Bioactive TNIIIA2 Sequence in Tenascin-C Is Responsible for Macrophage Foam Cell Transformation; Potential of FNIII14 Peptide Derived from Fibronectin in Suppression of Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation
Abstract
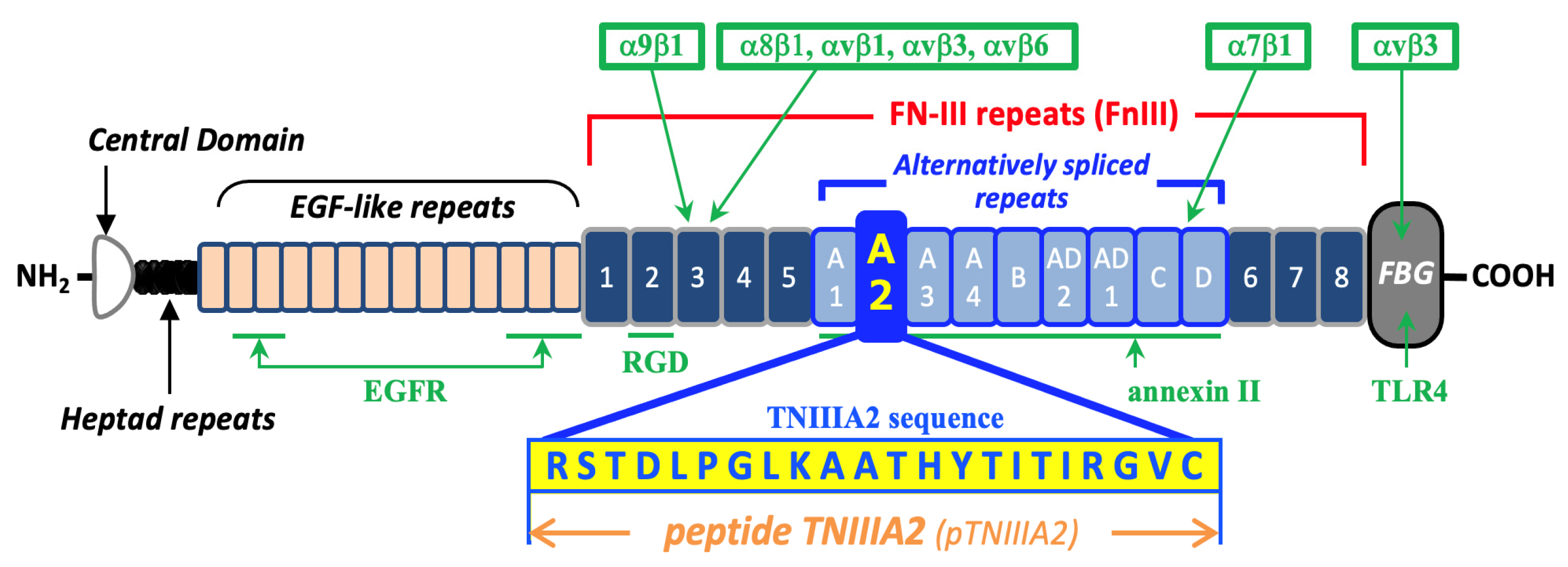
1. Introduction
2. Results
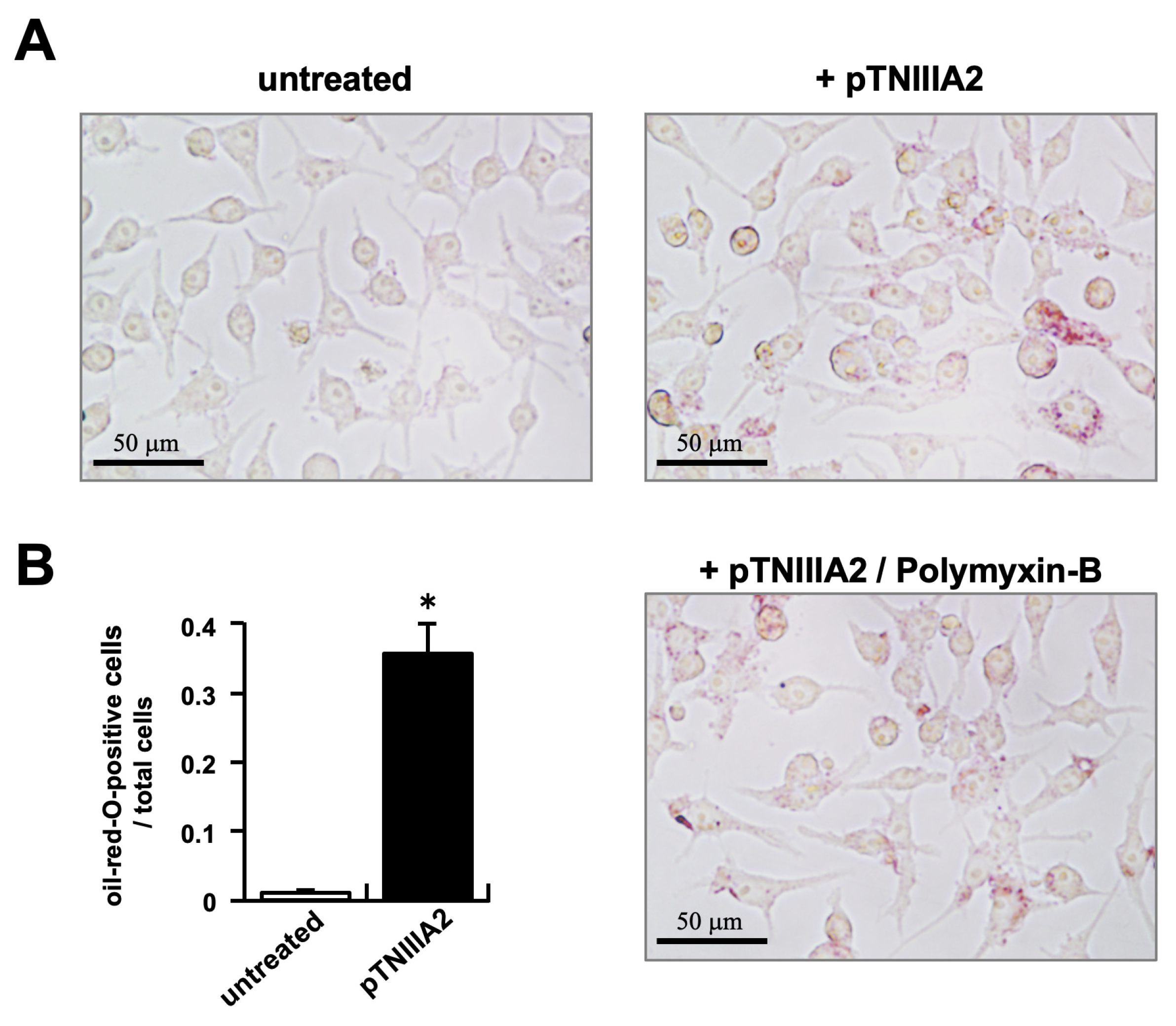
2.1. TNIIIA2 Stimulation in Intracellular Lipid Accumulation
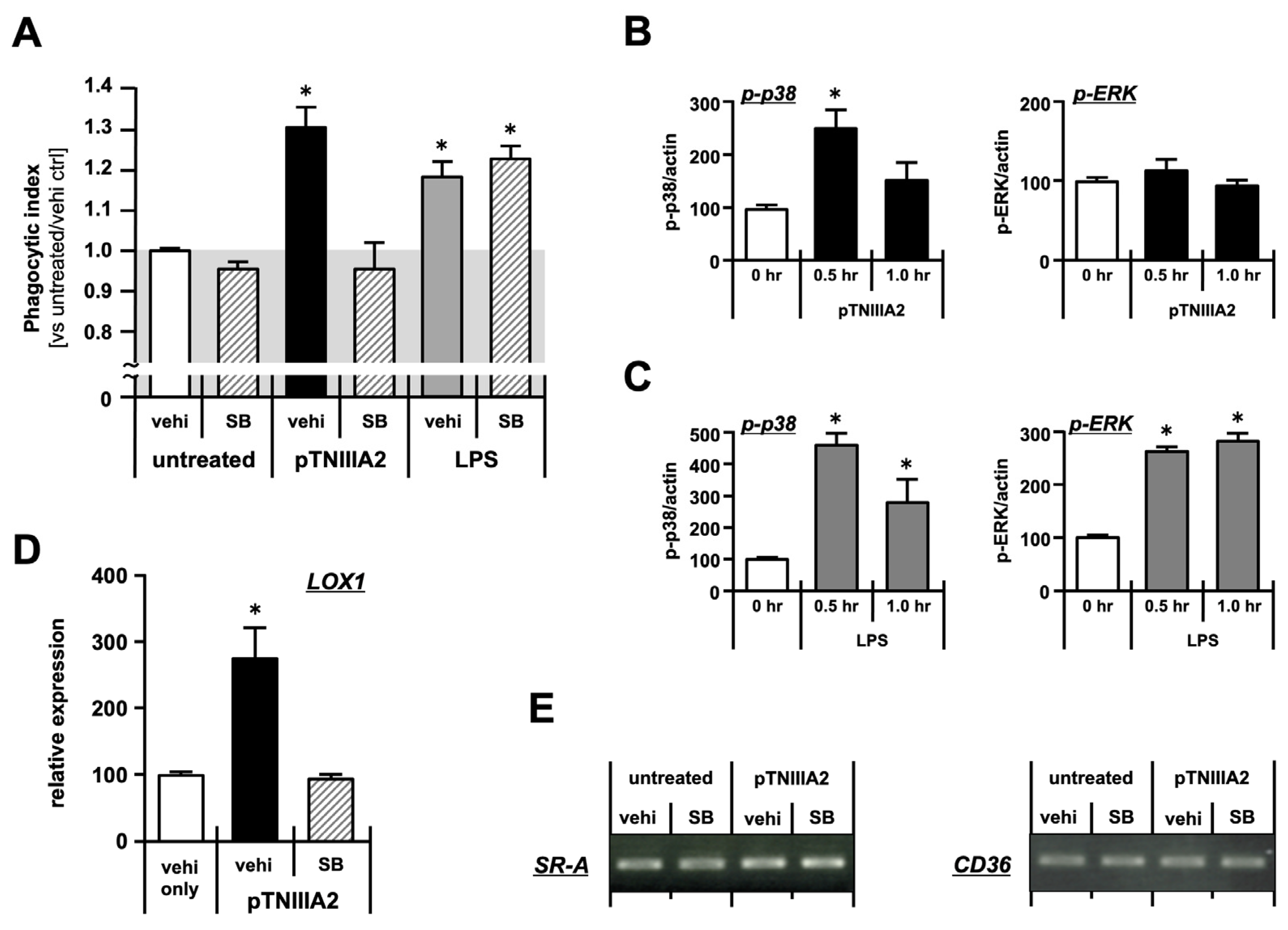
2.2. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Macrophage Foam Cell Formation
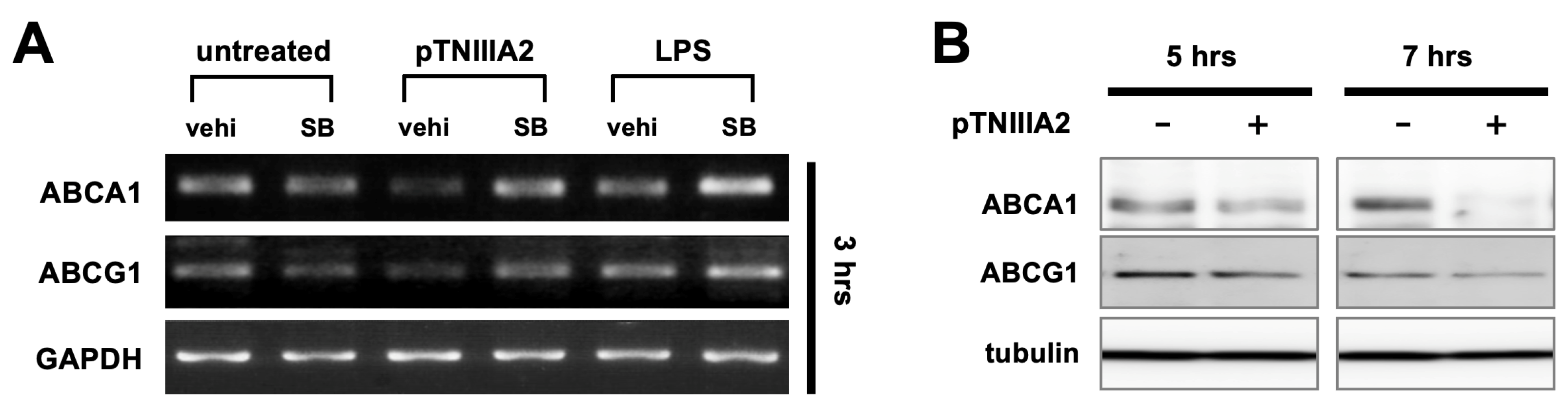
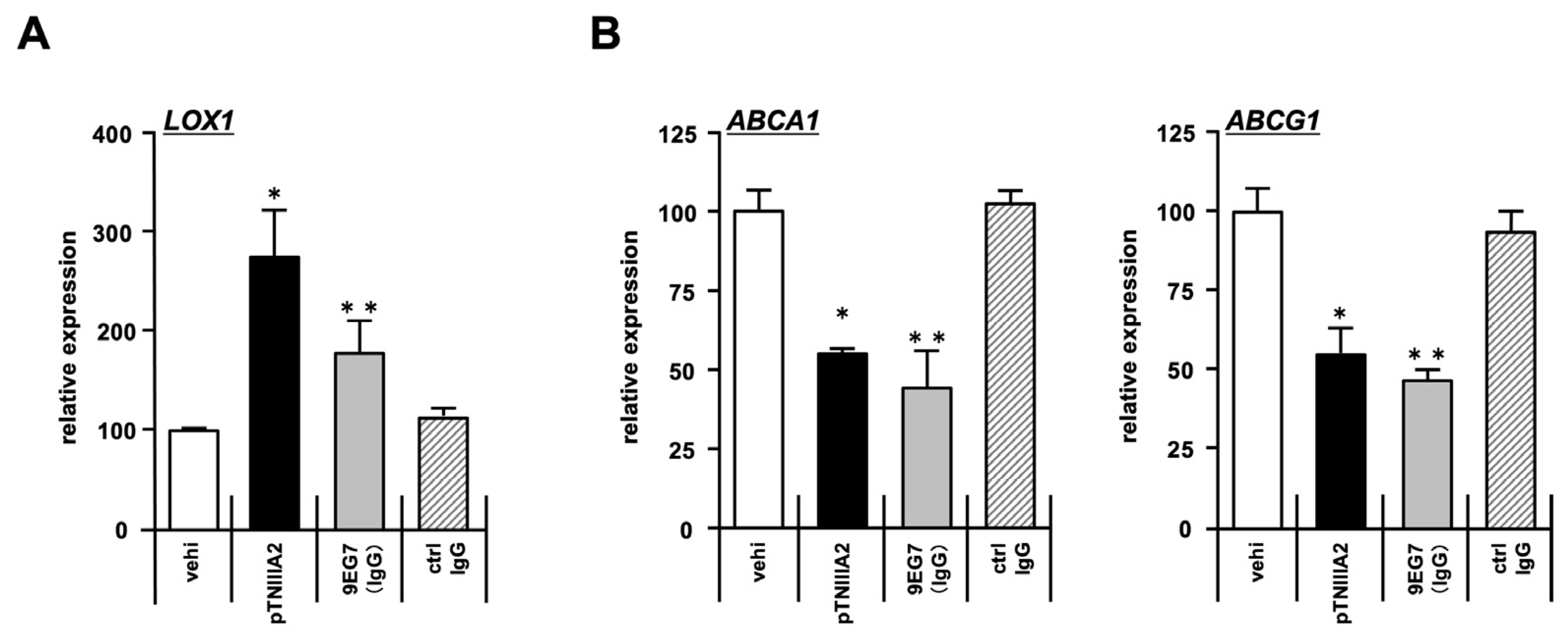
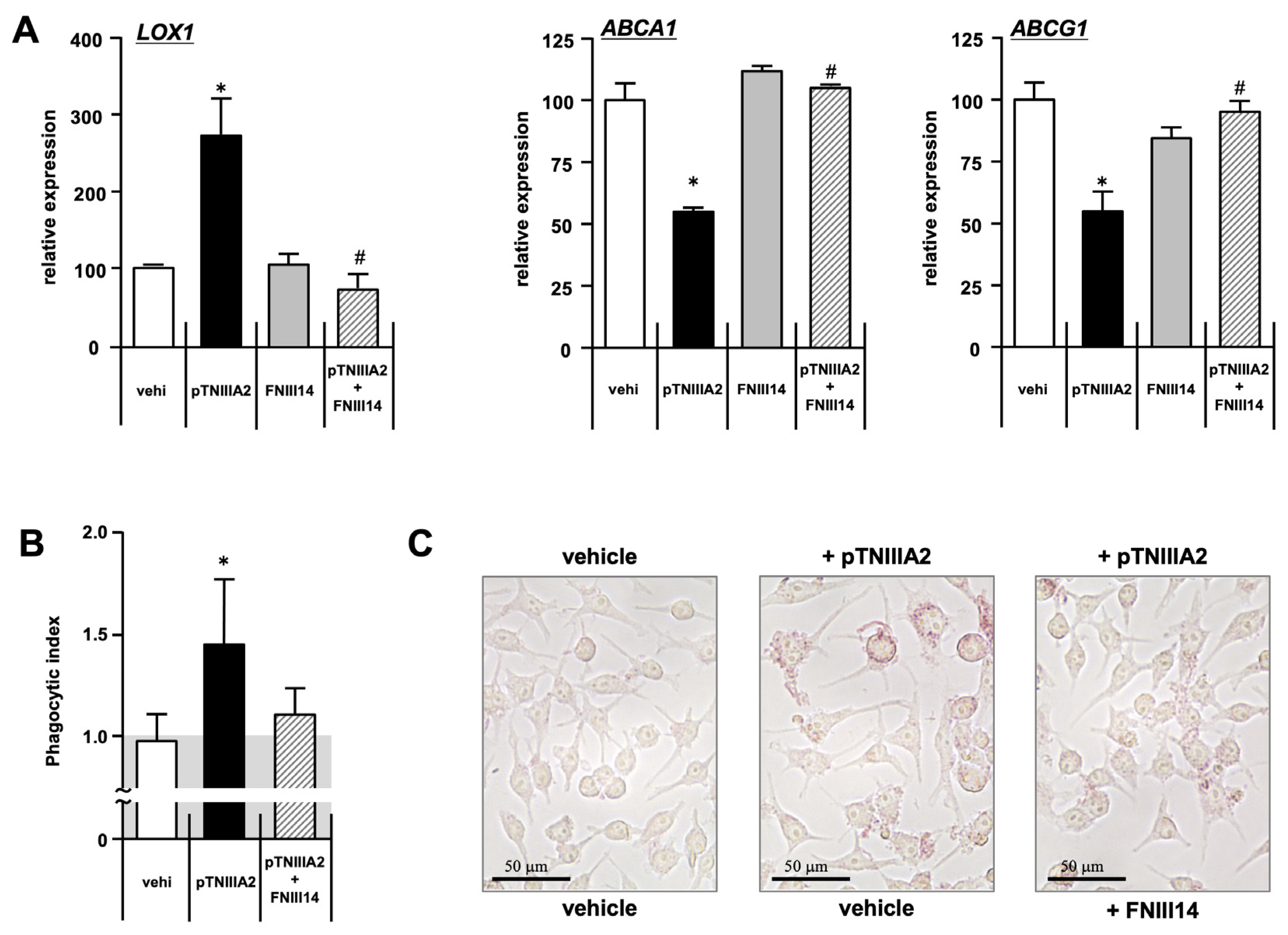
2.3. Effect of pTNIIIA2 on Lipid Transporter Expression
2.4. β1-Integrin Activation in TNIIIA2-Mediated Macrophage Foam Cell Transformation
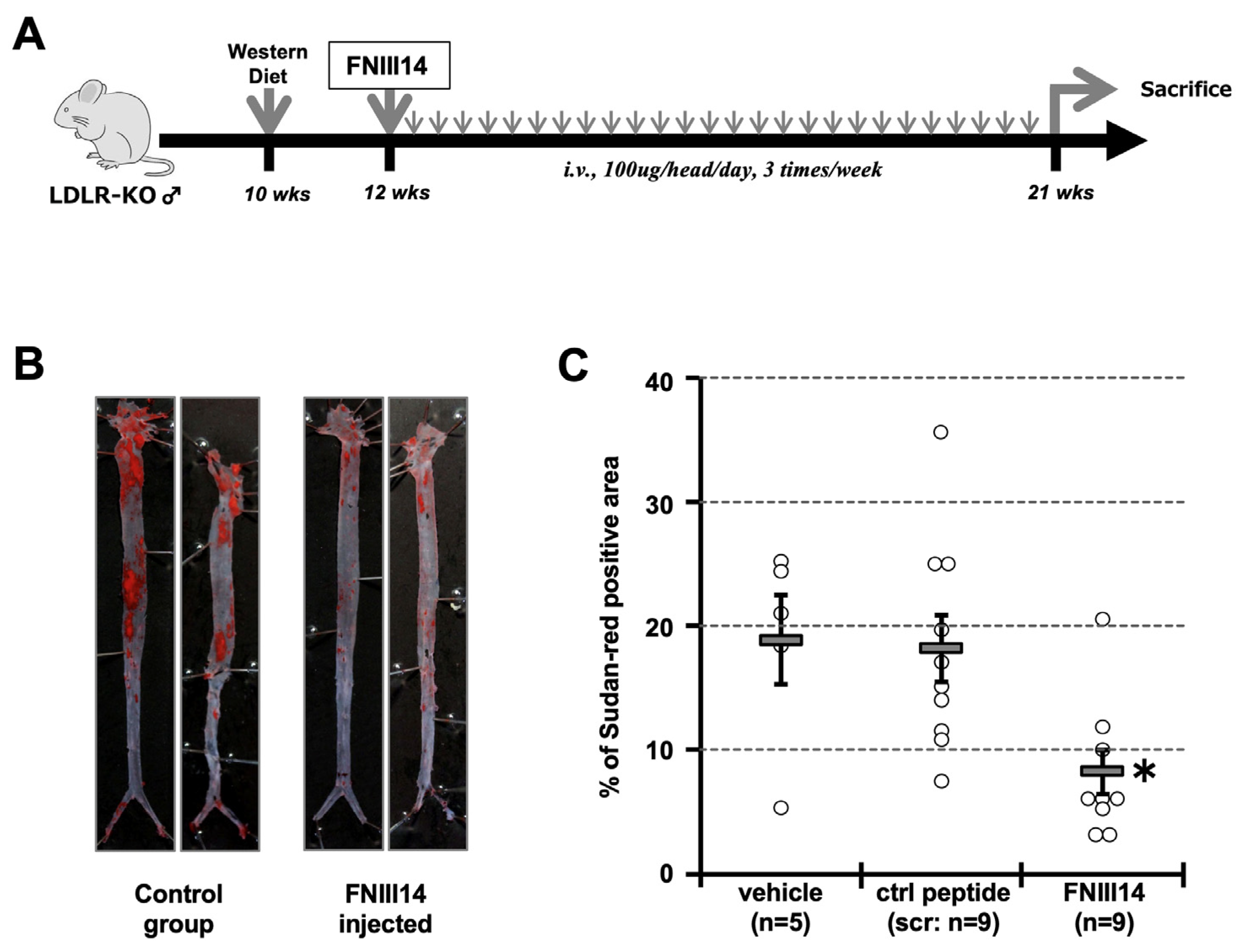
2.5. Forced Inactivation of β1-Integrin in Atherosclerosis Model Mouse
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and ox-LDL Loading
4.3. Phagocytic Assay
4.4. Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay
4.5. Animal Study
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chi, Z.; Melendez, A.J. Role of cell adhesion molecules and immune-cell migration in the initiation, Onset and development of atherosclerosis. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2007, 1, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.S.; Thiagarajan, R.; Willerson, J.T.; Yeh, E.T.H. Inhibition of α4 integrin and ICAM-1 markedly attenuate macrophage homing to atherosclerotic plaques in ApoE-deficient mice. Circulation 1998, 97, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quehenberger, O. Thematic review series: The immune system and atherogenesis. Molecular mechanisms regulating monocyte recruitment in atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiriou, S.N.; Orlova, V.V.; Al-Fakhri, N.; Ihanus, E.; Economopoulou, M.; Isermann, B.; Bdeir, K.; Nawroth, P.P.; Preissner, K.T.; Gahmberg, C.G.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic plaques recruits inflammatory cells through interaction with Mac-1 integrin. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merched, A.; Tollefson, K.; Chan, L. β2 integrins modulate the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 85, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, K.; Ardell, C.L.; Podolnikova, N.P.; Yakubenko, V.P. Distinct migratory properties of M1, M2, and resident macrophages are regulated by αDβ2and αMβ2 integrin-mediated adhesion. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, K.; Podolnikova, N.P.; Bailey, W.; Szmuc, E.; Podrez, E.A.; Byzova, T.V.; Yakubenko, V.P. Inhibition of integrin αDβ2–mediated macrophage adhesion to end product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) oxidation prevents macrophage accumulation during inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 14370–14382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, L.; Huo, Y.; Jung, U.; Ghosh, S.; Manka, D.R.; Sarembock, I.J. Direct Demonstration of P-Selectin– and VCAM-1–dependent mononuclear cell rolling in early atherosclerotic lesions of apolipoprotein E–deficient mice. Circ. Res. 1999, 84, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.; Hafzi-Moghadam, A.; Ley, K. Role of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and fibronectin connecting segment-1 in monocyte rolling and adhesion on early atherosclerotic lesions. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, G.G.; MacPherson, J.A.; Sanders, J.M.; Hesselbacher, S.E.; Feldman, M.J.; MacNamara, C.A.; Gimple, L.W.; Powers, E.R.; Mousa, S.A.; Sarembock, I.J. Selective αvβ3-receptor blockade reduces macrophage infiltration and restenosis after balloon angioplasty in the atherosclerotic rabbit. Circuration 2001, 103, 1906–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkina, E.; Ley, K. Vascular Adhesion Molecules in Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 2292–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, K.; Li, C.; Shah, P.K.; Fishbein, M.C.; Forrester, J.S.; Kaul, S.; Sharifi, B.G. Tenascin-C is Expressed in macrophage-rich human coronary atherosclerotic plaque. Circulation 1999, 99, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanaka-Yoshida, K. Tenascin-C in cardiovascular tissue remodeling: From development to inflammation and repair. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 2513–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satta, J.; Soini, Y.; Pollanen, R.; Paakko, P.; Juvonan, T. Tenascin expression is associated with a chronic inflammation process in abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 1997, 26, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kimra, T.; Yoshimira, K.; Aoki, H.; Imanaka-Yoshida, K.; Yoshida, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Morikage, N.; Endo, H.; Hamano, K.; Imaizumi, T.; et al. Tenascin-C is expressed in abdominal aortic aneurysm tissue with active degradation process. Pathol. Int. 2011, 61, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giblin, S.P.; Midwood, K.S. Tenascin-C: Form versus function. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2015, 9, 48–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Imazeki, H.; Miura, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Okutsu, H.; Harada, Y.; Ohwaki, T.; Nagao, O.; Kamiya, S.; Hayashi, R.; et al. A peptide derived from tenascin-C induces beta1 integrin activation through syndecan-4. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34929–34937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyoda, T.; Fujita, M.; Fukai, F. Biologically Active TNIIIA2 Region in Tenascin-C Molecule: A Major contributor to elicit aggressive malignant phenotypes from tumors/tumor Stroma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 610096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Seki, Y.; Saito, Y.; Kamiya, S.; Fujita, M.; Okutsu, H.; Iyoda, T.; Takai, T.; Owaki, T.; Yajima, H.; et al. Tenascin-C-derived peptide TNIIIA2 highly enhances cell survival and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-dependent cell proliferation through potentiated and sustained activation of integrin α5β1. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 17699–17708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Ito-Fujita, Y.; Iyoda, T.; Sasada, M.; Okada, Y.; Ishibashi, K.; Osawa, T.; Kodama, H.; Fukai, F.; Suzuki, H. Peptide TNIIIA2 derived from tenascin-C contributes to malignant progression in colitis-associated colorectal cancer via β1-integrin activation in fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Iyoda, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Nagai, R.; Kudo, C.; Sasada, M.; Kodama, H.; Fukai, F. Autocrine Production of PDGF Stimulated by the Tenascin-C-derived peptide TNIIIA2 induces hyper-proliferation in glioblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Sasada, M.; Eguchi, M.; Iyoda, T.; Okuyama, S.; Osawa, T.; Tsuzuranuki, K.; Sakamoto, M.; Hagihara, Y.; Matsumura, M.; et al. Induction of cellular senescence in fibroblasts through β1-integrin activation by tenascin-C-derived peptide and its protumor effect. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 4364–4379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Midwood, K.S.; Sacre, S.; Piccinini, A.M.; Inglis, J.; Trebaul, A.; Chan, E.; Drexler, S.; Sofat, N.; Kashiwagi, M.; Orend, G.; et al. Tenascin-C is an endogenous activator of Toll-like receptor 4 that is essential for maintaining inflammation in arthritic joint disease. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shah, P.K.; Wang, W.; Song, L.; Yang, M.; Sharifi, B.G. Tenascin-C deficiency in apo E−/− mouse increases eotaxin levels: Implications for atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2013, 227, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, D.; Zhou, R.; Cai, N.; Lai, Q.; Han, Q.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Lu, J.; Bao, W.; et al. Alginate enhances Toll-like receptor 4-mediated phagocytosis by murin RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, F.; Takahashi, H.; Habu, Y.; Kubushiro, N.; Katayama, T. Fibronectin harbors anti cell adhesive activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 220, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Kamiya, S.; Saito, Y.; Wada, S.; Hayashi, R.; Taira, J.; Kodama, H.; Yajima, H.; Ueki, M.; Fukai, F. Antiadhesive sites present in the fibronectin type III-like repeats of human plasma fibronectin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Shah, P.K.; Song, L.; Yang, M.; Sharifi, B.G. Deletion of tenascin-C gene exacerbates atherosclerosis and induces intraplaque hemorrhage in Apo-E-deficient mice. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2012, 21, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Shiraishi, K.; Furusho, A.; Ito, S.; Hirakata, S.; Nishida, N.; Yoshimura, K.; Imanaka-Yoshida, K.; Yoshida, T.; Ikeda, Y.; et al. Tenascin C protects aorta from acute dissection in mice. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; He, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Ren, Y.; Han, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Tenascin-C Produced by Oxidized LDL-stimulated macrophages increases foam cell formation through Toll-like receptor-4. Mol. Cells 2012, 34, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Onoda, K.; Sawada, Y.; Fujinaga, K.; Imanaka-Yoshida, K.; Simpo, H.; Yoshida, T.; Yada, I. Tenascin-C is an essential factor for neointimal hyperplasia after aortotomy in mice. Cadiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, Y.; Onoda, K.; Imanaka-Yoshida, K.; Maruyama, J.; Yamamoto, K.; Yoshida, T.; Simpo, H. Tenascin-C synthesized in both donor grafts and recipients accelerates artery graft stenosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 74, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinini, A.M.; Zuliani-Alvarez, L.; Lim, J.M.P.; Midwood, K.S. Distinct microenvironmental cues stimulate divergent TLR4-mediated signaling pathways in macrophages. Sci. Signal 2017, 9, ra86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Qiao, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Ma, N. ATF3 inhibits Tenascin-C-induced foam cell formation in LPS-stimulated THP-1 macrophages by suppressing TLR-4. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2015, 22, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Liu, L. HDL slowing down endothelial progenitor cells senescence: A novel anti-atherogenic property of HDL. Med. Hypothesis 2008, 70, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Dinh, A.; Diallo, D.; Delbosc, S.; Maria Varela-Perez, L.; Dang, Q.B.; Lapergie, B.; Burillo, E.; Michel, J.B.; Levoye, A.; Martin-Ventura, J.L.; et al. HDL and endothelial protection. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Ansell, B.J.; Barter, B.J.; Chapman, M.J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Kontush, A.; Tall, A.R.; Webb, N.R. Dysfunctional HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwanska, A.; Grall, D.; Schaub, S.; Divonne, S.B.F.; Ciais, D.; Rekima, S.; Rupp, T.; Sudaka, A.; Orend, G.; Van Obberghen-Schilling, E. Counterbalancing anti-adhesive effect of Tenascin-C through fibronectin expression in endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Ryu, S.Y.; Jung, I.; Lee, Y.; Kang, K.J.; Lee, M.; Lee, M.; Sonn, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.; et al. Evaluation of VCAM-1 antibodies as therapeutic agent for atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis 2012, 3, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, K.D.; Allen, M.D.; McDonald, T.O.; Chait, A.; Harlan, J.M.; Fishbein, D.; McCarty, J.; Ferguson, M.; Hudkins, K.; Benjamin, C.D. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 is expressed in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Implications for the mode of progression of advanced coronary atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, P.T.; Brennan, M.; Vora, D.K.; Territo, M.C.; Strahl, D.; Elices, M.J.; Lusis, A.J.; Berliner, J.A. Blocking Very late antigen-4 integrin decreases leukocyte entry and fatty streak formation in mice fed an atherogenic diet. Circ. Res. 1999, 84, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, Y.; Raines, E.W.; Plump, A.S.; Breslow, J.L.; Ross, R. Upregulation of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 at atherosclerosis-prone sites on the endothelium in the ApoE-deficient mouse. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, T.; Nitzan, R.; Atkinson, W.J.; Deway, C.F., Jr.; Gimbrone, M.A., Jr. Shere stress selectivily upregulates intracellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in cultured human vascular endothelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Ishida, T.; Yasuda, T.; Toh, R.; Hara, T.; Cangara, H.M.; Rikitake, Y.; Taira, K.; Sun, L.; Kundu, R.K.; et al. Endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule modulates atherosclerosis through plaque angio-genesis and monocyte–endothelial interaction. Microvasc. Res. 2010, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, S.E.; O’Connell, R.M.; Miranda, G.A.; Vaidya, S.A.; Chow, E.K.; Liu, P.T.; Suzuki, S.; Suzuki, N.; Modlin, R.L.; Yeh, W.; et al. Toll-loke receptors induce a phagocytic gene program through p38. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 199, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, M.D.; Shaposhnik, Z.; Meng, Y.; Rosales, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Ratiner, B.; Zadini, F.; Zadini, G.; Lusis, A.J. Hyodeoxycholic acid improves HDL function and inhibits atherosclerotic lesion formation in LDLR-knockout mice. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 3805–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.D.; Brown, K.K.; Silvestre, M.J.; Willson, T.M.; Palinski, W.; Glass, C.K. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ ligands inhibit development of atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2000, 106, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOX1 | Fw: | 5′- | GTGGACACAATTACGCCAGGTA | -3′ |
| Rv: | 5′- | GCCCTTCCAGGATACGATCC | -3′ | |
| ABCA1 | Fw: | 5′- | CTTCCCACATTTTTGCCTGG | -3′ |
| Rv: | 5′- | AAGGTTCCGTCCTACCAAGTC | -3′ | |
| ABCG1 | Fw: | 5′- | CTGTCTGATG GCCGCTTTCT | -3′ |
| Rv: | 5′- | CTGGACACGACCTCGTCCAC | -3′ | |
| SR-A | Fw: | 5′- | CATGAACGAGAGGATGCTGACT | -3′ |
| Rv: | 5′- | GGAAGGGATGCTGTCATTGAA | -3′ | |
| CD36 | Fw: Rv: | 5′- 5’- | TCCAGCCAATGCCTTTGC TGGAGATTACTTTTCAGTGCAGAA | -3′ -3’ |
| GAPDH | Fw: | 5′- | TTCACCACCATGGAGAAGGC | -3′ |
| Rv: | 5′- | GGCATGGACTGTGGTCATGA | -3′ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iyoda, T.; Ohishi, A.; Wang, Y.; Yokoyama, M.-S.; Kazama, M.; Okita, N.; Inouye, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Shimano, H.; Fukai, F. Bioactive TNIIIA2 Sequence in Tenascin-C Is Responsible for Macrophage Foam Cell Transformation; Potential of FNIII14 Peptide Derived from Fibronectin in Suppression of Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031825
Iyoda T, Ohishi A, Wang Y, Yokoyama M-S, Kazama M, Okita N, Inouye S, Nakagawa Y, Shimano H, Fukai F. Bioactive TNIIIA2 Sequence in Tenascin-C Is Responsible for Macrophage Foam Cell Transformation; Potential of FNIII14 Peptide Derived from Fibronectin in Suppression of Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(3):1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031825
Chicago/Turabian StyleIyoda, Takuya, Asayo Ohishi, Yunong Wang, Miyabi-Shara Yokoyama, Mika Kazama, Naoyuki Okita, Sachiye Inouye, Yoshimi Nakagawa, Hitoshi Shimano, and Fumio Fukai. 2024. "Bioactive TNIIIA2 Sequence in Tenascin-C Is Responsible for Macrophage Foam Cell Transformation; Potential of FNIII14 Peptide Derived from Fibronectin in Suppression of Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 3: 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031825
APA StyleIyoda, T., Ohishi, A., Wang, Y., Yokoyama, M.-S., Kazama, M., Okita, N., Inouye, S., Nakagawa, Y., Shimano, H., & Fukai, F. (2024). Bioactive TNIIIA2 Sequence in Tenascin-C Is Responsible for Macrophage Foam Cell Transformation; Potential of FNIII14 Peptide Derived from Fibronectin in Suppression of Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(3), 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25031825








