Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Metabolomic Analysis of Ilex Rotunda Extracted by Supercritical Fluid Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
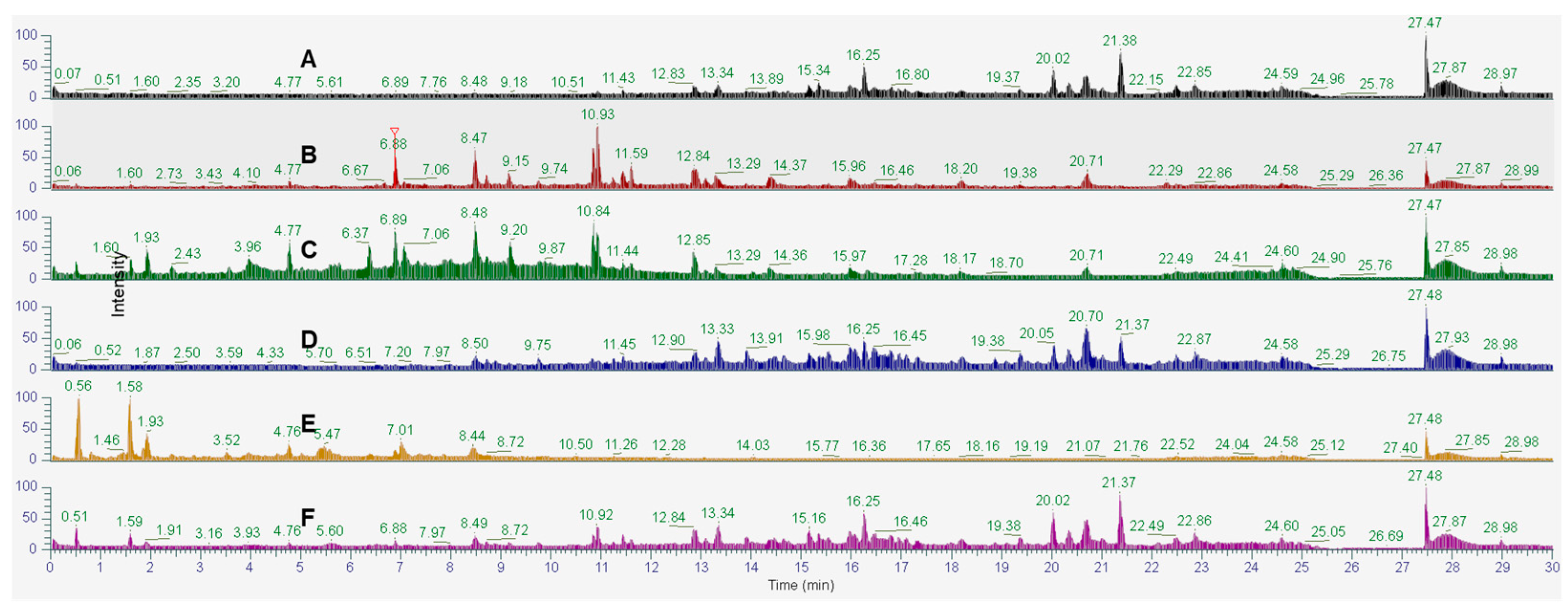
2.1. Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE)
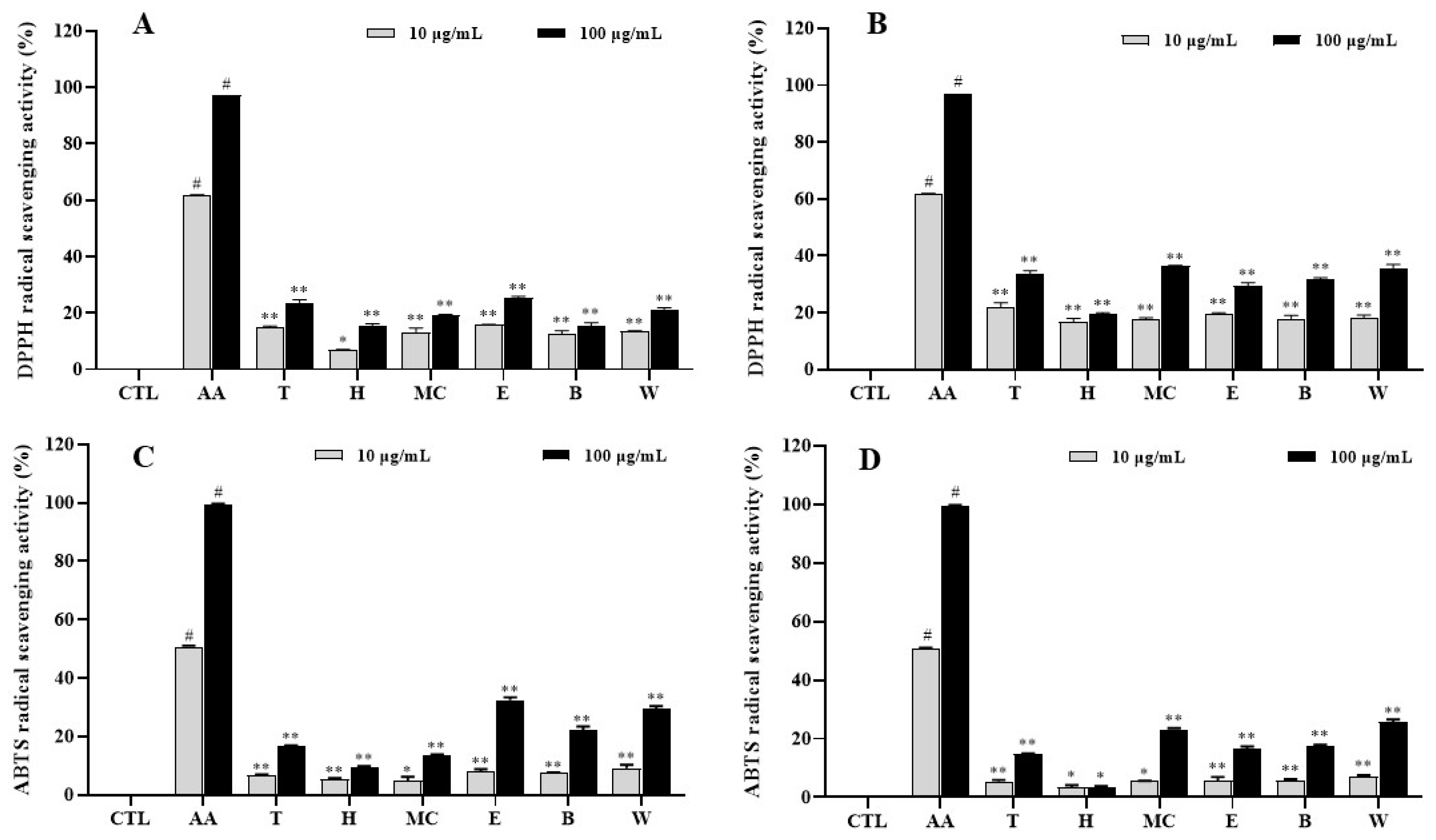
2.2. Antioxidative Effects of Extracts and Fractions
2.3. Effects of Leaf and Twig Extracts and Their Fractions on Cell Viability
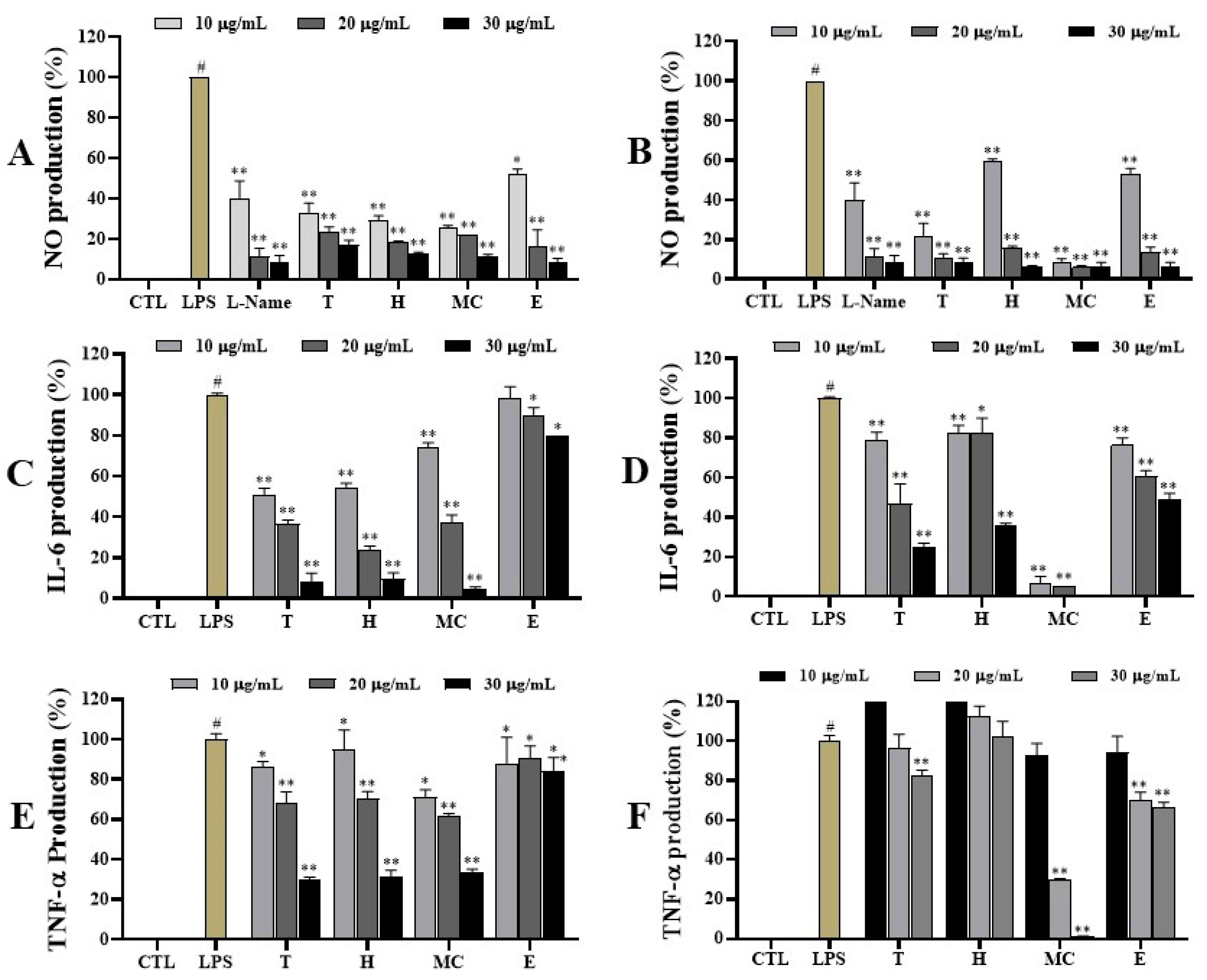
2.4. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
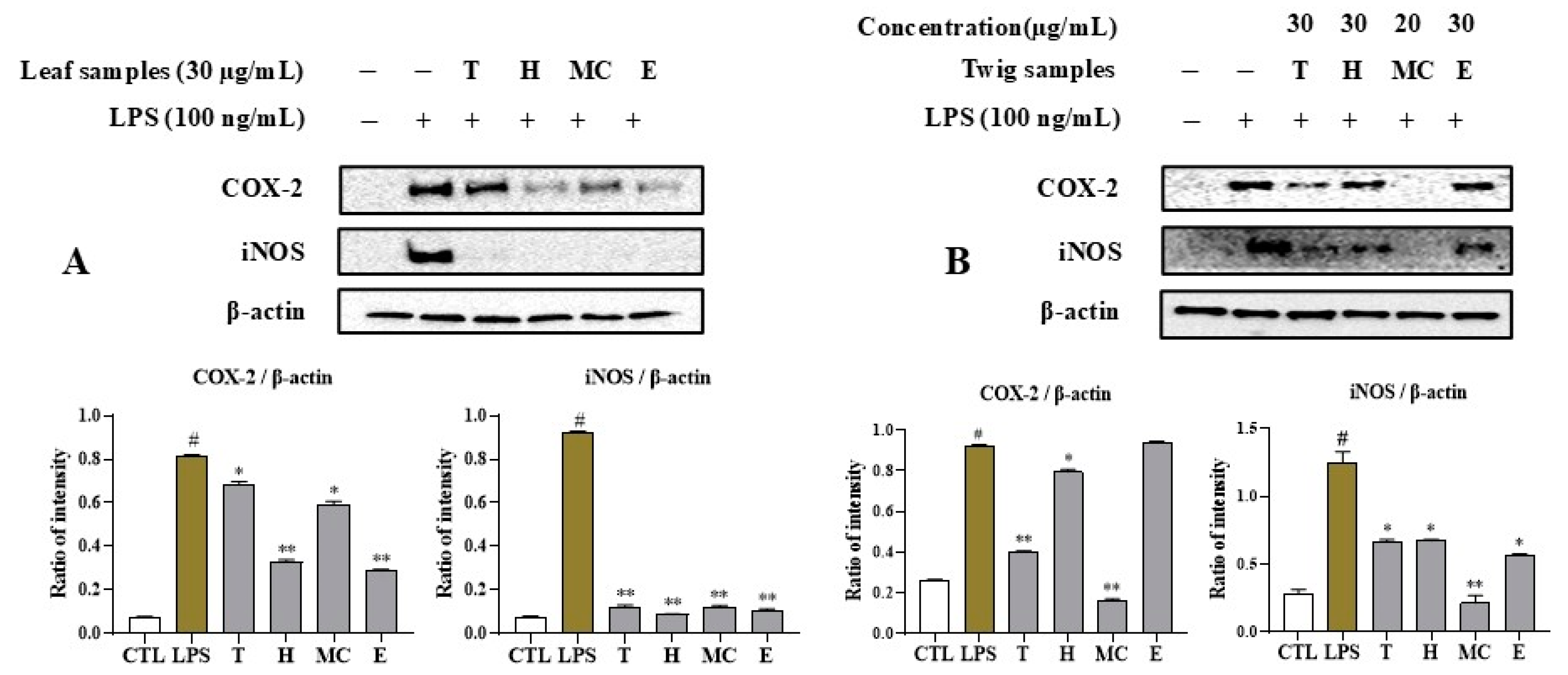
2.5. MNM Extract and Fractions Regulate iNOS and COX-2 Expression
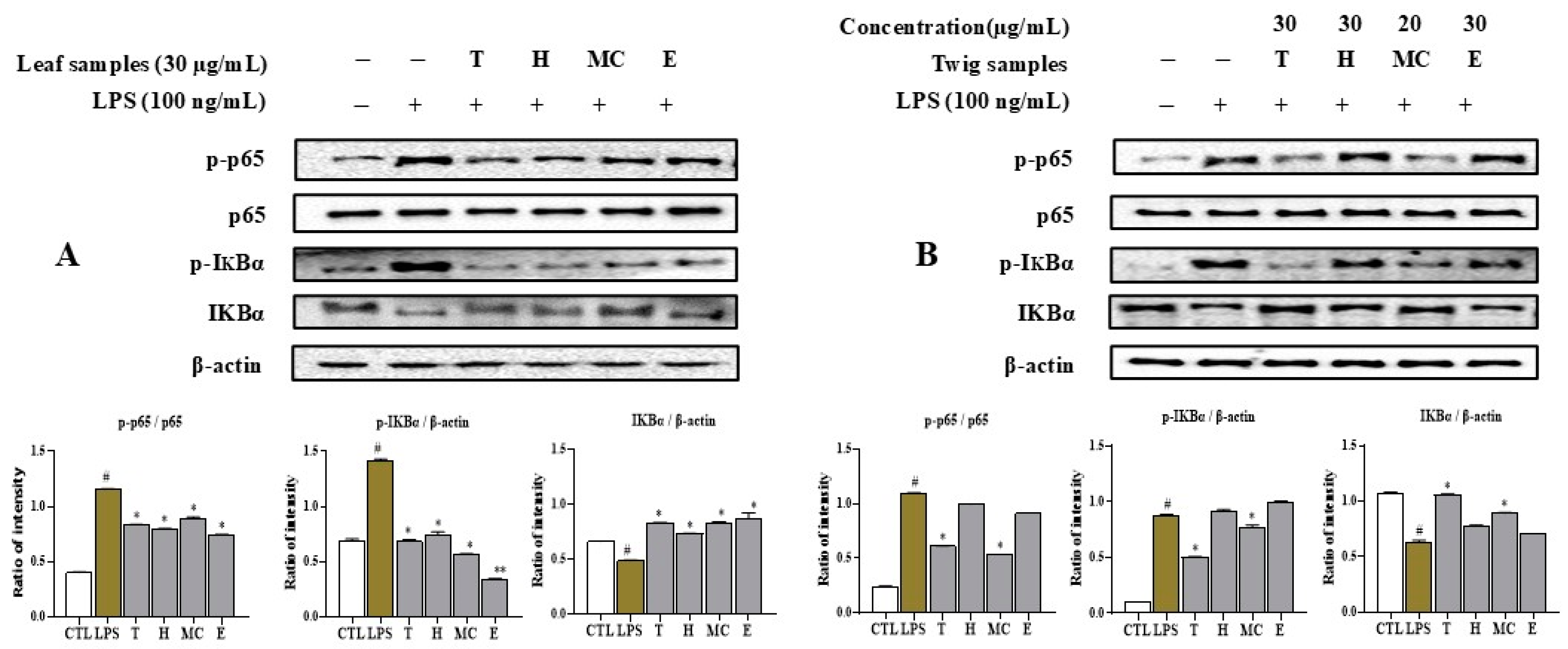
2.6. Leaf and Twig Extracts and Their Fractions Downregulate LPS-Induced NFκB Activation in RAW264.7 Macrophages
2.7. MNM Extracts and Fractions Mediate LPS-Induced MAPK Activation in RAW264.7 Cells
2.8. MNM Mediates CD3/CD28-Induced IL-2 Production in Jurkat T Cells
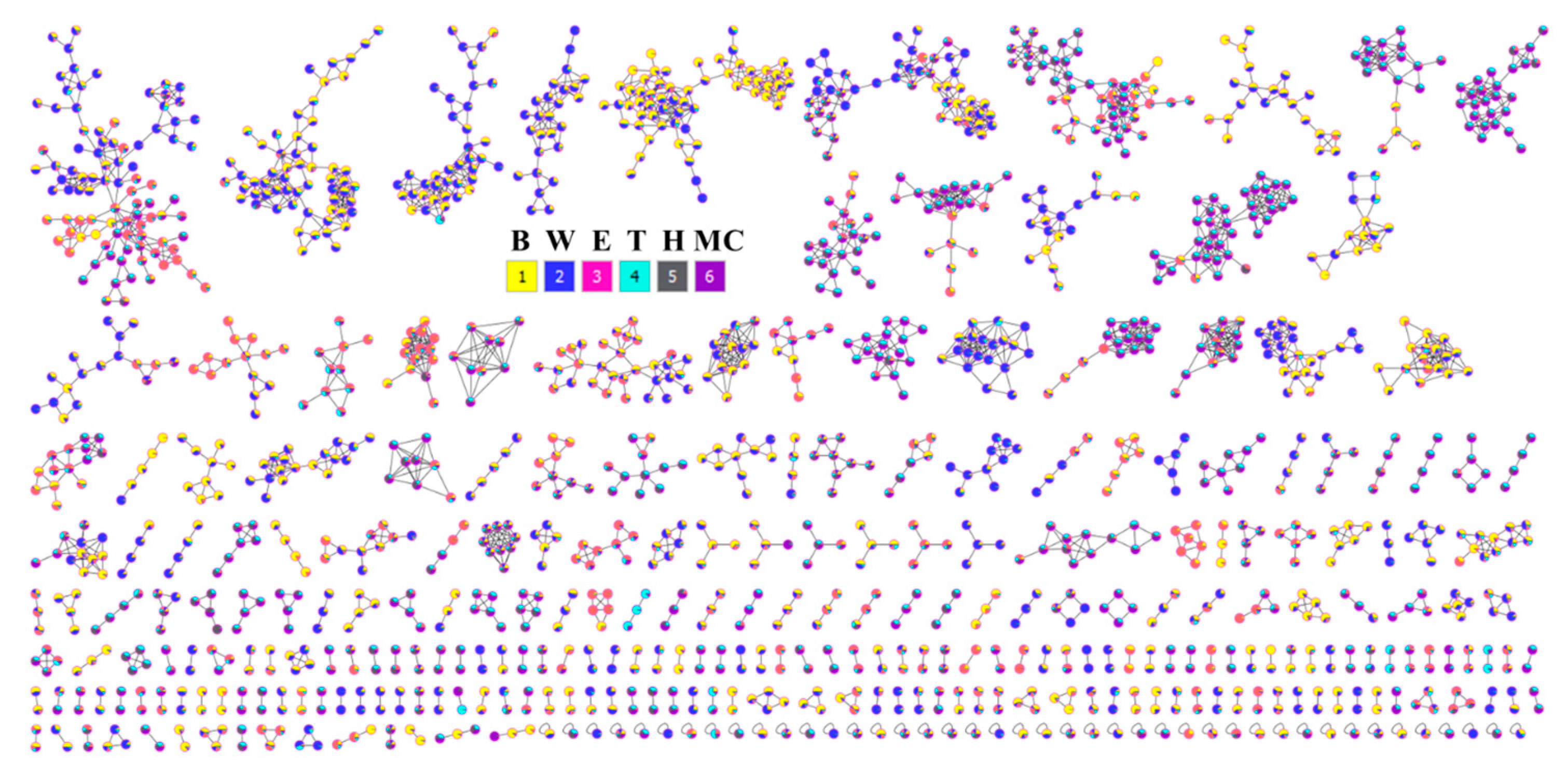
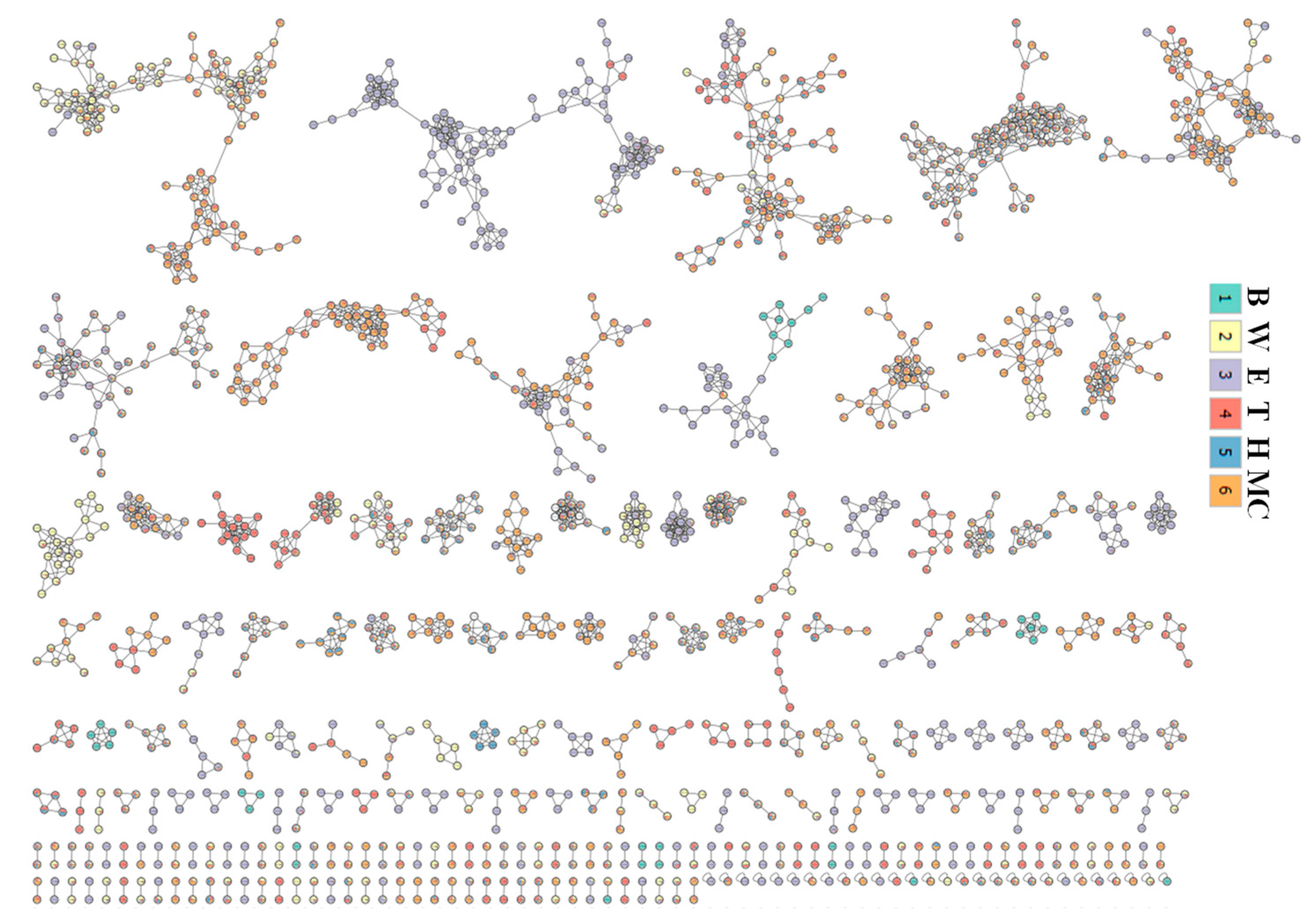
2.9. Phytochemical Profiling and Prediction of Compounds Using Open-Source Tools
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Extraction and Fractionation Conditions
4.3. Biological Assays
4.3.1. Determination of Anti-Inflammatory Mediator and Cytokines
Cell Culture and Viability
Measurement of NO Production
ELISA Assay
4.3.2. Western Blot Assay
4.4. LC-MS/MS Data Analysis
4.4.1. LC-MS/MS Conditions
4.4.2. Molecular Networking
4.4.3. LC-MS Annotations
4.4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhonghu, R.; Gongheguo, W.; Sheng, B.-Y.; Dian, W.; Yuan, H. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xiong, T.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.; Tan, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Jin, J. Antiplatelet aggregation triterpene saponins from the barks of Ilex rotunda. Fitoterapia 2015, 101, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Jung, E.B.; Lee, M.S.; Seo, S.J.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, M.W.; Lee, C.S. Rotundarpene inhibits Toll-like receptor 2 activation-induced production of inflammatory mediators in keratinocytes by suppressing the Akt and NF-κB pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 18, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Huang, C.-W.; Chang, P.-C.; Shiau, J.-P.; Lin, I.-P.; Lin, M.-Y.; Lai, C.-C.; Chen, C.-Y. Reactive oxygen species mediate the chemopreventive effects of syringin in breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 61, 152844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Li, S.; Qin, J.; Xie, L.; Gan, L.; Jie, F.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, Q. Kuijieling regulates the differentiation of Treg and Th17 cells to ameliorate experimental colitis in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gu, H.; Jia, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Shi, Q. Syringin protects against colitis by ameliorating inflammation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 680, 108242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Zhao, F.; Hu, M.; Xu, Z.; Yang, B.; Guo, J.; Sun, S.; et al. Pedunculoside attenuates pathological phenotypes of fibroblast-like synoviocytes and protects against collagen-induced arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 48, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X.; Yuan, R.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Han, S.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Yang, S.; Gao, H. Rotundic acid reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury in vitro and in vivo through regulating TLR4 dimer. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 4485–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Alhamlan, F.S.; Al-Qahtani, A.A. Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory interleukins in infectious diseases: A comprehensive review. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, L.; Warner, N.; Viani, K.; Nuñez, G. Function of Nod-like receptors in microbial recognition and host defense. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 227, 106–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiu To, Y.; Faisal, A.; Angelica, G.-C.; Sandro, A. Signaling Pathways in Inflammation and Anti-inflammatory Therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1449–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisoncik Jennifer, R.; Korth Marcus, J.; Simmons Cameron, P.; Farrar, J.; Martin Thomas, R.; Katze Michael, G. Into the eye of the cytokine storm. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.J.; Gong, J.P.; Zhang, W. Transcriptional co-regulator RIP140: An important mediator of the inflammatory response and its associated diseases (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. Anti-Inflammatory therapeutic mechanisms of natural products: Insight from rosemary diterpenes, carnosic acid and carnosol. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Du, H.; Liu, D.; Ma, Z. Editorial: The role of natural products in chronic inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 901538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anklam, E.; Berg, H.; Mathiasson, L.; Sharman, M.; Ulberth, F. Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) in food analysis: A review. Food Addit. Contam. 1998, 15, 729–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwineza, P.A.; Waśkiewicz, A. Recent advances in supercritical fluid extraction of natural bioactive compounds from natural plant materials. Molecules 2020, 25, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrona, O.; Rafińska, K.; Możeński, C.; Buszewski, B. Supercritical fluid extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 1624–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F. Strategies for targeting cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennyson, A.G.; Lippard, S.J. Generation, translocation, and action of nitric oxide in living systems. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, R.K.; Wilson, K.T. Nitric oxide in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2003, 9, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, S.G.; Romão, P.R.T.; Figueiredo, F.; Morais, R.H.; Lima, H.C.; Ferreira, S.H.; Cunha, F.Q. TNF-α mediates the induction of nitric oxide synthase in macrophages but not in neutrophils in experimental cutaneous leishmaniasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 2297–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purwata, T.E. High TNF-alpha plasma levels and macrophages iNOS and TNF-alpha expression as risk factors for painful diabetic neuropathy. J. Pain Res. 2011, 4, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Min, J.-S.; Kim, B.; Chae, U.-B.; Yun, J.W.; Choi, M.-S.; Kong, I.-K.; Chang, K.-T.; Lee, D.-S. Mitochondrial ROS govern the LPS-induced pro-inflammatory response in microglia cells by regulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 584, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, B. MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy—From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1754, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, M.; Ryan, M.P.; Watson, A.J.; Schramek, H.; Healy, E. Role of MAP kinase pathways in mediating IL-6 production in human primary mesangial and proximal tubular cells. Kidney Int. 1999, 56, 1366–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.D.; Kim, Y.-R.; Yu, S.; Dang, T.; Lee, K.-T.; Lee, M. Phytochemical and bioactivities of promising flavonoid glycosides and their content from unmatured fruits of Vicia bungei with their bioactivity. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, K.E.; Feerick, A.; Braun, J.M.; Feng, Y.-L.; Hall, A.; Koelmel, J.; Manzano, C.; Newton, S.R.; Pennell, K.D.; Place, B.J.; et al. Non-targeted analysis (NTA) and suspect screening analysis (SSA): A review of examining the chemical exposome. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagoskina, N.V.; Zubova, M.Y.; Nechaeva, T.L.; Kazantseva, V.V.; Goncharuk, E.A.; Katanskaya, V.M.; Baranova, E.N.; Aksenova, M.A. Polyphenols in plants: Structure, biosynthesis, abiotic stress regulation, and practical applications (Review). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prado-Audelo, M.L.; Cortés, H.; Caballero-Florán, I.H.; González-Torres, M.; Escutia-Guadarrama, L.; Bernal-Chávez, S.A.; Giraldo-Gomez, D.M.; Magaña, J.J.; Leyva-Gómez, G. Therapeutic applications of terpenes on inflammatory diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 704197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Câmara, J.S.; Perestrelo, R.; Ferreira, R.; Berenguer, C.V.; Pereira, J.A.M.; Castilho, P.C. Plant-derived terpenoids: A plethora of bioactive compounds with several health functions and industrial applications—A comprehensive overview. Molecules 2024, 29, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambriz-Pérez, D.L.; Leyva-López, N.; Gutierrez-Grijalva, E.P.; Heredia, J.B. Phenolic compounds: Natural alternative in inflammation treatment. A Review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1131412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Phenolic acids: Natural versatile molecules with promising therapeutic applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24, e00370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toschi, A.; Rossi, B.; Tugnoli, B.; Piva, A.; Grilli, E. Nature-identical compounds and organic acids ameliorate and prevent the damages induced by an inflammatory challenge in Caco-2 cell culture. Molecules 2020, 25, 4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.D.; Han, S.; Yu, J.; Ahn, J.; Kim, C.-K.; Lee, M. Iridoid derivatives from Vitex rotundifolia L. f. with their anti-inflammatory activity. Phytochemistry 2023, 210, 113649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, D.D.; Jang, Y.S.; Truong, V.; Dinh, T.; Dang, T.; Yu, S.; Lee, M. Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Metabolomic Analysis of Ilex Rotunda Extracted by Supercritical Fluid Extraction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11965. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252211965
Le DD, Jang YS, Truong V, Dinh T, Dang T, Yu S, Lee M. Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Metabolomic Analysis of Ilex Rotunda Extracted by Supercritical Fluid Extraction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(22):11965. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252211965
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Duc Dat, Young Su Jang, Vinhquang Truong, Thientam Dinh, Thinhulinh Dang, Soojung Yu, and Mina Lee. 2024. "Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Metabolomic Analysis of Ilex Rotunda Extracted by Supercritical Fluid Extraction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 22: 11965. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252211965
APA StyleLe, D. D., Jang, Y. S., Truong, V., Dinh, T., Dang, T., Yu, S., & Lee, M. (2024). Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Metabolomic Analysis of Ilex Rotunda Extracted by Supercritical Fluid Extraction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(22), 11965. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252211965




