Molecular and Cellular Neurobiology of Spreading Depolarization/Depression and Migraine: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
Aim of the Review
2. History of the Discovery of CSD
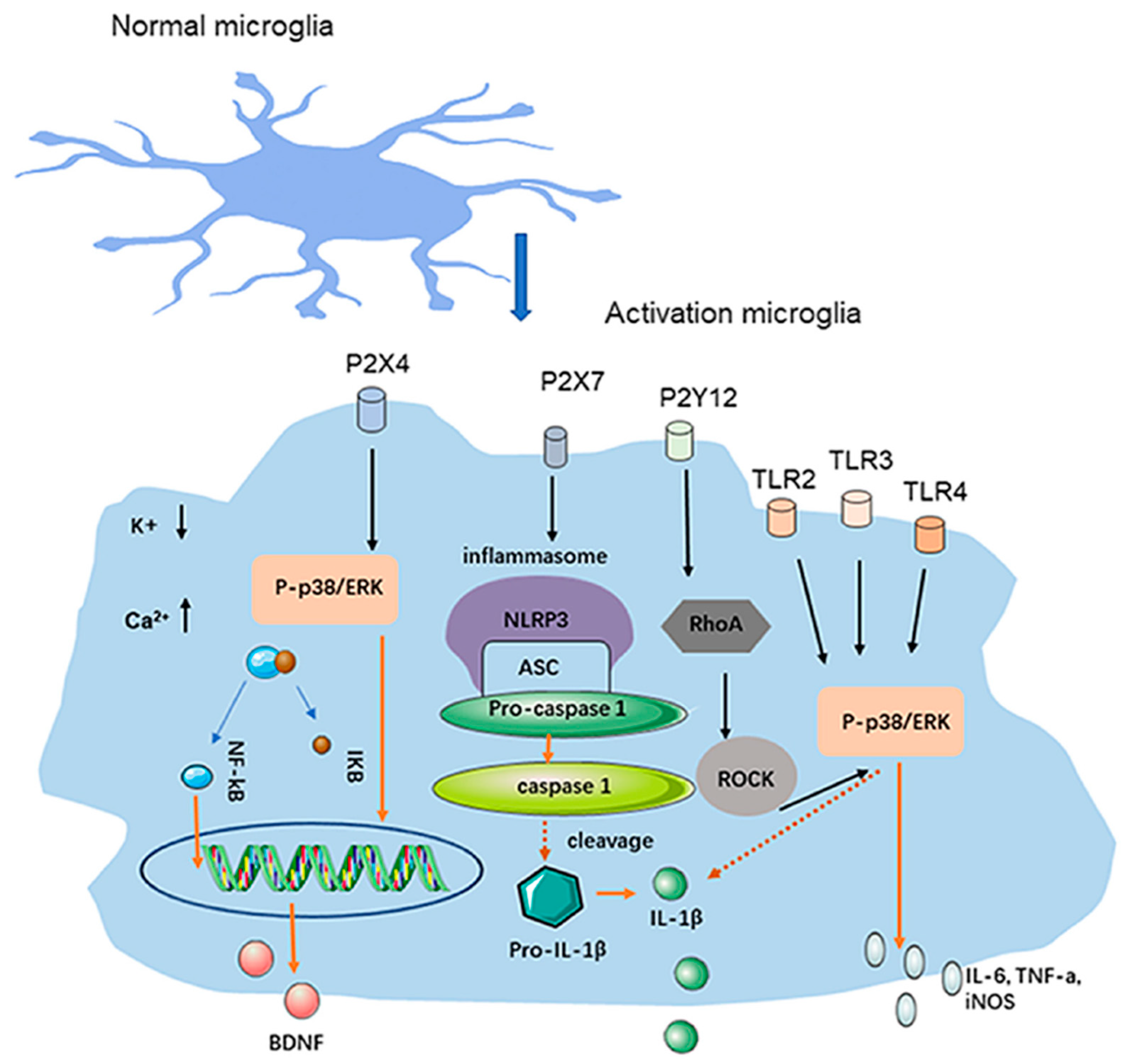
3. Microglia and Neuroinflammation in CSD
4. Animal Studies and CSD
5. What Are the Cellular Level Consequences of the Emergence of CSD?
6. Relationship of CSD to the Trigeminal Nervous System and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP)
7. CSD and Threshold
8. CSD and Migraine Treatment
9. CSD and the Role of Epigenetics
10. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSD | Cortical Spreading Depolarization |
| MWA | Migraine with Aura |
| MWoA | Migraine without Aura |
| CBF | Cerebral Blood Flow |
| BBB | Blood-Brain Barrier |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| CGRP | Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide |
| MMP-9 | Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 |
| iVNS | Invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation |
| nVNS | Non-Invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 Beta |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| iNOS | Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| NMDA | N-Methyl-D-Aspartate |
| DC | Direct Current |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| NTS | Nucleus Tractus Solitarius |
| TRN | Thalamic Reticular Nucleus |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| GWAS | Genome-Wide Association Studies |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| DMR | Differentially Methylated Region |
References
- Ashina, M.; Katsarava, Z.; Do, T.P.; Buse, D.C.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; Ozge, A.; Krymchantowski, A.V.; Lebedeva, E.R.; Ravishankar, K.; Yu, S.; et al. Migraine: Epidemiology and systems of care. Lancet 2021, 397, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina, M.; Ropper, A.H. Migraine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1866–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayata, C.; Jin, H.; Kudo, C.; Dalkara, T.; Moskowitz, M.A. Suppression of cortical spreading depression in migraine prophylaxis. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T.J.; Stovner, L.J.; Jensen, R.; Uluduz, D.; Katsarava, Z. Lifting the Burden: The Global Campaign against H. Migraine remains second among the world’s causes of disability, and first among young women: Findings from GBD2019. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina, M.; Terwindt, G.M.; Al-Karagholi, M.A.; de Boer, I.; Lee, M.J.; Hay, D.L.; Schulte, L.H.; Hadjikhani, N.; Sinclair, A.J.; Ashina, H.; et al. Migraine: Disease characterisation, biomarkers, and precision medicine. Lancet 2021, 397, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, A.C.; Baca, S.M. Cortical spreading depression and migraine. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodick, D.W. A Phase-by-Phase Review of Migraine Pathophysiology. Headache 2018, 58 (Suppl. S1), 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.R.; Fujii, T.; Ohiorhenuan, I.; Liu, C.Y. Cortical spreading depolarization: Pathophysiology, implications, and future directions. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 24, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritzen, M. Pathophysiology of the migraine aura. The spreading depression theory. Brain 1994, 117 Pt 1, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.A.; Panonnummal, R. Cortical spreading depression: Culprits and mechanisms. Exp. Brain Res. 2022, 240, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, T.; Ayata, C.; Chen, S.P. Therapeutic implications of cortical spreading depression models in migraine. Prog. Brain Res. 2020, 255, 29–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashley, K. Patterns of cerebral integration indicated by the scotoma of migraine. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1941, 42, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, A. Spreading depression of activity in the cerebral cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 1944, 78, 359–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, P.M. Note on a possible correspondence between the scotomas of migraine and spreading depression of Leao. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1958, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.; Larsen, B.; Lauritzen, M. Focal hyperemia followed by spreading oligemia and impaired activation of rCBF in classic migraine. Ann. Neurol. 1981, 9, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjikhani, N.; Sanchez Del Rio, M.; Wu, O.; Schwartz, D.; Bakker, D.; Fischl, B.; Kwong, K.K.; Cutrer, F.M.; Rosen, B.R.; Tootell, R.B.H.; et al. Mechanisms of migraine aura revealed by functional MRI in human visual cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4687–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, R.P.; Iacoboni, M.; Mazziotta, J.C. Brief report: Bilateral spreading cerebral hypoperfusion during spontaneous migraine headache. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denuelle, M.; Fabre, N.; Payoux, P.; Chollet, F.; Geraud, G. Posterior cerebral hypoperfusion in migraine without aura. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.D.; Haan, J.; Blokland, J.A.; Arndt, J.W.; Minnee, P.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Pauwels, E.K.J.; Saxena, P.R. Cerebral blood flow during migraine attacks without aura and effect of sumatriptan. Arch. Neurol. 1995, 52, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez del Rio, M.; Bakker, D.; Wu, O.; Agosti, R.; Mitsikostas, D.D.; Østergaard, L.; Wells, W.; Rosen, B.R.; Sorensen, G.; Moskowitz, M.A.; et al. Perfusion weighted imaging during migraine: Spontaneous visual aura and headache. Cephalalgia 1999, 19, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolay, H.; Reuter, U.; Dunn, A.K.; Huang, Z.; Boas, D.A.; Moskowitz, M.A. Intrinsic brain activity triggers trigeminal meningeal afferents in a migraine model. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, G.; Reuter, U.; Kinze, S.; Wolf, T.; Einhaupl, K.M. Migraine with aura shows gadolinium enhancement which is reversed following prophylactic treatment. Cephalalgia 1998, 18, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, J.S.; Varallyay, C.G.; Dosa, E.; Gahramanov, S.; Hamilton, B.; Rooney, W.D.; Muldoon, L.L.; A Neuwelt, E.A. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging and potential therapeutic applications in neurooncology and central nervous system inflammatory pathologies, a review. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2010, 30, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.M.; Hougaard, A.; Cramer, S.P.; Christensen, C.E.; Wolfram, F.; Larsson, H.B.W.; Ashina, M. Intact blood-brain barrier during spontaneous attacks of migraine without aura: A 3T DCE-MRI study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hougaard, A.; Amin, F.M.; Christensen, C.E.; Younis, S.; Wolfram, F.; Cramer, S.P.; Ashina, M. Increased brainstem perfusion, but no blood-brain barrier disruption, during attacks of migraine with aura. Brain 2017, 140, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, K.; Takeshima, T.; Fusayasu, E.; Nakashima, K. Increased plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 levels in migraineurs. Headache 2008, 48, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Oliveira, A.; Speciali, J.G.; Dach, F.; Marcaccini, A.M.; Goncalves, F.M.; Gerlach, R.F.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Different circulating metalloproteinases profiles in women with migraine with and without aura. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 408, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, D.S.; Mainero, C.; Ichijo, E.; Ward, N.; Granziera, C.; Zurcher, N.R.; Akeju, O.; Bonnier, G.; Price, J.; Hooker, J.M.; et al. Imaging of neuroinflammation in migraine with aura: A [(11)C]PBR28 PET/MRI study. Neurology 2019, 92, e2038–e2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreier, J.P.; Jurkat-Rott, K.; Petzold, G.C.; Tomkins, O.; Klingebiel, R.; Kopp, U.A.; Lehmann-Horn, F.; Friedman, A.; Dichgans, M. Opening of the blood-brain barrier preceding cortical edema in a severe attack of FHM type II. Neurology 2005, 64, 2145–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Amin, F.M.; Fliedner, F.P.; Christensen, C.E.; Tolnai, D.; Younis, S.; Olinger, A.C.R.; Birgens, H.; Daldrup-Link, H.; Kjær, A.; et al. Investigating macrophage-mediated inflammation in migraine using ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced 3T magnetic resonance imaging. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Suzuki, N. Exploring the role of microglia in cortical spreading depression in neurological disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2017, 37, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. The status of knowledge on migraines: The role of microglia. J. Neuroimmunol. 2023, 381, 578118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosche, B.; Graf, R.; Ernestus, R.I.; Dohmen, C.; Reithmeier, T.; Brinker, G.; Strong, A.J.; Dreier, J.P.; Woitzik, J. Recurrent spreading depolarizations after subarachnoid hemorrhage decreases oxygen availability in human cerebral cortex. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohmen, C.; Sakowitz, O.W.; Fabricius, M.; Bosche, B.; Reithmeier, T.; Ernestus, R.I.; Brinker, G.; Dreier, J.P.; Woitzik, J.; Strong, A.J.; et al. Spreading depolarizations occur in human ischemic stroke with high incidence. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartings, J.A.; Bullock, M.R.; Okonkwo, D.O.; Murray, L.S.; Murray, G.D.; Fabricius, M.; Maas, A.I.; Woitzik, J.; Sakowitz, O.; Mathern, B.; et al. Spreading depolarisations and outcome after traumatic brain injury: A prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.P.; Ay, I.; Lopes de Morais, A.; Qin, T.; Zheng, Y.; Sadeghian, H.; Oka, F.; Simon, B.; Eikermann-Haerter, K.; Ayata, C. Vagus nerve stimulation inhibits cortical spreading depression. Pain 2016, 157, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chever, O.; Zerimech, S.; Scalmani, P.; Lemaire, L.; Pizzamiglio, L.; Loucif, A.; Ayrault, M.; Krupa, M.; Desroches, M.; Duprat, F.; et al. Initiation of migraine-related cortical spreading depolarization by hyperactivity of GABAergic neurons and NaV1.1 channels. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Fischer, P.; Bohm, M.; Takizawa, T.; Sadeghian, H.; Morais, A.; Harriott, A.; Oka, F.; Qin, T.; et al. Real-time non-invasive in vivo visible light detection of cortical spreading depolarizations in mice. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 309, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiz, A.; Tepe, N.; Eftekhari, S.; Boran, H.E.; Dilekoz, E.; Edvinsson, L.; Bolay, H. CGRP receptor antagonist MK-8825 attenuates cortical spreading depression induced pain behavior. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, Y.Y.; Zitzow, L.A.; Kraig, R.P. Intranasally administered IGF-1 inhibits spreading depression in vivo. Brain Res. 2017, 1677, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, E.; Kanazawa, N.; Hamada, J. Hyperleptinemia increases the susceptibility of the cortex to generate cortical spreading depression. Cephalalgia 2015, 35, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Carrillo, A.; Schain, A.J.; Stratton, J.; Strassman, A.M.; Burstein, R. Fremanezumab and its isotype slow propagation rate and shorten cortical recovery period but do not prevent occurrence of cortical spreading depression in rats with compromised blood-brain barrier. Pain 2020, 161, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Tian, G.F.; Peng, W.; Lou, N.; Lovatt, D.; Hansen, A.J.; Kasischke, K.; Nedergaard, M. Cortical spreading depression causes and coincides with tissue hypoxia. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tye, A.E.; Zhao, J.; Ma, D.; Raddant, A.C.; Bu, F.; Spector, B.L.; Winslow, N.K.; Wang, M.; Russo, A.F. Induction of calcitonin gene-related peptide expression in rats by cortical spreading depression. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
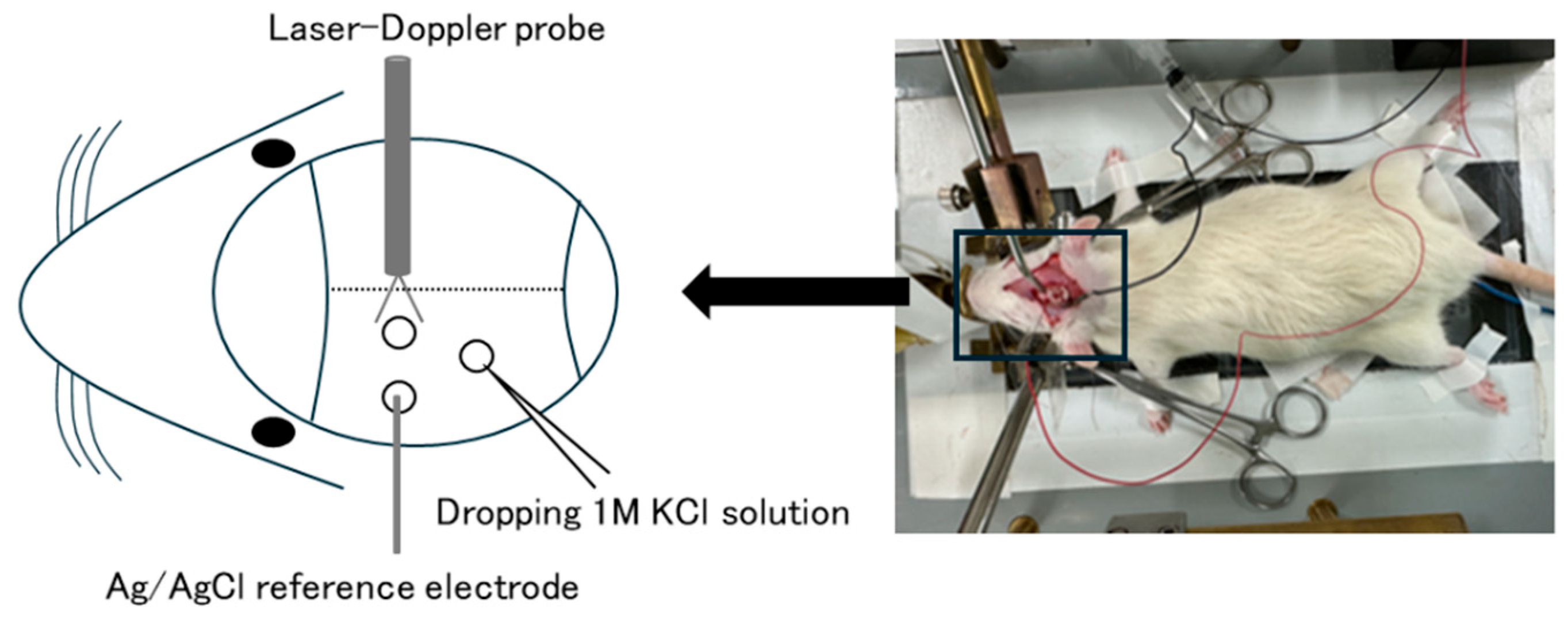
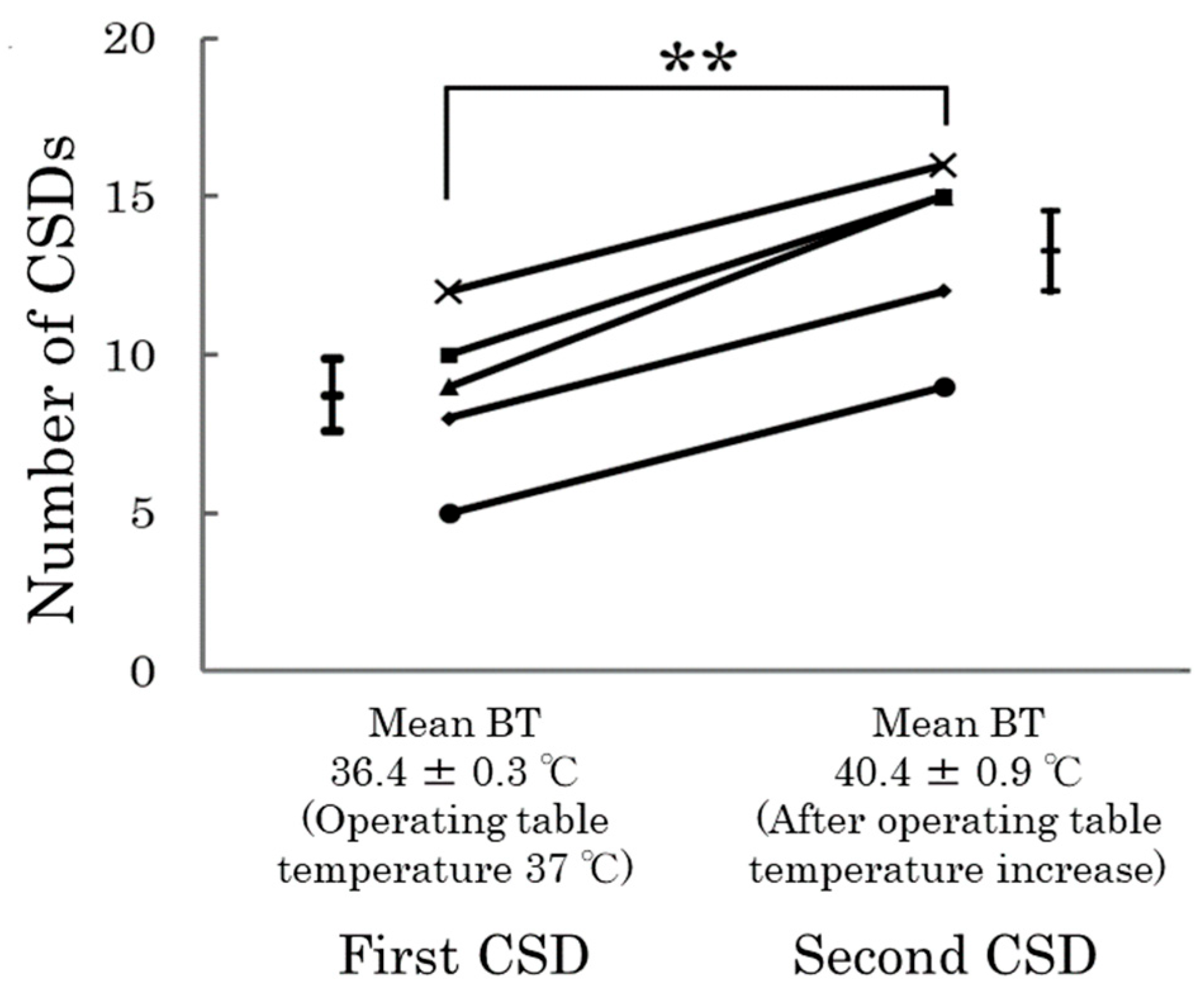
- Kitamura, E.; Kanazawa, N.; Iizuka, T.; Nishiyama, K. Elevation in body temperature may increase susceptibility to cortical spreading depression in a rat model. Neurosci. Res. 2024, 206, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harriott, A.M.; Takizawa, T.; Chung, D.Y.; Chen, S.P. Spreading depression as a preclinical model of migraine. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Dilli, E. Migraine Aura: Updates in Pathophysiology and Management. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, O.; Marchese, M.; Trovato, F.; Pracucci, E.; Ratto, G.M.; Buzzi, M.G.; Sicca, F.; Santorelli, F.M. Understanding Spreading Depression from Headache to Sudden Unexpected Death. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Kitagawa, S.; Unekawa, M.; Takizawa, T.; Nakahara, J. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide mRNA Synthesis in Trigeminal Ganglion Neurons after Cortical Spreading Depolarization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Pan, C.; Ghasemigharagoz, A.; Todorov, M.I.; Forstera, B.; Zhao, S.; Bhatia, H.S.; Parra-Damas, A.; Mrowka, L.; Theodorou, D.; et al. Panoptic imaging of transparent mice reveals whole-body neuronal projections and skull-meninges connections. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapunda, J.A.; Pareja, J.; Vladymyrov, M.; Bouillet, E.; Helie, P.; Pleskač, P.; Barcos, S.; Andrae, J.; Vestweber, D.; McDonald, D.M.; et al. VE-cadherin in arachnoid and pia mater cells serves as a suitable landmark for in vivo imaging of CNS immune surveillance and inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringstad, G.; Eide, P.K. Cerebrospinal fluid tracer efflux to parasagittal dura in humans. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustenhoven, J.; Drieu, A.; Mamuladze, T.; de Lima, K.A.; Dykstra, T.; Wall, M.; Papadopoulos, Z.; Kanamori, M.; Salvador, A.F.; Baker, W.; et al. Functional characterization of the dural sinuses as a neuroimmune interface. Cell 2021, 184, 1000–1016.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, L.C.D.; Xu, D.; Okar, S.V.; Dykstra, T.; Rustenhoven, J.; Papadopoulos, Z.; Bhasiin, K.; Kim, M.W.; Drieu, A.; Mamuladze, T.; et al. Identification of direct connections between the dura and the brain. Nature 2024, 627, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaag Rasmussen, M.; Mollgard, K.; Bork, P.A.R.; Weikop, P.; Esmail, T.; Drici, L.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; Carlsen, J.F.; Huynh, N.P.T.; Ghitani, N.; et al. Trigeminal ganglion neurons are directly activated by influx of CSF solutes in a migraine model. Science 2024, 385, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikermann-Haerter, K.; Dilekoz, E.; Kudo, C.; Savitz, S.I.; Waeber, C.; Baum, M.J.; Ferrari, M.D.; Maagdenberg, A.M.v.D.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Ayata, C. Genetic and hormonal factors modulate spreading depression and transient hemiparesis in mouse models of familial hemiplegic migraine type 1. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grech, O.; Sassani, M.; Terwindt, G.; Lavery, G.G.; Mollan, S.P.; Sinclair, A.J. Alterations in metabolic flux in migraine and the translational relevance. J. Headache Pain 2022, 23, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeghi Jahromi, S.; Ghorbani, Z.; Martelletti, P.; Lampl, C.; Togha, M. School of Advanced Studies of the European Headache F. Association of diet and headache. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, M.; Tatsumoto, M.; Kimoto, K.; Iiyama, T.; Tajima, M.; Munakata, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Shimazu, T. Investigating the effects of weather on headache occurrence using a smartphone application and artificial intelligence: A retrospective observational cross-sectional study. Headache 2023, 63, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, P.B.; Rapoport, A.M.; Sheftell, F.D.; Tepper, S.J.; Bigal, M.E. The Effect of Weather on Headache. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2004, 44, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, L.; Kraig, R.P. Insulin-like growth factor-1 inhibits spreading depression-induced trigeminal calcitonin gene related peptide, oxidative stress & neuronal activation in rat. Brain Res. 2020, 1732, 146673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, A.; Liu, T.T.; Qin, T.; Sadhegian, H.; Ay, I.; Yagmur, D.; da Silva, R.M.; Chung, D.; Simon, B.; Guedes, R.; et al. Vagus nerve stimulation inhibits cortical spreading depression exclusively through central mechanisms. Pain 2020, 161, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, H.G.; Albury, C.L.; Griffiths, L.R. Advances in genetics of migraine. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautakangas, H.; Winsvold, B.S.; Ruotsalainen, S.E.; Bjornsdottir, G.; Harder, A.V.E.; Kogelman, L.J.A.; Thomas, L.F.; Noordam, R.; Benner, C.; Gormley, P.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of 102,084 migraine cases identifies 123 risk loci and subtype-specific risk alleles. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, R.; Noseda, R.; Borsook, D. Migraine: Multiple processes, complex pathophysiology. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 6619–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, V.J.; Vila-Pueyo, M.; Pozo-Rosich, P. The impact of epigenetic mechanisms in migraine: Current knowledge and future directions. Cephalalgia 2023, 43, 03331024221145916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerring, Z.F.; McRae, A.F.; Montgomery, G.W.; Nyholt, D.R. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling in whole blood reveals epigenetic signatures associated with migraine. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsvold, B.S.; Palta, P.; Eising, E.; Page, C.M.; International Headache Genetics, C.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Palotie, A.; Zwart, J.-A. Epigenetic DNA methylation changes associated with headache chronification: A retrospective case-control study. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labruijere, S.; Stolk, L.; Verbiest, M.; de Vries, R.; Garrelds, I.M.; Eilers, P.H.; Danser, A.H.J.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. Methylation of migraine-related genes in different tissues of the rat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerman, S.; Goadsby, P.J. Topiramate inhibits cortical spreading depression in rat and cat: Impact in migraine aura. Neuroreport 2005, 16, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Pueyo, M.; Cuenca-Leon, E.; Queiros, A.C.; Kulis, M.; Sintas, C.; Cormand, B.; Martín-Subero, J.I.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; Fernàndez-Castillo, N.; Macaya, A. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis in an antimigraine-treated preclinical model of cortical spreading depolarization. Cephalalgia 2023, 43, 3331024221146317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kitamura, E.; Imai, N. Molecular and Cellular Neurobiology of Spreading Depolarization/Depression and Migraine: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011163
Kitamura E, Imai N. Molecular and Cellular Neurobiology of Spreading Depolarization/Depression and Migraine: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(20):11163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011163
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitamura, Eiji, and Noboru Imai. 2024. "Molecular and Cellular Neurobiology of Spreading Depolarization/Depression and Migraine: A Narrative Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 20: 11163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011163
APA StyleKitamura, E., & Imai, N. (2024). Molecular and Cellular Neurobiology of Spreading Depolarization/Depression and Migraine: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(20), 11163. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252011163






