The Immune Response to the Myxozoan Parasite Myxobolus cerebralis in Salmonids: A Review on Whirling Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical and Histopathological Changes in Diseased Fish
3. Innate Immune Response
3.1. Role of Physical Barrier in Immunity against M. cerebralis
3.2. Cellular Immunity
3.2.1. Macrophages
3.2.2. Lymphocytes
3.2.3. Granulocytes
3.2.4. Mast Cells
3.2.5. Rodlet Cells
3.3. Humoral Immunity
3.4. Cytokine Response
4. Adaptive Immune Responses to M. cerebralis
4.1. T Cells
4.2. B Cells
5. Immune Modulation in WD-Resistant and Susceptible Fish
6. Immune Modulation in Response to Co-Infection
7. Immune Modulation Due to Environmental Factors
8. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bianchi, M.C.G.; Camilleri, M.; Chopin, F.; Farme, T.; Franz, N.; Fuentevilla, C.; Garibaldi, L.; Grainger, R.; Hishamunda, N.; Jara, F.; et al. FAO: The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014; pp. 1–230. [Google Scholar]
- Sudhagar, A.; Kumar, G.; El-Matbouli, M. The malacosporean myxozoan parasite Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae: A threat to wild salmonids. Pathogens 2019, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomew, J.L.; Reno, P.W. The history and dissemination of whirling disease. In American Fisheries Society Symposium; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Fish immune response to Myxozoan parasites. Parasite 2008, 15, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, B.W.; Winkelman, D.L.; Fetherman, E.R. Survival of Whirling-Disease-Resistant Rainbow Trout Fry in the Wild: A Comparison of Two Strains. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2018, 30, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaylock, R.B.; Bullard, S.A. Counter-insurgents of the blue revolution? parasites and diseases affecting aquaculture and science. J. Parasitol. 2014, 100, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwell, L.C.S.; Stromberg, K.E.; Ryce, E.K.; Bartholomew, J.L. Whirling disease in the United States: A summary of progress in research and management. In Proceedings of the Wild Trout X Symposium, West Yellowstone, MT, USA, 28–39 September 2010; p. 203. [Google Scholar]
- Halliday, M.M. The biology of Myxosoma cerebralis: The causative organism of whirling disease of salmonids. J. Fish Biol. 1976, 9, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.G.; Smith, M.J.; Ridenhour, B.J. Whirling disease dynamics: An analysis of intervention strategies. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 113, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grodnick, J.J. Susceptibility of various salmonids to whirling disease (Myxosoma cerebralis). Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1979, 108, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grodnick, J.J. Susceptibility studies of various salmonids in whirling disease: Histologic staining and spore concentration procedures. US Natl. Mar. Fish. Serv. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1978, 40, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, H.; Hipp, E.; Sedlmeier, U.A. Aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of the freshwater oligochaete Tubifex sp. Hydrobiologia 1987, 155, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, R.P.; El-Matbouli, M. Recent advances with taxonomy, life cycle, and development of Myxobolus cerebralis in the fish and oligochaete hosts. In American Fisheries Society Symposium; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002; pp. 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, T.J.; Vincent, E.R.; Silflow, R.M.; Stanek, D. Myxobolus cerebralis infection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and brown trout (Salmo trutta) exposed under natural stream conditions. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2000, 12, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrick, R.P.; McDowell, T.S.; Mukkatira, K.; Georgiadis, M.P.; MacConnell, E. Susceptibility of selected inland salmonids to experimentally induced infections with Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of whirling disease. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1999, 11, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.; Kallert, D.; Hedrick, R.; El-Matbouli, M. Whirling disease revisited: Pathogenesis, parasite biology and disease intervention. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 114, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiw, M. Portals of entry for salmonid whirling disease in rainbow trout. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1989, 6, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.A.; Granath, W.O., Jr. Whirling disease of salmonid fish: Life cycle, biology, and disease. J. Parasitol. 2003, 89, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiw, M.E. Whirling disease: Earliest susceptible age of rainbow trout to the triactinomyxid of Myxobolus cerebralis. Aquaculture 1991, 92, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.A.; Granath, W.O., Jr. Persistent infection of Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of salmonid whirling disease, in Tubifex tubifex. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 87, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Matbouli, M.; Hoffmann, R.W.; Mandok, C. Light and electron microscopic observations on the route of the triactinomyxon-sporoplasm of Myxobolus cerebralis from epidermis into rainbow trout cartilage. J. Fish Biol. 1995, 46, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Matbouli, M.; Hoffmann, R.W.; Schoel, H.; McDowell, T.S.; Hedrick, R.P. Whirling disease:host specificity and interaction between the actinosporean stage of Myxobolus cerebralis and rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.R.M.C.; Staines, N.A.; Hernandez-Blazquez, F.J.; Porto-Neto, L.R.; Borges, J.C.S. Phagocytosis and giant cell formation at 0 °C by macrophage (MØ) of Notothenia coriiceps. J. Fish Biol. 2002, 60, 466–478. [Google Scholar]
- Secombes, C.J.; Wang, T. The innate and adaptive immune system of fish. In Infectious Disease in Aquaculture; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 3–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lom, J. Myxosporea: A new look at long-known parasites of fish. Parasitol. Today 1987, 3, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, C.; Folch, H.; Enriquez, R.; Moran, G. Innate and adaptive immunity in teleost fish: A review. Vet. Med. 2011, 56, 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Alvarez-Pellitero, P. Pathologic effects of Sphaerospora dicentrarchi Sitjà-Bobadilla and Alvarez-Pellitero, 1992 and S. testicularis Sitjà-Bobadilla and Alvarez-Pellitero, 1990 (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) parasitic in the Mediterranean sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax L. (Teleostei: Serranidae) and the cell-mediated immune reaction: A light and electron microscopy study. Parasitol. Res. 1993, 79, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucker, U.; El-Matbouli, M. Sequence analysis of OmNramp α and quantitative expression of Nramp homologues in different trout strains after infection with Myxobolus cerebralis. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 76, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.; Montero, R.; Kumar, G.; Sudhagar, A.; Friedl, A.; Köllner, B.; El-Matbouli, M. Kinetics of local and systemic immune cell responses in whirling disease infection and resistance in rainbow trout. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.; Friedl, A.; Srivastava, M.; Secombes, C.J.; El-Matbouli, M. Modulation of local and systemic immune responses in brown trout (Salmo trutta) following exposure to Myxobolus cerebralis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovey, M.G.; Lallemand, C. Adjuvant activity of cytokines. In Vaccine Adjuvants: Methods and Protocols; Humana: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 287–309. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, M.; Friedl, A.; Srivastava, M.; Soliman, H.; Secombes, C.J.; El-Matbouli, M. STAT3/SOCS3 axis contributes to the outcome of salmonid whirling disease. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Pellitero, P. Fish immunity and parasite infections: From innate immunity to immunoprophylactic prospects. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 126, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Living off a fish: A trade-off between parasites and the immune system. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerwald, M.R. Temporal expression patterns of rainbow trout immune-related genes in response to Myxobolus cerebralis exposure. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kotob, M.H.; El-Matbouli, M. A RNAi-based therapeutic proof of concept targets salmonid whirling disease in vivo. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.; Holland, J.W.; Secombes, C.J.; Tafalla, C. A portrait of the immune response to proliferative kidney disease (PKD) in rainbow trout. Parasite Immunol. 2020, 42, e12730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Matbouli, M.; Hoffmann, R. Light and electron microscopic studies on the chronological development of Myxobolus cerebralis to the actinosporean stage in Tubifex tubifex. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.D.; Marrs, G.S.; Lewis, C.; Schisler, G. Whirling disease behavior and its relation to pathology of brain stem and spinal cord in rainbow trout. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2000, 12, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K. Salmonid Whirling Disease; US Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, Division of Fishery Research: Lincoln, NE, USA, 1985; Volume 69.
- Kotob, M.H.; Gorgoglione, B.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae and Myxobolus cerebralis co-infections on pathology in rainbow trout. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, C. The peripheral vestibular system in fishes. In Fish Neurobiology; Northcutt, R.G., Davis, R.E., Eds.; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1983; pp. 89–124. [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen Recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, S.K. The innate immune response of finfish–A review of current knowledge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 1127–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turvey, S.E.; Broide, D.H. Innate immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S24–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadóttir, B. Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A. Innate host defense mechanisms of fish against viruses and bacteria. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnadottir, B. Immunological control of fish diseases. Mar. Biotechnol. 2010, 12, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.Á. An Overview of the immunological defenses in fish skin. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 853470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveinbjornsson, B.; Olsen, R.; Paulsen, S. Immunocytochemical localization of lysozyme in intestinal eosinophilic granule cells (EGCs) of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J. Fish Dis. 1996, 19, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, U.; Utke, K.; Somamoto, T.; Köllner, B.; Ototake, M.; Nakanishi, T. Cytotoxic activities of fish leucocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallert, D.; Eszterbauer, E.; Grabner, D.; El-Matbouli, M. In vivo exposure of susceptible and non-susceptible fish species to Myxobolus cerebralis actinospores reveals non-specific invasion behaviour. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 84, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Wahli, T.; Holland, J.W.; Secombes, C.J. Fish immune responses to Myxozoa. In Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 253–280. [Google Scholar]
- Estensoro, I.; Mulero, I.; Redondo, M.J.; Álvarez-Pellitero, P.; Mulero, V.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Modulation of leukocytic populations of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) by the intestinal parasite Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa: Myxosporea). Parasitology 2014, 141, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania, P.W.; Evensen, O.; Larsen, T.B.; Buchmann, K. Molecular and immunohistochemical studies on epidermal responses in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. induced by Gyrodactylus salaris Malmberg, 1957. J. Helminthol. 2010, 84, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, T. The nonspecific immune system: Humoral defense. In The Fish Immune System: Organism, Pathogen, Environment; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 105–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kallert, D.M.; Borrelli, J.; Haas, W. Biostatic activity of piscine serum and mucus on myxozoan fish infective stages. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.R.M. The occurrence and mechanisms of innate immunity against parasites in fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, R.P.; Adkison, M.A.; El-Matbouli, M.; MacConnell, E. Whirling disease: Re-emergence among wild trout. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 166, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, G.O.; Adkison, M.A.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Hedrick, R.P. Myxobolus cerebralis: Identification of a cathepsin Z-like protease gene (MyxCP-1) expressed during parasite development in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Exp. Parasitol. 2003, 105, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, G.; Zagmutt-Vergara, F.; Leutenegger, C.; Adkison, M.; Baxa, D.; Hedrick, R. Identification of a serine protease gene expressed by Myxobolus cerebralis during development in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2004, 59, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörfler, C.; El-Matbouli, M. Isolation of a subtilisin-like serine protease gene (MyxSubtSP) from spores of Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of whirling disease. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 73, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtar, D.M.; Zaccone, G.; Alesci, A.; Kuciel, M.; Hussein, M.T.; Sayed, R.K.A. Main components of fish immunity: An overview of the fish immune system. Fishes 2023, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secombes, C.; Fletcher, T. The role of phagocytes in the protective mechanisms of fish. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1992, 2, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secombes, C.; Wang, T.; Hong, S.; Peddie, S.; Crampe, M.; Laing, K.; Cunningham, C.; Zou, J. Cytokines and innate immunity of fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severin, V.I.C.; Soliman, H.; El-Matbouli, M. Expression of immune-regulatory genes, arginase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), in two rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) strains following exposure to Myxobolus cerebralis. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 106, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerink, M.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Wiegertjes, G.F. Evolutionary conservation of alternative activation of macrophages: Structural and functional characterization of arginase 1 and 2 in carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, C.P.; Grody, W.W.; Cederbaum, S.D. Comparative properties of arginases. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1996, 114, 107–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, R.P.; McDowell, T.S.; Marty, G.D.; Fosgate, G.T.; Mukkatira, K.; Myklebust, K.; El-Matbouli, M. Susceptibility of two strains of rainbow trout (one with suspected resistance to whirling disease) to Myxobolus cerebralis infection. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 55, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.T.; Barton, C.H.; E Biggs, T. A negative autoregulatory link between Nramp 1 function and expression. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 67, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, T.H.; Cooper, L.F.; Wrathmell, A.B.; Roper, J.; Evenden, A.J.; Gilpin, M.L. Host responses to Renibacterium salmoninarum and specific components of the pathogen reveal the mechanisms of immune suppression and activation. Immunology 2002, 106, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigh, J.; Lindenstrøm, T.; Buchmann, K. Expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during an infection with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 17, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overturf, K.; LaPatra, S. Quantitative expression (Walbaum) of immunological factors in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), after infection with either Flavobacterium psychrophilum, Aeromonas salmonicida, or infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, M.J.; Nakanishi, T. The specific immune system: Cellular defences. In The Fish Immune System; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Utke, K.; Bergmann, S.; Lorenzen, N.; Köllner, B.; Ototake, M.; Fischer, U. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, infected with viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Densmore, C.L.; Blazer, V.S.; Waldrop, T.B.; Pooler, P.S. Effects of Whirling Disease on Selected Hematological Parameters in Rainbow Trout. J. Wildl. Dis. 2001, 37, 375–378. Available online: http://meridian.allenpress.com/jwd/article-pdf/37/2/375/2233840/0090-3558-37_2_375.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, F.; Razquin, B.; Villena, A.; Fierro, P.L.; Zapata, A. Alterations in the peripheral lymphoid organs and differential leukocyte counts in Saprolegnia-infected brown trout, Salmo trutta fario. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1988, 18, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas, J.; Santos, Y.; Bruno, D.W.; Toranzo, A.E.; Anadon, R. Non-specific cellular responses of rainbow trout to Vibrio anguillarum and its extracellular products (ECPs). J. Fish Biol. 1994, 45, 839–854. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, P.T.; Dixon, D.G. Changes in circulating blood cell levels of rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson, following acute and chronic exposure to copper. J. Fish Biol. 1985, 26, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeay, D. Effects of cortisol and dexamethasone on the pituitary-interrenal axis and abundance of white blood cell types in juvenile coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1973, 21, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, A. Cortisol-induced lymphocytopenia in brown trout, Salmo trutta L. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1984, 53, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, A.; Houston, A. Leucocytes and leucopoietic capacity in goldfish, Carassius auratus, exposed to sublethal levels of cadmium. Aquat. Toxicol. 1988, 13, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Densmore, C.L.; Ottinger, C.A.; Blazer, V.S.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Smith, D.R. Immunomodulation and disease resistance in postyearling rainbow trout infected with Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of whirling disease. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2004, 16, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, R.; McDowell, T.; Gay, M.; Marty, G.; Georgiadis, M.; MacConnell, E. Comparative susceptibility of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and brown trout Salmo trutta to Myxobolus cerebralis, the cause of salmonid whirling disease. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 37, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrick, R.P.; McDowell, T.S.; Mukkatira, K.; Georgiadis, M.P.; MacConnell, E. Susceptibility of three species of anadromous salmonids to experimentally induced infections with Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of whirling disease. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2001, 13, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, A. Fish granulocytes: Morphology, distribution, and function. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1992, 2, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Matbouli, M.; Fischer-Scherl, T.; Hoffmann, R.W. Present knowledge on the life cycle, taxonomy, pathology, and therapy of some Myxosporea spp. important for freshwater fish. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1992, 2, 367–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andree, K.B.; El-Matbouli, M.; Hoffman, R.W.; Hedrick, R.P. Comparison of 18S and ITS-1 rDNA sequences of selected geographic isolates of Myxobolus cerebralis. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, D.M. Fish Histology: From Cells to Organs; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtar, D.M. Characterization of the fish ovarian stroma during the spawning season: Cytochemical, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauriano, E.R.; Calò, M.; Silvestri, G.; Zaccone, D.; Pergolizzi, S.; Cascio, P.L. Mast cells in the intestine and gills of the sea bream, Sparus aurata, exposed to a polychlorinated biphenyl, PCB 126. Acta Histochem. 2012, 114, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reite, O.B. Mast cells/eosinophilic granule cells of teleostean fish: A review focusing on staining properties and functional responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1998, 8, 489–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, B.S.; Giari, L.; Konecny, R.; Jaeger, P.; Manera, M. Immunohistochemistry, ultrastructure and pathology of gills of Abramis brama from Lake Mondsee, Austria, infected with Ergasilus sieboldi (Copepoda). Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2003, 53, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siderits, D.; Bielek, E. Rodlet cells in the thymus of the zebrafish Danio rerio (Hamilton, 1822). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leino, R.L. Reaction of rodlet cells to a myxosporean infection in kidney of the bluegill, Lepomis macrochirus. Can. J. Zool. 1996, 74, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reite, O.B. The rodlet cells of teleostean fish: Their potential role in host defence in relation to the role of mast cells/eosinophilic granule cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2005, 19, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, P.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Alvarez-Pellitero, P. Cellular and humoral immune response of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) (Teleostei: Serranidae) immunized with Sphaerospora dicentrarchi (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida). Parasitology 2000, 120, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reite, O.B. Mast cells/eosinophilic granule cells of salmonids: Staining properties and responses to noxious agents. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1997, 7, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P.; Cuesta, A.; Athanassopoulou, F.; Golomazou, H.; Crespo, S.; Padrós, F.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Albiñana, G.; Esteban, M.; Alvarez-Pellitero, P.; et al. Sharpsnout sea bream (Diplodus puntazzo) humoral immune response against the parasite Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Secombes, C.J. The cytokine networks of adaptive immunity in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1703–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabalgoity, J.A.; Baz, A.; Rial, A.; Grille, S. The relevance of cytokines for development of protective immunity and rational design of vaccines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007, 18, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Carrington, A.; Collet, B.; Dijkstra, J.M.; Yoshiura, Y.; Bols, N.; Secombes, C. Identification and bioactivities of IFN-γ in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss: The first Th1-type cytokine characterized functionally in fish. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2484–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoua, J.; Grabowski, P.S.; Cunningham, C.; Secombes, C.J. Molecular cloning of interleukin 1β from rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss reveals no evidence of an ice cut site. Cytokine 1999, 11, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, K.J.; Secombes, C.J. Chemokines. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, K.J.; Wang, T.; Zou, J.; Holland, J.; Hong, S.; Bols, N.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T.; Secombes, C.J. Cloning and expression analysis of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss tumour necrosis factor-α. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severin, V.I.C.; El-Matbouli, M. Relative quantification of immune-regulatory genes in two rainbow trout strains, Oncorhynchus mykiss, after exposure to Myxobolus cerebralis, the causative agent of whirling disease. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerwald, M.R.; Welsh, A.B.; Hedrick, R.P.; May, B. Discovery of genes implicated in whirling disease infection and resistance in rainbow trout using genome-wide expression profiling. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.D.; Alder, M.N. The evolution of adaptive immune systems. Cell 2006, 124, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flajnik, M.F. A cold-blooded view of adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 438–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauley, G.B. Fish Sporozoa: Extraction of Antigens from Myxosoma cerebralis Spores Which Mimic Tissue Antigens of Rainhow Trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1974, 31, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, M.M. Studies on Myxosoma cerebralis, a parasite of salmonids. 4. A preliminary immunofluorescent investigation of the spores of Myxosoma cerebralis. Nord. Vet. Med. 1974, 26, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bartholomew, J.L.; Smith, C.E.; Rohovec, J.S.; Fryer, J.L. Characterization of a host response to the myxosporean parasite, Ceratomyxa shasta (Noble), by histology, scanning electron microscopy and immunological techniques. J. Fish Dis. 1989, 12, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; Ogawa, K.; Wakabayashi, H. Humoral immune response of carp Cyprinus carpio to Myxobolus artus (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) infection. J. Fish Biol. 1993, 43, 150–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulnier, D.; de Kinkelin, P. Antigenic and biochemical study of PKX, the myxosporean causative agent of proliferative kidney disease of salmonid fish. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1996, 27, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, S.J.; Teichmann, S.A.; Ferreira, L.; Macaulay, I.C.; Stubbington, M.J.; Cvejic, A.; Gfeller, D. Single-cell transcriptome analysis of fish immune cells provides insight into the evolution of vertebrate immune cell types. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Shibasaki, Y.; Matsuura, Y. T cells in fish. Biology 2015, 4, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, H.; Soliman, H.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. CD4: A vital player in the teleost fish immune system. Vet. Res. 2019, 50, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. The function of fish cytokines. Biology 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Alnabulsi, A.; Alnabulsi, A.; Scott, C.; Tafalla, C.; Secombes, C.J.; Wang, T. Characterisation and analysis of IFN-gamma producing cells in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 117, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.A.; McKenzie, A.N.J. TH2 cell development and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braden, L.M.; Koop, B.F.; Jones, S.R. Signatures of resistance to Lepeophtheirus salmonis include a TH2-type response at the louse-salmon interface. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 48, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewski, T.F.; Fitch, F.W. Anti-proliferative effect of IFN-gamma in immune regulation. I. IFN-gamma inhibits the proliferation of Th2 but not Th1 murine helper T lymphocyte clones. J. Immunol. 1988, 140, 4245–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oriss, T.B.; A McCarthy, S.; Morel, B.F.; A Campana, M.; A Morel, P. Crossregulation between T helper cell (Th)1 and Th2: Inhibition of Th2 proliferation by IFN-gamma involves interference with IL-1. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 3666–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottiglione, F.; Dee, C.T.; Lea, R.; Zeef, L.A.H.; Badrock, A.P.; Wane, M.; Bugeon, L.; Dallman, M.J.; Allen, J.E.; Hurlstone, A.F.L. Zebrafish IL-4–like cytokines and IL-10 suppress inflammation but only IL-10 is essential for gill homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 994–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignali, D.A.A.; Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Cross-regulation of Signaling Pathways by Interferon-γ: Implications for Immune Responses and Autoimmune Diseases. Immunity 2009, 31, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magadan, S.; Sunyer, O.J.; Boudinot, P. Unique features of fish immune repertoires: Particularities of adaptive immunity within the largest group of vertebrates. In Pathogen-Host Interactions: Antigenic Variation v. Somatic Adaptations; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 235–264. [Google Scholar]
- Mashoof, S.; Criscitiello, M.F. Fish immunoglobulins. Biology 2016, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Qin, Z.; Liu, H.; Lin, L.; Ye, J.; Li, J. Recent advances on phagocytic B cells in teleost fish. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.-J.; Chen, D.-D.; Sunyer, J.O.; Zhang, Y.-A. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of three subclasses of IgT in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 70, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Takizawa, F.; Parra, D.; Gómez, D.; Jørgensen, L.v.G.; LaPatra, S.E.; Sunyer, J.O. Mucosal immunoglobulins at respiratory surfaces mark an ancient association that predates the emergence of tetrapods. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Jouneau, L.; Pham, H.-P.; Bouchez, O.; Giudicelli, V.; Lefranc, M.-P.; Quillet, E.; Benmansour, A.; Cazals, F.; Six, A.; et al. Teleost fish mount complex clonal IgM and IgT responses in spleen upon systemic viral infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzon, M.C.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Pereiro, P.; Estensoro, I.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Gómez-Casado, E.; Novoa, B.; Mulero, V.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Differential Modulation of IgT and IgM upon Parasitic, Bacterial, Viral, and Dietary Challenges in a Perciform Fish. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryce, E.K.N. Factors Affecting the Resistance of Juvenile Rainbow Trout to Whirling Disease; Montana State University: Bozeman, MT, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, B.R.; Davis, E.M. Myxosoma cerebralis: Detection of Circulating Antibodies in Infected Rainbow Trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1978, 35, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, G.L. Myxobolus cerebralis, a worldwide cause of salmonid whirling disease. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1990, 2, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacConnell, E.; Vincent, E.R. The effects of Myxobolus cerebralis on the salmonid host. In American Fisheries Society Symposium; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002; pp. 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, D.; Zlotnik, A. The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotob, M.H.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of co-infections on fish: A review. Vet. Res. 2017, 47, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, F.E.G. Concomitant infections, parasites and immune responses. Parasitology 2001, 122, S23–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotob, M.H.; Kumar, G.; Saleh, M.; Gorgoglione, B.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Differential modulation of host immune genes in the kidney and cranium of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in response to Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae and Myxobolus cerebralis co-infections. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoglione, B.; Wang, T.; Secombes, C.J.; Holland, J.W. Immune gene expression profiling of Proliferative Kidney Disease in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss reveals a dominance of anti-inflammatory, antibody and T helper cell-like activities. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.W.; Gould, C.R.W.; Jones, C.S.; Noble, L.R.; Secombes, C.J. The expression of immune-regulatory genes in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, during a natural outbreak of proliferative kidney disease (PKD). Parasitology 2003, 126, S95–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilmonczyk, S.; Monge, D.; De Kinkelin, P. Proliferative kidney disease: Cellular aspects of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), response to parasitic infection. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.J.; Molnár, K.; Longshaw, M.; Adams, A. Immunostaining of spores and plasmodia of disparate myxozoan genera with comments on the properties of the sporular mucus envelope. Parasitology 2006, 132, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.T. Immunological responses of fish to parasitic organisms. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1992, 2, 339–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Marel, M.; Adamek, M.; Gonzalez, S.F.; Frost, P.; Rombout, J.H.W.M.; Wiegertjes, G.F.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Steinhagen, D. Molecular cloning and expression of two β-defensin and two mucin genes in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) and their up-regulation after β-glucan feeding. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malachowicz, M.; Wenne, R.; Burzynski, A. De novo assembly of the sea trout (Salmo trutta m. trutta) skin transcriptome to identify putative genes involved in the immune response and epidermal mucus secretion. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveen, L.R.; Grammes, F.T.; Ytteborg, E.; Takle, H.; Jørgensen, S.M. Genome-wide analysis of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) mucin genes and their role as biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-López, M.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Mirimin, L.; MacCarthy, E.; Rodger, H.D.; O’Connor, I.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Piazzon, M.C. Gene expression analysis of Atlantic salmon gills reveals mucin 5 and interleukin 4/13 as key molecules during amoebic gill disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schisler, G.J.; Bergersen, E.P.; Walker, P.G. Effects of multiple stressors on morbidity and mortality of fingerling rainbow trout infected with Myxobolus cerebralis. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2000, 129, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, E.R. The relationship of time, temperature, and fish life histories to whirling disease infections. In Proceedings of the Whirling Disease Symposium: Research in Progress, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 19–21 February 1998; pp. 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wahli, T.; Bernet, D.; Segner, H.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H. Role of altitude and water temperature as regulating factors for the geographical distribution of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae infected fishes in Switzerland. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 73, 2184–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markkula, S.E.; Karvonen, A.; Salo, H.; Valtonen, E.T.; Jokinen, E.I. Ultraviolet B irradiation affects resistance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) against bacterium yersinia ruckeri and trematode Diplostomum spathaceum. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 83, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, R.; McDowell, T.; Marty, G.; Mukkatira, K.; Antonio, D.; Andree, K.; Bukhari, Z.; Clancy, T. Ultraviolet irradiation inactivates the waterborne infective stages of Myxobolus cerebralis: A treatment for hatchery water supplies. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2000, 42, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, R.P.; McDowell, T.S.; Adkison, M.A.; Myklebust, K.A.; Mardones, F.O.; Petri, B. Invasion and initial replication of ultraviolet irradiated waterborne infective stages of Myxobolus cerebralis results in immunity to whirling disease in rainbow trout. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, E.H.; Nabuurs, S.B.; Bury, N.R.; Sturm, A.; Flik, G.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Kemenade, B.L.V.-V. Stress and innate immunity in carp: Corticosteroid receptors and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 46, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemenade, B.V.-V.; Ribeiro, C.; Chadzinska, M. Neuroendocrine–immune interaction in fish: Differential regulation of phagocyte activity by neuroendocrine factors. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 172, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katharios, P.; Garaffo, M.; Sarter, K.; Athanassopoulou, F.; Mylonas, C.C. A case of high mortality due to heavy infestation of Ceratomyxa diplodae in sharpsnout sea bream (Diplodus puntazzo) treated with reproductive steroids. Bull.-Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2007, 27, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, M.L.; Hedrick, R.P. Effects of cortisol implants on the PKX myxosporean causing proliferative kidney disease in rainbow trout, salmo gairdneri. J. Parasitol. 1987, 73, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.T.; Veillard, M.F.; Martens, A.M.; Pila, E.A.; Turnbull, A.; Hanington, P.; Luek, A.; Alexander, J.; Nehring, R.B. Whirling disease in the Crowsnest River: An emerging threat to wild salmonids in Alberta. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 78, 1855–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheesh, P.; LaFrentz, B.; Call, D.R.; Siems, W.; LaPatra, S.; Wiens, G.; Cain, K. Identification of potential vaccine target antigens by immunoproteomic analysis of a virulent and a non-virulent strain of the fish pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 74, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, R.; Jeyabaskar, S.; Michael, D.; Paul, A.V.; Sitharaman, G. Computer-aided vaccine designing approach against fish pathogens Edwardsiella tarda and Flavobacterium columnare using bioinformatics softwares. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A. Progress, challenges and opportunities in fish vaccine development. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

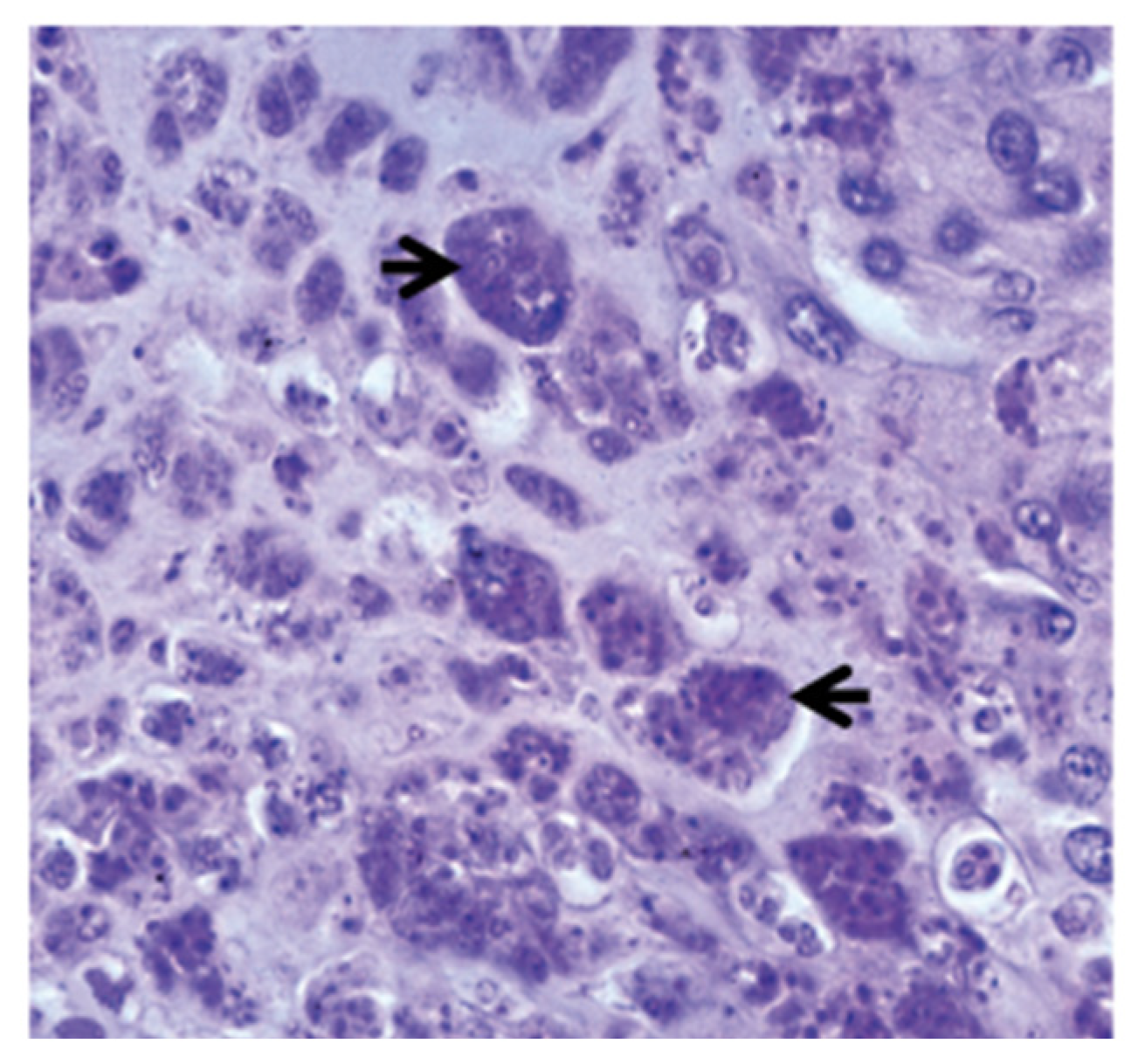









| Immune Cells Studied | Fish Spp. | Immune Modulation | Techniques Used | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphocytes | Rainbow trout | Lower propagation of lymphocyte in M. cerebralis infected fish against bioactive proteins. | Bromodeoxyuridine (BrDU) incorporation assay | [83] |
| Granulocytes | Brown trout and rainbow trout | Eosinophilic granular leucocytes were noticed in the root ganglia of infected brown trout, but not of rainbow trout. | Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry | [84] |
| Mast cells | Chinook salmon, Coho salmon, and rainbow trout | Coho salmon, but not rainbow trout or chinook salmon susceptible to M. cerebralis infection, exhibited an abundance of many eosinophilic granule cells (EGC) or mast cells in lesions caused by parasites or ganglia containing parasitic stages. | Histological analyses | [85] |
| Eosinophilic granular leucocytes | Brown trout and rainbow trout | Eosinophilic granular leukocytes were more noticeable in brown trout compared to rainbow trout. | Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry | [84] |
| Myeloid cells, B cells and T cells | Rainbow trout | The study expressed that in the TL strain, there were overall increases in CF, HK, and SP myeloid cells, alongside drops in B cells and T cells in the SP and HK at carious time periods. Conversely, the HO strain primarily experienced an increase in T cells across CF, HK, and SP at various times. | FACS | [29] |
| Cytokines Studied | Fish Spp. | Immune Modulation | Technique Used | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ubiquitin-like protein, metallothionein B | Rainbow trout strains | After pathogen exposure, ubiquitin-like protein 1 exhibited a more than 100-fold upregulation, and interferon-regulating factor 1 demonstrated a more than 15-fold upregulation in both strains. The expression of metallothionein B was increased by more than 5-fold in the Hofer strain, whereas it remained unchanged in the Troutlodge strain after pathogen exposure. | qRT-PCR | [107] |
| Serine protease (MyxSP-1) and cysteine protease (MyxCP-1) | Rainbow trout | Post-infection upregulation of these genes in gills and dorsal fins exposed the enzymatic action in host tissue | qRT-PCR | [60,61,107] |
| Nramp α & β | Rainbow trout and Brown trout | A notable reduction in the expression of both genes was observed at various time intervals in the susceptible rainbow trout that were infected, in comparison to the noninfected cohort. | qRT-PCR | [28] |
| Arginase 2, iNOS | Rainbow trout | The expression level of both genes was upregulated in both the strains. | cDNA microarrays | [66] |
| iNOS | Rainbow trout | The susceptible American strain had increased expression only at one time point, while resistant HO strain had stimulation at two PE time intervals. | qRT-PCR | [35] |
| TGF-β | Rainbow trout | Resistant HO strain expressed more TGF- β in comparison to the susceptible TL strain. | qRT-PCR | [106] |
| IL-1β and IFN-γ | Brown trout | IL-1β and IFN-γ were upregulated in HK, SP, and CF at various time intervals post exposure to M. cerebralis. IL-1β increased during initial time points while IFN-γ elevated at initial and later times (including 2 dpe, when the lowest parasite quantity was detected). | qRT-PCR | [30] |
| IFNγ | Rainbow trout | Upregulation in M. cerebralis-infected rainbow trout and resistant fish showed a more rapid induction. | qRT-PCR | [35] |
| STAT3, IL-17A | Rainbow trout | In susceptible strains, the greatest expression of IL-17A was noticed in 2 dpe interacting with the highest parasite burden, in contrast to resistant strain. | qRT-PCR | [32] |
| KLF2, IL-1b, and innate immune response genes (IRF1, IFN-g, and iNOS) | Resistant (H) and susceptible (TL) rainbow trout | IFN-g, IL-1b, IRF1, and iNOS were upregulated post exposure to M. cerebralis for one or both strains over various time points. IFN-g and IRF1 showed a continuous increase in the TL strain in comparison to the HO strain. STAT3 was the sole gene with persistent elevated expression in the HO strain after infection, while remaining stable in the TL strain. | qRT-PCR | [35] |
| SOCS1 and SOCS3 | Rainbow trout | The parasite induced the expression of SOCS1, IL-6-dependent SOCS3, IL-10 and Treg-associated transcription factor FOXP3 in a susceptible strain of rainbow trout, which caused limited STAT1 and STAT3 action, thereby having an effect on Th17 balance. | qRT-PCR | [32] |
| Fish Spp. | Parasites | Co-Infection | Outcomes of Infection | Techniques Used | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainbow trout | M. cerebralis and T. bryosalmonae | First, infection with M. cerebralis, followed by T. bryoslamonae | A greater number of parasites were observed in the posterior kidney and cranial cartilage. Upregulation of all immune genes (SOCS-1 and -3, JAK-1 and STAT-3) occurred in the kidney and crania. There was overexpression of SOCS1 and SOCS3 genes in the cranium. Increased expression of RPL18 was evident. | RT-qPCR | [141] |
| Co-infection with T. bryosalmonae followed by M. cerebralis | There were a lesser number of parasites in infected organs. All immune genes showed higher expression, but this group elicited the downregulation of the RPL18 gene. | ||||
| Rainbow trout | M. cerebralis and Y. ruckeri | M. cerebralis-infected fish challenged with Y. ruckeri | The higher bactericidal activity of already M. cerebralis-infected rainbow trout against Y. ruckeri was observed. | Bromodeoxyuridine (BrDU) incorporation assay and Histological technique | [83] |
| Rainbow trout | T. bryosalmonae and M. cerebralis | Infection with M. cerebralis in conjunction with T. bryosalmonae | More severe pathological progression of each parasite with high mortality was observed. Along with more intense cartilage loss and displacement, a pronounced kidney swelling index of grade 4 was observed. | Histology and immunohistochemistry | [41] |
| Infected with T. bryosalmonae concurrently with M. cerebralis | Typical pathological alterations associated with both parasitic diseases with a reduced mortality rate, similar to those caused by single M. cerebralis or T. bryosalmonae infection. Mild WD clinical signs without skeletal deformities were noticeable, and the kidney swelling index was grade 2 to 3. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akram, N.; El-Matbouli, M.; Saleh, M. The Immune Response to the Myxozoan Parasite Myxobolus cerebralis in Salmonids: A Review on Whirling Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417392
Akram N, El-Matbouli M, Saleh M. The Immune Response to the Myxozoan Parasite Myxobolus cerebralis in Salmonids: A Review on Whirling Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417392
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkram, Naveed, Mansour El-Matbouli, and Mona Saleh. 2023. "The Immune Response to the Myxozoan Parasite Myxobolus cerebralis in Salmonids: A Review on Whirling Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417392
APA StyleAkram, N., El-Matbouli, M., & Saleh, M. (2023). The Immune Response to the Myxozoan Parasite Myxobolus cerebralis in Salmonids: A Review on Whirling Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417392








