Development of Novel Peptidyl Nitriles Targeting Rhodesain and Falcipain-2 for the Treatment of Sleeping Sickness and Malaria
Abstract
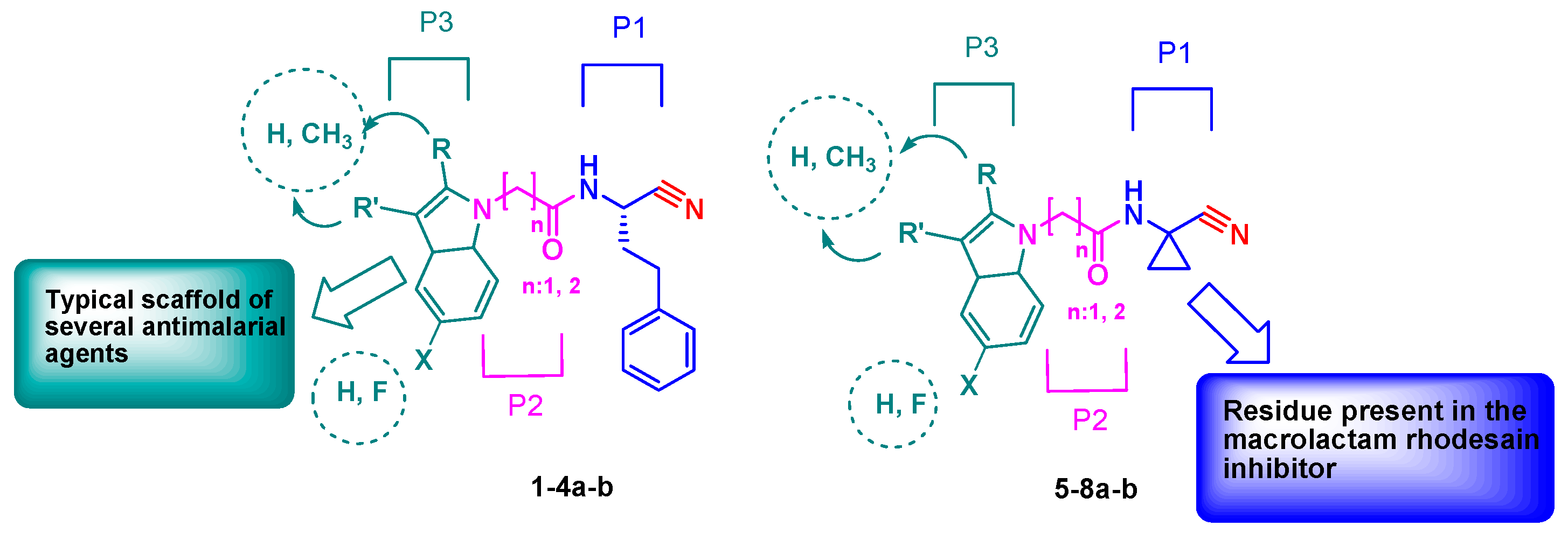
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
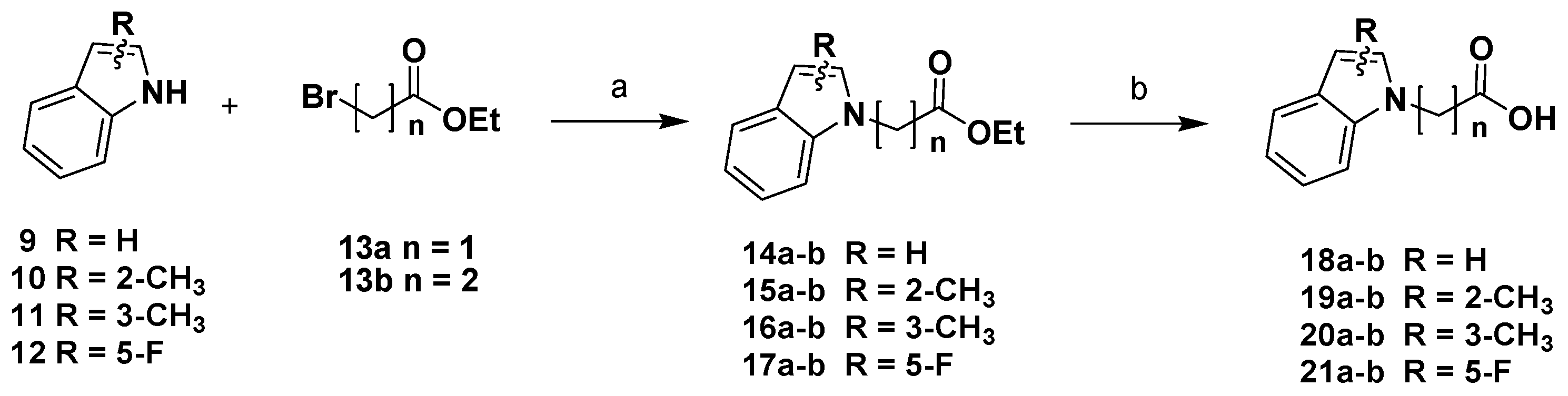
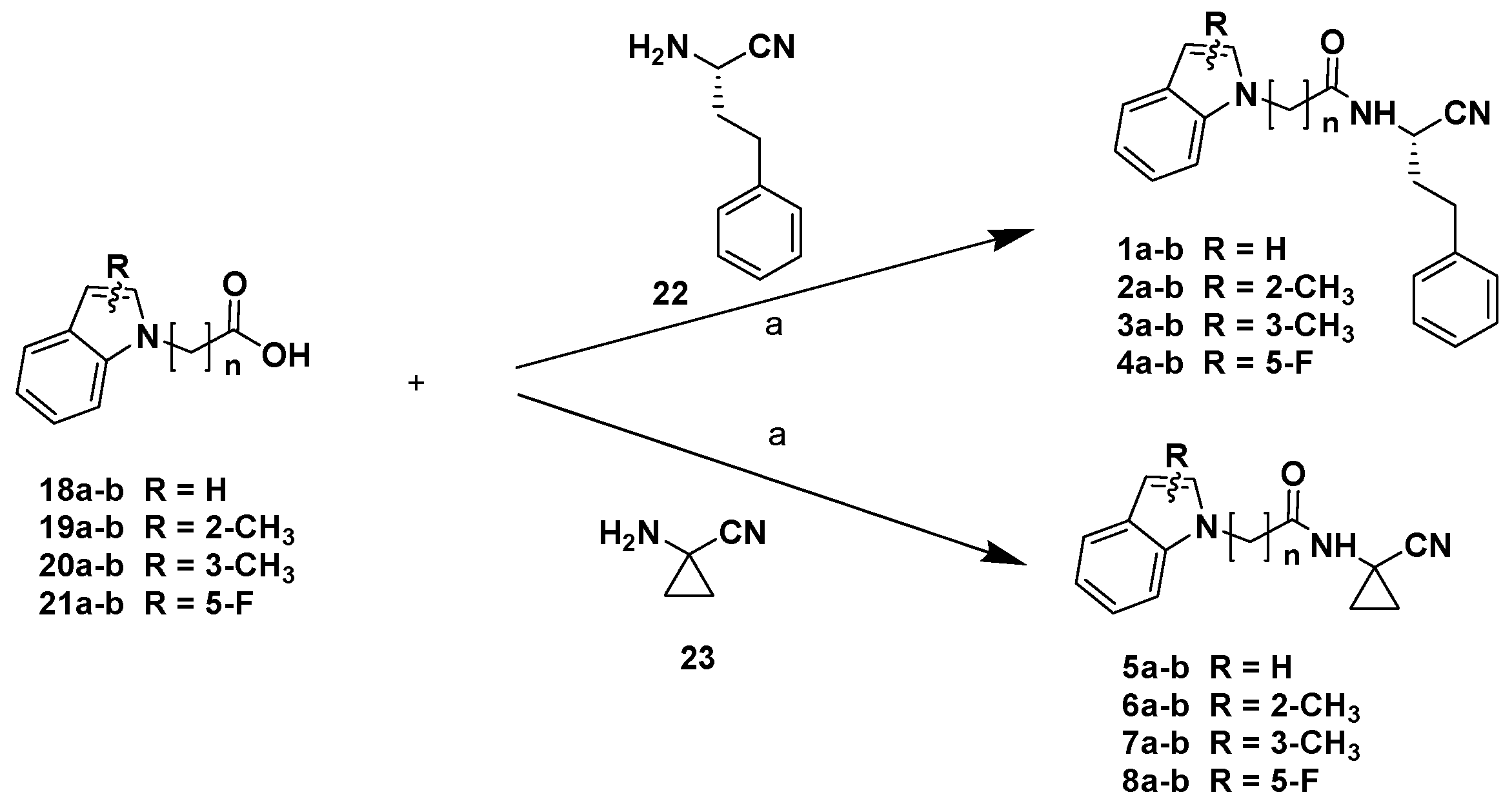
Chemistry
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Enzyme Assays against Rhodesain
3.3. FP-2 Inhibition
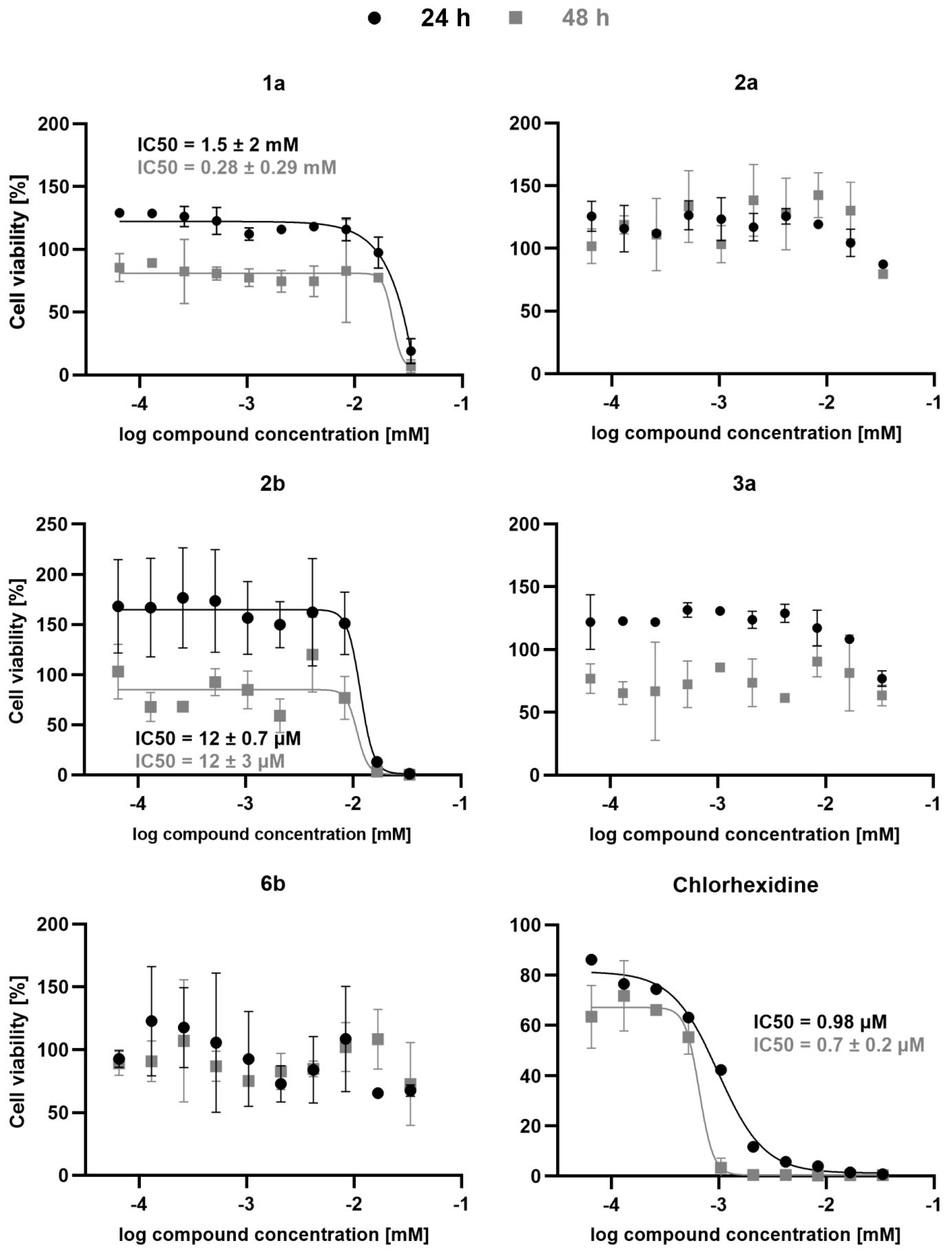
3.4. Antitrypanosomal Activity
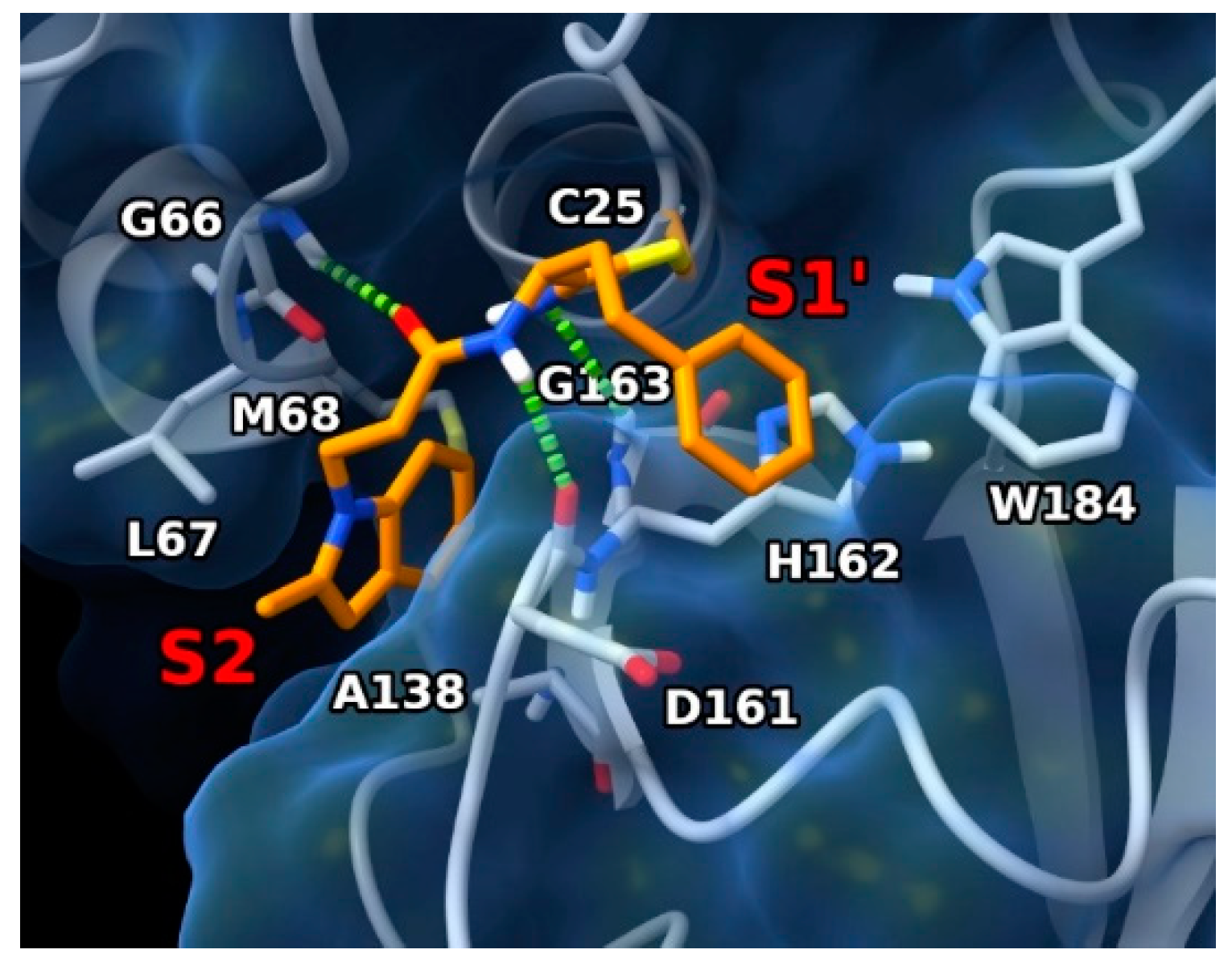
3.5. Docking Experiments
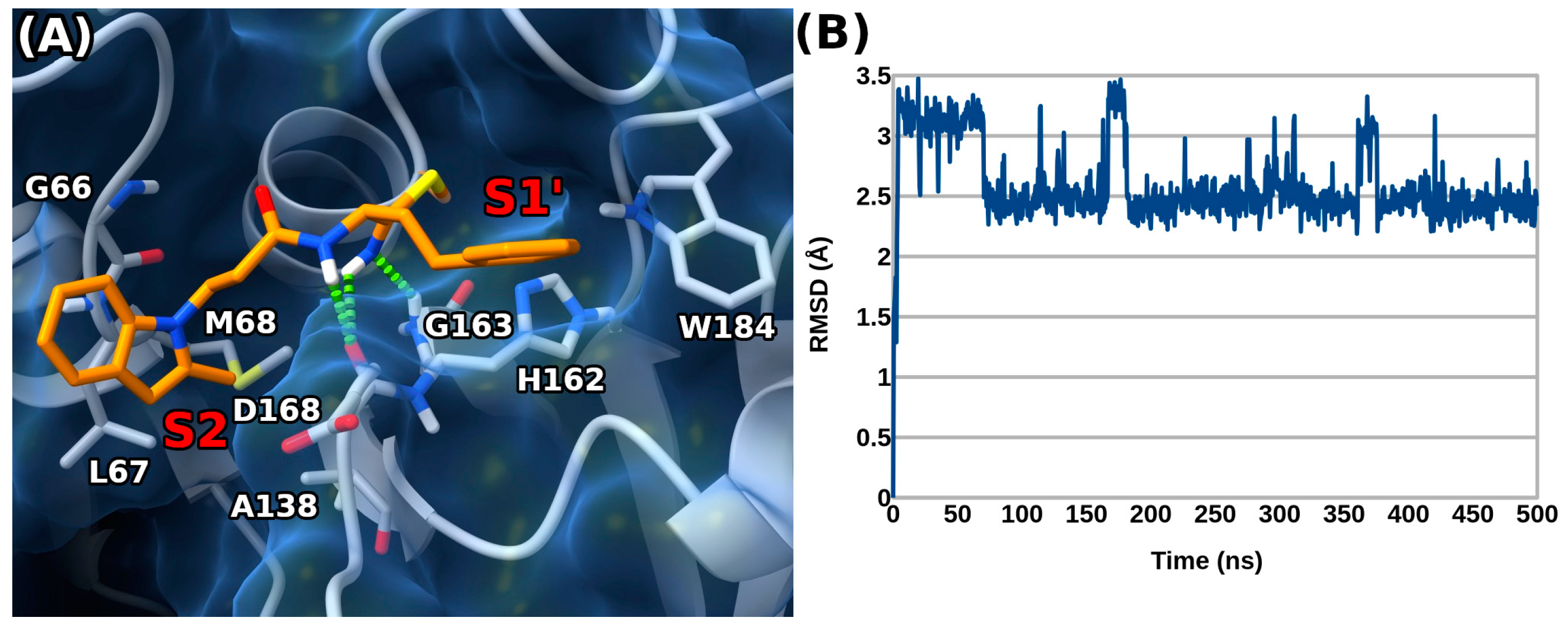
3.6. Molecular Dynamics Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Neglected Tropical Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/neglected-tropical-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 29 January 2024).
- World Health Organization. Human African Trypanosomiasis (Sleeping Sickness). Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/human-african-trypanosomiasis#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 29 January 2024).
- World Health Organization. Malaria. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malaria (accessed on 29 January 2024).
- Babokhov, P.; Sanyaolu, A.O.; Oyibo, W.A.; Fagbenro-Beyioku, A.F.; Iriemenam, N.C. A current analysis of chemotherapy strategies for the treatment of human African trypanosomiasis. Pathog. Glob. Health 2013, 107, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priotto, G.; Kasparian, S.; Mutombo, W.; Ngouama, D.; Ghorashian, S.; Arnold, U.; Ghabri, S.; Baudin, E.; Buard, V.; Kazadi-Kyanza, S.; et al. Nifurtimox-eflornithine combination therapy for second-stage African Trypanosoma brucei gambiense trypanosomiasis: A multicentre, randomised, phase III, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2009, 374, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, E.D. Fexinidazole: First global approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, B.J.; Wieten, R.W.; Kroon, D.; Nagel, I.M.; Belard, S.; van Vugt, M.; Grobusch, M.P. Efficacy and safety of artemisinin combination therapy (ACT) for non-falciparum malaria: A systematic review. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, P.J.; Asua, V.; Conrad, M.D. Emergence, transmission dynamics and mechanisms of artemisinin partial resistance in malaria parasites in Africa. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettari, R.; Previti, S.; Tamborini, L.; Cullia, G.; Grasso, S.; Zappalà, M. The inhibition of cysteine proteases rhodesain and TbCatB: A valuable approach to treat Human African Trypanosomiasis. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1374–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettari, R.; Tamborini, L.; Angelo, I.C.; Micale, N.; Pinto, A.; De Micheli, C.; Conti, P. Inhibition of rhodesain as a novel therapeutic modality for human African trypanosomiasis. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5637–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolskaia, O.V.; de Lima, A.A.P.; Kim, Y.V.; Lonsdale-Eccles, J.D.; Fukuma, T.; Scharfstein, J.; Grab, D.J. Blood-brain barrier traversal by African trypanosomes requires calcium signaling induced by parasite cysteine protease. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, J.D.; McCulloch, R. Antigenic variation in trypanosomes: Enhanced phenotypic variation in a eukaryotic parasite. Adv. Parasitol. 2001, 49, 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ettari, R.; Previti, S.; Di Chio, C.; Zappalà, M. Falcipain-2 and falcipain-3 inhibitors as promising antimalarial agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 3010–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettari, R.; Bova, F.; Zappalà, M.; Grasso, S.; Micale, N. Falcipain-2 inhibitors. Med. Res. Rev. 2010, 30, 136–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degotte, G.; Pendeville, H.; Di Chio, C.; Ettari, R.; Pirotte, B.; Frederich, M.; Francotte, P. Dimeric polyphenols to pave the way for new antimalarial drugs. RSC Med. Chem. 2023, 14, 715–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Previti, S.; Ettari, R.; Di Chio, C.; Legac, J.; Bogacz, M.; Zimmer, C.; Schirmeister, T.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Zappala, M. Influence of amino acid size at the P3 position of N-Cbz-tripeptide Michael acceptors targeting falcipain-2 and rhodesain for the treatment of malaria and human african trypanosomiasis. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 137, 106587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Previti, S.; Ettari, R.; Calcaterra, E.; Di Chio, C.; Ravichandran, R.; Zimmer, C.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Wagner, A.; Cosconati, S.; Schirmeister, T.; et al. Development of urea bond-containing Michael acceptors as antitrypanosomal agents targeting rhodesain. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Chio, C.; Previti, S.; Amendola, G.; Ravichandran, R.; Wagner, A.; Cosconati, S.; Hellmich, U.A.; Schirmeister, T.; Zappalà, M.; Ettari, R. Development of novel dipeptide nitriles as inhibitors of rhodesain of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 236, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Previti, S.; Ettari, R.; Di Chio, C.; Ravichandran, R.; Bogacz, M.; Hellmich, U.A.; Schirmeister, T.; Cosconati, S.; Zappalà, M. Development of reduced peptide bond pseudopeptide Michael acceptors for the treatment of Human African Trypanosomiasis. Molecules 2022, 27, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiorana, S.; Ettari, R.; Previti, S.; Amendola, G.; Wagner, A.; Cosconati, S.; Hellmich, U.A.; Schirmeister, T.; Zappalà, M. Peptidyl vinyl ketone irreversible inhibitors of rhodesain: Modifications of the P2 fragment. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Chio, C.; Previti, S.; Amendola, G.; Cosconati, S.; Schirmeister, T.; Zappala, M.; Ettari, R. Development of novel benzodiazepine-based peptidomimetics as inhibitors of rhodesain from Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettari, R.; Previti, S.; Maiorana, S.; Amendola, G.; Wagner, A.; Cosconati, S.; Schirmeister, T.; Hellmich, U.A.; Zappalà, M. Optimization strategy of novel peptide-based Michael acceptors for the treatment of Human African Trypanosomiasis. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 10617–10629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previti, S.; Ettari, R.; Cosconati, S.; Amendola, G.; Chouchene, K.; Wagner, A.; Hellmich, U.A.; Ulrich, K.; Krauth-Siegel, R.L.; Wich, P.R.; et al. Development of novel peptide-based Michael acceptors targeting rhodesain and falcipain-2 for the treatment of Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs). J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 6911–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettari, R.; Previti, S.; Cosconati, S.; Maiorana, S.; Schirmeister, T.; Grasso, S.; Zappalà, M. Development of novel 1,4-benzodiazepine-based Michael acceptors as antitrypanosomal agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3453–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettari, R.; Previti, S.; Cosconati, S.; Kesselring, J.; Schirmeister, T.; Grasso, S.; Zappalà, M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel peptidomimetics as rhodesain inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettari, R.; Pinto, A.; Previti, S.; Tamborini, L.; Angelo, I.C.; La Pietra, V.; Marinelli, L.; Novellino, E.; Schirmeister, T.; Zappalà, M.; et al. Development of novel dipeptide-like rhodesain inhibitors containing the 3-bromoisoxazoline warhead in a constrained conformation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 7053–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettari, R.; Pinto, A.; Tamborini, L.; Angelo, I.C.; Grasso, S.; Zappalà, M.; Capodicasa, N.; Yzeiraj, L.; Gruber, E.; Aminake, M.N.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of papain-family cathepsin L-like cysteine protease inhibitors containing a 1,4-benzodiazepine scaffold as antiprotozoal agents. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettari, R.; Tamborini, L.; Angelo, I.C.; Grasso, S.; Schirmeister, T.; Lo Presti, L.; De Micheli, C.; Pinto, A.; Conti, P. Development of rhodesain inhibitors with a 3-bromoisoxazoline warhead. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 2070–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettari, R.; Zappalà, M.; Micale, N.; Schirmeister, T.; Gelhaus, C.; Leippe, M.; Evers, A.; Grasso, S. Synthesis of novel peptidomimetics as inhibitors of protozoan cysteine proteases falcipain-2 and rhodesain. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3228–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bova, F.; Ettari, R.; Micale, N.; Carnovale, C.; Schirmeister, T.; Gelhaus, C.; Leippe, M.; Grasso, S.; Zappalà, M. Constrained peptidomimetics as antiplasmodial falcipain-2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 4928–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettari, R.; Micale, N.; Grazioso, G.; Bova, F.; Schirmeister, T.; Grasso, S.; Zappalà, M. Synthesis and molecular modeling studies of derivatives of a highly potent peptidomimetic vinyl ester as falcipain-2 inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 1594–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surur, A.S.; Huluka, S.A.; Mitku, M.L.; Asres, K. Indole: The after next scaffold of antiplasmodial agents? Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 4855–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroud, M.; Kuhn, B.; Saint-Auret, S.; Kuratli, C.; Martin, R.E.; Schuler, F.; Diederich, F.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Schirmeister, T.; et al. 2 H-1,2,3-Triazole-based dipeptidyl nitriles: Potent, selective, and trypanocidal rhodesain inhibitors by structure-based design. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3370–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffrey, C.R.; Hansell, E.; Lucas, K.D.; Brinen, L.S.; Alvarez Hernandez, A.; Cheng, J.; Gwaltney, S.L., 2nd; Roush, W.R.; Stierhof, Y.D.; Bogyo, M.; et al. Active site mapping, biochemical properties and subcellular localization of rhodesain, the major cysteine protease of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2001, 118, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, I.D.; Wu, P.; Marion-Tsukamaki, R.; Mackey, Z.B.; Brinen, L.S. Crystal Structures of TbCatB and rhodesain, potential chemotherapeutic targets and major cysteine proteases of Trypanosoma brucei. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berteotti, A.; Vacondio, F.; Lodola, A.; Bassi, M.; Silva, C.; Mor, M.; Cavalli, A. Predicting the reactivity of nitrile-carrying compounds with cysteine: A combined computational and experimental study. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sijwali, P.S.; Brinen, L.S.; Rosenthal, P.J. Systematic optimization of expression and refolding of the Plasmodium falciparum cysteine protease falcipain-2. Protein Expr. Purif. 2001, 22, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Le, T.A.; Brennich, M.; Klein, P.; Bader, N.; Diehl, E.; Paszek, D.; Weickhmann, A.K.; Dirdjaja, N.; Krauth-Siegel, R.L.; et al. Inhibitor-induced dimerization of an essential oxidoreductase from african trypanosomes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 3640–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, P.; Barthels, F.; Johe, P.; Wagner, A.; Tenzer, S.; Distler, U.; Le, T.A.; Schmid, P.; Engel, V.; Engels, B.; et al. Naphthoquinones as covalent reversible inhibitors of cysteine proteases-studies on inhibition mechanism and kinetics. Molecules 2020, 25, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, G.; Forli, S.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Covalent docking using autodock: Two-point attractor and flexible side chain methods. Protein Sci. 2016, 25, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Maestro, Release 2022-1: Schrödinger; LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2022.
- Harder, E.; Damm, W.; Maple, J.; Wu, C.; Reboul, M.; Xiang, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Lupyan, D.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Knight, J.L.; et al. OPLS3: A force field providing broad coverage of drug-like small molecules and proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoover, W.G. Canonical dynamics: Equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys. Rev. A Gen. Phys. 1985, 31, 1695–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosé, S. A molecular dynamics method for simulations in the canonical ensemble. Mol. Phys. 1984, 52, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tuckerman, M.E.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Explicit reversible integrators for extended systems dynamics. Mol. Phys. 1996, 87, 1117–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 4177–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckerman, M.; Berne, B.J.; Martyna, G.J. Reversible multiple time scale molecular dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cmpds. | n | Rhodesain Percentage of Inhibition at 100 μM or Ki µM | Falcipain-2 IC50 µM |
| 1a | n = 1 | 13.11 ± 0.23 | >50 µM |
| 1b | n = 2 | n.i. | >50 µM |
| 2a | n = 1 | 6.56 ± 0.37 | >50 µM |
| 2b | n = 2 | 5.06 ± 0.14 | 40.43 µM |
| 3a | n = 1 | 10.31 ± 0.4 | >50 µM |
| 3b | n = 2 | 7.8% | 50 µM |
| 4a | n = 1 | 18.7% | 50 µM |
| 4b | n = 2 | 1.9% | 50 µM |
| 5a | n = 1 | 6.2% | >50 µM |
| 5b | n = 2 | 4.4% | >50 µM |
| 6a | n = 1 | n.i. | >50 µM |
| 6b | n = 2 | 8.18 ± 0.58 | 50 µM |
| 7a | n = 1 | n.i. | >50 µM |
| 7b | n = 2 | 9.5% | 50 µM |
| 8a | n = 1 | 4.5% | 50 µM |
| 8b | n = 2 | 9.6% | 50 µM |
| E-64 | 0.033 ± 0.007 | 0.051 µM | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Chio, C.; Starvaggi, J.; Totaro, N.; Previti, S.; Natale, B.; Cosconati, S.; Bogacz, M.; Schirmeister, T.; Legac, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; et al. Development of Novel Peptidyl Nitriles Targeting Rhodesain and Falcipain-2 for the Treatment of Sleeping Sickness and Malaria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084410
Di Chio C, Starvaggi J, Totaro N, Previti S, Natale B, Cosconati S, Bogacz M, Schirmeister T, Legac J, Rosenthal PJ, et al. Development of Novel Peptidyl Nitriles Targeting Rhodesain and Falcipain-2 for the Treatment of Sleeping Sickness and Malaria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(8):4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084410
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Chio, Carla, Josè Starvaggi, Noemi Totaro, Santo Previti, Benito Natale, Sandro Cosconati, Marta Bogacz, Tanja Schirmeister, Jenny Legac, Philip J. Rosenthal, and et al. 2024. "Development of Novel Peptidyl Nitriles Targeting Rhodesain and Falcipain-2 for the Treatment of Sleeping Sickness and Malaria" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 8: 4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084410
APA StyleDi Chio, C., Starvaggi, J., Totaro, N., Previti, S., Natale, B., Cosconati, S., Bogacz, M., Schirmeister, T., Legac, J., Rosenthal, P. J., Zappalà, M., & Ettari, R. (2024). Development of Novel Peptidyl Nitriles Targeting Rhodesain and Falcipain-2 for the Treatment of Sleeping Sickness and Malaria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(8), 4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084410









