Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Yap/Taz Activity during Embryonic Development in Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Wnt/β-Catenin and Hippo-Yap/Taz Pathways Are Characterized by an Overlapping Spatial Expression during Zebrafish Development
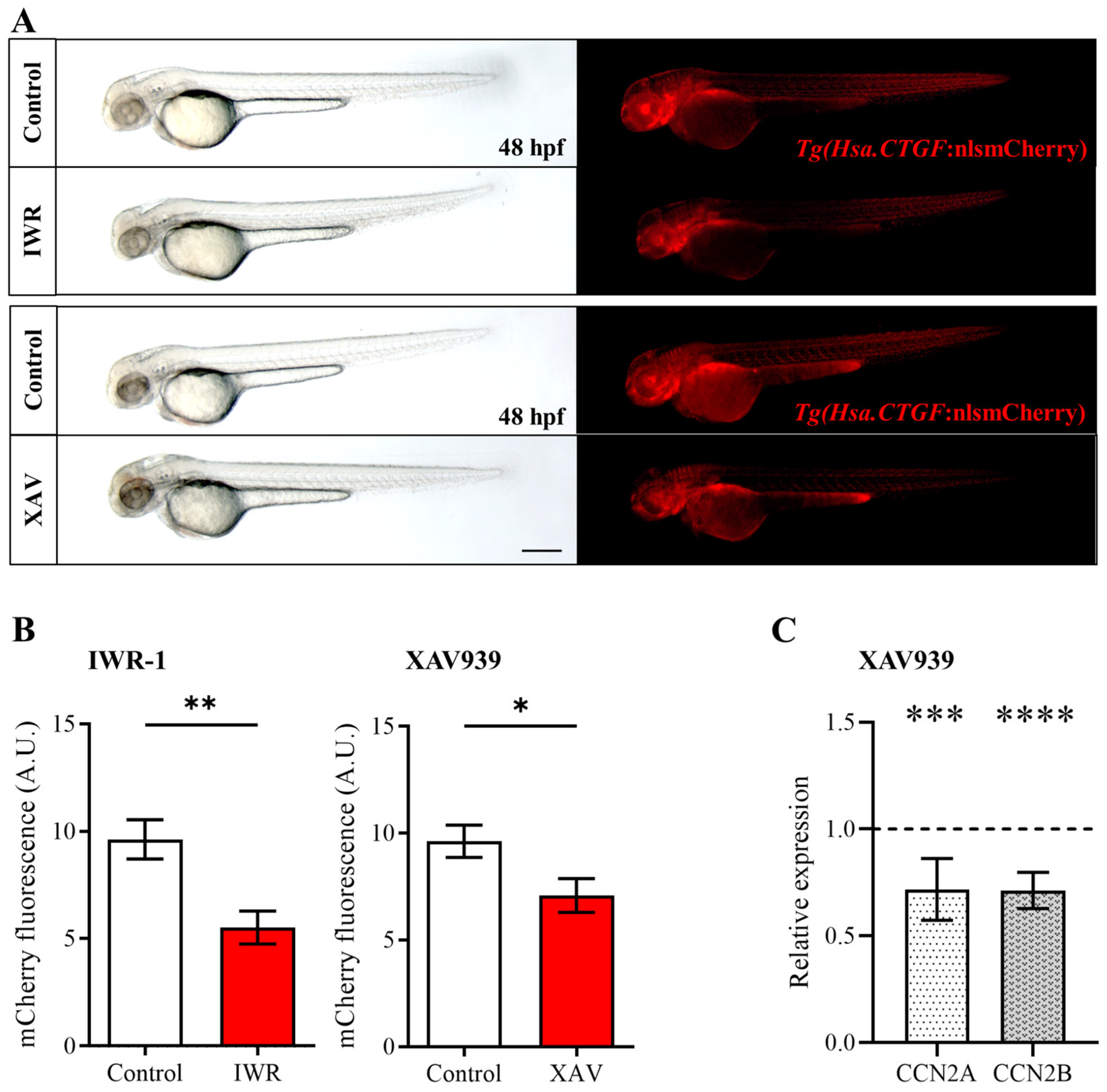
2.2. Pharmacological Inhibition of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Reduces Yap/Taz Activity during Zebrafish Embryonic Development
2.3. Genetic Inhibition of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Reduces Yap/Taz Activity during Zebrafish Embryonic Development
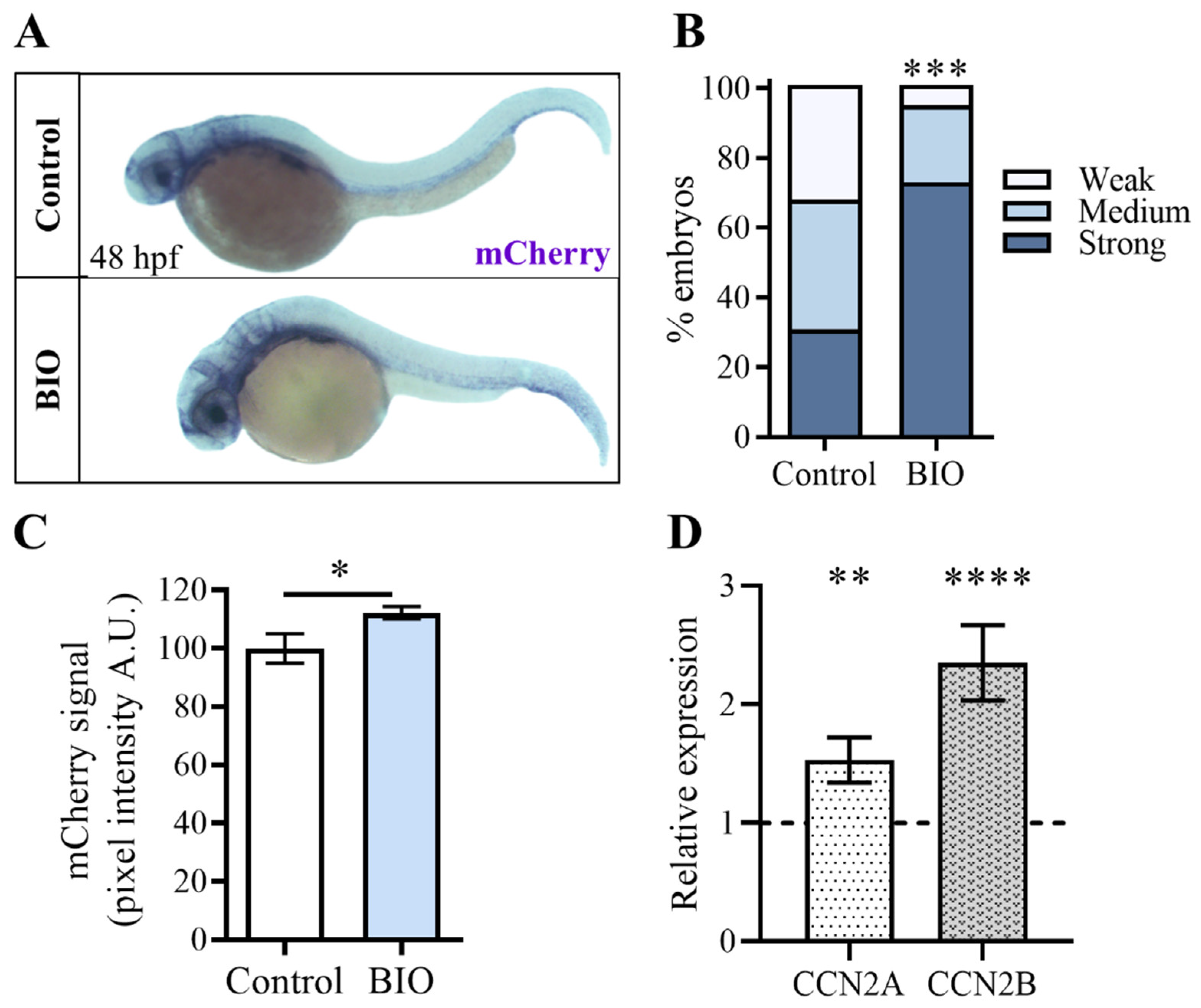
2.4. Pharmacological Inhibition of β-Catenin Kinase GSK3 during Zebrafish Embryonic Development Increases Yap/Taz Activity
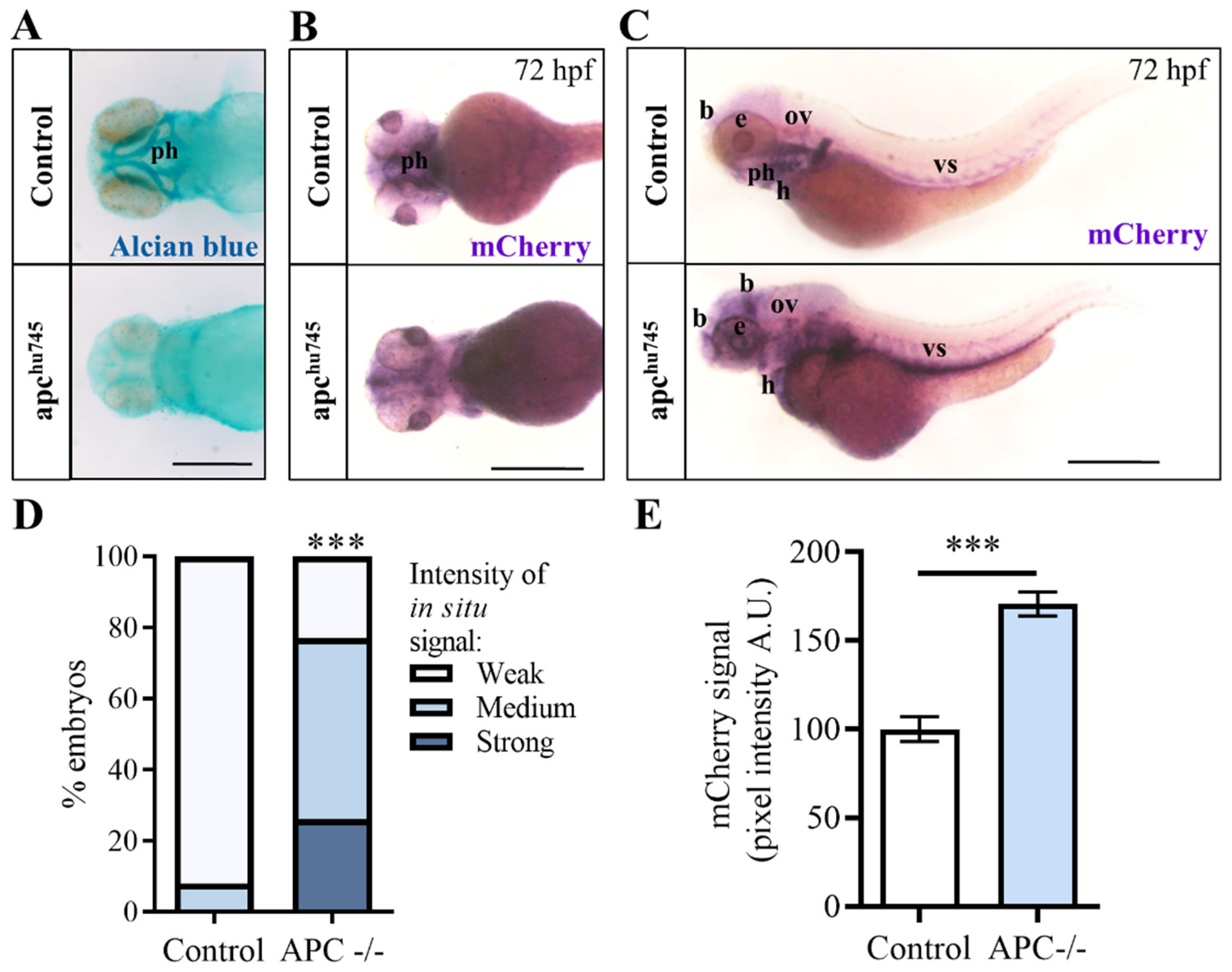
2.5. Activation of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway through Apc Depletion Increases Yap/Taz Activity during Zebrafish Development
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Chemical Treatments
4.3. Fluorescence Image Acquisition and Analysis
4.4. Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization (WISH) and Quantification
4.5. Alcian Blue Staining
4.6. Heat-Shock Treatments
4.7. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacDonald, B.T.; Tamai, K.; He, X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, D. The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mo, J.S.; Park, H.W.; Guan, K.L. The Hippo signaling pathway in stem cell biology and cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santinon, G.; Pocaterra, A.; Dupont, S. Control of YAP/TAZ Activity by Metabolic and Nutrient-Sensing Pathways. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piccolo, S.; Dupont, S.; Cordenonsi, M. The biology of YAP/TAZ: Hippo signaling and beyond. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1287–1312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moroishi, T.; Park, H.W.; Qin, B.; Chen, Q.; Meng, Z.; Plouffe, S.W.; Taniguchi, K.; Yu, F.X.; Karin, M.; Pan, D.; et al. A YAP/TAZ-induced feedback mechanism regulates Hippo pathway homeostasis. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, E.H.; Nousiainen, M.; Chalamalasetty, R.B.; Schafer, A.; Nigg, E.A.; Sillje, H.H. The Ste20-like kinase Mst2 activates the human large tumor suppressor kinase Lats1. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Feldmann, G.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, N.; Comerford, S.A.; Gayyed, M.F.; Anders, R.A.; Maitra, A.; Pan, D. Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in Drosophila and mammals. Cell 2007, 130, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, S.; Morsut, L.; Aragona, M.; Enzo, E.; Giulitti, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Zanconato, F.; Le Digabel, J.; Forcato, M.; Bicciato, S.; et al. Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature 2011, 474, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Zha, Z.Y.; Bai, F.; Pei, X.H.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, Y.; Guan, K.L. TAZ promotes cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is inhibited by the hippo pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 2426–2436. [Google Scholar]
- Praskova, M.; Xia, F.; Avruch, J. MOBKL1A/MOBKL1B phosphorylation by MST1 and MST2 inhibits cell proliferation. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.X.; Guan, K.L. The Hippo pathway: Regulators and regulations. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Udan, R.S.; Yang, Q.; Kim, J.; Xie, J.; Ikenoue, T.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; et al. Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2747–2761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clevers, H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 2006, 127, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konsavage, W.M., Jr.; Yochum, G.S. Intersection of Hippo/YAP and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Azzolin, L.; Panciera, T.; Soligo, S.; Enzo, E.; Bicciato, S.; Dupont, S.; Bresolin, S.; Frasson, C.; Basso, G.; Guzzardo, V.; et al. YAP/TAZ incorporation in the beta-catenin destruction complex orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell 2014, 158, 157–170. [Google Scholar]
- Azzolin, L.; Zanconato, F.; Bresolin, S.; Forcato, M.; Basso, G.; Bicciato, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. Role of TAZ as mediator of Wnt signaling. Cell 2012, 151, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Varelas, X.; Miller, B.W.; Sopko, R.; Song, S.; Gregorieff, A.; Fellouse, F.A.; Sakuma, R.; Pawson, T.; Hunziker, W.; McNeill, H.; et al. The Hippo pathway regulates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 579–591. [Google Scholar]
- Imajo, M.; Miyatake, K.; Iimura, A.; Miyamoto, A.; Nishida, E. A molecular mechanism that links Hippo signalling to the inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Shang, Y.; Lin, J. YAP-mediated crosstalk between the Wnt and Hippo signaling pathways (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 4101–4106. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Lu, N.; Xie, C. The Hippo and Wnt signalling pathways: Crosstalk during neoplastic progression in gastrointestinal tissue. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 3745–3756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cayuso, J.; Xu, Q.; Addison, M.; Wilkinson, D.G. Actomyosin regulation by Eph receptor signaling couples boundary cell formation to border sharpness. Elife 2019, 8, e49696. [Google Scholar]
- Voltes, A.; Hevia, C.F.; Engel-Pizcueta, C.; Dingare, C.; Calzolari, S.; Terriente, J.; Norden, C.; Lecaudey, V.; Pujades, C. Yap/Taz-TEAD activity links mechanical cues to progenitor cell behavior during zebrafish hindbrain segmentation. Development 2019, 146, dev176735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ward, D.; Montes Olivas, S.; Fletcher, A.; Homer, M.; Marucci, L. Cross-talk between Hippo and Wnt signalling pathways in intestinal crypts: Insights from an agent-based model. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 230–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, W.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Hou, N. Role of Hippo-YAP1/TAZ pathway and its crosstalk in cardiac biology. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2454–2463. [Google Scholar]
- Heallen, T.; Morikawa, Y.; Leach, J.; Tao, G.; Willerson, J.T.; Johnson, R.L.; Martin, J.F. Hippo signaling impedes adult heart regeneration. Development 2013, 140, 4683–4690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernascone, I.; Martin-Belmonte, F. Crossroads of Wnt and Hippo in epithelial tissues. Trends Cell Biol. 2013, 23, 380–389. [Google Scholar]
- Doloi, R.; Gupta, S.M. MicroRNAs: The key players regulating the crosstalk between Hippo and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways in breast cancer. Life Sci. 2023, 329, 121980. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Jin, D.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, D.; Xue, J.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, X.; Lian, F. The critical role of the Hippo signaling pathway in kidney diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 988175. [Google Scholar]
- Sileo, P.; Simonin, C.; Melnyk, P.; Chartier-Harlin, M.C.; Cotelle, P. Crosstalk between the Hippo Pathway and the Wnt Pathway in Huntington’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells 2022, 11, 3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astone, M.; Lai, J.K.H.; Dupont, S.; Stainier, D.Y.R.; Argenton, F.; Vettori, A. Zebrafish mutants and TEAD reporters reveal essential functions for Yap and Taz in posterior cardinal vein development. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10189. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.W.; Kim, Y.C.; Yu, B.; Moroishi, T.; Mo, J.S.; Plouffe, S.W.; Meng, Z.; Lin, K.C.; Yu, F.X.; Alexander, C.M.; et al. Alternative Wnt Signaling Activates YAP/TAZ. Cell 2015, 162, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dicipulo, R.; Selland, L.G.; Carpenter, R.G.A.J.W. Functional Role for Taz during Hindbrain Ventricle Morphogenesis. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4039852 (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Bao, R.; Christova, T.; Song, S.; Angers, S.; Yan, X.; Attisano, L. Inhibition of tankyrases induces Axin stabilization and blocks Wnt signalling in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48670. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Dodge, M.E.; Tang, W.; Lu, J.; Ma, Z.; Fan, C.W.; Wei, S.; Hao, W.; Kilgore, J.; Williams, N.S.; et al. Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fearon, E.R. PARsing the phrase ”all in for Axin”- Wnt pathway targets in cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, S.J.; Smith, S. Tankyrase function at telomeres, spindle poles, and beyond. Biochimie 2008, 90, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.M.; Mishina, Y.M.; Liu, S.; Cheung, A.; Stegmeier, F.; Michaud, G.A.; Charlat, O.; Wiellette, E.; Zhang, Y.; Wiessner, S.; et al. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature 2009, 461, 614–620. [Google Scholar]
- Stoick-Cooper, C.L.; Weidinger, G.; Riehle, K.J.; Hubbert, C.; Major, M.B.; Fausto, N.; Moon, R.T. Distinct Wnt signaling pathways have opposing roles in appendage regeneration. Development 2007, 134, 479–489. [Google Scholar]
- Halder, G.; Dupont, S.; Piccolo, S. Transduction of mechanical and cytoskeletal cues by YAP and TAZ. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 591–600. [Google Scholar]
- Hurlstone, A.F.; Haramis, A.P.; Wienholds, E.; Begthel, H.; Korving, J.; Van Eeden, F.; Cuppen, E.; Zivkovic, D.; Plasterk, R.H.; Clevers, H. The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway regulates cardiac valve formation. Nature 2003, 425, 633–637. [Google Scholar]
- Panciera, T.; Azzolin, L.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. Mechanobiology of YAP and TAZ in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Totaro, A.; Panciera, T.; Piccolo, S. YAP/TAZ upstream signals and downstream responses. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Soldt, B.J.; Cardoso, W.V. Hippo-Yap/Taz signaling: Complex network interactions and impact in epithelial cell behavior. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2020, 9, e371. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, V. Mechanotransduction involving multimodular proteins: Converting force into biochemical signals. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2006, 35, 459–488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moro, E.; Ozhan-Kizil, G.; Mongera, A.; Beis, D.; Wierzbicki, C.; Young, R.M.; Bournele, D.; Domenichini, A.; Valdivia, L.E.; Lum, L.; et al. In vivo Wnt signaling tracing through a transgenic biosensor fish reveals novel activity domains. Dev. Biol. 2012, 366, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Facchinello, N.; Schiavone, M.; Vettori, A.; Argenton, F.; Tiso, N. Monitoring Wnt Signaling in Zebrafish Using Fluorescent Biosensors. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1481, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bolte, S.; Cordelières, F.P. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 224, 213–232. [Google Scholar]
- Thisse, C.; Thisse, B.; Schilling, T.F.; Postlethwait, J.H. Structure of the zebrafish snail1 gene and its expression in wild-type, spadetail and no tail mutant embryos. Development 1993, 119, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Astone, M.; Tesoriero, C.; Schiavone, M.; Facchinello, N.; Tiso, N.; Argenton, F.; Vettori, A. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Yap/Taz Activity during Embryonic Development in Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251810005
Astone M, Tesoriero C, Schiavone M, Facchinello N, Tiso N, Argenton F, Vettori A. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Yap/Taz Activity during Embryonic Development in Zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(18):10005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251810005
Chicago/Turabian StyleAstone, Matteo, Chiara Tesoriero, Marco Schiavone, Nicola Facchinello, Natascia Tiso, Francesco Argenton, and Andrea Vettori. 2024. "Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Yap/Taz Activity during Embryonic Development in Zebrafish" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 18: 10005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251810005
APA StyleAstone, M., Tesoriero, C., Schiavone, M., Facchinello, N., Tiso, N., Argenton, F., & Vettori, A. (2024). Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Yap/Taz Activity during Embryonic Development in Zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(18), 10005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251810005








