Sex and Age-Dependent Effects of miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir on Ischemic Stroke Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
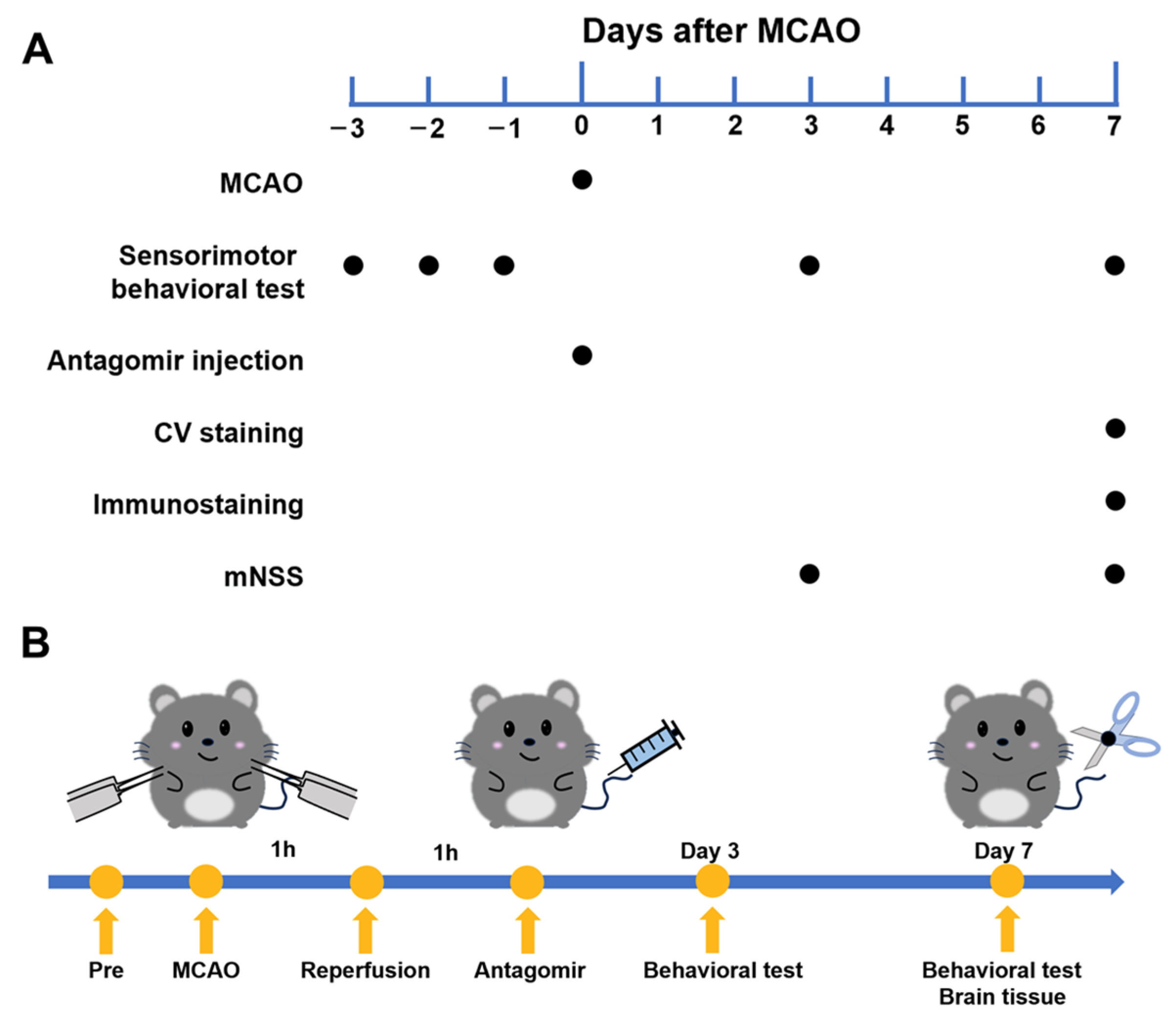
2.1. Experimental Flowchart
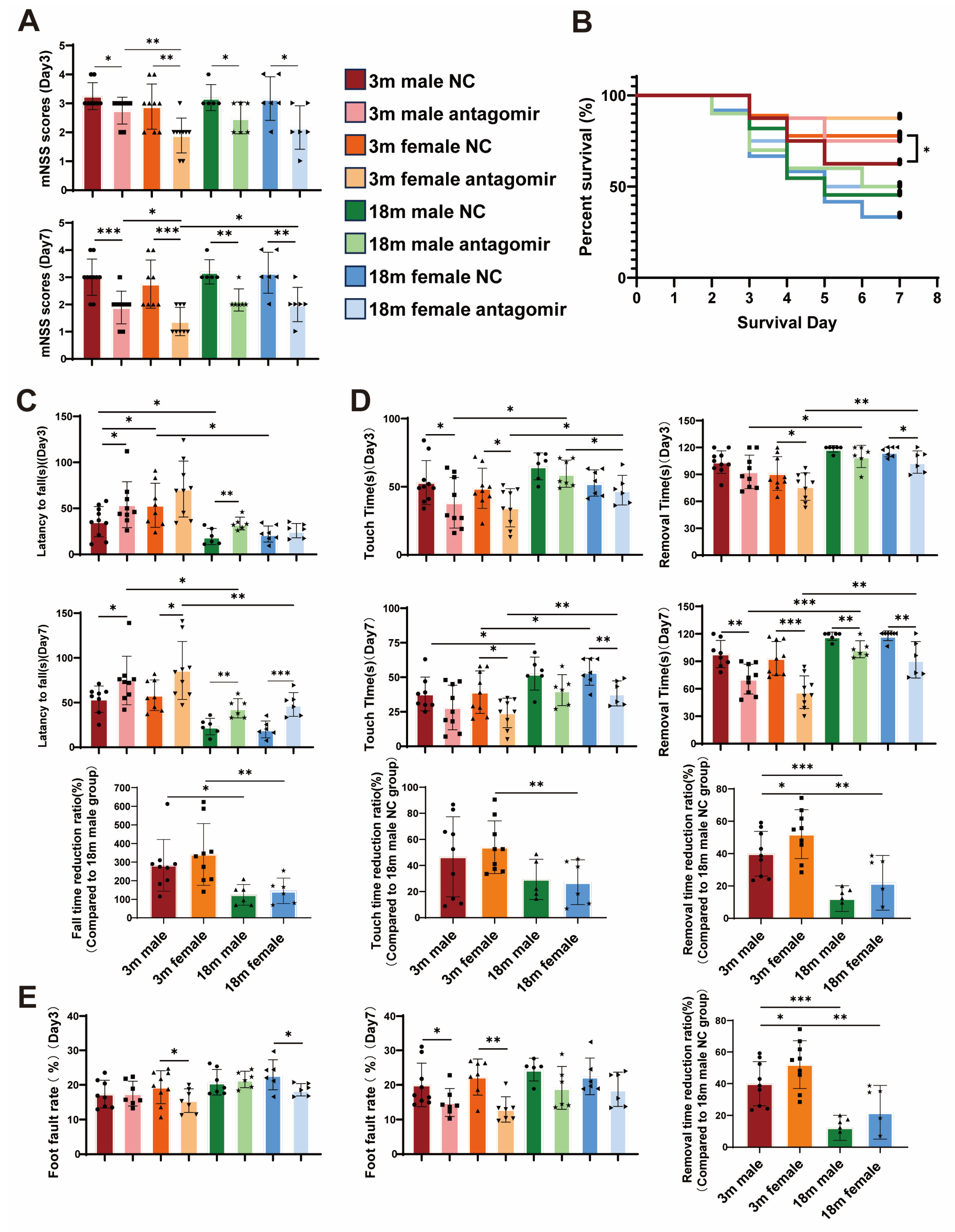
2.2. miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir Improves Sensorimotor Behavior in Mice After tMCAO
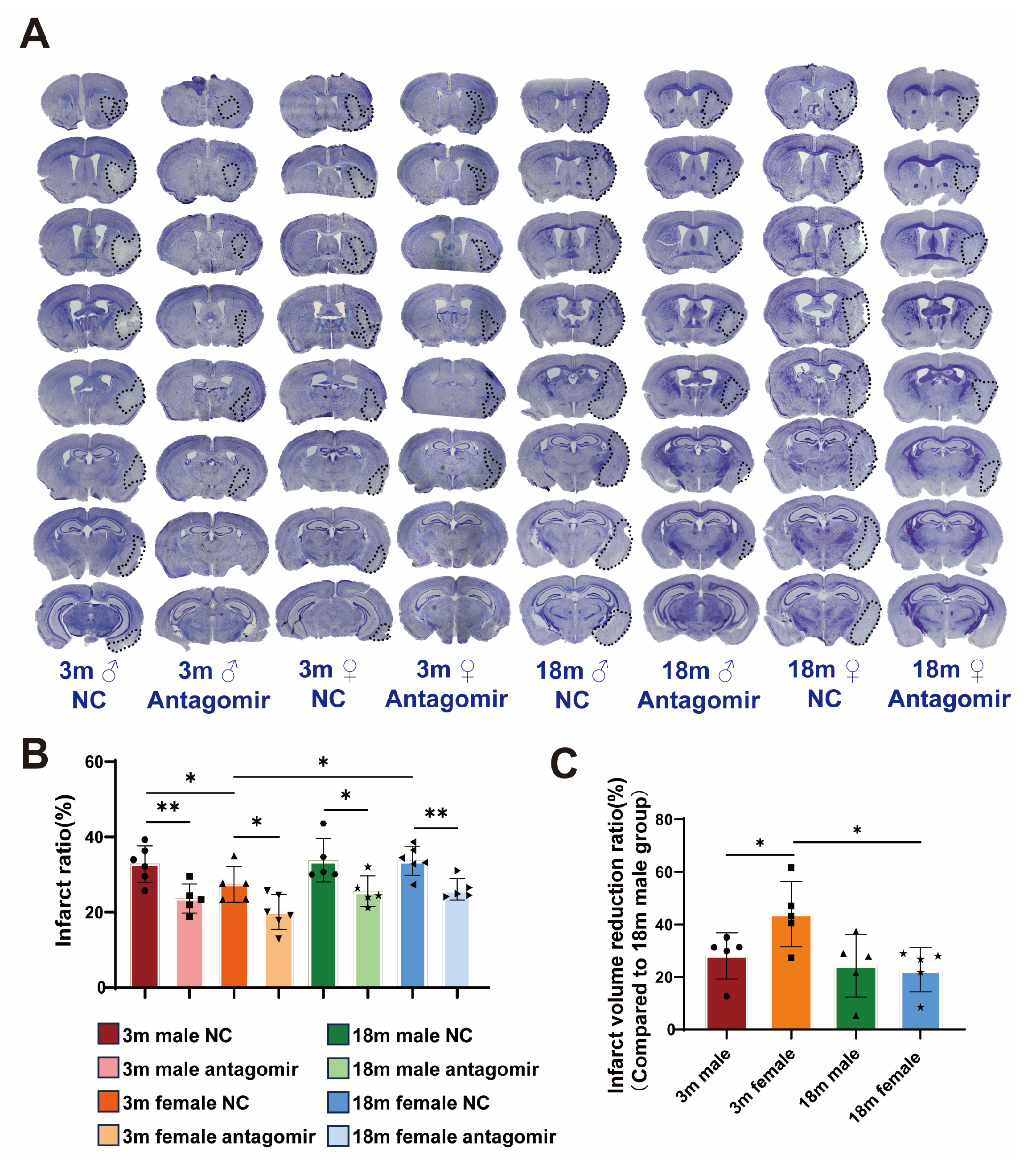
2.3. miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir Reduces Brain Infarct Volume in Mice 7 Days After tMCAO
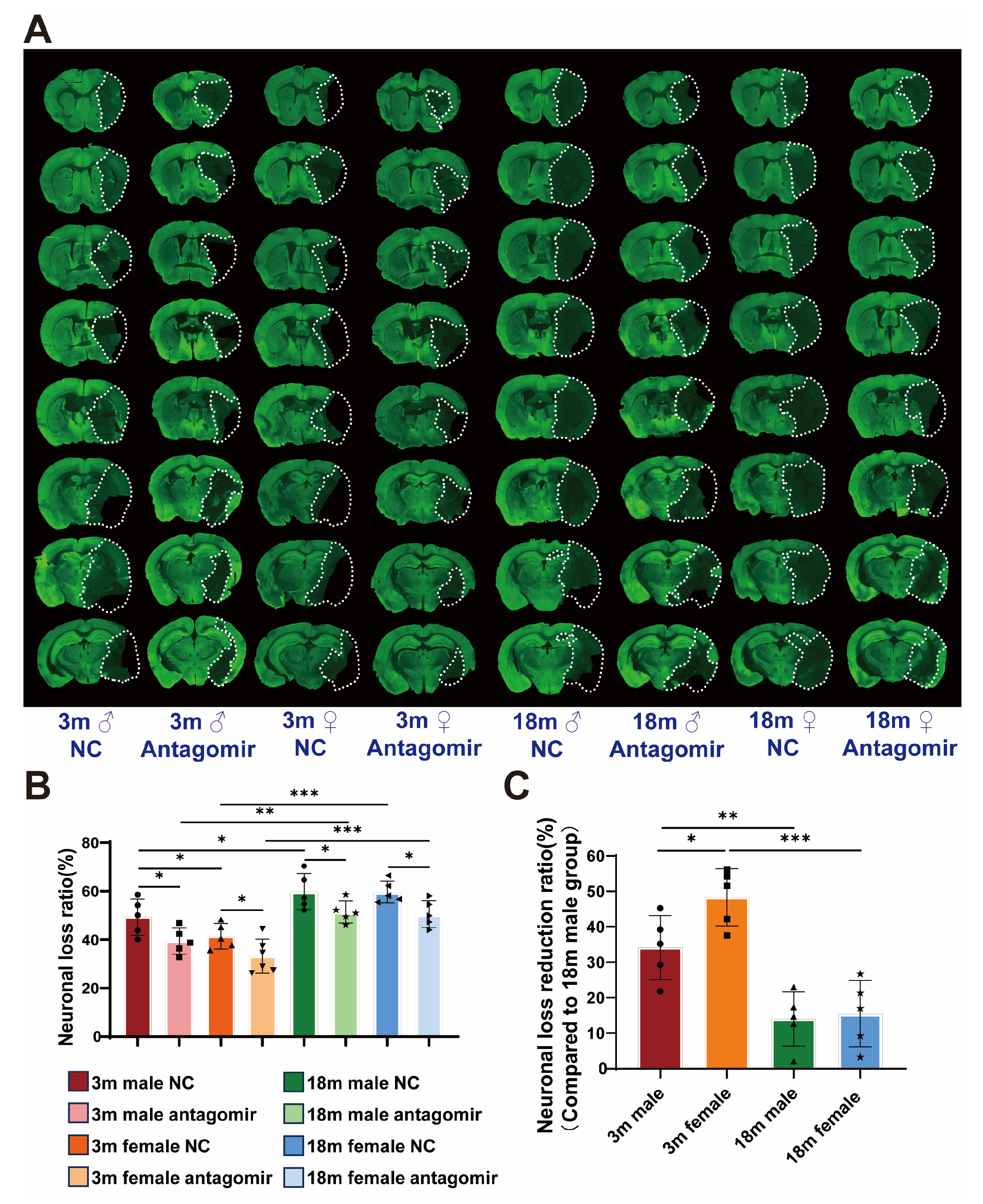
2.4. miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir Reduces Neuronal Loss Volume in Mice 7 Days After tMCAO
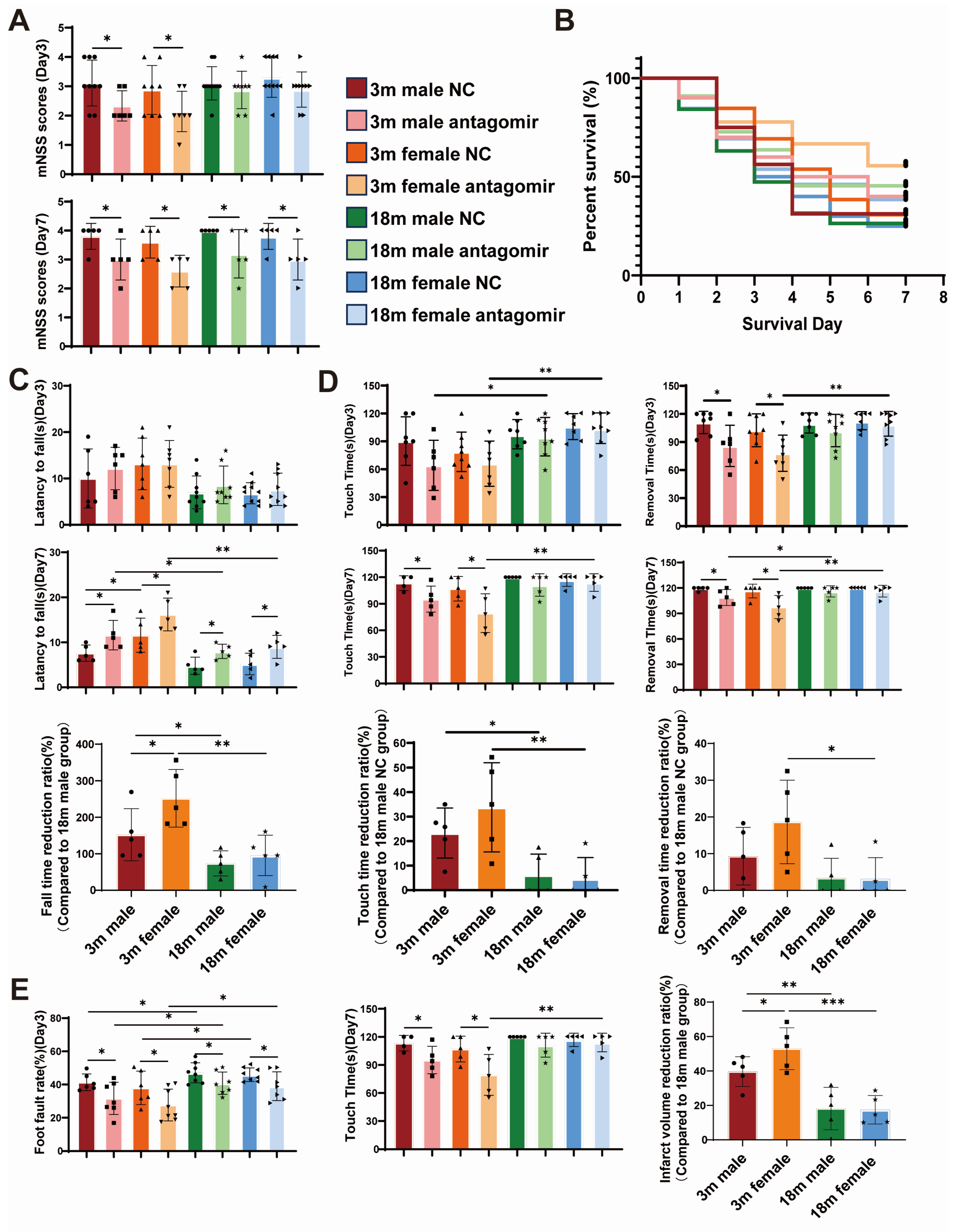
2.5. miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir Improves Sensorimotor Behavior in Mice After pMCAO
2.6. miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir Reduces Brain Infarct Volume in Mice 7 Days After pMCAO
2.7. miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir Reduces Neuronal Loss Volume in Mouse 7 Days After pMCAO
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Mouse Model of Transient/Permanent Focal Cerebral Ischemia
4.3. Intravenous Administration of miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir
4.4. Neurobehavioral Tests
4.5. Cresyl Violet (CV) Staining
4.6. MAP2 Immunostaining
4.7. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Abate, M.D.; Abate, Y.H.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdelkader, A.; Abdelmasseh, M.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Abdi, P.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Stroke and Its Risk Factors, 1990–2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 973–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, P.M.; Steinberg, G.K. Novel Stroke Therapeutics: Unraveling Stroke Pathophysiology and Its Impact on Clinical Treatments. Neuron 2015, 87, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; Khatri, P. Stroke. Lancet 2020, 396, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkor, E.S. Stroke in the 21st Century: A Snapshot of the Burden, Epidemiology, and Quality of Life. Stroke Res. Treat. 2018, 2018, 3238165. [Google Scholar]
- Feigin, V.L.; Norrving, B.; Mensah, G.A. Global Burden of Stroke. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qiu, N.; Ni, A.; Hamblin, M.H.; Yin, K.J. Role of Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs in Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurochem. Int. 2024, 172, 105643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkoly, E.; Ståhle, M.; Pivarcsi, A. MicroRNAs and Immunity: Novel Players in the Regulation of Normal Immune Function and Inflammation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, B.; Wollheim, C. MicroRNAs: ‘ribo-regulators’ of glucose homeostasis. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, D.Z.; Jickling, G.C.; Sharp, F.R.; Yin, K.J. MicroRNA-Based Therapeutics in Central Nervous System Injuries. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 1125–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Cui, W.; Shi, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhou, J.; Han, L.; et al. Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicular MiR-143-3p Dampens Autophagic Degradation of Endothelial Adhesion Molecules and Promotes Neutrophil Transendothelial Migration after Acute Brain Injury. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2305339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestro, S.; Mazzon, E. MiRNAs as Promising Translational Strategies for Neuronal Repair and Regeneration in Spinal Cord Injury. Cells 2022, 11, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.L.; He, X.S.; Liu, J.R.; Zheng, C.B.; Wang, Y.T.; Yang, G.Y. Lentivirus-Mediated Overexpression of MicroRNA-210 Improves Long-Term Outcomes after Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Morris-Blanco, K.C.; Lopez, M.S.; Yang, T.; Zhao, H.; Vemuganti, R.; Luo, Y. Impact of MicroRNAs on Ischemic Stroke: From Pre- to Post-Disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 163–164, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.-B.; Stary, C.M.; Yang, G.-Y.; Giffard, R. MicroRNAs: Innovative Targets for Cerebral Ischemia and Stroke. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.-J.; Hamblin, M.; Eugene Chen, Y. Angiogenesis-Regulating MicroRNAs and Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 13, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artimovič, P.; Špaková, I.; Macejková, E.; Pribulová, T.; Rabajdová, M.; Mareková, M.; Zavacká, M. The Ability of MicroRNAs to Regulate the Immune Response in Ischemia/Reperfusion Inflammatory Pathways. Genes. Immun. 2024, 25, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Qiu, N.; Sun, P.; Hamblin, M.H.; Dixon, C.E.; Chen, J.; Yin, K.J. Loss of MicroRNA-15a/16-1 Function Promotes Neuropathological and Functional Recovery in Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e178650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tang, X.; Sun, P.; Shi, Y.; Liu, K.; Hassan, S.H.; Stetler, R.A.; Chen, J.; Yin, K.J. MicroRNA-15a/16-1 Antagomir Ameliorates Ischemic Brain Injury in Experimental Stroke. Stroke 2017, 48, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Pu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, Q.; Shi, Y. Inhibition of TGFβ-Activated Kinase 1 Promotes Inflammation-Resolving Microglial/Macrophage Responses and Recovery after Stroke in Ovariectomized Female Mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 151, 105257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinge, C.M. MiRNAs and Estrogen Action. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexrode, K.M.; Madsen, T.E.; Yu, A.Y.X.; Carcel, C.; Lichtman, J.H.; Miller, E.C. The Impact of Sex and Gender on Stroke. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, K.; Hassan, S.H.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Pu, H.; Stetler, R.A.; Chen, J.; Yin, K.J. Endothelium-Targeted Deletion of MicroRNA-15a/16-1 Promotes Poststroke Angiogenesis and Improves Long-Term Neurological Recovery. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1040–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Sun, P.; Zhang, X.; Hamblin, M.H.; Yin, K.-J. Endothelium-Targeted Deletion of the MiR-15a/16-1 Cluster Ameliorates Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Ischemic Stroke. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaay5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ospina, J.A.; Krause, D.N.; Duckles, S.P. 7-Estradiol Increases Rat Cerebrovascular Prostacyclin Synthesis by Elevating Cyclooxygenase-1 and Prostacyclin Synthase. Stroke 2002, 33, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsialtas, I.; Georgantopoulos, A.; Karipidou, M.E.; Kalousi, F.D.; Karra, A.G.; Leonidas, D.D.; Psarra, A.M.G. Anti-Apoptotic and Antioxidant Activities of the Mitochondrial Estrogen Receptor Beta in N2a Neuroblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.K.; Jones, C.K.; Newhouse, P.A. The Role of Estrogen in Brain and Cognitive Aging. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichaya, E.G.; Ford, B.G.; Moltenkine, J.M.; Taniguchi, C.M.; Phillip West, A.; Dantzer, R. Sex Differences in the Behavioral and Immune Responses of Mice to Tumor Growth and Cancer Therapy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 98, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, A.; Gelosa, P.; Castiglioni, L.; Cimino, M.; Rizzi, N.; Pepe, G.; Lolli, F.; Marcello, E.; Sironi, L.; Vegeto, E.; et al. Sex-Specific Features of Microglia from Adult Mice. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3501–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, P.M.; Dubal, D.B.; Wilson, M.E.; Rau, S.W.; Böttner, M.; Böttner, B. Minireview: Neuroprotective Effects of Estrogen-New Insights into Mechanisms of Action. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Sert, N.P.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The Arrive Guidelines 2.0: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Sun, P.; Hamblin, M.H.; Yin, K.J. Genetic Deletion of Krüppel-like Factor 11 Aggravates Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Li, S.; Qiu, N.; Ni, A.; Xiong, T.; Xue, J.; Yin, K.-J. Sex and Age-Dependent Effects of miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir on Ischemic Stroke Outcomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111765
Huang X, Li S, Qiu N, Ni A, Xiong T, Xue J, Yin K-J. Sex and Age-Dependent Effects of miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir on Ischemic Stroke Outcomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(21):11765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111765
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xinlei, Shun Li, Na Qiu, Andrew Ni, Tianqing Xiong, Jia Xue, and Ke-Jie Yin. 2024. "Sex and Age-Dependent Effects of miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir on Ischemic Stroke Outcomes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 21: 11765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111765
APA StyleHuang, X., Li, S., Qiu, N., Ni, A., Xiong, T., Xue, J., & Yin, K.-J. (2024). Sex and Age-Dependent Effects of miR-15a/16-1 Antagomir on Ischemic Stroke Outcomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(21), 11765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111765




