Immune Profiling of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis through Targeted Proteomic Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Participants
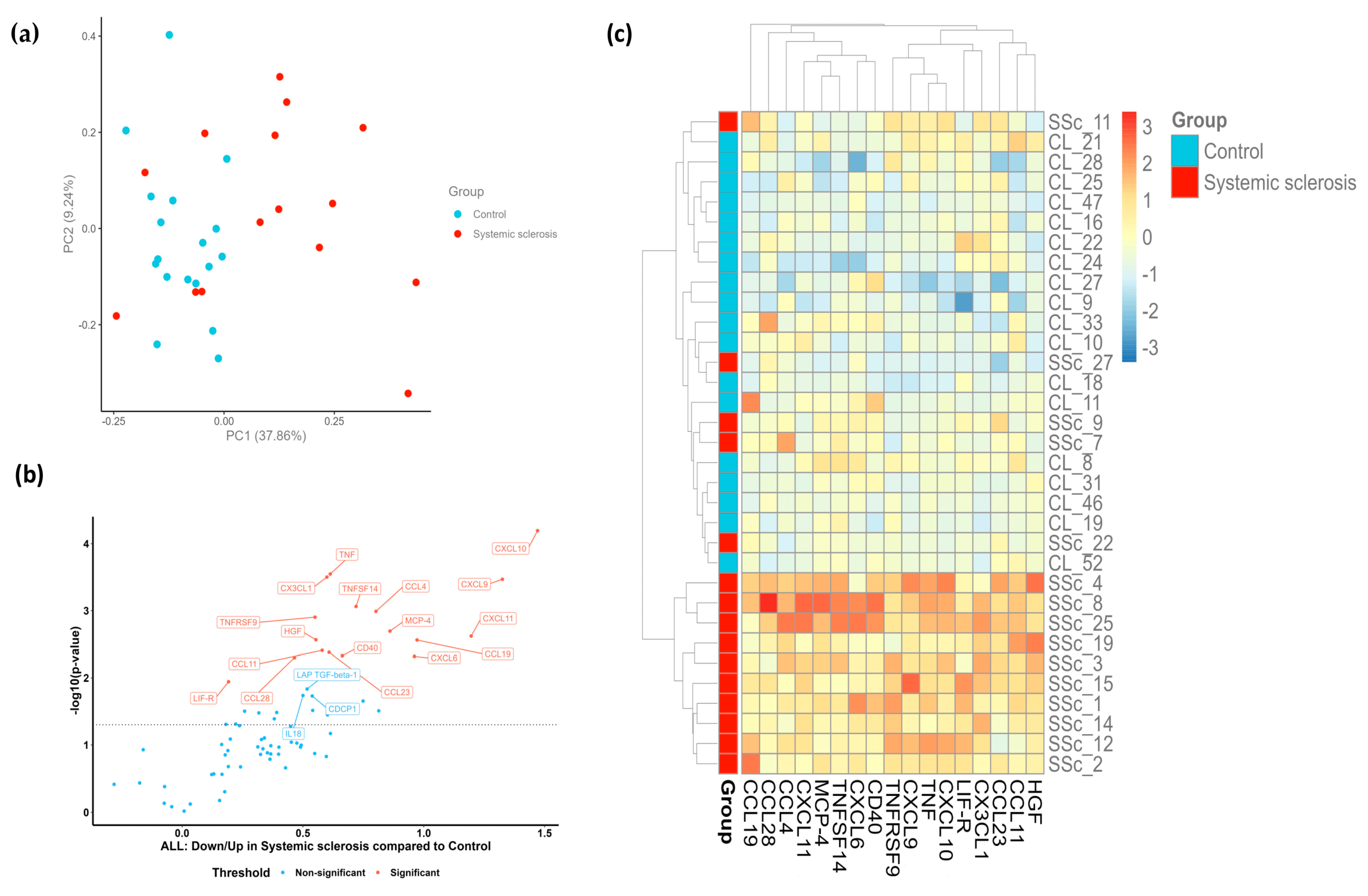
2.2. Patients with SSc Demonstrate a Distinct Proteomic Profile
2.3. Portrayal of Inflammatory Endotypes Based on the Identified Protein Signature
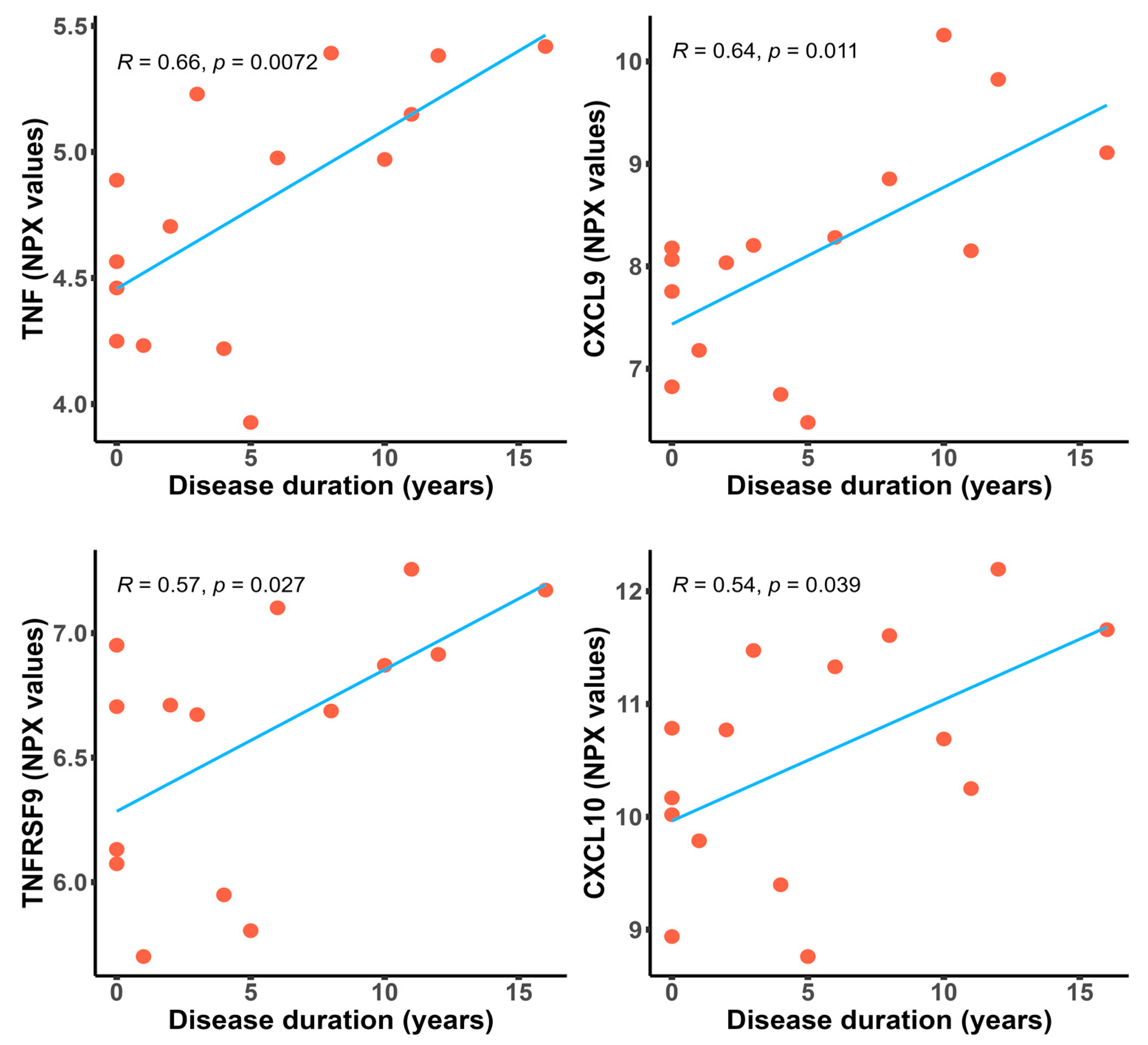
2.4. Inflammatory Proteins Are Significantly Upregulated in Patients with a Longer Disease Duration
2.5. Performance of Differentially Expressed Proteins for the Diagnosis of SSc
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design, Setting, and Participants
4.2. Variables and Data Collection
4.3. Sample Collection and Assessment of Inflammation Biomarkers
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bălănescu, P.; Bălănescu, A.; Bălănescu, E.; Băicuş, C. Candidate proteomic biomarkers in systemic sclerosis discovered using mass-spectrometry: An update of a systematic review (2014–2020). Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 59, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, L.M.; Mantero, J.C.; Stifano, G.; Ziemek, J.; Simms, R.W.; Gordon, J.; Domsic, R.; Lafyatis, R. A Proteome-Derived Longitudinal Pharmacodynamic Biomarker for Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellocchi, C.; Assassi, S.; Lyons, M.; Marchini, M.; Mohan, C.; Santaniello, A.; Beretta, L. Proteomic aptamer analysis reveals serum markers that characterize preclinical systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients at risk for progression toward definite SSc. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piera-Velazquez, S.; Dillon, S.T.; Gu, X.; Libermann, T.A.; Jimenez, S.A. Aptamer proteomics of serum exosomes from patients with Primary Raynaud’s and patients with Raynaud’s at risk of evolving into Systemic Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0279461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanges, S.; Rice, L.; Tu, L.; Valenzi, E.; Cracowski, J.L.; Montani, D.; Mantero, J.C.; Ternynck, C.; Marot, G.; Bujor, A.M.; et al. Biomarkers of haemodynamic severity of systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension by serum proteome analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farutin, V.; Kurtagic, E.; Pradines, J.R.; Capila, I.; Mayes, M.D.; Wu, M.; Manning, A.M.; Assassi, S. Multiomic study of skin, peripheral blood, and serum: Is serum proteome a reflection of disease process at the end-organ level in systemic sclerosis? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, D.H.; Robbins, J.M.; Deng, S.; Tahir, U.A.; Bick, A.G.; Pampana, A.; Yu, Z.; Ngo, D.; Benson, M.D.; Chen, Z.-Z.; et al. Proteomic profiling platforms head to head: Leveraging genetics and clinical traits to compare aptamer- and antibody-based methods. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.E.; Denton, C.P.; Johnson, S.R.; Fernandez-Codina, A.; Hudson, M.; Nevskaya, T. State-of-the-art evidence in the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, N.M.; Liem, S.I.E.; Maurits, M.P.; Ninaber, M.; Marsan, N.A.; Allaart, C.F.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Knevel, R.; de Vries-Bouwstra, J.K. Disease progression in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 1565–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roofeh, D.; Khanna, D. Management of systemic sclerosis: The first five years. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2020, 32, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Turk, M.A.; Pope, J.E. Factors associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann-Vold, A.M.; Allanore, Y.; Alves, M.; Brunborg, C.; Airó, P.; Ananieva, L.P.; Czirják, L.; Guiducci, S.; Hachulla, E.; Li, M.; et al. Progressive interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease in the EUSTAR database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann-Vold, A.M.; Brunborg, C.; Airò, P.; Ananyeva, L.P.; Czirják, L.; Guiducci, S.; Hachulla, E.; Li, M.; Mihai, C.; Riemekasten, G.; et al. Pos0063 Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease Is Frequent Also in Late Disease Stages in Systemic Sclerosis Patients from Eustar. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81 (Suppl. S1), 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Huang, S.; Sancho, J.J.A.; Carreira, P.; Engelhart, M.; Hachulla, E.; Henes, J.; Kerzberg, E.; Pozzi, M.R.; Riemekasten, G.; et al. Pos0914 Late Skin Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis: A Study from the Eustar Cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81 (Suppl. S1), 756–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchetet, M.E.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Current Concepts on the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Clinic Rev. Allerg. Immunol. 2023, 64, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairta, P.P.; Nicolaou, P.; Christodoulou, K. Enrichr in silico analysis of MS-based extracted candidate proteomic biomarkers highlights pathogenic pathways in systemic sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, C.; Wang, S.Y.; Sheban, F.; Zada, M.; Li, B.; Kharouf, F.; Peleg, H.; Aamar, S.; Yalin, A.; Kirschenbaum, D.; et al. LGR5 expressing skin fibroblasts define a major cellular hub perturbed in scleroderma. Cell 2022, 185, 1373–1388.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferri, C.; Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Giuggioli, D.; Colaci, M.; Manfredi, A.; Frascerra, S.; Franzoni, F.; Galetta, F.; et al. CXCL10 (alpha) and CCL2 (beta) chemokines in systemic sclerosis—A longitudinal study. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Asano, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Yamashita, T.; Saigusa, R.; Ichimura, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Toyama, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; Sato, S. Fli1 Deficiency Induces CXCL6 Expression in Dermal Fibroblasts and Endothelial Cells, Contributing to the Development of Fibrosis and Vasculopathy in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umehara, H.; Bloom, E.; Okazaki, T.; Domae, N.; Imai, T. Fractalkine and vascular injury. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volin, M.V.; Woods, J.M.; Amin, M.A.; Connors, M.A.; Harlow, L.A.; Koch, A.E. Fractalkine: A novel angiogenic chemokine in rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathes, A.L.; Christmann, R.B.; Stifano, G.; Affandi, A.J.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Farina, G.A.; Padilla, C.; McLaughlin, S.; Lafyatis, R. Global chemokine expression in systemic sclerosis (SSc): CCL19 expression correlates with vascular inflammation in SSc skin. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, P.; Ammar, R.; Thompson, J.R.; Luo, Y.; Streltsov, D.; Porteous, M.; McCoubrey, C.; Cantu, E., III; Beers, M.F.; Jarai, G.; et al. Integrated plasma proteomics and lung transcriptomics reveal novel biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habiel, D.M.; Espindola, M.S.; Jones, I.C.; Coelho, A.L.; Stripp, B.; Hogaboam, C.M. CCR10+ epithelial cells from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis lungs drive remodeling. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e122211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Domínguez-Andrés, J.; Barreiro, L.B.; Chavakis, T.; Divangahi, M.; Fuchs, E.; Joosten, L.A.B.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Mhlanga, M.M.; Mulder, W.J.M.; et al. Defining trained immunity and its role in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochando, J.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Madsen, J.C.; Netea, M.G.; Duivenvoorden, R. Trained immunity—Basic concepts and contributions to immunopathology. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeljeli, M.; Riccio, L.G.C.; Doridot, L.; Chêne, C.; Nicco, C.; Chouzenoux, S.; Joosten, L.A.B.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Mhlanga, M.M.; Mulder, W.J.M.; et al. Trained immunity modulates inflammation-induced fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, R.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Patel, M.C.; Yang, Y.; Ouda, R.; Joosten, L.A.B.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Mhlanga, M.M.; Mulder, W.J.M.; et al. Interferon stimulation creates chromatin marks and establishes transcriptional memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E9162–E9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.K.; Ju, S.A.; Lee, S.C.; Park, S.M.; Choe, S.Y.; Kwon, B.; Kwon, B.S.; Kim, B.-S. LIGHT enhances the bactericidal activity of human monocytes and neutrophils via HVEM. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindzienska-Sieskiewicz, E.; Distler, O.; Reszec, J.; Jordan, S.; Bielecki, P.; Sieskiewicz, A.; Sulik, A.; Lukasik, M.; Bielecki, M.; Kowal, K.; et al. Increased expression of the TNF superfamily member LIGHT/TNFSF14 and its receptors (HVEM and LTßR) in patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, A.; Bruns, H.; Fuchs, M.; Völkl, S.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Kunz, M.; Peipp, M.; Mackensen, A.; Mougiakakos, D. CD137 (4-1BB) stimulation leads to metabolic and functional reprogramming of human monocytes/macrophages enhancing their tumoricidal activity. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3482–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukasawa, C.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Harigai, M.; Sugiura, T.; Takagi, K.; Kawamoto, M.; Hara, M.; Kamatani, N. Increased CD40 expression in skin fibroblasts from patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc): Role of CD40-CD154 in the phenotype of SSc fibroblasts. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 2792–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komura, K.; Fujimoto, M.; Matsushita, T.; Yanaba, K.; Kodera, M.; Kawasuji, A.; Hasegawa, M.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Increased serum soluble CD40 levels in patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 34, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rea, I.M.; Gibson, D.S.; McGilligan, V.; McNerlan, S.E.; Alexander, H.D.; Ross, O.A. Age and Age-Related Diseases: Role of Inflammation Triggers and Cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Parini, P.; Giuliani, C.; Santoro, A. Inflammaging: A new immune-metabolic viewpoint for age-related diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, N.; Huang, Y.; Nguyen, K.; Krejciova-Rajaniemi, Z.; Grawe, A.P.; Gao, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Hastie, T.; Alpert, A.; Cui, L.; et al. An inflammatory aging clock (iAge) based on deep learning tracks multimorbidity, immunosenescence, frailty and cardiovascular aging. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, F.F.; Lima Torres, K.C.; Viana Peixoto, S.; Pinho Ribeiro, A.L.; Vaz Melo Mambrini, J.; Bortolo Rezende, V.; Silva, M.L.L.; Filho, A.I.L.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; Lima-Costa, M.F.; et al. CXCL9 and CXCL10 display an age-dependent profile in Chagas patients: A cohort study of aging in Bambui, Brazil. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyahu, Y.; Hekselman, I.; Eizenberg-Magar, I.; Berner, O.; Strominger, I.; Schiller, M.; Mittal, K.; Nemirovsky, A.; Eremenko, E.; Vital, A.; et al. Aging promotes reorganization of the CD4 T cell landscape toward extreme regulatory and effector phenotypes. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliprantis, A.O.; Wang, J.; Fathman, J.W.; Lemaire, R.; Dorfman, D.M.; Lafyatis, R.; Glimcher, L.H. Transcription factor T-bet regulates skin sclerosis through its function in innate immunity and via IL-13. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2827–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavalia, C.; Scaletti, C.; Romagnani, P.; Carossino, A.M.; Pignone, A.; Emmi, L.; Pupilli, C.; Pizzolo, G.; Maggi, E.; Romagnani, S. Type 2 helper T-cell predominance and high CD30 expression in systemic sclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Parel, Y.; Aurrand-Lions, M.; Scheja, A.; Dayer, J.M.; Roosnek, E.; Chizzolini, C. Presence of CD4+CD8+ double-positive T cells with very high interleukin-4 production potential in lesional skin of patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3459–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Longitudinal analysis of serum cytokine concentrations in systemic sclerosis: Association of interleukin 12 elevation with spontaneous regression of skin sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bauer, Y.; de Bernard, S.; Hickey, P.; Ballard, K.; Cruz, J.; Cornelisse, P.; Chadha-Boreham, H.; Distler, O.; Rosenberg, D.; Doelberg, M.; et al. Identifying early pulmonary arterial hypertension biomarkers in systemic sclerosis: Machine learning on proteomics from the DETECT cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2002591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.O.; Pilar, F.U.; Martinez-Monllor, M.; Muñoz-Barrera, L.; Sanchez-Pareja, I.; Ábalos-Aguilera, M.C.; Barbarroja, N.; Collantes-Estevez, E.; Aguirre-Zamorano, M.Á.; Pérez-Sánchez, C.; et al. Pos0488 Identification of Novel Disease Biomarkers in Systemic Sclerosis Through High-Throughput Proteomics. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81 (Suppl. S1), 498–499. [Google Scholar]
- LeRoy, E.C.; Medsger, T.A. Criteria for the classification of early systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 1573–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Noordegraaf, A.V.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Kardiol. Pol. 2015, 73, 1127–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | SSc, n = 15 1 |
|---|---|
| Age | 53 (48, 60) |
| Gender | |
| female | 15 (100%) |
| SSc subtype | |
| diffuse cutaneous | 6 (40%) |
| limited cutaneous | 9 (60%) |
| Disease duration (years) | 4 (0.5, 9.0) |
| Disease duration (early ≤ 3 years; late >3 years) | |
| early | 7 (47%) |
| late | 8 (53%) |
| Calcinosis | 2 (13%) |
| Telangiectasis | 9 (60%) |
| Digital ulcers (previous, current, never) | |
| previous | 7 (47%) |
| current | 2 (13%) |
| never | 6 (40%) |
| ILD | 8 (53%) |
| Arrythmias requiring therapy | 4 (27%) |
| Conduction blocks | 2 (13%) |
| PAH requiring therapy | 1 (6.7%) |
| Esophagitis | 5 (33%) |
| ANA | |
| positive | 15 (100%) |
| anti-Scl-70 antibodies | |
| positive | 8 (53%) |
| anti-centromere antibodies | |
| positive | 5 (33%) |
| Variable | Pearson’s Coefficient | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| TNF | 0.6615 | 0.0072 |
| CXCL9 | 0.6371 | 0.0106 |
| TNFRSF9 | 0.5697 | 0.0266 |
| CXCL10 | 0.5365 | 0.0392 |
| LIF-R | 0.4778 | 0.0716 |
| CXCL11 | 0.4188 | 0.1203 |
| CD40 | 0.3497 | 0.2013 |
| HGF | 0.3129 | 0.2562 |
| CCL28 | 0.2872 | 0.2993 |
| TNSF14 | 0.2814 | 0.3097 |
| CCL19 | 0.2770 | 0.3175 |
| CCL4 | 0.2463 | 0.3763 |
| MCP-4 | 0.2196 | 0.4315 |
| CXCL6 | 0.1976 | 0.4801 |
| CCL11 | 0.1439 | 0.6090 |
| CX3CL1 | 0.0891 | 0.7523 |
| CCL23 | 0.0008 | 0.9978 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szabo, I.; Badii, M.; Gaál, I.O.; Szabo, R.; Sîrbe, C.; Humiță, O.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Crișan, T.O.; Rednic, S. Immune Profiling of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis through Targeted Proteomic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417601
Szabo I, Badii M, Gaál IO, Szabo R, Sîrbe C, Humiță O, Joosten LAB, Crișan TO, Rednic S. Immune Profiling of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis through Targeted Proteomic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417601
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzabo, Iulia, Medeea Badii, Ildikó O. Gaál, Robert Szabo, Claudia Sîrbe, Oana Humiță, Leo A. B. Joosten, Tania O. Crișan, and Simona Rednic. 2023. "Immune Profiling of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis through Targeted Proteomic Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417601
APA StyleSzabo, I., Badii, M., Gaál, I. O., Szabo, R., Sîrbe, C., Humiță, O., Joosten, L. A. B., Crișan, T. O., & Rednic, S. (2023). Immune Profiling of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis through Targeted Proteomic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17601. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417601









