Structure, Evolution, and Mitochondrial Genome Analysis of Mussel Species (Bivalvia, Mytilidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
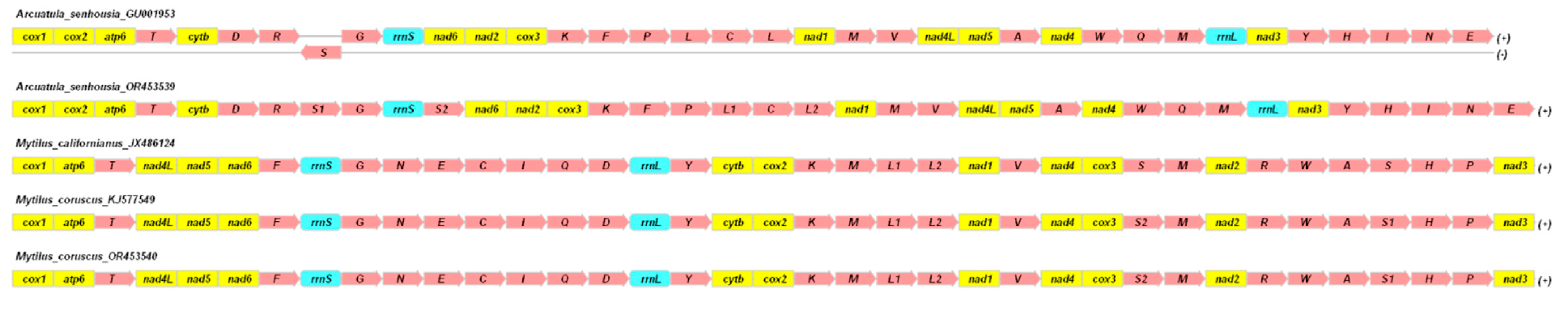
2.1. Structure and Variability of the Mitochondrial Genome of Arcuatula senhousia, Mytilus coruscus, and Other Representatives of the Mytilidae Family
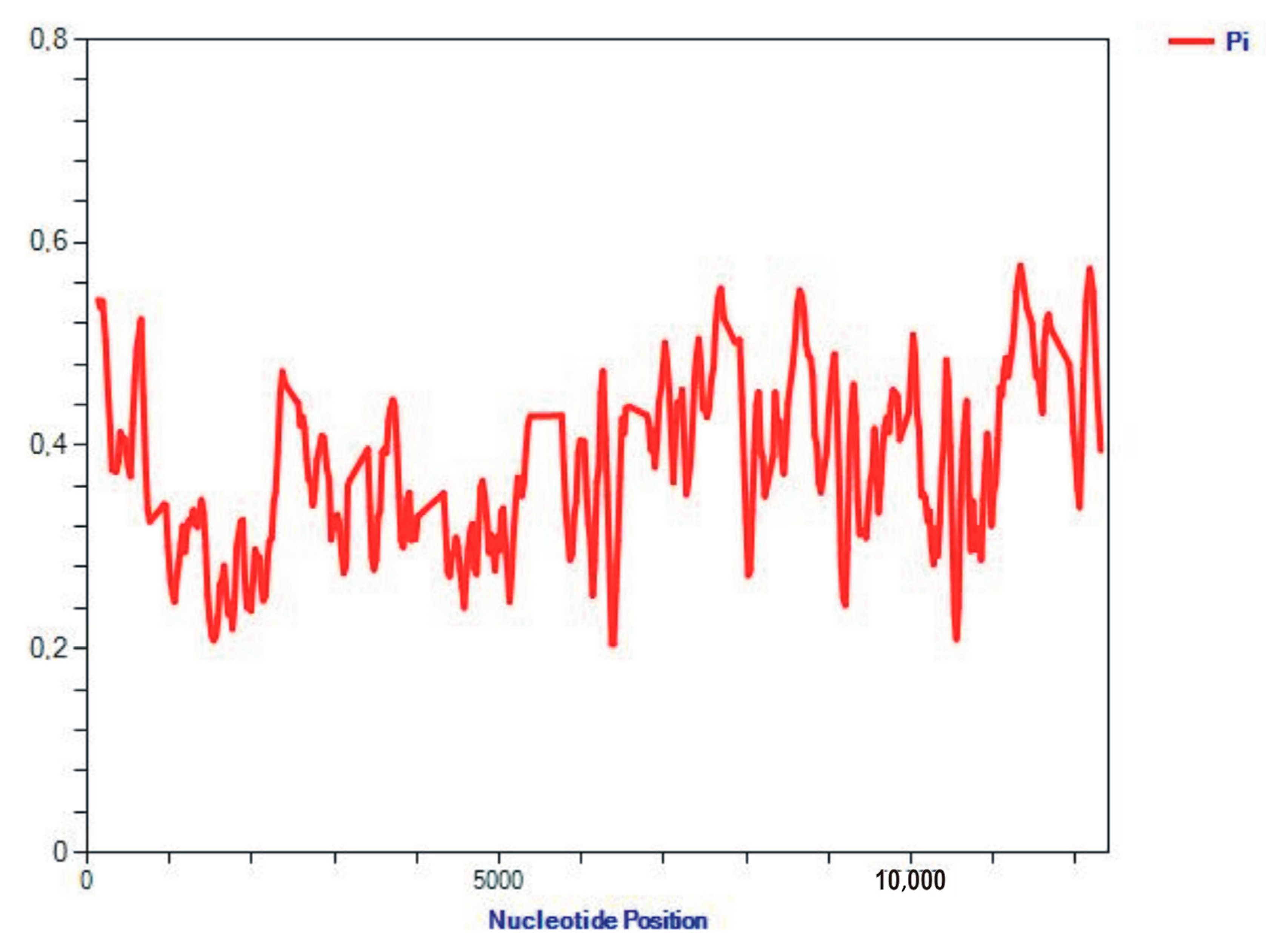
2.2. Analysis of the Sequence Properties
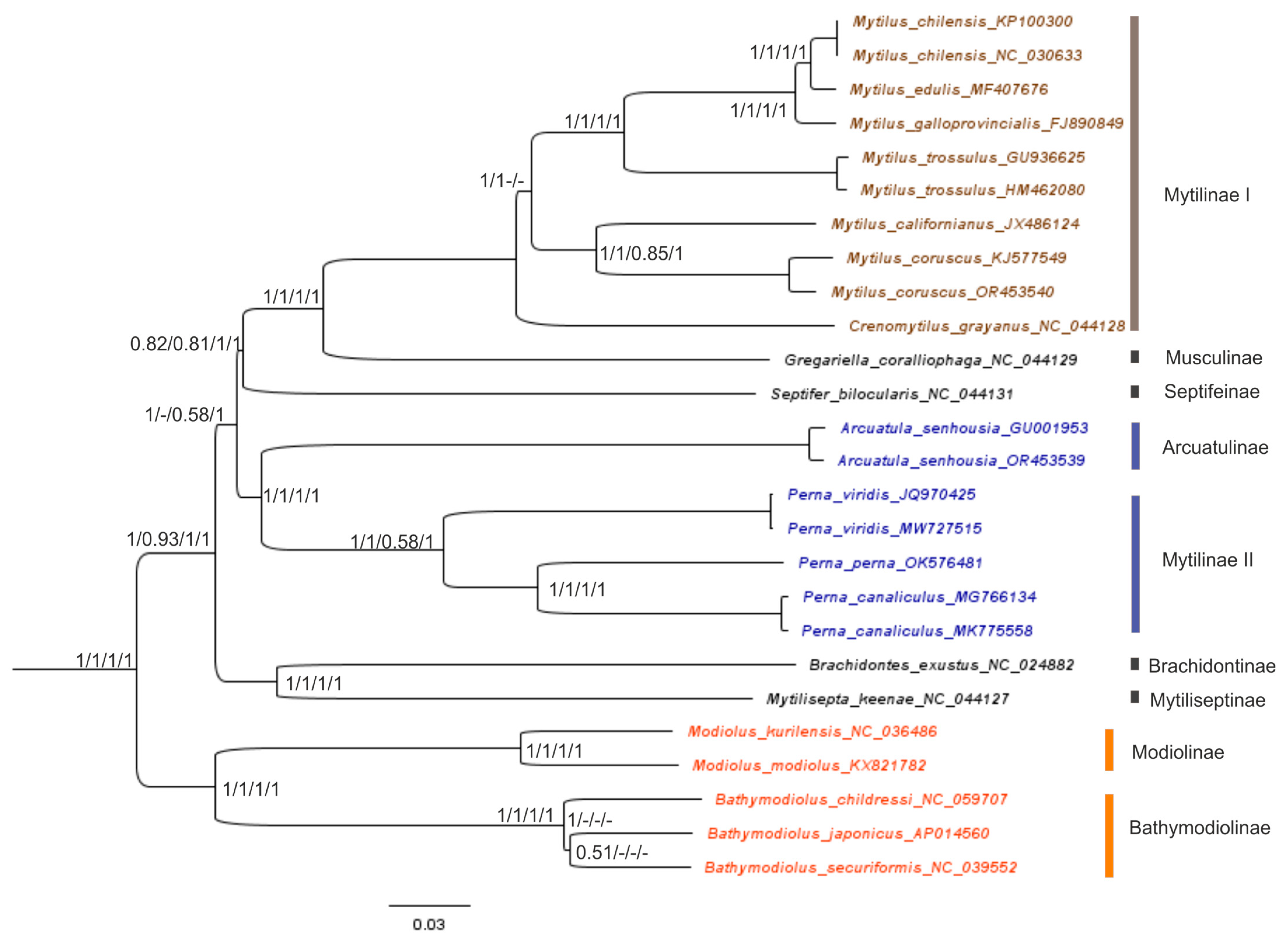
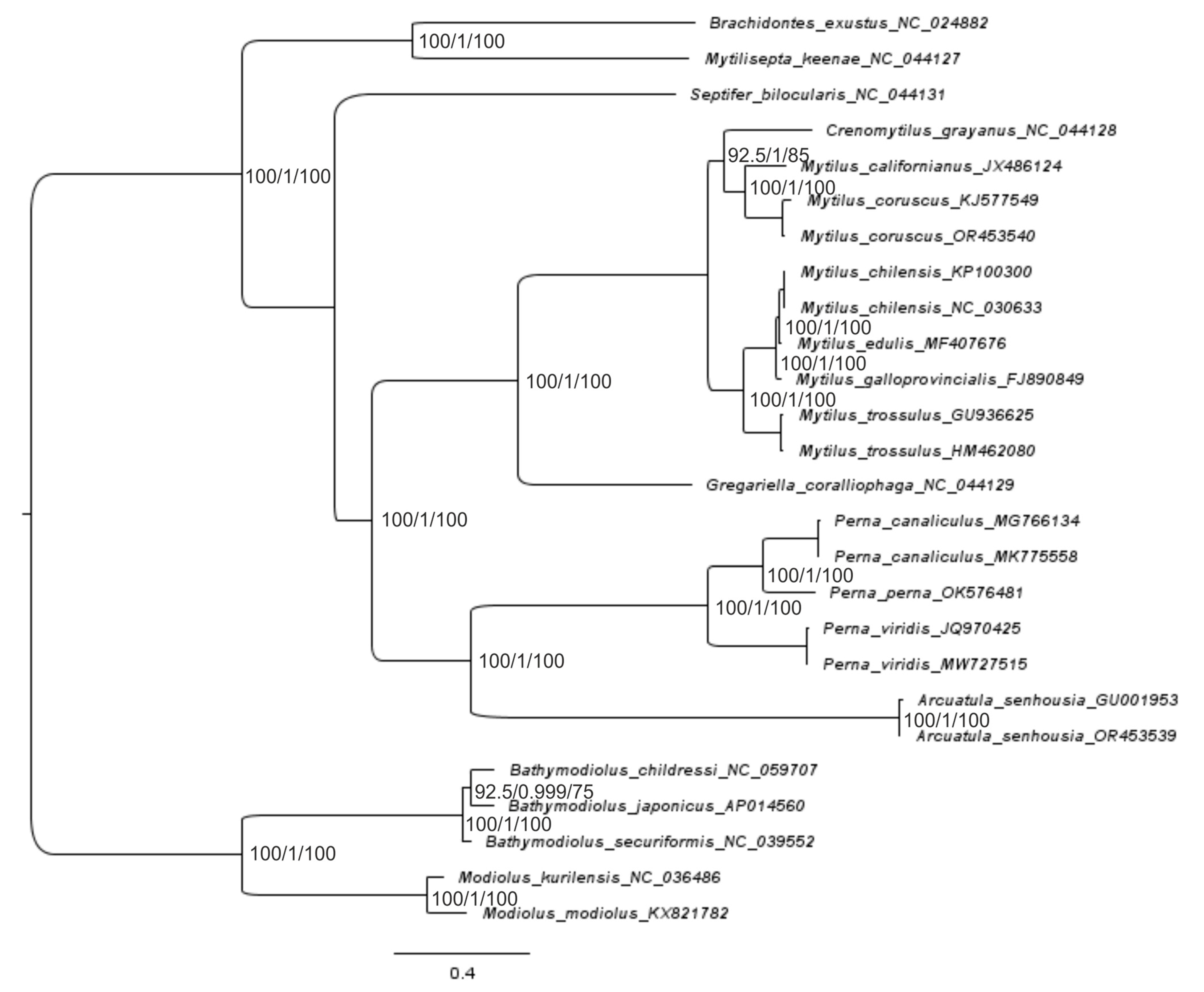
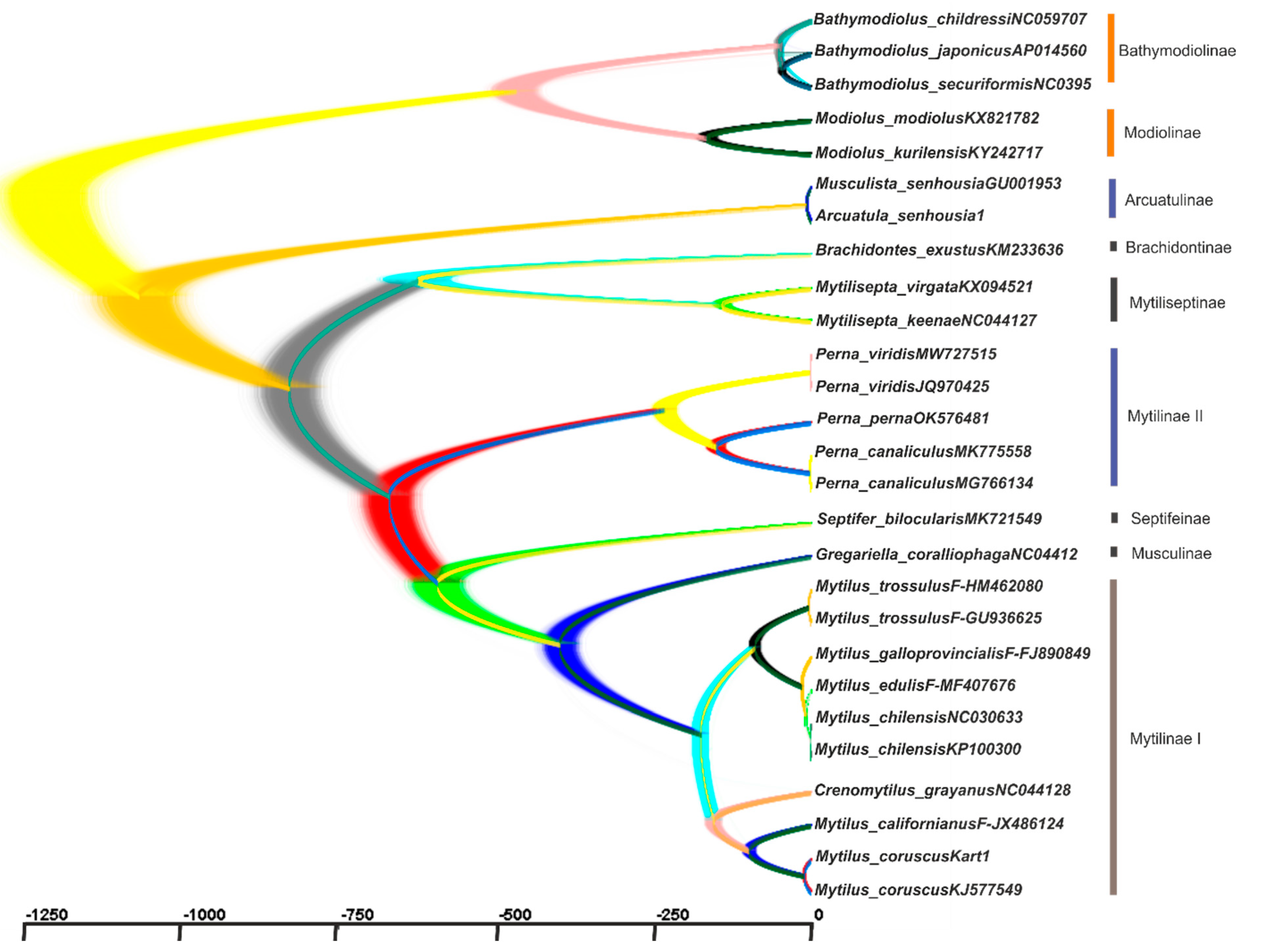
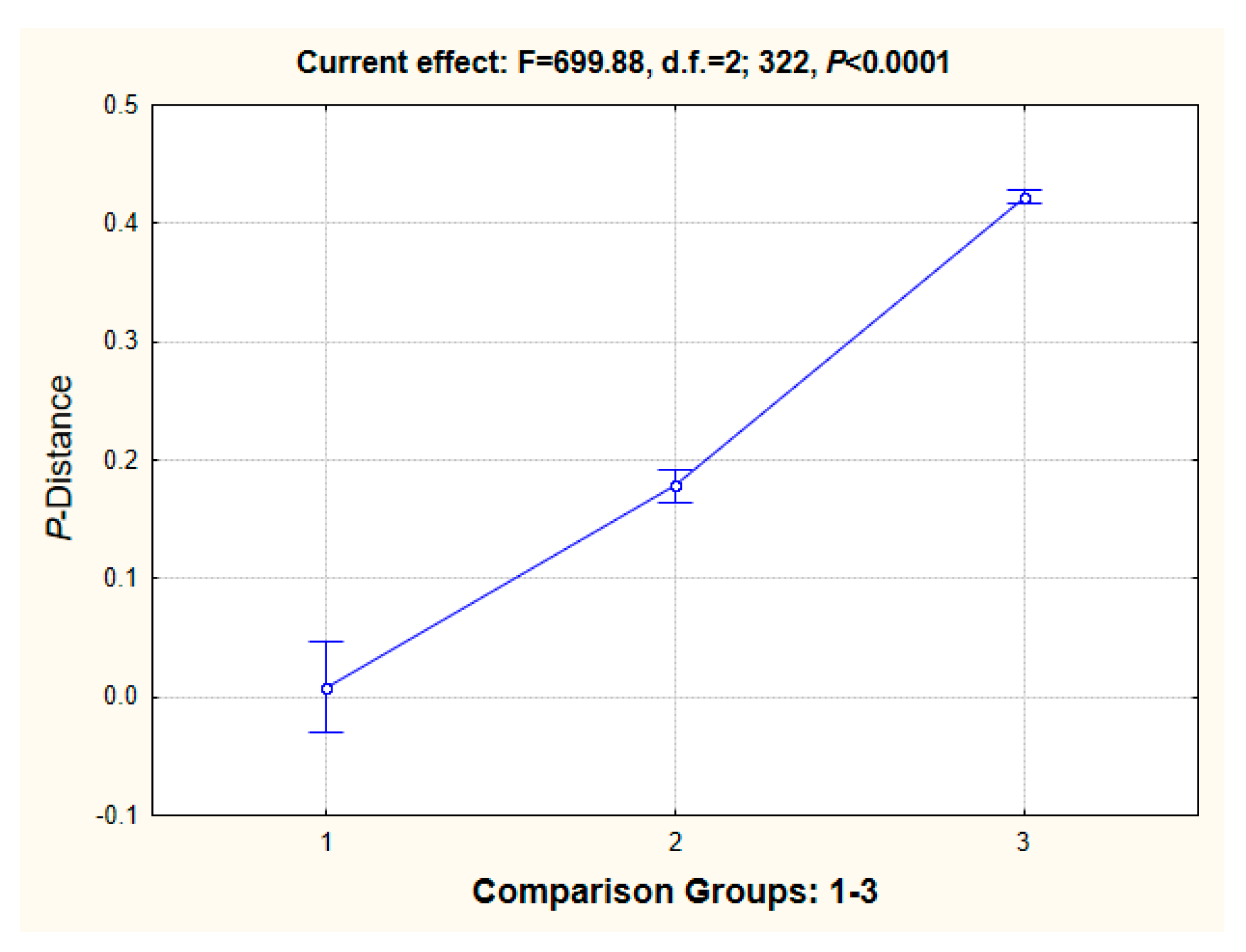
2.3. Reconstruction of the Gene Trees and Analysis of the Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships
3. Discussion
3.1. Structure and Variability of the Mitochondrial Genome of Arcuatula senhousia, Mytilus coruscus, and Other Representatives of the Mytilidae Family
3.2. Analysis of the Properties of Sequences
3.3. Reconstruction of Gene Trees and an Analysis of the Molecular Phylogenetic Relationships
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and General Approaches
4.2. Analysis of the Sequence Properties
4.3. Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Chichvarkhin, A.Y.; Kijima, A.; Hanzawa, N.; Park, I.-S. Allozyme and morphometric analysis of two commonmussel species of Mytilus genus (Mollusca, Mytilidae) in Korea, Japan and Russia waters. Korean J. Genet. 2005, 27, 289–306. [Google Scholar]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Katolikova, M.V.; Sharina, S.N.; Chichvarkhina, O.V.; Masalkova, N.A. A population genetic study of the hybrid zone of Mytilus trossulus Gould, 1850 and an introduced species, M. galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819, (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) in peter the great bay in the Sea of Japan. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2014, 40, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Sharina, S.N.; Chichvarkhin, A.Y.; Chichvarkhina, O.V.; Masalkova, N.A.; Lutaenko, K.A.; Oliveira, C. Genetic Divergence of Mussels (Mollusca, Mytilidae) Based on the 28S rRNA, 18S rRNA, and H3 Nuclear Gene Sequences. Russ. J. Genet. 2018, 54, 652–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Masalkova, N.A.; Katolikova, M.V. Genetic-and-morphometric variability in the settlements of two mussel species (Mytilus ex. gr. edulis), M. trossulus and M. galloprovincialis, in North-West Japan Sea. J. Shellfish Res. 2018, 37, 103–119. [Google Scholar]
- Katolikova, M.; Khaitov, V.; Vainola, R. Genetic, ecological and morphological distinctness of the blue mussels Mytilus trossulus Gould and M. edulis L. in the White Sea. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraín, M.A.; Zbawicka, M.; Araneda, C.; Gardner, J.P.A.; Wenne, R. Native and invasive taxa on the Pacific coast of South America: Impacts on aquaculture, traceability and biodiversity of blue mussels (Mytilus spp.). Evol. Appl. 2018, 11, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraín, M.A.; González, P.; Pérez, C.; Araneda, C. Comparison between single and multi-locus approaches for specimen identification in Mytilus mussels. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boss, K.J. How Many Species of Mollusks are There? Am. Malacol. Union Annu. Rep. 1971, 41. [Google Scholar]
- WoRMS. 2024. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=224589 (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Distel, D.L. Phylogenetic relationships among Mytilidae (Bivalvia): 18S RNA data suggest convergence in mytilid body plans. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2000, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, N.D. Classification of Bivalvia. In Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology; Moore, R.C., Ed.; Mollusca 6: Bivalvia, Kansas; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1969; Volume 1, pp. 205–224. [Google Scholar]
- Chichvarkhin, A. Phylogeny and taxonomy of marine mussels: Comments on the paper by Distel (2000). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2002, 22, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafanov, A.I.; Drozdov, A.L. Comparative sperm morphology and phylogenetic classification of recent Mytiloidea (Bivalvia). Malacologia 1998, 39, 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P. Some examples of the use of molecular markers for needs of basic biology and modern society. Animals 2021, 11, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouros, E.; Freeman, K.R.; Ball, A.O.; Pogson, G.H. Direct evidence for extensive paternal mitochondrial DNA inheritance in the marine mussel Mytilus. Nature 1992, 359, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawson, P.D.; Hilbish, T.J. Evolutionary relationships among the male and female mitochondrial DNA lineages in the Mytilus edulis species complex. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1995, 12, 893–901. [Google Scholar]
- Zouros, E. Biparental inheritance through uniparental transmission: The doubly uniparental inheritance (DUI) of mitochondrial DNA. Evol. Biol. 2013, 40, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.H. Evolution, systematics, and the unnatural history of mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2021, 32, 126–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, G.; Hammer, S. Molecular phylogeny of the Bivalvia inferred from 18S rDNA sequences with particular reference to the Pteriomorphia. In The Evolutionary Biology of the Bivalvia; Harpre, E.M., Taylor, J.D., Crame, J.A., Eds.; Geological Society Special Publications: London, UK, 2000; pp. 11–29. [Google Scholar]
- Giribet, G.; Wheeler, W. On bivalve phylogeny: A high-level analysis of the Bivalvia (Mollusca) based on combined morphology and DNA sequence data. Invertebr. Biol. 2002, 121, 271–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owada, M. Functional morphology and phylogeny of the rock-boring bivalves Leiosolenus and Lithophaga (Bivalvia: Mytilidae): A third functional clade. Mar. Biol. 2007, 150, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, S.; Quemere, E.; Lorion, J.; Tillier, A.; von Cosel, R.; Lopez, P.; Cruaud, C.; Couloux, A.; Boisselier-Dubayle, M.C. Molecular phylogeny in mytilids supports the wooden steps to deep-sea vents hypothesis. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2007, 330, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, G.; Shimamura, S.; Takaki, Y.; Yokobori, S.I.; Ohara, Y.; Takishita, K.; Maruyama, T.; Fujikura, K.; Yoshida, T. Updated mitochondrial phylogeny of Pteriomorph and Heterodont Bivalvia, including deep-sea chemosymbiotic Bathymodiolus mussels, vesicomyid clams and the thyasirid clam Conchocele cf. bisecta. Mar. Geonom. 2017, 31, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H. Phylogeny and evolutionary radiation of the marine mussels (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) based on mitochondrial and nuclear genes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 126, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kwak, H.; Shin, J.; Kim, S.-C.; Kim, T.; Park, J.-K. A mitochondrial genome phylogeny of Mytilidae (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 139, 106533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soot-Ryen, T. Superfamily Mytilacea Rafinesque, 1815. In Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology; Moore, R.C., Ed.; Mollusca 6: Bivalvia, Kansas; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1969; pp. 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Soot-Ryen, T. A report on the family Mytilidae (Pelecypoda). Allan Hancock Pac. Exped. 1955, 20, 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- WoRMS. 2024. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=211 (accessed on 8 April 2024).
- Skarlato, O.A. Dvustvorchatye Mollyuski Umerennykh Shirot Zapadnoi Chasti Tikhogo Okeana (Bivalve Mollusks of Temperate Latitudes of the Western Pacific Ocean); Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Skarlato, O.A.; Starobogatov, A.I. The systematic position and distribution of mussels. In Promyslovye Dvustvorchatye Mollyuski–midii i Ikh Rol’ v Ekosistemakh (Commercial Bivalve Molluscan Mussels and Their Role in the Ecosystem); Scarlato, O.A., Ed.; Zool. Inst. Akad. Nauk USSR: Leningrad, Russia, 1979; pp. 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Starobogatov, A.I. Morphological basis for phylogenyand classification of Bivalvia. Ruthenica 1992, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Coan, E.V.; Scott, P.V.; Bernard, F.R. BivalveSeashells of Western North America: Marine Bivalve Mollusks from Arctic Alaska to Baja California; Santa Barbara: Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 153–190. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, J.G.; Altaba, C.R.; Anderson, L.C. Paleontological Contributions: A Synoptical Classification of the Bivalvia (Mollusca); Kansas: University of Kansas: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2011; Available online: http://paleo.ku.edu/contributions (accessed on 8 April 2024).
- Kafanov, A.I. Subfamily Mytilinae Rafinisque, 1815 (Bivalvia, Mytilidae) in Cainozoe of North Pacific. In Fauna and Distribution of Mollusks: North Pacific and Polar Basin; Far East Center Publisher: Vladivostok, Russia, 1987; pp. 65–103. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; 512p. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.H. Molecular Evolution; Sinauer Ass.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tajima, F.; Nei, M. Biases of the estimates of DNA divergence obtained by the restriction enzyme technique. J. Mol. Evol. 1982, 18, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.; Crease, T. The analysis of population survey data on DNA sequence variation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1990, 7, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hudson, R.R.; Slatkin, M.; Maddison, W.P. Estimation of levels of gene flow from DNA sequence data. Genetics 1992, 132, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xie, Z.; Salemi, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. An index of substitution saturation and its application. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Lemey, P. Assessing substitution saturation with DAMBE. In The Phylogenetic Handbook; Lemey, P., Salemi, M., Vandamme, A.-M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 615–630. [Google Scholar]
- Steel, M.; Szekely, L.; Erdos, P.L.; Waddell, P. A complete family of phylogenetic invariants for any number of taxa under Kimura’s 3ST model. N. Z. J. Bot. 1993, 31, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, P.; Hu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. The complete mitochondrial genome of a marine mussel, Modiolus comptus (Mollusca: Mytilidae), and its phylogenetic implication. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 4057–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Gao, S.; Zhao, M.; Lv, H.; Song, J.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, J. Mitochondrial genomic analyses provide new insights into the “missing” atp8 and adaptive evolution of Mytilidae. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, K.; Gillespie, J.; Toari, Y.N. A profile of Drosophila species’ enzymes assayed by electrophoresis. I. Number of alleles, heterozygosities, and linkage disequilibrium in glucose-metabolizing systems and some other enzymes. Biochem. Genet. 1970, 4, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewontin, R.C. The Genetic Basis of Evolutionary Change; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, S.; Kang, H.-E.; Kim, A.R.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, E.-B.; Amin, M.H.F.; Andriyono, S.; Kim, H.-W.; Kang, K. Mitogenomic Characterization and Phylogenetic Placement of African Hind, Cephalopholis taeniops: Shedding Light on the Evolution of Groupers (Serranidae: Epinephelinae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.F.; Ta, K.W.; Zhang, N.N.; Liu, S.S.; Meng, L.; Liu, K.Q.; Cai, C.Y.; Peng, X.T.; Shao, C.W. Molecular phylogenetic relationships based on mitochondrial genomes of novel deep-sea corals (Octocorallia: Alcyonacea): Insights into slow evolution and adaptation to extreme deep-sea environments. Zool. Res. 2024, 45, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, N.I.; DeLeo, D.M.; Horowitz, J.; McFadden, C.S.; Quattrini, A.M. Selection in coral mitogenomes, with insights into adaptations in the deep sea. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Lee, J.-S. Analysis of nucleotide diversity at genes Cyt-b and Co-1 on population, species, and genera levels. Russ. J. Genet. 2006, 42, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotova, A.O.; Kartavtsev, Y.P. Analysis of sequence divergence in redfin (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae, Tribolodon) based on mtDNA and nDNA markers with inferences in systematics and genetics of speciation. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2018, 29, 975–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Cai, H.; Li, C.; Gao, T. Molecular phylogenetics of genus Mytilus based on COI and 16S rRNA sequences. South China Fish. Sci. 2010, 5, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenet; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; 333p. [Google Scholar]
- Swofford, D.L.; Olsen, G.J.; Waddel, P.J.; Hillis, D.M. Phylogenetic inference. In Molecular Systematics; Hillis, D.M., Moritz, C., Mable, B., Eds.; Sinauer. Assoc. Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 407–514. [Google Scholar]
- Hillis, D.M.; Mable, B.K.; Moritz, C. Application of molecular systematics: The state of the field and a look to the future. In Molecular Systematics; Hillis, D.M., Moritz, C., Mable, B., Eds.; Sinauer. Assoc. Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1996; Volume 12, pp. 515–543. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, B. Phylogenetic Trees Made Easy: A How-To Manual for Molecular Biologists, 4th ed.; Sinauer Assoc. Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2011; p. 282. [Google Scholar]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P. Molecular Evolution and Population Genetics. In A Course for Marine Biology Students; Johnson, M.S., Ed.; CRS Press, Taylor & Francis Publ. Group: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chichvarkhin, A.Y.; Kartavtsev, Y.F.; Kafanov, A.I. Genetic Relationships among Some Species of Mytilidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia) from the Northern Pacific Ocean. Russ. J. Genet. 2000, 36, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Kafanov, A.I. Pacifimytilus [Mytilidae Rafinesque, 1815]. In Typespecies—Mytilus californianus Conrad, 1837; 1984; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Kafanov, A.I. Crenomytilini [Mytilidae Rafinesque, 1815; Mytilinae Rafinesque, 1815]. In By Name Formation—Crenomytilus Soot–Ryen, 1955; 1984; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Lutaenko, K.A. Molluscan taxa of Alexander, I. In The Bulletin of the Russian Far East Malacological Society; 2007; Volume 11, pp. 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Koehn, R. The genetics and taxonomy of species in the genus Mytilus. Aquaculture 1991, 94, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y. Some current concerns of NeoDarvinism: Gene introgression throughout a species border. J. Phylogenet. Evol. Biol. 2013, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Smietanka, B.; Burzynski, A.; Hummel, H.; Wenne, R. Glacial history of the European marine mussels Mytilus, inferred from distribution of mitochondrial DNA lineages. Heredity 2014, 113, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbawicka, M.; Wenne, R.; Burzynski, A. Mitogenomics of recombinant mitochondrial genomes of Baltic Sea Mytilus mussels. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbawicka, M.; Trucco, M.I.; Wenne, R. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in native South American Atlantic coast populations of smooth shelled mussels: Hybridization with invasive European Mytilus galloprovincialis. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P. Sequence divergence at Co-1 and Cyt-b mtDNA on different taxonomic levels and genetics of speciation in animals. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2011, 2, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P. Sequence Diversity at Cyt-b and Co-1 mtDNA Genes in Animal Taxa Proved Neo-Darwinism. Phylogenet. Evol. Biol. 2013, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Redin, A.D. Estimates of genetic introgression, gene tree reticulation, taxon divergence, and sustainability of DNA barcoding based on genetic molecular markers. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2019, 9, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redin, A.D.; Kartavtsev, Y.P. The Mitogenome Structure of Righteye Flounders (Pleuronectidae): Molecular Phylogeny and Systematics of the Family in East Asia. Diversity 2022, 14, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GenBank. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- WoRMS. 2024. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=211 (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- WoRMS. 2024. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=506159 (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes De Novo Assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MITOS Web Server (uni-leipzig.de). Available online: http://mitos.bioinf.uni-leipzig.de (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Rozas, J.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Messegyer, X.; Rozas, R. DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2496–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian Phylogenet. with BEAUti and the BEAST 1. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.-H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Bouckaert, R.R. Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis with BEAST; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchêne, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kühnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovli’c, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary Phylogenet. studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadya, G.; Lohman, D.J.; Meier, R. SequenceMatrix: Concatenation software for the fast assembly of multi-gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickins, J.M. Permian Pelecypods and Gastropods from Western Australia, 2nd ed.; Australian Govt. Pub. Service: Canberra, Australia, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, K.M.; Finney, S.C.; Gibbard, P.L.; Fan, J.-X. The ICS International Chronostratigraphic Chart. Epis. J. Int. Geosci. 2013, 36, 199–204. Available online: https://paleobiodb.org/classic/displayTimescale?interval=139 (accessed on 8 April 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Phillips, M.J.; Rambaut, A. Relaxed Phylogenet. and Dating with Confidence. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindat. 2024. Available online: https://www.mindat.org/taxon-3476.html (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- Mindat, 2024. Main Source: Vokes, H.E. Genera of the Bivalvia: A Systematic and Bibliographic Catalogue. Genera of the Bivalvia: A Systematic and Bibliographic Catalogue. 1980. Available online: https://www.mindat.org/taxon-2285647.html (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1.4.4. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GenBank NCBI. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 19 April 2024).



| Genome Content/Sequences | Arcuatula senhousia, Ar2 OR453539 | Mytilus coruscus, Kart1 OR453540 | Mytilus californianus JX486124 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size (bp) | 17,675 | 16,629 | 16,729 |
| Gene number, PCGs | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Gene number, rRNA | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Gene number, tRNA | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| AT skew (PCGs, ratio) | 0.5795 | 0.7109 | 0.7130 |
| GC skew (PCGs, ratio) | 1.7258 | 1.7179 | 1.7569 |
| T + C:A + G ratio (PCGs, %) | 54.02:45.97 | 50.19:49.81 | 50.24:49.76 |
| CR (D-loop) | 1653–2111 (+) | 1–60 (+) | N/A |
| nad3 | 43–390 (ATG/TAA, +) | 8314–8664 (ATG/TAA, +) | 7314–7664 (ATG/TAA, +) |
| trnY | 626–691 (+) | 1115–1181 (+) | 1–67 (+) |
| trnH | 1235–1299 (+) | 8181–8244 (+) | 7181–7245 (+) |
| trnI | 1316–1381 (+) | 15,154–14,216 (+) | 14,150–14,216 (+) |
| trnN | 1393–1456 (+) | 14,955–15,019 (+) | 13,951–14,015 (+) |
| trnE | 1566–1630 (+) | 15,020–15,084 (+) | 14,016–14,080 (+) |
| cox1 | 1870–3432 (ATT/TAA, +) | 8950–10,605 (ATG/TAA, +) | 7947–9602 (ATG/TAA, +) |
| cox2 | 3763–4470 (ATT/TAA, +) | 2493–3221 (ATG/TAA, +) | 1378–2109 (ATG/TAA, +) |
| atp6 | 4787–5461 (ATG/TAG, +) | 10,621–11,331 (ATA/TAA, +) | 9612–10,328 (ATG/TAA, +) |
| trnT | 5488–5554 (+) | 11,336–11,398 (+) | 10,333–10,395 (+) |
| cytb | 5597–6727 (ATT/TAA, +) | 1183–2317 (ATG/T, +) | 69–1376 (ATG/TAA, +) |
| trnD | 6746–6810 (+) | 15,322–15,383 (+) | 14,316–14,380 (+) |
| trnR | 6820–6885 (+) | 7909–7971 (+) | 6909–6973 (+) |
| trnS1 | 6887–6944 (+) | 8113–8180 (+) | N/A |
| trnG | 6966–7031 (+) | 14,892–14,950 (+) | 13,885–13,950 (+) |
| rrnS | 7936–8825 (+) | 14,885–15,817 (+) | 13,884–14,829 (+) |
| trnS2 | 7938–7996 (+) | 6826–6888 (+) | N/A |
| nad6 | 8038–8475 (ATA/TAA, +) | 13,406–13,861 (ATA/TAA, +) | 12,394–12,858 (ATG/TAG, +) |
| nad2 | 8457–7905 (ATT/TAA, +) | 6958–7905 (ATG/TAA, +) | 5960–6907 (ATG/TAA, +) |
| cox3 | 9553–10,407 (ATG/TAA, +) | 6028–6810 (ATG/TAG, +) | 4877–5812 (ATG/TAA, +) |
| trnK | 10,421–10,487 (+) | 3223–3291 (+) | 2111–2179 (+) |
| trnF | 10,492–10,559 (+) | 13,877–13,944 (+) | 12,872–12,939 (+) |
| trnP | 10,575–10,637 (+) | 8246–8310 (+) | 7247–7310 (+) |
| trnL1 | 10,672–10,736 (+) | 3366–3431 (+) | 2254–2319 (+) |
| trnC | 10,743–10,806 (+) | 15,086–15,153 (+) | 14,082–14,149 (+) |
| trnL2 | 10,854–10,917 (+) | 3437–3502 (+) | 2325–2390 (+) |
| nad1 | 11,011–11,946 (ATG/TAA, +) | 3569–4492 (ATA/TAA, +) | 2569–3492 (ATA/TAA, +) |
| trnM | 12,080–12,142 (+) | 3295–3362 (+) | 2183–2250 (+) |
| trnV | 12,182–12,243 (+) | 4496–4562 (+) | 3497–3562 (+) |
| nad4L | 12,324–12,605 (ATT/TAA, +) | 11,399–11,680 (ATG/TAA, +) | 10,396–10,677 (ATG/TAA, +) |
| nad5 | 12,698–14,432 (ATT/T, +) | 11,688–13,397 (ATT/TAA, +) | 10,685–12,394 (ATT/TAA, +) |
| trnA | 14,433–14,433 (+) | 8046–8046 (+) | 7046–7046 (+) |
| Species | Mean Frequencies of Nucleotides (%) Combined for the Three Codon Positions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | A | G | Length of Sequence (bp) | |
| All PCG sequences | |||||
| Arcuatula senhousia GU001953 | 40.9 | 12.8 | 24.0 | 22.2 | 11,212 |
| Arcuatula senhousia OR453539 | 41.2 | 12.8 | 23.9 | 22.1 | 10,971 |
| Bathymodiolus childressi NC 059707 | 40.5 | 14.5 | 21.9 | 23.1 | 10,866 |
| Bathymodiolus japonicus AP014560 | 41.3 | 13.7 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 10,842 |
| Bathymodiolus securiformis NC 039552 | 41.4 | 13.5 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 10,872 |
| Brachidontes exustus NC 024882 | 40.9 | 13.8 | 25 | 20.3 | 11,100 |
| Crenomytilus grayanus NC 044128 | 36.3 | 13.8 | 24.7 | 25.2 | 11,298 |
| Gregariella coralliophaga NC 044129 | 40.1 | 12.1 | 26.9 | 20.9 | 11,181 |
| Modiolus kurilensis NC 036486 | 40.8 | 12 | 23.1 | 24.1 | 10,929 |
| Modiolus modiolus KX821782 | 40.6 | 12.1 | 22.8 | 24.4 | 10,839 |
| Mytilisepta keenae NC 044127 | 45.2 | 9.5 | 23.1 | 22.2 | 10,914 |
| Mytilus californianus JX486124 | 36.8 | 13.4 | 26.2 | 23.6 | 11,301 |
| Mytilus chilensis KP100300 | 35.4 | 15 | 25.2 | 24.5 | 11,297 |
| Mytilus chilensis NC 030633 | 35.4 | 15 | 25.2 | 24.5 | 11,297 |
| Mytilus coruscus KJ577549 | 36.1 | 14 | 25.8 | 24 | 11,294 |
| Mytilus coruscus OR453540 | 36.3 | 13.9 | 25.8 | 24 | 10,959 |
| Mytilus edulis MF407676 | 35.3 | 15 | 25.2 | 24.5 | 11,451 |
| Mytilus galloprovincialis FJ890849 | 35.3 | 15 | 25.1 | 24.6 | 11,451 |
| Mytilus trossulus GU936625 | 34.5 | 15.5 | 24.9 | 25.1 | 11,451 |
| Mytilus trossulus HM462080 | 34.5 | 15.5 | 25 | 25.1 | 11,451 |
| Perna canaliculus MG766134 | 40.5 | 12.5 | 26.3 | 20.8 | 11,022 |
| Perna canaliculus MK775558 | 40.5 | 12.5 | 26.1 | 20.8 | 10,914 |
| Perna perna OK576481 | 40.4 | 12.8 | 25.9 | 20.9 | 10,911 |
| Perna viridis JQ970425 | 42.4 | 10.2 | 24.7 | 22.7 | 11,004 |
| Perna viridis MW727515 | 42.4 | 10.2 | 24.7 | 22.7 | 11,004 |
| Septifer bilocularis NC 044131 | 44.8 | 11.1 | 24.6 | 19.5 | 11,250 |
| Average, n = 26 | 39.18 ± 1.48 | 13.18 ± 0.79 | 24.67 ± 0.32 | 22.96 ± 0.69 | 11,118 |
| Average, n = 26; T + C, A + G | 26.18 ± 1.14 | 23.82 ± 0.50 | 11,118 | ||
| PCG sequences for the singleton positions only | |||||
| Arcuatula senhousia GU001953 | 47.3 | 10.41 | 21.0 | 21.56 | 538 |
| Arcuatula senhousia OR453539 | 49.48 | 9.1 | 19.92 | 21.59 | 477 |
| Bathymodiolus childressi NC 059707 | 49.47 | 10.53 | 18.53 | 21.47 | 475 |
| Bathymodiolus japonicus AP014560 | 47.68 | 12.3 | 18.78 | 21.52 | 474 |
| Bathymodiolus securiformis NC 039552 | 50.73 | 9.15 | 19.33 | 20.79 | 481 |
| Brachidontes exustus NC 024882 | 40.8 | 15.72 | 21.2 | 23.18 | 509 |
| Crenomytilus grayanus NC 044128 | 42.60 | 11.59 | 22.64 | 23.17 | 561 |
| Gregariella coralliophaga NC 044129 | 44.26 | 11.48 | 23.68 | 20.58 | 549 |
| Modiolus kurilensis NC 036486 | 48.91 | 10.14 | 19.9 | 21.87 | 503 |
| Modiolus modiolus KX821782 | 49.18 | 9.39 | 19.39 | 22.4 | 490 |
| Mytilisepta keenae NC 044127 | 46.61 | 10.36 | 20.12 | 22.91 | 502 |
| Mytilus californianus JX486124 | 46.22 | 9.67 | 22.67 | 21.44 | 569 |
| Mytilus chilensis KP100300 | 46.30 | 9.15 | 22.89 | 21.65 | 568 |
| Mytilus chilensis NC 030633 | 46.30 | 9.15 | 22.89 | 21.65 | 568 |
| Mytilus coruscus KJ577549 | 44.1 | 9.86 | 23.59 | 22.54 | 568 |
| Mytilus coruscus OR453540 | 45.90 | 9.14 | 23.24 | 21.71 | 525 |
| Mytilus edulis MF407676 | 45.42 | 9.82 | 23.13 | 21.63 | 601 |
| Mytilus galloprovincialis FJ890849 | 45.42 | 9.98 | 22.80 | 21.80 | 601 |
| Mytilus trossulus GU936625 | 45.59 | 9.82 | 23.13 | 21.46 | 601 |
| Mytilus trossulus HM462080 | 45.9 | 10.32 | 22.96 | 21.63 | 601 |
| Perna canaliculus MG766134 | 50.69 | 9.43 | 19.25 | 20.63 | 509 |
| Perna canaliculus MK775558 | 50.42 | 9.49 | 18.57 | 21.52 | 474 |
| Perna perna OK576481 | 48.95 | 11.76 | 18.7 | 21.22 | 476 |
| Perna viridis JQ970425 | 50.21 | 9.58 | 18.75 | 21.46 | 480 |
| Perna viridis MW727515 | 50.21 | 9.58 | 18.75 | 21.46 | 480 |
| Septifer bilocularis NC 044131 | 41.57 | 13.22 | 20.50 | 24.71 | 522 |
| Average. n = 26 | 46.72 ± 1.48 | 10.36 ± 0.79 | 21.10 ± 0.32 | 21.82 ± 0.69 | 527 |
| Average. n = 26; T + C. A + G | 26.18 ± 1.14 | 23.82 ± 0.50 | 527 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Masalkova, N.A. Structure, Evolution, and Mitochondrial Genome Analysis of Mussel Species (Bivalvia, Mytilidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136902
Kartavtsev YP, Masalkova NA. Structure, Evolution, and Mitochondrial Genome Analysis of Mussel Species (Bivalvia, Mytilidae). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(13):6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136902
Chicago/Turabian StyleKartavtsev, Yuri Phedorovich, and Natalia A. Masalkova. 2024. "Structure, Evolution, and Mitochondrial Genome Analysis of Mussel Species (Bivalvia, Mytilidae)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 13: 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136902
APA StyleKartavtsev, Y. P., & Masalkova, N. A. (2024). Structure, Evolution, and Mitochondrial Genome Analysis of Mussel Species (Bivalvia, Mytilidae). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(13), 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25136902





