Correlation of MR-Based Metabolomics and Molecular Profiling in the Tumor Microenvironment of Temozolomide-Treated Orthotopic GL261 Glioblastoma in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
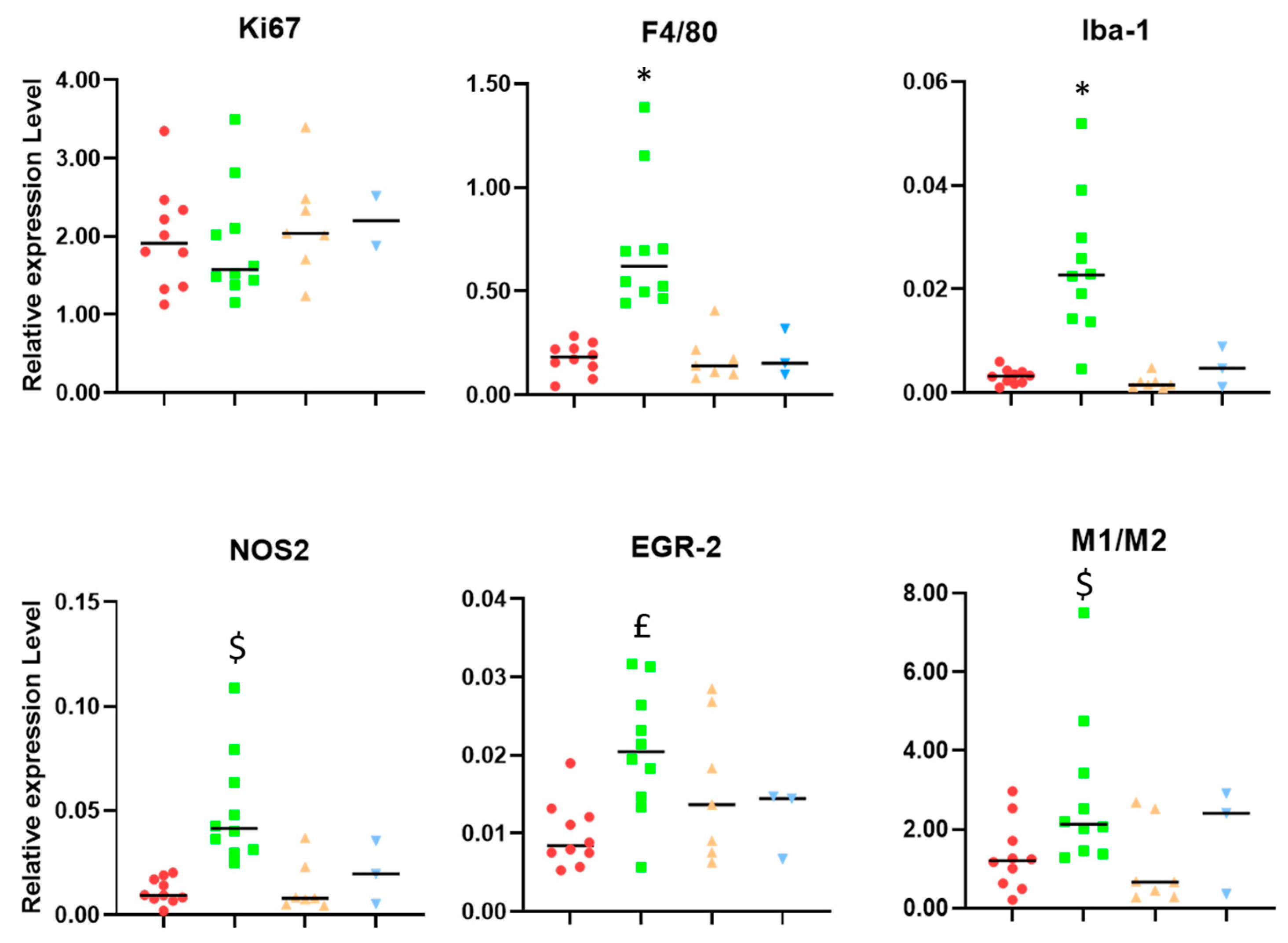
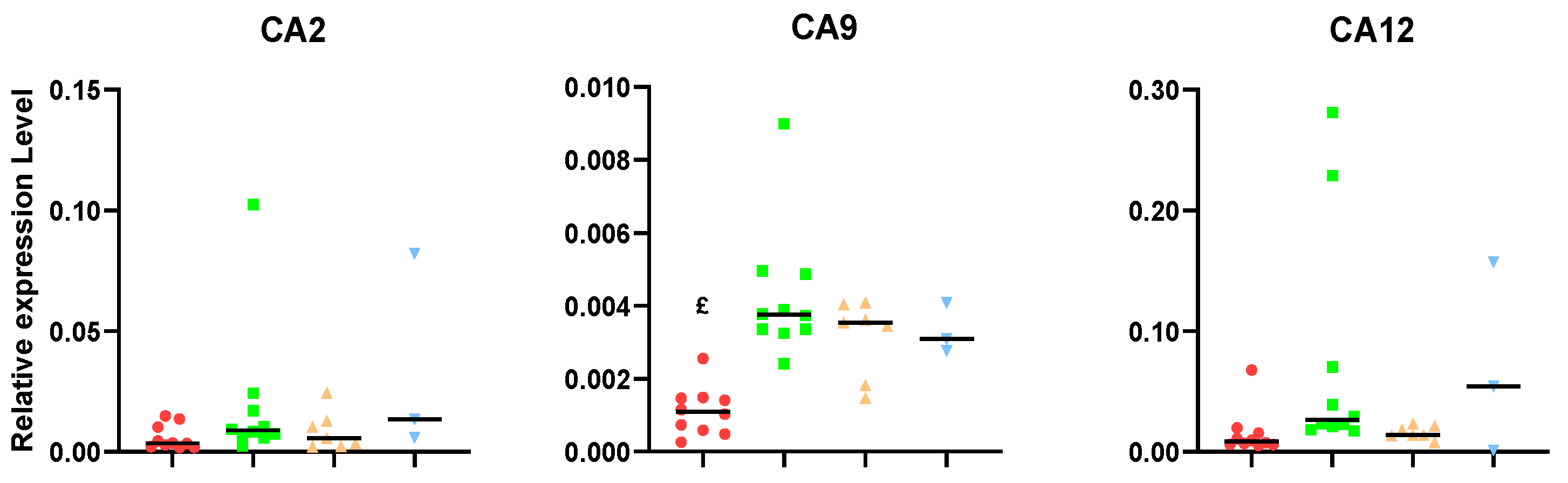
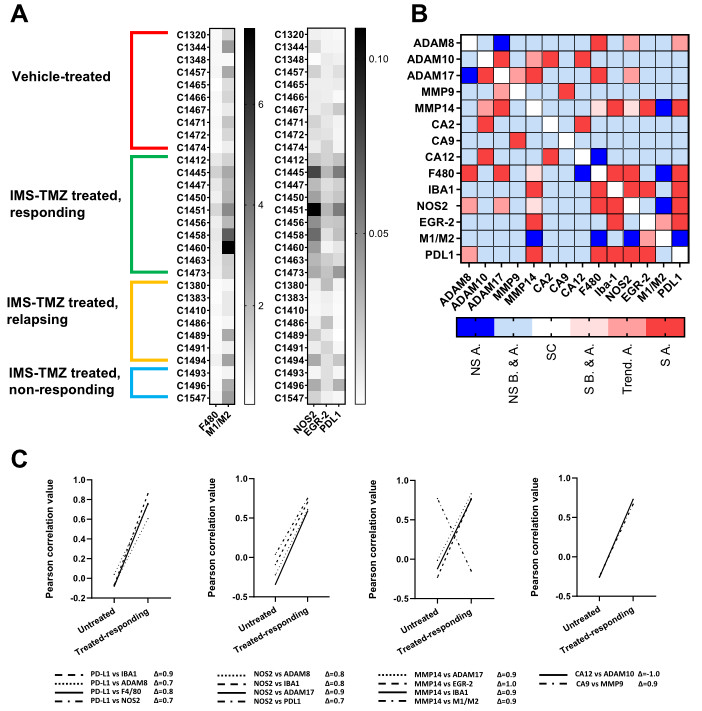
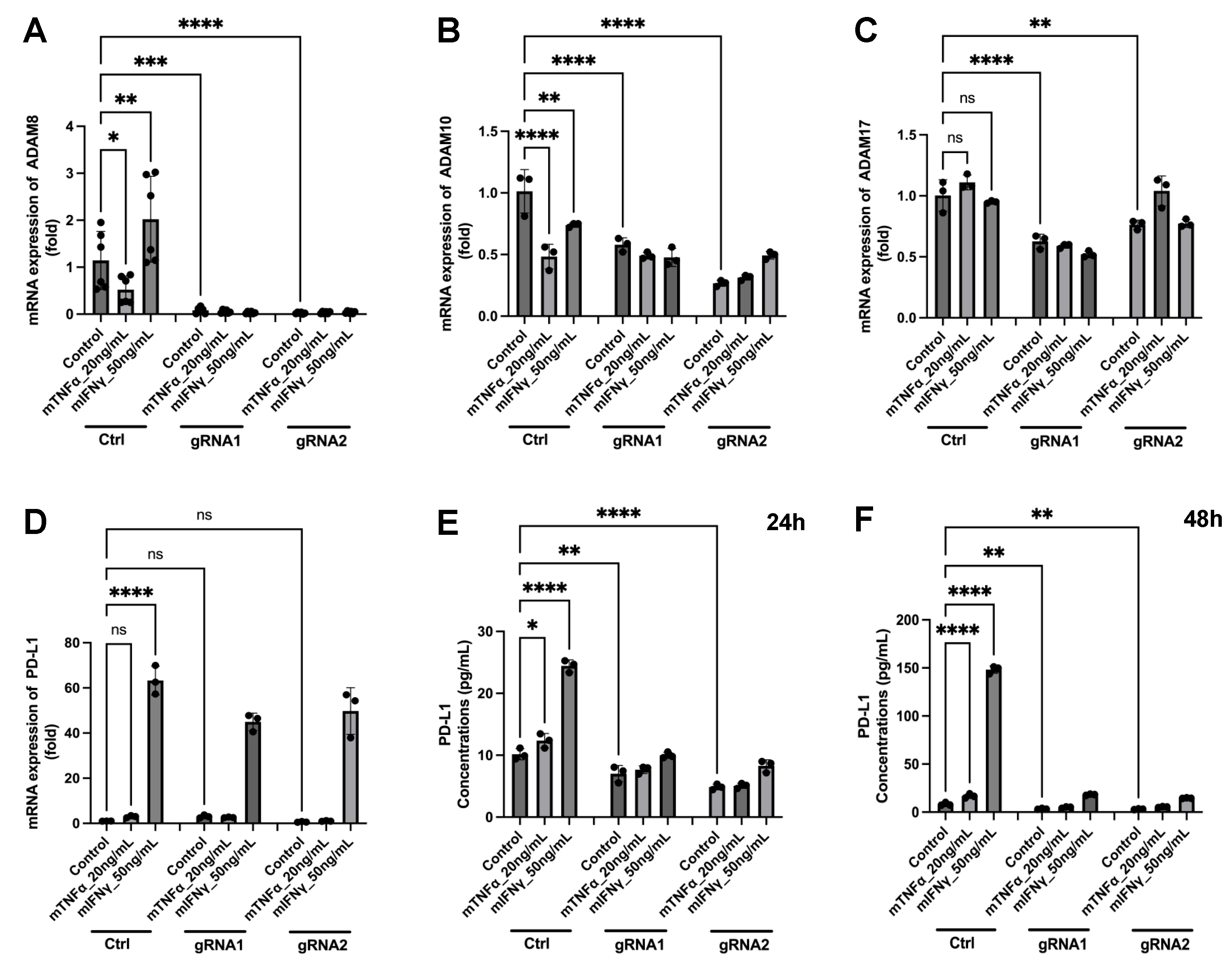
2. Results
Non-Invasive Follow-Up of Tumor Progression in Mice and Inclusion Criteria
3. Discussion
3.1. Microglia/Macrophage Populations Present Changes in Their Infiltration Behavior and Phenotypic Characteristics during Successful Response to IMS-TMZ Treatment
3.2. Carbonic Anhydrase Results Suggest That Unresponsive Tumors Could Overexpress This Gene
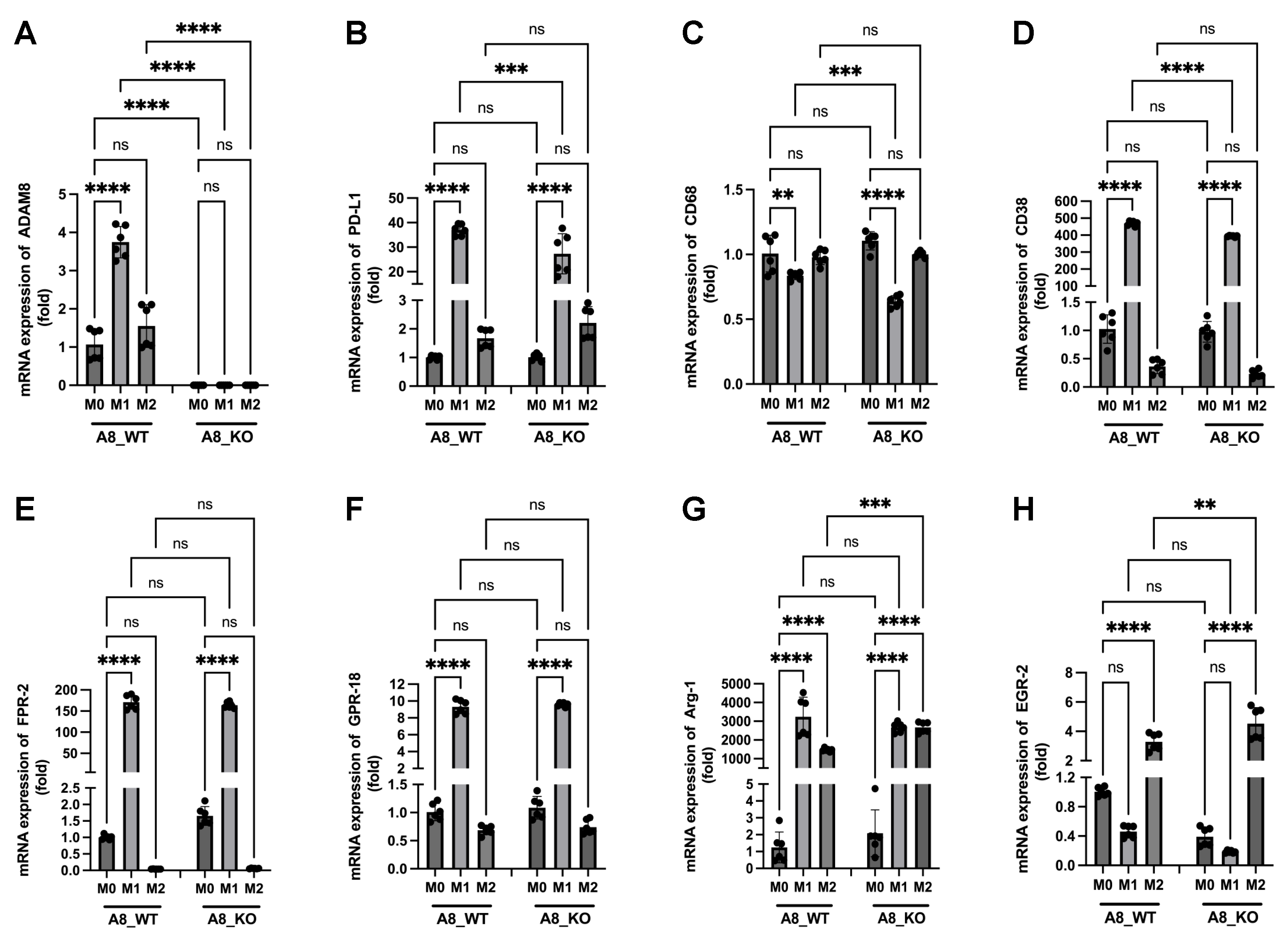
3.3. Changes in the Expression of Metalloproteases Can Shape TME, and Relevant Differences Are Found during Response to IMS-TMZ
3.4. Correlation between the Expression Levels of Different Genes Showed Unexpected Links
3.5. Microenvironment Changes during Sustained Response to IMS-TMZ Were Translated into Metabolomic Changes Noninvasively Assessed with MRSI
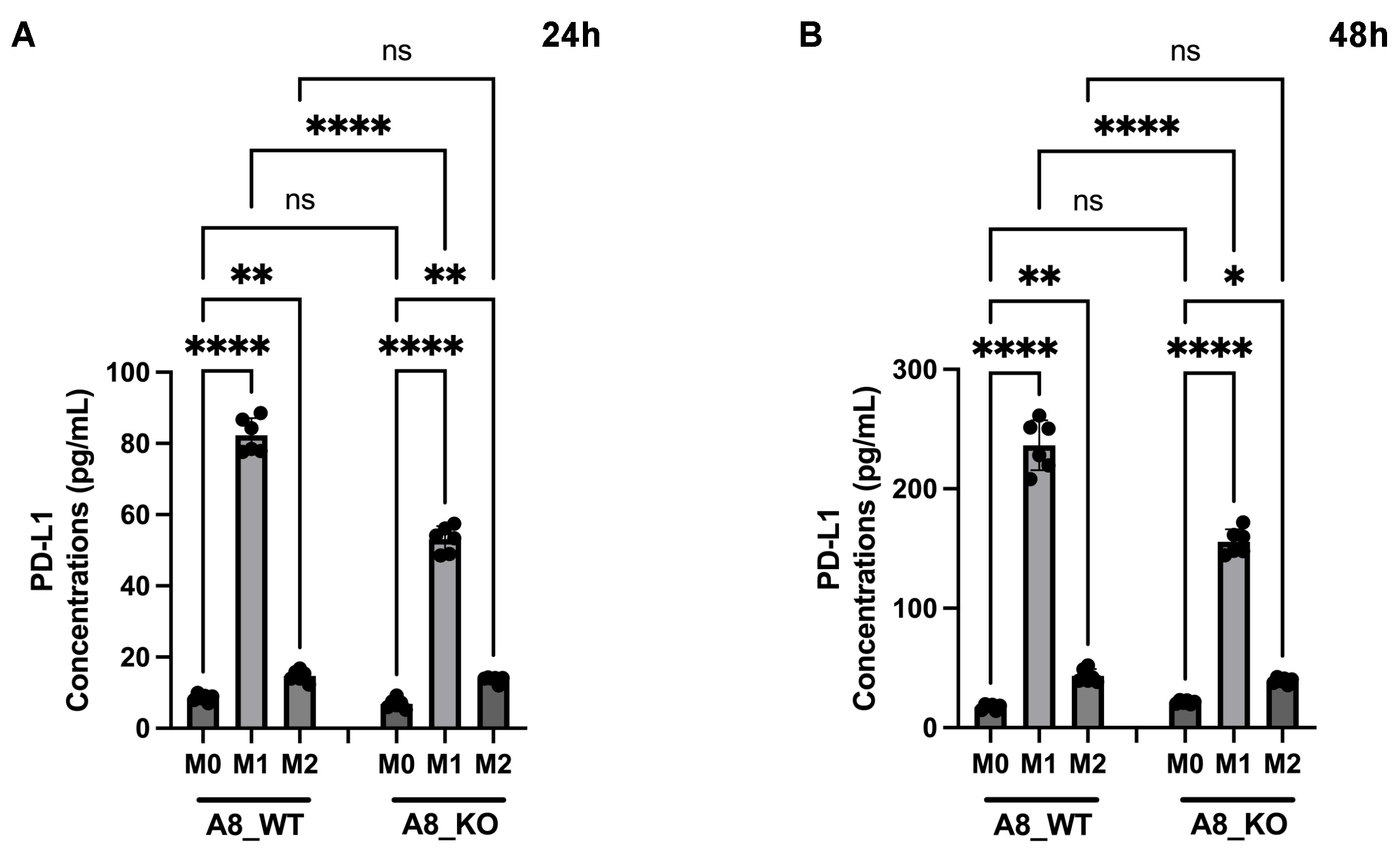
3.6. A New Therapeutic Target Emerges from the ADAM8/PD-L1 Relationship
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. GL261 Cell Culture
4.2. Preclinical GL261 GB Model and IMS-TMZ Treatment
4.3. MR Data Acquisition (MRI and MRSI), Processing, and Postprocessing, and Murine Tumor Sample Collection
4.4. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and RT-PCR from Mouse Brain Tissue
4.5. Construction of Stable GL261 ADAM8 Knockout Cells
4.6. RNA Extraction, cDNA Transcription, and RT-PCR from GL261 Cells
4.7. ELISA Measurements
4.8. In Vitro Polarization of Macrophages
4.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.10. Statistics, Algorithms, and Tools Used for Data Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oronsky, B.; Reid, T.R.; Oronsky, A.; Sandhu, N.; Knox, S.J. A Review of Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 574012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCordova, S.; Shastri, A.; Tsolaki, A.G.; Yasmin, H.; Klein, L.; Singh, S.K.; Kishore, U. Molecular Heterogeneity and Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Glioblastoma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.F.; Carter, T.J.; Ottaviani, D.; Mulholland, P. Harnessing the immune system in glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himes, B.T.; Geiger, P.A.; Ayasoufi, K.; Bhargav, A.G.; Brown, D.A.; Parney, I.F. Immunosuppression in Glioblastoma: Current Understanding and Therapeutic Implications. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 770561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikfalvi, A.; da Costa, C.A.; Avril, T.; Barnier, J.V.; Bauchet, L.; Brisson, L.; Cartron, P.F.; Castel, H.; Chevet, E.; Chneiweiss, H.; et al. Challenges in glioblastoma research: Focus on the tumor microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvalaggio, A.; Silvestri, E.; Sansone, G.; Pinton, L.; Magri, S.; Briani, C.; Anglani, M.; Lombardi, G.; Zagonel, V.; Della Puppa, A.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlates of Immune Microenvironment in Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 823812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedros, B.; Ijare, O.B.; Nikulin, A.E.; Somorjai, R.L.; Smith, I.C.P. MRS-based Metabolomics in Cancer Research. Magn. Reson. Insights 2014, 7, MRI-S13755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Ramos, N.; Ferrer-Font, L.; Lope-Piedrafita, S.; Mocioiu, V.; Julià-Sapé, M.; Pumarola, M.; Arús, C.; Candiota, A.P. Metabolomics of therapy response in preclinical glioblastoma: A multi-slice MRSI-based volumetric analysis for noninvasive assessment of temozolomide treatment. Metabolites 2017, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Calero-Pérez, P.; Villamañan, L.; Arias-Ramos, N.; Pumarola, M.; Ortega-Martorell, S.; Julià-Sapé, M.; Arús, C.; Candiota, A.P. Anti-tumour immune response in GL261 glioblastoma generated by Temozolomide Immune-Enhancing Metronomic Schedule monitored with MRSI-based nosological images. NMR Biomed. 2020, 33, e4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candiota, A.P.; Arús, C. Establishing Imaging Biomarkers of Host Immune System Efficacy during Glioblastoma Therapy Response: Challenges, Obstacles and Future Perspectives. Metabolites 2022, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjorgjevski, M.; Hannen, R.; Carl, B.; Li, Y.; Landmann, E.; Buchholz, M.; Bartsch, J.W.; Nimsky, C. Molecular profiling of the tumor microenvironment in glioblastoma patients: Correlation of microglia / macrophage polarization state with metalloprotease expression profiles and survival. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20182361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda-Goncalves, V.; Reis, R.M.; Baltazar, F. Lactate Transporters and pH Regulation: Potential Therapeutic Targets in Glioblastomas. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2016, 16, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Schäfer, A.; Zhang, Z.; Elsässer, K.; Culmsee, C.; Zhong, J.L.; Pagenstecher, A.; Nimsky, C.; Bartsch, J.W. Inhibition of Carbonic Anhydrase 2 Overcomes Temozolomide Resistance in Glioblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannen, R.; Selmansberger, M.; Hauswald, M.; Pagenstecher, A.; Nist, A.; Stiewe, T.; Acker, T.; Carl, B.; Nimsky, C.; Bartsch, J.W. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of Temozolomide resistant primary GBM Stem-like cells and recurrent GBM identifies up-regulation of the Carbonic Anhydrase CA2 gene as resistance factor. Cancers 2019, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Calero-Pérez, P.; Arús, C.; Candiota, A.P. Anti-pd-1 immunotherapy in preclinical gl261 glioblastoma: Influence of therapeutic parameters and non-invasive response biomarker assessment with mrsi-based approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero-Pérez, P.; Wu, S.; Arús, C.; Candiota, A.P. Immune system-related changes in preclinical GL261 glioblastoma under TMZ treatment: Explaining MRSI-based nosological imaging findings with RT-PCR analyses. Cancers 2021, 13, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Waxman, D.J. Metronomic cyclophosphamide eradicates large implanted GL261 gliomas by activating antitumor Cd8+ T-cell responses and immune memory. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1005521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Waxman, D.J. Medium dose intermittent cyclophosphamide induces immunogenic cell death and cancer cell autonomous type I interferon production in glioma models. Cancer Lett. 2020, 470, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Goñi, T.; Ortega-Martorell, S.; Ciezka, M.; Olier, I.; Candiota, A.P.; Julià-Sapé, M.; Fernández, F.; Pumarola, M.; Lisboa, P.J.; Arús, C. MRSI-based molecular imaging of therapy response to temozolomide in preclinical glioblastoma using source analysis. NMR Biomed. 2016, 29, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proescholdt, M.A.; Merrill, M.J.; Stoerr, E.M.; Lohmeier, A.; Pohl, F.; Brawanski, A. Function of carbonic anhydrase IX in glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro. Oncol. 2012, 14, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Cruz-López, K.G.; Castro-Muñoz, L.J.; Reyes-Hernández, D.O.; García-Carrancá, A.; Manzo-Merino, J. Lactate in the Regulation of Tumor Microenvironment and Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, J.P.; Koch, B.J.; Benson, P.D.; Varughese, E.; Monterey, M.D.; Lee, A.E.; Dave, A.M.; Kiousis, S.; Sloan, A.E.; Mathupala, S.P. pH, Lactate, and Hypoxia: Reciprocity in Regulating High-Affinity Monocarboxylate Transporter Expression in Glioblastoma 1. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haapasalo, J.; Nordfors, K.; Haapasalo, H.; Parkkila, S. The Expression of Carbonic Anhydrases II, IX and XII in Brain Tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bache, M.; Rot, S.; Kessler, J.; Güttler, A.; Wichmann, H.; Greither, T.; Wach, S.; Taubert, H.; Söling, A.; Bilkenroth, U.; et al. mRNA expression levels of hypoxia-induced and stem cell-associated genes in human glioblastoma. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 3155–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mboge, M.Y.; Mahon, B.P.; McKenna, R.; Frost, S.C. Carbonic Anhydrases: Role in pH Control and Cancer. Metabolites 2018, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haapasalo, J.; Nordfors, K.; Järvelä, S.; Bragge, H.; Rantala, I.; Parkkila, A.K.; Haapasalo, H.; Parkkila, S. Carbonic anhydrase II in the endothelium of glial tumors: A potential target for therapy. Neuro. Oncol. 2007, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonfiglioli, A.; Hambardzumyan, D. Macrophages and microglia: The cerberus of glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, F.; Xu, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, R.; Chu, Y. The IFN-γ/PD-L1 axis between T cells and tumor microenvironment: Hints for glioma anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Ma, L.; You, Z. Inflammatory cytokines IL-17 and TNF-α up-regulate PD-L1 expression in human prostate and colon cancer cells. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 184, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.R.; Maute, R.L.; Dulken, B.W.; Hutter, G.; George, B.M.; McCracken, M.N.; Gupta, R.; Tsai, J.M.; Sinha, R.; Corey, D.; et al. PD-1 expression by tumour-associated macrophages inhibits phagocytosis and tumour immunity. Nature 2017, 545, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, W.; Xiao, J.; Ma, Q.; Miao, J.; Cao, M.; Chen, L.; Shi, Y.; Yao, X.; Yu, S.; Liu, X.; et al. Combination of p38 MAPK inhibitor with PD-L1 antibody effectively prolongs survivals of temozolomide-resistant glioma-bearing mice via reduction of infiltrating glioma-associated macrophages and PD-L1 expression on resident glioma-associated microglia. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2021, 38, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, M.; Xin, H.B. Polarizing macrophages in vitro. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1784, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jablonski, K.A.; Amici, S.A.; Webb, L.M.; Ruiz-Rosado, J.D.D.; Popovich, P.G.; Partida-Sanchez, S.; Guerau-De-arellano, M. Novel Markers to Delineate Murine M1 and M2 Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakumäki, J.M.; Poptani, H.; Sandmair, A.M.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Kauppinen, R.A. 1H MRS detects polyunsaturated fatty acid accumulation during gene therapy of glioma: Implications for the in vivo detection of apoptosis. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelio, I.; Cutruzzolá, F.; Antonov, A.; Agostini, M.; Melino, G. Serine and glycine metabolism in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Durán, R.V. Glutamine metabolism in cancer therapy. Cancer Drug Resist. 2018, 1, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, A.; Munari, F.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Scolaro, T.; Castegna, A. The metabolic signature of macrophage responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattigan, K.M.; Pountain, A.W.; Regnault, C.; Achcar, F.; Vincent, I.M.; Goodyear, C.S.; Barrett, M.P. Metabolomic profiling of macrophages determines the discrete metabolomic signature and metabolomic interactome triggered by polarising immune stimuli. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Aaroe, A.; Liang, J.; Puduvalli, V.K. Tumor microenvironment in glioblastoma: Current and emerging concepts. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2023, 5, vdad009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobecki, M.; Mrouj, K.; Camasses, A.; Parisis, N.; Nicolas, E.; Llères, D.; Gerbe, F.; Prieto, S.; Krasinska, L.; David, A.; et al. The cell proliferation antigen Ki-67 organises heterochromatin. eLife 2016, 5, e13722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrouj, K.; Andrés-Sánchez, N.; Dubra, G.; Singh, P.; Sobecki, M.; Chahar, D.; Al Ghoul, E.; Aznar, A.B.; Prieto, S.; Pirot, N.; et al. Ki-67 regulates global gene expression and promotes sequential stages of carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2026507118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlrot, R.H.; Bangsø, J.A.; Petersen, J.K.; Rosager, A.M.; Sørensen, M.D.; Reifenberger, G.; Hansen, S.; Kristensen, B.W. Prognostic role of Ki-67 in glioblastomas excluding contribution from non-neoplastic cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Humeau, J.; Buqué, A.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunostimulation with chemotherapy in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karachi, A.; Dastmalchi, F.; Mitchell, D.A.; Rahman, M. Temozolomide for immunomodulation in the treatment of glioblastoma. Neuro. Oncol. 2018, 20, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.G.; Kim, C.H.; Park, J.S.; Park, S.D.; Kim, C.K.; Chung, D.S.; Hong, Y.K. Immunological factors relating to the antitumor effect of temozolomide chemoimmunotherapy in a murine glioma model. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamañan, L.; Martínez-escardó, L.; Arús, C.; Yuste, V.J.; Candiota, A.P. Successful partnerships: Exploring the potential of immunogenic signals triggered by TMZ, CX-4945, and combined treatment in Gl261 glioblastoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Geng, X.; Hou, J.; Wu, G. New insights into M1/M2 macrophages: Key modulators in cancer progression. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Mantovani, A. Science in medicine Macrophage plasticity and polarization: In vivo veritas. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Yin, F.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ji, N.; et al. RACK1 promotes cancer progression by increasing the M2/M1 macrophage ratio via the NF-κB pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisenberger, C.; Mock, A.; Warta, R.; Rapp, C.; Schwager, C.; Korshunov, A.; Nied, A.K.; Capper, D.; Brors, B.; Jungk, C.; et al. Molecular profiling of long-term survivors identifies a subgroup of glioblastoma characterized by chromosome 19/20 co-gain. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 130, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmour, K.M.; Perry, S.F. Carbonic anhydrase and acid-base regulation in fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 1647–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alterio, V.; Di Fiore, A.; D’Ambrosio, K.; Supuran, C.T.; De Simone, G. Multiple binding modes of inhibitors to carbonic anhydrases: How to design specific drugs targeting 15 different isoforms? Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4421–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, H.M.; Hagemann, C.; Staab, A.; Stojic, J.; Kühnel, S.; Vince, G.H.; Flentje, M.; Roosen, K.; Vordermark, D. Expression patterns of the hypoxia-related genes osteopontin, CA9, erythropoietin, VEGF and HIF-1alpha in human glioma in vitro and in vivo. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 83, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, H.M.; Hagemann, C.; Carta, F.; Katzer, A.; Polat, B.; Staab, A.; Scozzafava, A.; Anacker, J.; Vince, G.H.; Flentje, M.; et al. Hypoxia induced CA9 inhibitory targeting by two different sulfonamide derivatives including acetazolamide in human glioblastoma. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3949–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, N.H.; Walker, K.; Fried, J.; Hackney, J.R.; McDonald, P.C.; Benavides, G.A.; Spina, R.; Audia, A.; Scott, S.E.; Libby, C.J.; et al. Addition of carbonic anhydrase 9 inhibitor SLC-0111 to temozolomide treatment delays glioblastoma growth in vivo. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e92928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaroglio, I.C.; Mujumdar, P.; Annovazzi, L.; Kopecka, J.; Mellai, M.; Schiffer, D.; Poulsen, S.A.; Riganti, C. Carbonic Anhydrase XII Inhibitors Overcome P-Glycoprotein-Mediated Resistance to Temozolomide in Glioblastoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 2598–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G. The ADAMs: Signalling scissors in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Hu, M.; Khalil, R.A. Biochemical and Biological Attributes of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 147, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niland, S.; Riscanevo, A.X.; Eble, J.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases Shape the Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J.; Mullooly, M.; O’Donovan, N.; Sukor, S.; Crown, J.; Pierce, A.; McGowan, P.M. The ADAMs family of proteases: New biomarkers and therapeutic targets for cancer? Clin. Proteom. 2011, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watters, J.J.; Schartner, J.M.; Badie, B. Microglia function in brain tumors. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 81, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesolowska, A.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Slomnicki, L.; Dembinski, M.; Master, A.; Sliwa, M.; Franciszkiewicz, K.; Chouaib, S.; Kaminska, B. Microglia-derived TGF- b as an important regulator of glioblastoma invasion-an inhibition of TGF- b -dependent effects by shRNA against human TGF- b type II receptor. Oncogene 2008, 27, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnosa, S.P.; Blasco, L.P.; Piotrowski, K.B.; Freiberg, M.L.; Savickas, S.; Madsen, D.H.; auf dem Keller, U.; Kronqvist, P.; Kveiborg, M. ADAM17-mediated EGFR ligand shedding directs macrophage-promoted cancer cell invasion. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e155296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Gong, Q.; Huang, J.; Gong, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wei, D.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Song, J.; Meng, L. ADAM-10 Regulates MMP-12 during Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response in Macrophages. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 3012218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.; Sengelmann, M.; Winkler, B.; Nagl, C.; Koch, S.; Schlomann, U.; Slater, E.P.; Miller, M.A.; von Strandmann, E.P.; Dörsam, B.; et al. ADAM8-Dependent Extracellular Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment Involves Regulated Release of Lipocalin 2 and MMP-9. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Sala-Newby, G.B.; Susana, A.; Johnson, J.L.; Newby, A.C. Classical Macrophage Activation Up-Regulates Several Matrix Metalloproteinases through Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases and Nuclear Factor-κB. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingleton, B. Matrix metalloproteinases as regulators of inflammatory processes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 2036–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Q.; Liu, F.; Qiu, X.Y.; Chen, X.Q. The prognostic and therapeutic value of PD-L1 in glioma. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Chen, G.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, W.; et al. PD-L1 Expression in Glioblastoma, the Clinical and Prognostic Significance: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, F.; Tritschler, I.; Steinle, A.; Weller, M.; Eisele, G. A disintegrin and metalloproteinases 10 and 17 modulate the immunogenicity of glioblastoma-initiating cells. Neuro. Oncol. 2014, 16, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shinchi, Y.; Ishizuka, S.; Komohara, Y.; Matsubara, E.; Mito, R.; Pan, C.; Yoshii, D.; Yonemitsu, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Ikeda, K.; et al. The expression of PD-1 ligand 1 on macrophages and its clinical impacts and mechanisms in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 2645–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, P.; Lokensgard, J.R. Glial Cell Expression of PD-L1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, Y.; Wise, R.; Zolkiewska, A. Proteolytic processing of PD-L1 by ADAM proteases in breast cancer cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Eibach, M.; Bartsch, J.W.; Dolga, A.M.; Schlomann, U.; Conrad, C.; Schieber, S.; Schilling, O.; Biniossek, M.L.; Culmsee, C.; et al. The metalloprotease-disintegrin ADAM8 contributes to temozolomide chemoresistance and enhanced invasiveness of human glioblastoma cells. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 1474–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, R.V.; García-Martín, M.L.; Cerdán, S.; Arús, C. Perturbation of mouse glioma MRS pattern by induced acute hyperglycemia. NMR Biomed. 2008, 21, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, S.; Porzia, A.; Mainiero, F.; Di Angelantonio, S.; Cortese, B.; Basilico, B.; Pagani, F.; Cignitti, G.; Chece, G.; Maggio, R.; et al. Environmental stimuli shape microglial plasticity in glioma. eLife 2017, 6, e33415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, A.; Evers, L.; Meier, L.; Schlomann, U.; Bopp, M.H.A.; Dreizner, G.L.; Lassmann, O.; Ben Bacha, A.; Benescu, A.C.; Pojskic, M.; et al. The Metalloprotease-Disintegrin ADAM8 Alters the Tumor Suppressor miR-181a-5p Expression Profile in Glioblastoma Thereby Contributing to Its Aggressiveness. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 826273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, J.F.; Alieva, M.; Wellens, L.M.; Ariese, H.C.R.; Jamieson, P.R.; Vonk, A.M.; Amatngalim, G.D.; Hu, H.; Oost, K.C.; Snippert, H.J.G.; et al. High-resolution 3D imaging of fixed and cleared organoids. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1756–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Group | Total Number of Cases | Evolution | Cases with RT-PCR Studies | Cases with Immunofluorescence Studies | Tumor Volume at Therapy Starting Point (11 p.i. *) (mm3) | Tumor Volume at Euthanasia (mm3) | Euthanasia Day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMS-TMZ-treated responding, maximum of MRSI-based biomarker (high TRI) ** | 17 ** | Tumor volume met criteria for “stable disease” according to RECIST [19]; adapted as described in [20] and showing TRI values > 60% | 12 | 5 | 7.9 ± 3.1 | 54.2 ± 24.2 | 23 ± 1 |
| Control (vehicle-treated, low TRI) | 15 *** | Tumor volumes increased exponentially as expected, showing TRI values close to 0% | 10 | 5 | 10.3 ± 8.3 | 74.4 ± 24.3 | 18 ± 3 |
| IMS-TMZ-treated, relapsing | 7 | Tumors transiently responded to treatment and subsequently escaped therapy, showing clear regrowth | 7 | 0 | 8.1 ± 4.1 | 149.7 ± 33.0 | 40 ± 4 |
| IMS-TMZ-treated, unresponsive | 3 | Tumor volumes increased fast, and no signs of transient growth arrest were observed | 3 | 0 | 13.7 ± 4.7 | 179.4 ± 36.1 | 22 ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, K.; Calero-Pérez, P.; Bopp, M.H.A.; Möschl, V.; Pagenstecher, A.; Mulero-Acevedo, M.; Vázquez, M.; Barcia, C.; Arús, C.; Nimsky, C.; et al. Correlation of MR-Based Metabolomics and Molecular Profiling in the Tumor Microenvironment of Temozolomide-Treated Orthotopic GL261 Glioblastoma in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417628
Zhao K, Calero-Pérez P, Bopp MHA, Möschl V, Pagenstecher A, Mulero-Acevedo M, Vázquez M, Barcia C, Arús C, Nimsky C, et al. Correlation of MR-Based Metabolomics and Molecular Profiling in the Tumor Microenvironment of Temozolomide-Treated Orthotopic GL261 Glioblastoma in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417628
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Kai, Pilar Calero-Pérez, Miriam H. A. Bopp, Vincent Möschl, Axel Pagenstecher, Marta Mulero-Acevedo, Mario Vázquez, Carlos Barcia, Carles Arús, Christopher Nimsky, and et al. 2023. "Correlation of MR-Based Metabolomics and Molecular Profiling in the Tumor Microenvironment of Temozolomide-Treated Orthotopic GL261 Glioblastoma in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417628
APA StyleZhao, K., Calero-Pérez, P., Bopp, M. H. A., Möschl, V., Pagenstecher, A., Mulero-Acevedo, M., Vázquez, M., Barcia, C., Arús, C., Nimsky, C., Rusch, T., Bartsch, J. W., & Candiota, A. P. (2023). Correlation of MR-Based Metabolomics and Molecular Profiling in the Tumor Microenvironment of Temozolomide-Treated Orthotopic GL261 Glioblastoma in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417628












