Cytokines in Spondyloarthritis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Epidemiology and Classification
1.2. Overview on Pathogenesis
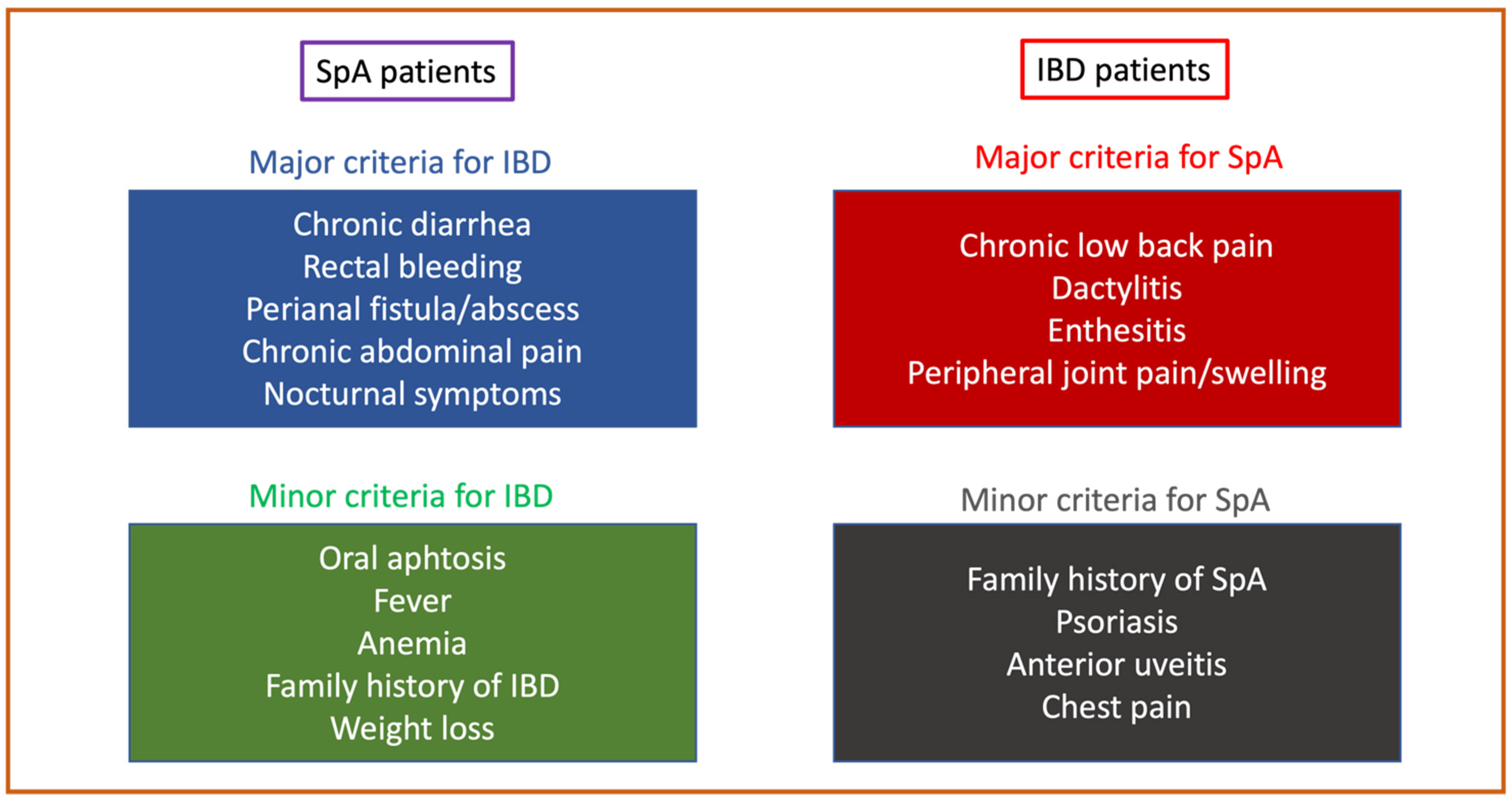
1.3. Principles of Diagnosis
2. Cytokines in Spondyloarthritis
3. Cytokines in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
4. Cytokine-Based Therapeutic Scenarios in IBD and SpA
5. Dual Targeted Therapy
| Reference | Year | Disease | N Patients | Combination | Control Arm | Outcome | Safety | Follow-up (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sands et al. [97] | 2007 | CD | 79 | Natalizumab + infliximab | Infliximab monotherapy | Safety | No differences in AEs | 10 weeks |
| Sands et al. [98] | 2022 | UC | 214 | Guselkumab + golimumab | Guselkumab or golimumab monotherapy | Clinical response (Mayo score) at week 12 | No differences in AEs | 3 |
| Genovese et al. [91] | 2004 | RA | 242 | Etanercept + anakinra | Etanercept monotherapy | ACR 50 at week 24 | Increased rate of AEs in combo therapy | 6 |
| Weinblatt et al. [101,102] | 2006 | RA | 167 | Abatacept + TNFi abatacept + anakinra | TNFi or anakinra monotherapy | Safety | Increased rate of AEs in combo therapy | 12 |
| Weinblatt et al. [102] | 2007 | RA | 121 | Abatacept + etanercept | Etanercept monotherapy | ACR 20 at 6 months | Increased rate of AEs in combo therapy | 12 |
| Blank et al. [103] | 2009 | RA | 18 | Rituximab + etanercept | Rituximab monotherapy | Safety | No differences in AEs | 8 |
| Greenwald et al. [104] | 2011 | RA | 51 | TNFi + rituximab | TNFi monotherapy | Safety | No differences in AEs | 6 |
| Glatt et al. [105] | 2019 | RA | 79 | Certolizumab + bimekizumab (anti-IL-17A and IL-17F) | Certolizumab monotherapy | DAS28 (CRP) and safety | Increased rate of AEs in combo therapy | 4 |
| Genovese et al. [92] | 2018 | RA | 222 | ABT-122 (dual TNF and IL-17A inhibitor) | Adalimumab | ACR20 at week 12 | No differences in AEs | 3 |
| NCT00845832 [106] | 2013 | RA | 24 | Rituximab + tocilizumab | Tocilizumab monotherapy | LDA at week 16 | No differences in AEs | 12 |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stolwijk, C.; van Onna, M.; Boonen, A.; van Tubergen, A. Global Prevalence of Spondyloarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, G.G.; Windsor, J.W. The four epidemiological stages in the global evolution of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coward, S.; Clement, F.; Benchimol, E.I.; Bernstein, C.N.; Avina-Zubieta, J.A.; Bitton, A.; Carroll, M.W.; Hazlewood, G.; Jacobson, K.; Jelinski, S.; et al. Past and Future Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Based on Modeling of Population-Based Data. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1345–1353 e1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karreman, M.C.; Luime, J.J.; Hazes, J.M.W.; Weel, A. The Prevalence and Incidence of Axial and Peripheral Spondyloarthritis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, C.; Pugliese, D.; Papparella, L.G.; Pizzolante, F.; Onori, E.; Gasbarrini, A.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Guidi, L.; Armuzzi, A. Clinical management of rheumatologic conditions co-occurring with inflammatory bowel diseases. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, C.; Leccese, P.; Scudeller, L.; Lubrano, E.; Cantini, F.; Castiglione, F.; Gionchetti, P.; Orlando, A.; Salvarani, C.; Scarpa, R.; et al. Red flags for appropriate referral to the gastroenterologist and the rheumatologist of patients with inflammatory bowel disease and spondyloarthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 196, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armuzzi, A.; Felice, C.; Lubrano, E.; Cantini, F.; Castiglione, F.; Gionchetti, P.; Orlando, A.; Salvarani, C.; Scarpa, R.; Marchesoni, A.; et al. Multidisciplinary management of patients with coexisting inflammatory bowel disease and spondyloarthritis: A Delphi consensus among Italian experts. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, I.; Cantini, F.; Castiglione, F.; Felice, C.; Gionchetti, P.; Orlando, A.; Salvarani, C.; Scarpa, R.; Vecchi, M.; Armuzzi, A. Italian Expert Panel on the management of patients with coexisting spondyloarthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudwaleit, M.; van der Heijde, D.; Landewe, R.; Akkoc, N.; Brandt, J.; Chou, C.T.; Dougados, M.; Huang, F.; Gu, J.; Kirazli, Y.; et al. The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for peripheral spondyloarthritis and for spondyloarthritis in general. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.F.; Bungau, S.G. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Cells 2021, 10, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, E.R.; Hong, S.N.; Chang, D.K.; Yang, M.; Kim, S.; Shin, M.H.; Kim, Y.H. Comorbid immune-mediated diseases in inflammatory bowel disease: A nation-wide population-based study. Aliment. Pharm. 2019, 49, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisinger, C.; Freuer, D. Rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 55, 151992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinghaus, D.; Jostins, L.; Spain, S.L.; Cortes, A.; Bethune, J.; Han, B.; Park, Y.R.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Pouget, J.G.; Hubenthal, M.; et al. Analysis of five chronic inflammatory diseases identifies 27 new associations and highlights disease-specific patterns at shared loci. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zundler, S.; Gunther, C.; Kremer, A.E.; Zaiss, M.M.; Rothhammer, V.; Neurath, M.F. Gut immune cell trafficking: Inter-organ communication and immune-mediated inflammation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Pile, K.D.; Kennedy, L.G.; Calin, A.; Darke, C.; Bell, J.; Wordsworth, B.P.; Cornelis, F. HLA class I associations of ankylosing spondylitis in the white population in the United Kingdom. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1996, 55, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reveille, J.D. Genetics of spondyloarthritis--beyond the MHC. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmi, M.; Jalkanen, S. Human leukocyte subpopulations from inflamed gut bind to joint vasculature using distinct sets of adhesion molecules. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4650–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Rizzo, A.; Alessandro, R.; Luchetti, M.M.; Milling, S.; Saieva, L.; Cypers, H.; Stampone, T.; Di Benedetto, P.; et al. Dysbiosis and zonulin upregulation alter gut epithelial and vascular barriers in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracey, E.; Vereecke, L.; McGovern, D.; Frohling, M.; Schett, G.; Danese, S.; De Vos, M.; Van den Bosch, F.; Elewaut, D. Publisher Correction: Revisiting the gut-joint axis: Links between gut inflammation and spondyloarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leirisalo-Repo, M.; Turunen, U.; Stenman, S.; Helenius, P.; Seppala, K. High frequency of silent inflammatory bowel disease in spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, M.; Sternes, P.R.; Costello, M.E.; Karstens, L.; Diamond, S.; Martin, T.M.; Li, Z.; Marshall, M.S.; Spector, T.D.; le Cao, K.A.; et al. HLA Alleles Associated With Risk of Ankylosing Spondylitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Influence the Gut Microbiome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, F.M.; Vesa, C.M.; Gheorghe, G.; Diaconu, C.C.; Stoicescu, M.; Munteanu, M.A.; Babes, E.E.; Tit, D.M.; Toma, M.M.; Bungau, S. Highlighting the Relevance of Gut Microbiota Manipulation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, Y.; Takeda, K. Host-microbiota interactions in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breban, M.; Tap, J.; Leboime, A.; Said-Nahal, R.; Langella, P.; Chiocchia, G.; Furet, J.P.; Sokol, H. Faecal microbiota study reveals specific dysbiosis in spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, T.; Asquith, M.; Brooks, S.R.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Colbert, R.A. Effects of HLA-B27 on Gut Microbiota in Experimental Spondyloarthritis Implicate an Ecological Model of Dysbiosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, J.U.; Ubeda, C.; Artacho, A.; Attur, M.; Isaac, S.; Reddy, S.M.; Marmon, S.; Neimann, A.; Brusca, S.; Patel, T.; et al. Decreased bacterial diversity characterizes the altered gut microbiota in patients with psoriatic arthritis, resembling dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacquard-Bouder, C.; Ittah, M.; Breban, M. Animal models of HLA-B27-associated diseases: New outcomes. Jt. Bone Spine 2006, 73, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragsnaes, M.S.; Kjeldsen, J.; Horn, H.C.; Munk, H.L.; Pedersen, J.K.; Just, S.A.; Ahlquist, P.; Pedersen, F.M.; de Wit, M.; Moller, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of faecal microbiota transplantation for active peripheral psoriatic arthritis: An exploratory randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schett, G.; McInnes, I.B.; Neurath, M.F. Reframing Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaser, C.; Sturm, A.; Vavricka, S.R.; Kucharzik, T.; Fiorino, G.; Annese, V.; Calabrese, E.; Baumgart, D.C.; Bettenworth, D.; Borralho Nunes, P.; et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglione, F.; Mainenti, P.P.; De Palma, G.D.; Testa, A.; Bucci, L.; Pesce, G.; Camera, L.; Diaferia, M.; Rea, M.; Caporaso, N.; et al. Noninvasive diagnosis of small bowel Crohn’s disease: Direct comparison of bowel sonography and magnetic resonance enterography. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cope, A.P.; Aderka, D.; Doherty, M.; Engelmann, H.; Gibbons, D.; Jones, A.C.; Brennan, F.M.; Maini, R.N.; Wallach, D.; Feldmann, M. Increased levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in the sera and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1992, 35, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, F.M.; Chantry, D.; Jackson, A.; Maini, R.; Feldmann, M. Inhibitory effect of TNF alpha antibodies on synovial cell interleukin-1 production in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1989, 2, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleuran, B.W.; Chu, C.Q.; Field, M.; Brennan, F.M.; Mitchell, T.; Feldmann, M.; Maini, R.N. Localization of tumor necrosis factor receptors in the synovial tissue and cartilage-pannus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Implications for local actions of tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1992, 35, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breedveld, F.C.; Emery, P.; Keystone, E.; Patel, K.; Furst, D.E.; Kalden, J.R.; St Clair, E.W.; Weisman, M.; Smolen, J.; Lipsky, P.E.; et al. Infliximab in active early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, K.; Sato, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Aizaki, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Sekikawa, M.; Kozu, N.; Kadono, Y.; Oda, H.; Mimura, T. Characterization and Function of Tumor Necrosis Factor and Interleukin-6-Induced Osteoclasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gengenbacher, M.; Sebald, H.J.; Villiger, P.M.; Hofstetter, W.; Seitz, M. Infliximab inhibits bone resorption by circulating osteoclast precursor cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambre, I.; Gaublomme, D.; Burssens, A.; Jacques, P.; Schryvers, N.; De Muynck, A.; Meuris, L.; Lambrecht, S.; Carter, S.; de Bleser, P.; et al. Mechanical strain determines the site-specific localization of inflammation and tissue damage in arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watad, A.; Rowe, H.; Russell, T.; Zhou, Q.; Anderson, L.K.; Khan, A.; Dunsmuir, R.; Loughenbury, P.; Borse, V.; Rao, A.; et al. Normal human enthesis harbours conventional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells with regulatory features and inducible IL-17A and TNF expression. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lories, R.J.; Derese, I.; Luyten, F.P. Modulation of bone morphogenetic protein signaling inhibits the onset and progression of ankylosing enthesitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, F.; Natura, G.; Ebbinghaus, M.; von Banchet, G.S.; Hensellek, S.; Konig, C.; Brauer, R.; Schaible, H.G. Interleukin-17 sensitizes joint nociceptors to mechanical stimuli and contributes to arthritic pain through neuronal interleukin-17 receptors in rodents. Arthritis. Rheum. 2012, 64, 4125–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeten, D.; Sieper, J.; Braun, J.; Baraliakos, X.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Deodhar, A.; Porter, B.; Martin, R.; Andersson, M.; et al. Secukinumab, an Interleukin-17A Inhibitor, in Ankylosing Spondylitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2534–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougados, M.; Wei, J.C.; Landewe, R.; Sieper, J.; Baraliakos, X.; Van den Bosch, F.; Maksymowych, W.P.; Ermann, J.; Walsh, J.A.; Tomita, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab through 52 weeks in two phase 3, randomised, controlled clinical trials in patients with active radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (COAST-V and COAST-W). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Mease, P.J.; Kirkham, B.; Kavanaugh, A.; Ritchlin, C.T.; Rahman, P.; van der Heijde, D.; Landewe, R.; Conaghan, P.G.; Gottlieb, A.B.; et al. Secukinumab, a human anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriatic arthritis (FUTURE 2): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heijde, D.; Gladman, D.D.; Kishimoto, M.; Okada, M.; Rathmann, S.S.; Moriarty, S.R.; Shuler, C.L.; Carlier, H.; Benichou, O.; Mease, P.J. Efficacy and Safety of Ixekizumab in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: 52-week Results from a Phase III Study (SPIRIT-P1). J. Rheumatol. 2018, 45, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Kavanaugh, A.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Puig, L.; Rahman, P.; Ritchlin, C.; Brodmerkel, C.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Mendelsohn, A.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab in patients with active psoriatic arthritis: 1 year results of the phase 3, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled PSUMMIT 1 trial. Lancet 2013, 382, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deodhar, A.; Gensler, L.S.; Sieper, J.; Clark, M.; Calderon, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Leu, J.H.; Campbell, K.; Sweet, K.; et al. Three Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Ustekinumab in Axial Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestein, G.S.; Alvaro-Gracia, J.M.; Maki, R. Quantitative analysis of cytokine gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 1990, 144, 3347–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Beaulieu, A.; Rubbert-Roth, A.; Ramos-Remus, C.; Rovensky, J.; Alecock, E.; Woodworth, T.; Alten, R.; Investigators, O. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 2008, 371, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huizinga, T.W.; Fleischmann, R.M.; Jasson, M.; Radin, A.R.; van Adelsberg, J.; Fiore, S.; Huang, X.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Stahl, N.; Genovese, M.C. Sarilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody against IL-6Ralpha in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate: Efficacy and safety results from the randomised SARIL-RA-MOBILITY Part A trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieper, J.; Porter-Brown, B.; Thompson, L.; Harari, O.; Dougados, M. Assessment of short-term symptomatic efficacy of tocilizumab in ankylosing spondylitis: Results of randomised, placebo-controlled trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alten, R.; Gomez-Reino, J.; Durez, P.; Beaulieu, A.; Sebba, A.; Krammer, G.; Preiss, R.; Arulmani, U.; Widmer, A.; Gitton, X.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the human anti-IL-1beta monoclonal antibody canakinumab in rheumatoid arthritis: Results of a 12-week, Phase II, dose-finding study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuki, G.; Bresnihan, B.; Bear, M.B.; McCabe, D.; European Group Of Clinical, I. Long-term safety and maintenance of clinical improvement following treatment with anakinra (recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Extension phase of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2838–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.M.; Bonelli, M.; Gadina, M.; O’Shea, J.J. Type I/II cytokines, JAKs, and new strategies for treating autoimmune diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispino, N.; Ciccia, F. JAK/STAT pathway and nociceptive cytokine signalling in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoyiannis, D.; Pasparakis, M.; Pizarro, T.T.; Cominelli, F.; Kollias, G. Impaired on/off regulation of TNF biosynthesis in mice lacking TNF AU-rich elements: Implications for joint and gut-associated immunopathologies. Immunity 1999, 10, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, G.; Douni, E.; Kassiotis, G.; Kontoyiannis, D. The function of tumour necrosis factor and receptors in models of multi-organ inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1999, 58 (Suppl. S1), I32–I39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, K.; Robinson, D.; Zonin, F.; Hartley, S.B.; Macatonia, S.E.; Somoza, C.; Hunter, C.A.; Murphy, K.M.; O’Garra, A. IL-1 alpha and TNF-alpha are required for IL-12-induced development of Th1 cells producing high levels of IFN-gamma in BALB/c but not C57BL/6 mice. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Hanauer, S.B.; Katz, S.; Safdi, M.; Wolf, D.G.; Baerg, R.D.; Tremaine, W.J.; Johnson, T.; Diehl, N.N.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Etanercept for active Crohn’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraoui, B.; Krelenbaum, M. Emergence of Crohn’s disease during treatment with the anti-tumor necrosis factor agent etanercept for ankylosing spondylitis: Possible mechanisms of action. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 39, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, R.; Zimmer, M.; Bartsch, B.; Waldner, M.J.; Atreya, I.; Neumann, H.; Hildner, K.; Hoffman, A.; Kiesslich, R.; Rink, A.D.; et al. Antibodies against tumor necrosis factor (TNF) induce T-cell apoptosis in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases via TNF receptor 2 and intestinal CD14(+) macrophages. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 2026–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerr, R.H.; Taylor, K.D.; Brant, S.R.; Rioux, J.D.; Silverberg, M.S.; Daly, M.J.; Steinhart, A.H.; Abraham, C.; Regueiro, M.; Griffiths, A.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science 2006, 314, 1461–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elson, C.O.; Cong, Y.; Weaver, C.T.; Schoeb, T.R.; McClanahan, T.K.; Fick, R.B.; Kastelein, R.A. Monoclonal anti-interleukin 23 reverses active colitis in a T cell-mediated model in mice. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2359–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahern, P.P.; Schiering, C.; Buonocore, S.; McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Maloy, K.J.; Powrie, F. Interleukin-23 drives intestinal inflammation through direct activity on T cells. Immunity 2010, 33, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, M.; Panaccione, R.; Baert, F.; Bossuyt, P.; Colombel, J.F.; Danese, S.; Dubinsky, M.; Feagan, B.G.; Hisamatsu, T.; Lim, A.; et al. Risankizumab as maintenance therapy for moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease: Results from the multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, withdrawal phase 3 FORTIFY maintenance trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 2031–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Haens, G.; Panaccione, R.; Baert, F.; Bossuyt, P.; Colombel, J.F.; Danese, S.; Dubinsky, M.; Feagan, B.G.; Hisamatsu, T.; Lim, A.; et al. Risankizumab as induction therapy for Crohn’s disease: Results from the phase 3 ADVANCE and MOTIVATE induction trials. Lancet 2022, 399, 2015–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; D’Haens, G.R.; Reinisch, W.; Panes, J.; Chan, D.; Gonzalez, S.; Weisel, K.; Germinaro, M.; Frustaci, M.E.; Yang, Z.; et al. Guselkumab for the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease: Induction Results From the Phase 2 GALAXI-1 Study. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1650–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, J.R.; Zhang, Y.; Brown, W.A.; Smith, C.L.; Byrne, F.R.; Fiorino, M.; Stevens, E.; Bigler, J.; Davis, J.A.; Rottman, J.B.; et al. Differential Roles for Interleukin-23 and Interleukin-17 in Intestinal Immunoregulation. Immunity 2015, 43, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Tato, C.M.; Joyce-Shaikh, B.; Gulen, M.F.; Cayatte, C.; Chen, Y.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Judo, M.; Ayanoglu, G.; McClanahan, T.K.; et al. Interleukin-23-Independent IL-17 Production Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Permeability. Immunity 2015, 43, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueber, W.; Sands, B.E.; Lewitzky, S.; Vandemeulebroecke, M.; Reinisch, W.; Higgins, P.D.; Wehkamp, J.; Feagan, B.G.; Yao, M.D.; Karczewski, M.; et al. Secukinumab, a human anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody, for moderate to severe Crohn’s disease: Unexpected results of a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Gut 2012, 61, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauny, M.; Moulin, D.; D’Amico, F.; Netter, P.; Petitpain, N.; Arnone, D.; Jouzeau, J.Y.; Loeuille, D.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Paradoxical gastrointestinal effects of interleukin-17 blockers. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Vermeire, S.; Hellstern, P.; Panaccione, R.; Rogler, G.; Fraser, G.; Kohn, A.; Desreumaux, P.; Leong, R.W.; Comer, G.M.; et al. Randomised trial and open-label extension study of an anti-interleukin-6 antibody in Crohn’s disease (ANDANTE I and II). Gut 2019, 68, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, S.; Aden, K.; Bernardes, J.P.; Conrad, C.; Tran, F.; Hoper, H.; Volk, V.; Mishra, N.; Blase, J.I.; Nikolaus, S.; et al. Therapeutic Interleukin-6 Trans-signaling Inhibition by Olamkicept (sgp130Fc) in Patients With Active Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2354–2366 e2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F. Targeting immune cell circuits and trafficking in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, S.; Rudzinski, J.; Brandt, W.; Dupas, J.L.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Bouhnik, Y.; Kleczkowski, D.; Uebel, P.; Lukas, M.; Knutsson, M.; et al. Tralokinumab for moderate-to-severe UC: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIa study. Gut 2015, 64, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisch, W.; Panes, J.; Khurana, S.; Toth, G.; Hua, F.; Comer, G.M.; Hinz, M.; Page, K.; O’Toole, M.; Moorehead, T.M.; et al. Anrukinzumab, an anti-interleukin 13 monoclonal antibody, in active UC: Efficacy and safety from a phase IIa randomised multicentre study. Gut 2015, 64, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedin, C.R.H.; Vavricka, S.R.; Stagg, A.J.; Schoepfer, A.; Raine, T.; Puig, L.; Pleyer, U.; Navarini, A.; van der Meulen-de Jong, A.E.; Maul, J.; et al. The Pathogenesis of Extraintestinal Manifestations: Implications for IBD Research, Diagnosis, and Therapy. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.M.; Kanno, Y.; Villarino, A.; Ward, M.; Gadina, M.; O’Shea, J.J. JAK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for immune and inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Van Assche, G.; Gomez-Ulloa, D.; Garcia-Alvarez, L.; Lara, N.; Black, C.M.; Kachroo, S. Systematic Review of Tumor Necrosis Factor Antagonists in Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 25–36 e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavricka, S.R.; Gubler, M.; Gantenbein, C.; Spoerri, M.; Froehlich, F.; Seibold, F.; Protic, M.; Michetti, P.; Straumann, A.; Fournier, N.; et al. Anti-TNF Treatment for Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the Swiss IBD Cohort Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, D.; Daperno, M.; Fiorino, G.; Savarino, E.; Mosso, E.; Biancone, L.; Testa, A.; Sarpi, L.; Cappello, M.; Bodini, G.; et al. Real-life effectiveness of ustekinumab in inflammatory bowel disease patients with concomitant psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis: An IG-IBD study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liefferinckx, C.; Verstockt, B.; Gils, A.; Noman, M.; Van Kemseke, C.; Macken, E.; De Vos, M.; Van Moerkercke, W.; Rahier, J.F.; Bossuyt, P.; et al. Long-term Clinical Effectiveness of Ustekinumab in Patients with Crohn’s Disease Who Failed Biologic Therapies: A National Cohort Study. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biemans, V.B.C.; van der Meulen-de Jong, A.E.; van der Woude, C.J.; Lowenberg, M.; Dijkstra, G.; Oldenburg, B.; de Boer, N.K.H.; van der Marel, S.; Bodelier, A.G.L.; Jansen, J.M.; et al. Ustekinumab for Crohn’s Disease: Results of the ICC Registry, a Nationwide Prospective Observational Cohort Study. J. Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursi, A.; Mocci, G.; Maconi, G. Effect of Ustekinumab on Extraintestinal Diseases in Refractory Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, 1399–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narula, N.; Aruljothy, A.; Wong, E.C.L.; Homenauth, R.; Alshahrani, A.A.; Marshall, J.K.; Reinisch, W. The impact of ustekinumab on extraintestinal manifestations of Crohn’s disease: A post hoc analysis of the UNITI studies. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Galan, C.; Truyens, M.; Peeters, H.; Mesonero Gismero, F.; Elorza, A.; Torres, P.; Vandermeulen, L.; Amezaga, A.J.; Ferreiro-Iglesias, R.; Holvoet, T.; et al. The Impact of Vedolizumab and Ustekinumab on Articular Extra-Intestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: A Real-Life Multicentre Cohort Study. J. Crohns Colitis 2022, 16, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrom, U.; Olofsson, T.; Wedren, S.; Qirjazo, I.; Askling, J. Impact of extra-articular spondyloarthritis manifestations and comorbidities on drug retention of a first TNF-inhibitor in ankylosing spondylitis: A population-based nationwide study. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, M.H.; Dean, L.; Jones, G.T.; Siebert, S.; Gaffney, K. Predictors of extra-articular manifestations in axial spondyloarthritis and their influence on TNF-inhibitor prescribing patterns: Results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register in Ankylosing Spondylitis. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, H.; Billmeier, U.; Dieterich, W.; Rath, T.; Sonnewald, S.; Reid, S.; Hirschmann, S.; Hildner, K.; Waldner, M.J.; Mudter, J.; et al. Expansion of IL-23 receptor bearing TNFR2+ T cells is associated with molecular resistance to anti-TNF therapy in Crohn’s disease. Gut 2019, 68, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivernini, S.; Pugliese, D.; Tolusso, B.; Bui, L.; Petricca, L.; Guidi, L.; Mirone, L.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Federico, F.; Ferraccioli, G.; et al. Paradoxical arthritis occurring during anti-TNF in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Histological and immunological features of a complex synovitis. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, M.C.; Cohen, S.; Moreland, L.; Lium, D.; Robbins, S.; Newmark, R.; Bekker, P.; Study, G. Combination therapy with etanercept and anakinra in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have been treated unsuccessfully with methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.C.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Aelion, J.A.; Mansikka, H.T.; Peloso, P.M.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Othman, A.A.; Khatri, A.; Khan, N.S.; et al. ABT-122, a Bispecific Dual Variable Domain Immunoglobulin Targeting Tumor Necrosis Factor and Interleukin-17A, in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis With an Inadequate Response to Methotrexate: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleto, G.; Kanagaratnam, L.; Drame, M.; Salmon, J.H. Safety of combination therapy with two bDMARDs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Galati, J.; Kumar, A.; Christos, P.J.; Longman, R.; Lukin, D.J.; Scherl, E.; Battat, R. Dual Biologic or Small Molecule Therapy for Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e361–e379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alayo, Q.A.; Fenster, M.; Altayar, O.; Glassner, K.L.; Llano, E.; Clark-Snustad, K.; Patel, A.; Kwapisz, L.; Yarur, A.J.; Cohen, B.L.; et al. Systematic Review With Meta-analysis: Safety and Effectiveness of Combining Biologics and Small Molecules in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Crohns. Colitis 360 2022, 4, otac002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolinger, M.T.; Spencer, E.A.; Lai, J.; Dunkin, D.; Dubinsky, M.C. Dual Biologic and Small Molecule Therapy for the Treatment of Refractory Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, B.E.; Kozarek, R.; Spainhour, J.; Barish, C.F.; Becker, S.; Goldberg, L.; Katz, S.; Goldblum, R.; Harrigan, R.; Hilton, D.; et al. Safety and tolerability of concurrent natalizumab treatment for patients with Crohn’s disease not in remission while receiving infliximab. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, B.E.; Feagan, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J.; Shipitofsky, N.; Marko, M.; Sheng, S.; Johanns, J.; Germinaro, M.; Vetter, M.; Panés, J. OP36 Efficacy and safety of combination induction therapy with guselkumab and golimumab in participants with moderately-to-severely active Ulcerative Colitis: Results through week 12 of a phase 2a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, parallel-grou. Proc. ECCO Congr. 2022, 16, i42–i43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privitera, G.; Pugliese, D.; Onali, S.; Petito, V.; Scaldaferri, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Danese, S.; Armuzzi, A. Combination therapy in inflammatory bowel disease-from traditional immunosuppressors towards the new paradigm of dual targeted therapy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillo, L.; Abreu, M.; Panaccione, R.; Sandborn, W.J.; Azevedo, V.F.; Gensler, L.; Moghaddam, B.; Ahuja, V.; Ali, S.A.; Allez, M.; et al. Endpoints for extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease trials: The EXTRA consensus from the International Organization for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinblatt, M.; Combe, B.; Covucci, A.; Aranda, R.; Becker, J.C.; Keystone, E. Safety of the selective costimulation modulator abatacept in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving background biologic and nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: A one-year randomized, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2807–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinblatt, M.; Schiff, M.; Goldman, A.; Kremer, J.; Luggen, M.; Li, T.; Chen, D.; Becker, J.C. Selective costimulation modulation using abatacept in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis while receiving etanercept: A randomised clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, N.; Max, R.; Schiller, M.; Briem, S.; Lorenz, H.M. Safety of combination therapy with rituximab and etanercept for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, M.W.; Shergy, W.J.; Kaine, J.L.; Sweetser, M.T.; Gilder, K.; Linnik, M.D. Evaluation of the safety of rituximab in combination with a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor and methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: Results from a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatt, S.; Taylor, P.C.; McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G.; Landewe, R.; Baeten, D.; Ionescu, L.; Strimenopoulou, F.; Watling, M.I.L.; Shaw, S. Efficacy and safety of bimekizumab as add-on therapy for rheumatoid arthritis in patients with inadequate response to certolizumab pegol: A proof-of-concept study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Study of Combination Treatment with MabThera (Rituximab) and RoActemra (Tocilizumab) Vrsus RoActemra in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with an Incomplete Response to Methotrexate. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00845832 (accessed on 10 February 2023).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Felice, C.; Dal Buono, A.; Gabbiadini, R.; Rattazzi, M.; Armuzzi, A. Cytokines in Spondyloarthritis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043957
Felice C, Dal Buono A, Gabbiadini R, Rattazzi M, Armuzzi A. Cytokines in Spondyloarthritis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):3957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043957
Chicago/Turabian StyleFelice, Carla, Arianna Dal Buono, Roberto Gabbiadini, Marcello Rattazzi, and Alessandro Armuzzi. 2023. "Cytokines in Spondyloarthritis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 3957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043957
APA StyleFelice, C., Dal Buono, A., Gabbiadini, R., Rattazzi, M., & Armuzzi, A. (2023). Cytokines in Spondyloarthritis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043957







