The Landscape of Global Ocean Microbiome: From Bacterioplankton to Biofilms
Abstract
1. Introduction
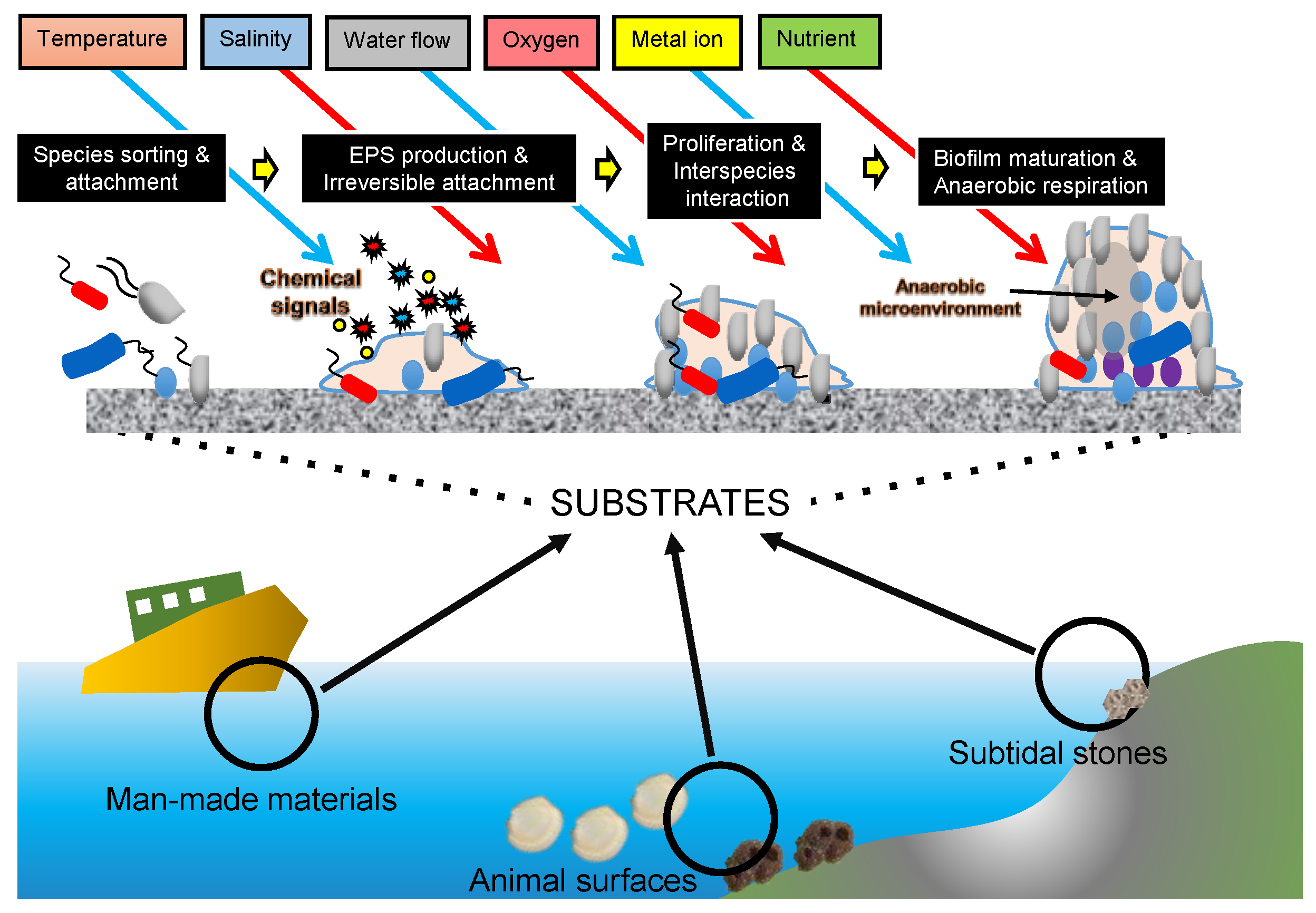
2. What Ocean Environments Have Been Analyzed
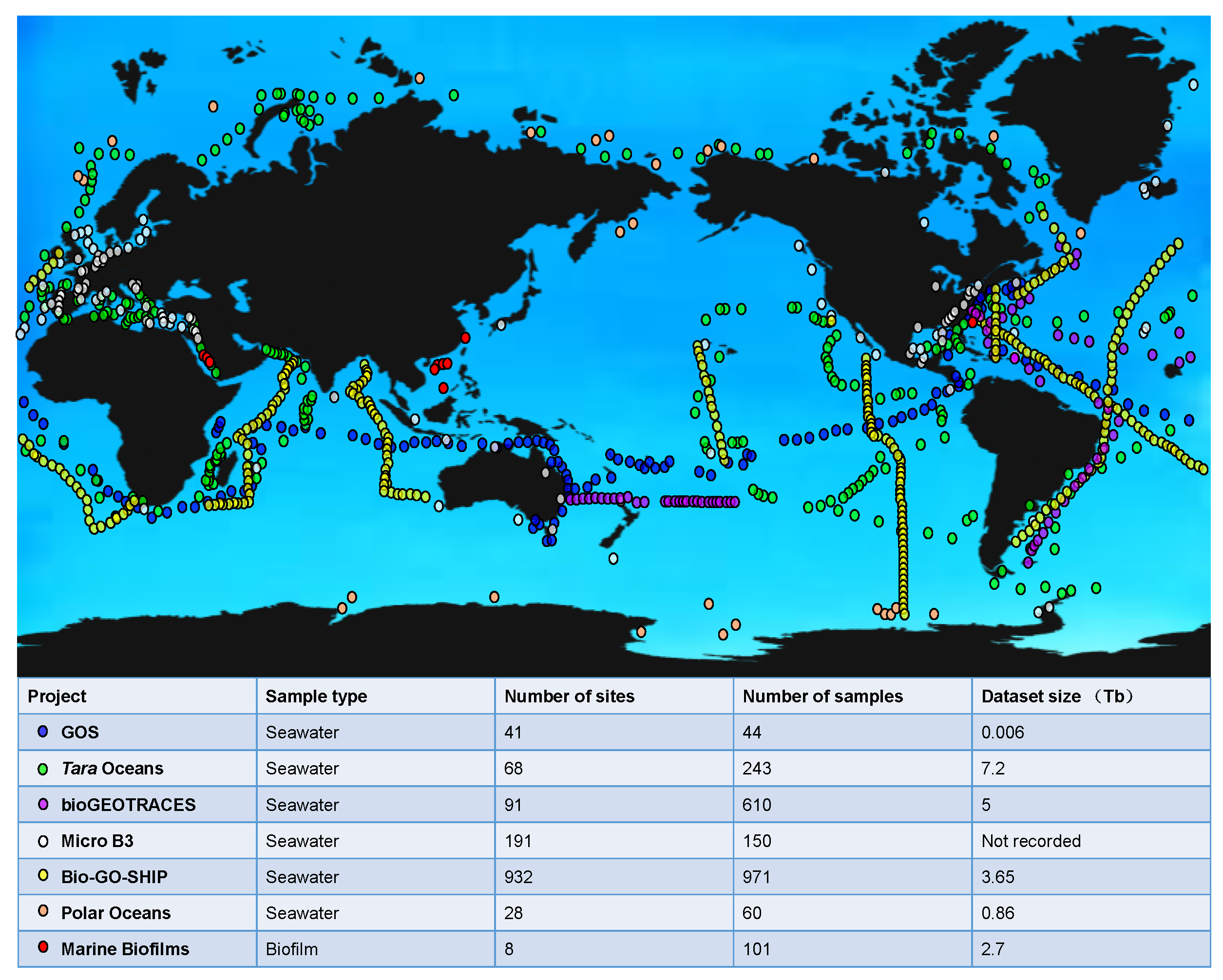
3. Global Ocean Datasets beyond Metagenomes
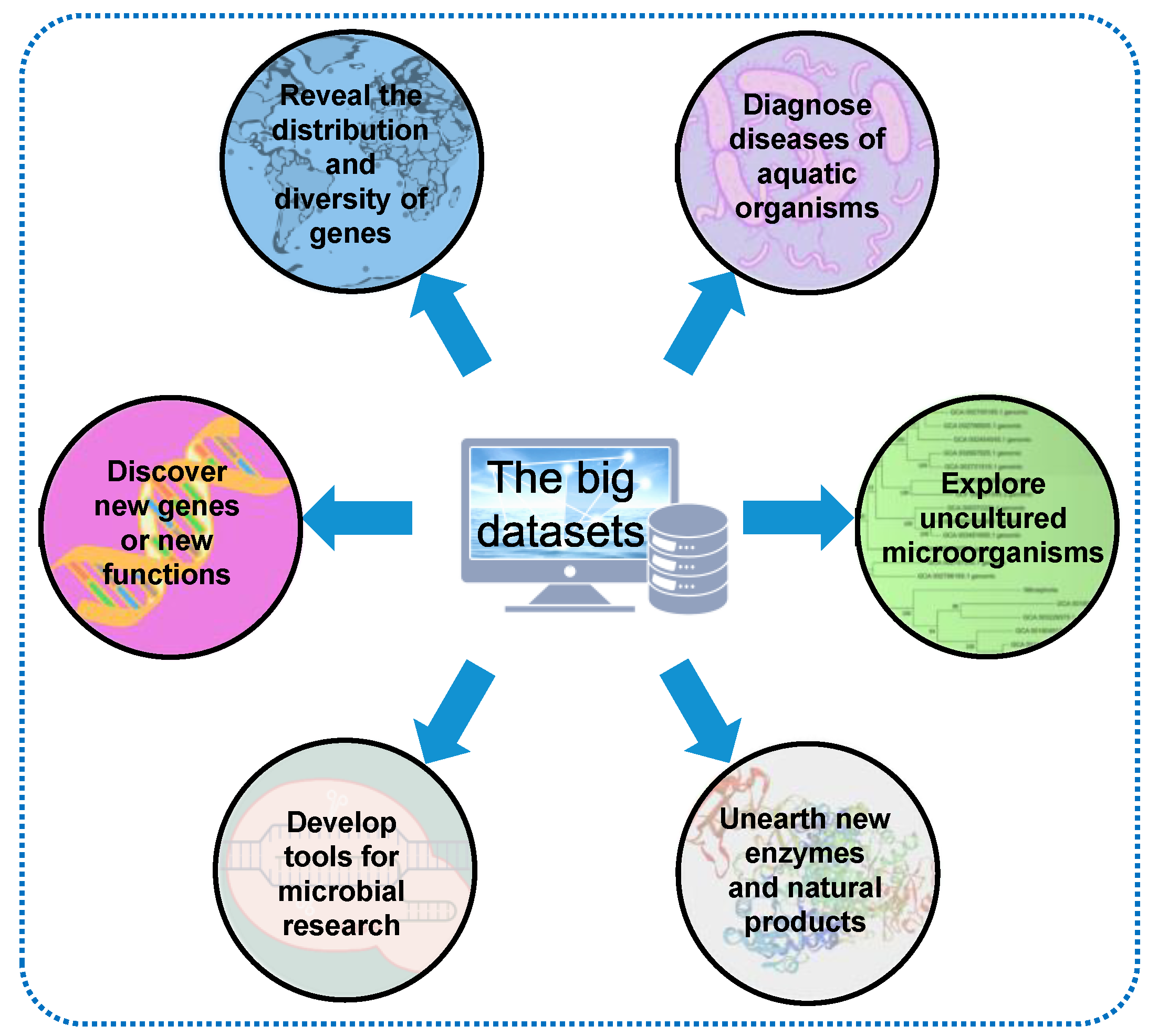
4. Transformation of the Large Datasets
5. Bottlenecks and Future Directions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harwani, D. The Great Plate Count Anomaly and the Unculturable Bacteria. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2012, 2, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.M.; DeLong, E.F.; Pace, N.R. Analysis of a marine picoplankton community by 16S rRNA gene cloning and sequencing. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 4371–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelsman, J.; Rondon, M.R.; Brady, S.F.; Clardy, J.; Goodman, R.M. Molecular biological access to the chemistry of unknown soil microbes: A new frontier for natural products. Chem. Biol. 1998, 5, R245–R249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amann, R.I.; Binder, B.J.; Olson, R.J.; Chisholm, S.W.; Devereux, R.; Stahl, D.A. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amann, R.I.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H. Phylogenetic identification and in-situ detection of individual microbial-cells without cultivation. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 59, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martiny, A.C. High proportions of bacteria are culturable across major biomes. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2125–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, A.D.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Carini, P.; DeAngelis, K.M.; Fierer, N.; Lloyd, K.G.; Thrash, J.C. High proportions of bacteria and archaea across most biomes remain uncultured. ISME J. 2019, 13, 3126–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiny, A. The “1% cultivability paradigm” needs to be carefully defined. ISME J. 2020, 14, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, G.W.; Chapman, J.; Hugenholtz, P.; Allen, E.E.; Ram, R.J.; Richardson, P.M.; Solovyev, V.V.; Rubin, E.M.; Rokhsar, D.S.; Banfield, J.F. Community structure and metabolism through reconstruction of microbial genomes from the environment. Nature 2004, 428, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, J.C.; Remington, K.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Halpern, A.L.; Rusch, D.; Eisen, J.A.; Wu, D.; Paulsen, I.T.; Nelson, K.E.; Nelson, W.; et al. Environmental Genome Shotgun Sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science 2004, 304, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Gilbert, J.; Meyer, F. Metagenomics—A guide from sampling to data analysis. Microb. Inform. Exp. 2012, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, F.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, M.; Sun, F.; Yang, L.; Bi, X.; Lin, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hao, H.; et al. Advances in Metagenomics and Its Application in Environmental Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 766364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flombaum, P.; Gallegos, J.L.; Gordillo, R.A.; Rincón, J.; Zabala, L.L.; Jiao, N.; Karl, D.M.; Li, W.K.W.; Lomas, M.W.; Veneziano, D.; et al. Present and future global distributions of the marine Cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9824–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigo, K.R. Marine microorganisms and global nutrient cycles. Nature 2004, 437, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnosti, C. Microbial Extracellular Enzymes and the Marine Carbon Cycle. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.A.; Beman, J.M.; Kuypers, M.M.M. New processes and players in the nitrogen cycle: The microbial ecology of anaerobic and archaeal ammonia oxidation. ISME J. 2007, 1, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehr, J.P.; Ward, B.B. Nitrogen Cycling in the Ocean: New Perspectives on Processes and Paradigms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehr, J.P.; Capone, D.G. Changing perspectives in marine nitrogen fixation. Science 2020, 368, aay9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, S.; Ramos, R. Processes and Microorganisms Involved in the Marine Nitrogen Cycle: Knowledge and Gaps. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.A.; Durham, B.P. Sulfur metabolites in the pelagic ocean. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 17, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasmund, K.; Mußmann, M.; Loy, A. The life sulfuric: Microbial ecology of sulfur cycling in marine sediments. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2017, 9, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, E.L. Microorganisms and their roles in fundamental biogeochemical cycles. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchioli, R.; Ostrowski, M.; Fegatella, F.; Goodchild, A.; Guixa-Boixereu, N. Life under Nutrient Limitation in Oligotrophic Marine Environments: An Eco/Physiological Perspective of Sphingopyxis alaskensis (formerly Sphingomonas alaskensis). Microb. Ecol. 2003, 46, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.-C.; Giovannoni, S.J.; Allgaier, M.; Uphoff, H.; Felske, A.; Wagner-Döbler, I. Cultivation and Growth Characteristics of a Diverse Group of Oligotrophic Marine Gammaproteobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5051–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, J.-C.; Collins, T.; D’Amico, S.; Feller, G.; Gerday, C. Cold-Adapted Enzymes from Marine Antarctic Microorganisms. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 9, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, A.; Finore, I.; Romano, I.; Gioiello, A.; Lama, L.; Nicolaus, B. Microbial Diversity in Extreme Marine Habitats and Their Biomolecules. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A.; Anzelmo, G.; Nicolaus, B. Bacterial Exopolysaccharides from Extreme Marine Habitats: Production, Characterization and Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1779–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikoshi, K. Barophiles: Deep-sea microorganisms adapted to an extreme environment. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1998, 1, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, D.H. Microbial life at high pressures. Sci. Prog. 1992, 76, 479–496. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, A.G.; Garcia, C.A.; Martiny, A.C. Increased biofilm formation due to high-temperature adaptation in marine Roseobacter. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.; Rose, A. Temperature Effects on Microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1967, 21, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A. Microbial life at high salt concentrations: Phylogenetic and metabolic diversity. Saline Syst. 2008, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Fu, H.-H.; Li, C.-Y.; Qin, Q.-L.; Liang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; et al. TCA cycle enhancement and uptake of monomeric substrates support growth of marine Roseobacter at low temperature. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint, I.; Mühling, M.; Querellou, J. Culturing marine bacteria—An essential prerequisite for biodiscovery. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.H.; Tahon, G.; Geesink, P.; Sousa, D.Z.; Ettema, T.J.G. Innovations to culturing the uncultured microbial majority. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 19, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ding, W.; Li, Y.-X.; Tam, C.; Bougouffa, S.; Wang, R.; Pei, B.; Chiang, H.; Leung, P.; Lu, Y.; et al. Marine biofilms constitute a bank of hidden microbial diversity and functional potential. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunagawa, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Chaffron, S.; Kultima, J.R.; Labadie, K.; Salazar, G.; Djahanschiri, B.; Zeller, G.; Mende, D.R.; Alberti, A.; et al. Ocean Plankton. Structure and function of the global ocean microbiome. Science 2015, 348, 1261359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, W.; Ding, W.; Wang, M.; Fan, S.; Yang, B.; Mcminn, A.; Wang, M.; Xie, B.-B.; Qin, Q.-L.; et al. Structure and function of the Arctic and Antarctic marine microbiota as revealed by metagenomics. Microbiome 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.A.; Kujawinski, E.B.; Stubbins, A.; Fatland, R.; Aluwihare, L.I.; Buchan, A.; Crump, B.C.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Dyhrman, S.T.; Hess, N.J.; et al. Deciphering ocean carbon in a changing world. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3143–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannes, R.; Cavaud, L.; Lopez, P.; Bapteste, E. Marine Ultrasmall Prokaryotes Likely Affect the Cycling of Carbon, Methane, Nitrogen, and Sulfur. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 13, evaa261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlusich, J.J.P.; Pelletier, E.; Lombard, F.; Carsique, M.; Dvorak, E.; Colin, S.; Picheral, M.; Cornejo-Castillo, F.M.; Acinas, S.G.; Pepperkok, R.; et al. Global distribution patterns of marine nitrogen-fixers by imaging and molecular methods. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.-J.; Qin, Q.-L.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Fu, H.-H.; Wang, P.; Lan, M.; Luo, G.; He, J.; McMinn, A.; et al. Biogeographic traits of dimethyl sulfide and dimethylsulfoniopropionate cycling in polar oceans. Microbiome 2021, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, S.; Coordinators, T.O.; Brum, J.R.; Dutilh, B.E.; Sunagawa, S.; Duhaime, M.B.; Loy, A.; Poulos, B.T.; Solonenko, N.; Lara, E.; et al. Ecogenomics and potential biogeochemical impacts of globally abundant ocean viruses. Nature 2016, 537, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, F.H.; Silveira, C.B.; Gregoracci, G.B.; Thompson, C.C.; Edwards, R.A.; Brussaard, C.P.D.; Dutilh, B.E.; Thompson, F.L. Marine viruses discovered via metagenomics shed light on viral strategies throughout the oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Pérez, M.; Jayakumar, J.M.; Haro-Moreno, J.M.; Zaragoza-Solas, A.; Reddi, G.; Rodriguez-Valera, F.; Shapiro, O.H.; Alam, M.; Almagro-Moreno, S. Evolutionary Model of Cluster Divergence of the Emergent Marine Pathogen Vibrio vulnificus: From Genotype to Ecotype. Mbio 2019, 10, e02852-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Wang, R.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Qian, P.-Y.; Zhang, W. Expanding our understanding of marine viral diversity through metagenomic analyses of biofilms. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Jiang, W.; Shi, Y.; Cai, W. Metagenomic Sequencing Revealed the Potential Pathogenic Threats of Banknotes. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 3499–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harik, A.-M.G.; Griffiths, Z.; Hazen, T.C. Omics of oil biodegradation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2022, 36, 100800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, F.; Guo, L.; Chen, Z.; Sievert, S.M.; Meng, J.; Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Yan, Q.; Wu, S.; et al. Comparative metagenomics of microbial communities inhabiting deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimneys with contrasting chemistries. ISME J. 2010, 5, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokke, R.; Dahle, H.; Roalkvam, I.; Wissuwa, J.; Daae, F.L.; Tooming-Klunderud, A.; Thorseth, I.H.; Pedersen, R.B.; Steen, I.H. Functional interactions among filamentous Epsilonproteobacteria and Bacteroidetes in a deep-sea hydrothermal vent biofilm. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4063–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, M.; Goecke, F.; Labes, A.; Dobretsov, S.; Weinberger, F. The Second Skin: Ecological Role of Epibiotic Biofilms on Marine Organisms. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.G.; Apprill, A.; Lebaron, P.; Robbins, J.; Romano, T.A.; Overton, E.; Rong, Y.; Yuan, R.; Pollara, S.; Whalen, K.E. Characterizing the culturable surface microbiomes of diverse marine animals. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiab040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decho, A.W. Microbial biofilms in intertidal systems: An overview. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 20, 1257–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, J.; Stippkugel, A.; Lenz, M.; Wirtz, K.; Engel, A. Rapid aggregation of biofilm-covered microplastics with marine biogenic particles. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2018, 285, 20181203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N. A short history of microbial biofilms and biofilm infections. Apmis 2017, 125, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basili, M.; Quero, G.M.; Giovannelli, D.; Manini, E.; Vignaroli, C.; Avio, C.G.; De Marco, R.; Luna, G.M. Major Role of Surrounding Environment in Shaping Biofilm Community Composition on Marine Plastic Debris. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wuertz, S. Bacteria and archaea on Earth and their abundance in biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Tian, X. Quorum Sensing and Bacterial Social Interactions in Biofilms. Sensors 2012, 12, 2519–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgani, L.; Tsapakis, M.; Pitta, P.; Tsiola, A.; Tzempelikou, E.; Kalantzi, I.; Esposito, C.; Loiselle, A.; Tsotskou, A.; Zivanovic, S.; et al. Microplastics increase the marine production of particulate forms of organic matter. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelhofer, G.; Jirón, T.S.; Yeh, T.-C.; Steniczka, G.; Pucher, M. Dissolved Organic Matter Quality and Biofilm Composition Affect Microbial Organic Matter Uptake in Stream Flumes. Water 2020, 12, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Lovell, C.R. Microbial Surface Colonization and Biofilm Development in Marine Environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 91–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.P.; Wang, Y.; Tian, R.M.; Bougouffa, S.; Yang, B.; Cao, H.L.; Zhang, G.; Wong, Y.H.; Xu, W.; Batang, Z.; et al. Species sorting during biofilm assembly by artificial substrates deployed in a cold seep system. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Bougouffa, S.; Tian, R.; Cao, H.; Li, Y.; Cai, L.; Wong, Y.H.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, G.; et al. Synchronized dynamics of bacterial niche-specific functions during biofilm development in a cold seep brine pool. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4089–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Tian, R.; Bo, Y.; Cao, H.; Cai, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Al-Suwailem, A.; et al. Environmental switching during biofilm development in a cold seep system and functional determinants of species sorting. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1958–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, D.B.; Halpern, A.L.; Sutton, G.; Heidelberg, K.; Williamson, S.; Yooseph, S.; Wu, D.; Eisen, J.A.; Hoffman, J.M.; Remington, K.; et al. The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling Expedition: Northwest Atlantic through Eastern Tropical Pacific. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yooseph, S.; Sutton, G.; Rusch, D.B.; Halpern, A.L.; Williamson, S.J.; Remington, K.; Eisen, J.A.; Heidelberg, K.; Manning, G.; Li, W.; et al. The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling Expedition: Expanding the Universe of Protein Families. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimmler, A.; Korn, R.; de Vargas, C.; Audic, S.; Stoeck, T. The Tara Oceans voyage reveals global diversity and distribution patterns of marine planktonic ciliates. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, R. Marine Microbes See a Sea of Gradients. Science 2012, 338, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.F.; Mawji, E.; Cutter, G.A.; Measures, C.I.; Jeandel, C. GEOTRACES changing the way we explore ocean chemistry. Oceanography 2014, 27, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, A.; Bicak, M.; Kottmann, R.; Schnetzer, J.; Kostadinov, I.; Lehmann, K.; Fernandez-Guerra, A.; Jeanthon, C.; Rahav, E.; Ullrich, M.; et al. The ocean sampling day consortium. Gigascience 2015, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoopen, P.T.; Pesant, S.; Kottmann, R.; Kopf, A.; Bicak, M.; Claus, S.; Deneudt, K.; Borremans, C.; Thijsse, P.; Dekeyzer, S.; et al. Marine microbial biodiversity, bioinformatics and biotechnology (M2B3) data reporting and service standards. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2015, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, S.; Alexander, H.; Graff, J.R.; Poulton, N.J.; Thompson, L.R.; Benway, H.; Boss, E.; Martiny, A. Bio-GO-SHIP: The Time Is Right to Establish Global Repeat Sections of Ocean Biology. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, A.A.; Garcia, C.A.; Garcia, N.; Brock, M.L.; Lee, J.A.; Ustick, L.J.; Barbero, L.; Carter, B.R.; Sonnerup, R.E.; Talley, L.D.; et al. High spatial resolution global ocean metagenomes from Bio-GO-SHIP repeat hydrography transects. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobanov, V.; Gobet, A.; Joyce, A. Ecosystem-specific microbiota and microbiome databases in the era of big data. Environ. Microbiome 2022, 17, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, C.L.; McCrow, J.; Valas, R.E.; Moustafa, A.; Walworth, N.; Goodenough, U.; Roth, R.; Hogle, S.; Bai, J.; Johnson, Z.; et al. Genomes and gene expression across light and productivity gradients in eastern subtropical Pacific microbial communities. ISME J. 2014, 9, 1076–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, F.J.; Ulloa, O.; DeLong, E.F. Microbial metatranscriptomics in a permanent marine oxygen minimum zone. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, G.; Paoli, L.; Alberti, A.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Ruscheweyh, H.-J.; Cuenca, M.; Field, C.M.; Coelho, L.P.; Cruaud, C.; Engelen, S.; et al. Gene Expression Changes and Community Turnover Differentially Shape the Global Ocean Metatranscriptome. Cell 2019, 179, 1068–1083.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.M.; Nunn, B.; Frazar, C.; Goodlett, D.R.; Ting, Y.; Rocap, G. Comparative metaproteomics reveals ocean-scale shifts in microbial nutrient utilization and energy transduction. ISME J. 2010, 4, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, A.K.; Brewer, H.M.; Norbeck, A.D.; Paša-Tolić, L.; Hallam, S.J. Metaproteomics reveals differential modes of metabolic coupling among ubiquitous oxygen minimum zone microbes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11395–11400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, J.; Cao, H.; Tian, R.; Cai, L.; Ding, W.; Qian, P.-Y. Post-translational modifications are enriched within protein functional groups important to bacterial adaptation within a deep-sea hydrothermal vent environment. Microbiome 2016, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podar, M.; Gilmour, C.C.; Brandt, C.C.; Soren, A.; Brown, S.D.; Crable, B.R.; Palumbo, A.V.; Somenahally, A.C.; Elias, D.A. Global prevalence and distribution of genes and microorganisms involved in mercury methylation. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Sun, Y.; Pei, B.; Gao, Z.; Qian, P.Y. Distribution, diversity and functional dissociation of the mac genes in marine biofilms. Biofouling 2019, 35, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatosy, S.M.; Martiny, A.C. The Ocean as a Global Reservoir of Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7593–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, C.G.; Bardischewsky, F.; Rother, D.; Quentmeier, A.; Fischer, J. Prokaryotic sulfur oxidation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, A.; Rusch, D.B. Distribution of microbial terpenoid lipid cyclases in the global ocean metagenome. ISME J. 2008, 3, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; Ding, W.; Liang, Z.; Long, L.; Wong, W.C.; Qian, P.-Y. Profiling Signal Transduction in Global Marine Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 768926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobecky, P.A.; Hazen, T.H. Horizontal Gene Transfer and Mobile Genetic Elements in Marine Systems. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 532, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.J.; Roux, S.; Hwang, C.Y.; Sul, W.J. Marine DNA methylation patterns are associated with microbial community composition and inform virus-host dynamics. Microbiome 2022, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNichol, J.; Berube, P.M.; Biller, S.J.; Fuhrman, J.A. Evaluating and Improving Small Subunit rRNA PCR Primer Coverage for Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes Using Metagenomes from Global Ocean Surveys. Msystems 2021, 6, e00565-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayfach, S.; Roux, S.; Seshadri, R.; Udwary, D.; Varghese, N.; Schulz, F.; Wu, D.; Paez-Espino, D.; Chen, I.-M.; Huntemann, M.; et al. A genomic catalog of Earth’s microbiomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 39, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, L.; Ruscheweyh, H.-J.; Forneris, C.C.; Hubrich, F.; Kautsar, S.; Bhushan, A.; Lotti, A.; Clayssen, Q.; Salazar, G.; Milanese, A.; et al. Biosynthetic potential of the global ocean microbiome. Nature 2022, 607, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, M.; Ding, W.; Li, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Zhang, W. Scientific and technological progress in the microbial exploration of the hadal zone. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 4, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tian, R.-M.; Sun, J.; Bougouffa, S.; Ding, W.; Cai, L.; Lan, Y.; Tong, H.; Li, Y.; Jamieson, A.J.; et al. Genome Reduction in Psychromonas Species within the Gut of an Amphipod from the Ocean’s Deepest Point. Msystems 2018, 3, e00009-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Watanabe, H.K.; Ding, W.; Lan, Y.; Tian, R.-M.; Sun, J.; Chen, C.; Cai, L.; Li, Y.; Oguri, K.; et al. Gut Microbial Divergence between Two Populations of the Hadal Amphipod Hirondellea gigas. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02032-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, D.; Raab, N.; Pinto, Y.; Rothschild, D.; Zanir, G.; Godneva, A.; Mellul, N.; Futorian, D.; Gal, D.; Leviatan, S.; et al. Diversity and functional landscapes in the microbiota of animals in the wild. Science 2021, 372, abb5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.M.; Cavanaugh, C.M. CO 2 Uptake and Fixation by Endosymbiotic Chemoautotrophs from the Bivalve Solemya velum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kletzin, A.; Urich, T.; Müller, F.; Bandeiras, T.; Gomes, C.M. Dissimilatory Oxidation and Reduction of Elemental Sulfur in Thermophilic Archaea. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2004, 36, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyben, D.; Sun, L.; Moccia, R.; Kiessling, A.; Dicksved, J.; Lundh, T. Dietary live yeast and increased water temperature influence the gut microbiota of rainbow trout. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1377–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-F.; Xu, J.-K.; Chen, Y.-W.; Ding, W.-Y.; Shao, A.-Q.; Liang, X.; Zhu, Y.-T.; Yang, J.-L. Characterization of Gut Microbiome in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in Response to Thermal Stress. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.A.; Grant, F.; Ferguson, C.M.J.; Gallacher, S. Biotransformations of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins by Bacteria Isolated from Bivalve Molluscs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2345–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, H.P.; Forster, S.C.; Anonye, B.O.; Kumar, N.; Neville, B.A.; Stares, M.D.; Goulding, D.; Lawley, T.D. Culturing of ‘unculturable’ human microbiota reveals novel taxa and extensive sporulation. Nature 2016, 533, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, V.C.; Gong, C.; Shanmugam, R.; Lee, J.-K. Prospecting Microbial Genomes for Biomolecules and Their Applications. Indian J. Microbiol. 2022, 62, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-K.; Kalia, V.C. Mapping Microbial Capacities for Bioremediation: Genes to Genomics. Indian J. Microbiol. 2019, 60, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, C.; Ding, W.; Zhang, W. The Landscape of Global Ocean Microbiome: From Bacterioplankton to Biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076491
Lu J, Shu Y, Zhang H, Zhang S, Zhu C, Ding W, Zhang W. The Landscape of Global Ocean Microbiome: From Bacterioplankton to Biofilms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076491
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jie, Yi Shu, Heng Zhang, Shangxian Zhang, Chengrui Zhu, Wei Ding, and Weipeng Zhang. 2023. "The Landscape of Global Ocean Microbiome: From Bacterioplankton to Biofilms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076491
APA StyleLu, J., Shu, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, S., Zhu, C., Ding, W., & Zhang, W. (2023). The Landscape of Global Ocean Microbiome: From Bacterioplankton to Biofilms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076491







