Angiotensin-(1-7) and Central Control of Cardiometabolic Outcomes: Implications for Obesity Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Angiotensin II Pathways
3. Angiotensin-(1-7) Pathways
3.1. Angiotensin-(1-7) Mas Receptors
3.2. Cardiometabolic Effects of Systemic Angiotensin-(1-7) Administration
4. Central Angiotensin-(1-7) and MasR
Cardiometabolic Effects of Intracerebroventricular Angiotensin-(1-7) Administration
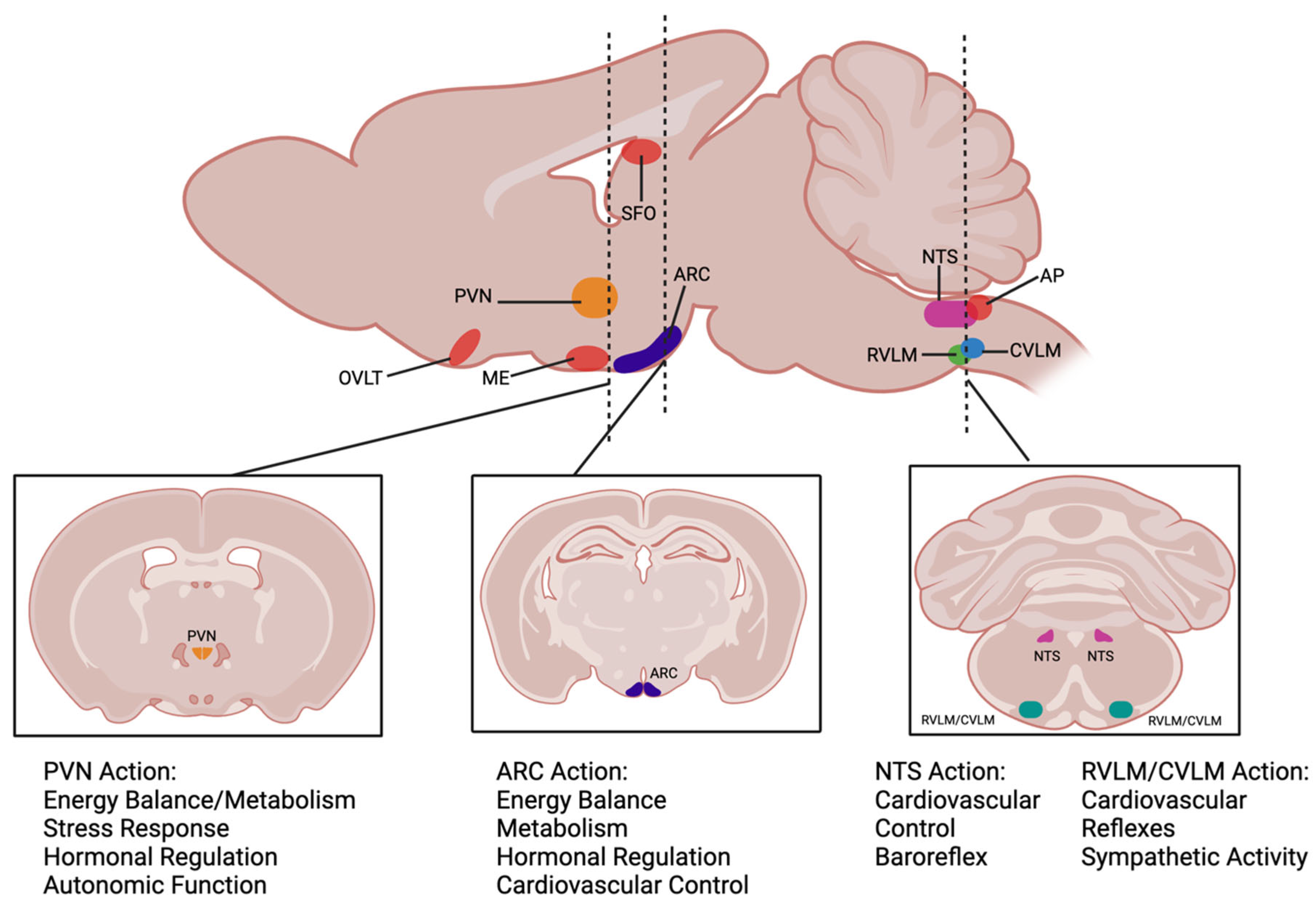
5. Ang-(1-7) Modulation of Cardiometabolic Function via the Brainstem and Hypothalamus
5.1. Nucleus Tractus Solitarius
5.2. Caudal Ventrolateral Medulla
5.3. Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla
5.4. Arcuate Nucleus
5.5. Paraventricular Nucleus
6. Clinical Implications
7. Conclusions and Future Directions for Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esunge, P.M. From Blood Pressure to Hypertension: The History of Research. J. R. Soc. Med. 1991, 84, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saklayen, M.G.; Deshpande, N.V. Timeline of History of Hypertension Treatment. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, W.C. Discovery of the Cardiovascular System: From Galen to William Harvey. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9 (Suppl. S1), 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.S.; Podolsky, S.H.; Greene, J.A. The Burden of Disease and the Changing Task of Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalen, J.E.; Alpert, J.S.; Goldberg, R.J.; Weinstein, R.S. The Epidemic of the 20th Century: Coronary Heart Disease. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The Global Epidemiology of Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvanova, A.; Reseghetti, E.; Abbate, M.; Ruggenenti, P. Mechanisms and Treatment of Obesity-Related Hypertension-Part 1: Mechanisms. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfad282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariq, O.A.; McKenzie, T.J. Obesity-Related Hypertension: A Review of Pathophysiology, Management, and the Role of Metabolic Surgery. Gland. Surg. 2020, 9, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marketou, M.; Gupta, Y.; Jain, S.; Vardas, P. Differential Metabolic Effects of Beta-Blockers: An Updated Systematic Review of Nebivolol. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2017, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; Gadde, K.M. Weight Loss Medications in the Treatment of Obesity and Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2019, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Blüher, M.; Tschöp, M.H.; DiMarchi, R.D. Anti-Obesity Drug Discovery: Advances and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.J.; Arnold, A.C. The Renin–Angiotensin System in Cardiovascular Autonomic Control: Recent Developments and Clinical Implications. Clin. Auton. Res. 2019, 29, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, F.P.; Gironacci, M.M.; Narvaez Pardo, J.A. Therapeutic Opportunities in Targeting the Protective Arm of the Renin-Angiotensin System to Improve Insulin Sensitivity: A Mechanistic Review. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.C.; Fleeman, R.; Arnold, A.C. Sex Differences in the Metabolic Effects of the Renin-Angiotensin System. Biol. Sex. Differ. 2019, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.A. Angiotensin-(1-7). Hypertension 2014, 63, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, D.; Arnold, A.C. Angiotensin-(1-7): Translational Avenues in Cardiovascular Control. Am. J. Hypertens. 2019, 32, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-H.; Mohammadmoradi, S.; Chen, J.Z.; Sawada, H.; Daugherty, A.; Lu, H.S. Renin-Angiotensin System and Cardiovascular Functions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, e108–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, G.A.; Esnault, V.L.M.; Van Obberghen, E. Modulation of Glucose Metabolism by the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E435–E449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiderski, J.; Gadanec, L.K.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Moore, G.J.; Kelaidonis, K.; Matsoukas, J.M.; Zulli, A. Role of Angiotensin II in Cardiovascular Diseases: Introducing Bisartans as a Novel Therapy for Coronavirus 2019. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, L.; Menikdiwela, K.; LeMieux, M.; Dufour, J.M.; Kaur, G.; Kalupahana, N.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. The Renin Angiotensin System, Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Function in Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, J.S.; Randhawa, A.K.; Wharton, S.; Edgell, H.; Kuk, J.L. The Association between Antihypertensive Medication Use and Blood Pressure is Influenced by Obesity. J. Obes. 2018, 2018, 4573258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acelajado, M.C.; Hughes, Z.H.; Oparil, S.; Calhoun, D.A. Treatment of Resistant and Refractory Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendse, L.B.; Danser, A.H.J.; Poglitsch, M.; Touyz, R.M.; Burnett, J.C.; Llorens-Cortes, C.; Ehlers, M.R.; Sturrock, E.D. Novel Therapeutic Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System and Associated Peptides in Hypertension and Heart Failure. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 539–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, B.; Jadhav, U.; Singhai, P.; Sadhanandham, S.; Shah, N. ACEI-Induced Cough: A Review of Current Evidence and Its Practical Implications for Optimal CV Risk Reduction. Indian Heart J. 2020, 72, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, C.; Cicero, A.F.; Agnoletti, D.; Fiorini, G. Pathophysiology of Cough with Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors: How to Explain within-Class Differences? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 110, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostchega, Y.; Fryar, C.D.; Nwankwo, T.; Nguyen, D.T. Hypertension Prevalence Among Adults Aged 18 and Over: United States, 2017–2018; NCHS Data Brief, no 364; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2020.
- Allred, A.J.; Diz, D.I.; Ferrario, C.M.; Chappell, M.C. Pathways for Angiotensin-(1-7) Metabolism in Pulmonary and Renal Tissues. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2000, 279, F841–F850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loloi, J.; Miller, A.J.; Bingaman, S.S.; Silberman, Y.; Arnold, A.C. Angiotensin-(1-7) Contributes to Insulin-Sensitizing Effects of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition in Obese Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E1204–E1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.A.S.; Sampaio, W.O.; Alzamora, A.C.; Motta-Santos, D.; Alenina, N.; Bader, M.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. The ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS Axis of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Focus on Angiotensin-(1-7). Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 505–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.B.; Zhong, J.-C.; Grant, M.B.; Oudit, G.Y. Role of the ACE2/Angiotensin 1–7 Axis of the Renin–Angiotensin System in Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regenhardt, R.W.; Desland, F.; Mecca, A.P.; Pioquinto, D.J.; Afzal, A.; Mocco, J.; Sumners, C. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Angiotensin-(1-7) in Ischemic Stroke. Neuropharmacology 2013, 71, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benter, I.F.; Ferrario, C.M.; Morris, M.; Diz, D.I. Antihypertensive Actions of Angiotensin-(1-7) in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 269, H313–H319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loot, A.E.; Roks, A.J.M.; Henning, R.H.; Tio, R.A.; Suurmeijer, A.J.H.; Boomsma, F.; van Gilst, W.H. Angiotensin-(1-7) Attenuates the Development of Heart Failure after Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Circulation 2002, 105, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, H.; Mori, J.; Nakajima, H.; Kawabe, Y.; Tsuma, Y.; Fukuhara, S.; Kodo, K.; Ikoma, K.; Matoba, S.; Oudit, G.Y.; et al. Angiotensin 1–7 Stimulates Brown Adipose Tissue and Reduces Diet-Induced Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 314, E131–E138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ren, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, B.; Han, Y. Angiotensin-(1-7) Abrogates Angiotensin II-Induced Proliferation, Migration and Inflammation in VSMCs through Inactivation of ROS-Mediated PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Yang, F.; Huang, X.; Meng, J.; Chen, J.; Bader, M.; Penninger, J.M.; Fung, E.; Yu, X.; Lan, H. Dual Deficiency of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme-2 and Mas Receptor Enhances Angiotensin II-induced Hypertension and Hypertensive Nephropathy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 13093–13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, R.; Bader, M.; Ludwig, T.; Berberich, C.; Bunnemann, B.; Ganten, D. Expression of the Mouse and Rat Mas Proto-Oncogene in the Brain and Peripheral Tissues. FEBS Lett. 1995, 357, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.A.S.; Simoes e Silva, A.C.; Maric, C.; Silva, D.M.R.; Machado, R.P.; de Buhr, I.; Heringer-Walther, S.; Pinheiro, S.V.B.; Lopes, M.T.; Bader, M.; et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) Is an Endogenous Ligand for the G Protein-Coupled Receptor Mas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8258–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, W.O.; Henrique de Castro, C.; Santos, R.A.S.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Touyz, R.M. Angiotensin-(1-7) Counterregulates Angiotensin II Signaling in Human Endothelial Cells. Hypertension 2007, 50, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, W.O.; Souza dos Santos, R.A.; Faria-Silva, R.; da Mata Machado, L.T.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Touyz, R.M. Angiotensin-(1-7) through Receptor Mas Mediates Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Activation via Akt-Dependent Pathways. Hypertension 2007, 49, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, L.T.; Gallagher, P.E.; Ann Tallant, E. Angiotensin-(1-7) Attenuates Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiac Remodeling Associated with Upregulation of Dual-Specificity Phosphatase 1. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H801–H810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povlsen, A.; Grimm, D.; Wehland, M.; Infanger, M.; Krüger, M. The Vasoactive Mas Receptor in Essential Hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, M.; Alenina, N.; Young, D.; Santos, R.A.S.; Touyz, R.M. The Meaning of Mas. Hypertension 2018, 72, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galandrin, S.; Denis, C.; Boularan, C.; Marie, J.; M’Kadmi, C.; Pilette, C.; Dubroca, C.; Nicaise, Y.; Seguelas, M.-H.; N’Guyen, D.; et al. Cardioprotective Angiotensin-(1–7) Peptide Acts as a Natural-Biased Ligand at the Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor. Hypertension 2016, 68, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.B.; Parreiras-E-Silva, L.T.; Bruder-Nascimento, T.; Duarte, D.A.; Simões, S.C.; Costa, R.M.; Rodríguez, D.Y.; Ferreira, P.A.B.; Silva, C.A.A.; Abrao, E.P.; et al. Ang-(1-7) Is an Endogenous β-Arrestin-Biased Agonist of the AT1 Receptor with Protective Action in Cardiac Hypertrophy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, R.D.; Lima, C.V.; Khosla, M.C.; Santos, R.A. Angiotensin-(1-7) Potentiates the Hypotensive Effect of Bradykinin in Conscious Rats. Hypertension 1995, 26, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, P.E.; Gaspari, T.A.; Widdop, R.E. Angiotensin-(1-7) Acts as a Vasodepressor Agent via Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptors in Conscious Rats. Hypertension 2005, 45, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feterik, K.; Smith, L.; Katusic, Z.S. Angiotensin-(1-7) Causes Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation in Canine Middle Cerebral Artery. Brain Res. 2000, 873, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzner, A.; Gebolys, K.; Meinert, C.; Klein, S.; Uhlich, A.; Trebicka, J.; Villacañas, Ó.; Walther, T. G-Protein-Coupled Receptor MrgD Is a Receptor for Angiotensin-(1-7) Involving Adenylyl Cyclase, cAMP, and Phosphokinase A. Hypertension 2016, 68, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayorh, M.A.; Eatman, D.; Walton, M.; Socci, R.R.; Thierry-Palmer, M.; Emmett, N. 1A-779 Attenuates Angiotensin-(1-7) Depressor Response in Salt-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Peptides 2002, 23, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, C.-X.; Chen, X.-R.; Liu, B.-X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.-Z.; Sun, W.; Li, P.; Kong, X.-Q. Alamandine Attenuates Hypertension and Cardiac Hypertrophy in Hypertensive Rats. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Luo, M.; Yong, Y.; Zhong, S.; Li, P. Alamandine Alleviates Hypertension and Renal Damage via Oxidative-Stress Attenuation in Dahl Rats. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesus, I.C.G.; Scalzo, S.; Alves, F.; Marques, K.; Rocha-Resende, C.; Bader, M.; Santos, R.A.S.; Guatimosim, S. Alamandine Acts via MrgD to Induce AMPK/NO Activation against ANG II Hypertrophy in Cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2018, 314, C702–C711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, I.M.; Otero, Y.F.; Bracy, D.P.; Wasserman, D.H.; Biaggioni, I.; Arnold, A.C. Chronic Angiotensin-(1-7) Improves Insulin Sensitivity in High-Fat Fed Mice Independent of Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2016, 67, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.A.; Barbosa, C.M.; Lima, T.C.; Dos Santos, R.A.S.; Alzamora, A.C. The Novel Angiotensin-(1-7) Analog, A-1317, Improves Insulin Resistance by Restoring Pancreatic β-Cell Functionality in Rats with Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerri, G.C.; Santos, S.H.S.; Bader, M.; Santos, R.A.S. Brown Adipose Tissue Transcriptome Unveils an Important Role of the Beta-Alanine/Alamandine Receptor, MrgD, in Metabolism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 114, 109268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecca, A.P.; Regenhardt, R.W.; O’Connor, T.E.; Joseph, J.P.; Raizada, M.K.; Katovich, M.J.; Sumners, C. Cerebroprotection by Angiotensin-(1-7) in Endothelin-1-Induced Ischaemic Stroke. Exp. Physiol. 2011, 96, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhns, R.P.; Sulaiman, M.I.; Gaub, M.; Bae, E.H.; Davidson Knapp, R.B.; Larson, A.R.; Smith, A.; Coleman, D.L.; Staatz, W.D.; Sandweiss, A.J.; et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) Improves Cognitive Function and Reduces Inflammation in Mice Following Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 903980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittimalli, K.; Jahan, J.; Sakamuri, A.; McAdams, Z.L.; Ericsson, A.C.; Jarajapu, Y.P.R. Restoration of the Gut Barrier Integrity and Restructuring of the Gut Microbiome in Aging by Angiotensin-(1-7). Clin. Sci. 2023, 137, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütten, M.T.J.; Houben, A.J.H.M.; de Leeuw, P.W.; Stehouwer, C.D.A. The Link Between Adipose Tissue Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Signaling and Obesity-Associated Hypertension. Physiology 2017, 32, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.K.; Etelvino, G.M.; Walther, T.; Santos, R.A.S.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. Immunofluorescence Localization of the Receptor Mas in Cardiovascular-Related Areas of the Rat Brain. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H1416–H1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleegal-DeMotta, M.A.; Doghu, S.; Banks, W.A. Angiotensin II Modulates BBB Permeability via Activation of the AT1 Receptor in Brain Endothelial Cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2009, 29, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Fang, C.; Ma, Y.; Chang, J. Obesity-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction: Phenotypes and Mechanisms. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancardi, V.C.; Stern, J.E. Compromised Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability: Novel Mechanism by Which Circulating Angiotensin II Signals to Sympathoexcitatory Centres during Hypertension. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhea, E.M.; Salameh, T.S.; Logsdon, A.F.; Hanson, A.J.; Erickson, M.A.; Banks, W.A. Blood-Brain Barriers in Obesity. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Venegas, V.; Flores-Torres, R.P.; Rodríguez-Cortés, Y.M.; Rodríguez-Retana, D.; Ramírez-Carreto, R.J.; Concepción-Carrillo, L.E.; Pérez-Flores, L.J.; Alarcón-Aguilar, A.; López-Díazguerrero, N.E.; Gómez-González, B.; et al. The Obese Brain: Mechanisms of Systemic and Local Inflammation, and Interventions to Reverse the Cognitive Deficit. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 798995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancardi, V.C.; Son, S.J.; Ahmadi, S.; Filosa, J.A.; Stern, J.E. Circulating Angiotensin II Gains Access to the Hypothalamus and Brain Stem during Hypertension via Breakdown of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Hypertension 2014, 63, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, A.; Lazartigues, E. The Compensatory Renin-Angiotensin System in the Central Regulation of Arterial Pressure: New Avenues and New Challenges. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 9, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, M.C.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Diz, D.I.; Ferrario, C.M. Identification of Angiotensin-(1-7) in Rat Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 16518–16523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.; Eldahshan, W.; Fagan, S.C.; Ergul, A. Within the Brain: The Renin Angiotensin System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, M.; Walther, T.; von Bohlen und Halbach, O. Immunohistochemical Localization of the Angiotensin-(1-7) Receptor Mas in the Murine Forebrain. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 348, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Heringer, S.B.; Batista, E.N.; Khosla, M.C.; Santos, R.A. Differential Baroreceptor Reflex Modulation by Centrally Infused Angiotensin Peptides. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 263, R89–R94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nautiyal, M.; Shaltout, H.A.; de Lima, D.C.; do Nascimento, K.; Chappell, M.C.; Diz, D.I. Central Angiotensin-(1-7) Improves Vagal Function Independent of Blood Pressure in Hypertensive (mRen2)27 Rats. Hypertension 2012, 60, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, J.M.; Allen, M.; Herbert, J.; Fitzsimons, J.T. The Association of Thirst, Sodium Appetite and Vasopressin Release with c-Fos Expression in the Forebrain of the Rat after Intracerebroventricular Injection of Angiotensin II, Angiotensin-(1-7) or Carbachol. Neuroscience 1995, 69, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimaraes, P.S.; Santiago, N.M.; Xavier, C.H.; Velloso, E.P.P.; Fontes, M.A.P.; Santos, R.A.S.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. Chronic Infusion of Angiotensin-(1-7) into the Lateral Ventricle of the Brain Attenuates Hypertension in DOCA-Salt Rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 303, H393–H400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangussu, L.M.; Guimaraes, P.S.; Nadu, A.P.; Melo, M.B.; Santos, R.A.S.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. Activation of Angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas Axis in the Brain Lowers Blood Pressure and Attenuates Cardiac Remodeling in Hypertensive Transgenic (mRen2)27 Rats. Neuropharmacology 2015, 97, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Gao, L.; Shi, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Angiotensin-(1-7) Modulates Renin-Angiotensin System Associated with Reducing Oxidative Stress and Attenuating Neuronal Apoptosis in the Brain of Hypertensive Rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 67, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangussu, L.M.; Melo-Braga, M.N.; de Souza Lima, B.S.; Santos, R.A.S.; de Andrade, H.M.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. Angiotensin-(1-7) Central Mechanisms After ICV Infusion in Hypertensive Transgenic (mRen2)27 Rats. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 624249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendricks, A.S.; Lawson, M.J.; Figueroa, J.P.; Chappell, M.C.; Diz, D.I.; Shaltout, H.A. Central ANG-(1-7) Infusion Improves Blood Pressure Regulation in Antenatal Betamethasone-Exposed Sheep and Reveals Sex-Dependent Effects on Oxidative Stress. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 316, H1458–H1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villela, D.C.; Passos-Silva, D.G.; Santos, R.A.S. Alamandine: A New Member of the Angiotensin Family. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimaraes, P.S.; Oliveira, M.F.; Braga, J.F.; Nadu, A.P.; Schreihofer, A.; Santos, R.A.S.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. Increasing Angiotensin-(1-7) Levels in the Brain Attenuates Metabolic Syndrome-Related Risks in Fructose-Fed Rats. Hypertension 2014, 63, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, F.S.; Bartness, T.J. Central Angiotensin 1-7 Triggers Brown Fat Thermogenesis. Physiol. Rep. 2023, 11, e15621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapouckey, S.A.; Deng, G.; Sigmund, C.D.; Grobe, J.L. Potential Mechanisms of Hypothalamic Renin-Angiotensin System Activation by Leptin and DOCA-Salt for the Control of Resting Metabolism. Physiol. Genom. 2017, 49, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dampney, R.A.; Michelini, L.C.; Li, D.-P.; Pan, H.-L. Regulation of Sympathetic Vasomotor Activity by the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus in Normotensive and Hypertensive States. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H1200–H1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dampney, R.A.L. Central Neural Control of the Cardiovascular System: Current Perspectives. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2016, 40, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccal, D.B.; Furuya, W.I.; Bassi, M.; Colombari, D.S.A.; Colombari, E. The Nucleus of the Solitary Tract and the Coordination of Respiratory and Sympathetic Activities. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Diz, D.I.; Santos, R.A.; Khosla, M.C.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Ferrario, C.M. Cardiovascular Effects of Angiotensin-(1-7) Injected into the Dorsal Medulla of Rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1989, 257, H324–H329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz, D.I.; Garcia-Espinosa, M.A.; Gallagher, P.E.; Ganten, D.; Ferrario, C.M.; Averill, D.B. Angiotensin-(1-7) and Baroreflex Function in Nucleus Tractus Solitarii of (mRen2)27 Transgenic Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 51, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, G.Z.; Caligiorne, S.M.; Santos, R.A.; Khosla, M.C.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. Modulation of the Baroreflex Control of Heart Rate by Angiotensin-(1-7) at the Nucleus Tractus Solitarii of Normotensive and Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. J. Hypertens. 2000, 18, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, T.S.; Sato, M.A.; Takakura, A.C.T.; Menani, J.V.; Colombari, E. Role of Pressor Mechanisms from the NTS and CVLM in Control of Arterial Pressure. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 289, R1416–R1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cravo, S.L.; Morrison, S.F.; Reis, D.J. Differentiation of Two Cardiovascular Regions within Caudal Ventrolateral Medulla. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 261, R985–R994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cangussu, L.M.; de Castro, U.G.M.; do Pilar Machado, R.; Silva, M.E.; Ferreira, P.M.; dos Santos, R.A.S.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Alzamora, A.C. Angiotensin-(1-7) Antagonist, A-779, Microinjection into the Caudal Ventrolateral Medulla of Renovascular Hypertensive Rats Restores Baroreflex Bradycardia. Peptides 2009, 30, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, G.G.; Barbosa, M.A.; Barbosa, C.M.; Lima, T.C.; Souza Dos Santos, R.A.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Alzamora, A.C. Different Reactive Species Modulate the Hypotensive Effect Triggered by Angiotensins at CVLM of 2K1C Hypertensive Rats. Peptides 2020, 134, 170409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerrato, B.D.; Frasch, A.P.; Nakagawa, P.; Longo-Carbajosa, N.; Peña, C.; Höcht, C.; Gironacci, M.M. Angiotensin-(1-7) Upregulates Central Nitric Oxide Synthase in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Brain Res. 2012, 1453, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzamora, A.C.; Santos, R.a.S.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. Hypotensive Effect of ANG II and ANG-(1-7) at the Caudal Ventrolateral Medulla Involves Different Mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 283, R1187–R1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, E.R.; Barbosa, C.M.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Santos, R.a.S.; Alzamora, A.C. Hypotensive Effect Induced by Microinjection of Alamandine, a Derivative of Angiotensin-(1-7), into Caudal Ventrolateral Medulla of 2K1C Hypertensive Rats. Peptides 2017, 96, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyenet, P.G.; Stornetta, R.L.; Holloway, B.B.; Souza, G.M.P.R.; Abbott, S.B.G. Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla and Hypertension. Hypertension 2018, 72, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, M.; Zhu, M.; Jing, H.; Fang, J.; Shen, L.; Zhu, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, J. The Effects of Angiotensin II and Angiotensin-(1-7) in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla of Rats on Stress-Induced Hypertension. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lautner, R.Q.; Villela, D.C.; Fraga-Silva, R.A.; Silva, N.; Verano-Braga, T.; Costa-Fraga, F.; Jankowski, J.; Jankowski, V.; Sousa, F.; Alzamora, A.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of Alamandine: A Novel Component of the Renin–Angiotensin System. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilodeau, M.S.; Leiter, J.C. Angiotensin 1-7 in the Rostro-Ventrolateral Medulla Increases Blood Pressure and Splanchnic Sympathetic Nerve Activity in Anesthetized Rats. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2018, 247, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Sun, H.-J.; Cui, B.-P.; Zhou, Y.-B.; Han, Y. Angiotensin-(1-7) in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Modulates Enhanced Cardiac Sympathetic Afferent Reflex and Sympathetic Activation in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 2013, 61, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.-M.; Shi, Z.; Gao, J.; Han, Y.; Yuan, N.; Gao, X.-Y.; Zhu, G.-Q. Angiotensin-(1-7) and Angiotensin II in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Modulate the Cardiac Sympathetic Afferent Reflex and Sympathetic Activity in Rats. Pflug. Arch. 2010, 459, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.C.; Fontes, M.A.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Khosla, M.C.; Campos, R.R.; Guertzenstein, P.G.; Santos, R.A. Cardiovascular Effects Produced by Micro-Injection of Angiotensin-(1-7) on Vasopressor and Vasodepressor Sites of the Ventrolateral Medulla. Brain Res. 1993, 613, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazato, M.; Yamazato, Y.; Sun, C.; Diez-Freire, C.; Raizada, M.K. Overexpression of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Causes Long-Term Decrease in Blood Pressure in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 2007, 49, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmouni, K. Cardiovascular Regulation by the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus: Neurocircuitry and Signaling Systems. Hypertension 2016, 67, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Deng, G.; Grobe, J.L.; Cui, H. Hypothalamic GPCR Signaling Pathways in Cardiometabolic Control. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 691226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehay, D.; Silberman, Y.; Arnold, A.C. The Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus and Metabolic Regulation: An Emerging Role for Renin–Angiotensin Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, S.B.R.; Wagner, V.A.; Nakagawa, P.; Segar, J.L.; Sigmund, C.D.; Morselli, L.L.; Grobe, J.L. Angiotensin in the Arcuate: Mechanisms Integrating Cardiometabolic Control: The 2022 COH Mid-Career Award for Research Excellence. Hypertension 2024, 81, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Stornetta, D.S.; Stornetta, R.L.; Brooks, V.L. Arcuate Angiotensin II Increases Arterial Pressure via Coordinated Increases in Sympathetic Nerve Activity and Vasopressin Secretion. eNeuro 2022, 9, ENEURO.0404–21.2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, B.; Murphy, D.; Japundžić-Žigon, N. The Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus in Control of Blood Pressure and Blood Pressure Variability. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 858941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, C.Y.; Wainford, R.D. Hypothalamic Signaling Mechanisms in Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2015, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.-J.; Li, P.; Chen, W.-W.; Xiong, X.-Q.; Han, Y. Angiotensin II and Angiotensin-(1-7) in Paraventricular Nucleus Modulate Cardiac Sympathetic Afferent Reflex in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, S.; Fraidenburg, D.R.; Tang, H.; Han, Y. Angiotensin-(1-7) in Paraventricular Nucleus Contributes to the Enhanced Cardiac Sympathetic Afferent Reflex and Sympathetic Activity in Chronic Heart Failure Rats. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2523–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.-J.; Miao, Y.-W.; Li, H.-B.; Su, Q.; Liu, K.-L.; Fu, L.-Y.; Hou, Y.-K.; Shi, X.-L.; Li, Y.; Mu, J.-J.; et al. Blockade of Endogenous Angiotensin-(1-7) in Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates High Salt-Induced Sympathoexcitation and Hypertension. Neurosci. Bull. 2019, 35, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Sun, H.-J.; Li, P.; Gao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gao, X.-Y.; Zhu, G.-Q. Angiotensin-(1-7) in Paraventricular Nucleus Modulates Sympathetic Activity and Cardiac Sympathetic Afferent Reflex in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriramula, S.; Cardinale, J.P.; Lazartigues, E.; Francis, J. ACE2 Overexpression in the Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 92, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-H.; Chen, X.-R.; Yang, C.-X.; Liu, B.-X.; Li, P. Alamandine Injected into the Paraventricular Nucleus Increases Blood Pressure and Sympathetic Activation in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Peptides 2018, 103, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, P.; Gomez, J.; Grobe, J.L.; Sigmund, C.D. The Renin-Angiotensin System in the Central Nervous System and Its Role in Blood Pressure Regulation. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2020, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.J.; Zinkevich, N.S.; Riedel, M.; Gutterman, D.D.; Nasci, V.L.; Salato, V.K.; Hijjawi, J.B.; Reuben, C.F.; North, P.E.; Beyer, A.M. Vascular Actions of Angiotensin 1–7 in the Human Microcirculation: Novel Role for Telomerase. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Castillo, A.; Tobon-Cornejo, S.; Del Valle-Mondragon, L.; Torre-Villalvazo, I.; Schcolnik-Cabrera, A.; Guevara-Cruz, M.; Pichardo-Ontiveros, E.; Fuentes-Romero, R.; Bader, M.; Alenina, N.; et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) Induces Beige Fat Thermogenesis through the Mas Receptor. Metabolism 2020, 103, 154048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, M.; Steckelings, U.M.; Alenina, N.; Santos, R.A.S.; Ferrario, C.M. Alternative Renin-Angiotensin System. Hypertension 2024, 81, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Kararigas, G. Mechanistic Pathways of Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usselman, C.W.; Lindsey, M.L.; Robinson, A.T.; Habecker, B.A.; Taylor, C.E.; Merryman, W.D.; Kimmerly, D.; Bender, J.R.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Moreau, K.L.; et al. Guidelines on the Use of Sex and Gender in Cardiovascular Research. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2024, 326, H238–H255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalenga, C.Z.; Ramesh, S.; Dumanski, S.M.; MacRae, J.M.; Nerenberg, K.; Metcalfe, A.; Sola, D.Y.; Ahmed, S.B. Sex Influences the Effect of Adiposity on Arterial Stiffness and Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System Activity in Young Adults. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 5, e00317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundemer, G.L.; Agharazii, M.; Madore, F.; Piché, M.-E.; Gagnon, C.; Bussières, A.; St-Jean, M.; Leung, A.A.; Kline, G.A.; Sood, M.M.; et al. Sex-Specific Associations of Aldosterone and Renin with Body Composition: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, dgae566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, D.; Mehay, D.; Arnold, A.C. Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Actions of the Renin-Angiotensin System. Clin. Auton. Res. 2020, 30, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Location | Blood Pressure | Sympathetic Activity | BRS | Metabolic Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systemic | ⇓ | ⇓ | ⇑ | ⇑ |
| Icv | ⇓ | ⇓ | ⇑ | ⇑ |
| Intra-NTS | ⇓ | UNK | ⇑ | UNK |
| Intra-CVLM | ⇓ | UNK | UNK | UNK |
| Intra-RVLM | ⇑ | ⇑ | UNK | UNK |
| Intra-ARC | UNK | UNK | UNK | UNK |
| Intra-PVN | ⇑ | ⇑ | UNK | UNK |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vernail, V.L.; Lucas, L.; Miller, A.J.; Arnold, A.C. Angiotensin-(1-7) and Central Control of Cardiometabolic Outcomes: Implications for Obesity Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413320
Vernail VL, Lucas L, Miller AJ, Arnold AC. Angiotensin-(1-7) and Central Control of Cardiometabolic Outcomes: Implications for Obesity Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(24):13320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413320
Chicago/Turabian StyleVernail, Victoria L., Lillia Lucas, Amanda J. Miller, and Amy C. Arnold. 2024. "Angiotensin-(1-7) and Central Control of Cardiometabolic Outcomes: Implications for Obesity Hypertension" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 24: 13320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413320
APA StyleVernail, V. L., Lucas, L., Miller, A. J., & Arnold, A. C. (2024). Angiotensin-(1-7) and Central Control of Cardiometabolic Outcomes: Implications for Obesity Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413320







