Time-Restricted Feeding Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice Under Chronic Light Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
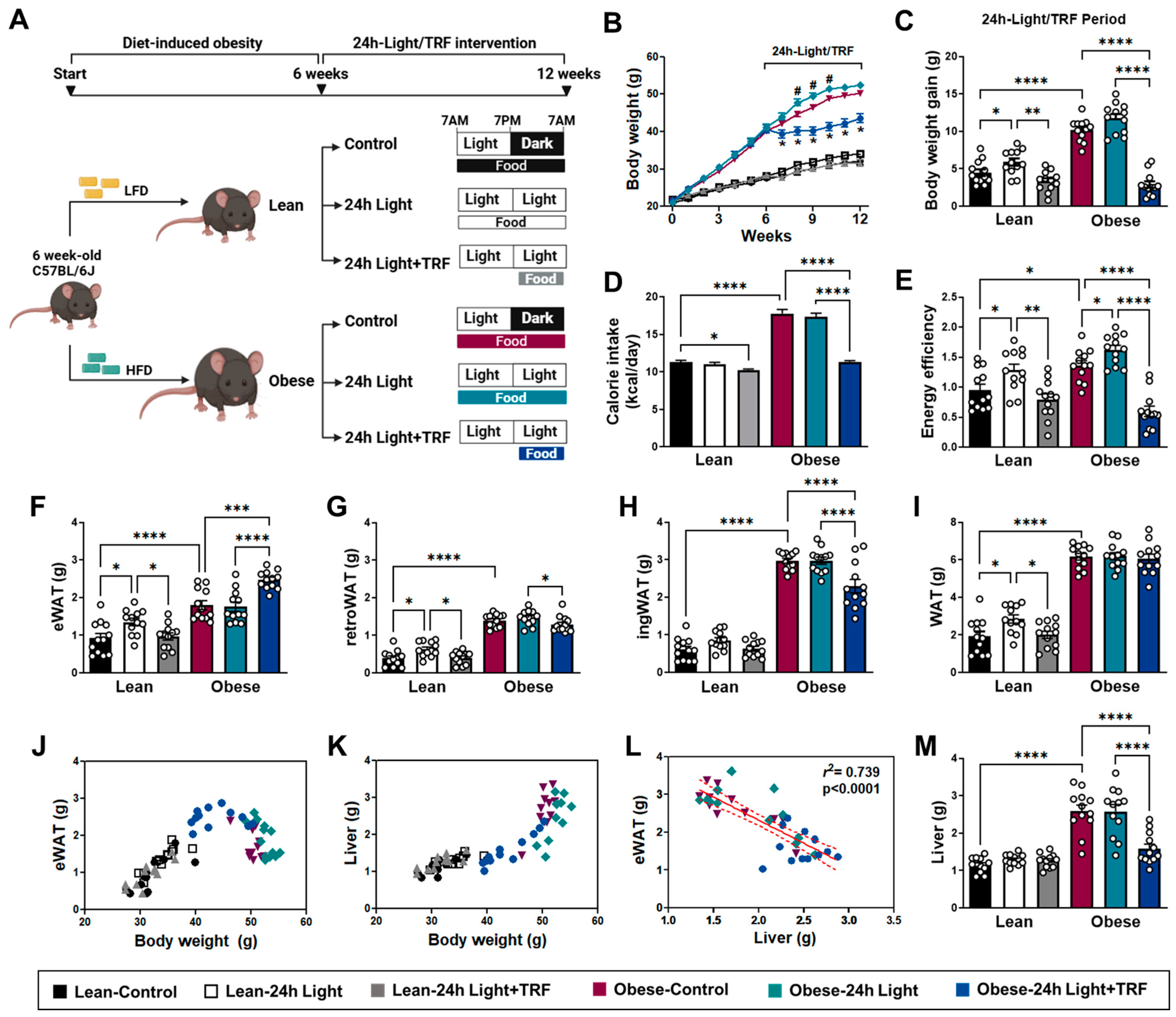
2.1. Effects of Chronic Light Exposure and TRF on Body Weight and Tissue Mass
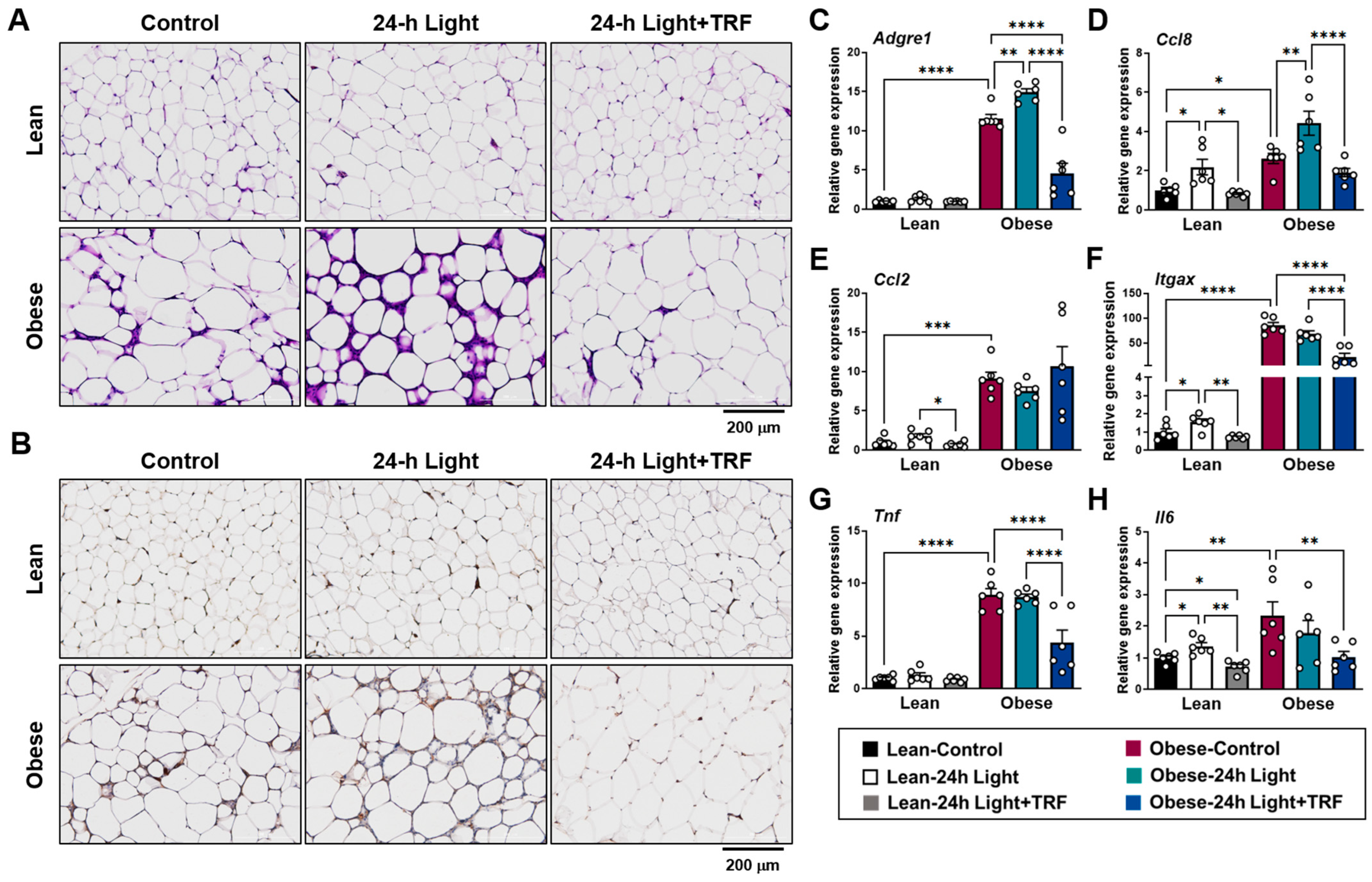
2.2. Effects of Chronic Light Exposure and TRF on Adipose Tissue Inflammation
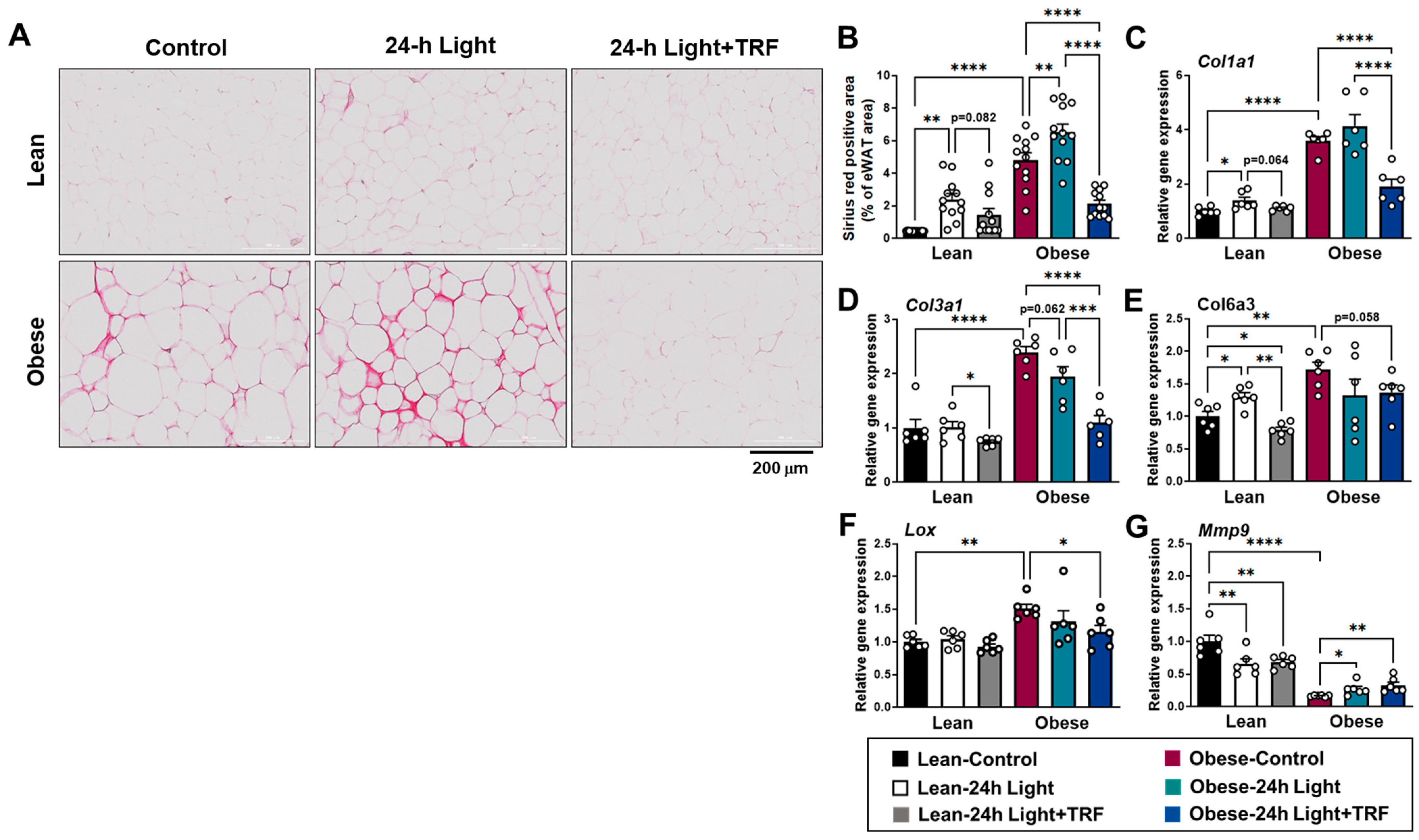
2.3. Effects of Chronic Light Exposure and TRF on Collagen Deposition and Fibrosis-Related Gene Expression in eWAT
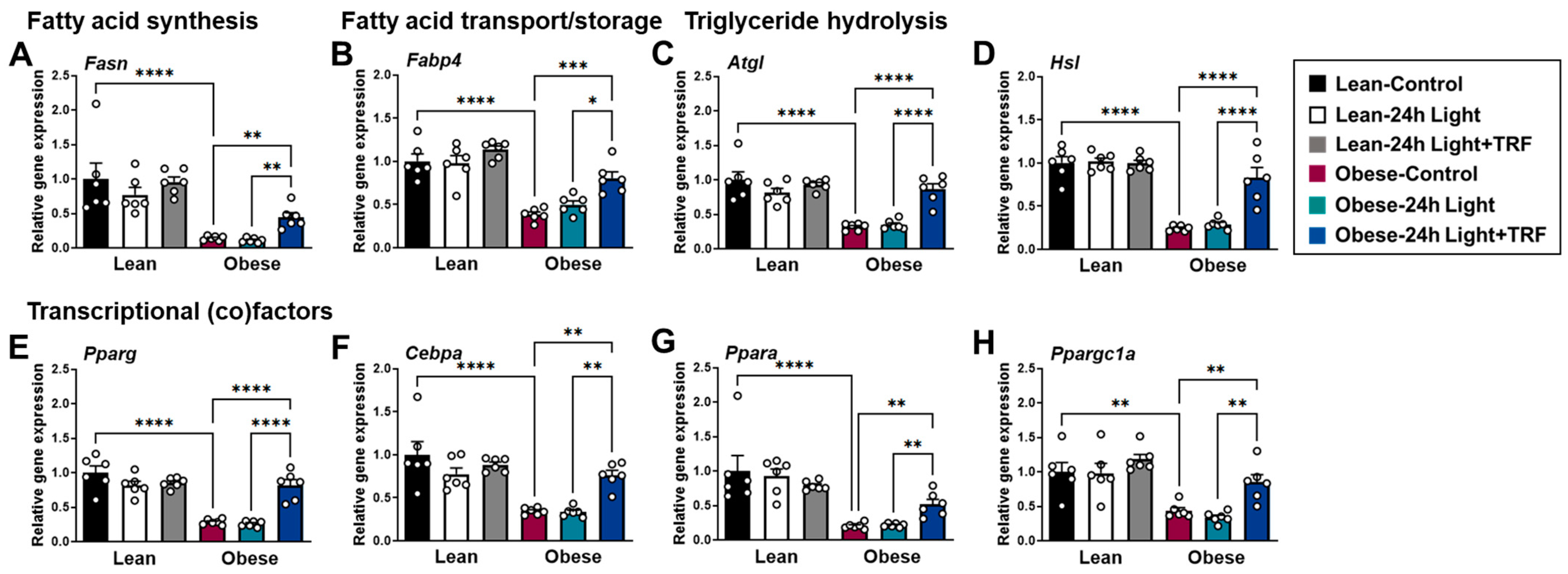
2.4. Effects of Chronic Light Exposure and TRF on the Expression of Genes Involved in Lipid Metabolism in eWAT
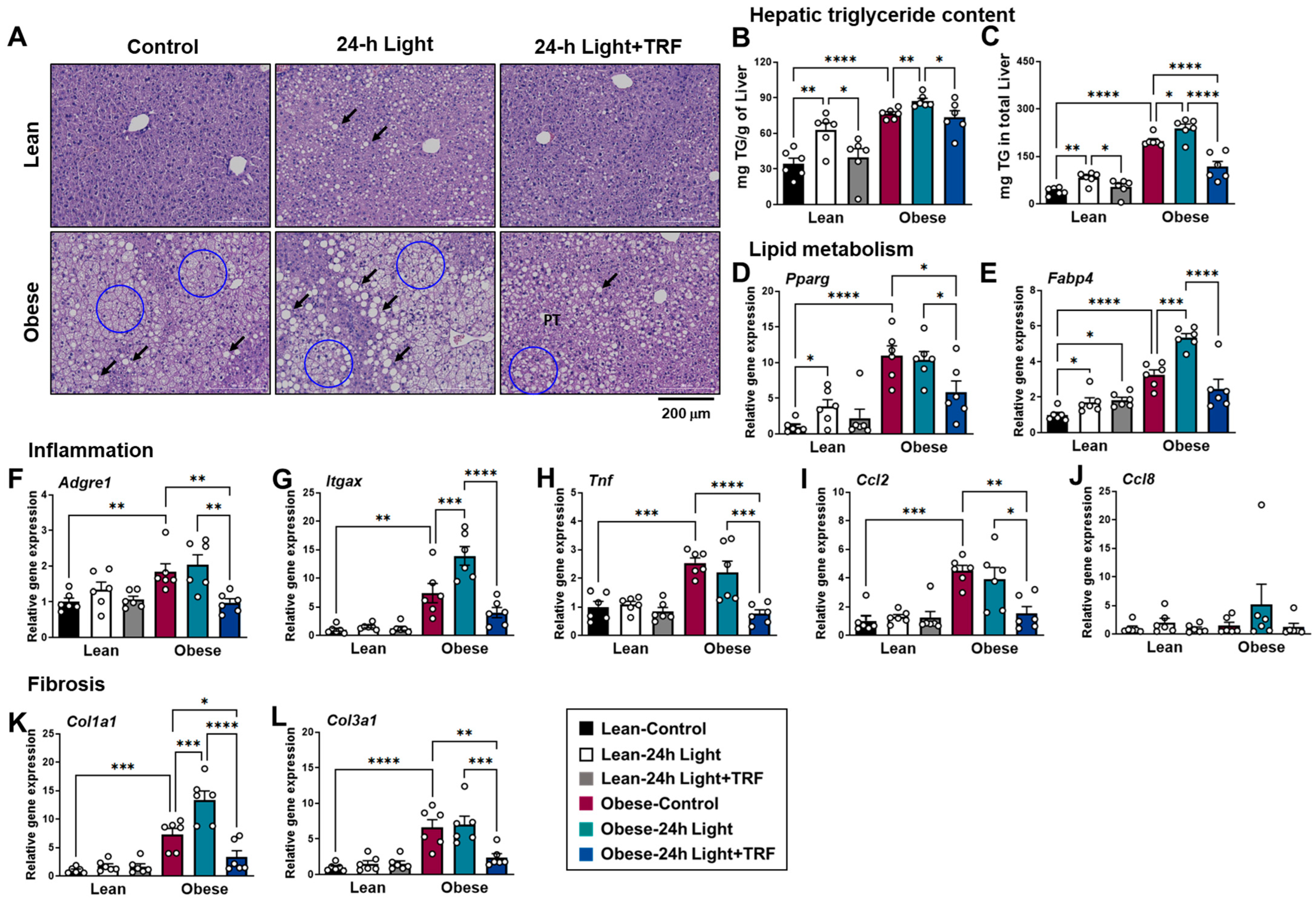
2.5. Effects of Chronic Light Exposure and TRF on Hepatic Steatosis, Inflammation, and Fibrosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2. Body Weight, Food Intake, and EER
4.3. Tissue Collection
4.4. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Hepatic Triglyceride
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muscogiuri, G.; Poggiogalle, E.; Barrea, L.; Tarsitano, M.G.; Garifalos, F.; Liccardi, A.; Pugliese, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Alviggi, C.; et al. Exposure to artificial light at night: A common link for obesity and cancer? Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 173, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybnikova, N.A.; Haim, A.; Portnov, B.A. Does artificial light-at-night exposure contribute to the worldwide obesity pandemic? Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonken, L.K.; Workman, J.L.; Walton, J.C.; Weil, Z.M.; Morris, J.S.; Haim, A.; Nelson, R.J. Light at night increases body mass by shifting the time of food intake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18664–18669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.-M.M.; White, A.J.; Jackson, C.L.; Weinberg, C.R.; Sandler, D.P. Association of Exposure to Artificial Light at Night While Sleeping with Risk of Obesity in Women. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brum, M.C.B.; Filho, F.F.D.; Schnorr, C.C.; Bertoletti, O.A.; Bottega, G.B.; Rodrigues, T.d.C. Night shift work, short sleep and obesity. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coomans, C.P.; Houben, T.; Klinken, J.; Pronk, A.C.M.; Havekes, L.M.; Romijn, J.A.; Dijk, K.W.; Biermasz, N.R.; Meijer, J.H.; Berg, S.A.A.v.D.; et al. Detrimental effects of constant light exposure and high-fat diet on circadian energy metabolism and insulin sensitivity. FASEB J. 2012, 27, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.R.; Sen, S.K.; Mazzone, A.; Her, T.K.; Xiong, Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Javeed, N.; Colwell, C.S.; Rakshit, K.; LeBrasseur, N.K.; et al. Time-restricted feeding prevents deleterious metabolic effects of circadian disruption through epigenetic control of β cell function. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonken, L.K.; Lieberman, R.A.; Weil, Z.M.; Nelson, R.J. Dim Light at Night Exaggerates Weight Gain and Inflammation Associated with a High-Fat Diet in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3817–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, V.D.; Panda, S. Fasting, circadian rhythms, and time-restricted feeding in healthy lifespan. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, E.F.; Beyl, R.; Early, K.S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early time-restricted feeding improves insulin sensitivity, blood pressure, and oxidative stress even without weight loss in men with prediabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1212–1221.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatori, M.; Vollmers, C.; Zarrinpar, A.; DiTacchio, L.; Bushong, E.A.; Gill, S.; Leblanc, M.; Chaix, A.; Joens, M.; Fitzpatrick, J.A.; et al. Time-Restricted Feeding without Reducing Caloric Intake Prevents Metabolic Diseases in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Xu, H.; Xie, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H.; Hu, D.; Mao, Y. Time-Restricted Feeding Reduces the Detrimental Effects of a High-Fat Diet, Possibly by Modulating the Circadian Rhythm of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 596285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, N.; Nah, J.; Lee, M.N.; Wu, D.; Pae, M. Post-Effects of Time-Restricted Feeding against Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obese Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaix, A.; Chaix, A.; Lin, T.; Lin, T.; Le, H.D.; Le, H.D.; Chang, M.W.; Chang, M.W.; Panda, S.; Panda, S. Time-Restricted Feeding Prevents Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Mice Lacking a Circadian Clock. Cell Metab. 2018, 29, 303–319.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, M.; Wu, D.; Pae, M. Time-Restricted Feeding Restores Obesity-Induced Alteration in Adipose Tissue Immune Cell Phenotype. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M.N.; Nah, J.; Yun, N.; Wu, D.; Pae, M. Time-restricted feeding reduces monocyte production by controlling hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the bone marrow during obesity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1054875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.-Q.; Ansari, T.S.; McGuinness, O.P.; Wasserman, D.H.; Johnson, C.H. Circadian Disruption Leads to Insulin Resistance and Obesity. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, S.; Berg, R.v.D.; Ramkisoensing, A.; Boon, M.R.; Kuipers, E.N.; Loef, M.; Zonneveld, T.C.M.; Lucassen, E.A.; Sips, H.C.M.; Chatzispyrou, I.A.; et al. Prolonged daily light exposure increases body fat mass through attenuation of brown adipose tissue activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6748–6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opperhuizen, A.-L.; van Kerkhof, L.W.M.; Proper, K.I.; Rodenburg, W.; Kalsbeek, A. Rodent models to study the metabolic effects of shiftwork in humans. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strissel, K.J.; Stancheva, Z.; Miyoshi, H.; Perfield, J.W.; DeFuria, J.; Jick, Z.; Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Adipocyte Death, Adipose Tissue Remodeling, and Obesity Complications. Diabetes 2007, 56, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushman, T.; Lin, T.-Y.; Chen, X. Depot-Dependent Impact of Time-Restricted Feeding on Adipose Tissue Metabolism in High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Male Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, M.M.; A Rossetti, M.; Nayer, B.; Puig, A.; Zagallo, P.; Ortega, L.M.; Johnson, K.B.; McNamara, G.; Reiser, J.; Mendez, A.J.; et al. Apoptosis, mastocytosis, and diminished adipocytokine gene expression accompany reduced epididymal fat mass in long-standing diet-induced obese mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelin, G.; Gautier, E.L.; Clément, K. Adipose Tissue Fibrosis in Obesity: Etiology and Challenges. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 84, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crewe, C.; An, Y.A.; Scherer, P.E. The ominous triad of adipose tissue dysfunction: Inflammation, fibrosis, and impaired angiogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBari, M.K.; Abbott, R.D. Adipose Tissue Fibrosis: Mechanisms, Models, and Importance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.; Muise, E.S.; Iyengar, P.; Wang, Z.V.; Chandalia, M.; Abate, N.; Zhang, B.B.; Bonaldo, P.; Chua, S.; Scherer, P.E. Metabolic Dysregulation and Adipose Tissue Fibrosis: Role of Collagen VI. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 1575–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Tordjman, J.; Clément, K.; Scherer, P.E. Fibrosis and Adipose Tissue Dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2020, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Bernlohr, D.A. Metabolic functions of FABPs—mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Guo, W.; Zhou, Z. Adipose Triglyceride Lipase in Hepatic Physiology and Pathophysiology. Biomolecules 2021, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Akazawa, N.; Park, I.; Kwak, H.-B.; Tokuyama, K.; Maeda, S. Effects of nocturnal light exposure on circadian rhythm and energy metabolism in healthy adults: A randomized crossover trial. Chrono- Int. 2021, 39, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Rust, B.M.; Palmer, D.G. Time-restricted feeding restores metabolic flexibility in adult mice with excess adiposity. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1340735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsouris, D.; Li, P.-P.; Thapar, D.; Chapman, J.; Olefsky, J.M.; Neels, J.G. Ablation of CD11c-Positive Cells Normalizes Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Insulin Resistant Animals. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, C.; Shi, T.; Cai, Q.; Wang, T.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Lu, M.; Chen, Z.; et al. FAP expression in adipose tissue macrophages promotes obesity and metabolic inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2303075120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, H.; Tateya, S.; Tamori, Y.; Kotani, K.; Hiasa, K.-I.; Kitazawa, R.; Kitazawa, S.; Miyachi, H.; Maeda, S.; Egashira, K.; et al. MCP-1 contributes to macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliniak, C.M.; Pedersen, L.; E Scherer, P. Adipose tissue fibrosis: The unwanted houseguest invited by obesity. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 259, e230180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, J.; Löffler, M.; Bilban, M.; Reimers, M.; Kadl, A.; Todoric, J.; Zeyda, M.; Geyeregger, R.; Schreiner, M.; Weichhart, T.; et al. Prevention of high-fat diet-induced adipose tissue remodeling in obese diabetic mice by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 31, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisinger, K.; Girke, P.; Buechler, C.; Krautbauer, S. Adipose tissue depot specific expression and regulation of fibrosis-related genes and proteins in experimental obesity. Mamm. Genome 2023, 35, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Page, A.J.; Hatzinikolas, G.; Chen, M.; Wittert, G.A.; Heilbronn, L.K. Intermittent Fasting Improves Glucose Tolerance and Promotes Adipose Tissue Remodeling in Male Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, I.K.; Badin, P.-M.; Marques, M.-A.; Monbrun, L.; Lefort, C.; Mir, L.; Louche, K.; Bourlier, V.; Roussel, B.; Gui, P.; et al. Immune Cell Toll-like Receptor 4 Mediates the Development of Obesity- and Endotoxemia-Associated Adipose Tissue Fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, Y.; Tomaru, U.; Miyoshi, A.; Ito, T.; Fukaya, S.; Miyoshi, H.; Atsumi, T.; Ishizu, A. Overexpression of TNF-α converting enzyme promotes adipose tissue inflammation and fibrosis induced by high fat diet. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2014, 97, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, C.; Lu, F.; Liao, Y.; Cai, J.; Gao, J. Challenges and opportunities in obesity: The role of adipocytes during tissue fibrosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1365156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Vishvanath, L.; Busbuso, N.C.; Hepler, C.; Shan, B.; Sharma, A.X.; Chen, S.; Yu, X.; An, Y.A.; Zhu, Y.; et al. De novo adipocyte differentiation from Pdgfrβ+ preadipocytes protects against pathologic visceral adipose expansion in obesity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, T.D.; Kipp, Z.A.; Xu, M.; Yiannikouris, F.B.; Morris, A.J.; Stec, D.F.; Wahli, W.; Stec, D.E. Adipose-Specific PPARα Knockout Mice Have Increased Lipogenesis by PASK–SREBP1 Signaling and a Polarity Shift to Inflammatory Macrophages in White Adipose Tissue. Cells 2021, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Cai, G.H.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.P.; Mitchell, G.A.; Wu, J.W. Adipose tissue deficiency of hormone-sensitive lipase causes fatty liver in mice. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinelli, P.; Videla, L.A. Up-Regulation of PPAR-γ mRNA Expression in the Liver of Obese Patients: An Additional Reinforcing Lipogenic Mechanism to SREBP-1c Induction. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Vedia, J.; Girona, J.; Ibarretxe, D.; Masana, L.; Rodríguez-Calvo, R. Unveiling the Role of the Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 in the Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Escoté, X.; Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Miranda, M.; Clemente-Postigo, M.; Pérez-Pérez, R.; Peral, B.; Cardona, F.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; et al. FABP4 Dynamics in Obesity: Discrepancies in Adipose Tissue and Liver Expression Regarding Circulating Plasma Levels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosquet, A.; Guaita-Esteruelas, S.; Saavedra, P.; Rodríguez-Calvo, R.; Heras, M.; Girona, J.; Masana, L. Exogenous FABP4 induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in HepG2 liver cells. Atherosclerosis 2016, 249, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.; Lam, K.S.L.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, D.; Ding, K.; Wang, Y.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Xu, A. Adipocyte Fatty Acid-binding Protein Modulates Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages through a Positive Feedback Loop Involving c-Jun NH2-terminal Kinases and Activator Protein-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10273–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Cong, X.; Zhu, L.; Ning, Z. Inhibition of FABP4 attenuates cardiac fibrosis through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Tao, S.; Guo, F.; Liu, J.; Huang, R.; Tan, Z.; Zeng, X.; Ma, L.; Fu, P. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of fatty acid-binding protein 4 alleviated inflammation and early fibrosis after toxin induced kidney injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, Y. Oxidative stress in the light-exposed retina and its implication in age-related macular degeneration. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Goyal, R. Long-term exposure to constant light induces dementia, oxidative stress and promotes aggregation of sub-pathological Aβ42 in Wistar rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 192, 172892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. Monochromatic blue light not green light exposure is associated with continuous light-induced hepatic steatosis in high fat diet fed-mice via oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Lee, E.; Moon, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.-J. Circadian disruption and increase of oxidative stress in male and female volunteers after bright light exposure before bed time. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early, J.O.; Menon, D.; Wyse, C.A.; Cervantes-Silva, M.P.; Zaslona, Z.; Carroll, R.G.; Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; Angiari, S.; Ryan, D.G.; Corcoran, S.E.; et al. Circadian clock protein BMAL1 regulates IL-1β in macrophages via NRF2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8460–E8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; E Stubbins, R.; Smith, R.R.; E Harvey, A.; Núñez, N.P. Differential susceptibility to obesity between male, female and ovariectomized female mice. Nutr. J. 2009, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pae, M.; Baek, Y.; Lee, S.; Wu, D. Loss of ovarian function in association with a high-fat diet promotes insulin resistance and disturbs adipose tissue immune homeostasis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 57, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, S.; Yasoshima, A.; Doi, K.; Nakayama, H.; Uetsuka, K. Involvement of Sex, Strain and Age Factors in High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in C57BL/6J and BALB/cA Mice. Exp. Anim. 2007, 56, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaix, A.; Deota, S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Lin, T.; Panda, S. Sex- and age-dependent outcomes of 9-hour time-restricted feeding of a Western high-fat high-sucrose diet in C57BL/6J mice. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nah, J.; Yun, N.; Yoo, H.; Park, S.; Pae, M. Time-Restricted Feeding Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice Under Chronic Light Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111524
Nah J, Yun N, Yoo H, Park S, Pae M. Time-Restricted Feeding Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice Under Chronic Light Exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(21):11524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111524
Chicago/Turabian StyleNah, Jiyeon, Narae Yun, Hyunjin Yoo, Surin Park, and Munkyong Pae. 2024. "Time-Restricted Feeding Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice Under Chronic Light Exposure" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 21: 11524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111524
APA StyleNah, J., Yun, N., Yoo, H., Park, S., & Pae, M. (2024). Time-Restricted Feeding Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice Under Chronic Light Exposure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(21), 11524. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252111524





