Predicting and Monitoring Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy Using Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
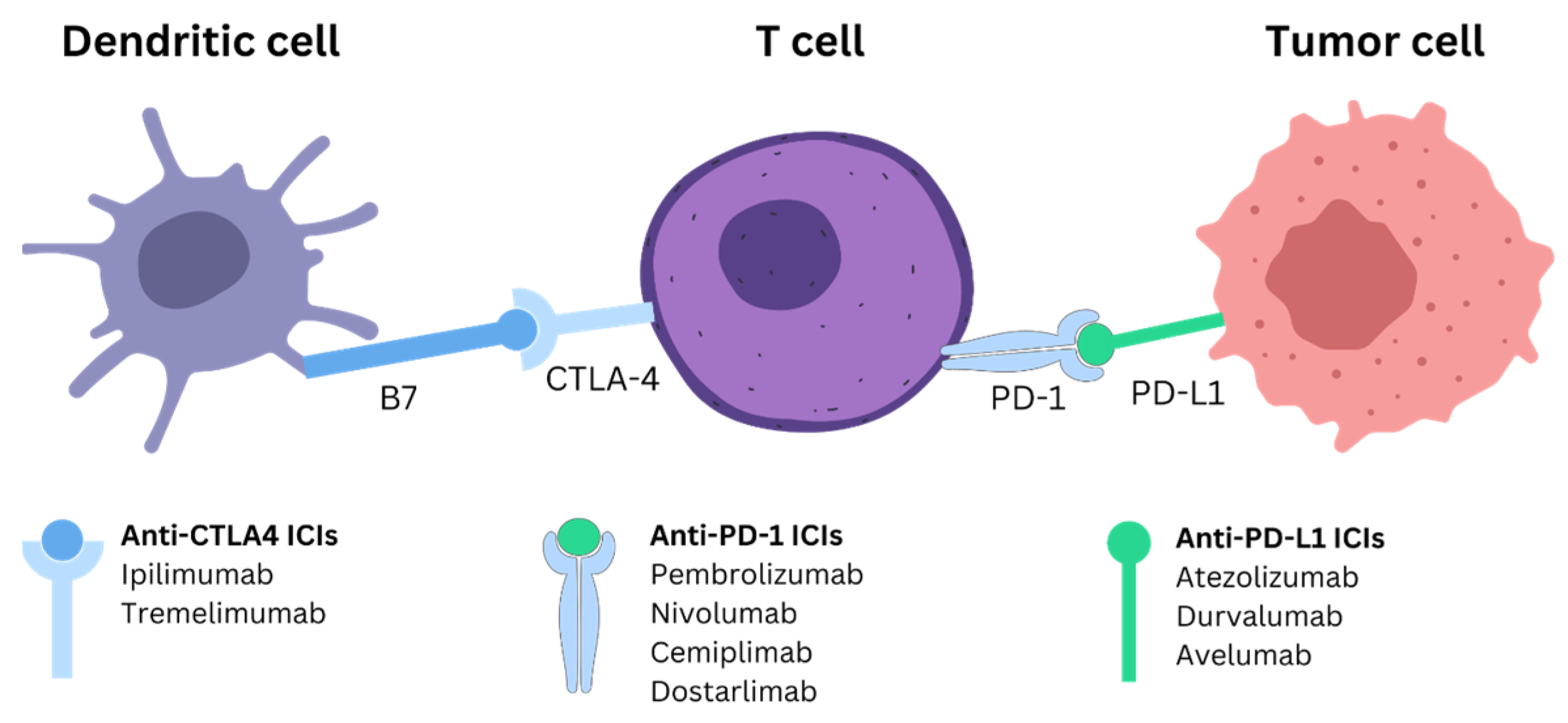
2. ICI Mechanism and Treatment for PDAC
2.1. PD-1/PD-L1
2.2. CTLA-4
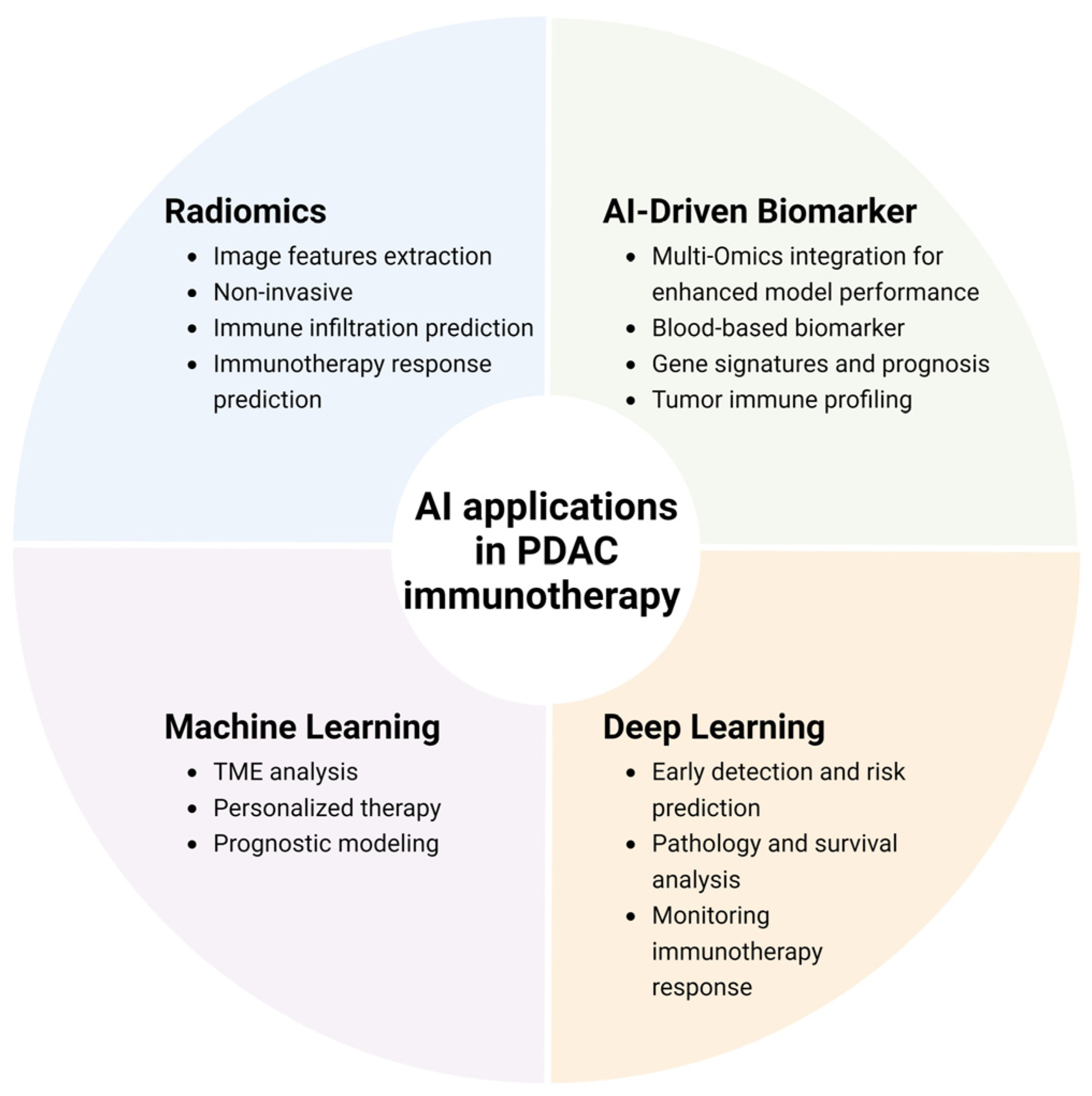
3. AI in Detecting and Monitoring Immunotherapy Responses
3.1. The Need for AI in PDAC Detection and Monitoring
3.2. AI-Driven Improvement in Biomarkers
3.3. Radiomics-Based Prediction of Immunotherapy Response in PDAC
3.4. Machine Learning Applications for PDAC Immunotherapy
3.5. Deep Learning-Based Surveillance of Risk, Early Detection, and Immunotherapy Response/Outcomes of PDAC
4. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahib, L.; Wehner, M.R.; Matrisian, L.M.; Nead, K.T. Estimated Projection of US Cancer Incidence and Death to 2040. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e214708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhi, A.D.; Koay, E.J.; Chari, S.T.; Maitra, A. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2024–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, V.L.; Burotto, M. Pseudoprogression and Immune-Related Response in Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3541–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L.H.; Litière, S.; de Vries, E.; Ford, R.; Gwyther, S.; Mandrekar, S.; Shankar, L.; Bogaerts, J.; Chen, A.; Dancey, J.; et al. RECIST 1.1-Update and clarification: From the RECIST committee. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 62, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, L.; Bogaerts, J.; Perrone, A.; Ford, R.; Schwartz, L.H.; Mandrekar, S.; Lin, N.U.; Litiere, S.; Dancey, J.; Chen, A.; et al. iRECIST: Guidelines for response criteria for use in trials testing immunotherapeutics. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e143–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; Ballinger, M.; Lyons, B.; Soria, J.C.; Nishino, M.; Tabernero, J.; Powles, T.; Smith, D.; Hoos, A.; McKenna, C.; et al. Immune-Modified Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (imRECIST): Refining Guidelines to Assess the Clinical Benefit of Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eresen, A.; Yang, J.; Shangguan, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Sun, C.; Velichko, Y.; Yaghmai, V.; Benson, A.B., 3rd; Zhang, Z. MRI radiomics for early prediction of response to vaccine therapy in a transgenic mouse model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Li, M.; Yang, J.; Hou, W.; Du, M.; Chen, K.; Qu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Contrast-enhanced CT radiomics for predicting lymph node metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A pilot study. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, S.; Yuan, R.; Engleman, E.G. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer: Clinical Impact and Mechanisms of Response and Resistance. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2021, 16, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naimi, A.; Mohammed, R.N.; Raji, A.; Chupradit, S.; Yumashev, A.V.; Suksatan, W.; Shalaby, M.N.; Thangavelu, L.; Kamrava, S.; Shomali, N.; et al. Tumor immunotherapies by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); the pros and cons. Cell Commun. Signal 2022, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, T.; Honjo, T. PD-1 and PD-1 ligands: From discovery to clinical application. Int. Immunol. 2007, 19, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Leach, D.R.; Krummel, M.F.; Allison, J.P. Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science 1996, 271, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C. A decade of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Geng, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, Z.; Ling, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L. Hot and cold tumors: Immunological features and the therapeutic strategies. MedComm 2023, 4, e343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhai, J.; Zhang, Z. Clinical application of immunogenic cell death inducers in cancer immunotherapy: Turning cold tumors hot. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1363121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Yang, Z.H.; Guo, Q.Q. Immune checkpoint inhibition for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Limitations and prospects: A systematic review. Cell Commun. Signal 2021, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki Vareki, S. High and low mutational burden tumors versus immunologically hot and cold tumors and response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Uram, J.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Kemberling, H.; Eyring, A.D.; Skora, A.D.; Luber, B.S.; Azad, N.S.; Laheru, D.; et al. PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Itoh, F.; Nakamura, H.; Fukushima, H.; Sasaki, S.; Perucho, M.; Imai, K. Genetic and clinical features of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas with widespread microsatellite instability. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3139–3144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Luo, H.; Huang, L.; Luo, H.; Zhu, X. Microsatellite instability: A review of what the oncologist should know. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taïeb, J.; Sayah, L.; Heinrich, K.; Kunzmann, V.; Boileve, A.; Cirkel, G.; Lonardi, S.; Chibaudel, B.; Turpin, A.; Beller, T.; et al. Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in microsatellite unstable/mismatch repair-deficient advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: An AGEO European Cohort. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 188, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C.; Ben-Shachar, R.; Gao, Y.; Hyun, S.W.; Rivers, Z.; Epstein, C.; Kaneva, K.; Sangli, C.; Nimeiri, H.; Patel, J. Assessment of Tumor Mutational Burden and Outcomes in Patients With Diverse Advanced Cancers Treated With Immunotherapy. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2311181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y. Autophagy, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, N.A.; Burchard, P.R.; Dunne, R.F.; Linehan, D.C. Immunologic Strategies in Pancreatic Cancer: Making Cold Tumors Hot. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2789–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Kong, L.; Shi, F.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J. Abscopal effect of radiotherapy combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrouzieh, S.; Sheida, F.; Rezaei, N. Review of the recent clinical trials for PD-1/PD-L1 based lung cancer immunotherapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2021, 21, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Xiong, G.; Cao, Z.; Yang, G.; Zheng, S.; Song, X.; You, L.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y. PD-1/PD-L1 and immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 407, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moral, J.A.; Leung, J.; Rojas, L.A.; Ruan, J.; Zhao, J.; Sethna, Z.; Ramnarain, A.; Gasmi, B.; Gururajan, M.; Redmond, D.; et al. ILC2s amplify PD-1 blockade by activating tissue-specific cancer immunity. Nature 2020, 579, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.-Y.; Fu, Z.-J.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Q.-W.; An, J.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. Probiotics functionalized with a gallium-polyphenol network modulate the intratumor microbiota and promote anti-tumor immune responses in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, K.A.; Mick, R.; Teitelbaum, U.; O’Hara, M.; Schneider, C.; Massa, R.; Karasic, T.; Tondon, R.; Onyiah, C.; Gosselin, M.K.; et al. Niraparib plus nivolumab or niraparib plus ipilimumab in patients with platinum-sensitive advanced pancreatic cancer: A randomised, phase 1b/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosein, P.J.; Datta, J.; Ezenwajiaku, N.; Zhou, Z.; Yow, M.V.; Boone, M.; Nagathihalli, N.; Reis, I.M.; Merchant, N.B. A phase 1 trial of combined MEK, STAT3 and PD-1 inhibition in metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, TPS713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, L.A.; Sethna, Z.; Soares, K.C.; Olcese, C.; Pang, N.; Patterson, E.; Lihm, J.; Ceglia, N.; Guasp, P.; Chu, A.; et al. Personalized RNA neoantigen vaccines stimulate T cells in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2023, 618, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shao, Q.; Hao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; He, Y.; Gao, W.; Mao, H. CTLA-4 positive breast cancer cells suppress dendritic cells maturation and function. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13703–13715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengsch, F.; Knoblock, D.M.; Liu, A.; McAllister, F.; Beatty, G.L. CTLA-4/CD80 pathway regulates T cell infiltration into pancreatic cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.J.; Tchekmedyian, N.S.; Rini, B.I.; Fong, L.; Lowy, I.; Allison, J.P. A pilot trial of CTLA-4 blockade with human anti-CTLA-4 in patients with hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1810–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, L.F.; Clay, T.M.; Morse, M.A. Update on anti-CTLA-4 antibodies in clinical trials. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2007, 7, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, S.D.; Kalyan, A.; Kircher, S.; Nimeiri, H.; Fought, A.J.; Benson, A., 3rd; Mulcahy, M. Ipilimumab and Gemcitabine for Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Phase Ib Study. Oncologist 2020, 25, e808–e815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal, R.E.; Levy, C.; Turner, K.; Mathur, A.; Hughes, M.; Kammula, U.S.; Sherry, R.M.; Topalian, S.L.; Yang, J.C.; Lowy, I.; et al. Phase 2 trial of single agent Ipilimumab (anti-CTLA-4) for locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Immunother. 2010, 33, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.C.; Yarchoan, M.; Durham, J.N.; Yusko, E.C.; Rytlewski, J.A.; Robins, H.S.; Laheru, D.A.; Le, D.T.; Lutz, E.R.; Jaffee, E.M. T cell receptor repertoire features associated with survival in immunotherapy-treated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e122092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Dey, M.K.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. Biomarkers in Cancer Detection, Diagnosis, and Prognosis. Sensors 2023, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, F.; Suzuki, K.; Noda, H.; Rikiyama, T. Liquid biopsy leads to a paradigm shift in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 6478–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shaheri, F.N.; Alhamdani, M.S.S.; Bauer, A.S.; Giese, N.; Büchler, M.W.; Hackert, T.; Hoheisel, J.D. Blood biomarkers for differential diagnosis and early detection of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 96, 102193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Eresen, A.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yaghmai, V.; Zhang, Z. Dendritic cell vaccination combined with irreversible electroporation for treating pancreatic cancer-a narrative review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2024, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lin, X.; Shen, Q.; Qian, X. Combined Spiral Transformation and Model-Driven Multi-Modal Deep Learning Scheme for Automatic Prediction of TP53 Mutation in Pancreatic Cancer. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatate, Y.; Hoshino, I.; Yokota, H.; Ishige, F.; Itami, M.; Mori, Y.; Chiba, S.; Arimitsu, H.; Yanagibashi, H.; Nagase, H.; et al. Radiogenomics for predicting p53 status, PD-L1 expression, and prognosis with machine learning in pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Ge, J.; Tang, G.; Xiong, D.; Zhu, D.; Ding, X.; Zhou, X.; Sang, M. Machine learning-based identification of biomarkers and drugs in immunologically cold and hot pancreatic adenocarcinomas. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Materka, A.; Langs, G.; Häggström, I.; Szczypiński, P.; Gibbs, P.; Cook, G. Introduction to Radiomics. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Xue, H.; Jin, Z. Radiomics in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A state of art review. J. Pancreatol. 2020, 3, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, B.; Kudryashova, O.; Kravets, A.; Thalji, S.; Malarkannan, S.; Kurzrock, R.; Chernyavskaya, E.; Gusakova, M.; Kravchenko, D.; Tychinin, D.; et al. Transcriptomic-Based Microenvironment Classification Reveals Precision Medicine Strategies for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2024, 166, 859–871.e853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Meng, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Feng, X.; et al. Preoperative Radiomics Approach to Evaluating Tumor-Infiltrating CD8(+) T Cells in Patients With Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Using Noncontrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 2022, 55, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Shang, N.; Shangguan, J.; Figini, M.; Xing, W.; Wang, B.; Sun, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, S.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging monitoring therapeutic response to dendritic cell vaccine in murine orthotopic pancreatic cancer models. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 562–573. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Wu, G.; Miao, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Shentu, D.; Xue, S.; Xia, Q.; Wang, Y.; et al. The radiomics nomogram predicts the prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients with hepatic metastasis after chemoimmunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2024, 73, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blise, K.E.; Sivagnanam, S.; Betts, C.B.; Betre, K.; Kirchberger, N.; Tate, B.J.; Furth, E.E.; Dias Costa, A.; Nowak, J.A.; Wolpin, B.M.; et al. Machine Learning Links T-cell Function and Spatial Localization to Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy and Clinical Outcome in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2024, 12, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, R.; Shi, J.; Yang, C.; Ma, P.; Min, J.; Zhao, T.; Hua, L.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Machine learning-based integration develops a metabolism-derived consensus model for improving immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. J. ImmunoTherapy Cancer 2023, 11, e007466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Dollinger, E.; Nie, Q. Machine Learning of Single Cell Transcriptomic Data From anti-PD-1 Responders and Non-responders Reveals Distinct Resistance Mechanisms in Skin Cancers and PDAC. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 806457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Chen, C.; Ouyang, Q.; Han, R.; Sun, P.; Chen, H. Machine learning models for predicting of PD-1 treatment efficacy in Pan-cancer patients based on routine hematologic and biochemical parameters. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Q. Establishment and Verification of a Novel Gene Signature Connecting Hypoxia and Lactylation for Predicting Prognosis and Immunotherapy of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients by Integrating Multi-Machine Learning and Single-Cell Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ta, N.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Zhu, X.; Kong, L.; Gong, X.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y. Unraveling pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma immune prognostic signature through a naive B cell gene set. Cancer Lett. 2024, 594, 216981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Lopez, R.; Ghaffari Laleh, N.; Mahmood, F.; Kather, J.N. A guide to artificial intelligence for cancer researchers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2024, 24, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, S.S.; Aerts, H.J. Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, R150–R166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placido, D.; Yuan, B.; Hjaltelin, J.X.; Zheng, C.; Haue, A.D.; Chmura, P.J.; Yuan, C.; Kim, J.; Umeton, R.; Antell, G.; et al. A deep learning algorithm to predict risk of pancreatic cancer from disease trajectories. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Xia, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, X.; Lambert, L.; Zhang, T.; Tang, W.; Jin, G.; Jiang, H.; Fang, X.; et al. Large-scale pancreatic cancer detection via non-contrast CT and deep learning. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, H.; Han, I.W.; Song, S.; Shin, J.; Song, H.; Park, S.; Pereira, S.; Shin, S.H.; et al. Artificial intelligence (AI) –powered spatial analysis of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) for prediction of prognosis in resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Man, Q.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Hou, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, J.; Wei, X.; Bai, W.; Liu, Z.; et al. Artificial intelligence-based comprehensive analysis of immune-stemness-tumor budding profile to predict survival of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol. Med. 2023, 20, 196–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanguri, R.S.; Luo, J.; Aukerman, A.T.; Egger, J.V.; Fong, C.J.; Horvat, N.; Pagano, A.; Araujo-Filho, J.A.B.; Geneslaw, L.; Rizvi, H.; et al. Multimodal integration of radiology, pathology and genomics for prediction of response to PD-(L)1 blockade in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.; Kulkarni, A.; Agorku, D.; Midelashvili, T.; Hardt, O.; Legler, T.J.; Ströbel, P.; Conradi, L.C.; Alves, F.; Ramos-Gomes, F.; et al. OrganoIDNet: A deep learning tool for identification of therapeutic effects in PDAC organoid-PBMC co-cultures from time-resolved imaging data. Cell Oncol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Park, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Jun, E.; Song, K.B.; Hwang, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, K.; Kim, N.; Lee, S.S.; et al. Preoperative data-based deep learning model for predicting postoperative survival in pancreatic cancer patients. Int. J. Surg. 2022, 105, 106851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; He, Y.; Li, F.; Han, L.; You, C.; Wang, B. Segment anything in medical images. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wong, C.; Zhang, S.; Usuyama, N.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Naumann, T.; Poon, H.; Gao, J. LLaVA-Med: Training a Large Language-and-Vision Assistant for Biomedicine in One Day. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.00890. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Yavuz, M.C.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Yuille, A.; Tang, Y.; et al. Universal and extensible language-vision models for organ segmentation and tumor detection from abdominal computed tomography. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 97, 103226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ICIs Type | ICIs Name | Other Treatments | NCT | Phase | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTLA-4 | Ipilimumab | KRAS peptide vaccine | NCT04117087 | PHASE1 | RECRUITING |
| Niraparib + Ipilimumab | NCT03404960 | PHASE1|PHASE2 | ACTIVE_NOT_RECRUITING | ||
| PD-1 | Niraparib + Nivolumab | NCT03404960 | PHASE1|PHASE2 | ACTIVE_NOT_RECRUITING | |
| Nivolumab | BMS-813160, Gemcitabine, Nab-paclitaxel, Biopsy, Peripheral blood | NCT03496662 | PHASE1|PHASE2 | ACTIVE_NOT_RECRUITING | |
| Stereotactic Body Radiation (SBRT), CCR2/CCR5 dual antagonist, GVAX | NCT03767582 | PHASE1|PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| Irreversible Electroporation (IRE), Toll-Like Receptor 9 | NCT04612530 | PHASE1 | RECRUITING | ||
| KRAS peptide vaccine | NCT04117087 | PHASE1 | RECRUITING | ||
| Albumin-bound paclitaxel, Paricalcitol, Cisplatin, Gemcitabine | NCT02754726 | PHASE2 | ACTIVE_NOT_RECRUITING | ||
| BMS-986416 | NCT04943900 | PHASE1 | ACTIVE_NOT_RECRUITING | ||
| RO7496353, Capecitabine, S-1, Oxaliplatin, Nab-paclitaxel, Gemcitabine | NCT05867121 | PHASE1 | RECRUITING | ||
| Daratumumab, KRAS vaccine | NCT06015724 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| Fluorouracil, Irinotecan, Irinotecan Hydrochloride, Leucovorin, Leucovorin Calcium, Oxaliplatin, Therapeutic Conventional Surgery | NCT03970252 | EARLY_PHASE1 | ACTIVE_NOT_RECRUITING | ||
| Regorafenib, (Stivarga, BAY73-4506) | NCT04704154 | PHASE2 | ACTIVE_NOT_RECRUITING | ||
| SX-682 | NCT04477343 | PHASE1 | RECRUITING | ||
| Pembrolizumab | Defactinib | NCT03727880 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | |
| PEGPH20 | NCT03634332 | PHASE2 | UNKNOWN | ||
| GEN1042, Cisplatin, Carboplatin, 5-FU, Gemcitabine, Nab paclitaxel, Pemetrexed, Paclitaxel | NCT04083599 | PHASE1|PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| Folfirinox | NCT05132504 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| BXCL701 | NCT05558982 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| Olaparib | NCT04666740 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| Lenvatinib Mesylate | NCT04887805 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| Belzutifan, Lenvatinib | NCT04976634 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| Imiquimod, Sotigalimab, Synthetic Tumor-Associated Peptide Vaccine Therapy, Computed Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging | NCT02600949 | PHASE1 | RECRUITING | ||
| Epacadostat | NCT03432676 | PHASE2 | WITHDRAWN | ||
| Lenvatinib | NCT05273554 | PHASE1 | RECRUITING | ||
| PF-07934040, Gemcitabine, Nab-paclitaxel, Cetuximab, Fluorouracil, Oxaliplatin, Leucovorin, Bevacizumab, pemetrexed, Cisplatin, Paclitaxel, Carboplatin | NCT06447662 | PHASE1 | NOT_YET_RECRUITING | ||
| Nab-paclitaxel, Gemcitabine, Cisplatin, Irinotecan, Capecitabine, Olaparib | NCT04753879 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| Epacadostat, Oxaliplatin, Leucovorin, 5-Fluorouracil, Gemcitabine, nab-Paclitaxel, Carboplatin, Paclitaxel, Pemetrexed, Cyclophosphamide, Carboplatin, Cisplatin, 5-Fluorouracil, investigator’s choice of platinum agent | NCT03085914 | PHASE1|PHASE2 | COMPLETED | ||
| Futibatinib, Cisplatin, 5-FU, Oxaliplatin, Leucovorin, Levoleucovorin, Irinotecan | NCT05945823 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| PD-L1 | Atezolizumab | PEGPH20 | NCT03979066 | PHASE2 | TERMINATED |
| Tumor Treating Fields, Gemcitabine, Nab-paclitaxel | NCT06390059 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| RO7496353, Capecitabine, S-1, Oxaliplatin, Nab-paclitaxel, Gemcitabine | NCT05867121 | PHASE1 | RECRUITING | ||
| Autogene cevumeran, mFOLFIRINOX | NCT05968326 | PHASE2 | RECRUITING | ||
| Nab-paclitaxel, Gemcitabine, Oxaliplatin, Leucovorin, Fluorouracil, Cobimetinib, PEGPH20, BL-8040, Selicrelumab, Bevacizumab, RO6874281, AB928, Tiragolumab, Tocilizumab | NCT03193190 | PHASE1|PHASE2 | ACTIVE_NOT_RECRUITING | ||
| Durvalumab | Rintatolimod | NCT05927142 | PHASE1|PHASE2 | RECRUITING | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Eresen, A.; Hou, Q.; Amirrad, F.; Webster, S.; Nauli, S.; Yaghmai, V.; Zhang, Z. Predicting and Monitoring Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy Using Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212038
Yu G, Zhang Z, Eresen A, Hou Q, Amirrad F, Webster S, Nauli S, Yaghmai V, Zhang Z. Predicting and Monitoring Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy Using Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(22):12038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212038
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Guangbo, Zigeng Zhang, Aydin Eresen, Qiaoming Hou, Farideh Amirrad, Sha Webster, Surya Nauli, Vahid Yaghmai, and Zhuoli Zhang. 2024. "Predicting and Monitoring Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy Using Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 22: 12038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212038
APA StyleYu, G., Zhang, Z., Eresen, A., Hou, Q., Amirrad, F., Webster, S., Nauli, S., Yaghmai, V., & Zhang, Z. (2024). Predicting and Monitoring Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy Using Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(22), 12038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252212038








