Deficiency of AP1 Complex Ap1g1 in Zebrafish Model Led to Perturbation of Neurodevelopment, Female and Male Fertility; New Insight to Understand Adaptinopathies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Generation of Ap1g1 Mutant Line
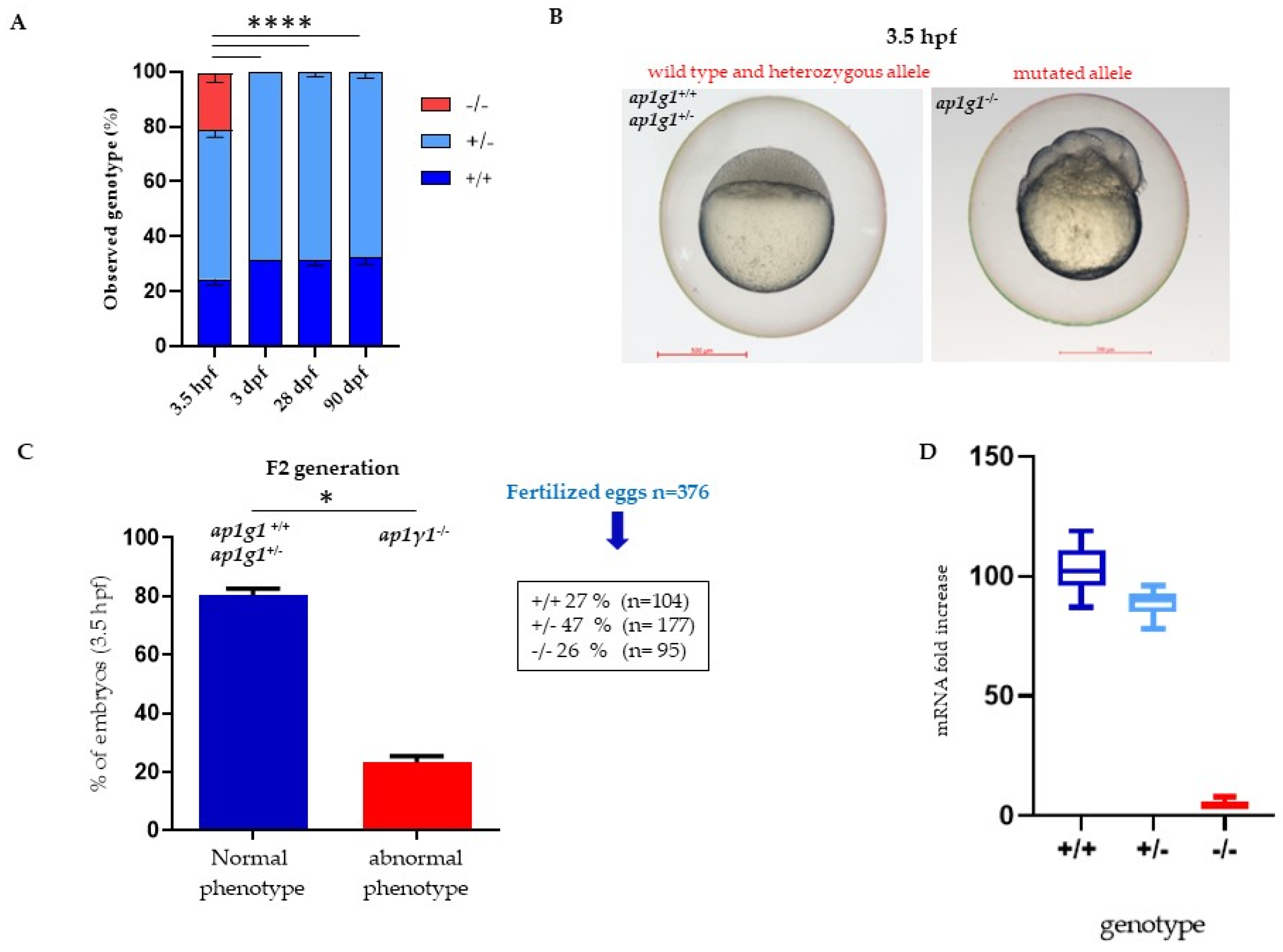
2.2. Lethality of ap1g1 Mutants during Development
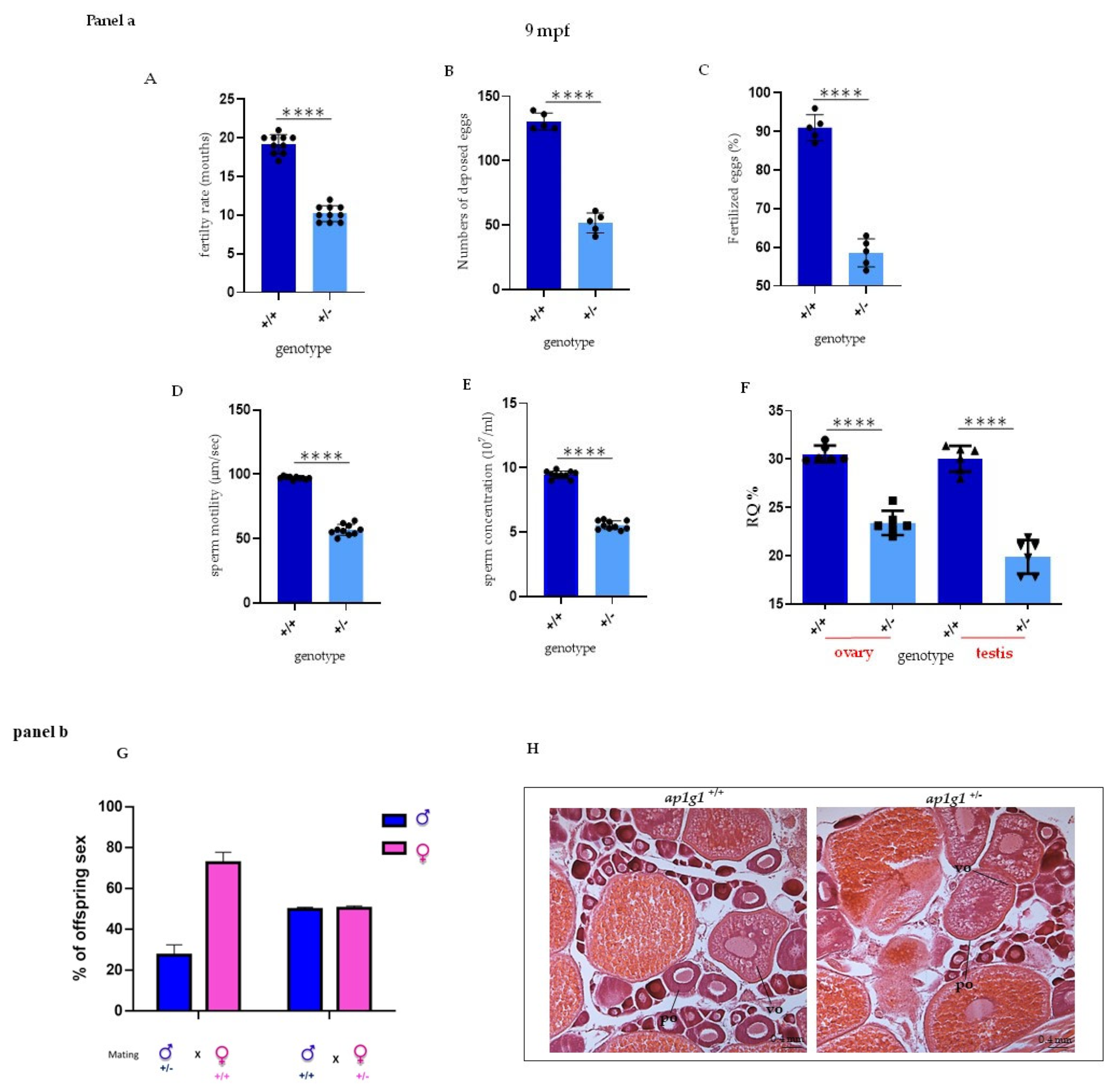
2.3. Reduced Fertility of ap1g1+/− Animals
2.4. Loss of Ap1g1subunit Affects the Development of Intestinal Epithelium in Heterozygous Fish
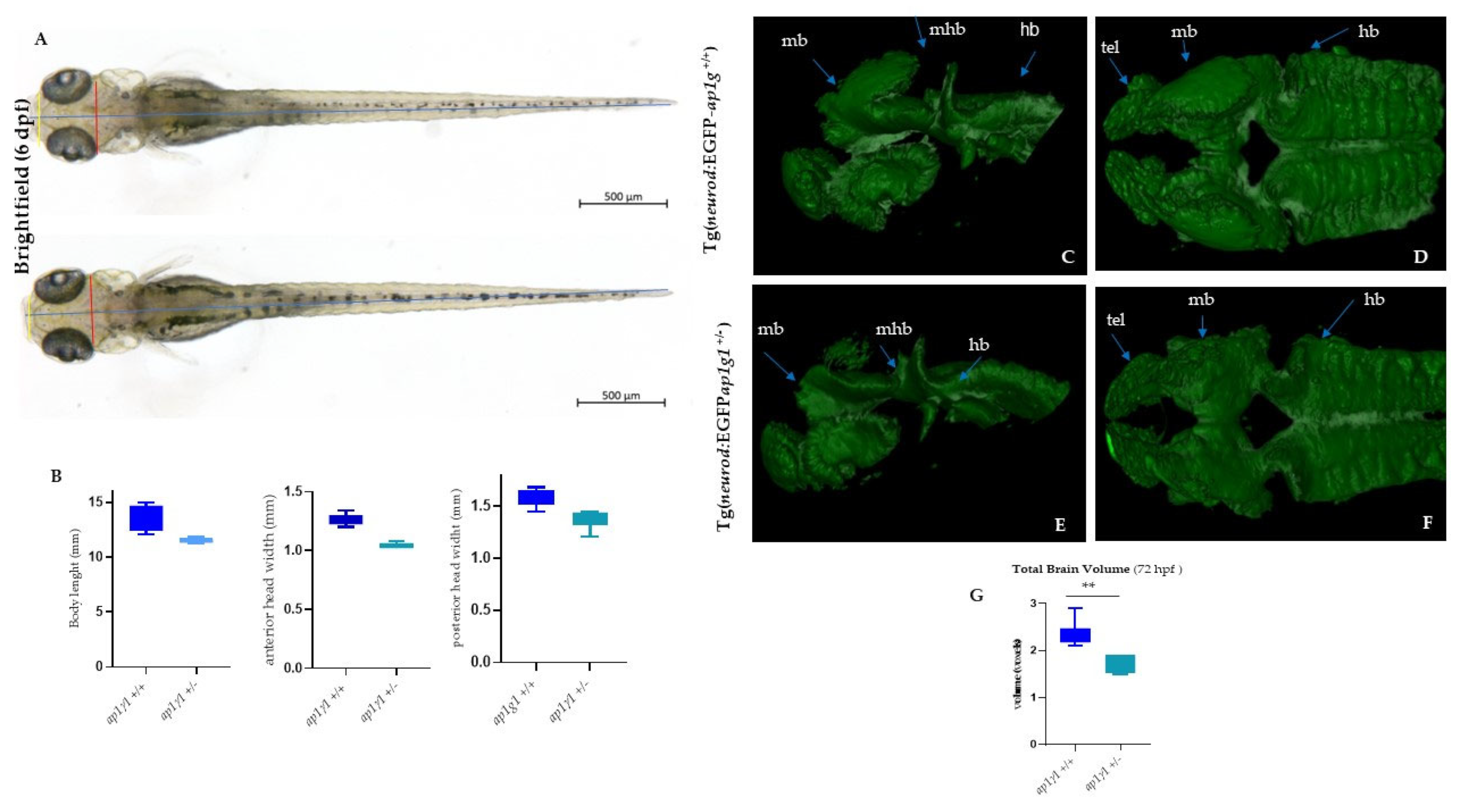
2.5. Impaired Neuronal Development of Ap1g1+/− Zebrafish Embryos
2.6. Reduced E-Cadherin and BMPs Expression in Zebrafish Ap1g1+/− Larvae
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Maintenance and Handling of Zebrafish Lines
4.2. Generation and Genotyping of Zebrafish ap1γ1 Mutant Line
4.3. Generation of Heterozygous ap1g1 Mutant Transgenic Zebrafish Line
4.4. Mendelian Analysis
4.5. Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization (WISH)
4.6. Histological Analysis
4.7. RNA Extraction and qPCR
4.8. Ejaculate Collection
4.9. Sperm Concentration
4.10. Sperm Velocity
4.11. Acridine Orange Staining
4.12. Microscopy
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonifacino, J.S.; Glick, B.S. The mechanisms of vesicle budding and fusion. Cell 2004, 116, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zizioli, D.; Meyer, C.; Guhde, G.; Saftig, P.; von Figura, K.; Schu, P. Early embryonic death of mice deficient in γ-adaptin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 5385–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zizioli, D.; Geumann, C.; Kratzke, M.; Mishra, R.; Borsani, G.; Finazzi, D.; Candiello, E.; Schu, P. γ2AP-1 and γ1AP-1 complexes: Different essential functions and regulatory mechanisms in clathrin-dependent protein sorting. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 96, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hase, K.; Nakatsu, F.; Ohmae, M.; Sugihara, K.; Shioda, N.; Takahashi, D.; Obata, Y.; Furusawa, Y.; Fujimura, Y.; Yamashita, T.; et al. AP1B-mediated protein sorting regulates polarity and proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glyvuk, N.; Tsytsyura, Y.; Geumann, C.; D’Hooge, R.; Hüve, J.; Kratzke, M.; Baltes, J.; Boening, D.; Klingauf, J.; Schu, P. AP-1/σ1B-adaptin mediates endosomal synaptic vesicle recycling, learning and memory. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.P.; Spang, A. Protein sorting from endosomes to the tgn. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1140605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farías, G.G.; Britt, D.J.; Bonifacino, J.S. Imaging the polarized sorting of proteins from the golgi complex in live neurons. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1496, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, M.; Bonifacino, J.S. Genetic analyses of adaptin function from yeast to mammals. Gene 2002, 286, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Arias, D.A.; McCarty, N.; Lu, L.; Maldonado, R.A.; Shinohara, M.L.; Cantor, H. Unexpected role of clathrin adaptor AP-1 in mhc-dependent positive selection of t cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2556–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.R.; Gagnon, L.H.; Chang, B. A hypomorphic mutation of the γ1 adaptin gene (Ap1g1) causes inner ear, retina, thyroid, and testes abnormalities in mice. Mamm. Genome 2016, 27, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H.; Tomemori, T.; Nakatsu, F.; Okazaki, Y.; Aguilar, R.C.; Foelsch, H.; Mellman, I.; Saito, T.; Shirasawa, T.; Bonifacino, J.S. μ1B, a novel adaptor medium chain expressed in polarized epithelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1999, 449, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, D.; Hase, K.; Kimura, S.; Nakatsu, F.; Ohmae, M.; Mandai, Y.; Sato, T.; Date, Y.; Ebisawa, M.; Kato, T.; et al. The epithelia-specific membrane trafficking factor AP1B controls gut immune homeostasis in mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskelinen, E.L.; Meyer, C.; Ohno, H.; von Figura, K.; Schu, P. The polarized epithelia-specific μ1B-adaptin complements μ1B-deficiency in fibroblasts. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.; Zizioli, D.; Lausmann, S.; Eskelinen, E.L.; Hamann, J.; Saftig, P.; von Figura, K.; Schu, P. μ1A-adaptin-deficient mice: Lethality, loss of AP-1 binding and rerouting of mannose 6-phosphate receptors. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Eskelinen, E.L.; Guruprasad, M.R.; von Figura, K.; Schu, P. μ1A deficiency induces a profound increase in MPR300 receptor internalization rate. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 4469–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittnenzweig, M.; Mayshar, Y.; Cheng, S.; Ben-Yair, R.; Hadas, R.; Rais, Y.; Chomsky, E.; Reines, N.; Uzonyi, A.; Lumerman, L.; et al. A single-embryo, single-cell time-resolved model for mouse gastrulation. Cell 2021, 184, 2825.e2822–2842.e2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candiello, E.; Kratzke, M.; Wenzel, D.; Cassel, D.; Schu, P. Ap-1/σ1a and ap-1/σ1b adaptor-proteins differentially regulate neuronal early endosome maturation via the rab5/vps34-pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpey, P.S.; Stevens, C.; Teague, J.; Edkins, S.; O’Meara, S.; Avis, T.; Barthorpe, S.; Buck, G.; Butler, A.; Cole, J.; et al. Mutations in the gene encoding the sigma 2 subunit of the adaptor protein 1 complex, ap1s2, cause x-linked mental retardation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 79, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saillour, Y.; Zanni, G.; Des Portes, V.; Heron, D.; Guibaud, L.; Iba-Zizen, M.T.; Pedespan, J.L.; Poirier, K.; Castelnau, L.; Julien, C.; et al. Mutations in the ap1s2 gene encoding the sigma 2 subunit of the adaptor protein 1 complex are associated with syndromic x-linked mental retardation with hydrocephalus and calcifications in basal ganglia. J. Med. Genet. 2007, 44, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, D.; Dionisi-Vici, C. Ap1s1 defect causing mednik syndrome: A new adaptinopathy associated with defective copper metabolism. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1314, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montpetit, A.; Côté, S.; Brustein, E.; Drouin, C.A.; Lapointe, L.; Boudreau, M.; Meloche, C.; Drouin, R.; Hudson, T.J.; Drapeau, P.; et al. Disruption of ap1s1, causing a novel neurocutaneous syndrome, perturbs development of the skin and spinal cord. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmani, M.A.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Magini, P.; Pienkowski, V.M.; Rasmussen, K.J.; Hernan, R.; Rasheed, F.; Hussain, M.; Shahzad, M.; Lanpher, B.C.; et al. De novo and bi-allelic variants in ap1g1 cause neurodevelopmental disorder with developmental delay, intellectual disability, and epilepsy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyden, L.M.; Atzmony, L.; Hamilton, C.; Zhou, J.; Lim, Y.H.; Hu, R.; Pappas, J.; Rabin, R.; Ekstien, J.; Hirsch, Y.; et al. Recessive mutations in ap1b1 cause ichthyosis, deafness, and photophobia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vornweg, J.; Gläser, S.; Ahmad-Anwar, M.; Zimmer, A.D.; Kuhn, M.; Hörer, S.; Korenke, G.C.; Grothaus, J.; Ott, H.; Fischer, J. Identification of compound heterozygous mutations in AP1B1 leading to the newly described recessive keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness (kidar) syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 1190–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaif, H.S.; Al-Owain, M.; Barrios-Llerena, M.E.; Gosadi, G.; Binamer, Y.; Devadason, D.; Ravenscroft, J.; Suri, M.; Alkuraya, F.S. Homozygous loss-of-function mutations in Ap1b1, encoding β1 subunit of adaptor-related protein complex 1, cause mednik-like syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens Grisham, R.; Kindt, K.; Finger-Baier, K.; Schmid, B.; Nicolson, T. Mutations in Ap1b1 cause mistargeting of the Na(+)/K(+)-Atpase pump in sensory hair cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klee, K.M.C.; Janecke, A.R.; Civan, H.A.; Rosipal, Š.; Heinz-Erian, P.; Huber, L.A.; Müller, T.; Vogel, G.F. Ap1s1 missense mutations cause a congenital enteropathy via an epithelial barrier defect. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariano, G.; Guarienti, M.; Bresciani, R.; Borsani, G.; Carola, G.; Monti, E.; Giuliani, R.; Rezzani, R.; Bonomini, F.; Preti, A.; et al. Analysis of three μ1-AP1 subunits during zebrafish development. Dev. Dyn. 2014, 243, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizioli, D.; Forlanelli, E.; Guarienti, M.; Nicoli, S.; Fanzani, A.; Bresciani, R.; Borsani, G.; Preti, A.; Cotelli, F.; Schu, P. Characterization of the AP-1 μ1A and μ1B adaptins in zebrafish (danio rerio). Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, J.A.; Valen, E.; Thyme, S.B.; Huang, P.; Akhmetova, L.; Pauli, A.; Montague, T.G.; Zimmerman, S.; Richter, C.; Schier, A.F. Efficient mutagenesis by cas9 protein-mediated oligonucleotide insertion and large-scale assessment of single-guide rnas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliodori, A.; Beffagna, G.; Marchetto, G.; Fornetto, C.; Vanzi, F.; Toppo, S.; Facchinello, N.; Santimaria, M.; Vettori, A.; Rizzo, S.; et al. Loss of cardiac wnt/β-catenin signalling in desmoplakin-deficient ac8 zebrafish models is rescuable by genetic and pharmacological intervention. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1082–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Farías, G.G.; Bonifacino, J.S. Polarized sorting of the copper transporter ATP7B in neurons mediated by recognition of a dileucine signal by AP-1. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, T.; Wullimann, M.F. Anatomy of neurogenesis in the early zebrafish brain. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 2003, 140, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzh, V.; Sleptsova, I.; Liao, J.; He, J.; Gong, Z. Expression of zebrafish bhlh genes ngn1 and nrd defines distinct stages of neural differentiation. Dev. Dyn. 1998, 213, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.L.; Ochocinska, M.J.; Hitchcock, P.F.; Thummel, R. Using the tg(nrd:Egfp)/albino zebrafish line to characterize in vivo expression of neurod. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riethmacher, D.; Brinkmann, V.; Birchmeier, C. A targeted mutation in the mouse E-cadherin gene results in defective preimplantation development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von der Hardt, S.; Bakkers, J.; Inbal, A.; Carvalho, L.; Solnica-Krezel, L.; Heisenberg, C.P.; Hammerschmidt, M. The bmp gradient of the zebrafish gastrula guides migrating lateral cells by regulating cell-cell adhesion. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, R.; Hellicar, J.; Woodman, P.G.; Lowe, M. Membrane trafficking in health and disease. Dis. Model. Mech. 2020, 13, dmm043448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setta-Kaffetzi, N.; Simpson, M.A.; Navarini, A.A.; Patel, V.M.; Lu, H.C.; Allen, M.H.; Duckworth, M.; Bachelez, H.; Burden, A.D.; Choon, S.E.; et al. Ap1s3 mutations are associated with pustular psoriasis and impaired toll-like receptor 3 trafficking. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 94, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, R.; Hofmeister, W.; Lindstrand, A. Zebrafish models of neurodevelopmental disorders: Limitations and benefits of current tools and techniques. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.R.; Kolligs, F.T. E-cadherin’s role in development, tissue homeostasis and disease: Insights from mouse models: Tissue-specific inactivation of the adhesion protein E-cadherin in mice reveals its functions in health and disease. Bioessays 2015, 37, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, Y.; Ozawa, M. A dileucine motif in its cytoplasmic domain directs β-catenin-uncoupled E-cadherin to the lysosome. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 4395–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, Y.; Ozawa, M. Increased internalization of p120-uncoupled E-cadherin and a requirement for a dileucine motif in the cytoplasmic domain for endocytosis of the protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11540–11548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L.; Weis, W.I. Structure and biochemistry of cadherins and catenins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a003053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltes, J.; Larsen, J.V.; Radhakrishnan, K.; Geumann, C.; Kratzke, M.; Petersen, C.M.; Schu, P. σ1B adaptin regulates adipogenesis by mediating the sorting of sortilin in adipose tissue. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 3477–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janvier, K.; Kato, Y.; Boehm, M.; Rose, J.R.; Martina, J.A.; Kim, B.Y.; Venkatesan, S.; Bonifacino, J.S. Recognition of dileucine-based sorting signals from HIV-1 Nef and Limp-II by the AP-1 γ-σ1 and AP-3 δ-σ3 hemicomplexes. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punovuori, K.; Malaguti, M.; Lowell, S. Cadherins in early neural development. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 4435–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.J.; Harris, T.J. Cadherin trafficking for tissue morphogenesis: Control and consequences. Traffic 2016, 17, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.; Bairstow, S.F.; Carbonara, C.; Turbin, D.A.; Huntsman, D.G.; Anderson, R.A. Type I γ-phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase modulates adherens junction and E-cadherin trafficking via a direct interaction with μ1B adaptin. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.; Wandinger-Ness, A.; Roitbak, T. Altered trafficking and epithelial cell polarity in disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2002, 12, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Angelica, E.C.; Bonifacino, J.S. Coatopathies: Genetic disorders of protein coats. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 35, 131–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleström, P.; D’Angelo, L.; Midtlyng, P.J.; Schorderet, D.F.; Schulte-Merker, S.; Sohm, F.; Warner, S. Zebrafish: Housing and husbandry recommendations. Lab. Anim. 2020, 54, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucenas, S.; Takada, N.; Park, H.C.; Woodruff, E.; Broadie, K.; Appel, B. Cns-derived glia ensheath peripheral nerves and mediate motor root development. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truett, G.E.; Heeger, P.; Mynatt, R.L.; Truett, A.A.; Walker, J.A.; Warman, M.L. Preparation of pcr-quality mouse genomic DNA with hot sodium hydroxide and tris (hotshot). Biotechniques 2000, 29, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, S.; Lu, L.; Ding, M.; Cheng, J.; Song, G.; Gao, X.; Yao, L.; Fan, D.; et al. An efficient genotyping method for genome-modified animals and human cells generated with crispr/cas9 system. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, B.D.; Nicholas, C.S.; Baye, L.M.; Link, B.A.; Dowling, J.E. Dazed gene is necessary for late cell type development and retinal cell maintenance in the zebrafish retina. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 233, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.; Marquart, G.D.; Horstick, E.J.; Tabor, K.M.; Pajevic, S.; Burgess, H.A. Morphometric analysis and neuroanatomical mapping of the zebrafish brain. Methods 2018, 150, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mignani, L.; Facchinello, N.; Varinelli, M.; Massardi, E.; Tiso, N.; Ravelli, C.; Mitola, S.; Schu, P.; Monti, E.; Finazzi, D.; et al. Deficiency of AP1 Complex Ap1g1 in Zebrafish Model Led to Perturbation of Neurodevelopment, Female and Male Fertility; New Insight to Understand Adaptinopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087108
Mignani L, Facchinello N, Varinelli M, Massardi E, Tiso N, Ravelli C, Mitola S, Schu P, Monti E, Finazzi D, et al. Deficiency of AP1 Complex Ap1g1 in Zebrafish Model Led to Perturbation of Neurodevelopment, Female and Male Fertility; New Insight to Understand Adaptinopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(8):7108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087108
Chicago/Turabian StyleMignani, Luca, Nicola Facchinello, Marco Varinelli, Elena Massardi, Natascia Tiso, Cosetta Ravelli, Stefania Mitola, Peter Schu, Eugenio Monti, Dario Finazzi, and et al. 2023. "Deficiency of AP1 Complex Ap1g1 in Zebrafish Model Led to Perturbation of Neurodevelopment, Female and Male Fertility; New Insight to Understand Adaptinopathies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087108
APA StyleMignani, L., Facchinello, N., Varinelli, M., Massardi, E., Tiso, N., Ravelli, C., Mitola, S., Schu, P., Monti, E., Finazzi, D., Borsani, G., & Zizioli, D. (2023). Deficiency of AP1 Complex Ap1g1 in Zebrafish Model Led to Perturbation of Neurodevelopment, Female and Male Fertility; New Insight to Understand Adaptinopathies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(8), 7108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087108








