Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Monocyte-Derived Interstitial Macrophages with a Pro-Fibrotic Phenotype in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
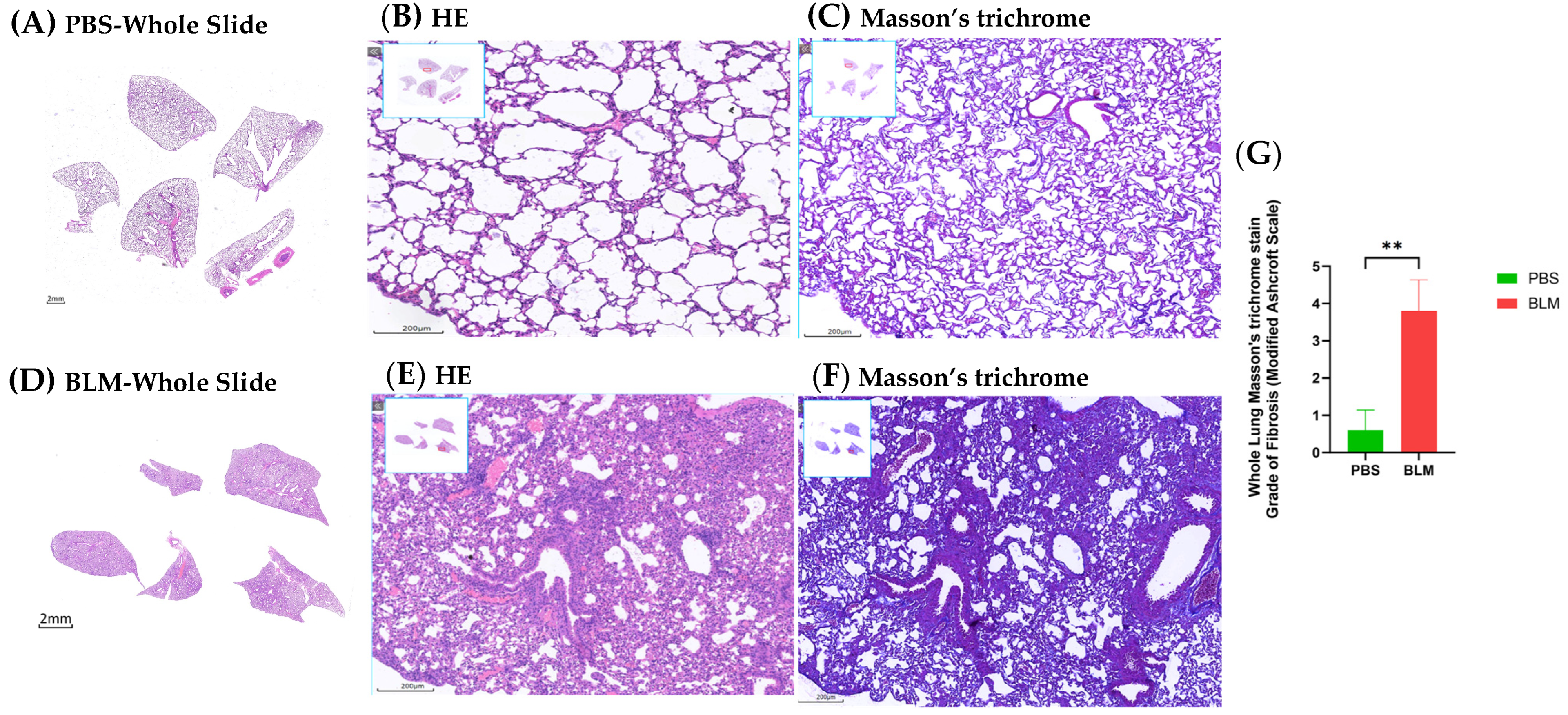
2.1. BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice
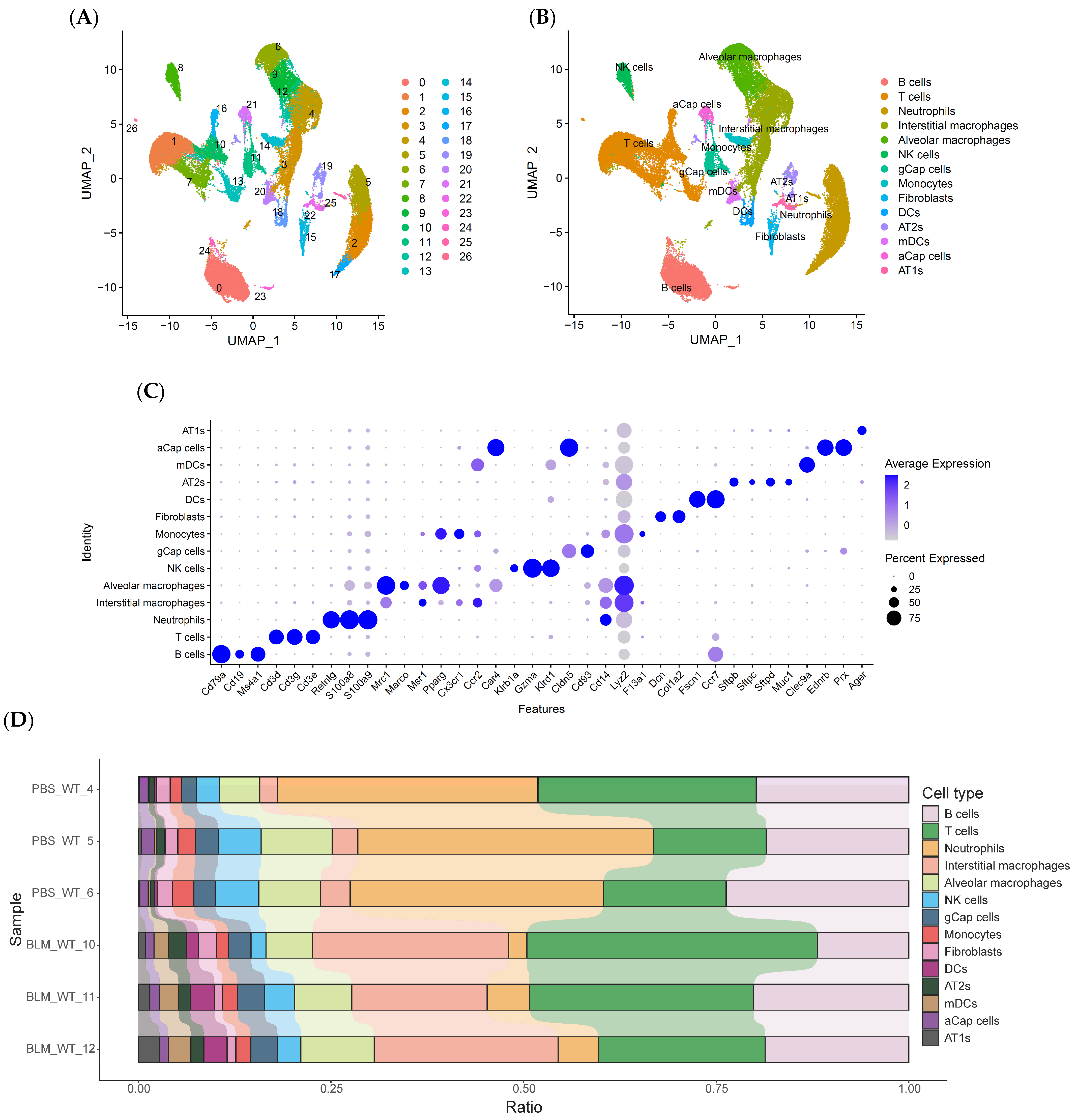
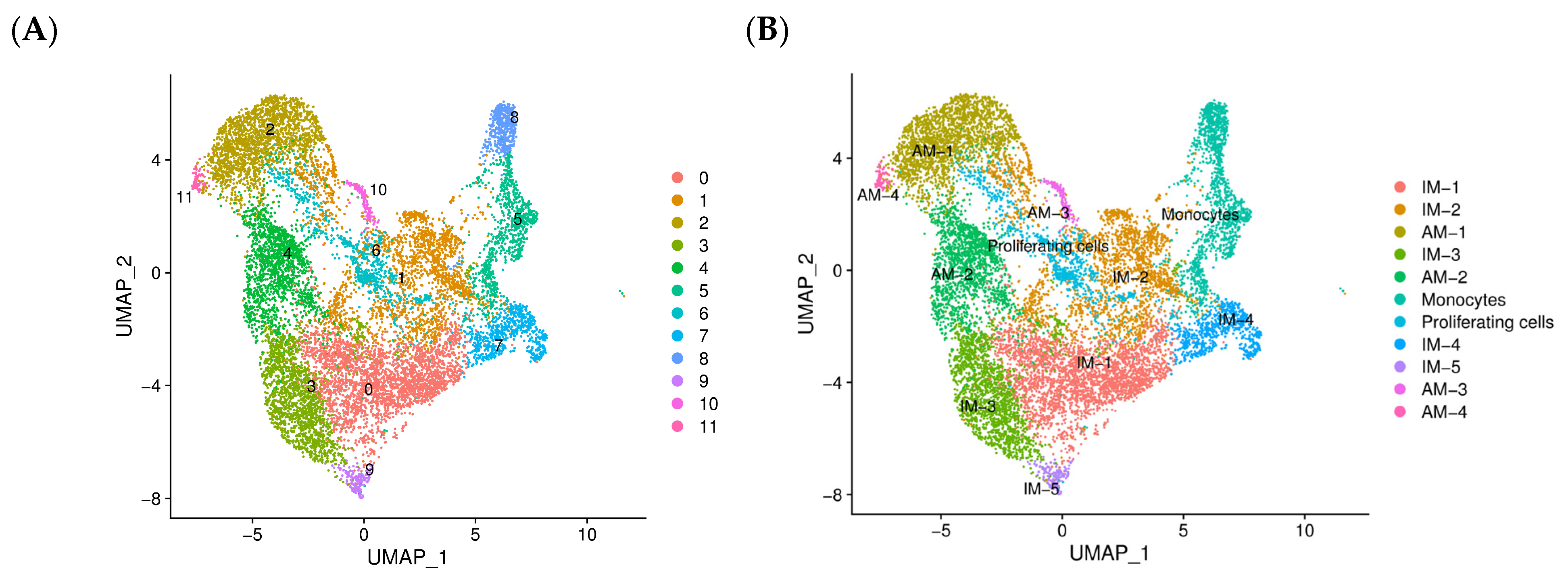
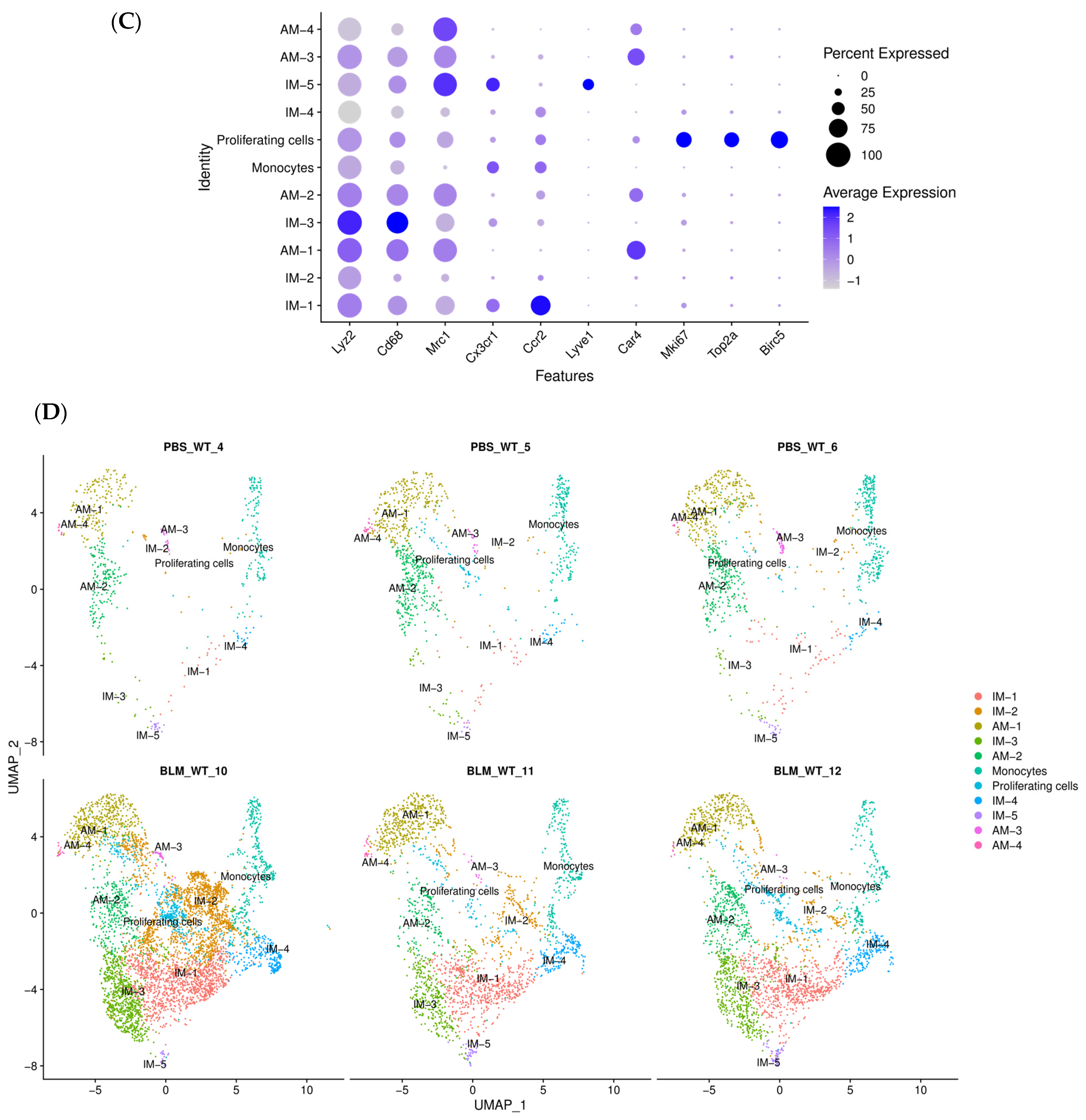
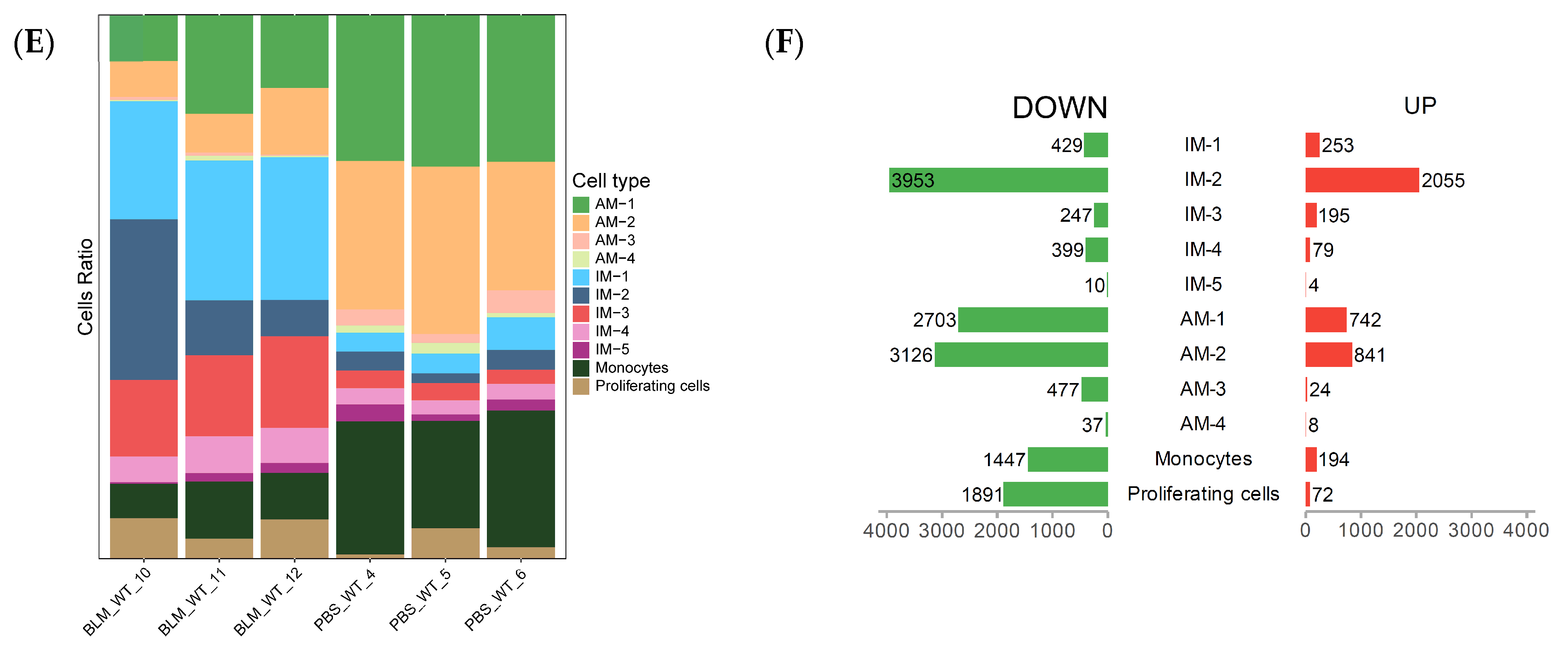
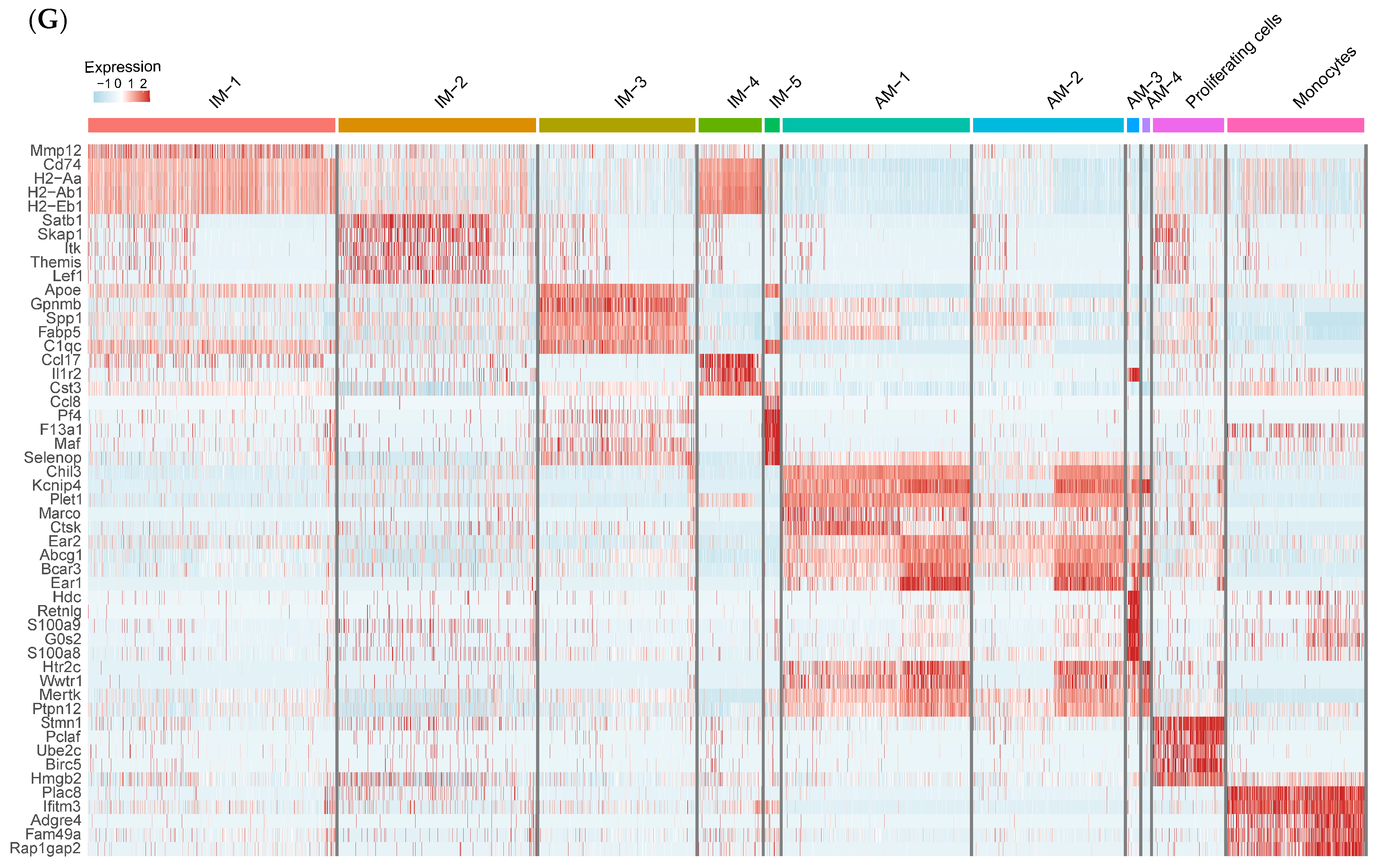
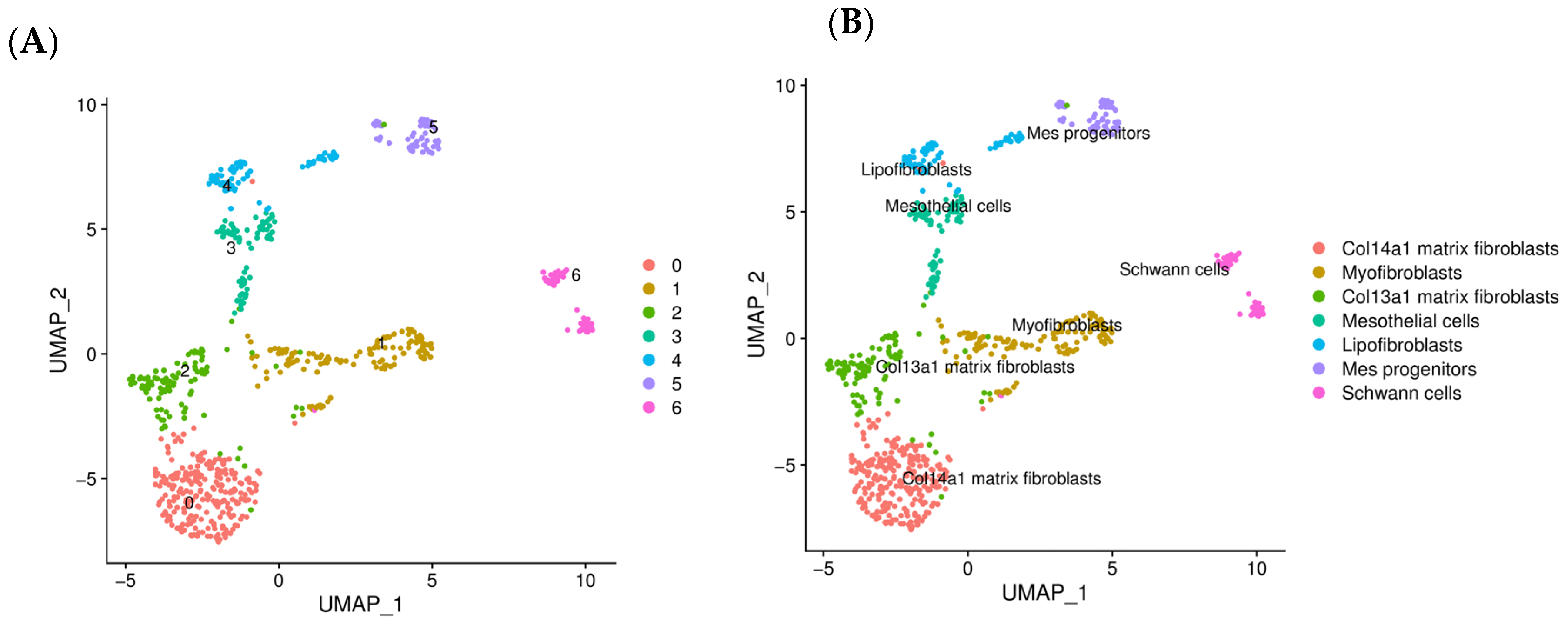
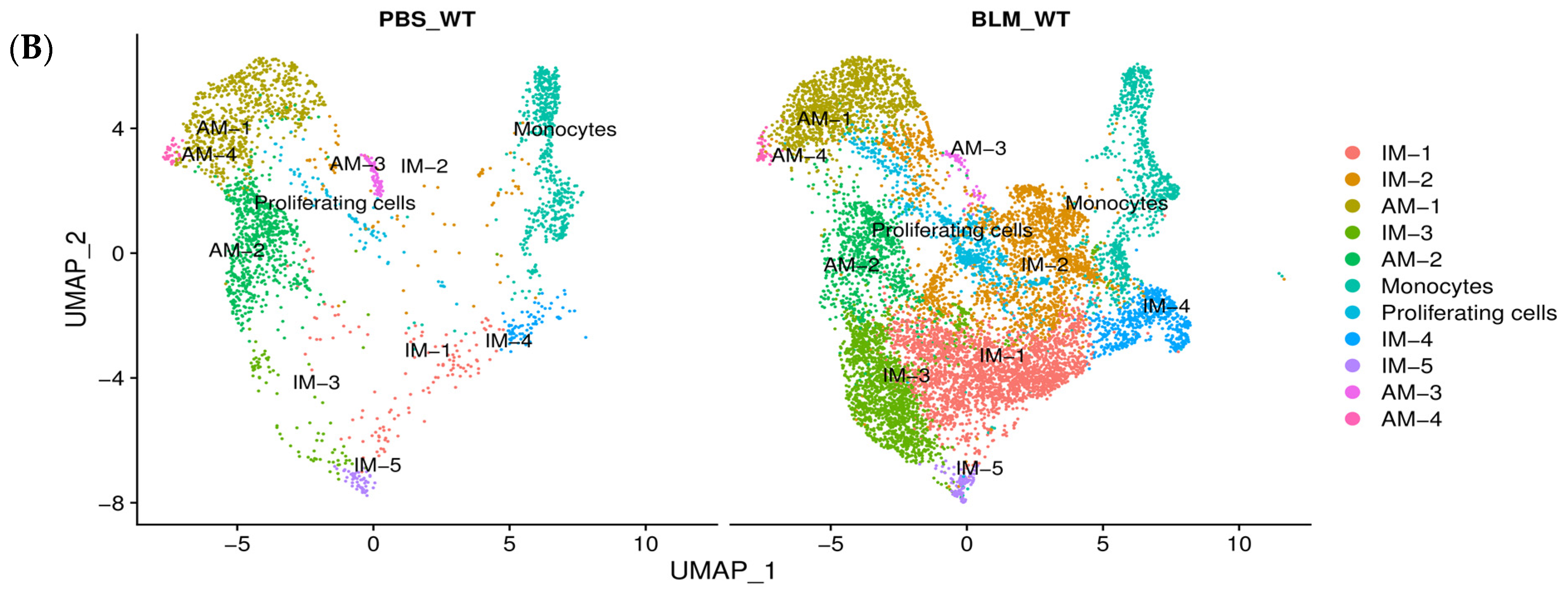
2.2. scRNA-Seq Reveals Distinct Subpopulations of IMs in BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
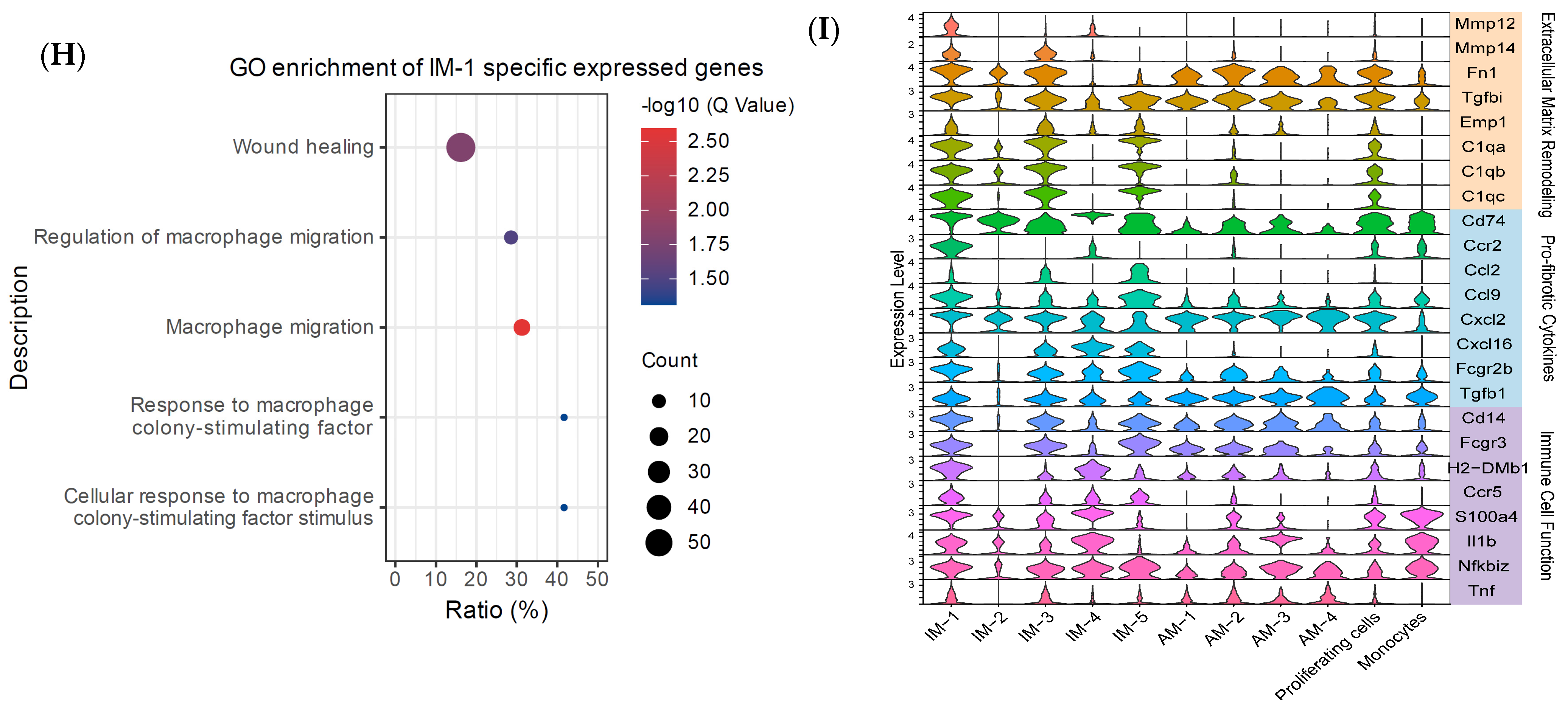
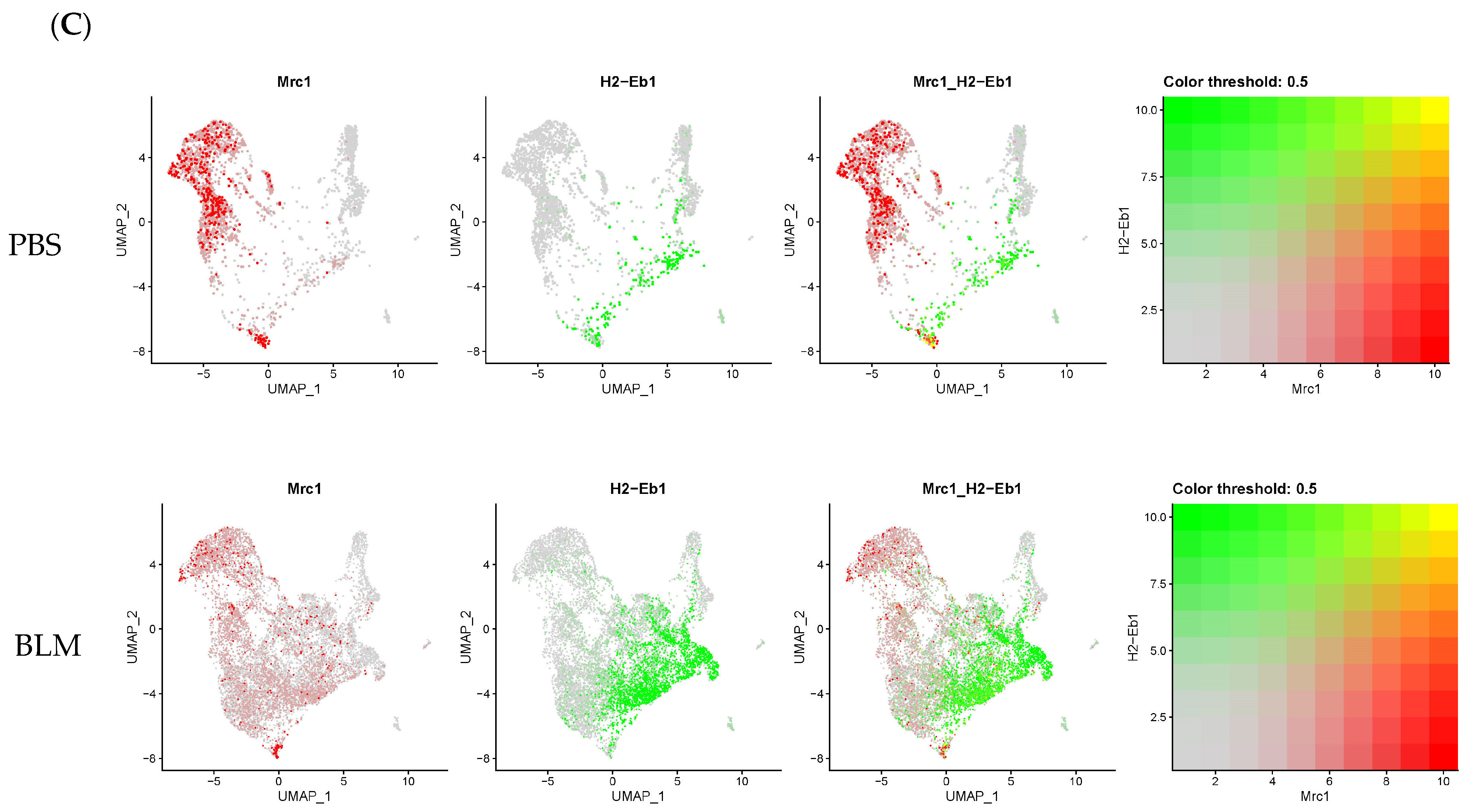
2.3. Monocyte-Derived Macrophages Exhibit a Pro-Fibrotic Gene Expression Profile
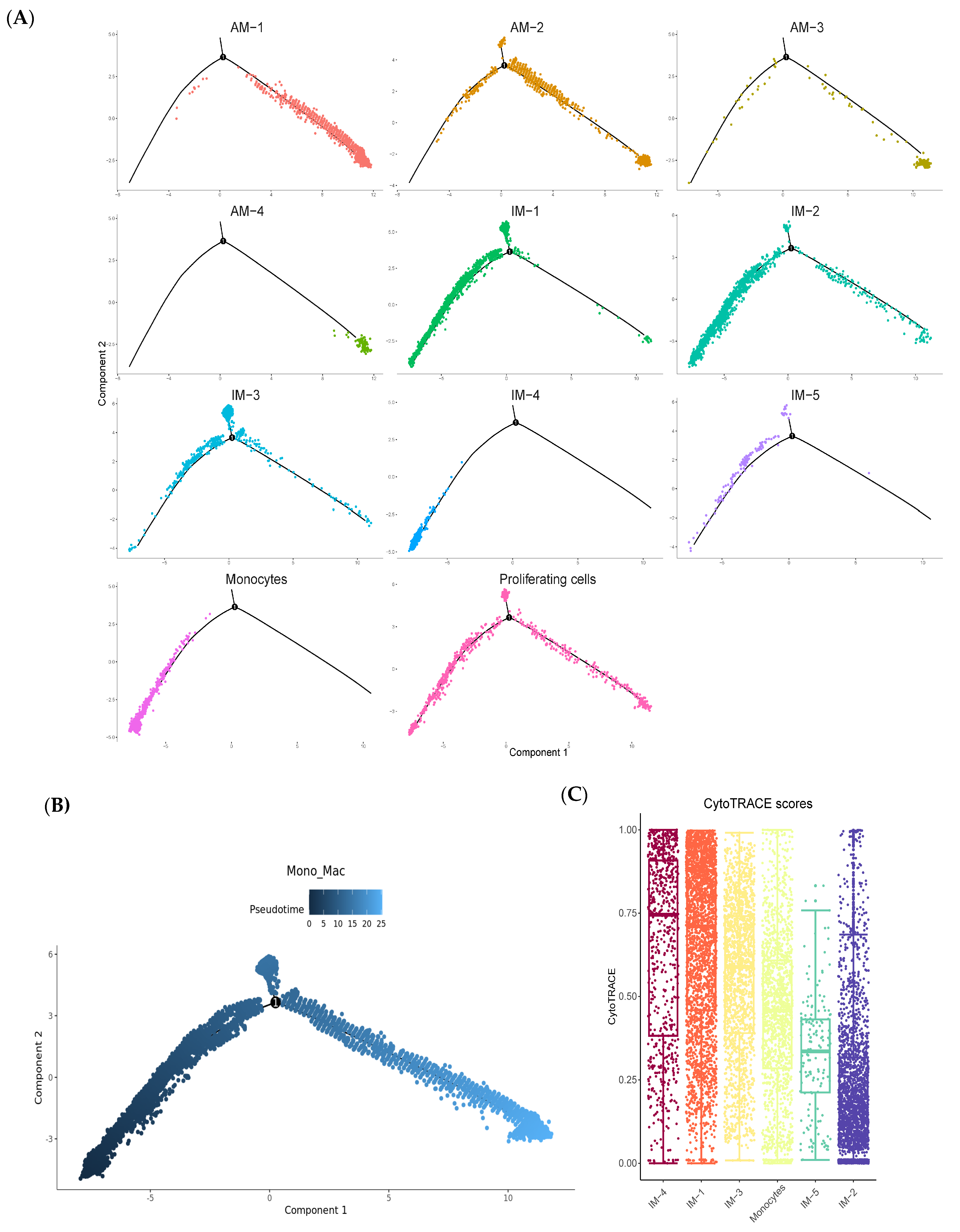
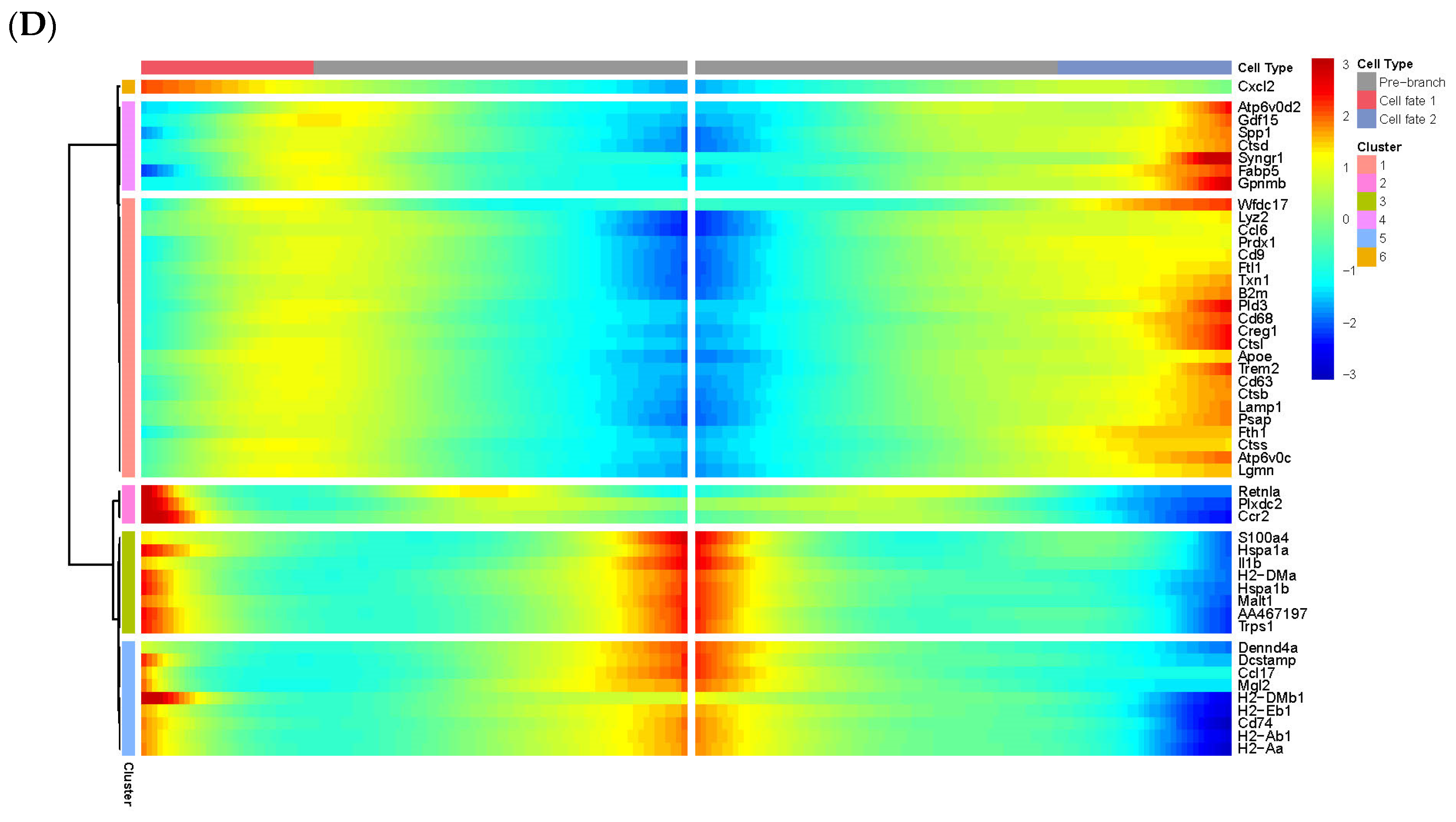
2.4. Pseudotime Analysis Reveals That IMs Originate from Monocytes
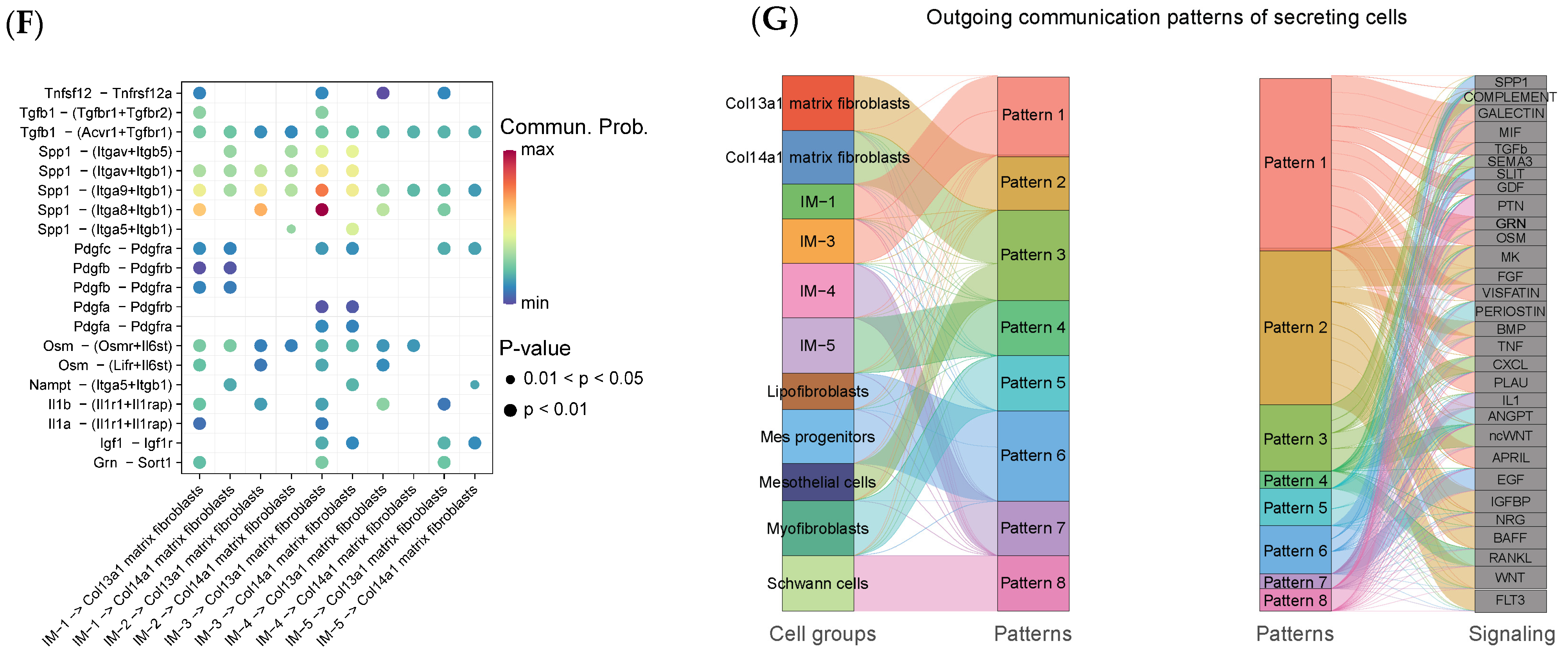
2.5. Cell–Cell Communication Analysis Reveals Strong Interactions Between Mo-IMs and Fibroblasts Through the TGFβ, SPP1, and PDGF Signaling Network
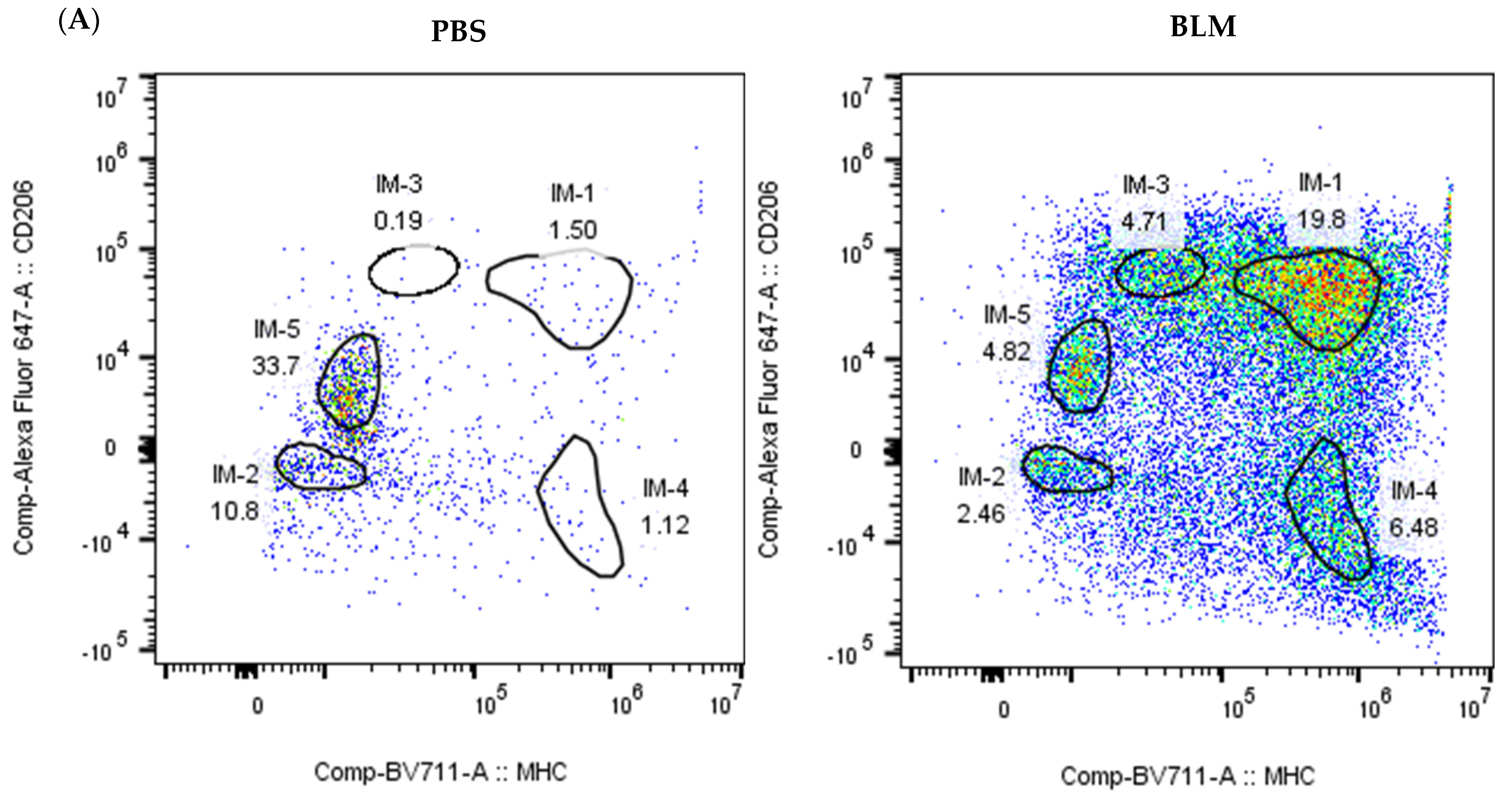
2.6. Flow Cytometry Analysis Validates the Presence of IM Subpopulations in BLM-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Histology and Masson’s Trichrome Staining
4.3. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Library Construction and Sequencing
4.4. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data Analysis
4.5. Single-Cell Pseudotime Analysis
4.6. Cell–Cell Interaction Analysis
4.7. Flow Cytometry
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lederer, D.J.; Martinez, F.J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.J.; Collard, H.R.; Pardo, A.; Raghu, G.; Richeldi, L.; Selman, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Taniguchi, H.; Wells, A.U. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnolo, P.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Bonella, F. The Management of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, O.; Winkler, J.; Minasyan, M.; Herzog, E.L. The Role of Immune and Inflammatory Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heukels, P.; Moor, C.C.; von der Thüsen, J.H.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Kool, M. Inflammation and immunity in IPF pathogenesis and treatment. Respir. Med. 2019, 147, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Vannella, K.M. Macrophages in Tissue Repair, Regeneration, and Fibrosis. Immunity 2016, 44, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginhoux, F.; Schultze, J.L.; Murray, P.J.; Ochando, J.; Biswas, S.K. New insights into the multidimensional concept of macrophage ontogeny, activation and function. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbings, S.L.; Thomas, S.M.; Atif, S.M.; McCubbrey, A.L.; Desch, A.N.; Danhorn, T.; Leach, S.M.; Bratton, D.L.; Henson, P.M.; Janssen, W.J.; et al. Three Unique Interstitial Macrophages in the Murine Lung at Steady State. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schyns, J.; Bai, Q.; Ruscitti, C.; Radermecker, C.; De Schepper, S.; Chakarov, S.; Farnir, F.; Pirottin, D.; Ginhoux, F.; Boeckxstaens, G.; et al. Non-classical tissue monocytes and two functionally distinct populations of interstitial macrophages populate the mouse lung. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran, D.; Looney, A.P.; Liu, L.; Wu, E.; Fong, V.; Hsu, A.; Chak, S.; Naikawadi, R.P.; Wolters, P.J.; Abate, A.R.; et al. Reference-based analysis of lung single-cell sequencing reveals a transitional profibrotic macrophage. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyfman, P.A.; Walter, J.M.; Joshi, N.; Anekalla, K.R.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Chiu, S.; Fernandez, R.; Akbarpour, M.; Chen, C.I.; Ren, Z.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Human Lung Provides Insights into the Pathobiology of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, B.; Lee, J.H.; Bang, D. Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies and bioinformatics pipelines. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luecken, M.D.; Theis, F.J. Current best practices in single-cell RNA-seq analysis: A tutorial. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2019, 15, e8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, J.A.; Scialdone, A.; Marioni, J.C. Using single-cell genomics to understand developmental processes and cell fate decisions. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2018, 14, e8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanay, A.; Regev, A. Scaling single-cell genomics from phenomenology to mechanism. Nature 2017, 541, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.S.; Schupp, J.C.; Poli, S.; Ayaub, E.A.; Neumark, N.; Ahangari, F.; Chu, S.G.; Raby, B.A.; DeIuliis, G.; Januszyk, M.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals ectopic and aberrant lung-resident cell populations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzi, E.; Bulik, M.; Tabib, T.; Morse, C.; Sembrat, J.; Trejo Bittar, H.; Rojas, M.; Lafyatis, R. Single-cell analysis reveals fibroblast heterogeneity and myofibroblasts in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyser, R.; MacDonnell, S.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, L.; Kim, Y.; Kaplan, T.; Ruan, Q.; Wei, Y.; Ni, M.; Adler, C.; et al. Defining the Activated Fibroblast Population in Lung Fibrosis Using Single-Cell Sequencing. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 61, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Wang, Y.; Deng, N.; Huang, G.; Taghavifar, F.; Geng, Y.; Liu, N.; Kulur, V.; Yao, C.; Chen, P.; et al. Single-Cell Deconvolution of Fibroblast Heterogeneity in Mouse Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 3625–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, R.H.; Gitter, W.; El Mokhtari, N.E.; Mathiak, M.; Both, M.; Bolte, H.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Bewig, B. Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological samples. Biotechniques 2008, 44, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misharin, A.V.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Reyfman, P.A.; Cuda, C.M.; Walter, J.M.; McQuattie-Pimentel, A.C.; Chen, C.I.; Anekalla, K.R.; Joshi, N.; Williams, K.J.N.; et al. Monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages drive lung fibrosis and persist in the lung over the life span. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2387–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgalla, G.; Iovene, B.; Calvello, M.; Ori, M.; Varone, F.; Richeldi, L. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Pathogenesis and management. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upagupta, C.; Shimbori, C.; Alsilmi, R.; Kolb, M. Matrix abnormalities in pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, C.; Tabib, T.; Sembrat, J.; Buschur, K.L.; Bittar, H.T.; Valenzi, E.; Jiang, Y.; Kass, D.J.; Gibson, K.; Chen, W.; et al. Proliferating SPP1/MERTK-expressing macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1802441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Kui, Z.; Ping, Z. Reviews and prospectives of signaling pathway analysis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redente, E.F.; Aguilar, M.A.; Black, B.P.; Edelman, B.L.; Bahadur, A.N.; Humphries, S.M.; Lynch, D.A.; Wollin, L.; Riches, D.W.H. Nintedanib reduces pulmonary fibrosis in a model of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2018, 314, L998–L1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modhukur, V.; Iljasenko, T.; Metsalu, T.; Lokk, K.; Laisk-Podar, T.; Vilo, J. MethSurv: A web tool to perform multivariable survival analysis using DNA methylation data. Epigenomics 2018, 10, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ma, R. Identifying the Potential Roles of PBX4 in Human Cancers Based on Integrative Analysis. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, D.T.M.; Wu, C.C.; Wang, W.J.; Hsu, H.P.; Ta, H.D.K.; Anuraga, G.; Chiao, C.C.; Wang, C.Y. Glutamine synthetase regulates the immune microenvironment and cancer development through the inflammatory pathway. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 20, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, J.; Rubio, G.A.; Limper, A.H.; Williams, K.; Elliot, S.J.; Ninou, I.; Aidinis, V.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Glassberg, M.K. Exploring Animal Models That Resemble Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrington, R.; Jordan, S.; Pitchford, S.C.; Page, C.P. Use of animal models in IPF research. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 51, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.E., Jr.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2011, 378, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Wang, R.; Herazo-Maya, J.D.; Ibarra, G.H.; Srivastava, A.; de Castro, J.P.W.; DeIuliis, G.; Ahangari, F.; Woolard, T.; et al. Thyroid hormone inhibits lung fibrosis in mice by improving epithelial mitochondrial function. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misharin, A.V.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Mutlu, G.M.; Budinger, G.R.; Perlman, H. Flow cytometric analysis of macrophages and dendritic cell subsets in the mouse lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, M.; Kamio, K.; Azuma, A.; Matsuda, K.; Kokuho, N.; Miura, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Nei, T.; Fujita, K.; Saito, Y.; et al. Pirfenidone inhibits fibrocyte accumulation in the lungs in bleomycin-induced murine pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Xiong, W.; Gu, W.; Wang, C.Y. Macrophages: Friend or foe in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.L.; Rojas, M.; Pardo, A.; Selman, M. Emerging therapies for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a progressive age-related disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Ma, T.; Cao, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Xiang, Z.; Han, X. TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation promotes myofibroblast differentiation of LR-MSCs and exacerbates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Fan, L.; Zeng, Y.; Han, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, D.; et al. GPRC5A reduction contributes to pollutant benzo[a]pyrene injury via aggravating murine fibrosis, leading to poor prognosis of IIP patients. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossarizza, A.; Chang, H.D.; Radbruch, A.; Abrignani, S.; Addo, R.; Akdis, M.; Andra, I.; Andreata, F.; Annunziato, F.; Arranz, E.; et al. Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies (third edition). Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 2708–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; You, Y.; He, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Min, H.; Li, C.; Chen, J. Crystalline Silica-Induced Proinflammatory Interstitial Macrophage Recruitment through Notch3 Signaling Promotes the Pathogenesis of Silicosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 14502–14514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Lei, Z.; Wang, T.; Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Bi, X.; Zheng, F.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Monocyte-Derived Interstitial Macrophages with a Pro-Fibrotic Phenotype in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111669
Wang S, Li J, Wu C, Lei Z, Wang T, Huang X, Zhang S, Liu Y, Bi X, Zheng F, et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Monocyte-Derived Interstitial Macrophages with a Pro-Fibrotic Phenotype in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(21):11669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111669
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shunli, Jie Li, Caixia Wu, Zhengyao Lei, Tong Wang, Xinxin Huang, Suxia Zhang, Yuting Liu, Xiaohan Bi, Fanshuo Zheng, and et al. 2024. "Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Monocyte-Derived Interstitial Macrophages with a Pro-Fibrotic Phenotype in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 21: 11669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111669
APA StyleWang, S., Li, J., Wu, C., Lei, Z., Wang, T., Huang, X., Zhang, S., Liu, Y., Bi, X., Zheng, F., Zhu, X., Huang, Z., & Yi, X. (2024). Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Monocyte-Derived Interstitial Macrophages with a Pro-Fibrotic Phenotype in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(21), 11669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111669





