Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Different Colors of Soybean Seed Coats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
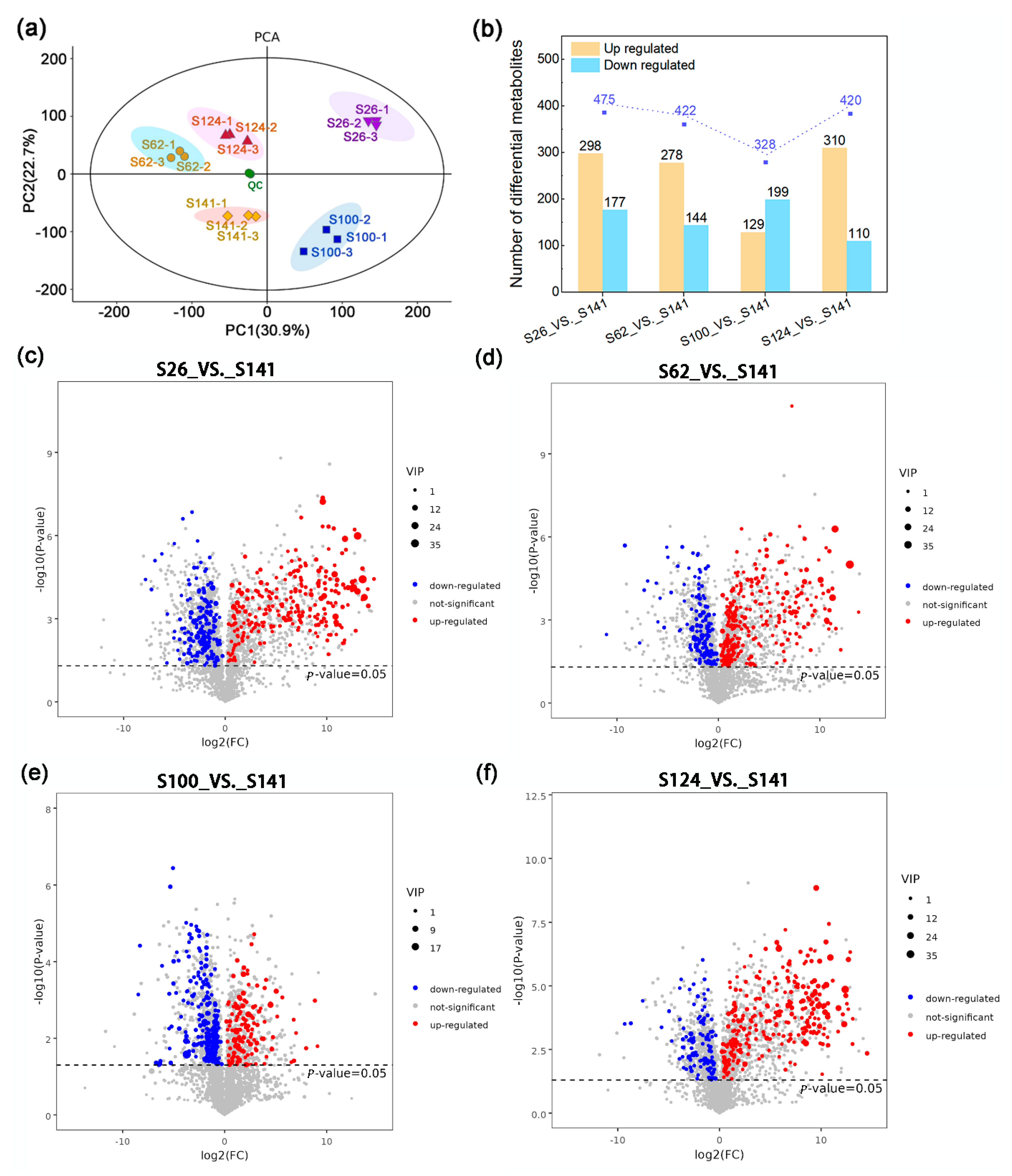
2.1. Metabolic Differences Among the Seed Coat of Soybean Germplasms
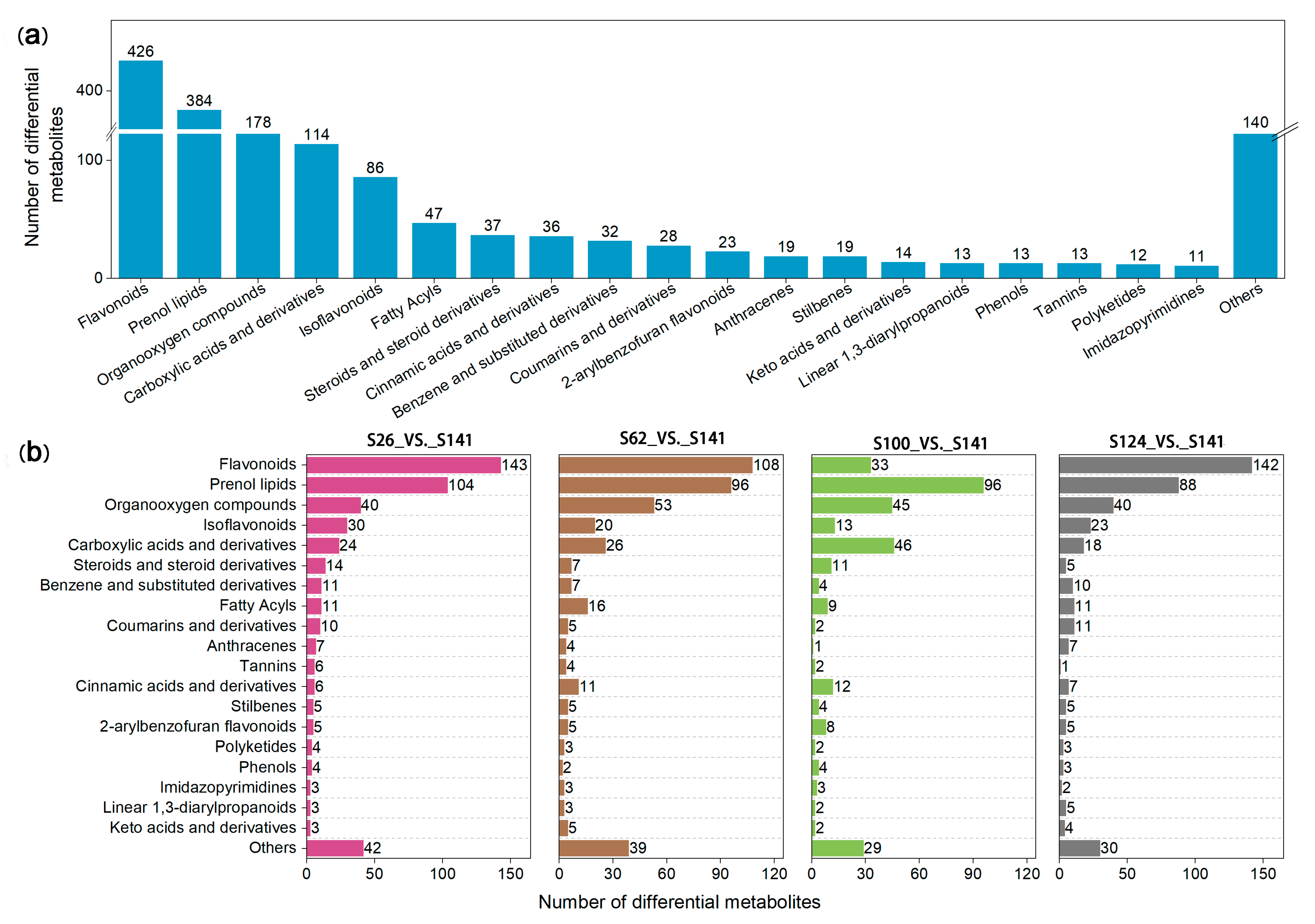
2.2. Analysis of the DAMs in the Flavonoid Biosynthetic Pathway
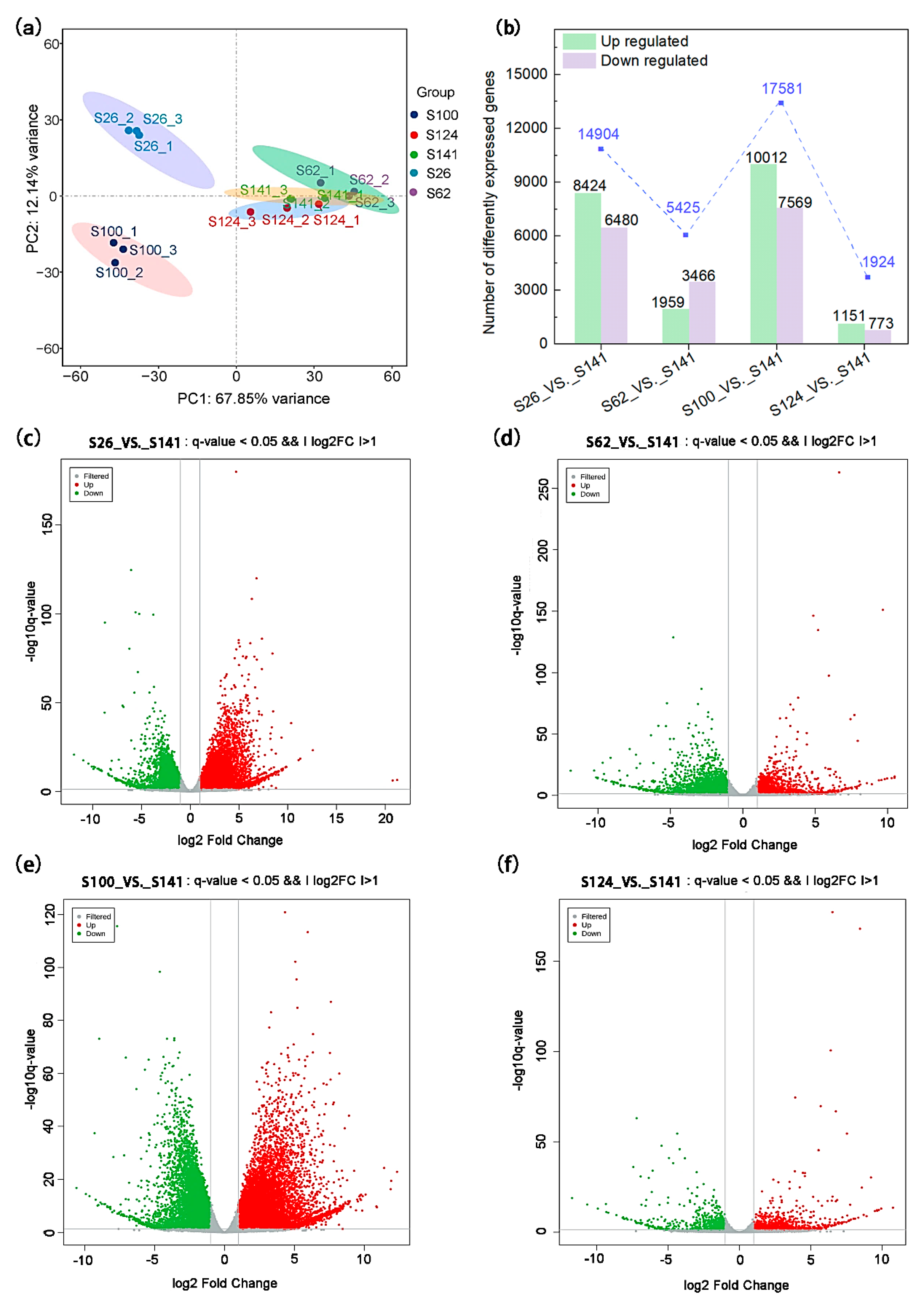
2.3. Transcriptomic Profiling of Soybean Seed Coat
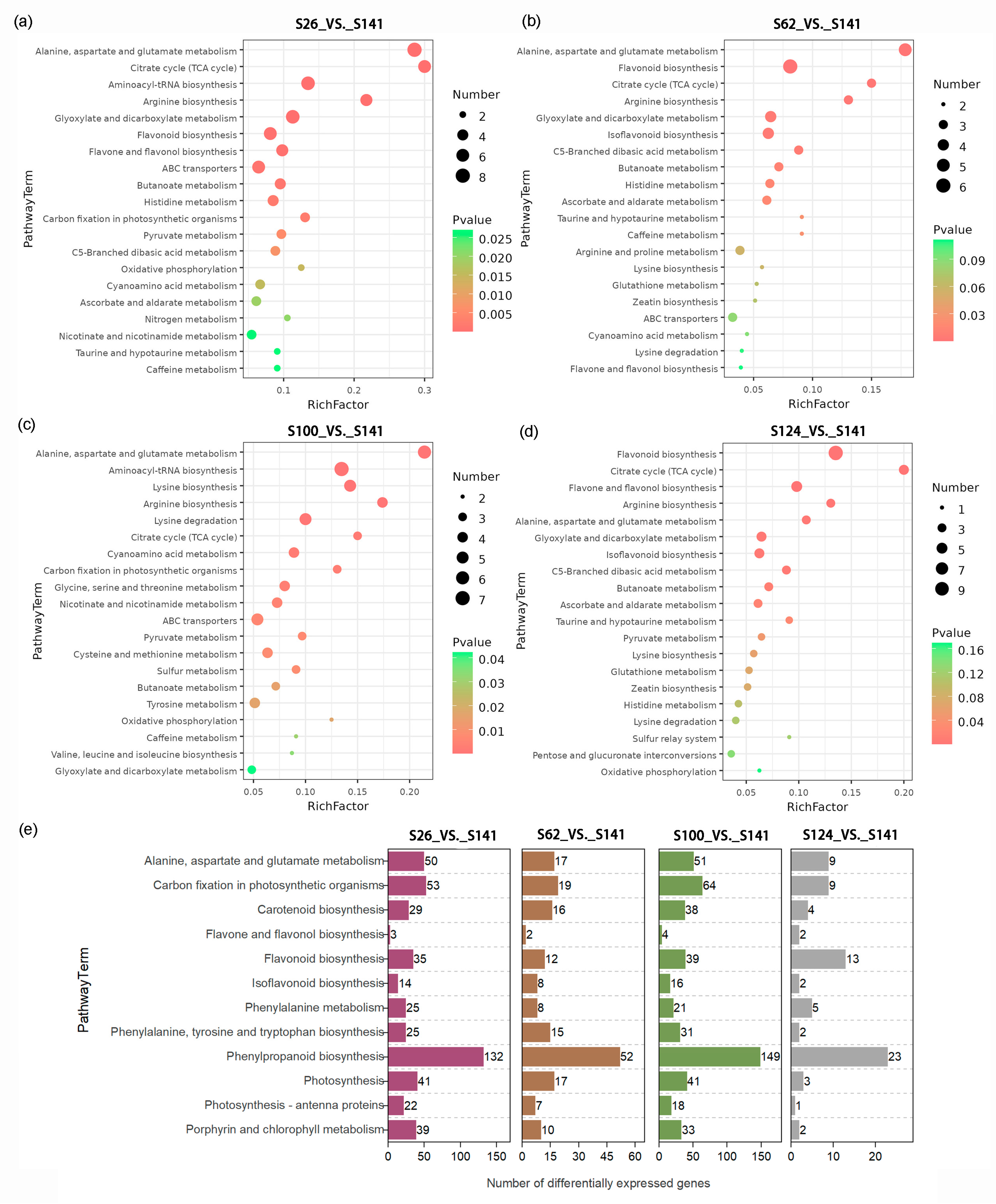
2.4. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis of the Expected Changes in DAMs and DEGs
2.5. Candidate Genes Related to the Flavonoid Biosynthetic Pathway
3. Discussion
3.1. Identification of Flavonoid Compounds in Soybean Seed Coat
3.2. DEGs Related to the Biosynthesis of Flavonoids in the Seed Coat of Soybean
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Experimental Site
4.2. Metabolome Measurement
4.3. Transcriptome Analysis
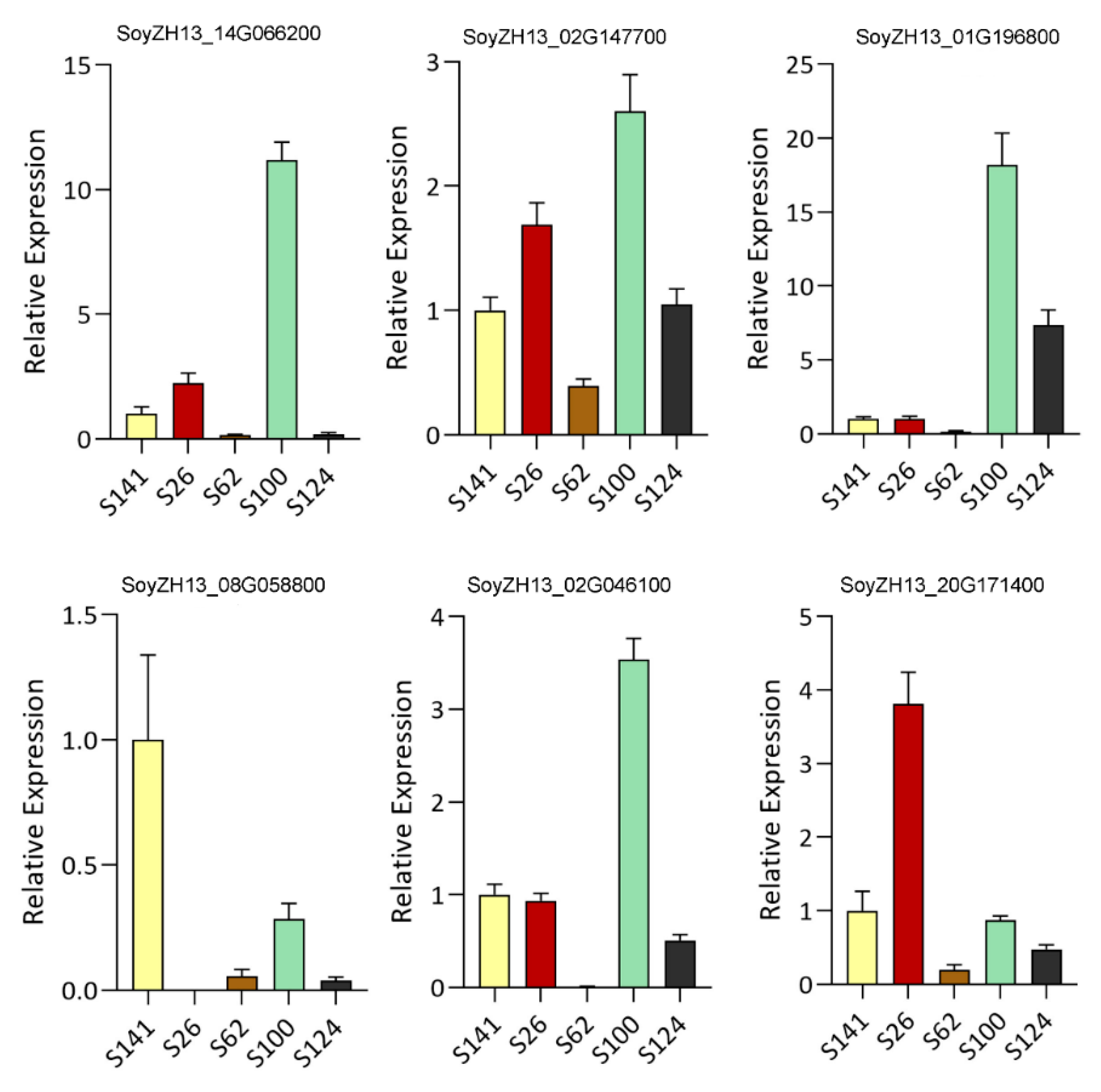
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whipps, J.M.; Davies, K.G. Success in Biological Control of Plant Pathogens and Nematodes by Microorganisms; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Desta, K.T.; Hur, O.S.; Lee, S.; Yoon, H.; Shin, M.J.; Yi, J.; Lee, Y.; Ro, N.Y.; Wang, X.; Choi, Y.M. Origin and seed coat color differently affect the concentrations of metabolites and antioxidant activities in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) seeds. Food Chem. 2022, 381, 132249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcclean, P.E.; Lee, R.K.; Otto, C.; Gepts, P.; Bassett, M.J. Molecular and Phenotypic Mapping of Genes Controlling Seed Coat Pattern and Color in Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Hered. 2002, 2, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, B.W.; Ha, T.J.; Bae, D.W.; Son, B.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Baek, S.B.; Kim, Y.C.; et al. Comparative proteomics analysis of seed coat from two black colored soybean cultivars during seed development. Plant Omics 2013, 6, 456–463. [Google Scholar]
- Toda, K.; Yang, D.; Yamanaka, N.; Watanabe, S.; Harada, K.; Takahashi, R. A single-base deletion in soybean flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase gene is associated with gray pubescence color. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 50, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Lu, S.; He, W.; Bi, T.; Li, J. Metabonomics analysis of flavonoids in seeds and sprouts of two Chinese soybean cultivars. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hwang, Y.S.; Kim, S.T.; Yoon, W.B.; Han, W.Y.; Kang, I.K.; Choung, M.G. Seed coat color and seed weight contribute differential responses of targeted metabolites in soybean seeds. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepiniec, L.; Debeaujon, I.; Routaboul, J.M.; Baudry, A.; Pourcel, L.; Nesi, N.; Caboche, M. Flavonoids and the regulation of seed size in Arabidopsis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Du, W.; Hao, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, M.; Sun, Z. Elucidation of the Regulatory Network of Flavonoid Biosynthesis by Profiling the Metabolome and Transcriptome in Tartary Buckwheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7218–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, Q.; Li, Z.; Jin, X.; Xing, W. Metabolic and transcriptomic analysis related to flavonoid biosynthesis during the color formation of Michelia crassipes tepal. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 938–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Li, C.; Duan, C.; Gu, C.; Zhang, Q. Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Flavonoid Regulatory Network by Eutrema EsMYB90. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Yang, X.; Zheng, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Tu, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Cheng, S.; et al. Unraveling the Regulatory Mechanism of Color Diversity in Camellia japonica Petals by Integrative Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 685136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shan, X.; Gao, R.; Han, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Kimani, S.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. MYB repressors and MBW activation complex collaborate to fine-tune flower coloration in Freesia hybrida. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Saeed, F.; Anjum, F.M.; Afzaal, M.; Tufail, T.; Bashir, M.S.; Ishtiaq, A.; Hussain, S.; Suleria, H.A. Natural polyphenols: An overview. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Han, T.; Xun, H.; Zeng, X.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Feng, X.; et al. MYB transcription factors GmMYBA2 and GmMYBR function in a feedback loop to control pigmentation of seed coat in soybean. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 4401–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zheng, J.; Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, H.; Fu, Q. Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptome and Metabolome Reveals the Flavonoid Metabolic Pathway Is Associated with Fruit Peel Coloration of Melon. Molecules 2021, 26, 2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.J.; Kwon, S.-J.; Qu, S.; Kim, D.-G.; Eom, S. Antioxidant Contributors in Seed, Seed Coat, and Cotyledon of γ-ray-Induced Soybean Mutant Lines with Different Seed Coat Colors. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Cao, S.; Shang, X.; Xie, X.; Zeng, W.; Lu, L.; Kong, Q.; Yan, H. Metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling reveals distinct nutritional properties of cassavas with different flesh colors. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2021, 2, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Qiao, G.; Wen, Z.; Deng, B.; Qiu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Wen, X. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals the molecular regulation underlying the adaptive mechanism of cherry (Cerasus pseudocerasus Lindl.) to shelter covering. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Yin, C.; Wang, F.; Chen, P.; Chen, H.; Ma, J.; Zhang, B.; Xu, J.; et al. iTRAQ-based analysis of developmental dynamics in the soybean leaf proteome reveals pathways associated with leaf photosynthetic rate. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Rao, J.; Shi, J.; Hu, C.; Cheng, F.; Wilson, Z.A.; Zhang, D.; Quan, S. Seed metabolomic study reveals significant metabolite variations and correlations among different soybean cultivars. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, K.; Qin, J.; Yang, C.; Qiao, Y. Identification of candidate genes for soybean seed coat-related traits using QTL mapping and GWAS. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1190503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofsky, J.; Zhang, H.; Song, B.H. The Untapped Genetic Reservoir: The Past, Current, and Future Applications of the Wild Soybean (Glycine soja). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, S.; Funatsuki, H.; Kasai, A.; Kurauchi, T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Takeuchi, T.; Yamazaki, H.; Kurosaki, H.; Shirai, S.; Miyoshi, T.; et al. Variation of GmIRCHS (Glycine max inverted-repeat CHS pseudogene) is related to tolerance of low temperature-induced seed coat discoloration in yellow soybean. TAG Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Li, B.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q. Integration of Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveals the Molecular Mechanisms of Flower Color Formation in Prunus mume. Plants 2024, 13, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Liao, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Sun, C. Integrated Metabolomic-Transcriptomic Analyses of Flavonoid Accumulation in Citrus Fruit under Exogenous Melatonin Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Hao, Y.; Fan, S.; Cai, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Zhu, X. Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Profiling Provide Novel Insights into Fruit Ripening and Ripening Disorder Caused by 1-MCP Treatments in Papaya. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Deng, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, S.; Fu, Y.; Yang, C.; Liao, Z.; Chen, M. An analytical pipeline to compare and characterise the anthocyanin antioxidant activities of purple sweet potato cultivars. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.E.; Azlan, A.; Tang, S.T.; Lim, S.M. Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: Colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1361779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, M.; Zhang, S.; Qi, J.; Abdelghany, A.M.; Shaibu, A.S.; Feng, Y.; Ghosh, S.; Agyenim-Boateng, K.G.; Liu, Y.; Yao, L.; et al. Effect of Origin, Seed Coat Color, and Maturity Group on Seed Isoflavones in Diverse Soybean Germplasm. Plants 2024, 13, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Luo, H.; Jiang, L.; Hou, J.; Zhang, T.; Dai, L.; Yu, Z. Integrative analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveals the possible mechanism of leaf yellowing in pak choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis) with 1-methylcyclopropene treatment during storage at 20 °C. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 169, 111300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; He, T.; Wang, X. Analysis of Dynamic Global Transcriptional Atlas Reveals Common Regulatory Networks of Hormones and Photosynthesis Across Nicotiana Varieties in Response to Long-Term Drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.W.; Oh, S.D.; Park, S.Y.; Jang, Y.; Lee, S.K.; Yun, D.W.; Chang, A.; Park, S.U.; Ha, S.H.; Kim, J.K. Metabolic profiling and antioxidant properties of hybrid soybeans with different seed coat colors, obtained by crossing β-carotene-enhanced (Glycine max) and wild (Glycine soja) soybeans. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2022, 16, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, S.; Ma, H.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y. Tree peony variegated flowers show a small insertion in the F3′H gene of the acyanic flower parts. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, S.; Chen, J.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, H.; Wen, Y. De novo Assembly of the Camellia nitidissima Transcriptome Reveals Key Genes of Flower Pigment Biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovinich, N.; Saleem, A.; Rintoul, T.L.; Brown, D.C.; Arnason, J.T.; Miki, B. Coloring genetically modified soybean grains with anthocyanins by suppression of the proanthocyanidin genes ANR1 and ANR2. Transgenic Res. 2012, 21, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, D.O.; Yang, H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Metabolome and Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis Reveals Anthocyanin Metabolism in Pink Flowers of Anthocyanin-Rich Tea (Camellia sinensis). Molecules 2019, 24, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Liao, D.; Wu, X.; Gao, R.; Fan, Y.; Raza, M.A.; Wang, X.; Yong, T.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; et al. Effect of aboveground and belowground interactions on the intercrop yields in maize-soybean relay intercropping systems. Field Crops Res. 2017, 203, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Hu, H.; Wei, G.; Cui, J.; Xu, J. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Reveal Differences in Terpenoid and Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Cryptomeria fortunei Needles Across Different Seasons. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 862746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xing, L.; Song, H.; Wei, Y.; Li, P.; Lu, Q.; Hu, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Large-scale metabolome analysis reveals dynamic changes of metabolites during foxtail millet grain filling. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Song, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, T.; Tang, B.; Dong, L.; Ding, N.; Zhang, Q.; et al. GSA: Genome Sequence Archive. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Code | Name | Seed Coat Color | 100-Seed Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S141 | Huangdou | Yellow | 16.4 |
| S26 | Hongpixiangdou | Red | 36.8 |
| S62 | Bendihuangdou | Brown | 19.7 |
| S100 | Bendilvhuangdou | Green | 20.5 |
| S124 | Heipidadou | Black | 20.7 |
| S26_vs._S141 | S62_vs._S141 | S100_vs._S141 | S124_vs._S141 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold Change | p-Value | Regu-lation | Fold Change | p-Value | Regu-lation | Fold Change | p-Value | Regu-lation | Fold Change | p-Value | Regu lation | |
| SoyZH13_02G120600(CHS6) | 8.65 | 0.010 | up | 1.54 | 0.660 | up | 17.30 | 0.000 | up | 11.24 | 0.000 | up |
| SoyZH13_11G010700(CHS) | 2.83 | 0.000 | up | 1.36 | 0.580 | up | 0.95 | 0.860 | down | 0.54 | 0.010 | down |
| SoyZH13_08G103500(CHS1) | 10.75 | 0.000 | up | 0.23 | 0.060 | down | 18.76 | 0.000 | up | 10.30 | 0.000 | up |
| SoyZH13_06G290900(UGT88F4) | 1.51 | 0.014 | up | 0.41 | 0.000 | down | 1.75 | 0.000 | up | 0.50 | 0.001 | down |
| SoyZH13_02G046100(FHT) | 5.35 | 0.000 | up | 0.12 | 0.000 | down | 7.71 | 0.000 | up | 1.51 | 0.260 | up |
| SoyZH13_14G066200(DFR) | 10.47 | 0.000 | up | 0.21 | 0.200 | down | 33.06 | 0.000 | up | 0.72 | 0.730 | down |
| SoyZH13_02G147700(DFR) | 7.51 | 0.000 | up | 0.57 | 0.220 | down | 5.87 | 0.000 | up | 1.71 | 0.100 | up |
| SoyZH13_01G196800(ANT17) | 3.17 | 0.000 | up | 0.08 | 0.010 | down | 16.61 | 0.000 | up | 12.17 | 0.000 | up |
| SoyZH13_08G058800(ANR) | 0.04 | 0.010 | down | 0.05 | 0.030 | down | 0.63 | 0.550 | down | 0.08 | 0.030 | down |
| SoyZH13_20G171400(LAR) | 18.82 | 0.000 | up | 0.68 | 0.580 | down | 9.39 | 0.000 | up | 0.19 | 0.030 | down |
| SoyZH13_05G078700(FLS) | 7.76 | 0.000 | up | 0.26 | 0.020 | down | 4.39 | 0.000 | up | 0.05 | 0.000 | down |
| SoyZH13_12G118300(FG3) | 78.61 | 0.000 | up | 26.24 | 0.000 | up | 6.81 | 0.000 | up | |||
| SoyZH13_20G225300(CHI2-A) | 7.42 | 0.000 | up | 7.42 | 0.000 | up | ||||||
| SoyZH13_05G020900(CYP75B2) | 9.275 | 0.002 | up | |||||||||
| SoyZH13_12G061300(CYP93B1) | 21.265 | 0.001 | up | |||||||||
| Time (min) | A% | B% |
|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 95 | 5 |
| 2 | 95 | 5 |
| 4 | 70 | 30 |
| 8 | 50 | 50 |
| 10 | 20 | 80 |
| 14 | 0 | 100 |
| 15 | 0 | 100 |
| 15.1 | 95 | 5 |
| 16 | 95 | 5 |
| Parameters | Positive Ion Mode | Negative Ion Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Mass scan range (m/z) | 100–1200 | 100–1200 |
| Resolution (full scan) | 70,000 | 70,000 |
| Resolution (HCD MS/MS scans) | 17,500 | 17,500 |
| Spray voltage (V) | 3800 | −3000 |
| Sheath gas flow rate (Arb) | 40 | 35 |
| Aux gas flow rate (Arb) | 10 | 8 |
| Capillary temperature (°C) | 320 | 320 |
| Auxiliary gas heater temperature (°C) | 350 | 350 |
| S-lens radio frequency (RF) level | 50 | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Hussain, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, M.; Zhong, X.; Tao, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, C. Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Different Colors of Soybean Seed Coats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010294
Fan Y, Hussain S, Wang X, Yang M, Zhong X, Tao L, Li J, Zhou Y, Xiang C. Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Different Colors of Soybean Seed Coats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010294
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yuanfang, Sajad Hussain, Xianshu Wang, Mei Yang, Xiaojuan Zhong, Lei Tao, Jing Li, Yonghang Zhou, and Chao Xiang. 2025. "Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Different Colors of Soybean Seed Coats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010294
APA StyleFan, Y., Hussain, S., Wang, X., Yang, M., Zhong, X., Tao, L., Li, J., Zhou, Y., & Xiang, C. (2025). Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Different Colors of Soybean Seed Coats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010294







