Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effect of Azalomycin F on 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene-Induced Mice and Potential Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
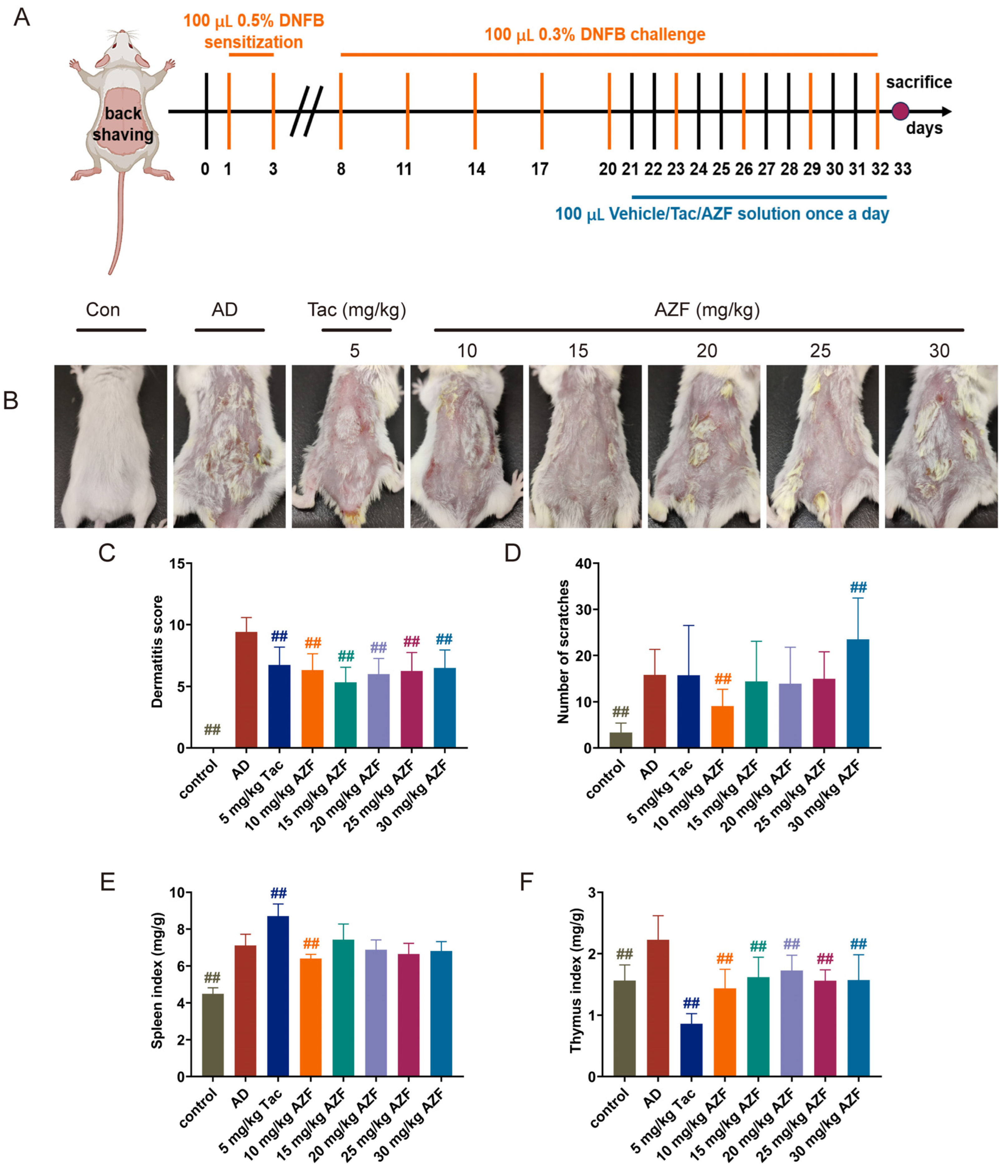
2.1. Effect of AZF Treatment on DNFB-Induced AD-like Clinical Symptoms
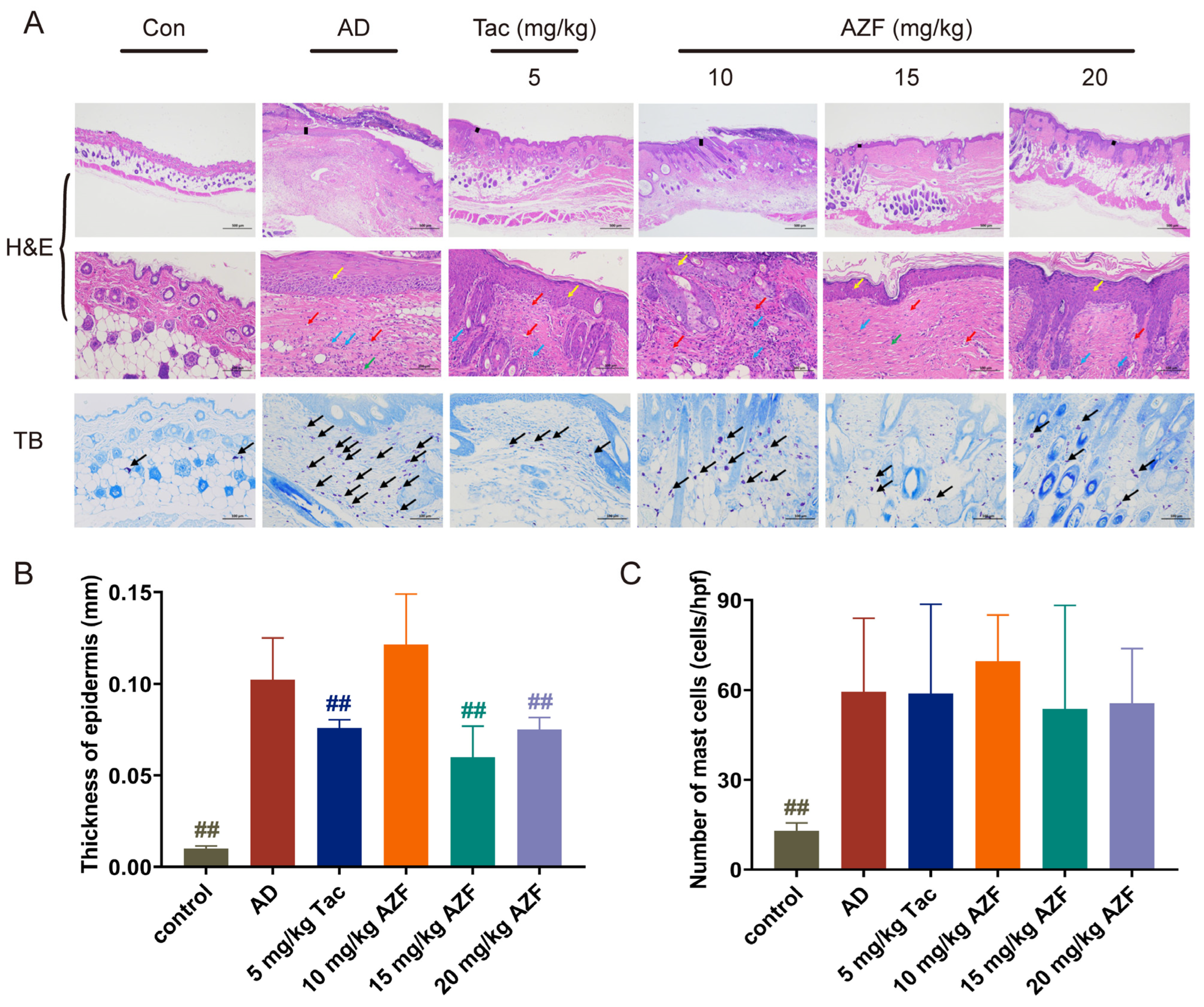
2.2. Effect of AZF Treatment on Histopathology of Skin Tissue
2.3. Effect of AZF on Serum IgE and Inflammatory Mediators
2.4. RAN-Seq Date Analyses
2.5. Go Annotation and KEGG Enrichment
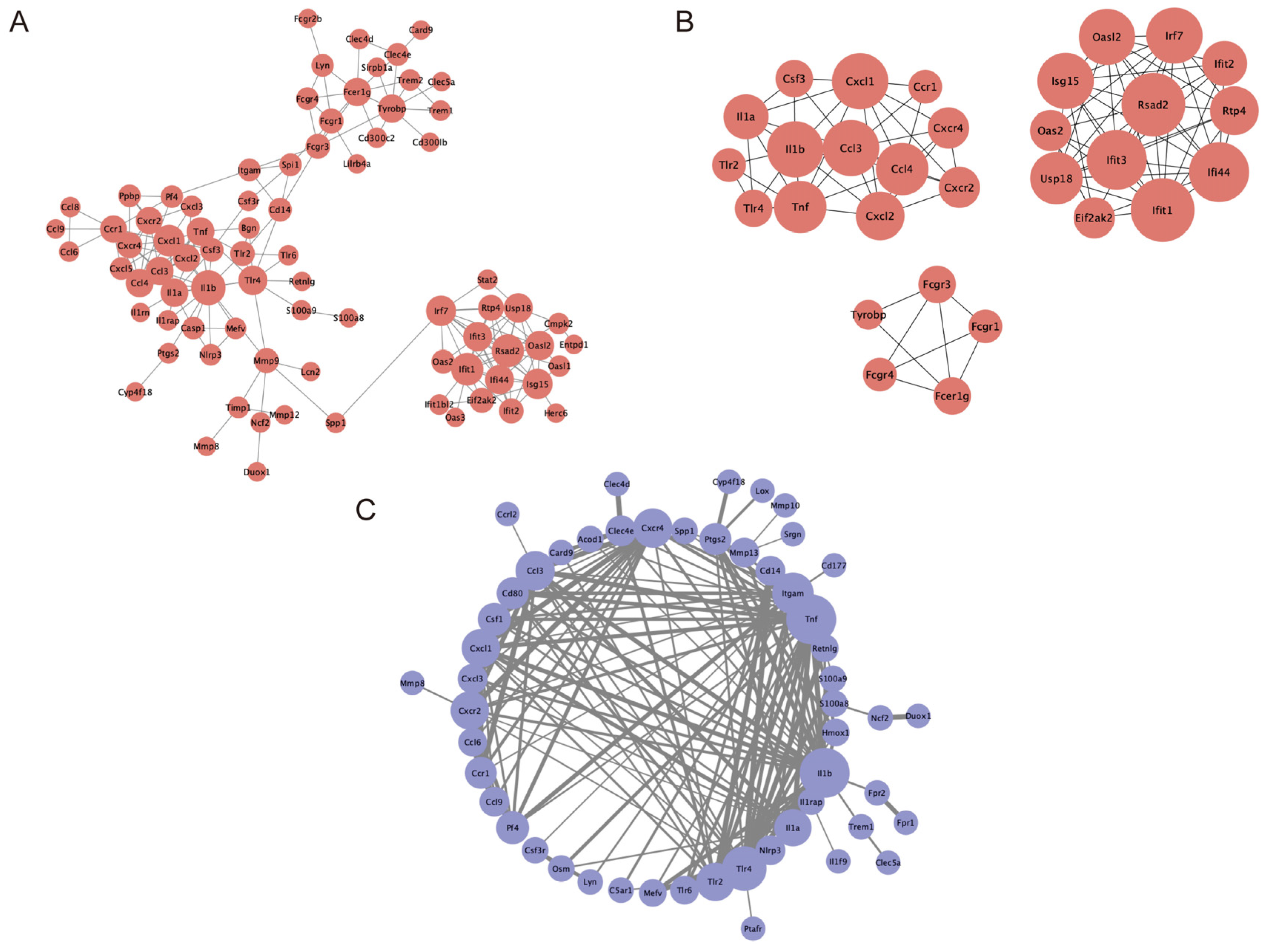
2.6. PPI Network Construction and Module Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Animal Modeling and Grouping
4.4. Evaluation of the Severity of Atopic Dermatitis and Analysis of Organ Index
4.5. Measurement of Inflammatory Factors Release in Serum
4.6. Histopathological Analysis
4.7. RNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Sequencing
4.8. Data Analysis of RNA Sequencing
4.9. GO Functional Annotation and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analyses
4.10. PPI Network Construction and Module Analyses
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langan, S.M.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yao, X.; Lu, Q. Global epidemiology of atopic dermatitis: A comprehensive systematic analysis and modelling study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 190, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Yuan, L.; Wang, S. Screening differentially expressed genes and the pathogenesis in atopic dermatitis using bioinformatics. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Li, P.; Tang, J.; Han, X.; Zou, X.; Xu, G.; Xu, Z.; Wei, F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, M.; et al. Prevalence of atopic dermatitis in chinese children aged 1–7 ys. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Pawar, M.; Bothra, A.; Choudhary, N. Overzealous hand hygiene during the COVID 19 pandemic causing an increased incidence of hand eczema among general population. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, e37–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Song, Z.; Miao, X.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Yang, J.; An, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; et al. Skin damage among health care workers managing coronavirus disease-2019. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1215–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedoszytko, B.; Reszka, E.; Gutowska-Owsiak, D.; Trzeciak, M.; Lange, M.; Jarczak, J.; Niedoszytko, M.; Jablonska, E.; Romantowski, J.; Strapagiel, D.; et al. Genetic and epigenetic aspects of atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demessant-Flavigny, A.L.; Connétable, S.; Kerob, D.; Moreau, M.; Aguilar, L.; Wollenberg, A. Skin microbiome dysbiosis and the role of Staphylococcus aureus in atopic dermatitis in adults and children: A narrative review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37 (Suppl. 5), 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.H.; Zhu, T.R.; Tran, K.A.; Sivamani, R.K.; Shi, V.Y. Epithelial barrier dysfunctions in atopic dermatitis: A skin-gut-lung model linking microbiome alteration and immune dysregulation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Seok, J.K.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. Skin barrier abnormalities and immune dysfunction in atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidinger, S.; Beck, L.A.; Bieber, T.; Kabashima, K.; Irvine, A.D. Atopic dermatitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Pang, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Peng, L.; Guo, J.; Zeng, J. A comprehensive review of natural products against atopic dermatitis: Flavonoids, alkaloids, terpenes, glycosides and other compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.H.; Chung, W.H.; Wu, P.C.; Chen, C.B. JAK-STAT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: An updated review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1068260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M. Regulation of filaggrin, loricrin, and involucrin by IL-4, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-22, AHR, and NRF2: Pathogenic implications in atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fyhrquist, N.; Muirhead, G.; Prast-Nielsen, S.; Jeanmougin, M.; Olah, P.; Skoog, T.; Jules-Clement, G.; Feld, M.; Barrientos-Somarribas, M.; Sinkko, H.; et al. Microbe-host interplay in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, E.; Gooderham, M.; Torres, T. New topical therapies in development for atopic dermatitis. Drugs 2022, 82, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Yao, Z. Update on the pathogenesis and therapy of atopic dermatitis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 61, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G. Screening of Macrolide-Producing Strains from Mangrove Actinomycetes, and Isolation, Identification and Bioactivity of Metabolites. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Hainan, Haikou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.; Hong, K.; Lin, H.; She, Z.; Li, J. New azalomycin F analogs from mangrove Streptomyces sp. 211726 with activity against microbes and cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Li, P.; Zhong, Q.; Xia, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, P.; Song, X.; Li, J.; et al. Azalomycin F5a, a polyhydroxy macrolide binding to the polar head of phospholipid and targeting to lipoteichoic acid to kill methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, Q.; Cai, G.; Xia, F.; et al. Targeting autophagy peptidase ATG4B with a novel natural product inhibitor Azalomycin F4a for advanced gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S. Pharmacokinetic, and Anti-Inflammatory, Antibacterial Activity of Azalomycin F. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi Agricultural University, Nanchang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.; Wang, Y.; LIiu, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Application of Azalomycin F in the Preparation of Drugs for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Patent: CN 105919995 B, 29 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, T.; Terayama. Clinical effects of anti-candida drug Azalomycin F. Jpn. J. Chemother. 1963, 11, 19–20. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.T.; Goodarzi, H.; Chen, H.Y. IgE, mast cells, and eosinophils in atopic dermatitis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 41, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, G.Y.; Kim, E.Y.; Hong, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, E.J.; Park, J.H.; Sohn, Y.; Jung, H.S. Lycopus lucidus Turcz ameliorates DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis in BALB/c mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.R.; Lei, D.; Yousaf, M.; Chavda, R.; Gabriel, S.; Janmohamed, S.R.; Silverberg, J.I. Reliability and longitudinal course of itch/scratch severity in adults with atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis 2021, 32, S28–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Ohn, J.; Kim, J.W.; Kang, S.M.; Jeon, D.; Heo, C.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kwon, O.; Kim, K.H. Caffeoyl-Pro-His amide relieve DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis-like phenotypes in BALB/c mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Ryu, H.W.; Yang, W.K.; Park, M.H.; Park, Y.C.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, S.R.; Kim, S.H. A combination of Olea europaea leaf extract and Spirodela polyrhiza extract alleviates atopic dermatitis by modulating immune balance and skin barrier function in a 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene-induced murine model. Phytomedicine 2021, 82, 153407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, T.; Yang, S.; Wen, X.; Jia, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Mechanism of dihuangyin in treatment of mice with atopic dermatitis by regulating JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2024, 30, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ye, H.; Su, T.; Hu, C.; Huang, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhong, Z.; Du, X.; Zheng, Y. Immunity and reproduction protective effects of Chitosan Oligosaccharides in Cyclophosphamide/Busulfan-induced premature ovarian failure model mice. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1185921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, E.B.; Cyr, S.L.; Arima, K.; McDonald, R.A.; Levit, N.A.; Nestle, F.O. Current and emerging strategies to inhibit type 2 inflammation in atopic dermatitis. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 1501–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scibiorek, M.; Mthembu, N.; Mangali, S.; Ngomti, A.; Ikwegbue, P.; Brombacher, F.; Hadebe, S. IL-4Rα signalling in B cells and T cells play differential roles in acute and chronic atopic dermatitis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Song, Z. Combined application of dinitrofluorobenzene and ovalbumin induced AD-like dermatitis with an increase in helper T-cell cytokines and a prolonged Th2 response. BMC Immunol. 2022, 23, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mócsai, G.; Gáspár, K.; Dajnoki, Z.; Tóth, B.; Gyimesi, E.; Bíró, T.; Maródi, L.; Szegedi, A. Investigation of skin barrier functions and allergic sensitization in patients with Hyper-IgE syndrome. J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Deng, F.; Chang, B.; Zhou, J.; Sun, L. The role of TSLP in atopic dermatitis: From pathogenetic molecule to therapeutical target. Mediators Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 7697699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.L.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Peeva, E. Role of innate immunity in allergic contact dermatitis: An update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Jeong, N.H.; Choi, Y.A.; Lee, B.; Jang, Y.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.H. Lupeol alleviates atopic dermatitis-like skin inflammation in 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene/Dermatophagoides farinae extract-induced mice. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 24, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanelli, S.; Corti, E.; Montanini, N.; Denaro, M.; Sarubbi, E. Inhibitors of type-I interleukin-1 receptor from microbial metabolites. J. Antibiot. 1997, 50, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Zhao, W.; Li, P.; Tu, W.; Hong, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, G. Pharmacokinetics of azalomycin F, a natural macrolide produced by streptomycete strains, in rats. Molecules 2021, 26, 6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Gong, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, S.; Tang, J.; Ge, H.; Wu, C.; Tang, H.; Wang, G.; et al. Dectin-1 aggravates neutrophil inflammation through caspase-11/4-mediated macrophage pyroptosis in asthma. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.F.; Galkina, E.; Ley, K.; Huo, Y. GRO family chemokines are specialized for monocyte arrest from flow. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1976–H1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damour, A.; Robin, B.; Deroche, L.; Broutin, L.; Bellin, N.; Verdon, J.; Lina, G.; Leclère, F.M.; Garcia, M.; Cremniter, J.; et al. Phenol-soluble modulins α are major virulence factors of Staphylococcus aureus secretome promoting inflammatory response in human epidermis. Virulence 2021, 12, 2474–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Paik, J.H.; Kwon, O.K.; Paryanto, I.; Yuniato, P.; Ryu, H.W.; Choi, S.H.; Oh, S.R.; Han, S.B.; Park, J.W.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Lagerstroemia ovalifolia Teijsm. & Binn. in TNFα/IFNγ-stimulated keratinocytes. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 2439231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.; Yang, W.; Park, S.; Yang, J.; Kim, S.; Lyu, J.H.; Kim, H. The Anti-inflammatory and skin barrier function recovery effects of schisandra chinensis in mice with atopic dermatitis. Medicina 2023, 59, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, F.; Dong, J.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, J.; Feng, Y.; Wu, B.; Xie, T.; Cheng, L. Qingxue jiedu formulation ameliorated DNFB-induced atopic dermatitis by inhibiting STAT3/MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 270, 113773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, R.; Chen, X.; Hu, J.; Fu, Y.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, P.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.; et al. Ghrelin protects against contact dermatitis and psoriasiform skin inflammation by antagonizing TNF-α/NF-κB signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Li, X.L.; Deng, Z.X.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, Y.H.; Li, J.; Ding, H. Conjugated linoleic acid attenuates 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice through dual inhibition of COX-2/5-LOX and TLR4/NF-κB signaling. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 81, 108379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, Q.; Huang, H.; Xu, X.; Du, B.; Li, P. Probiotic-fermented Portulaca oleracea L. alleviated DNFB-induced atopic dermatitis by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 313, 116613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, M.; Le, Y.; Chen, L.; Zheng, J. Topical emollient prevents the development of atopic dermatitis and atopic march in mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesiak, A.; Smolewski, P.; Sobolewska-Sztychny, D.; Sysa-Jedrzejowska, A.; Narbutt, J. The role of T-regulatory cells and Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in atopic dermatitis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2012, 76, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, H.; Kurashimo, S.; Chihara, J.; Matsukura, M.; Yudate, T.; Tezuka, T. Overexpression of CD11b on eosinophils in atopic dermatitis: Downregulation by cyclosporin A and upregulation by interleukin 5. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1999, 120 (Suppl. 1), 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Hong, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. 1H and 13C assignments of two new macrocyclic lactones isolated from Streptomyces sp. 211726 and revised assignments of azalomycins F3a, F4a and F5a. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Chang, H.; He, K.; Ni, Y.; Li, C.; Hou, M.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.; Chen, B.; Ji, M. Fucoidan from seaweed Fucus vesiculosus inhibits 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 75, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.W.; Wang, B.Y.; Xiao, W.L.; Sun, Y.J.; Yang, C.; Zhao, B.T. Different molecular weight hyaluronic acid alleviates inflammation response in DNFB-induced mice atopic dermatitis and LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Life Sci. 2022, 301, 120591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene_ID | Name | Con_vs_AD | Con_vs_AZF | AD_vs_AZF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSMUSG00000036931 | Nfkbid | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000040435 | Ppp1r15a | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000063889 | Crem | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000029373 | Pf4 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000000982 | Ccl3 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000047735 | Samd9l | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000079293 | Clec7a | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000034459 | Ifit1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000041735 | AAdacl4fm3 | down | - | up |
| ENSMUSG00000028874 | Fgr | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000027399 | Il1a | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000020077 | Srgn | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000026480 | Ncf2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000049130 | C5ar1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000043953 | Ccrl2 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000029379 | Cxcl3 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000027524 | Edn3 | down | - | up |
| ENSMUSG00000046223 | Plaur | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000042265 | Trem1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000048120 | Entpd1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000026177 | Slc11a1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000028859 | Csf3r | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000020120 | Plek | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000050931 | Sgms2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000027398 | Il1b | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000044103 | Il36g | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000029915 | Clec5a | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000051439 | Cd14 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000054404 | Slfn5 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000057933 | Gsta2 | down | - | up |
| ENSMUSG00000037946 | Fgd3 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000048455 | Sprr1b | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000042759 | Apobr | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000033268 | Duox1 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000022534 | Mefv | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000029304 | Spp1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000037731 | Themis2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000072620 | Slfn2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000005413 | Hmox1 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000049685 | Cyp2g1 | up | up | up |
| ENSMUSG00000029338 | Antxr2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000030155 | Clec2e | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000003484 | Cyp4f18 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000035861 | Tmprss11b | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000030144 | Clec4d | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000045502 | Hcar2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000051920 | Rspo2 | down | - | up |
| ENSMUSG00000052270 | Fpr2 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000094733 | Csta3 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000059657 | Stfa2l1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000019122 | Ccl9 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000051682 | Treml4 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000043939 | A530064D06Rik | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000025804 | Ccr1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000099398 | Ms4a14 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000050578 | Mmp13 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000079597 | Cstdc4 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000026535 | Ifi202b | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000064345 | mt-Nd2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000045382 | Cxcr4 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000031504 | Rab20 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000041324 | Inhba | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000064357 | mt-Atp6 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000027202 | Slc12a1 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000039232 | Stx11 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000024529 | Lox | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000022876 | Samsn1 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000064354 | mt-Co2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000022150 | Dab2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000024053 | Emilin2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000112023 | Lilrb4b | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000058755 | Osm | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000032515 | Csrnp1 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000112148 | Lilrb4a | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000065947 | mt-Nd4l | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000026180 | Cxcr2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000025473 | Adam8 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000029380 | Cxcl1 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000020407 | Upp1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000064367 | mt-Nd5 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000014599 | Csf1 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000029659 | Medag | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000047562 | Mmp10 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000045362 | Tnfrsf26 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000033777 | Tlr13 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000064368 | mt-Nd6 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000042622 | Maff | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000013974 | Mcemp1 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000030786 | Itgam | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000046203 | Sprr2g | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000018927 | Ccl6 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000032691 | Nlrp3 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000069792 | Wfdc17 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000025383 | Il23a | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000022126 | Acod1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000020641 | Rsad2 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000014329 | Bicc1 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000027995 | Tlr2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000070031 | Sp140 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000022026 | Olfm4 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000064363 | mt-Nd4 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000032487 | Ptgs2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000041754 | Trem3 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000064370 | mt-Cytb | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000067297 | Ifit1bl2 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000035004 | Igsf6 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000059013 | Sh2d3c | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000022514 | Il1rap | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000056054 | S100a8 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000026872 | Zeb2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000042228 | Lyn | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000052212 | Cd177 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000026271 | Gpr35 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000022651 | Retnlg | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000009633 | G0s2 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000045551 | Fpr1 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000026068 | Il18rap | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000096719 | Mrgpra2b | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000039005 | Tlr4 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000045566 | Sprr4 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000022902 | Stfa2 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000003153 | Slc2a3 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000075122 | Cd80 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000035183 | Slc24a5 | down | - | up |
| ENSMUSG00000079652 | Garin1a | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000055775 | Myh8 | up | up | up |
| ENSMUSG00000027737 | Slc7a11 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000056529 | Ptafr | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000003555 | Cyp17a1 | up | up | up |
| ENSMUSG00000056071 | S100a9 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000005800 | Mmp8 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000064341 | mt-Nd1 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000030142 | Clec4e | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000000204 | Slfn4 | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000051498 | Tlr6 | up | - | down |
| ENSMUSG00000027360 | Hdc | up | up | down |
| ENSMUSG00000024401 | Tnf | up | - | down |
| Pathway ID | Pathway Name | KEGG Class | Degs Number | Total Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmu04060 | Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction | Signaling molecules and interaction | 20 | 289 |
| mmu04061 | Viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor | Signaling molecules and interaction | 12 | 92 |
| mmu04064 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | Signal transduction | 8 | 105 |
| mmu04668 | TNF signaling pathway | Signal transduction | 6 | 113 |
| mmu04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | Immune system | 8 | 93 |
| mmu04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | 7 | 205 |
| mmu04062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | Immune system | 11 | 190 |
| mmu04625 | C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | 8 | 112 |
| mmu04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | 9 | 99 |
| mmu04610 | Complement and coagulation cascades | Immune system | 3 | 91 |
| mmu04640 | Hematopoietic cell lineage | Immune system | 7 | 94 |
| mmu04613 | Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | Immune system | 8 | 201 |
| mmu04623 | Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | Immune system | 2 | 63 |
| mmu04380 | Osteoclast differentiation | Development and regeneration | 5 | 124 |
| mmu05332 | Graft-versus-host disease | Immune disease | 4 | 56 |
| mmu05323 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Immune disease | 11 | 87 |
| mmu05321 | Inflammatory bowel disease | Immune disease | 7 | 62 |
| mmu05135 | Yersinia infection | Infectious disease: bacterial | 5 | 135 |
| mmu05152 | Tuberculosis | Infectious disease: bacterial | 10 | 179 |
| mmu05150 | Staphylococcus aureus infection | Infectious disease: bacterial | 5 | 120 |
| mmu05133 | Pertussis | Infectious disease: bacterial | 8 | 76 |
| mmu05134 | Legionellosis | Infectious disease: bacterial | 8 | 60 |
| mmu05162 | Measles | Infectious disease: viral | 4 | 146 |
| mmu05171 | Coronavirus disease—COVID-19 | Infectious disease: viral | 6 | 235 |
| mmu05164 | Influenza A | Infectious disease: viral | 6 | 173 |
| mmu05142 | Chagas disease | Infectious disease: parasitic | 6 | 103 |
| mmu05140 | Leishmaniasis | Infectious disease: parasitic | 8 | 70 |
| mmu05144 | Malaria | Infectious disease: parasitic | 4 | 55 |
| mmu05146 | Amoebiasis | Infectious disease: parasitic | 8 | 107 |
| mmu04940 | Type I diabetes mellitus | Endocrine and metabolic disease | 4 | 63 |
| mmu04936 | Alcoholic liver disease | Endocrine and metabolic disease | 7 | 139 |
| mmu05417 | Lipid and atherosclerosis | Cardiovascular disease | 12 | 216 |
| mmu05418 | Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | Cardiovascular disease | 6 | 145 |
| mmu04217 | Necroptosis | Cell growth and death | 5 | 174 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Zhu, J.; Luo, X.; Lian, F.; Yang, Y.; He, S.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, G. Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effect of Azalomycin F on 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene-Induced Mice and Potential Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312846
Zhao W, Zhu J, Luo X, Lian F, Yang Y, He S, Zhu J, Yuan G. Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effect of Azalomycin F on 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene-Induced Mice and Potential Mechanism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(23):12846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312846
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wenjia, Jianping Zhu, Xinrong Luo, Fengxian Lian, Yanli Yang, Su He, Jinzhou Zhu, and Ganjun Yuan. 2024. "Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effect of Azalomycin F on 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene-Induced Mice and Potential Mechanism" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 23: 12846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312846
APA StyleZhao, W., Zhu, J., Luo, X., Lian, F., Yang, Y., He, S., Zhu, J., & Yuan, G. (2024). Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effect of Azalomycin F on 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene-Induced Mice and Potential Mechanism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(23), 12846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252312846






