Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in the Treatment of Myocardial Injury
Abstract
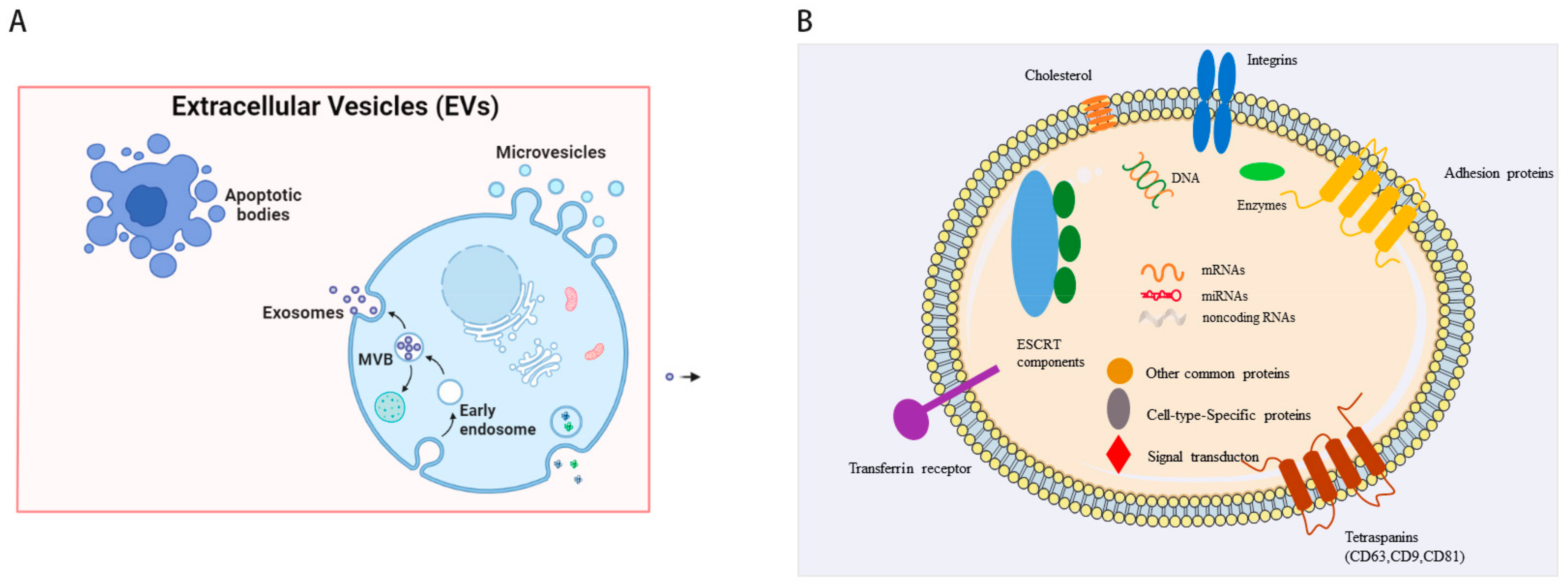
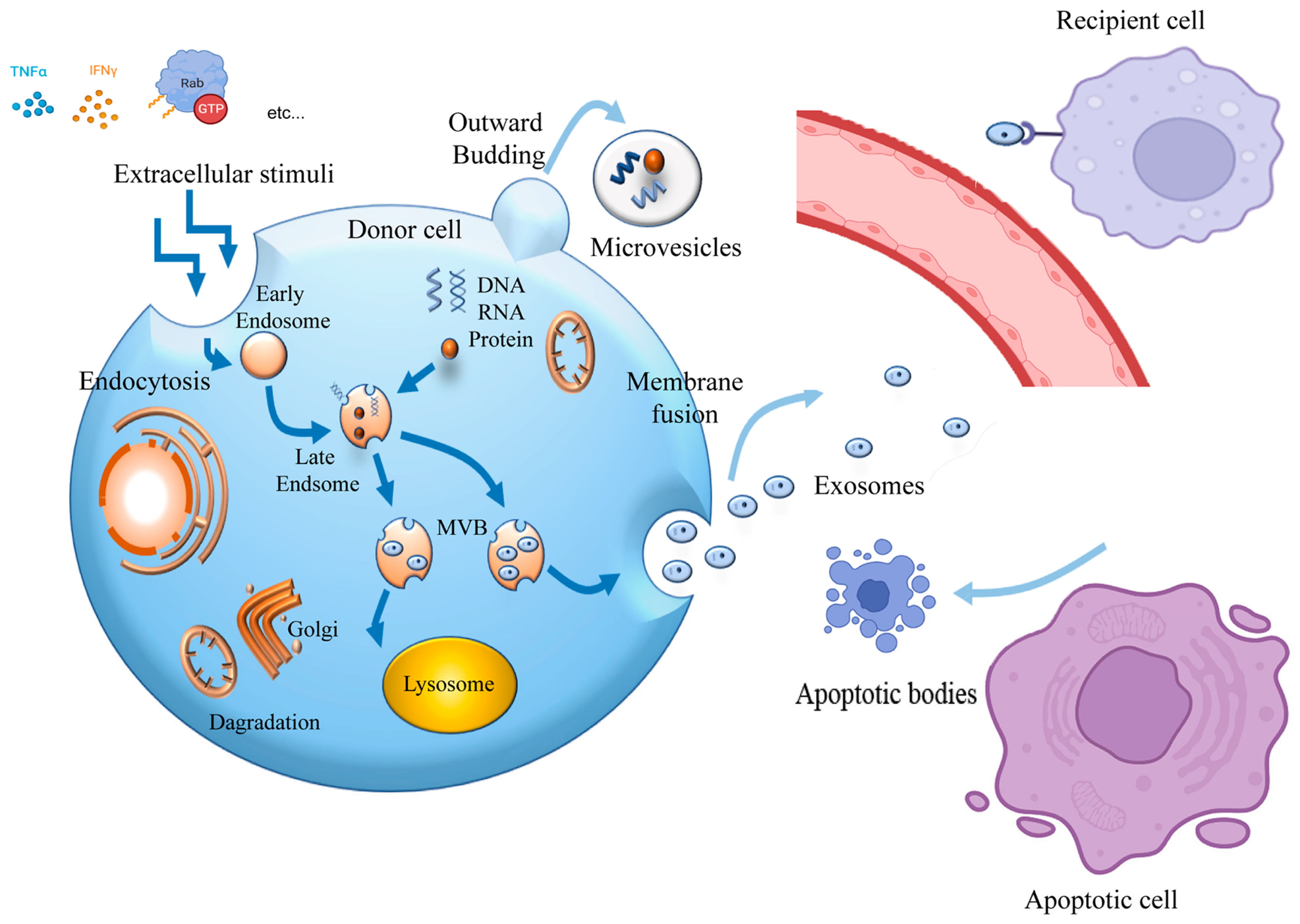
:1. Introduction
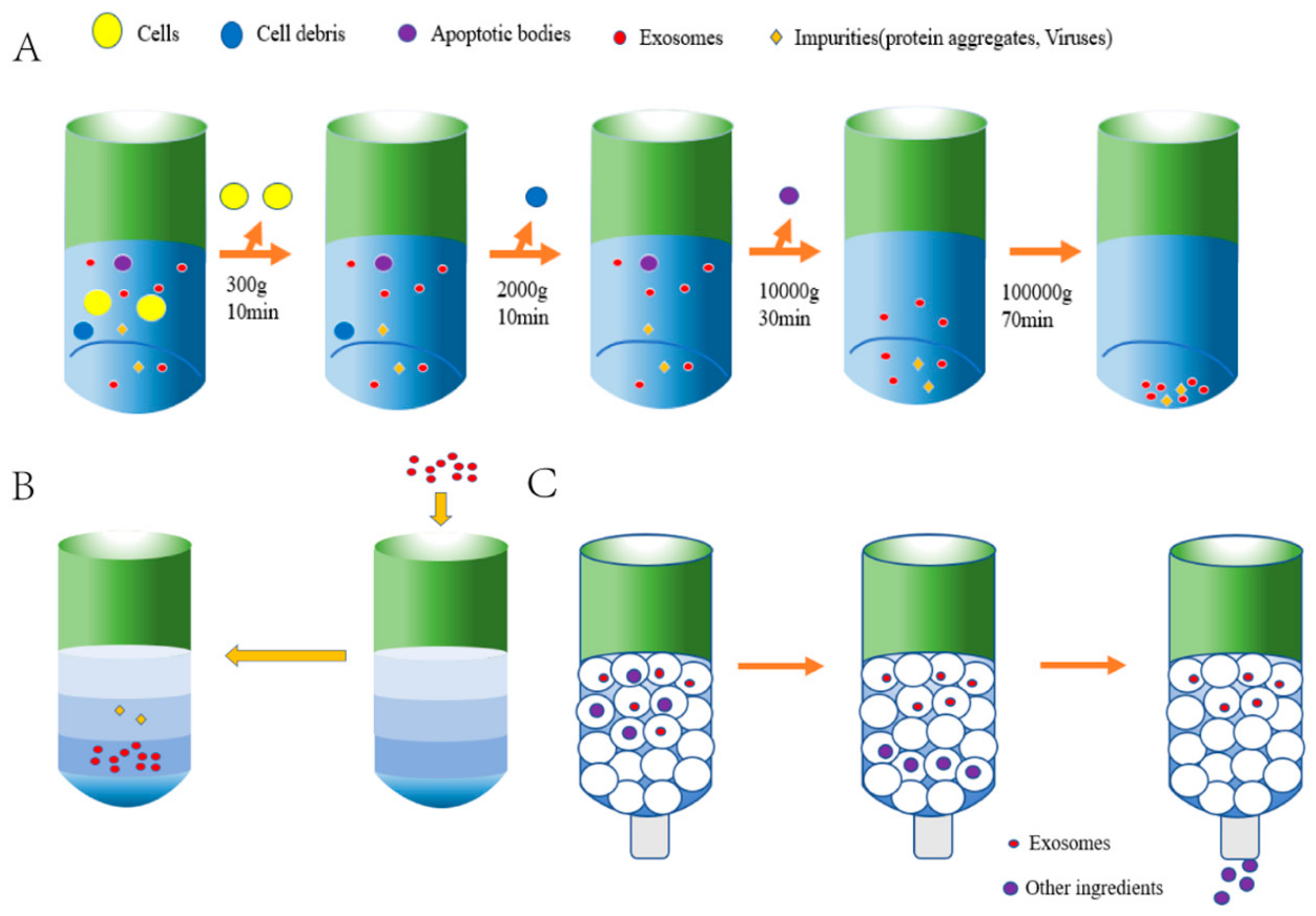
2. Isolation of sEVs from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
3. Drug Delivery of iPSC-sEVs in the Repair of Myocardial Injury
4. Mechanism of iPSC-sEVs in the Repair of Myocardial Injury
4.1. MI
4.2. MIRI
4.3. Coronary Heart Disease
4.4. HF
5. Challenges in the Treatment of CVD with IPSC-sEVs
6. Prospects and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kovacic, J.C.; Dimmeler, S.; Harvey, R.P.; Finkel, T.; Aikawa, E.; Krenning, G.; Baker, A.H. Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sureda, A.; Devkota, H.P.; Pittalà, V.; Barreca, D.; Silva, A.S.; Tewari, D.; Xu, S.; Nabavi, S.M. Curcumin, the golden spice in treating cardiovascular diseases. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 38, 107343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Du, L.; Wang, S.; Kong, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Du, G. Differences in the prevention and control of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, R.; Pattnaik, S.; Busi, S.; Nauli, S.M. Nanomaterials as Novel Cardiovascular Theranostics. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashvili, M.; Bosnjak, Z.J. Stem Cell Therapies in Cardiovascular Disease. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesthesia 2019, 33, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Inoue, H.; Wu, J.C.; Yamanaka, S. Induced pluripotent stem cell technology: A decade of progress. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Ikeya, M. Dental applications of induced pluripotent stem cells and their derivatives. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2022, 58, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deuse, T.; Hu, X.; Gravina, A.; Wang, D.; Tediashvili, G.; De, C.; Thayer, W.O.; Wahl, A.; Garcia, J.V.; Reichenspurner, H.; et al. Hypoimmunogenic derivatives of induced pluripotent stem cells evade immune rejection in fully immunocompetent allogeneic recipients. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doss, M.X.; Sachinidis, A. Current Challenges of iPSC-Based Disease Modeling and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2019, 8, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crow, D. Could iPSCs Enable "Off-the-Shelf" Cell Therapy? Cell 2019, 177, 1667–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Krishnamurthy, P.; Walcott, G.P.; Menasché, P.; Zhang, J. Exosomes secreted by hiPSC-derived cardiac cells improve recovery from myocardial infarction in swine. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Michowski, W.; Kolodziejczyk, A.; Sicinski, P. The cell cycle in stem cell proliferation, pluripotency and differentiation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Pol, E.; Böing, A.N.; Harrison, P.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veerman, R.E.; Teeuwen, L.; Czarnewski, P.; Güclüler Akpinar, G.; Sandberg, A.; Cao, X.; Pernemalm, M.; Orre, L.M.; Gabrielsson, S.; Eldh, M. Molecular evaluation of five different isolation methods for extracellular vesicles reveals different clinical applicability and subcellular origin. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.M.; Yellon, D.M. Exosomes and cardioprotection—A critical analysis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 60, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, M.; Kang, M.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Teng, L.; Qiu, L. Adult mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes: Sources, characteristics, and application in regenerative medicine. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 118002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi, Y.; Movassaghpour, A.; Zamani, M.; Talebi, M.; Mehdizadeh, A.; Yousefi, M. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived-exosomes in diseases treatment. Life Sci. 2019, 233, 116733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Chen, Y.; Shi, S.; Wen, H. Stem cell-derived and circulating exosomal microRNAs as new potential tools for diabetic nephropathy management. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiak, M.; Cheng, G.; Bobis-Wozowicz, S.; Zhao, L.; Kedracka-Krok, S.; Samanta, A.; Karnas, E.; Xuan, Y.T.; Skupien-Rabian, B.; Chen, X.; et al. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC)-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Are Safer and More Effective for Cardiac Repair Than iPSCs. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenson, B.H.; Hor, P.; Kaufman, D.S. iPSC-Derived Natural Killer Cell Therapies—Expansion and Targeting. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 841107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, J.; Anastasaki, C.; Chen, Z.; Shipman, T.; Papke, J.; Yin, K.; Gutmann, D.H.; Le, L.Q. Humanized neurofibroma model from induced pluripotent stem cells delineates tumor pathogenesis and developmental origins. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e139807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Greca, A.; Solari, C.; Furmento, V.; Lombardi, A.; Biani, M.C.; Aban, C.; Moro, L.; García, M.; Guberman, A.S.; Sevlever, G.E.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells acquire a stromal modulatory proteomic pattern during differentiation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.W.; Li, Q.; Niu, X.; Hu, B.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.M.; Guo, S.C.; Lang, H.L.; Zhang, C.Q.; Wang, Y.; et al. Exosomes secreted by human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate limb ischemia by promoting angiogenesis in mice. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, R.; Liu, Y.; Lu, M.; Ding, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Tian, X.; Lu, P.; Meng, D.; Sun, N.; et al. ALIX increases protein content and protective function of iPSC-derived exosomes. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzwald-Josefson, E.; Zeevi-Levin, N.; Rubchevsky, V.; Bechar Erdman, N.; Schwartz Rohaker, O.; Nahum, O.; Hochhauser, E.; Ben-Avraham, B.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Aravot, D.; et al. Cardiac Fibroblast-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as a Potential Therapeutic Mean for Heart Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzhrani, G.N.; Alanazi, S.T.; Alsharif, S.Y.; Albalawi, A.M.; Alsharif, A.A.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.S.; Elsherbiny, N. Exosomes: Isolation, characterization, and biomedical applications. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 1807–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandham, S.; Su, X.; Wood, J.; Nocera, A.L.; Alli, S.C.; Milane, L.; Zimmerman, A.; Amiji, M.; Ivanov, A.R. Technologies and Standardization in Research on Extracellular Vesicles. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1066–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.Y.; Sung, C.W.; Chen, C.; Cheng, C.M.; Lin, D.P.; Huang, C.T.; Hsu, M.Y. Advances in exosomes technology. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 493, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, K.; Minamisawa, T.; Suga, K.; Yajima, Y.; Shiba, K. Isolation of human salivary extracellular vesicles by iodixanol density gradient ultracentrifugation and their characterizations. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 30829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Böing, A.N.; van der Pol, E.; Grootemaat, A.E.; Coumans, F.A.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Single-step isolation of extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 23430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.N.; Yin, H. Polymer-Based Purification of Extracellular Vesicles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1660, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijerathne, H.; Witek, M.A.; Jackson, J.M.; Brown, V.; Hupert, M.L.; Herrera, K.; Kramer, C.; Davidow, A.E.; Li, Y.; Baird, A.E.; et al. Affinity enrichment of extracellular vesicles from plasma reveals mRNA changes associated with acute ischemic stroke. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Cheng, G.; Liu, X.; Hao, S.J.; Nisic, M.; Zhu, C.D.; Xia, Y.Q.; Li, W.Q.; Wang, Z.G.; Zhang, W.L.; et al. Rapid magnetic isolation of extracellular vesicles via lipid-based nanoprobes. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Zhao, X. Magnetic Soft Materials and Robots. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5317–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, N.; Nakamura, J.; Kaneda, T.; Tateno, H.; Shimoda, A.; Ichiki, T.; Furukawa, K.; Hirabayashi, J.; Akiyoshi, K.; Shiku, H. Distinguishing functional exosomes and other extracellular vesicles as a nucleic acid cargo by the anion-exchange method. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, J.Z.; Lee, Y.; Vader, P.; Mäger, I.; Johansson, H.J.; Heusermann, W.; Wiklander, O.P.; Hällbrink, M.; Seow, Y.; Bultema, J.J.; et al. Ultrafiltration with size-exclusion liquid chromatography for high yield isolation of extracellular vesicles preserving intact biophysical and functional properties. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staubach, S.; Bauer, F.N.; Tertel, T.; Börger, V.; Stambouli, O.; Salzig, D.; Giebel, B. Scaled preparation of extracellular vesicles from conditioned media. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 177, 113940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Sun, H.T.; Wang, S.; Huang, S.L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.Q.; Hu, B.Y.; Qin, W.; Zou, T.T.; Fu, Y.; et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes for cancer research. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Kalimuthu, S.; Gangadaran, P.; Oh, J.M.; Lee, H.W.; Baek, S.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.C. Exosomes Derived From Natural Killer Cells Exert Therapeutic Effect in Melanoma. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2732–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, P.; Kim, D.H.; Liu, B.F.; Demirci, U. Towards Microfluidic-Based Exosome Isolation and Detection for Tumor Therapy. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Tian, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Y. Exosomes from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived keratinocytes accelerate burn wound healing through miR-762 mediated promotion of keratinocytes and endothelial cells migration. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, M.; Bejoy, J.; Cheerathodi, M.R.; Sun, L.; York, S.B.; Zhao, J.; Kanekiyo, T.; Bu, G.; Meckes, D.G., Jr.; Li, Y. Differential Effects of Extracellular Vesicles of Lineage-Specific Human Pluripotent Stem Cells on the Cellular Behaviors of Isogenic Cortical Spheroids. Cells 2019, 8, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardiner, C.; Ferreira, Y.J.; Dragovic, R.A.; Redman, C.W.; Sargent, I.L. Extracellular vesicle sizing and enumeration by nanoparticle tracking analysis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 19671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobb, R.J.; Becker, M.; Wen, S.W.; Wong, C.S.; Wiegmans, A.P.; Leimgruber, A.; Möller, A. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Ishikawa, N.; Tatsuguchi, A.; Saichi, N.; Fujii, R.; Nakagawa, H. Antibody-coupled monolithic silica microtips for highthroughput molecular profiling of circulating exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pocsfalvi, G.; Stanly, C.; Vilasi, A.; Fiume, I.; Capasso, G.; Turiák, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Vékey, K. Mass spectrometry of extracellular vesicles. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rus Jacquet, A.; Tancredi, J.L.; Lemire, A.L.; DeSantis, M.C.; Li, W.P.; O’Shea, E.K. The LRRK2 G2019S mutation alters astrocyte-to-neuron communication via extracellular vesicles and induces neuron atrophy in a human iPSC-derived model of Parkinson’s disease. eLife 2021, 10, e73062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, J.M.; Barran, P.E.; Mackay, C.L.; Weidt, S.; Balmforth, C.; Walsh, T.S.; Chalmers, R.T.; Webb, D.J.; Dear, J.W. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human cerebrospinal fluid. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, R.; Du, L. Review on Strategies and Technologies for Exosome Isolation and Purification. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 811971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Zieren, R.C.; Horie, K.; Kim, C.J.; Mallick, E.; Jing, Y.; Feng, M.; Kuczler, M.D.; Green, J.; Amend, S.R.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of methods for small extracellular vesicles separation from human plasma, urine and cell culture medium. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 10, e12044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.Q.; Almughlliq, F.B.; Vaswani, K.; Peiris, H.N.; Mitchell, M.D. Exosome enrichment by ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2018, 23, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Yi, M.; Dong, B.; Tan, X.; Luo, S.; Wu, K. The role of exosomes in liquid biopsy for cancer diagnosis and prognosis prediction. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 2640–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Gu, J.; Xu, W.; Cai, H.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrop-Albrecht, E.J.; Taylor, W.R.; Huang, B.Q.; Kisiel, J.B.; Lucien, F. Assessment of extracellular vesicle isolation methods from human stool supernatant. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onódi, Z.; Pelyhe, C.; Terézia Nagy, C.; Brenner, G.B.; Almási, L.; Kittel, Á.; Manček-Keber, M.; Ferdinandy, P.; Buzás, E.I.; Giricz, Z. Isolation of High-Purity Extracellular Vesicles by the Combination of Iodixanol Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation and Bind-Elute Chromatography From Blood Plasma. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Gao, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, P.; Mao, L. Sizing Single Particles at the Orifice of a Nanopipette. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2351–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Lin, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; Wang, T.; Cui, Y. Establishment of a simplified dichotomic size-exclusion chromatography for isolating extracellular vesicles toward clinical applications. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, N.; Cvjetkovic, A.; Jang, S.C.; Crescitelli, R.; Hosseinpour Feizi, M.A.; Nieuwland, R.; Lötvall, J.; Lässer, C. Detailed analysis of the plasma extracellular vesicle proteome after separation from lipoproteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2873–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzner, D.; Schnaars, M.; van Rossum, D.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Dibaj, P.; Bakhti, M.; Regen, T.; Hanisch, U.K.; Simons, M. Selective transfer of exosomes from oligodendrocytes to microglia by macropinocytosis. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostrowski, M.; Carmo, N.B.; Krumeich, S.; Fanget, I.; Raposo, G.; Savina, A.; Moita, C.F.; Schauer, K.; Hume, A.N.; Freitas, R.P.; et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.; Morohashi, Y.; Yoshimura, S.; Manrique-Hoyos, N.; Jung, S.; Lauterbach, M.A.; Bakhti, M.; Grønborg, M.; Möbius, W.; Rhee, J.; et al. Regulation of exosome secretion by Rab35 and its GTPase-activating proteins TBC1D10A-C. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chutna, O.; Gonçalves, S.; Villar-Piqué, A.; Guerreiro, P.; Marijanovic, Z.; Mendes, T.; Ramalho, J.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Ventura, S.; Klucken, J.; et al. The small GTPase Rab11 co-localizes with α-synuclein in intracellular inclusions and modulates its aggregation, secretion and toxicity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 6732–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, B.H.; Ketova, T.; Hoshino, D.; Zijlstra, A.; Weaver, A.M. Directional cell movement through tissues is controlled by exosome secretion. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bobrie, A.; Krumeich, S.; Reyal, F.; Recchi, C.; Moita, L.F.; Seabra, M.C.; Ostrowski, M.; Théry, C. Rab27a supports exosome-dependent and -independent mechanisms that modify the tumor microenvironment and can promote tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4920–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.P.; Mardini, O.; Ericsson, M.; Prabhakar, S.; Maguire, C.; Chen, J.W.; Tannous, B.A.; Breakefield, X.O. Dynamic biodistribution of extracellular vesicles in vivo using a multimodal imaging reporter. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.P.; Kim, E.Y.; Badr, C.E.; Weissleder, R.; Mempel, T.R.; Tannous, B.A.; Breakefield, X.O. Visualization and tracking of tumour extracellular vesicle delivery and RNA translation using multiplexed reporters. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.; Peng, L.; Ming, X.; Wang, X.; Cui, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, D.; Sun, N.; Xiang, M.; et al. Enhanced wound healing promotion by immune response-free monkey autologous iPSCs and exosomes vs. their allogeneic counterparts. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Würdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendell, J.T. miRiad roles for the miR-17-92 cluster in development and disease. Cell 2008, 133, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, J.P.; Holme, M.N.; Stevens, M.M. Re-Engineering Extracellular Vesicles as Smart Nanoscale Therapeutics. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, R.; Liu, M.; Tan, T.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Men, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Xie, T.; et al. Emerging Significance and Therapeutic Potential of Extracellular vesicles. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2476–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xitong, D.; Xiaorong, Z. Targeted therapeutic delivery using engineered exosomes and its applications in cardiovascular diseases. Gene 2016, 575, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobis-Wozowicz, S.; Kmiotek, K.; Sekula, M.; Kedracka-Krok, S.; Kamycka, E.; Adamiak, M.; Jankowska, U.; Madetko-Talowska, A.; Sarna, M.; Bik-Multanowski, M.; et al. Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Microvesicles Transmit RNAs and Proteins to Recipient Mature Heart Cells Modulating Cell Fate and Behavior. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 2748–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, F.; Liu, W.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhu, B.; Yu, B. MiR-499 induces cardiac differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells through wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Ikeda, G.; Tada, Y.; von Bornstädt, D.; Santoso, M.R.; Wahlquist, C.; Rhee, S.; Jeon, Y.J.; Yu, A.C.; O’Brien, C.G.; et al. miR-106a-363 cluster in extracellular vesicles promotes endogenous myocardial repair via Notch3 pathway in ischemic heart injury. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2021, 116, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Gao, D.; Wang, P.; Lou, C.; Li, T.; Niu, W.; Gao, Y. Optimized culture methods for isolating small extracellular vesicles derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Li, Z.; Huang, K.; Caranasos, T.G.; Rossi, J.S.; Cheng, K. Minimally invasive delivery of therapeutic agents by hydrogel injection into the pericardial cavity for cardiac repair. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Qin, G.; He, S.H.; Zimmerman, A.; et al. Exosomes/microvesicles from induced pluripotent stem cells deliver cardioprotective miRNAs and prevent cardiomyocyte apoptosis in the ischemic myocardium. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 192, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeda, M.; Kanki, Y.; Masumoto, H.; Funakoshi, S.; Hatani, T.; Fukushima, H.; Izumi-Taguchi, A.; Matsui, Y.; Shimamura, T.; Yoshida, Y.; et al. Identification of Cardiomyocyte-Fated Progenitors from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Marked with CD82. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, B.W.; Ronan, G.; Ren, X.; Bahcecioglu, G.; Senapati, S.; Anderson, D.; Handberg, E.; March, K.L.; Chang, H.C.; Zorlutuna, P. Human Heart Anoxia and Reperfusion Tissue (HEART) Model for the Rapid Study of Exosome Bound miRNA Expression As Biomarkers for Myocardial Infarction. Small 2022, 18, e2201330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Sucharov, J.; Stauffer, B.L.; Miyamoto, S.D.; Sucharov, C.C. Exosomes from pediatric dilated cardiomyopathy patients modulate a pathological response in cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H818–H826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Aggarwal, P.; Matter, A.; Olson, B.; Gu, C.C.; Hunt, S.C.; Lewis, C.E.; Arnett, D.K.; Lorier, R.; Broeckel, U. Donor-specific phenotypic variation in hiPSC cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes impacts endothelial cell function. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2021, 320, H954–H968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Ivey, K.N. Potential of stem-cell-based therapies for heart disease. Nature 2006, 441, 1097–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartz, M.; Darlington, A.; Afzal, M.Z.; Strande, J.L. Exosomes exert cardioprotection in dystrophin-deficient cardiomyocytes via ERK1/2-p38/MAPK signaling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.H.; Chen, W.Y.; Shao, N.Y.; Xiao, D.; Qin, X.; Baker, N.; Bae, H.R.; Wei, T.T.; Wang, Y.; Shukla, P.; et al. Comparison of Non-Coding RNAs in Exosomes and Functional Efficacy of Human Embryonic Stem Cell- versus Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 2138–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Li, C.; Luo, H.; Xue, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chen, C. Exosomes from human induced pluripotent stem cells derived mesenchymal stem cells improved myocardial injury caused by severe acute pancreatitis through activating Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 axis. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guan, J.; Niu, X.; Hu, G.; Guo, S.; Li, Q.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Exosomes released from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived MSCs facilitate cutaneous wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Harane, N.; Kervadec, A.; Bellamy, V.; Pidial, L.; Neametalla, H.J.; Perier, M.-C.; Lima Correa, B.; Thiébault, L.; Cagnard, N.; Duché, A.; et al. Acellular therapeutic approach for heart failure: In vitro production of extracellular vesicles from human cardiovascular progenitors. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1835–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayourian, J.; Ceholski, D.K.; Gorski, P.A.; Mathiyalagan, P.; Murphy, J.F.; Salazar, S.I.; Stillitano, F.; Hare, J.M.; Sahoo, S.; Hajjar, R.J.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-21-5p Mediates Mesenchymal Stem Cell Paracrine Effects on Human Cardiac Tissue Contractility. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Fu, X.; Yang, P.C. Exosomes Generated From iPSC-Derivatives: New Direction for Stem Cell Therapy in Human Heart Diseases. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Li, D.; Chen, X.; Han, C.; Xu, L.; Huang, T.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, M. Extracellular vesicles from human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (hiPSC-MSCs) protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via delivering specificity protein (SP1) and transcriptional activating of sphingosine kinase 1 and inhibiting necroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dougherty, J.A.; Kumar, N.; Noor, M.; Angelos, M.G.; Khan, M.; Chen, C.A.; Khan, M. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Human Induced-Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes Promote Angiogenesis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zununi Vahed, S.; Barzegari, A.; Zuluaga, M.; Letourneur, D.; Pavon-Djavid, G. Myocardial infarction and gut microbiota: An incidental connection. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 129, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Nakada, Y.; Wei, Y.; Bian, W.; Chu, Y.; Borovjagin, A.V.; Xie, M.; Zhu, W.; Nguyen, T.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Cyclin D2 Overexpression Enhances the Efficacy of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes for Myocardial Repair in a Swine Model of Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2021, 144, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, J.; Rai, A.; Lees, J.G.; Fang, H.; Claridge, B.; Lim, S.Y.; Greening, D.W. Scalable Generation of Nanovesicles from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Cardiac Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Zhang, Y.; Buikema, J.W.; Serpooshan, V.; Chirikian, O.; Kosaric, N.; Churko, J.M.; Dzilic, E.; Shieh, A.; Burridge, P.W.; et al. Stage-specific Effects of Bioactive Lipids on Human iPSC Cardiac Differentiation and Cardiomyocyte Proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Gregorich, Z.R.; Zhu, W.; Mattapally, S.; Oduk, Y.; Lou, X.; Kannappan, R.; Borovjagin, A.V.; Walcott, G.P.; Pollard, A.E.; et al. Large Cardiac Muscle Patches Engineered From Human Induced-Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiac Cells Improve Recovery From Myocardial Infarction in Swine. Circulation 2018, 137, 1712–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.G.; Cheng, K.; Marbán, E. Exosomes as critical agents of cardiac regeneration triggered by cell therapy. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 2, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Ha, T.; Liu, L.; Zou, J.; Zhang, X.; Kalbfleisch, J.; Gao, X.; Williams, D.; Li, C. Increased expression of microRNA-146a decreases myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 97, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Liew, O.W.; Richards, A.M.; Chen, Y.T. Overview of MicroRNAs in Cardiac Hypertrophy, Fibrosis, and Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Fan, G.C. Extracellular/circulating microRNAs and their potential role in cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 1, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Tian, S.S.; Hang, P.Z.; Sun, C.; Guo, J.; Du, Z.M. Combination of microRNA-21 and microRNA-146a Attenuates Cardiac Dysfunction and Apoptosis During Acute Myocardial Infarction in Mice. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.H.; Wang, S.P.H.; Gao, Z.H.; Wu, S.N.; Chang, H.Y.; Yang, P.J.; Liu, P.Y.; Liu, Y.W. Efficient Cardiac Differentiation of Human Amniotic Fluid-Derived Stem Cells into Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Their Potential Immune Privilege. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taheri, B.; Soleimani, M.; Fekri Aval, S.; Esmaeili, E.; Bazi, Z.; Zarghami, N. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A novel approach for cell-free regenerative medicine. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8455–8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deanfield, J.E.; Halcox, J.P.; Rabelink, T.J. Endothelial function and dysfunction: Testing and clinical relevance. Circulation 2007, 115, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Feinberg, M.W. Regulation of endothelial cell metabolism: Just go with the flow. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jouda, H.; Larrea Murillo, L.; Wang, T. Current Progress in Vascular Engineering and Its Clinical Applications. Cells 2022, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rooij, E.; Olson, E.N. MicroRNA therapeutics for cardiovascular disease: Opportunities and obstacles. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Couto, G.; Gallet, R.; Cambier, L.; Jaghatspanyan, E.; Makkar, N.; Dawkins, J.F.; Berman, B.P.; Marbán, E. Exosomal MicroRNA Transfer Into Macrophages Mediates Cellular Postconditioning. Circulation 2017, 136, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Han, Z.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cai, B.; Yuan, Y. Potential Applications of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Godoy, M.A.; Saraiva, L.M.; de Carvalho, L.R.P.; Vasconcelos-Dos-Santos, A.; Beiral, H.J.V.; Ramos, A.B.; Silva, L.R.P.; Leal, R.B.; Monteiro, V.H.S.; Braga, C.V.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and cell-derived extracellular vesicles protect hippocampal neurons from oxidative stress and synapse damage induced by amyloid-β oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 1957–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, Q.; Sun, R.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, M.; Meng, D.; Sun, N.; Chen, A.F.; Chen, S. Protective effects of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived exosomes on high glucose-induced injury in human endothelial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 4791–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.; Krishnakumar, V.; Soni, N.; Rao, E.P.; Banerjee, A.; Mohanty, S. Comparative proteomic profiling of Small Extracellular vesicles derived from iPSCs and tissue specific mesenchymal stem cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 420, 113354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, M.M.; Cancemi, P.; Geraci, F. Mesenchymal and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: The New Frontier for Regenerative Medicine? Cells 2020, 9, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.A. Current status of cardiac transplantation. JAMA 1998, 280, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, C.; Gao, L.; Zucker, I.H. Regulation of Nrf2 signaling pathway in heart failure: Role of extracellular vesicles and non-coding RNAs. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 167, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Hu, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H.; Huang, K.; Li, Z.; Su, T.; Vandergriff, A.; Tang, J.; et al. microRNA-21-5p dysregulation in exosomes derived from heart failure patients impairs regenerative potential. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2237–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bär, C.; Chatterjee, S.; Falcão Pires, I.; Rodrigues, P.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; Boon, R.A.; Nevado, R.M.; Andrés, V.; Sansonetti, M.; de Windt, L.; et al. Non-coding RNAs: Update on mechanisms and therapeutic targets from the ESC Working Groups of Myocardial Function and Cellular Biology of the Heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1805–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viereck, J.; Bührke, A.; Foinquinos, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Kleeberger, J.A.; Xiao, K.; Janssen-Peters, H.; Batkai, S.; Ramanujam, D.; Kraft, T.; et al. Targeting muscle-enriched long non-coding RNA H19 reverses pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3462–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.R.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhong, Y.N.; Che, T.T.; Hu, Y.; Bao, J.; Meng, N. Protective Effect of Flavonoids from a Deep-Sea-Derived Arthrinium sp. against ox-LDL-Induced Oxidative Injury through Activating the AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnas, E.; Sekuła-Stryjewska, M.; Kmiotek-Wasylewska, K.; Bobis-Wozowicz, S.; Ryszawy, D.; Sarna, M.; Madeja, Z.; Zuba-Surma, E.K. Extracellular vesicles from human iPSCs enhance reconstitution capacity of cord blood-derived hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2964–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhya, R.; Madhu, L.N.; Rao, S.; Shetty, A.K. Proficiency of Extracellular Vesicles From hiPSC-Derived Neural Stem Cells in Modulating Proinflammatory Human Microglia: Role of Pentraxin-3 and miRNA-21-5p. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 845542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandy, M.; Rhee, J.W.; Ozen, M.O.; Williams, D.R.; Pepic, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Malisa, J.; Lau, E.; Demirci, U.; et al. Atlas of Exosomal microRNAs Secreted From Human iPSC-Derived Cardiac Cell Types. Circulation 2020, 142, 1794–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goversen, B.; van der Heyden, M.A.G.; van Veen, T.A.B.; de Boer, T.P. The immature electrophysiological phenotype of iPSC-CMs still hampers in vitro drug screening: Special focus on I(K1). Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 183, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaldson-Bouchard, K.; Ma, S.P.; Yeager, K.; Chen, T.; Song, L.; Sirabella, D.; Morikawa, K.; Teles, D.; Yazawa, M.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G. Advanced maturation of human cardiac tissue grown from pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2018, 556, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbassi, E.; Fenix, A.; Marchiano, S.; Muraoka, N.; Nakamura, K.; Yang, X.; Murry, C.E. Cardiomyocyte maturation: Advances in knowledge and implications for regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.; Boheler, K.R.; Li, R.A. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes for heart regeneration, drug discovery and disease modeling: From the genetic, epigenetic, and tissue modeling perspectives. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollý, D.; Klein, M.; Mazreku, M.; Zamborský, R.; Polák, Š.; Danišovič, Ľ.; Csöbönyeiová, M. Stem Cells and Their Derivatives-Implications for Alveolar Bone Regeneration: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Bai, X.; Fei, Q.; Zhang, L. Rapid human-derived iPSC osteogenesis combined with three-dimensionally printed Ti6Al4V scaffolds for the repair of bone defects. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 9763–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bec, N.; Bonhoure, A.; Henry, L.; Berry, L.; Larroque, C.; Coux, O.; Stoebner, P.E.; Vidal, M. Proteasome 19S RP and translation preinitiation complexes are secreted within exosomes upon serum starvation. Traffic 2019, 20, 516–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bister, N.; Pistono, C.; Huremagic, B.; Jolkkonen, J.; Giugno, R.; Malm, T. Hypoxia and extracellular vesicles: A review on methods, vesicular cargo and functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 10, e12002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachlas, A.L.Y.; Li, S.; Jha, R.; Singh, M.; Xu, C.; Davis, M.E. Human iPSC-derived mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in PEGDA hydrogels mature into valve interstitial-like cells. Acta Biomater. 2018, 71, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.; Shapira, A.; Edri, R.; Gal, I.; Wertheim, L.; Dvir, T. 3D Printing of Personalized Thick and Perfusable Cardiac Patches and Hearts. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabei, R.; Kawaguchi, S.; Kanazawa, H.; Tohyama, S.; Hirano, A.; Handa, N.; Hishikawa, S.; Teratani, T.; Kunita, S.; Fukuda, J.; et al. Development of a transplant injection device for optimal distribution and retention of human induced pluripotent stem cell–derived cardiomyocytes. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q.; Niu, X.; Hu, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Exosomes Secreted by Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Critical-Sized Bone Defects through Enhanced Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xiao, Z. Visualizing of the cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of exosomes by live-cell microscopy. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 111, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Zhao, W.L.; Ye, Y.Y.; Bai, X.C.; Liu, R.Q.; Chang, L.F.; Zhou, Q.; Sui, S.F. Cellular internalization of exosomes occurs through phagocytosis. Traffic 2010, 11, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xue, R.; Huang, P.; Wu, Y.; Fan, W.; He, X.; Dong, Y.; Liu, C. Modified Exosomes: A Good Transporter for miRNAs within Stem Cells to Treat Ischemic Heart Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2022, 15, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, F.; Ström, S.; Inzunza, J.; Baker, D.; Strömberg, A.M.; Rozell, B.; Feki, A.; Bergström, R.; Hovatta, O. An effective serum- and xeno-free chemically defined freezing procedure for human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Jehuda, R.; Shemer, Y.; Binah, O. Genome Editing in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells using CRISPR/Cas9. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2018, 14, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockemeyer, D.; Jaenisch, R. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Meet Genome Editing. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Wang, B.; Ono, M.; Kagita, A.; Fujii, K.; Sasakawa, N.; Ueda, T.; Gee, P.; Nishikawa, M.; Nomura, M.; et al. Targeted Disruption of HLA Genes via CRISPR-Cas9 Generates iPSCs with Enhanced Immune Compatibility. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 566–578.e567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeedi, S.; Israel, S.; Nagy, C.; Turecki, G. The emerging role of exosomes in mental disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Feng, R.; Fu, Q.; Xu, S.; Hao, X.; Qiu, Y.; Feng, T.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote healing via TNF-α-stimulated gene-6 in inflammatory bowel disease models. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Workman, M.J.; Troisi, E.; Targan, S.R.; Svendsen, C.N.; Barrett, R.J. Modeling Intestinal Epithelial Response to Interferon-γ in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Intestinal Organoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Mo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, B.; Liao, Q.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Xiong, W.; Li, G.; et al. Chronic Stress Promotes Cancer Development. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckerling, A.; Ricon-Becker, I.; Sorski, L.; Sandbank, E.; Ben-Eliyahu, S. Stress and cancer: Mechanisms, significance and future directions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 767–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M. Therapeutics targeting angiogenesis: Genetics and epigenetics, extracellular miRNAs and signaling networks (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Xia, P.; Cui, X.; Bai, X.; Lu, Z. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of exosomes in prostate cancer. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, J.C.; Hand, G.R.; Briner, A.; Li, C.; Götz, J. Exosomes induce endolysosomal permeabilization as a gateway by which exosomal tau seeds escape into the cytosol. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, B.; Lim, H.G. Exosomes and ultrasound: The future of theranostic applications. Mater. Today. Bio 2023, 19, 100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Lee, C.S.; Kim, S.; Chen, C.; Aghaloo, T.; Lee, M. Generation of Small RNA-Modulated Exosome Mimetics for Bone Regeneration. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 11973–11984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cell Sources | Characterization | Models | Therapeutic Effects | Cargos | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miPSCs | TEM | MI | Mitigate cardiac remodeling and improve cardiac functions post myocardial infarction | [81] | |
| miPSCs | WB (CD63, Tsg101) | MIRI | Prevent cardiomyocyte apoptosis in ischemic myocardium | miR21, HIF-1α-regulated miR210 | [82] |
| miPSCs | EM, FCM, RT-PCR | MIRI | Improve LV function and enhance angiogenesis | global miRNA and proteomic profiling performed | [21] |
| hiPSCs | FCM, BCA | MI | Reduce fibrosis in infarcted mice hearts | CD82 | [83] |
| hiPSCs | TEM, NTA | MI | Facilitate cardiac repair through circulating miRNAs | circulating miRNAs | [84] |
| hiPSCs | NTA, WB (CD63) | HF | Involved in the remodeling process and observed in primary cardiomyocytes | miRNA mRNA | [85] |
| hiPSCs | TEM, WB (CD63, CD9) | Endothelial cell in vitro | Improve cardiac function and repair | miRNA | [86] |
| hiPSCs | TEM, NTA | H9c2 in vitro | Protect against oxidative-stress-induced apoptosis | miRNA | [87] |
| hiCMs | WB (CD63, CD81) | Dys-iCMs In vitro | Decrease reactive oxygen species and delay mitochondrial permeability | [88] | |
| hiCMs | TEM, WB (CD63, CD81) | MI | Facilitate cardiac repair and avoid immune rejection | miRNA, LncRNA | [89] |
| hiCMs | WB (CD81, CD63, flotillin-1, TSTG101) | MI | Improve recovery from myocardial infarction in swine | [12] | |
| hiMSCs | EM, NanoFCM | MI | Promote cell viability through activating the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 axis and improve cardiac function | [90] | |
| hiMSCs | TEM, immunoblot | Rat skin wound model | Promote collagen synthesis and angiogenesis | [91] | |
| hiMSCs | EM, NTA | HF | Improve cardiac function and increased EF relative to baseline values | miRNA | [92] |
| hiMSCs | TEM, NTA, RT-PCR | Ischemic Adult Human Cardiomyocytes | Alter cardiac tissue-level remodeling | miR21-5p | [93] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, W.-T.; Guo, H.-D. Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in the Treatment of Myocardial Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054577
Meng W-T, Guo H-D. Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in the Treatment of Myocardial Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054577
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Wan-Ting, and Hai-Dong Guo. 2023. "Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in the Treatment of Myocardial Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054577
APA StyleMeng, W.-T., & Guo, H.-D. (2023). Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in the Treatment of Myocardial Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4577. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054577






