Joint QTL Mapping and Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis Reveal Candidate Genes for Salinity Tolerance in Oryza sativa L. ssp. Japonica Seedlings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
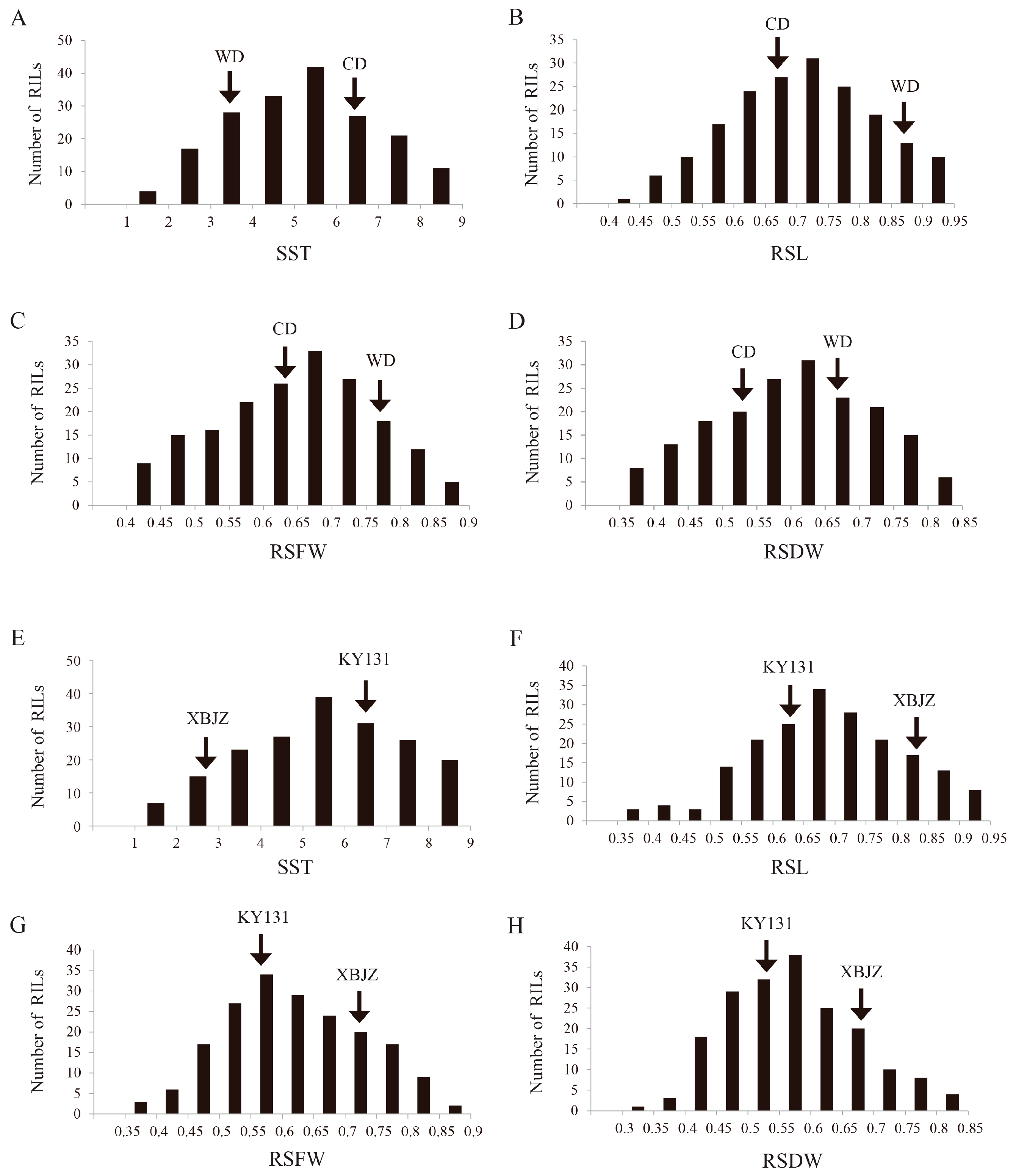
2.1. Phenotypic Variation
2.2. Linkage Mapping for Salinity Tolerance
2.3. RNA-Seq Statistics
2.4. Candidate Gene Mining
2.5. Validation of the LOC_Os12g29400 Mutant
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Plant Materials
5.2. Salinity Tolerance Evaluation at the Seedling Stage
5.3. QTL Mapping for Salinity Tolerance
5.4. RNA-Seq
5.5. Identification of Candidate Genes by Gene Expression and Sequence Analysis
5.6. LOC_Os12g29400 Mutant Plants
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R. Genes and salt tolerance: Bringing them together. New Phytol. 2005, 167, 645–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, S.J.; Stirnberg, P.M.; Hartley, S.E.; Maathuis, F.J.M. The Ability of Silicon Fertilisation to Alleviate Salinity Stress in Rice is Critically Dependent on Cultivar. Rice 2022, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, D.Z.; Zhang, G.P. Advances in studies on ion transporters involved in salt tolerance and breeding crop cultivars with high salt tolerance. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2020, 21, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, L.C.; Wei, X.; Wang, R.H.; Li, N.N.; Chen, G.L.; Fan, F.F.; Huang, S.Y.; Li, J.X.; Li, S.Q. Quantitative Trait Locus Mapping of Salt Tolerance in Wild Rice Oryza longistaminata. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, A.; Ali, A.; Bin Safdar, L.; Zafar, M.M.; Rui, Y.; Shakeel, A.; Shaukat, A.; Ashraf, M.; Gong, W.K.; Yuan, Y.L. Salt stress induces physiochemical alterations in rice grain composition and quality. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Kota, S.; Flowers, T.J. Salt tolerance in rice: Seedling and reproductive stage QTL mapping come of age. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 3495–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, S.; Kim, E.G.; Jang, Y.H.; Jan, R.; Kim, N.; Asaf, S.; Lubna; Farooq, M.; Kim, K.M. Identification of the OsCML4 Gene in Rice Related to Salt Stress Using QTL Analysis. Plants 2022, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.X.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, K.; Shen, C.C.; Zhao, X.Q.; Shabala, S.; Shabala, L.; Meinke, H.; Venkataraman, G.; Chen, Z.H.; et al. Identification of new QTL for salt tolerance from rice variety Pokkali. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 2020, 206, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, N.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Song, M.Q.; Zhao, C.Y.; Hu, H.T.; Cui, Y.T.; Wang, Z.W.; Yang, S.L.; Zhang, A.P.; et al. QTL analysis for rice salinity tolerance and fine mapping of a candidate locus qSL7 for shoot length under salt stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 90, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.X.; Zhu, M.Z.; Yano, M.; Gao, J.P.; Liang, Z.W.; Su, W.A.; Hu, X.H.; Ren, Z.H.; Chao, D.Y. QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-M.; Ju, H.-G.; Kwon, T.-R.; Oh, C.-S.; Ahn, S.-N. Mapping QTLs for Salt Tolerance in an Introgression Line Population between Japonica Cultivars in Rice. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 12, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehisa, H.; Shimodate, T.; Fukuta, Y.; Ueda, T.; Yano, M.; Yamaya, T.; Kameya, T.; Sato, T. Identification of quantitative trait loci for plant growth of rice in paddy field flooded with salt water. Field Crop. Res. 2004, 89, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.H.; Gao, J.P.; Li, L.G.; Cai, X.L.; Huang, W.; Chao, D.Y.; Zhu, M.Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Luan, S.; Lin, H.X. A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, M.J.; de Ocampo, M.; Egdane, J.; Rahman, M.A.; Sajise, A.G.; Adorada, D.L.; Tumimbang-Raiz, E.; Blumwald, E.; Seraj, Z.I.; Singh, R.K.; et al. Characterizing the Saltol Quantitative Trait Locus for Salinity Tolerance in Rice. Rice 2010, 3, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Chao, D.Y.; Gao, J.P.; Zhu, M.Z.; Shi, M.; Lin, H.X. A previously unknown zinc finger protein, DST, regulates drought and salt tolerance in rice via stomatal aperture control. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.D.; Xie, H.J.; Wei, X.J.; Dossa, K.; Yu, Y.Y.; Hui, S.Z.; Tang, G.H.; Zeng, X.S.; Yu, Y.H.; Hu, P.S.; et al. WGCNA Analysis of Salt-Responsive Core Transcriptome Identifies Novel Hub Genes in Rice. Genes 2019, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, T.; Du, Q.; Ma, X.D.; Cui, D.; Han, B.; Zhang, Q.X.; Han, L.Z. Integrating linkage mapping and comparative transcriptome analysis for discovering candidate genes associated with salt tolerance in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leon, T.B.; Linscombe, S.; Subudhi, P.K. Molecular Dissection of Seedling Salinity Tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Using a High-Density GBS-Based SNP Linkage Map. Rice 2016, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, K.; Rabiei, B.; Sabouri, H.; Sabouri, A. Mapping QTLs for Traits Related to Salinity Tolerance at Seedling Stage of Rice (Oryza sativa L.): An Agrigenomics Study of an Iranian Rice Population. Omics 2013, 17, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabouri, H.; Rezai, A.M.; Moumeni, A.; Kavousi, A.; Katouzi, M.; Sabouri, A. QTLs mapping of physiological traits related to salt tolerance in young rice seedlings. Biol. Plant. 2009, 53, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfatih, A.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jan, S.U.; Zhang, Z.S.; Xia, J.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Nazish, T.; Wu, J.; Zhao, P.X.; et al. Nitrate-responsive OsMADS27 promotes salt tolerance in rice. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, M.R.; Chen, L.; Wu, G.J.; Li, H.Q. Rapid generation of rice mutants via the dominant negative suppression of the mismatch repair protein OsPMS1. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, H.; Rahman, M.A.; Alam, M.S.; Singh, R.K. Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci Associated with Reproductive-Stage Salt Tolerance in Rice. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2015, 201, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, Q.H.; Zhang, H.S. Identification of a rice zinc finger protein whose expression is transiently induced by drought, cold but not by salinity and abscisic acid. DNA Seq. 2005, 16, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.R.; Wang, Y.; Meng, L.J.; Hu, X.; Cui, Y.R.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, L.H.; Ali, J.; Xu, J.L.; Li, Z.K. Identification of salt-tolerant QTLs with strong genetic background effect using two sets of reciprocal introgression lines in rice. Genome 2012, 55, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, T.; Kitamoto, H.K.; Nakamura, A.; Fukuda, A.; Tanaka, Y. Rice Shaker potassium channel OsKAT1 confers tolerance to salinity stress on yeast and rice cells. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Wang, J.F.; Bao, Y.M.; Wu, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.S. Quantitative trait loci controlling rice seed germination under salt stress. Euphytica 2011, 178, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Zhang, C.C.; Wei, C.C.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.G.; Yu, F.F.; Xie, Q.; Tu, J.M. The RING Finger Ubiquitin E3 Ligase OsHTAS Enhances Heat Tolerance by Promoting H2O2-Induced Stomatal Closure in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.F.; Duan, M.; Huang, S.D.; Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H.S. A Novel Nuclear Protein Phosphatase 2C Negatively Regulated by ABL1 is Involved in Abiotic Stress and Panicle Development in Rice. Mol. Biotechnol. 2013, 54, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbani, M.A.; Maruyama, K.; Abe, H.; Khan, M.A.; Katsura, K.; Ito, Y.; Yoshiwara, K.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Monitoring expression profiles of rice genes under cold, drought, and high-salinity stresses and abscisic acid application using cDNA microarray and RNA get-blot analyses. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 1755–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doerks, T.; Strauss, M.; Brendel, M.; Bork, P. GRAM, a novel domain in glucosyltransferases, myotubularins and other putative membrane-associated proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, K.N.; Schroeder, D.F.; Stasolla, C. GEm-Related 5 (GER5), an ABA and stress-responsive GRAM domain protein regulating seed development and inflorescence architecture. Plant Sci. 2014, 223, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.S.; Hwang, B.K. Proteomics and Functional Analyses of Pepper Abscisic Acid-Responsive 1 (ABR1), Which Is Involved in Cell Death and Defense Signaling. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Ramamoorthy, R.; Ramachandran, S. Comparative transcriptional profiling and evolutionary analysis of the GRAM domain family in eukaryotes. Dev. Biol. 2008, 314, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, N.; Fernández-Marcos, M.; Costas, C.; Desvoyes, B.; Pichel, A.; Caro, E.; Gutierrez, C. GEM, a member of the GRAM domain family of proteins, is part of the ABA signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Shweta, S.; Prasad, M.; Lata, C. Genome-wide investigation of GRAM-domain containing genes in rice reveals their role in plant-rhizobacteria interactions and abiotic stress responses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Zheng, H.L.; Wu, W.S.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, J.G.; Jia, Y.; Li, J.M.; Yang, L.M.; Lei, L.; Zou, D.T.; et al. QTL Mapping and Candidate Gene Analysis for Alkali Tolerance in Japonica Rice at the bud Stage Based on Linkage Mapping and Genome-Wide Association Study. Rice 2020, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Han, Z.H.; Cui, B.W.; Yang, L.M.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, J.G.; Zhao, H.W.; Xin, W.; Li, X.W.; Li, J.M.; et al. Mapping of a major QTL for salinity tolerance at the bud burst stage in rice (Oryza sativa L) using a high-density genetic map. Euphytica 2021, 217, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazee, A.C.; Pertea, G.; Jaffe, A.E.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L.; Leek, J.T. Ballgown bridges the gap between transcriptome assembly and expression analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Traits | QTLs | Left Marker | Right Marker | Chr. | LOD | R2 (%) | Additive Effect | Known QTLs | Known Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST | qSST4 | C4_32625360 | C4_32680426 | 4 | 2.98 | 5.85 | −0.41 | qDWT4.32 [20] | |
| qSST12-1 | C12_17379052 | C12_17572391 | 12 | 10.94 | 23.52 | −0.83 | qSNK-12 [21] | ||
| RSL | qRSL2 | C2_21864234 | C2_24239570 | 2 | 4.57 | 9.70 | 0.04 | qNA-2a [22] | OsMADS27 [23] OsPMS1 [24] |
| qRSL10 | C10_2404205 | C10_2549079 | 10 | 2.55 | 5.34 | −0.03 | qPF10.2 [25] | ||
| RSFW | qRSFW4 | C4_26190239 | C4_26579339 | 4 | 2.66 | 5.90 | −0.03 | ||
| qRSFW7 | C7_23130700 | C7_24094627 | 7 | 4.30 | 10.47 | −0.04 | ZFP245 [26] | ||
| RSDW | qRSDW11 | C11_23355381 | C11_23543062 | 11 | 4.70 | 11.67 | −0.04 |
| Traits | QTLs | Left Marker | Right Marker | Chr. | LOD | R2 (%) | Additive Effect | Known QTLs | Known Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST | qSST1 | C1_31761401 | C1_32601806 | 1 | 2.96 | 5.89 | −0.48 | qSKC1 [27] | OsKAT1 [28] |
| qSST11 | C11_25364222 | C11_25595354 | 11 | 3.88 | 7.68 | 0.55 | |||
| qSST12-2 | C12_16988462 | C12_17519826 | 12 | 5.25 | 10.60 | −0.04 | qSNK-12 [21] | ||
| RSL | qRSL4 | C4_21835179 | C4_22375729 | 4 | 3.71 | 7.19 | 0.03 | qDTF4.1s [27] | |
| qRSL12 | C12_16988462 | C12_17519826 | 12 | 9.26 | 17.83 | −0.06 | qSNK-12 [21] | ||
| RSFW | qRSFW9 | C9_9364678 | C9_9790798 | 9 | 2.77 | 7.40 | −0.03 | qGP-7-2 [29] | OsHTAs [30] OsSIPP2C1 [31] |
| RSDW | qRSDW3 | C3_26113568 | C3_28667135 | 3 | 2.77 | 6.35 | −0.03 | qCHL3.26 [20] | OsBIHD1 [20] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Xu, S.; Zheng, J.; Du, H.; Li, C.; Shen, S.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; et al. Joint QTL Mapping and Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis Reveal Candidate Genes for Salinity Tolerance in Oryza sativa L. ssp. Japonica Seedlings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417591
Li S, Xu S, Zheng J, Du H, Li C, Shen S, Liang S, Wang J, Liu H, Yang L, et al. Joint QTL Mapping and Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis Reveal Candidate Genes for Salinity Tolerance in Oryza sativa L. ssp. Japonica Seedlings. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417591
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuangshuang, Shanbin Xu, Jie Zheng, Haoqiang Du, Chong Li, Shen Shen, Shaoming Liang, Jingguo Wang, Hualong Liu, Luomiao Yang, and et al. 2023. "Joint QTL Mapping and Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis Reveal Candidate Genes for Salinity Tolerance in Oryza sativa L. ssp. Japonica Seedlings" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417591
APA StyleLi, S., Xu, S., Zheng, J., Du, H., Li, C., Shen, S., Liang, S., Wang, J., Liu, H., Yang, L., Xin, W., Jia, Y., Zou, D., & Zheng, H. (2023). Joint QTL Mapping and Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis Reveal Candidate Genes for Salinity Tolerance in Oryza sativa L. ssp. Japonica Seedlings. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417591






