Mechanistic Investigation of WWOX Function in NF-kB-Induced Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. WWOX Is Highly Expressed in Psoriatic Skin
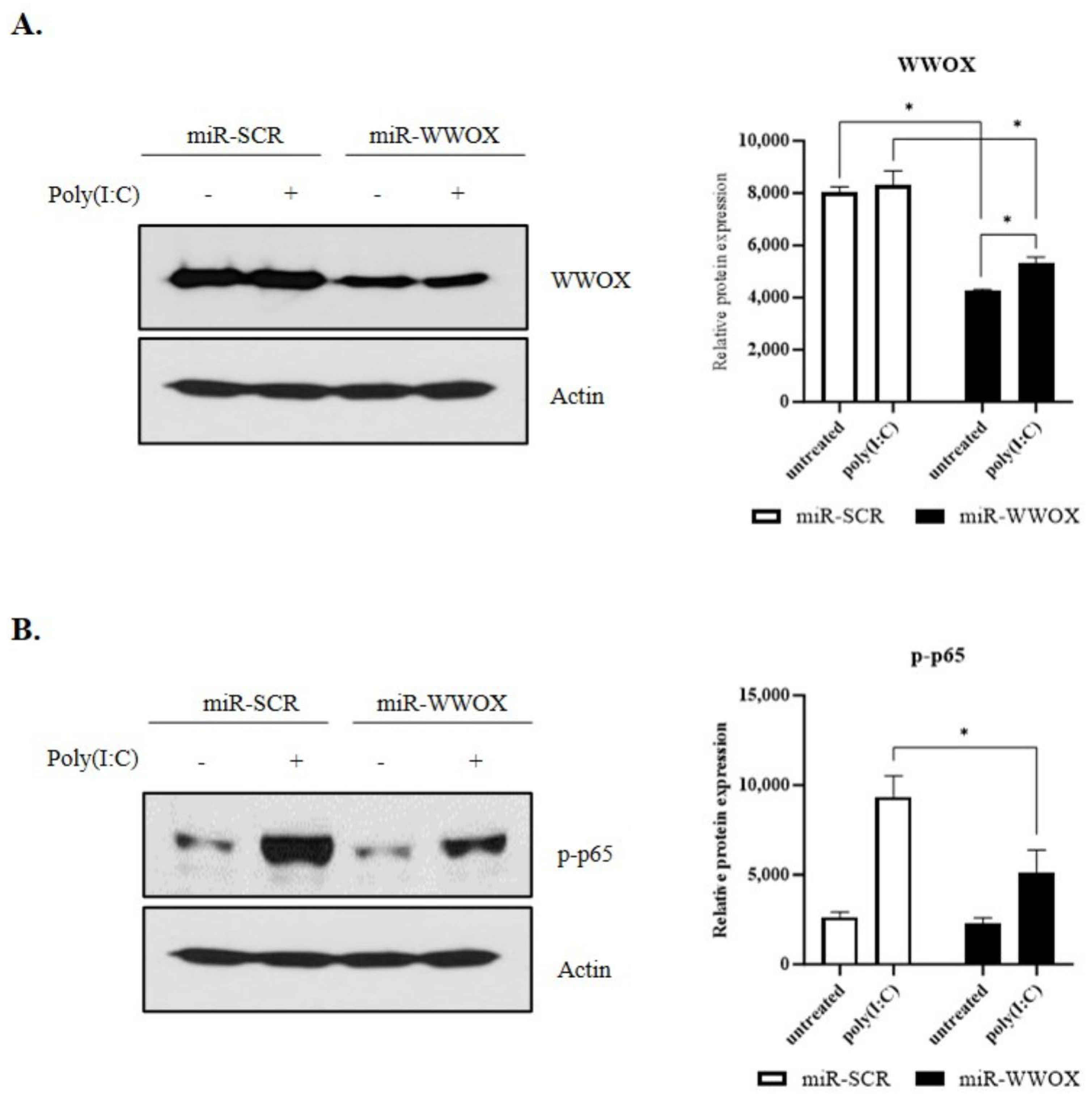
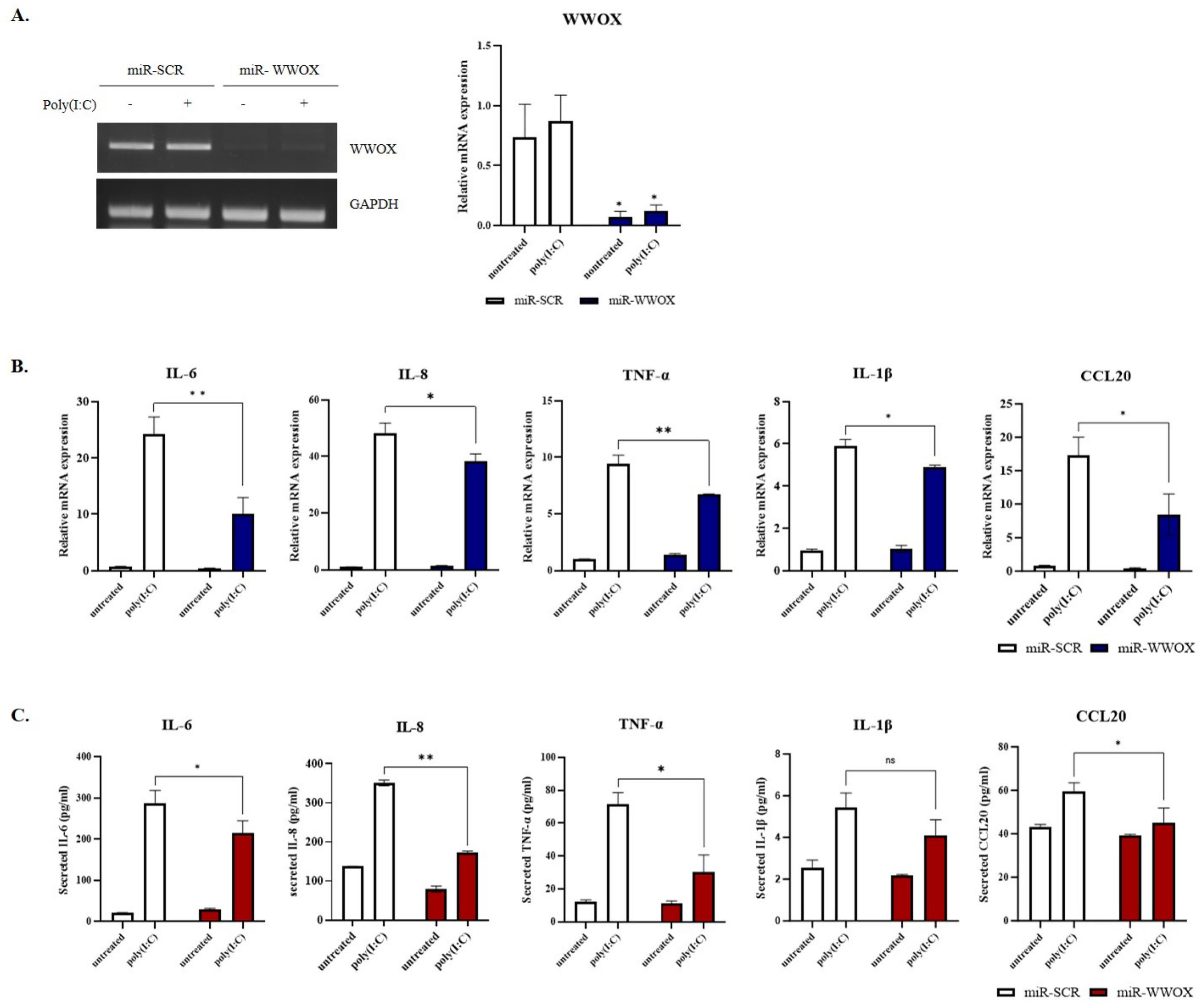
2.2. WWOX Knockdown Inhibits Poly(I:C)-Induced Inflammatory Response in Epidermal Keratinocytes
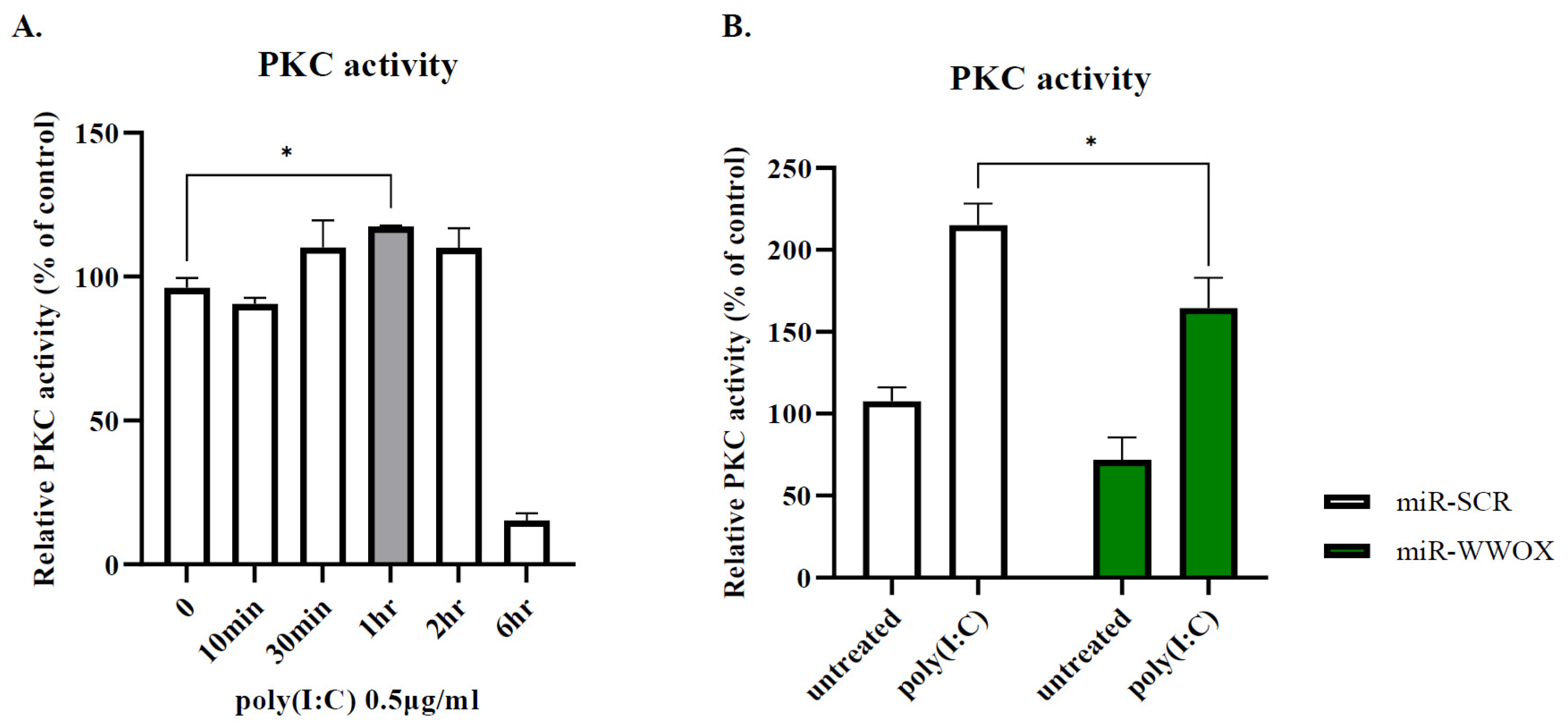
2.3. PKC Activity Is Decreased by WWOX Knockdown in Poly(I:C)-Treated Group
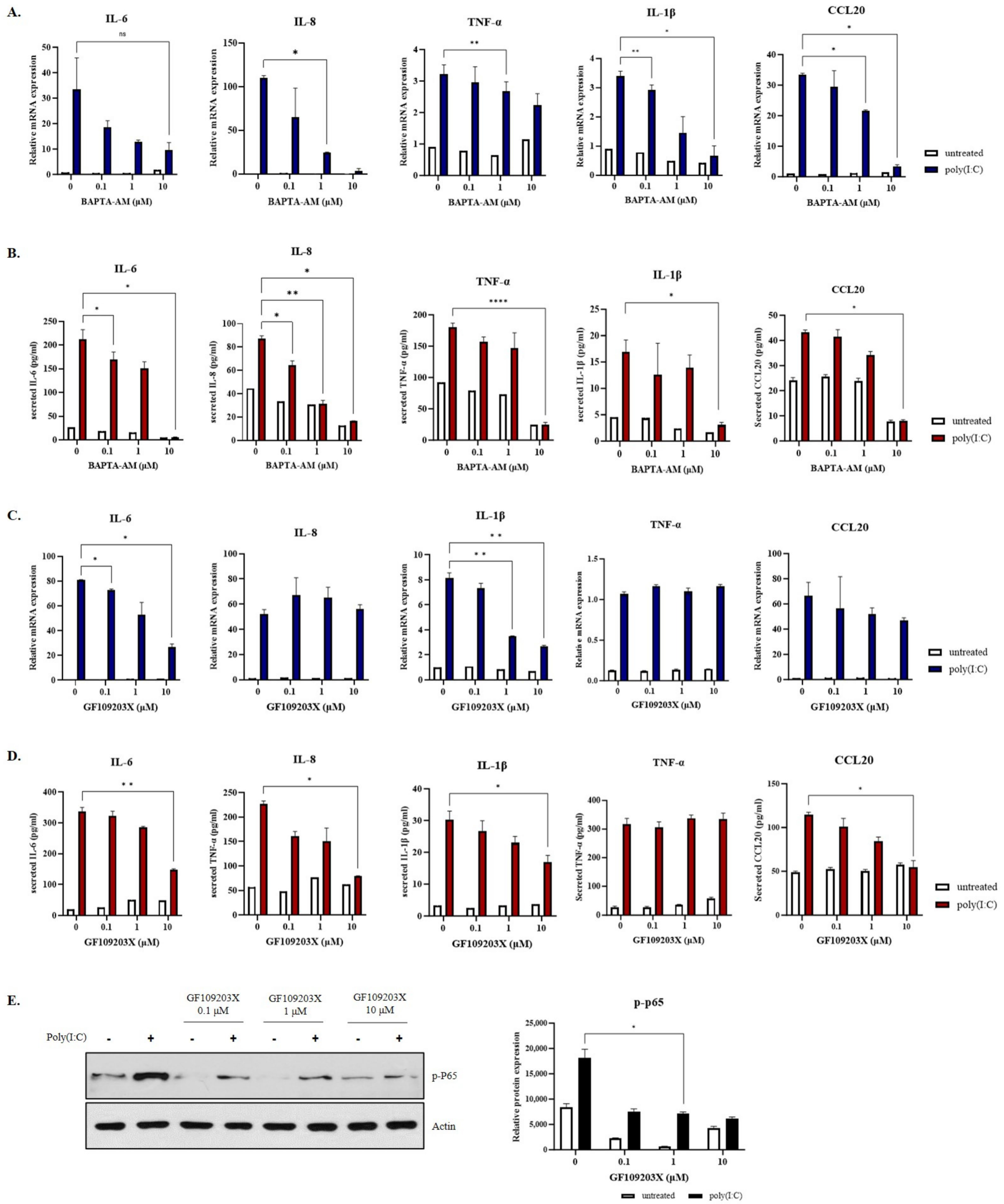
2.4. Inflammatory Response by Ca2+ and PKC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.2. Imiquimod (IMQ)-Induced Psoriasis Mouse Model
4.3. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.4. Recombinant Adenovirus Expressing a WWOX-Specific microRNA and WWOX Knockdown in Human Keratinocytes
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
- IL-6, CCATGCTACATTTGCCGA-3′ and 5′-CTGCGCAGCTTTAAGGAG-3′;
- IL-8, 5′-CCTTTCCACCCCAAATTTATCA-3′ and 5′-TTTCTGTGTTGGCGCAGTGT-3′;
- IL-1β, 5′-ACGAATCTCCGACCACCACTA-3′ and 5′-TCCATGGCCACAACAACTGA-3′;
- TNF-α, TGGCCCAGGCAGTCAGAT-3′ and 5′-GGTTTGCTACAACATGGGCTA-3′;
- CCL20, 5′-TGTGTATCCAAGACAGCAGTCAAA-3′ and 5′-CCACCTCTGCGGCGAAT-3′;
- WWOX, 5′-AGTCGCCTCTCTCCAACAAA-3′ and 5′-CGTCTCTTCGCTCTGAGCTT-3′
- GAPDH, 5’-TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAGC and 5’-GGCATGGACTGTGGTCATGAG.
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.8. PKC
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Gudjonsson, J.E.; Elder, J.T. Psoriasis: Epidemiology. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, M.A.; Bowcock, A.M.; Krueger, J.G. Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature 2007, 445, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudjonsson, J.E.; Johnston, A.; Sigmundsdottir, H.; Valdimarsson, H. Immunopathogenic mechanisms in psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 135, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, M.A.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Krueger, J.G. Immunology of psoriasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendon, A.; Schakel, K. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabat, R.; Philipp, S.; Hoflich, C.; Kreutzer, S.; Wallace, E.; Asadullah, K.; Volk, H.D.; Sterry, W.; Wolk, K. Immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 16, 779–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Papp, K.; Gottlieb, A.; Jarell, A.; Reich, K.; Maari, C.; Gordon, K.B.; Ferris, L.K.; Langley, R.G.; Tada, Y.; et al. A head-to-head comparison of ixekizumab vs. guselkumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: 12-week efficacy, safety and speed of response from a randomized, double-blinded trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasca, C.; Fornaro, L.; Martora, F.; Picone, V.; Fabbrocini, G.; Megna, M. Onset of vitiligo in a psoriasis patient on ixekizumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, A.; Picone, V.; Martora, F.; Fabbrocini, G.; Megna, M. Guselkumab, Risankizumab, and Tildrakizumab in the Management of Psoriasis: A Review of the Real-World Evidence. Clin. Cosmet Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M.; Puig, L.; Torres, T. JAK Inhibitors for Treatment of Psoriasis: Focus on Selective TYK2 Inhibitors. Drugs 2020, 80, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potestio, L.; Ruggiero, A.; Fabbrocini, G.; Martora, F.; Megna, M. Effectiveness and Safety of Deucravacitinib for the Management of Psoriasis: A Review of the Current Literature. Psoriasis 2023, 13, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.Q.; Spencer, R.K.; Reddy, V.; Bhutani, T.; Liao, W. Clinical Utility of Deucravacitinib for the Management of Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2023, 19, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schön, M.P.; Wilsmann-Theis, D. Current developments and perspectives in psoriasis. J. Dtsch Dermatol. Ges. 2023, 21, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Choo, A.; Dayan, S.; Richards, R.I.; O’Keefe, L.V. Molecular Biology of the WWOX Gene That Spans Chromosomal Fragile Site FRA16D. Cells 2021, 10, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarek, A.K.; Keck-Waggoner, C.L.; Daniel, R.L.; Laflin, K.J.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Kiguchi, K.; Brenner, A.J.; Aldaz, C.M. WWOX, the FRA16D gene, behaves as a suppressor of tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8068–8073. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Visschedijk, M.C.; Spekhorst, L.M.; Cheng, S.C.; van Loo, E.S.; Jansen, B.H.D.; Blokzijl, T.; Kil, H.; de Jong, D.J.; Pierik, M.; Maljaars, J.; et al. Genomic and Expression Analyses Identify a Disease-Modifying Variant for Fibrostenotic Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, S.; Chen, J.; Sethuraman, S.; Sysol, J.R.; Gampa, A.; Zhao, S.; Machado, R.F. Loss of lung WWOX expression causes neutrophilic inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, L903–L911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baryła, I.; Styczeń-Binkowska, E.; Płuciennik, E.; Kośla, K.; Bednarek, A.K. The WWOX/HIF1A Axis Downregulation Alters Glucose Metabolism and Predispose to Metabolic Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatan, I.; Choi, H.Y.; Ruel, I.; Reddy, M.V.; Kil, H.; Lee, J.; Odeh, M.A.; Salah, Z.; Abu-Remaileh, M.; Weissglas-Volkov, D.; et al. The WWOX gene modulates high-density lipoprotein and lipid metabolism. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baryła, I.; Kośla, K.; Bednarek, A.K. WWOX and metabolic regulation in normal and pathological conditions. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xu, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, M.; Qin, Y.; Wu, W.; Xia, Y.; Ji, C.; Guo, X.; et al. Genetic variants in PTPRD and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76101–76107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sakai, K.; Imamura, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Iwata, M.; Hirose, H.; Kaku, K.; Maegawa, H.; Watada, H.; Tobe, K.; Kashiwagi, A.; et al. Replication study for the association of 9 East Asian GWAS-derived loci with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in a Japanese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.S.; Chang, N.S. Phosphorylation/de-phosphorylation in specific sites of tumor suppressor WWOX and control of distinct biological events. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Ho, P.C.; Nagarajan, G.; Chen, Y.A.; Kuo, H.L.; Subhan, D.; Su, W.P.; Chang, J.Y.; Lu, C.Y.; Chang, K.T.; et al. WWOX Possesses N-Terminal Cell Surface-Exposed Epitopes WWOX7-21 and WWOX7-11 for Signaling Cancer Growth Suppression and Prevention In Vivo. Cancers 2019, 11, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Han, Q.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, K. EDIL3 influenced the αvβ3-FAK/MEK/ERK axis of endothelial cells in psoriasis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 5202–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, D.; Ekman, A.K.; Bivik Eding, C.; Enerbäck, C. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Profiling Identifies Differential Methylation in Uninvolved Psoriatic Epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Li, K.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Hayden, K.; Brodmerkel, C.; Krueger, J.G. Expanding the psoriasis disease profile: Interrogation of the skin and serum of patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2552–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.L.; Crumrine, D.A.; Man, M.Q.; Chang, W.; Elalieh, H.; You, M.; Elias, P.M.; Bikle, D.D. Ablation of the calcium-sensing receptor in keratinocytes impairs epidermal differentiation and barrier function. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendy, G.N.; Canaff, L. Calcium-sensing receptor, proinflammatory cytokines and calcium homeostasis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 49, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Delalio, L.J.; Best, A.K.; Macal, E.; Milstein, J.; Donnelly, I.; Miller, A.M.; McBride, M.; Shu, X.; Koval, M.; et al. Endothelial Pannexin 1 Channels Control Inflammation by Regulating Intracellular Calcium. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 2995–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscat, J.; Diaz-Meco, M.T.; Rennert, P. NF-kappaB activation by protein kinase C isoforms and B-cell function. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrero, M.; Planes, R.; Bahraoui, E. PKC-delta isoform plays a crucial role in Tat-TLR4 signalling pathway to activate NF-kappaB and CXCL8 production. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T.; Gilroy, D.W.; Colville-Nash, P.R.; Willoughby, D.A. Possible new role for NF-kappaB in the resolution of inflammation. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizzul, P.F.; Aphale, A.; Malaviya, R.; Sun, Y.; Masud, S.; Dombrovskiy, V.; Gottlieb, A.B. Differential expression of phosphorylated NF-kappaB/RelA in normal and psoriatic epidermis and downregulation of NF-kappaB in response to treatment with etanercept. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldminz, A.M.; Au, S.C.; Kim, N.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Lizzul, P.F. NF-κB: An essential transcription factor in psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 69, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindell, W.R.; Xing, X.; Stuart, P.E.; Chen, C.S.; Aphale, A.; Nair, R.P.; Voorhees, J.J.; Elder, J.T.; Johnston, A.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Heterogeneity of inflammatory and cytokine networks in chronic plaque psoriasis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommert, S.; Doenni, L.; Szudybill, P.; Zoeller, C.; Beyer, F.H.; Werfel, T. C3a and Its Receptor C3aR Are Detectable in Normal Human Epidermal Keratinocytes and Are Differentially Regulated via TLR3 and LL37. J. Innate Immun. 2021, 13, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prens, E.P.; Kant, M.; van Dijk, G.; van der Wel, L.I.; Mourits, S.; van der Fits, L. IFN-alpha enhances poly-IC responses in human keratinocytes by inducing expression of cytosolic innate RNA receptors: Relevance for psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimstad, O.; Husebye, H.; Espevik, T. TLR3 mediates release of IL-1beta and cell death in keratinocytes in a caspase-4 dependent manner. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 72, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogsaeter, E.; Tang, R.; Grimm, C. JPT2: The missing link between intracellular Ca(2+) release channels and NAADP? Cell Calcium 2021, 97, 102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.L. The Role of Calcium in Inflammation-Associated Bone Resorption. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mine, Y.; Zhang, H. Calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR)-mediated anti-inflammatory effects of L-amino acids in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9987–9995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarek, A.K.; Laflin, K.J.; Daniel, R.L.; Liao, Q.; Hawkins, K.A.; Aldaz, C.M. WWOX, a novel WW domain-containing protein mapping to human chromosome 16q23.3-24.1, a region frequently affected in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2140–2145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ried, K.; Finnis, M.; Hobson, L.; Mangelsdorf, M.; Dayan, S.; Nancarrow, J.K.; Woollatt, E.; Kremmidiotis, G.; Gardner, A.; Venter, D.; et al. Common chromosomal fragile site FRA16D sequence: Identification of the FOR gene spanning FRA16D and homozygous deletions and translocation breakpoints in cancer cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 1651–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, N.S.; Pratt, N.; Heath, J.; Schultz, L.; Sleve, D.; Carey, G.B.; Zevotek, N. Hyaluronidase induction of a WW domain-containing oxidoreductase that enhances tumor necrosis factor cytotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3361–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taouis, K.; Driouch, K.; Lidereau, R.; Lallemand, F. Molecular Functions of WWOX Potentially Involved in Cancer Development. Cells 2021, 10, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.T.; Lai, F.J.; Chang, N.S.; Hsu, L.J. Wwox Deficiency Causes Downregulation of Prosurvival ERK Signaling and Abnormal Homeostatic Responses in Mouse Skin. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 558432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Odeh, M.; Bar-Mag, T.; Huang, H.; Kim, T.; Salah, Z.; Abdeen, S.K.; Sudol, M.; Reichmann, D.; Sidhu, S.; Kim, P.M.; et al. Characterizing WW domain interactions of tumor suppressor WWOX reveals its association with multiprotein networks. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 8865–8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Qu, Z.; Yan, P.; Ishikawa, C.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Rabson, A.B.; Xiao, G. The tumor suppressor gene WWOX links the canonical and noncanonical NF-kappaB pathways in HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis. Blood 2011, 117, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaz, C.M.; Hussain, T. WWOX Loss of Function in Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoulis, G.E.; Siebert, S.; McInnes, I.B. Therapeutic Targeting of IL-17 and IL-23 Cytokines in Immune-Mediated Diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Bai, Y. Dendritic cells: The driver of psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Experimental study on the effect of luteolin on the proliferation, apoptosis and expression of inflammation-related mediators in lipopolysaccharide-induced keratinocytes. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 3946320231169175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, R.; Hu, L.; Li, S.; Wei, Z.; Song, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lei, X.; Yang, Y. Tiamulin inhibits TNF-alpha and alleviates psoriasis-like dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2022, 107, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudha Yalamarthi, S.; Puppala, E.R.; Abubakar, M.; Saha, P.; Challa, V.S.; Np, S.; Usn, M.; Gangasani, J.K.; Naidu, V.G.M. Perillyl alcohol inhibits keratinocyte proliferation and attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasis like skin-inflammation by modulating NF-kappaB and STAT3 signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 103, 108436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Lee, S.H. Skin Barrier and Calcium. Ann. Dermatol. 2018, 30, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D.; Jiang, Y.; Nguyen, T.; Oda, Y.; Tu, C.L. Disruption of Vitamin D and Calcium Signaling in Keratinocytes Predisposes to Skin Cancer. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubillos, S.; Norgauer, J. Low vitamin D-modulated calcium-regulating proteins in psoriasis vulgaris plaques: S100A7 overexpression depends on joint involvement. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.S.; Sutton, C.R.; Rao, S. Protein kinase C in the immune system: From signalling to chromatin regulation. Immunology 2015, 146, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataisson, C.; Joseloff, E.; Murillas, R.; Wang, A.; Atwell, C.; Torgerson, S.; Gerdes, M.; Subleski, J.; Gao, J.-L.; Murphy, P.M. Activation of cutaneous protein kinase Cα induces keratinocyte apoptosis and intraepidermal inflammation by independent signaling pathways. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 2703–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataisson, C.; Pearson, A.J.; Torgerson, S.; Nedospasov, S.A.; Yuspa, S.H. Protein kinase Cα-mediated chemotaxis of neutrophils requires NF-κB activity but is independent of TNFα signaling in mouse skin in vivo. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mo, X.; Piper, M.G.; Wang, H.; Parinandi, N.L.; Guttridge, D.; Marsh, C.B. M-CSF induces monocyte survival by activating NF-κB p65 phosphorylation at Ser276 via protein kinase C. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.-M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.K.; Choi, M.R.; Hwang, Y.L.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, Y.; Seo, Y.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, J.H. Potential Role of Cytosolic RNA Sensor MDA5 as an Inhibitor for Keratinocyte Differentiation in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Ann. Dermatol. 2021, 33, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, T.J.; Chang, Y.H.; Shin, Y.A.; Shin, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, S.K.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.G.; Yoon, T.J.; Kim, C.D. Identification of a possible susceptibility locus for UVB-induced skin tanning phenotype in K orean females using genomewide association study. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, M.-J.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, P.; Yang, N.-G.; Kim, J.-Y.; Eun, Y.-S.; Lee, W.; Kim, D.; Lee, Y.; Jung, K.-E.; et al. Mechanistic Investigation of WWOX Function in NF-kB-Induced Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010167
Shin M-J, Kim H-S, Lee P, Yang N-G, Kim J-Y, Eun Y-S, Lee W, Kim D, Lee Y, Jung K-E, et al. Mechanistic Investigation of WWOX Function in NF-kB-Induced Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(1):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010167
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Min-Jeong, Hyun-Sun Kim, Pyeongan Lee, Na-Gyeong Yang, Jae-Yun Kim, Yun-Su Eun, Whiin Lee, Doyeon Kim, Young Lee, Kyung-Eun Jung, and et al. 2024. "Mechanistic Investigation of WWOX Function in NF-kB-Induced Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 1: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010167
APA StyleShin, M.-J., Kim, H.-S., Lee, P., Yang, N.-G., Kim, J.-Y., Eun, Y.-S., Lee, W., Kim, D., Lee, Y., Jung, K.-E., Hong, D., Shin, J.-M., Lee, S.-H., Lee, S.-Y., Kim, C.-D., & Kim, J.-E. (2024). Mechanistic Investigation of WWOX Function in NF-kB-Induced Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010167





