Fed-Batch Strategy Achieves the Production of High Concentration Fermentable Sugar Solution and Cellulosic Ethanol from Pretreated Corn Stover and Corn Cob
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical Compositions of Lignocellulosic Substrates
2.2. Fed-Batch Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Cellulosic Substates to Produce High Concentration Fermentable Sugar Solution
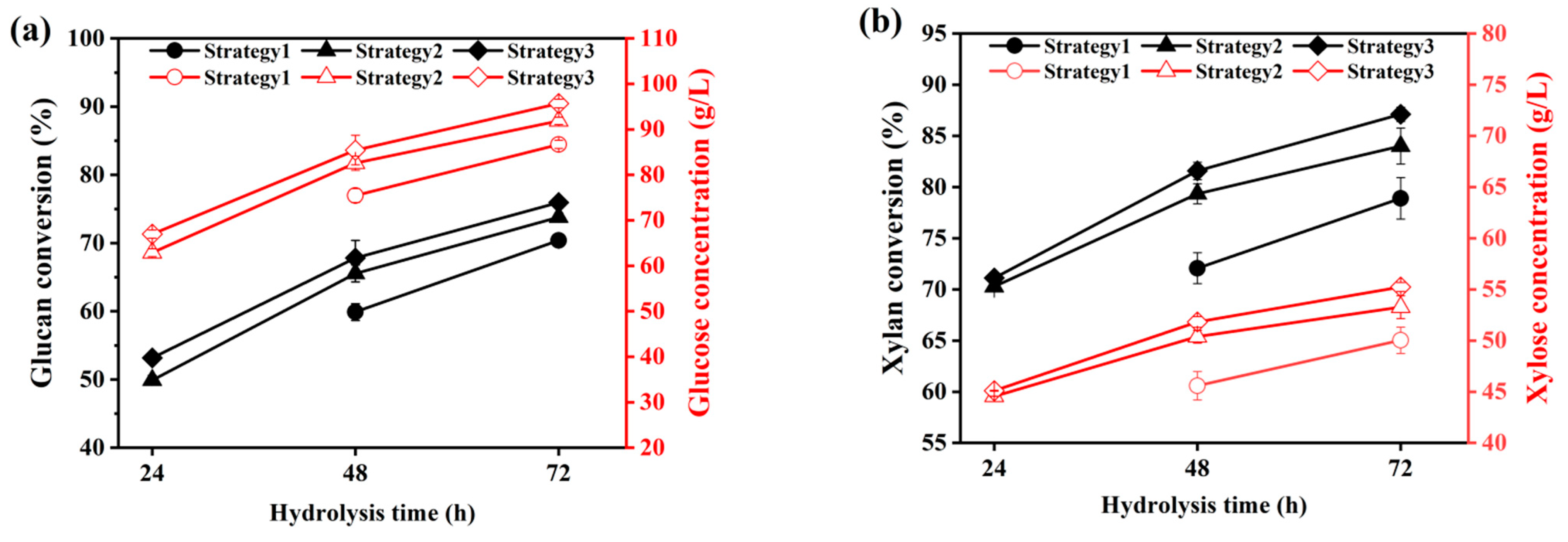
2.2.1. Fed-Batch Enzymatic Hydrolysis of ACSE-CS
Effect of Batch Feeding Strategy
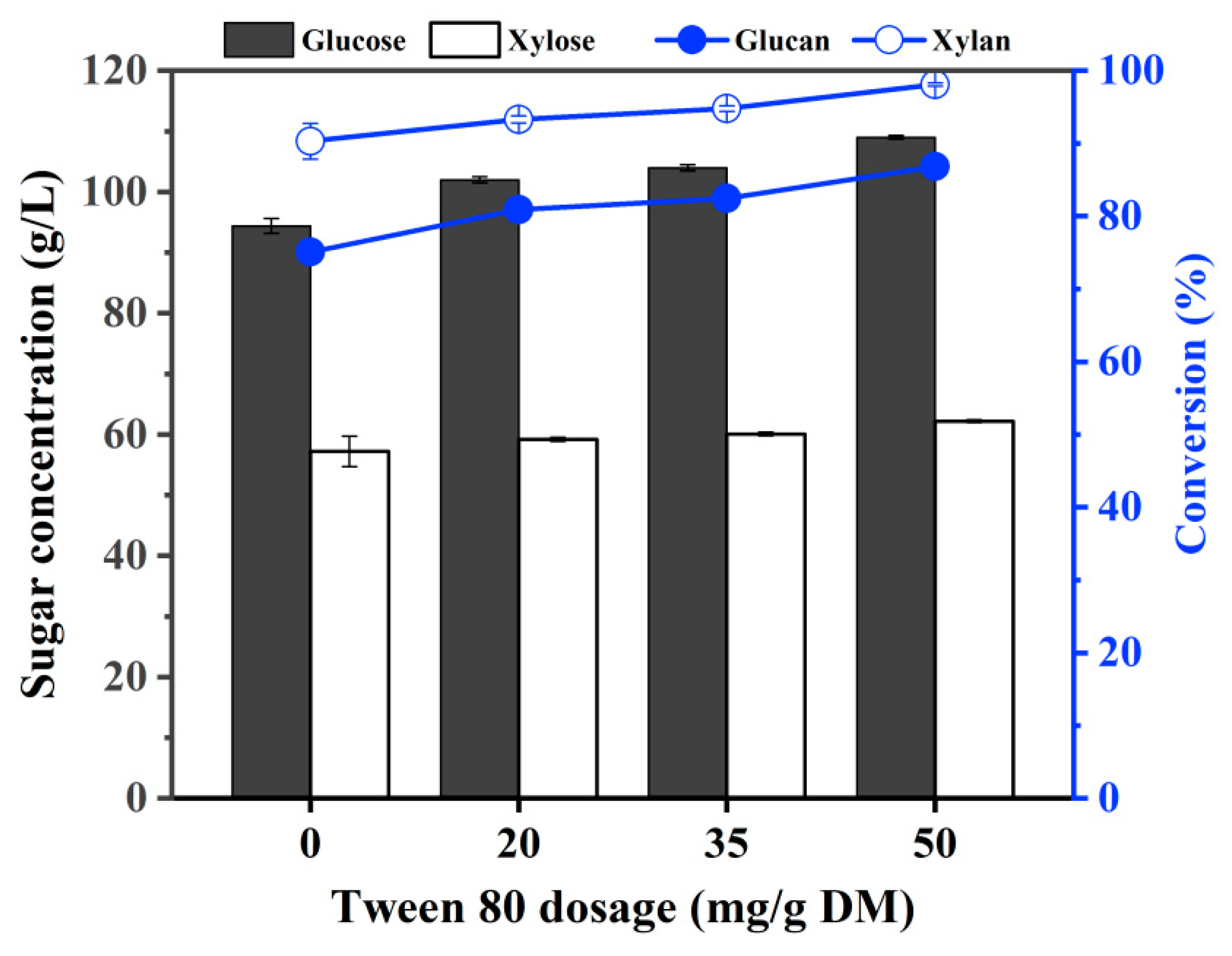
Effect of Tween 80 Addition on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of ACSE-CS
2.2.2. Fed-Batch Enzymatic Hydrolysis of CCR
2.3. Fed-Batch SSCF of ACSE-CS and CCR for Ethanol Production
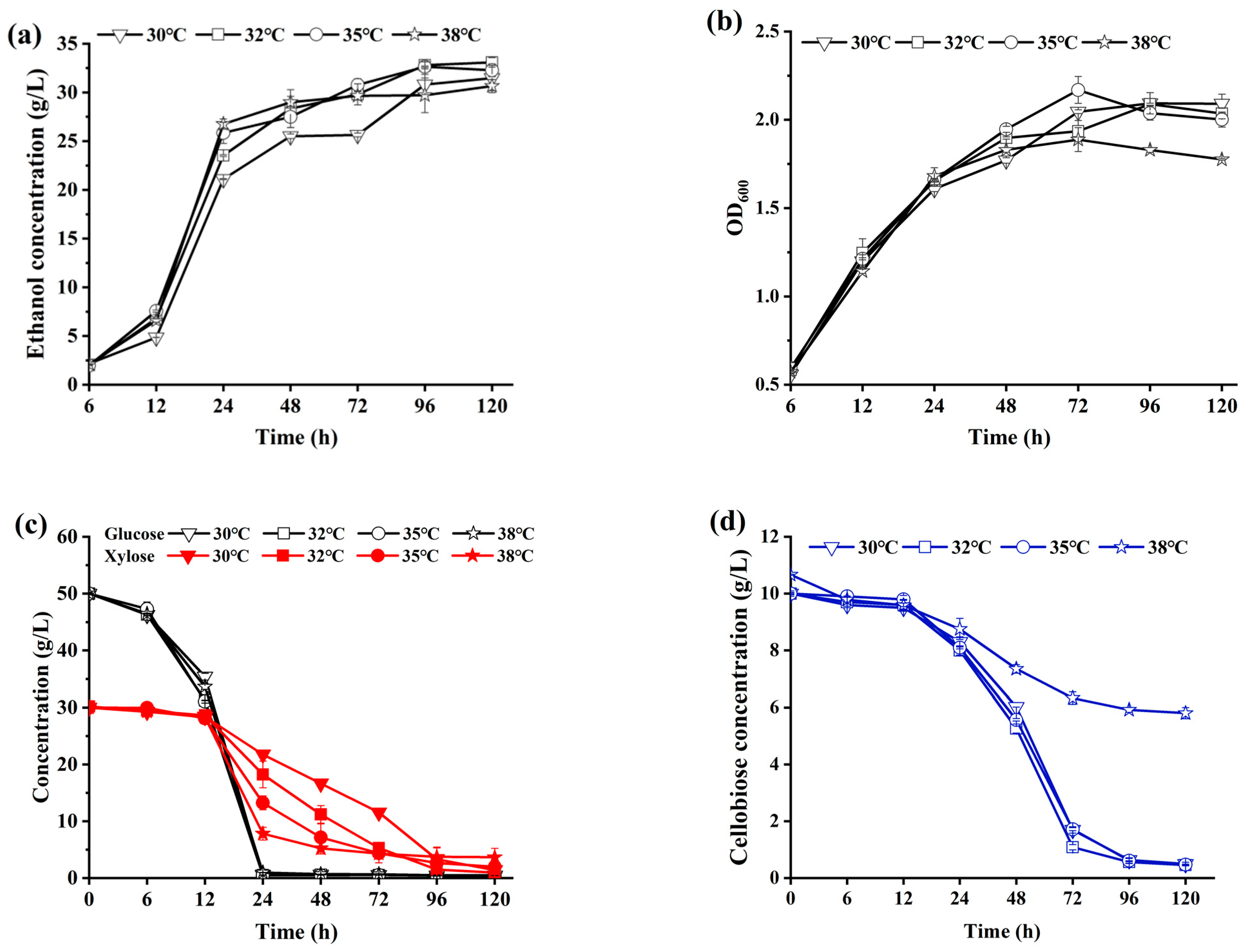
2.3.1. Selection of Fermentation Temperature
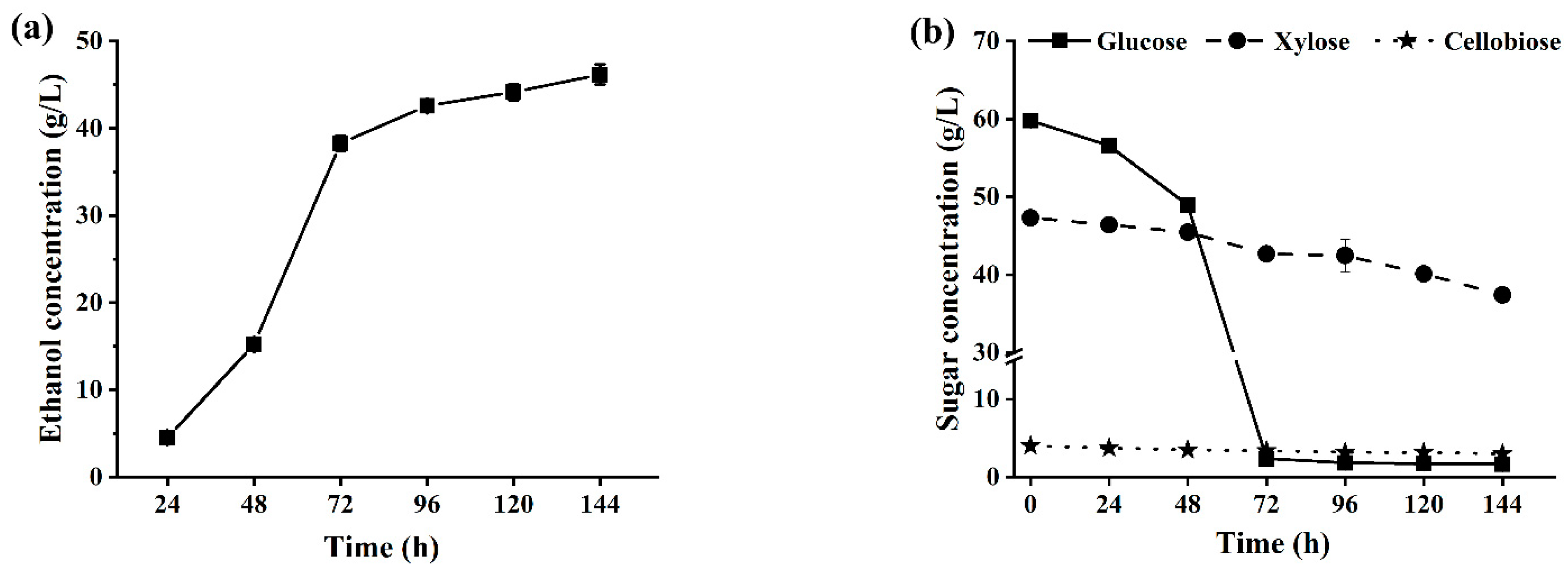
2.3.2. Fed-Batch SSCF of ACSE-CS for Producing Ethanol
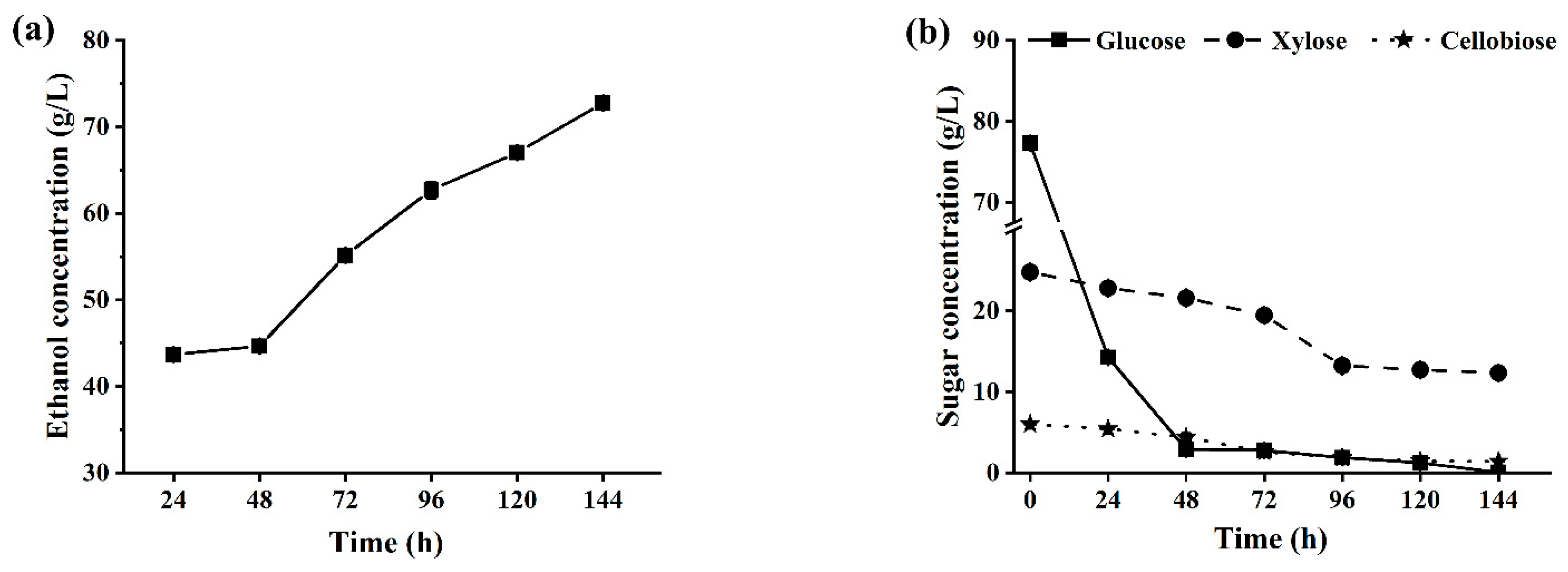
2.3.3. Fed-Batch SSCF of CCR for Producing Ethanol
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Strains
3.2. Analysis of Chemical Compositions of Lignocellulosic Materials
3.3. Fed-Batch Enzymatic Hydrolysis
3.4. Fed-Batch SSCF
3.5. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, E.; Khan, T.S.; Alam, M.I.; Pant, K.K.; Haider, M.A. Understanding Reaction Kinetics, Deprotonation and Solvation of Brnsted Acidic Protons in Heteropolyacid Catalyzed Synthesis of Biorenewable Alkyl Levulinates. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankar, A.R.; Pandey, A.; Modak, A.; Pant, K. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: A review on recent advances. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 334, 125235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varjani, S.; Shahbeig, H.; Popat, K.; Patel, Z.; Vyas, S.; Shah, A.V.; Barceló, D.; Ngo, H.H.; Sonne, C.; Lam, S.S.; et al. Sustainable management of municipal solid waste through waste-to-energy technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 355, 127247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.; Rathore, S.S.; Singh, R.; Kumar, S.; Singh, V.K.; Yadav, S.; Yadav, V.; Raj, R.; Yadav, D.; Shekhawat, K.; et al. Exploring agricultural waste biomass for energy, food and feed production and pollution mitigation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluchamy, C.; Kalamdhad, A.S.; Gilroyed, B.H. Advanced pretreatment strategies for bioenergy production from biomass and biowaste. In Handbook of Environmental Materials Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1507–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Humbird, D.; Mohagheghi, A.; Dowe, N.; Schell, D.J. Economic impact of total solids loading on enzymatic hydrolysis of dilute acid pretreated corn stover. Biotechnol. Prog. 2010, 26, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiva; Barba, F.C.; Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Sukumaran, R.K.; Ruiz, H.A. High-solids loading processing for an integrated lignocellulosic biorefinery: Effects of transport phenomena and rheology—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Xie, J. Optimization of high solids fed-batch saccharification of sugarcane bagasse based on system viscosity changes. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 211, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.K.; Chakraborty, S. Mixing effects on the kinetics and the dynamics of two-phase enzymatic hydrolysis of hemicellulose for biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, K.M.; Lavenson, D.M.; Tozzi, E.J.; McCarthy, M.J.; Jeoh, T. The effects of water interactions in cellulose suspensions on mass transfer and saccharification efficiency at high solids loadings. Cellulose 2011, 18, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Ana da Silva, A.; Fernandes de Souza, M.; Ballesteros, I.; Manzanares, P.; Ballesteros, M.; Bon, E.P. High-solids content enzymatic hydrolysis of hydrothermally pretreated sugarcane bagasse using a laboratory-made enzyme blend and commercial preparations. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1561–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotaniemi, V.-H.; Taskila, S.; Ojamo, H.; Tanskanen, J. Controlled feeding of lignocellulosic substrate enhances the performance of fed-batch enzymatic hydrolysis in a stirred tank reactor. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 91, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Jin, Y.; Jameel, H.; Park, S. Strategies to achieve high-solids enzymatic hydrolysis of dilute-acid pretreated corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 187, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, H.M.; Jung, Y.H.; Sukyai, P.; Kim, K.H. Pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification of oak at high solids loadings to obtain high titers and high yields of sugars. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 284, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Wang, X.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. Fed-batch enzymatic hydrolysis of alkaline organosolv-pretreated corn stover facilitating high concentrations and yields of fermentable sugars for microbial lipid production. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z. Enhancement of high-solids enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency of alkali pretreated sugarcane bagasse at low cellulase dosage by fed-batch strategy based on optimized accessory enzymes and additives. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 121993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Qin, Y. Pretreatment Strategies to Enhance Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Cellulosic Ethanol Production for Biorefinery of Corn Stover. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Fan, Y.; Shi, W.; Liu, X.; Shun, Q. Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of corn stover pretreated by H2O2 oxidative degradation for ethanol production. Energy 2019, 168, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Lau, M.W.; Balan, V.; Dale, B.E. Two-step SSCF to convert AFEX-treated switchgrass to ethanol using commercial enzymes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae 424A(LNH-ST). Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8171–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-H.; Chen, H.-Z. Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation for improving the xylose utilization of steam exploded corn stover at high solid loading. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 201, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppram, R.; Nielsen, F.; Albers, E.; Lambert, A.; Wännström, S.; Welin, L.; Zacchi, G.; Olsson, L. Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation for bioethanol production using corncobs at lab, PDU and demo scales. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, K.; Rudolf, A.; Lidén, G. Designing simultaneous saccharification and fermentation for improved xylose conversion by a recombinant strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 134, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, A.D.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; Ibarra, D.; Ballesteros, M.; Olsson, L. Fed-batch SSCF using steam-exploded wheat straw at high dry matter consistencies and a xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain: Effect of laccase supplementation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabed, H.M.; Akter, S.; Yun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, M.; Mofijur, M.; Awasthi, M.K.; Kalam, M.; Ragauskas, A.; Qi, X. Towards the sustainable conversion of corn stover into bioenergy and bioproducts through biochemical route: Technical, economic and strategic perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 400, 136699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, S.; Alavijeh, M.K.; Shafiei, M.; Karimi, K. A comprehensive review on bioethanol production from corn stover: Worldwide potential, environmental importance, and perspectives. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 161, 106447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D. Physico-chemical conversion of lignocellulose: Inhibitor effects and detoxification strategies: A mini review. Molecules 2018, 23, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, R.; Hu, J.; Saddler, J.N. What are the major components in steam pretreated lignocellulosic biomass that inhibit the efficacy of cellulase enzyme mixtures? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3429–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.P.; Bura, R.; Mabee, W.E.; Berlin, D.A.; Pan, X.; Saddler, J.N. Substrate pretreatment: The key to effective enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosics? Biofuels 2007, 108, 67–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Dong, H.; Hassanpour, M.; Zhang, K.; Xie, H.; Zhang, H.; Song, A.; Zhang, Z. Glycerol-assisted one-step instant catapult steam explosion enhances enzymatic digestibility of corn stover. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 157, 112907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, H. Screw extrude steam explosion: A promising pretreatment of corn stover to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Peng, H. Combined deacetylation and PFI refining pretreatment of corn cob for the improvement of a two-stage enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4661–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, B.; Du, H.; Lv, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, G.; Mu, X.; Peng, H. Properties of nanocellulose isolated from corncob residue using sulfuric acid, formic acid, oxidative and mechanical methods. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Liu, C.; Bi, Y.-H.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, B.; Cui, Q. A clean and effective potassium hydroxide pretreatment of corncob residue for the enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis at high solids loading. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 11558–11566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Han, X.; Qian, Y.; Liu, G.; Yao, G.; Zhong, Y.; Qu, Y. Proteomic analysis of the biomass hydrolytic potentials of Penicillium oxalicum lignocellulolytic enzyme system. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Liu, G.; Song, W.; Qu, Y. Production of sodium gluconate from delignified corn cob residue by on-site produced cellulase and co-immobilized glucose oxidase and catalase. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, R.; Wang, B.; Hu, Y.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wu, R. Comparative study on different pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis of corncob residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shi, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Yong, Q.; Ouyang, J.; Yu, S. Difference analysis of the enzymatic hydrolysis performance of acid-catalyzed steam-exploded corn stover before and after washing with water. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liu, L.; Li, W.-C.; Zhu, J.-Q.; Li, B.-Z.; Yuan, Y.-J. Evaluation of soluble fraction and enzymatic residual fraction of dilute dry acid, ethylenediamine, and steam explosion pretreated corn stover on the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, J. Adsorption and mechanism of cellulase enzymes onto lignin isolated from corn stover pretreated with liquid hot water. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Yao, Y.; Xu, N.; Jia, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, S.; Qu, Y. Pretreatment affects profits from xylanase during enzymatic saccharification of corn stover through changing the interaction between lignin and xylanase protein. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 754593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Feng, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, J. The adsorption properties of endoglucanase to lignin and their impact on hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, M.S.; Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Michelin, M.; Ruiz, H.A. Enhancement and modeling of enzymatic hydrolysis on cellulose from agave bagasse hydrothermally pretreated in a horizontal bioreactor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos-Rocha, M.S.R.; Pratto, B.; Corrêa, L.J.; Badino, A.C.; Almeida, R.M.R.G.; Cruz, A.J.G. Assessment of different biomass feeding strategies for improving the enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane straw. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, X.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, J. Xylo-oligosaccharides inhibit enzymatic hydrolysis by influencing enzymatic activity of cellulase from Penicillium oxalicum. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 9427–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, B.; Yan, B.; Gao, P. Mechanism of cellobiose inhibition in cellulose hydrolysis by cellobiohydrolase. Sci. China Life Sci. 2004, 47, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.S.; Patel, A.K.; Chen, C.-W.; Dong, C.-D.; Singhania, R.R. Strategies for Overcoming the Inhibition of Cellulose Hydrolysis. In Handbook of Biorefinery Research and Technology: Biomass Logistics to Saccharification; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, J.B.; Felby, C.; Jørgensen, H. Yield-determining factors in high-solids enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2009, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Shen, B.; Zhang, D.; Li, R.; Xu, X.; Wang, K.; Lai, C.; Yong, Q. Understanding of promoting enzymatic hydrolysis of combined hydrothermal and deep eutectic solvent pretreated poplars by Tween 80. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukasekuru, M.R.; Hu, J.; Zhao, X.; Sun, F.F.; Pascal, K.; Ren, H.; Zhang, J. Enhanced high-solids fed-batch enzymatic hydrolysis of sugar cane bagasse with accessory enzymes and additives at low cellulase loading. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12787–12796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, W.; Lai, C.; Yong, Q.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Meng, X. Revealing the mechanism of surfactant-promoted enzymatic hydrolysis of dilute acid pretreated bamboo. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J.; Qin, Y. Effects of NaOH-catalyzed organosolv pretreatment and surfactant on the sugar production from sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Dong, Y.; Ma, S.; Gan, L.; Lin, L.; Liu, J. Efficient enzymatic hydrolysis of active oxygen and solid alkali/dilute sulfuric acid-pretreated corn cob. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 220, 119202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Cai, D.; Luo, Z.; Qin, P.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Tan, T. Effect of acid pretreatment on different parts of corn stalk for second generation ethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanuso, E.; Ruiz, H.A.; Domingues, L.; Teixeira, J.A. Oscillatory flow bioreactor operating at high solids loading for enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 187, 108632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Hu, C.-H.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.-H.; Luo, J.-X.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Zheng, Y.-G. Efficient high-solids enzymatic hydrolysis of corncobs by an acidic pretreatment and a fed-batch feeding mode. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.-Q.; Qin, L.; Li, W.-C.; Zhang, J.; Bao, J.; Huang, Y.-D.; Li, B.-Z.; Yuan, Y.-J. Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of dry diluted acid pretreated corn stover at high dry matter loading: Overcoming the inhibitors by non-tolerant yeast. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Fu, G.; Li, B.; Guo, X.; Xiao, D. Efficient utilization of hemicellulose and cellulose in alkali liquor-pretreated corncob for bioethanol production at high solid loading by Spathaspora passalidarum U1-58. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Ma, Y.; Qi, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, F.; Du, R.; Yang, J.; Zhang, M.; He, Z. Ethanol production from high-solid SSCF of alkaline-pretreated corncob using recombinant Zymomonas mobilis CP4. BioEnergy Res. 2013, 6, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass; Report No. TP-510-42618; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; He, X.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Qu, Y. Combinatorial engineering of transcriptional activators in Penicillium oxalicum for improved production of corn-fiber-degrading enzymes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2539–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Materials | Glucan | Xylan | Lignin |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACSE-CS | 37.8 ± 0.7 | 18.6 ± 0.3 | 14.7 ± 0.3 |
| CCR | 75.1 ± 0.1 | 16.7 ± 4.6 | 8.67 ± 0.05 |
| Feeding Strategies | Hydrolysis Time (h) | Solid Loading (%) | Enzyme Dosage (FPU) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy 1 | 0–8 | 10 | 20 |
| 8–16 | 17 | 34 | |
| 16–24 | 24 | 48 | |
| 24–72 | 30 | 60 | |
| Strategy 2 | 0–3 | 15 | 30 |
| 3–6 | 23 | 46 | |
| 6–72 | 30 | 60 | |
| Strategy 3 | 0–3 | 15 | 60 |
| 3–6 | 23 | 60 | |
| 6–72 | 30 | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Qu, Y. Fed-Batch Strategy Achieves the Production of High Concentration Fermentable Sugar Solution and Cellulosic Ethanol from Pretreated Corn Stover and Corn Cob. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212306
Huang J, Li X, Zhao J, Qu Y. Fed-Batch Strategy Achieves the Production of High Concentration Fermentable Sugar Solution and Cellulosic Ethanol from Pretreated Corn Stover and Corn Cob. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(22):12306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212306
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jiamin, Xuezhi Li, Jian Zhao, and Yinbo Qu. 2024. "Fed-Batch Strategy Achieves the Production of High Concentration Fermentable Sugar Solution and Cellulosic Ethanol from Pretreated Corn Stover and Corn Cob" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 22: 12306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212306
APA StyleHuang, J., Li, X., Zhao, J., & Qu, Y. (2024). Fed-Batch Strategy Achieves the Production of High Concentration Fermentable Sugar Solution and Cellulosic Ethanol from Pretreated Corn Stover and Corn Cob. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(22), 12306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212306







