Regulation of T Lymphocyte Functions through Calcium Signaling Modulation by Nootkatone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Calcium Transporting CRAC Channel Activation Is Regulated by Nootkatone
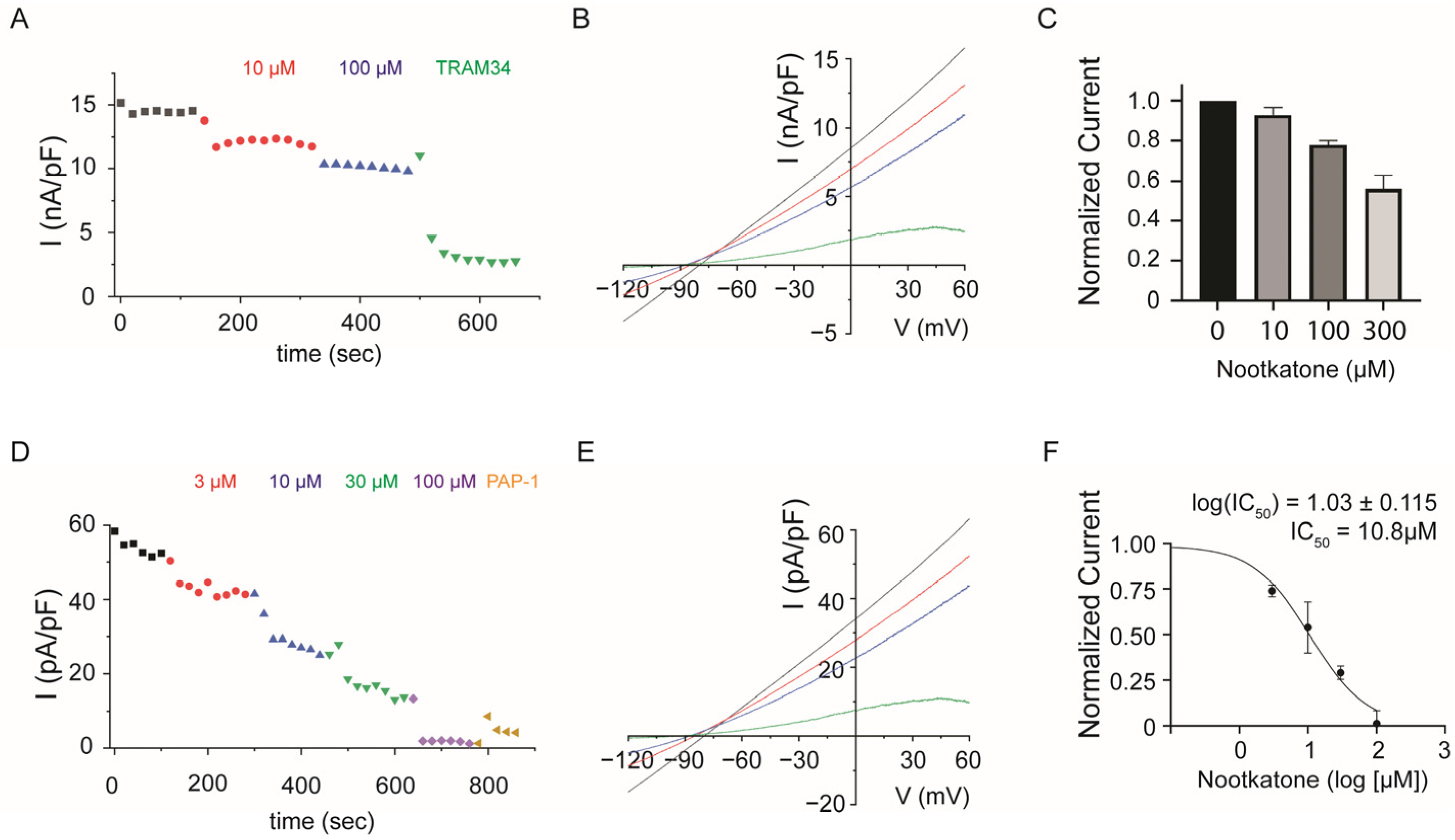
2.2. Potassium Channel KCa3.1 and KV1.3 Activation Is Regulated by Nootkatone
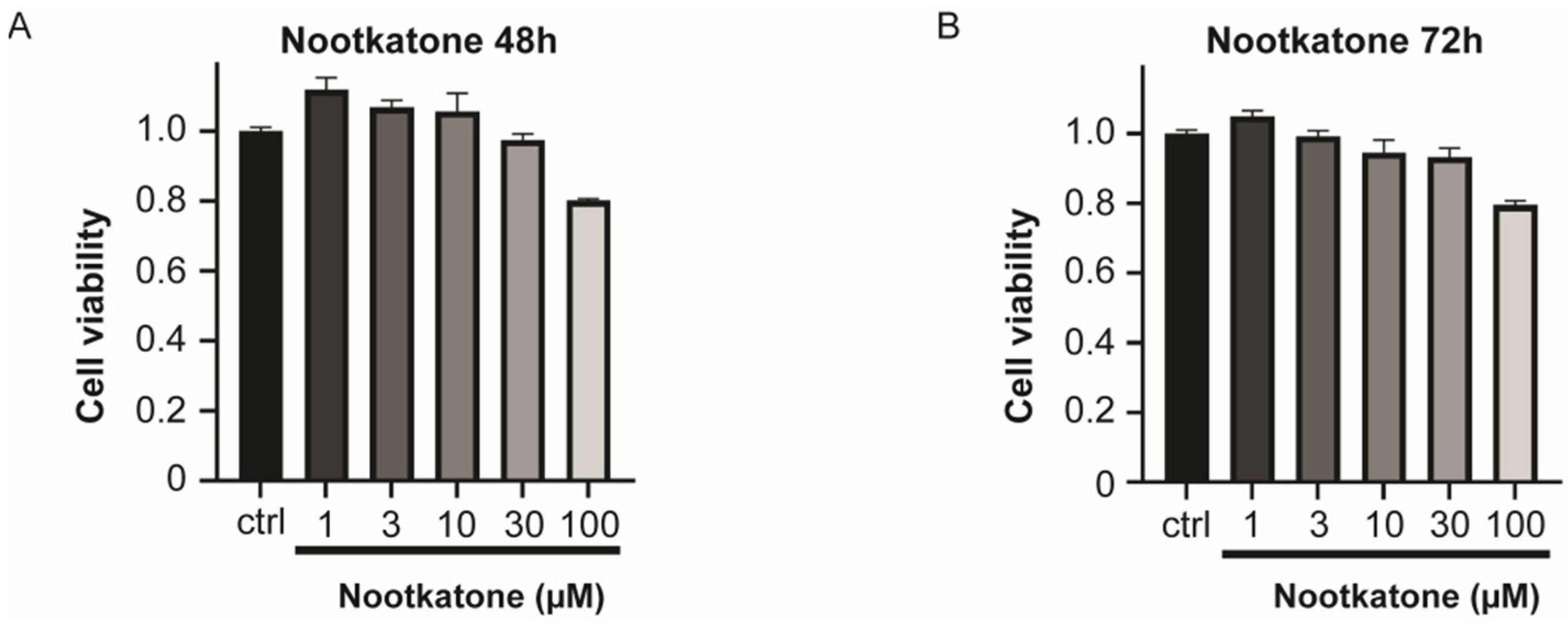
2.3. Store-Operated Calcium Entry Could Be Regulated by Nootkatone without Cytotoxicity
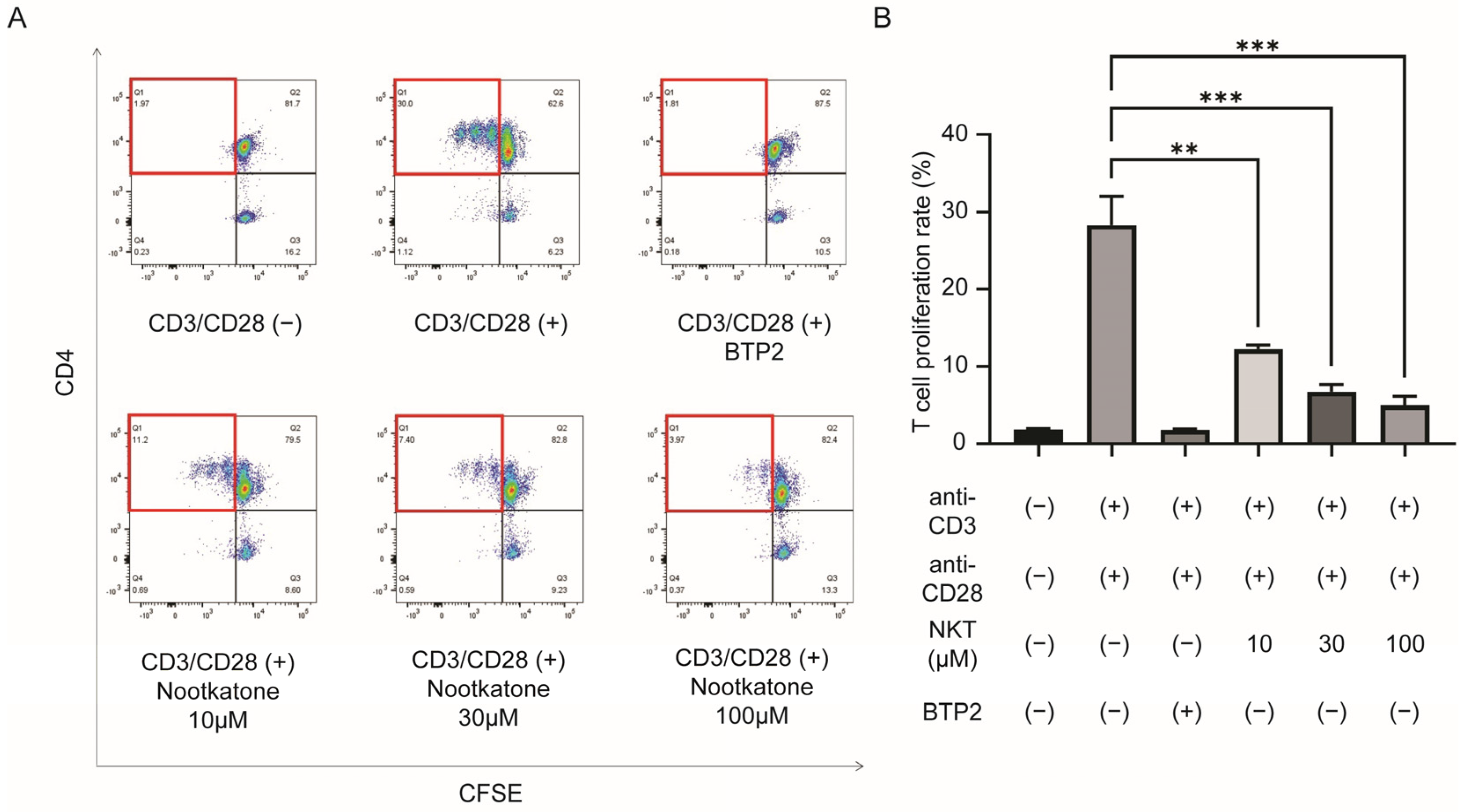
2.4. Nootkatone Inhibits T Lymphocyte Proliferation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Transient Transfection
4.3. Cell Cytotoxicity
4.4. Electrophysiology
4.5. Fura-2 Ca2+ Imaging
4.6. Human Primary CD4+ T Lymphocyte Isolation
4.7. T Cell Proliferation Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feske, S.; Wulff, H.; Skolnik, E.Y. Ion channels in innate and adaptive immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 291–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh-hora, M. Calcium signaling in the development and function of T-lineage cells. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 231, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakriya, M.; Lewis, R.S. Store-Operated Calcium Channels. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1383–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.L.; Yu, Y.; Roos, J.; Kozak, J.A.; Deerinck, T.J.; Ellisman, M.H.; Stauderman, K.A.; Cahalan, M.D. STIM1 is a Ca2+ sensor that activates CRAC channels and migrates from the Ca2+ store to the plasma membrane. Nature 2005, 437, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandy, K.G.; Wulff, H.; Beeton, C.; Pennington, M.; Gutman, G.A.; Cahalan, M.D. K+ channels as targets for specific immunomodulation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianna-Jorge, R.; Suarez-Kurtz, G. Potassium channels in T lymphocytes: Therapeutic targets for autoimmune disorders? BioDrugs 2004, 18, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Gairola, S.; Kundu, S.; Doye, P.; Syed, A.M.; Ram, C.; Kulhari, U.; Kumar, N.; Murty, U.S.; Sahu, B.D. Biological Activities, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicity of Nootkatone: A Review. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 2244–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.H.; Lee, D.U.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.P. Anti-allergic activity of sesquiterpenes from the rhizomes of Cyperus rotundus. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2011, 34, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.; Wulff, H. The Lymphocyte Potassium Channels Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 as Targets for Immunosuppression. Drug Dev. Res. 2011, 72, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panella, N.A.; Dolan, M.C.; Karchesy, J.J.; Xiong, Y.; Peralta-Cruz, J.; Khasawneh, M.; Montenieri, J.A.; Maupin, G.O. Use of novel compounds for pest control: Insecticidal and acaricidal activity of essential oil components from heartwood of Alaska yellow cedar. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemmar, A.; Al-Salam, S.; Beegam, S.; Yuvaraju, P.; Hamadi, N.; Ali, B.H. In Vivo Protective Effects of Nootkatone against Particles-Induced Lung Injury Caused by Diesel Exhaust Is Mediated via the NF-kappaB Pathway. Nutrients 2018, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, W.; Xia, B.; Wang, W.; Pan, X. Nootkatone protects cartilage against degeneration in mice by inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, C.T.; May, M.J.; Freedman, B.D. STIM- and Orai-mediated calcium entry controls NF-kappaB activity and function in lymphocytes. Cell Calcium 2018, 74, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feske, S. Calcium signalling in lymphocyte activation and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alansary, D.; Kilch, T.; Holzmann, C.; Peinelt, C.; Hoth, M.; Lis, A. Patch-clamp measurement of ICRAC and ORAI channel activity. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2014, 2014, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, Y.S. (+)-Nootkatone inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha/interferon gamma-induced production of chemokines in HaCaT cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 447, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoyi, K.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, H.G.; Lee, J.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Lee, D.U.; Chang, K.C. (+)-Nootkatone and (+)-valencene from rhizomes of Cyperus rotundus increase survival rates in septic mice due to heme oxygenase-1 induction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, S.Y.; Kim, M.R.; Lee, B.S.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, Y.C. Anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activities of Alpinia Oxyphylla Miquel extracts in animal models. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 260, 112985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaeth, M.; Kahlfuss, S.; Feske, S. CRAC Channels and Calcium Signaling in T Cell-Mediated Immunity. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 878–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butorac, C.; Krizova, A.; Derler, I. Review: Structure and Activation Mechanisms of CRAC Channels. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1131, 547–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feske, S. CRAC channels and disease—From human CRAC channelopathies and animal models to novel drugs. Cell Calcium 2019, 80, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feske, S. CRAC channelopathies. Pflug. Arch. 2010, 460, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aki, A.; Tanaka, K.; Nagaoka, N.; Kimura, T.; Baba, D.; Onodera, Y.; Wada, T.; Maeda, H.; Nakanishi, T.; Agatsuma, T.; et al. Anti-ORAI1 antibody DS-2741a, a specific CRAC channel blocker, shows ideal therapeutic profiles for allergic disease via suppression of aberrant T-cell and mast cell activation. FASEB Bioadv. 2020, 2, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.T.L.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, W.K.; Nam, J.H. Flos magnoliae constituent fargesin has an anti-allergic effect via ORAI1 channel inhibition. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 25, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.T.L.; Kim, H.J.; Jo, S.; Kim, W.K.; Namkung, W.; Nam, J.H. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Licochalcone A via Regulation of ORAI1 and K(+) Channels in T-Lymphocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, E.Y.; Li, T.; Jeet, S.; Peng, I.; Zhang, J.; Lee, W.P.; DeVoss, J.; Caplazi, P.; Chen, J.; Warming, S.; et al. Potassium channels Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 cooperatively and compensatorily regulate antigen-specific memory T cell functions. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradding, P.; Wulff, H. The K+ channels K(Ca)3.1 and K(v)1.3 as novel targets for asthma therapy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markakis, I.; Charitakis, I.; Beeton, C.; Galani, M.; Repousi, E.; Aggeloglou, S.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Pennington, M.W.; Chandy, K.G.; Poulopoulou, C. Kv1.3 Channel Up-Regulation in Peripheral Blood T Lymphocytes of Patients With Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 714841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yu, L.; Ji, Y.; Tao, J. Kv1.3 Channel as a Key Therapeutic Target for Neuroinflammatory Diseases: State of the Art and Beyond. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Srivastava, S.; Zhdanova, O.; Ding, Y.; Li, Z.; Wulff, H.; Lafaille, M.; Skolnik, E.Y. Inhibition of the K+ channel KCa3.1 ameliorates T cell-mediated colitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhao, Y.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Hao, W.J.; Zhu, R.D.; Wang, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhou, R.P. Regulatory role of KCa3.1 in immune cell function and its emerging association with rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 997621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.H.; Xu, J.R.; Wang, Y.X.; Xu, G.N.; Xu, Z.P.; Yang, K.; Wu, D.Z.; Cui, Y.Y.; Chen, H.Z. Targeted inhibition of KCa3.1 channel attenuates airway inflammation and remodeling in allergic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Tao, Y.; Liu, J.; Geng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, W.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. KCa3.1 Inhibition of Macrophages Suppresses Inflammatory Response Leading to Endothelial Damage in a Cell Model of Kawasaki Disease. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivas-Aguirre, M.; Cruz-Aguilar, L.H.; Pottosin, I.; Dobrovinskaya, O. Reduction of Ca2+ Entry by a Specific Block of KCa3.1 Channels Optimizes Cytotoxic Activity of NK Cells against T-ALL Jurkat Cells. Cells 2023, 12, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Li, C.; Sheng, W.; Li, Z.; Jiang, M. The cajanine derivative LJ101019C regulates the proliferation and enhances the activity of NK cells via Kv1.3 channel-driven activation of the AKT/mTOR pathway. Phytomedicine 2020, 66, 153113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.; Schlichter, L.C. Selective activation of KCa3.1 and CRAC channels by P2Y2 receptors promotes Ca2+ signaling, store refilling and migration of rat microglial cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbing, M.J.; Cottee, J.M.; Rana, I. The Role of Ion Channels in Microglial Activation and Proliferation—A Complex Interplay between Ligand-Gated Ion Channels, K+ Channels, and Intracellular Ca2+. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomina, A.F.; Nguyen, H.M.; Wulff, H. Kv1.3 inhibition attenuates neuroinflammation through disruption of microglial calcium signaling. Channels 2021, 15, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebak, M.; Kinet, J.P. Calcium signalling in T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Yoo, S.A.; Kim, M.; Kim, W.U. The Role of Calcium-Calcineurin-NFAT Signaling Pathway in Health and Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.; van de Kerkhof, P.; Czarnecka-Operacz, M. Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 7, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Nam, Y.R.; Kim, E.J.; Nam, J.H.; Kim, W.K. Spirodela polyrhiza and its Chemical Constituent Vitexin Exert Anti-Allergic Effect via ORAI1 Channel Inhibition. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 1243–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, B.J.; Warren, H.S.; Parish, C.R. Monitoring lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and in vivo with the intracellular fluorescent dye carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.M.; Kim, J.; Park, S.J.; Nam, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, W.K. Regulation of T Lymphocyte Functions through Calcium Signaling Modulation by Nootkatone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105240
Lee JM, Kim J, Park SJ, Nam JH, Kim HJ, Kim WK. Regulation of T Lymphocyte Functions through Calcium Signaling Modulation by Nootkatone. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(10):5240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105240
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji Min, Jintae Kim, Su Jin Park, Joo Hyun Nam, Hyun Jong Kim, and Woo Kyung Kim. 2024. "Regulation of T Lymphocyte Functions through Calcium Signaling Modulation by Nootkatone" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 10: 5240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105240
APA StyleLee, J. M., Kim, J., Park, S. J., Nam, J. H., Kim, H. J., & Kim, W. K. (2024). Regulation of T Lymphocyte Functions through Calcium Signaling Modulation by Nootkatone. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(10), 5240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25105240






