The Genetic Profile of Large B-Cell Lymphomas Presenting in the Ocular Adnexa
Abstract
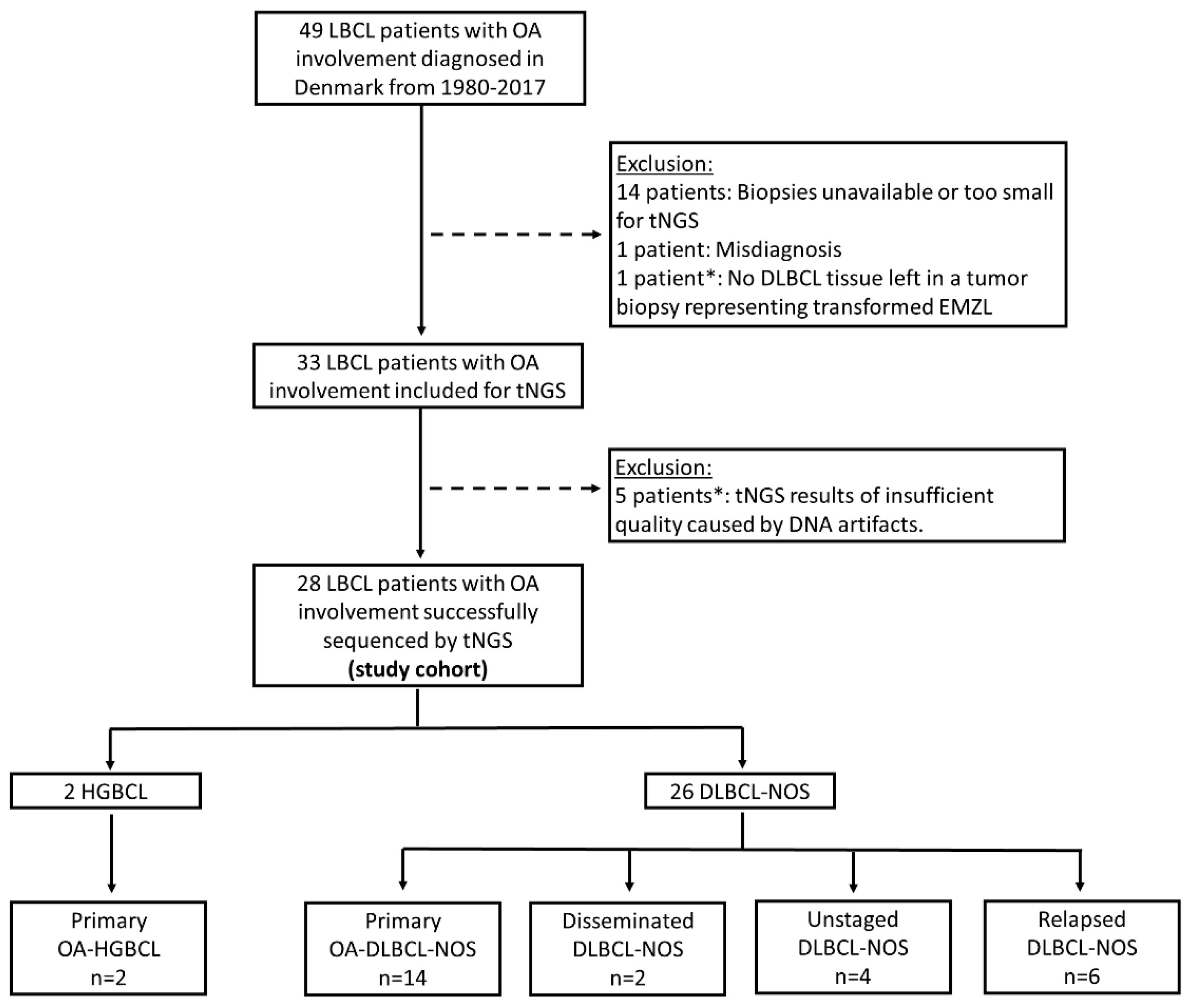
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Pathological Features
2.2. Patient Clinical Characteristics
| All n = 28 | HGBCL n = 2 | DLBCL-NOS n = 20 | Relapsed DLBCL-NOS 8,9 n = 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age 1 (years) | 74 (69–83) | 71 (69–74) | 75 (71–83) | 71 (66–84) |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 13 (46) | 0 (0) | 10 (50) | 3 (50) |
| Female | 15 (54) | 2 (100) | 10 (50) | 3 (50) |
| OA-LBCL location | ||||
| Orbit ± other OA location 2 | 25 (89) | 2 (100) | 18 (90) | 5 (83) |
| Lacrimal sac | 2 (7) | 0 (0) | 2 (10) | 0 (0) |
| Eyelid | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (17) |
| Cell-of-origin | ||||
| GCB | 13 (46) | 2 (100) | 11 (55) | 0 (0) |
| Non-GCB | 15 (54) | 0 (0) | 9 (45) | 6 (100) |
| Ann Arbor stage at OA-LBCL diagnosis | ||||
| IE-IIE | 19 (68) | 2 (100) | 14 (70) 7 | 3 (50) 10 |
| IV | 4 (14) | 0 (0) | 2 (10) | 2 (33) |
| Unstaged | 5 (18) | 0 (0) | 4 (20) | 1 (17) |
| Initial treatment of OA-LBCL | ||||
| Rituximab + chemotherapy ± RT 3 | 13 (46) | 1 (50) | 10 (50) | 2 (33) |
| RT ± prednisolone 4 | 9 (32) | 0 (0) | 7 (35) | 2 (33) |
| Chemotherapy ± RT 5 | 3 (11) | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 2 (33) |
| No treatment 6 | 3 (11) | 0 (0) | 3 (15) | 0 (0) |
| Recurrence or progression within 5 years of OA-LBCL diagnosis | ||||
| Yes | 9 (32) | 0 (0) | 6 (30) | 3 (50) |
| No | 16 (57) | 2 (100) | 12 (60) | 2 (33) |
| Unknown | 3 (11) | 0 (0) | 2 (10) | 1 (17) |
| Disease status at 5-year follow-up from OA-LBCL diagnosis | ||||
| Alive with complete remission | 12 (43) | 2 (100) | 8 (40) | 2 (33) |
| Dead from lymphoma | 9 (32) | 0 (0) | 6 (30) | 3 (50) |
| Dead from other cause | 4 (14) | 0 (0) | 3 (15) | 1 (17) |
| Dead from unknown cause | 2 (7) | 0 (0) | 2 (10) | 0 (0) |
| Unknown vital status | 1 (4) | 0(0) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) |
| Time to last follow-up from OA-LBCL diagnosis, months 1 | 30 (8–107) | 193 (170–216) | 25 (3–90) | 21 (8–83) |
2.3. Cell-of-Origin
2.4. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing

2.5. LymphGen Classification
2.6. Survival Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
4.2. Clinical Data
4.3. Tumor Samples and Histopathological Classification
4.4. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing
4.5. LymphGen Classification
4.6. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; International Agency for Research in Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Coiffier, B.; Lepage, E.; Brière, J.; Herbrecht, R.; Tilly, H.; Bouabdallah, R.; Morel, P.; Van Den Neste, E.; Salles, G.; Gaulard, P.; et al. CHOP Chemotherapy plus Rituximab Compared with CHOP Alone in Elderly Patients with Diffuse Large-B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. A Predictive Model for Aggressive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 987–994. [CrossRef]
- Ziepert, M.; Hasenclever, D.; Kuhnt, E.; Glass, B.; Schmitz, N.; Pfreundschuh, M.; Loeffler, M. Standard International prognostic index remains a valid predictor of outcome for patients with aggressive CD20+ B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.d.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leuk 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.; Zhang, J.; Davis, N.S.; Moffitt, A.B.; Love, C.L.; Waldrop, A.; Leppa, S.; Pasanen, A.; Meriranta, L.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.L.; et al. Genetic and Functional Drivers of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cell 2017, 171, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular Subtypes of Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma are Associated with Distinct Pathogenic Mechanisms and Outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, S.E.; Barrans, S.L.; Beer, P.A.; Painter, D.; Smith, A.G.; Roman, E.; Cooke, S.L.; Ruiz, C.; Glover, P.; Van Hoppe, S.J.L.; et al. Targeted sequencing in DLBCL, molecular subtypes, and outcomes: A Haematological Malignancy Research Network report. Blood 2020, 135, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.; Sehn, L.H.; Johnson, P.; Zinzani, P.L.; Hong, X.; Zhu, J.; Patti, C.; Belada, D.; Samoilova, O.; Suh, C.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Ibrutinib and Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone in Non–Germinal Center B-Cell Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.H.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Hodkinson, B.; Balasubramanian, S.; Fan, Y.; Vermeulen, J.; Shreeve, M.; Staudt, L.M. Effect of ibrutinib with R-CHOP chemotherapy in genetic subtypes of DLBCL. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1643–1653.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.C.; Tian, S.; Fu, D.; Wang, L.; Cheng, S.; Yi, H.M.; Jiang, X.F.; Song, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; et al. Genetic subtype-guided immunochemotherapy in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: The randomized GUIDANCE-01 trial. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1705–1716.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollila, T.A.; Olszewski, A.J. Extranodal Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma: Molecular Features, Prognosis, and Risk of Central Nervous System Recurrence. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2018, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.H.; Yoon, S.E.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, W.S.; Cho, J. Differences in mutational signature of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas according to the primary organ. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 19732–19743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vest, S.D.; Coupland, S.E.; Esmaeli, B.; Finger, P.T.; Graue, G.F.; Grossniklaus, H.E.; Hindso, T.G.; Holm, F.; Honavar, S.G.; Khong, J.J.; et al. Specific location of ocular adnexal lymphoma and mortality: An international multicentre retrospective study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 107, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferry, J.A.; Fung, C.Y.; Zukerberg, L.; Lucarelli, M.J.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Preffer, F.I.; Harris, N.L. Lymphoma of the Ocular Adnexa: A Study of 353 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, F.; Mikkelsen, L.H.; Kamper, P.; Rasmussen, P.K.; Larsen, T.S.; Sjö, L.D.; Heegaard, S. Ocular adnexal lymphoma in Denmark: A nationwide study of 387 cases from 1980 to 2017. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munch-Petersen, H.D.; Rasmussen, P.K.; Coupland, S.E.; Esmaeli, B.; Finger, P.T.; Graue, G.F.; Grossniklaus, H.E.; Honavar, S.G.; Khong, J.J.; McKelvie, P.A.; et al. Ocular Adnexal Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015, 133, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, M.K.; Minderman, M.; Sjö, L.D.; Pals, S.T.; Eriksen, P.R.G.; Heegaard, S. Prevalence and prognostic value of MYD88 and CD79B mutations in ocular adnexal large B-cell lymphoma: A reclassification of ocular adnexal large B-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 107, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, A.K.; Soliman, M.; Hovelson, D.H.; Liu, C.J.; McDaniel, A.S.; Haller, M.J.; Bratley, J.V.; Rahrig, S.E.; Li, Q.; Briceño, C.A.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiling of orbital and ocular adnexal lymphomas identifies frequent alterations in MYD88 and chromatin modifiers: New routes to targeted therapies. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vela, V.; Juskevicius, D.; Gerlach, M.M.; Meyer, P.; Graber, A.; Cathomas, G.; Dirnhofer, S.; Tzankov, A. High throughput sequencing reveals high specificity of TNFAIP3 mutations in ocular adnexal marginal zone B-cell lymphomas. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 38, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonese, I.; Takase, H.; Yoshimori, M.; Onozawa, E.; Tsuzura, A.; Miki, T.; Mochizuki, M.; Miura, O.; Arai, A. CD79B mutations in primary vitreoretinal lymphoma: Diagnostic and prognostic potential. Eur. J. Haematol. 2019, 102, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermaat, J.S.; Somers, S.F.; De Wreede, L.C.; Kraan, W.; De Groen, R.A.L.; Schrader, A.M.R.; Kerver, E.D.; Scheepstra, C.G.; Berenschot, H.; Deenik, W.; et al. MYD88 mutations identify a molecular subgroup of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with an unfavorable prognosis. Haematologica 2020, 105, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuy, B.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Stewart, C.; Tan, Y.; Abo, R.P.; Zhang, L.; Dunford, A.J.; Meredith, D.M.; Thorner, A.R.; Jordanova, E.S.; et al. Targetable genetic features of primary testicular and primary central nervous system lymphomas. Blood 2016, 127, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, N.; White, M.D.; Gill, C.M.; Lastrapes, M.; Bertalan, M.; Kaplan, A.; D’Andrea, M.R.; Bihun, I.; Kaneb, A.; Dietrich, J.; et al. MYD88 L265P mutation and CDKN2A loss are early mutational events in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, L. Genomic Mutation Landscape of Primary Breast Lymphoma: Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 6441139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, F.; González-Rincón, J.; Lavernia, J.; García, J.F.; Martín, P.; Bellas, C.; Piris, M.A.; Pedrosa, L.; Miramón, J.; Gómez-Codina, J.; et al. Mutational profile of primary breast diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareschal, S.; Pham-Ledard, A.; Viailly, P.J.; Dubois, S.; Bertrand, P.; Maingonnat, C.; Fontanilles, M.; Bohers, E.; Ruminy, P.; Tournier, I.; et al. Identification of Somatic Mutations in Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma, Leg Type by Massive Parallel Sequencing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, A.M.R.; de Groen, R.A.L.; Willemze, R.; Jansen, P.M.; Quint, K.D.; Cleven, A.H.G.; van Wezel, T.; van Eijk, R.; Ruano, D.; Veelken, J.H.; et al. Genetic Stability of Driver Alterations in Primary Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma, Leg Type and Their Relapses: A Rationale for the Use of Molecular-Based Methods for More Effective Disease Monitoring. Cancers 2022, 14, 5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Yoshida, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Iriyama, C.; Inoue, Y.; Sanada, M.; Kataoka, K.; Yuge, M.; Takagi, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; et al. Frequent genetic alterations in immune checkpoint-related genes in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2021, 137, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, A.M.R.; Jansen, P.M.; Willemze, R.; Vermeer, M.H.; Cleton-Jansen, A.M.; Somers, S.F.; Veelken, H.; Van Eijk, R.; Kraan, W.; Kersten, M.J.; et al. High prevalence of MYD88 and CD79B mutations in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2086–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Farre, B.; Ramis-Zaldivar, J.E.; Castrejón De Anta, N.; Rivas-Delgado, A.; Nadeu, F.; Salmeron-Villalobos, J.; Enjuanes, A.; Karube, K.; Balagué, O.; Cobo, F.; et al. Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma Genomic Profile Is Characterized by Alterations in Genes Regulating NF-κB and Immune Checkpoints. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 47, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- René Gerhard Eriksen, P.; de Groot, F.A.; Clasen-Linde, E.; de Nully Brown, P.; de Groen, R.A.L.; Melchior, L.; Maier, A.D.; Minderman, M.; Vermaat, J.S.P.; von Buchwald, C.; et al. Sinonasal DLBCL: Molecular profiling identifies subtypes with distinctive prognoses and targetable genetic features. Blood Adv. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolen, C.R.; Klanova, M.; Trnény, M.; Sehn, L.H.; He, J.; Tong, J.; Paulson, J.N.; Kim, E.; Vitolo, U.; Di Rocco, A.; et al. Prognostic impact of somatic mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and relationship to cell-of-origin: Data from the phase III GOYA study. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, D.; Imber, B.S.; Okwali, M.; Hamlin, P.A.; Kumar, A.; Lahoud, O.B.; Matasar, M.J.; Noy, A.; Owens, C.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. Long-term outcomes of patients with limited-stage ocular adnexal DLBCL treated with combined modality therapy in the rituximab era. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 200, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobillo, S.; Joffe, E.; Lavery, J.A.; Sermer, D.; Ghione, P.; Noy, A.; Caron, P.C.; Hamilton, A.; Hamlin, P.A.; Horwitz, S.M.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of extranodal stage I diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. Blood 2021, 137, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.M.; Young, K.H.; Visco, C.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Orazi, A.; Go, R.S.; Nielsen, O.; Gadeberg, O.V.; Mourits-Andersen, T.; Frederiksen, M.; et al. Immunohistochemical double-hit score is a strong predictor of outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3460–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.A.; Slack, G.W.; Savage, K.J.; Connors, J.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rogic, S.; Scott, D.W.; Tan, K.L.; Steidl, C.; Sehn, L.H.; et al. Concurrent Expression of MYC and BCL2 in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated With Rituximab Plus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, P.N.; Fu, K.; Greiner, T.C.; Smith, L.M.; Delabie, J.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Ott, G.; Rosenwald, A.; Braziel, R.M.; Campo, E.; et al. Immunohistochemical Methods for Predicting Cell of Origin and Survival in Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated With Rituximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaat, J.S.; Pals, S.T.; Younes, A.; Dreyling, M.; Federico, M.; Aurer, I.; Radford, J.; Kersten, M.J. Precision medicine in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Hitting the target. Haematologica 2015, 100, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Hong, F.; Scott, D.W.; Macon, W.R.; King, R.L.; Habermann, T.M.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Casulo, C.; Wade, J.L.; Nagargoje, G.G.; et al. Addition of Lenalidomide to R-CHOP Improves Outcomes in Newly Diagnosed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in a Randomized Phase II US Intergroup Study ECOG-ACRIN E1412. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartert, K.T.; Wenzl, K.; Krull, J.E.; Manske, M.; Sarangi, V.; Asmann, Y.; Larson, M.C.; Maurer, M.J.; Slager, S.; Macon, W.R.; et al. Targeting of Inflammatory Pathways with R2CHOP in High-Risk DLBCL. Leukemia 2021, 35, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arboe, B.; Josefsson, P.; Jørgensen, J.; Haaber, J.; Jensen, P.; Poulsen, C.; Rønnov-Jessen, D.; Pedersen, R.S.; Pedersen, P.; Frederiksen, M.; et al. Danish National Lymphoma Registry. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 8, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, P.P.; Kaplan, H.S.; Musshoff, K.; Smithers, D.W.; Tubiana, M. Report of the Committee on Hodgkin’s Disease Staging Classification. Cancer Res. 1971, 31, 1860–1861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Groen, A.L.; van Eijk, R.; Bohringer, S.; van Wezel, T.; Raghoo, R.; Ruano, D.; Jansen, P.M.; Briaire-De Bruijn, I.; de Groot, F.A.; Kleiverda, K.; et al. Frequent mutated B2M, EZH2, IRF8, and TNFRSF14 in primary bone diffuse large B-cell lymphoma reflect a GCB phenotype. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3760–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, B.A.; Spurdle, A.B.; Plazzer, J.P.; Greenblatt, M.S.; Akagi, K.; Al-Mulla, F.; Bapat, B.; Bernstein, I.; Capellá, G.; Den Dunnen, J.T.; et al. Application of a 5-tiered scheme for standardized classification of 2,360 unique mismatch repair gene variants in the InSiGHT locus-specific database. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzsch, P.; Witten, D.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD: Predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.; Hondelink, L.M.; Solleveld-Westerink, N.; Uljee, S.M.; Ruano, D.; Cleton-Jansen, A.M.; von der Thüsen, J.H.; Ramai, S.R.S.; Postmus, P.E.; Graadt van Roggen, J.F.; et al. Optimizing Mutation and Fusion Detection in NSCLC by Sequential DNA and RNA Sequencing. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardin, F.; Jais, J.P.; Molina, T.J.; Parmentier, F.; Picquenot, J.M.; Ruminy, P.; Tilly, H.; Bastard, C.; Salles, G.A.; Feugier, P.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas with CDKN2A deletion have a distinct gene expression signature and a poor prognosis under R-CHOP treatment: A GELA study. Blood 2010, 116, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runge, H.F.P.; Lacy, S.; Barrans, S.; Beer, P.A.; Painter, D.; Smith, A.; Roman, E.; Burton, C.; Crouch, S.; Tooze, R.; et al. Application of the LymphGen classification tool to 928 clinically and genetically-characterised cases of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, M.K. Ocular adnexal lymphoma: Subtype-specific clinical and genetic features. Acta Ophthalmol. 2022, 100, 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eijk, R.; Stevens, L.; Morreau, H.; van Wezel, T. Assessment of a fully automated high-throughput DNA extraction method from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue for KRAS, and BRAF somatic mutation analysis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 94, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Overall Survival | Progression-Free Survival | Disease-Specific Mortality | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-Rank | Cox Regression | Log-Rank | Cox Regression | Gray’s Test | Cox Regression | Competing Risk Regression | ||||||||||
| n | p | HR | 95% CI | p | p | HR | 95% CI | p | p | HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | |
| MYD88 mutation | 6 | 0.12 | 2.70 | 0.76–9.62 | 0.13 | 0.24 | 2.04 | 0.59–6.99 | 0.26 | 0.66 | 1.62 | 0.29–8.97 | 0.58 | 1.45 | 0.31–6.87 | 0.64 |
| LymphGen MCD | 6 | 0.12 | 3.19 | 0.68–15.0 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 3.19 | 0.68–15.0 | 0.14 | 0.88 | 1.25 | 0.08–20.0 | 0.88 | 1.25 | 0.10–16.4 | 0.87 |
| Cell-of-origin: non-GCB | 9 | 0.85 | 1.11 | 0.34–3.65 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.28–2.83 | 0.85 | 0.59 | 0.64 | 0.12, 3.52 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.13–3.01 | 0.57 |
| Double-expressor | 11 | 0.083 | 2.86 | 0.82–9.94 | 0.098 | 0.20 | 2.12 | 0.66–6.77 | 0.21 | 0.059 | 6.34 | 0.73–54.7 | 0.093 | 5.98 | 0.71–50.4 | 0.10 |
| Rituximab-based chemotherapy | 11 | 0.0089 | 0.19 | 0.05–0.74 | 0.017 | 0.023 | 0.26 | 0.08–0.89 | 0.031 | 0.005 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 5-Year Overall Survival | 5-Year Progression-Free Survival | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | |
| Rituximab | 11 | 0.14 | 0.03–0.59 | 0.008 | 0.21 | 0.06–0.77 | 0.019 |
| MYD88 mutation | 6 | 4.66 | 1.08–20.1 | 0.039 | 2.90 | 0.76–11.0 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vest, S.D.; Eriksen, P.R.G.; de Groot, F.A.; de Groen, R.A.L.; Kleij, A.H.R.; Kirkegaard, M.K.; Kamper, P.; Rasmussen, P.K.; von Buchwald, C.; de Nully Brown, P.; et al. The Genetic Profile of Large B-Cell Lymphomas Presenting in the Ocular Adnexa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063094
Vest SD, Eriksen PRG, de Groot FA, de Groen RAL, Kleij AHR, Kirkegaard MK, Kamper P, Rasmussen PK, von Buchwald C, de Nully Brown P, et al. The Genetic Profile of Large B-Cell Lymphomas Presenting in the Ocular Adnexa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(6):3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063094
Chicago/Turabian StyleVest, Stine Dahl, Patrick Rene Gerhard Eriksen, Fleur A. de Groot, Ruben A. L. de Groen, Anne H. R. Kleij, Marina Knudsen Kirkegaard, Peter Kamper, Peter Kristian Rasmussen, Christian von Buchwald, Peter de Nully Brown, and et al. 2024. "The Genetic Profile of Large B-Cell Lymphomas Presenting in the Ocular Adnexa" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 6: 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063094
APA StyleVest, S. D., Eriksen, P. R. G., de Groot, F. A., de Groen, R. A. L., Kleij, A. H. R., Kirkegaard, M. K., Kamper, P., Rasmussen, P. K., von Buchwald, C., de Nully Brown, P., Kiilgaard, J. F., Vermaat, J. S. P., & Heegaard, S. (2024). The Genetic Profile of Large B-Cell Lymphomas Presenting in the Ocular Adnexa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(6), 3094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063094








