Characteristics of Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes Based on Different Types of Pectin with Eudragit® EPO as Novel Carriers for Colon-Specific Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Turbidity Measurements
2.2. Apparent Viscosity Measurements and Gravimetry
2.3. Elemental Analyses
2.4. FTIR Spectroscopy
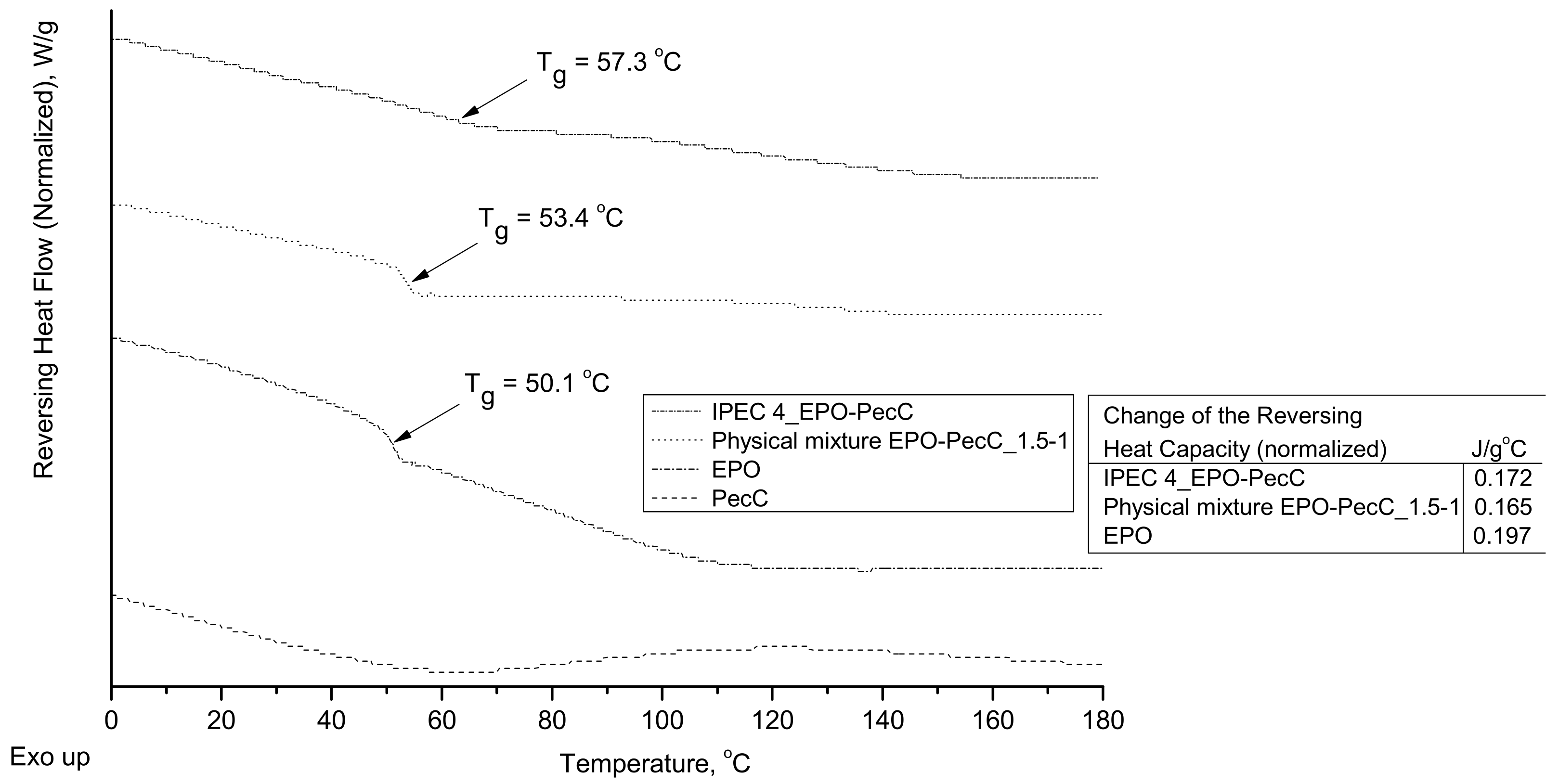
2.5. Thermal Analysis
2.6. Determination of the Degree of Swelling of Matrices
2.7. In Vitro Drug Release Test
3. Discussion
- y = D(x)—drug transport according to the diffusion equation;
- A1 = D(max)—maximum diffusion;
- A2 = D(min)—minimum diffusion;
- p = −λ·(x − σ)—the product of the inversely proportional width of the path of the drug (λ) from the tablet and the difference between the release value (x) and the location of the center of diffusion of the drug (σ) from the tablet;
- x0—release value at maximum diffusion.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Turbidity Measurements
4.2.2. Apparent Viscosity Measurements
- η—relative viscosity of the solution;
- τ—solution out flow time, s;
- τ0—solvent flow time, s.
4.2.3. Gravimetry
4.2.4. Synthesis of Solid IPEC
4.2.5. Elemental Analyses
4.2.6. FTIR Spectroscopy
4.2.7. Thermal Analysis
4.2.8. Preparation of Tablets
4.2.9. Determination of the Degree of Swelling of Matrices
4.2.10. In Vitro Drug Release Test
4.2.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinha, V.R.; Kumria, R. Polysaccharides in colon-specific drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 224, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martau, G.A.; Mihai, M.; Vodnar, D.C. The Use of Chitosan, Alginate, and Pectin in the Biomedical and Food Sector—Biocompatibility, Bioadhesiveness, and Biodegradability. Polymers 2019, 11, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z. Polysaccharides-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2008, 14, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rial-Hermida, M.I.; Rey-Rico, A.; Blanco-Fernandez, B.; Carballo-Pedrares, N.; Byrne, E.M.; Mano, J.F. Recent Progress on Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Controlled Delivery of Therapeutic Biomolecules. ASC Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4102–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S. Nanocomposites based on halloysite nanotubes and sulphated galactan from red seaweed Gloiopeltis: Properties and delivery capacity of sodium diclofenac. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, G.; Lazzara, G. Layered composite based on halloysite and natural polymers: A carrier for the pH controlled release of drugs. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 10887–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.M.P.; Coimbra, J.S.R.; Souza, V.G.L.; Sousa, R.C.S. Structure and Applications of Pectin in Food, Biomedical, and Pharmaceutical Industry: A Review. Coatings 2021, 11, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriamornsak, P. Review. Application of pectin in oral drug delivery. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liua, L.S.; Fishmana, M.L.; Kostb, J.; Hicks, K.B. Pectin-based systems for colon-specific drug delivery via oral route. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3333–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigucci, F.; Luppi, B.; Monaco, L.; Cerchiara, T.; Zecchi, V. Pectin-based microspheres for colon-specific delivery of vancomycin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.R.; Kumria, R. Microbially triggered drug delivery to the colon. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 18, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.W.; Colombo, G.; Sonvico, F. Pectin Matrix as Oral Drug Delivery Vehicle for Colon Cancer Treatment. Review Article. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vildanova, R.R.; Petrova, S.F.; Kolesov, S.V.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biodegradable Hydrogels Based on Chitosan and Pectin for Cisplatin Delivery. Gels 2023, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semde, R.; Amighi, K.; Pierre, D.; Devleeschouwer, M.J.; Moes, A.J. Leaching of pectin from mixed pectin/insoluble polymer films intended for colonic drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 174, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semde, R.; Amighi, K.; Michel, J.; Devleeschouwer, M.J.; Moes, A.J. Effect of pectinolytic enzymes on the theophylline release from pellets coated with water insoluble polymers containing pectin HM or calcium pectinate. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 197, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofori-Kwakye, K.; Fell, J.T. Leaching of pectin from mixed films containing pectin, chitosan and HPMC intended for biphasic drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 250, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafin, R.I. Interpolymer combinations of chemically complementary grades of Eudragit copolymers: A new direction in the design of peroral solid dosage forms of drug delivery systems with controlled release (review). Pharm. Chem. J. 2011, 45, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafine, R.I.; Sitenkov, A.Y.; Bukhovets, A.V.; Nasibullin, S.F.; Appeltans, B.; Kabanova, T.V.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Van den Mooter, G. Indomethacin-containing interpolyelectrolyte complexes based on Eudragit EPO/S100 copolymers as a novel drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 524, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmoro, A.; Sitenkov, A.Y.; Cascone, S.; Lamberti, G.; Barba, A.A.; Moustafine, R.I. Hydrophilic drug encapsulation in shell-core microcarriers by two stage polyelectrolyte complexation method. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 518, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmoro, A.; Sitenkov, A.Y.; Lamberti, G.; Barba, A.A.; Moustafine, R.I. Ultrasonic atomization and polyelectrolyte complexation to produce gastroresistant shell–core microparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcíaa, M.C.; Martinellic, M.; Ponced, N.E.; Sanmarcoe, L.M.; Aokie, M.P.; Manzo, R.H.; Jimenez-Kairuz, A.F. Multi-kinetic release of benznidazole-loaded multiparticulate drug delivery systems based on polymethacrylate interpolyelectrolyte complexes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 120, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sester, C.; Ofridam, F.; Lebaz, N.; Gagnière, E.; Mangin, D.; Elaissari, A. pH-Sensitive methacrylic acid–methyl methacrylate copolymer Eudragit L100 and dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, butyl methacrylate, and methyl methacrylate tri-copolymer Eudragit E100. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, B.; Dautzenberg, H.; Linow, K.-J.; Kötz, J.; Dawydoff, W. Polyelectrolyte complexes—Recent developments and open problems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1989, 14, 91–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, E. Formation of polyelectrolyte complexes and their structures. J. Macromol. Sci. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunemann, A.F.; Muller, M.; Dautzenberg, H.; Joanny, J.-F.; Lowen, H. Polyelectrolyte complexes. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2004, 166, 113–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergushov, D.V.; Müller, A.H.E.; Schacher, F.H. Micellar interpolyelectrolyte complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6888–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemenova, V.A.; Mustafin, R.I.; Alekseyev, K.V.; Scorodinskaya, A.M.; Zezin, A.B.; Tenchova, A.I.; Kabanov, V.A. Applying interpolymer complexes in pharmacy. Pharmacya 1991, 60, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hartig, M.S.; Greene, R.R.; Dikov, M.M.; Prokop, A.; Davidson, J.M. Multifunctional nanoparticulate polyelectrolyte complexes. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 2353–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankalapalli, S.; Kolapalli, V.R.M. Polyelectrolyte complexes: A review of their applicability in drug delivery technology. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 71, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Robertis, S.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Elviri, L.; Sandri, G.; Caramella, C.; Bettini, R. Advances in oral controlled drug delivery: The role of drug—Polymer and interpolymer non-covalent interactions. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Navaee, K.; Oskoui, M.; Bayati, K.; Rafiee-Tehrani, M. Preparation and characterization of free mixed-film of pectin/chitosan/Eudragit RS intended for sigmoidal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigucci, F.; Luppi, B.; Cerchiara, T.; Sorrenti, M.; Bettinetti, G.; Rodrigueza, L.; Zecchi, V. Chitosan/pectin polyelectrolyte complexes: Selection of suitable preparative conditions for colon-specific delivery of vancomycin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 35, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, P.B.V.; Choonara, Y.E.; du Toit, L.C.; Ndesendo, V.M.K.; Kumar, P. A Composite Polyelectrolytic Matrix for Controlled Oral Drug Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norcino, L.B.; de Oliveira, J.E.; Moreira, F.K.V.; Marconcini, J.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Rheological and thermo-mechanical evaluation of bio-based chitosan/pectin blends with tunable ionic cross-linking. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiorth, M.; Tho, I.; Sande, S.A. The formation and permeability of drugs across free pectin and chitosan films prepared by a spraying method. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Hervás, M.J.; Fell, J.T. Pectin/chitosan mixtures as coatings for colon-specific drug delivery: An in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 169, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshali, M.M.; Gabr, K.E. Effect of interpolymer complex formation of chitosan with pectin or acacia on the release behaviour of chlorpromazine HCl. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 89, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, G.S.; Collett, J.H.; Fell, J.T. The potential use of mixed films of pectin, chitosan and HPMC for bimodal drug release. J. Control. Release 1999, 58, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzoni, M.; Negri, A.; Brambilla, E.; Giussani, L.; Pitton, S.; Caccia, S.; Epis, S.; Bandi, C.; Locarno, S.; Lenardiad, C. Biodegradable floating hydrogel baits as larvicide delivery systems against mosquitoes. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 6443–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafine, R.I.; Zakharov, I.M. Diffusion transport properties of polymeric complex matrix systems based on Eudragit and sodium alginate. Pharm. Chem. J. 2004, 38, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafine, R.I.; Kemenova, V.A.; Van den Mooter, G. Characteristics of interpolyelectrolyte complexes of Eudragit E100 with sodium alginate. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 294, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafine, R.I.; Salachova, A.R.; Frolova, E.S.; Kemenova, V.A.; Van den Mooter, G. Interpolyelectrolyte complexes of Eudragit® E PO with sodium alginate as potential carriers for colonic drug delivery: Monitoring of structural transformation and composition changes during swellability and release evaluating. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusif, R.M.; Hashim, I.I.A.; El-Dahan, M.S. Some variables affecting the characteristics of Eudragit E-sodium alginate polyelectrolyte complex as a tablet matrix for diltiazem hydrochloride. Acta Pharm. 2014, 64, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunawattanakul, W.; Jaipakdee, N.; Rongthong, T.; Chansri, N.; Srisuk, P.; Chitropas, P.; Pongjanyakul, T. Sodium Alginate-Quaternary Polymethacrylate Composites: Characterization of Dispersions and Calcium Ion Cross-Linked Gel Beads. Gels 2022, 8, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngwuluka, N.C.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; Modi, G.; du Toit, L.C.; Pillay, V.A. Hybrid Methacrylate-Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose Interpolyelectrolyte Complex: Rheometry and in Silico Disposition for Controlled Drug Release. Materials 2013, 6, 4284–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngwuluka, N.C.; Choonara, Y.E.; Modi, G.; du Toit, L.C.; Kumar, P.; Ndesendo, V.M.K.; Pillay, V.A. Design of an Interpolyelectrolyte Gastroretentive Matrix for the Site-Specific Zero-Order Delivery of Levodopa in Parkinson’s Disease. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwuluka, N.C.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; du Toit, L.C.; Modi, G.; Pillay, V.A. Co-blended Locust Bean Gum and Polymethacrylate-NaCMC Matrix to Achieve Zero-Order Release via Hydro-Erosive Modulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, H.J.; Matulewicz, M.C.; Bonelli, P.; Cukierman, A.L. Basic butylated methacrylate copolymer/kappa-carrageenan interpolyelectrolyte complex: Preparation, characterization and drug release behaviour. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.H.; Prado, H.J.; Rodríguez, M.C.; Michetti, K.; Leonardi, P.I.; Matulewicz, M.C. Carrageenans from Sarcothalia crispata and Gigartina skottsbergii: Structural Analysis and Interpolyelectrolyte Complex Formation for Drug Controlled Release. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, H.J.; Matulewicz, M.C.; Bonelli, P.; Cukierman, A.L. Preparation and characterization of a novel starch-based interpolyelectrolyte complex as matrix for controlled drug release. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, H.J.; Matulewicz, M.C.; Bonelli, P.; Cukierman, A.L. Preparation and characterization of controlled release matrices based on novel seaweed interpolyelectrolyte complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 429, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Mooter, G. Colon drug delivery. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidon, S.; Brown, J.E.; Dave, V.S. Colon-Targeted Oral Drug Delivery Systems: Design Trends and Approaches. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Docler, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N. Mechanism of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisele, J.; Haynes, G.; Rosamilia, T. Characterisation and toxicological behaviour of Basic Methacrylate Copolymer for GRAS evaluation. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 61, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafine, R.I.; Bobyleva, V.L.; Bukhovets, A.V.; Garipova, V.R.; Kabanova, T.V.; Kemenova, V.A.; Van den Mooter, G. Structural transformations during swelling of polycomplex matrices based on countercharged (meth)acrylate copolymers (Eudragit® EPO/Eudragit® L100-55). J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafine, R.I.; Bukhovets, A.V.; Sitenkov, A.Y.; Kemenova, V.A.; Rombaut, P.; Van den Mooter, G. Eudragit® E PO as a complementary material for designing oral drug delivery systems with controlled release properties: Comparative evaluation of new interpolyelectrolyte complexes with countercharged Eudragit® L100 copolymers. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 2630–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafine, R.I.; Margulis, E.B.; Sibgatullina, L.F.; Kemenova, V.A.; Van den Mooter, G. Comparative evaluation of interpolyelectrolyte complexes of chitosan with Eudragit® L100 and Eudragit® L100-55 as potential carriers for oral controlled drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Lamoza, M.L.; Remunan-Lopez, C.; Vila-Jato, J.; Alonso, M.J. Design of microencapsulated chitosan microspheres for colonic drug delivery. J. Control. Release 1998, 52, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretti, G.; McGinty, S.; Pontrelli, G. Modelling smart drug release with functionally graded materials. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 164, 107294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| pH | EPO/PecC (mole/mole) | EPO/PecA (mole/mole) |
|---|---|---|
| 4.0 | 1:1.74 | 1:1.8 |
| 5.0 | 1:1.41 | 1:1.67 |
| 6.0 | 1:1.35 | 1:1.38 |
| 7.0 | 1.4:1 | 1.78:1 |
| Sample Symbol | Molar Ration of Polymers EPO/Pec | pH at Which IPEC Was Obtained |
|---|---|---|
| IPEC EPO/PecC_1 | 1:1.5 | 4.0 |
| IPEC EPO/PecC_2 | 1:1 | 5.0 |
| IPEC EPO/PecC_3 | 1:1 | 6.0 |
| IPEC EPO/PecC_4 | 1.5:1 | 7.0 |
| IPEC EPO/PecA_1 | 1:1.5 | 4.0 |
| IPEC EPO/PecA_2 | 1:1.5 | 5.0 |
| IPEC EPO/PecA_3 | 1:1 | 6.0 |
| IPEC EPO/PecA_4 | 4:1 | 7.0 |
| The Korsmeyer–Peppas Equation | Mt/M∞ = k·tn y = a·xb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | IPEC_EPO/PecC_1 | IPEC_EPO/PecC_2 | IPEC_EPO/PecC_3 | IPEC_EPO/PecC_4 |
| Exponential release (n) | 14.0 ± 1.8 | 4.8 ± 0.8 | 8.4 ± 0.9 | 16.4 ± 1.6 |
| Constant release (k) | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 |
| Correlation coefficient (R2) | 0.938 | 0.957 | 0.963 | 0.945 |
| Transport mechanism | Super Case II | Super Case II | Super Case II | Super Case II |
| IPEC_EPO/PecA_1 | IPEC_EPO/PecA_2 | IPEC_EPO/PecA_3 | IPEC_EPO/PecA_4 | |
| Exponential release (n) | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 5.1 ± 0.8 |
| Constant release (k) | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 |
| Correlation coefficient (R2) | 0.985 | 0.981 | 0.958 | 0.973 |
| Transport mechanism | Anomalous transport | Anomalous transport | Super Case II | Super Case II |
| Logistic equation | y = A2 + (A1 − A2)/(1 + x/x0)˄p | |||
| IPEC_EPO/PecC_1 | IPEC_EPO/PecC_2 | IPEC_EPO/PecC_3 | IPEC_EPO/PecC_4 | |
| A1 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 1.0 | 3.5 ± 0.9 | 6.4 ± 1.0 |
| A2 | 56.1 ± 1.0 | 63.6 ± 2.5 | 83.2 ± 1.3 | 76.2 ± 1.3 |
| X0 | 5.1 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.1 |
| P | 2.8 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.1 |
| Correlation coefficient (R2) | 0.998 | 0.996 | 0.998 | 0.997 |
| IPEC_EPO/PecA_1 | IPEC_EPO/PecA_2 | IPEC_EPO/PecA_3 | IPEC_EPO/PecA_4 | |
| A1 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 6.6 ± 0.1 |
| A2 | 46.5 ± 3.7 | 35.9 ± 1.3 | 43.2 ± 2.5 | 67.7 ± 4.2 |
| X0 | 5.5 ± 0.2 | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 4.4 ± 0.2 |
| P | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 4.5 ± 0.3 | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.4 |
| Correlation coefficient (R2) | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.993 | 0.995 |
| Mixing Order | Polymer Ratio | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPO/PecC(or PecA) | 9:1 | 8:2 | 7:3 | 6:4 | 5:5 | 4:6 | 3:7 | 2:8 | 1:9 |
| PecC(or PecA)/EPO | 9:1 | 8:2 | 7:3 | 6:4 | 5:5 | 4:6 | 3:7 | 2:8 | 1:9 |
| Molar Ratios EPO/PecC(or PecA) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6:1 | 5:1 | 4:1 | 3:1 | 2:1 | 1.5:1 | 1:1 | 1:1.5 | 1:2 | 1:3 | 1:4 | 1:5 | 1:6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasibullin, S.F.; Dunaeva, J.V.; Akramova, L.A.; Timergalieva, V.R.; Moustafine, R.I. Characteristics of Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes Based on Different Types of Pectin with Eudragit® EPO as Novel Carriers for Colon-Specific Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417622
Nasibullin SF, Dunaeva JV, Akramova LA, Timergalieva VR, Moustafine RI. Characteristics of Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes Based on Different Types of Pectin with Eudragit® EPO as Novel Carriers for Colon-Specific Drug Delivery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417622
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasibullin, Shamil F., Julia V. Dunaeva, Lilija A. Akramova, Venera R. Timergalieva, and Rouslan I. Moustafine. 2023. "Characteristics of Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes Based on Different Types of Pectin with Eudragit® EPO as Novel Carriers for Colon-Specific Drug Delivery" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417622
APA StyleNasibullin, S. F., Dunaeva, J. V., Akramova, L. A., Timergalieva, V. R., & Moustafine, R. I. (2023). Characteristics of Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes Based on Different Types of Pectin with Eudragit® EPO as Novel Carriers for Colon-Specific Drug Delivery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417622







