Gut Microbiota Composition of Insectivorous Synanthropic and Fructivorous Zoo Bats: A Direct Metagenomic Comparison
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
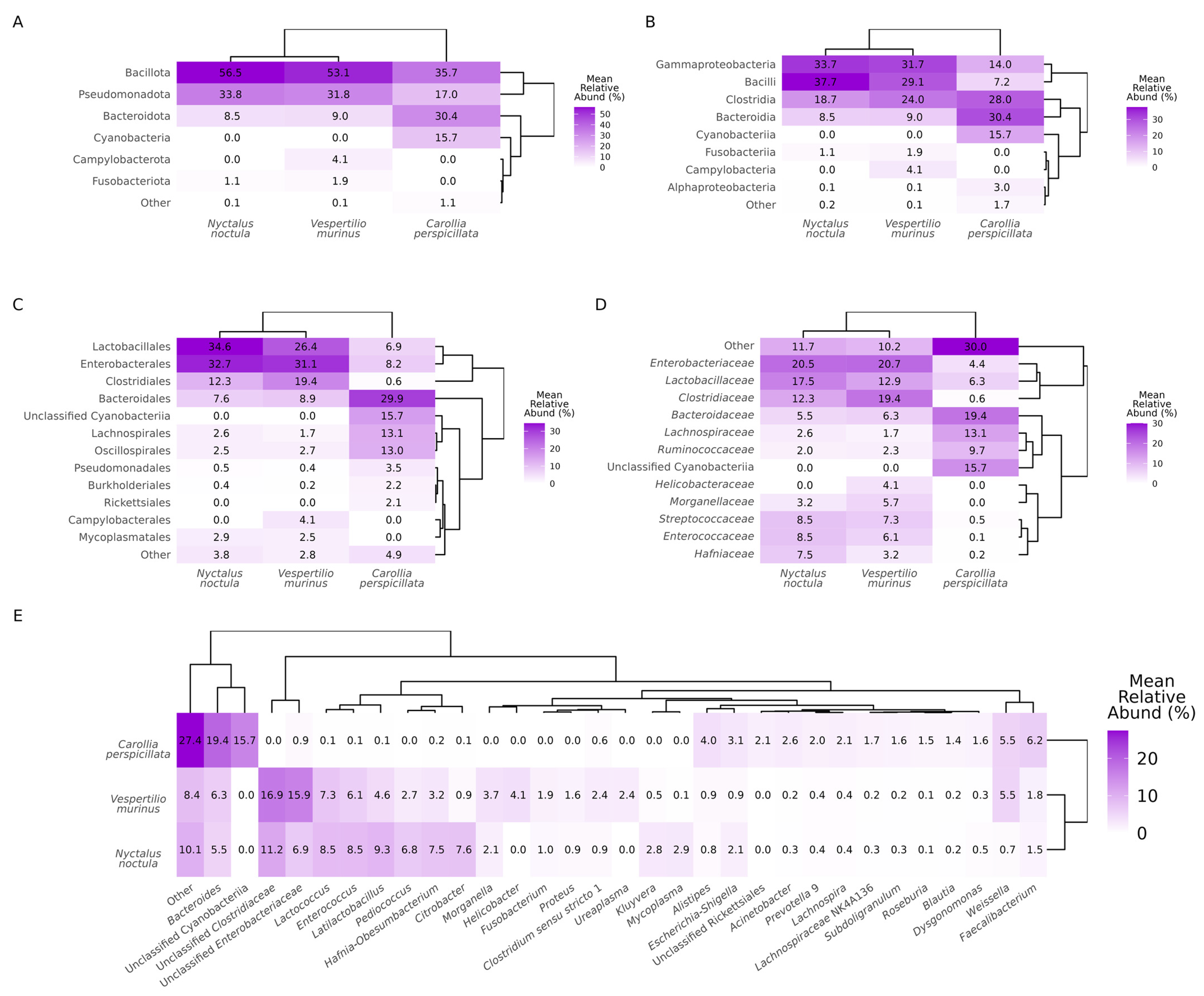
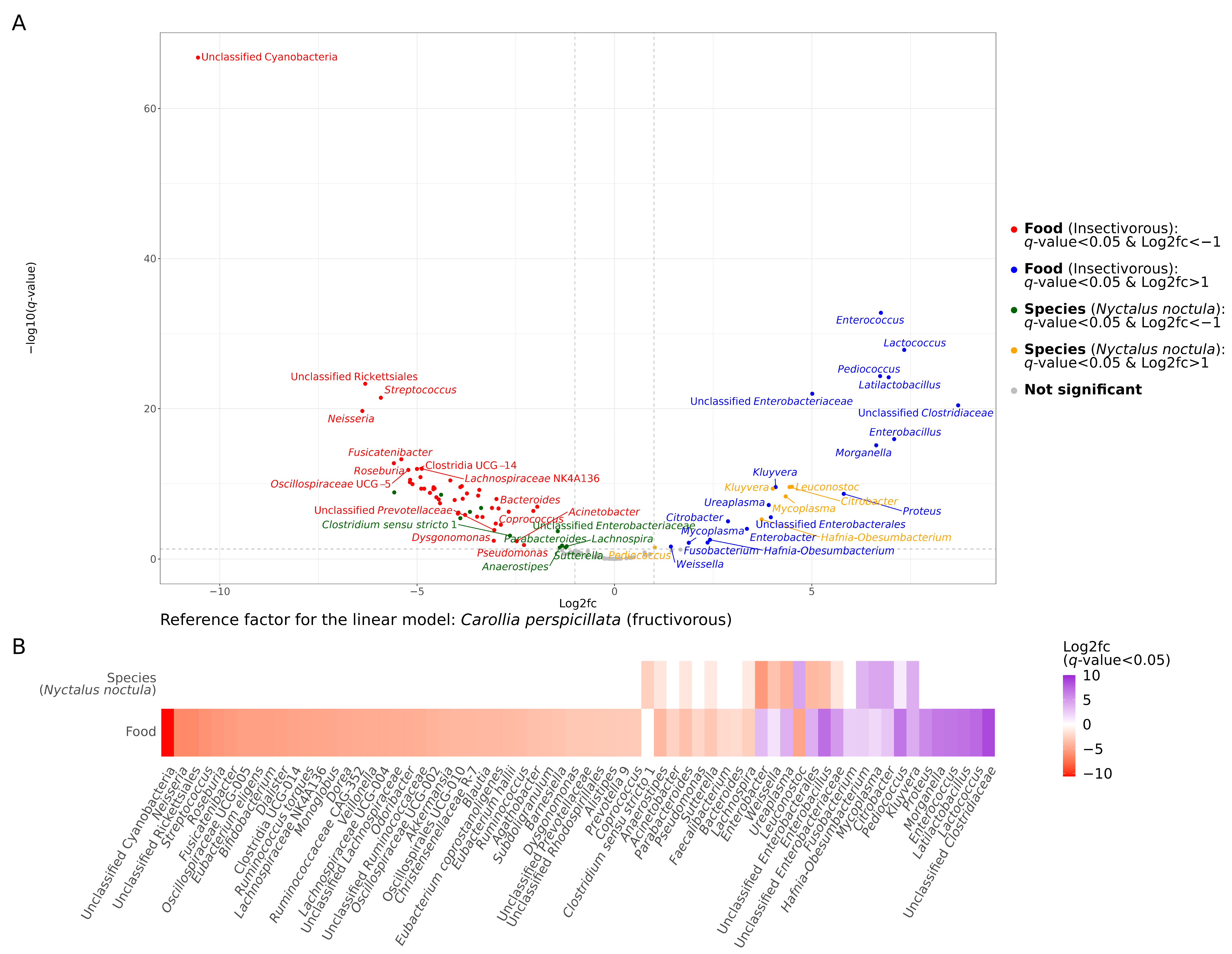
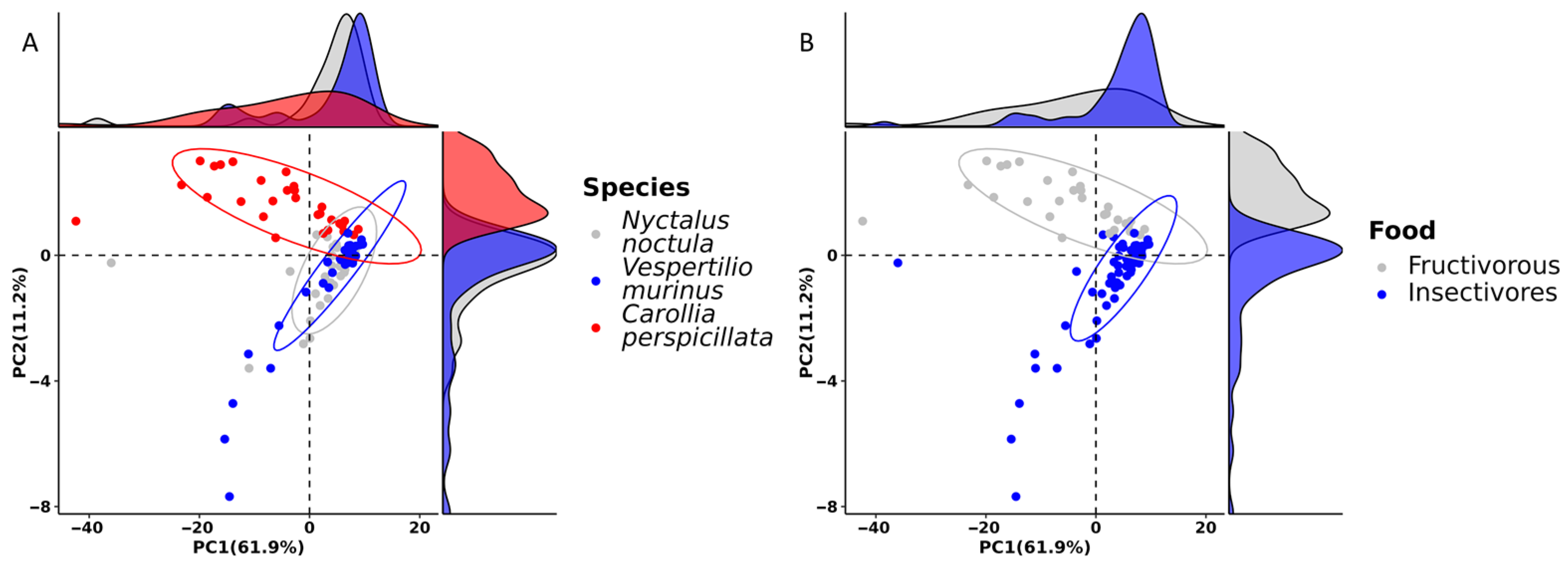
2.1. Gut Microbiota Composition
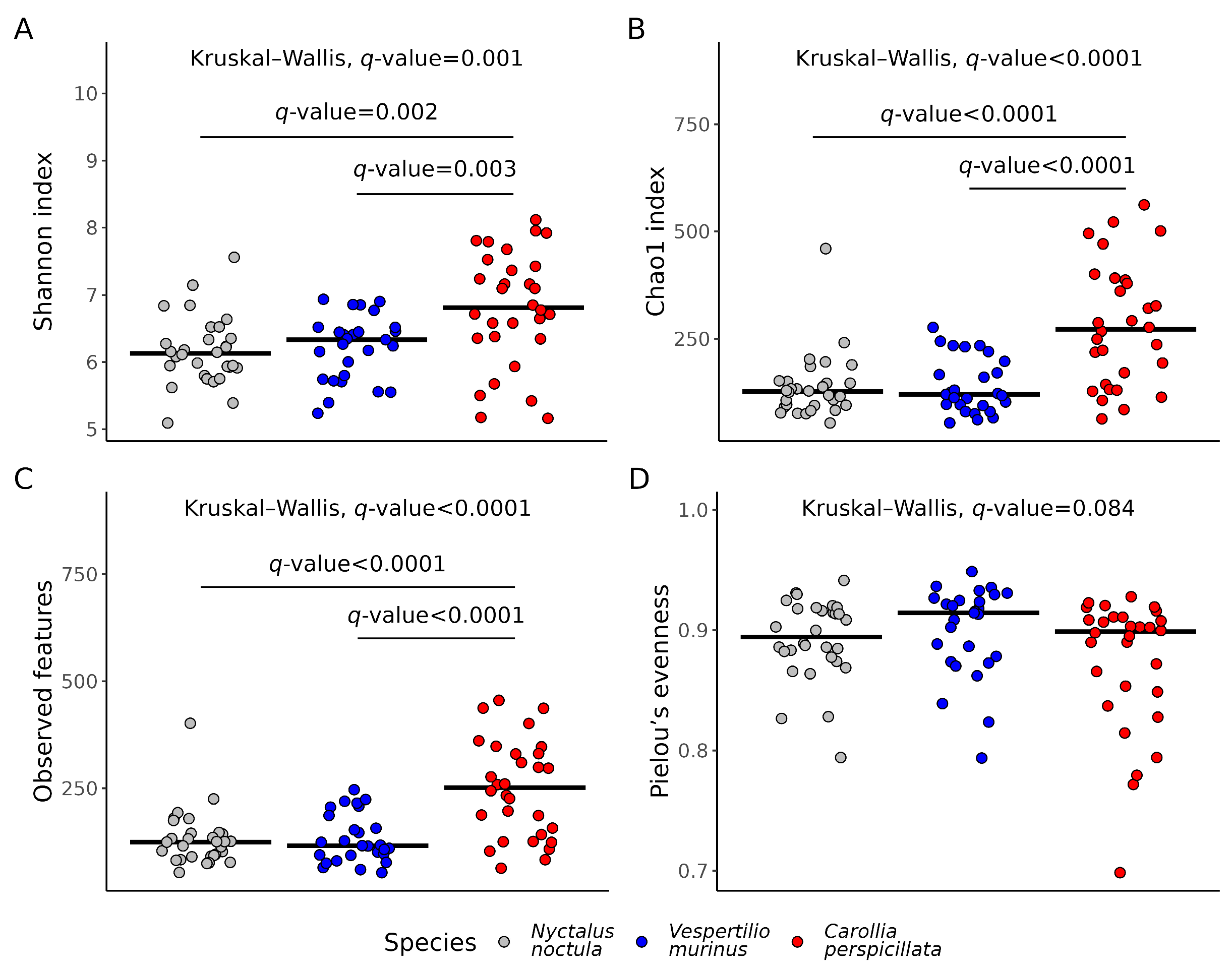
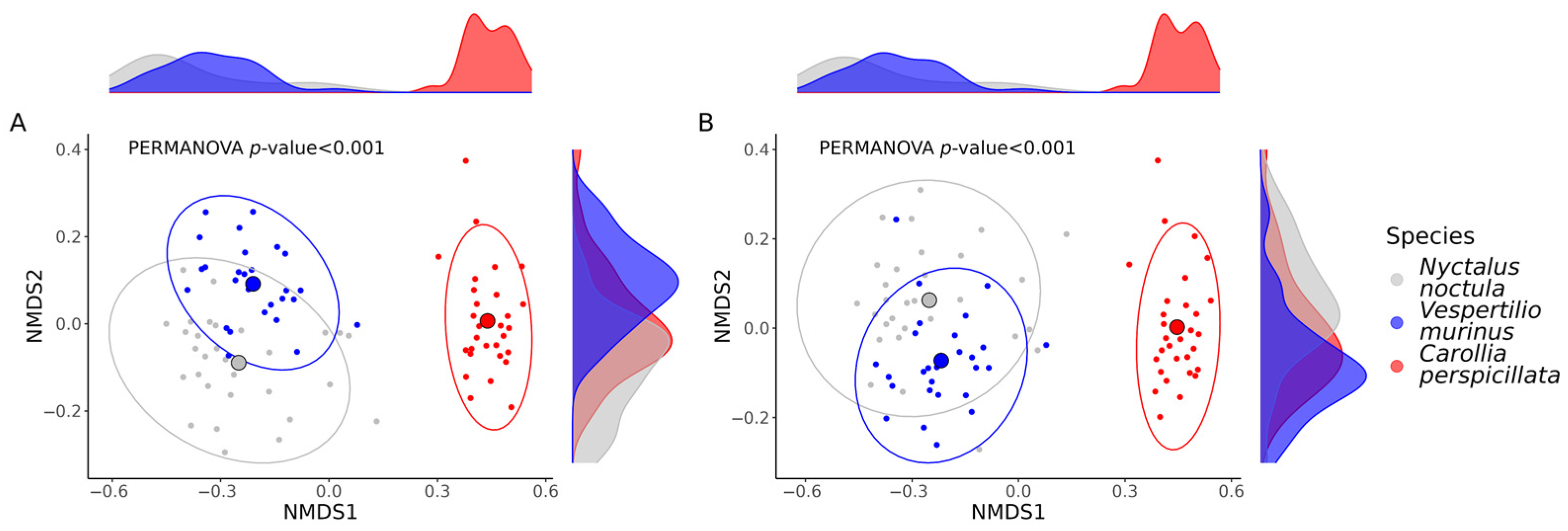
2.2. Gut Microbiota Richness and Diversity
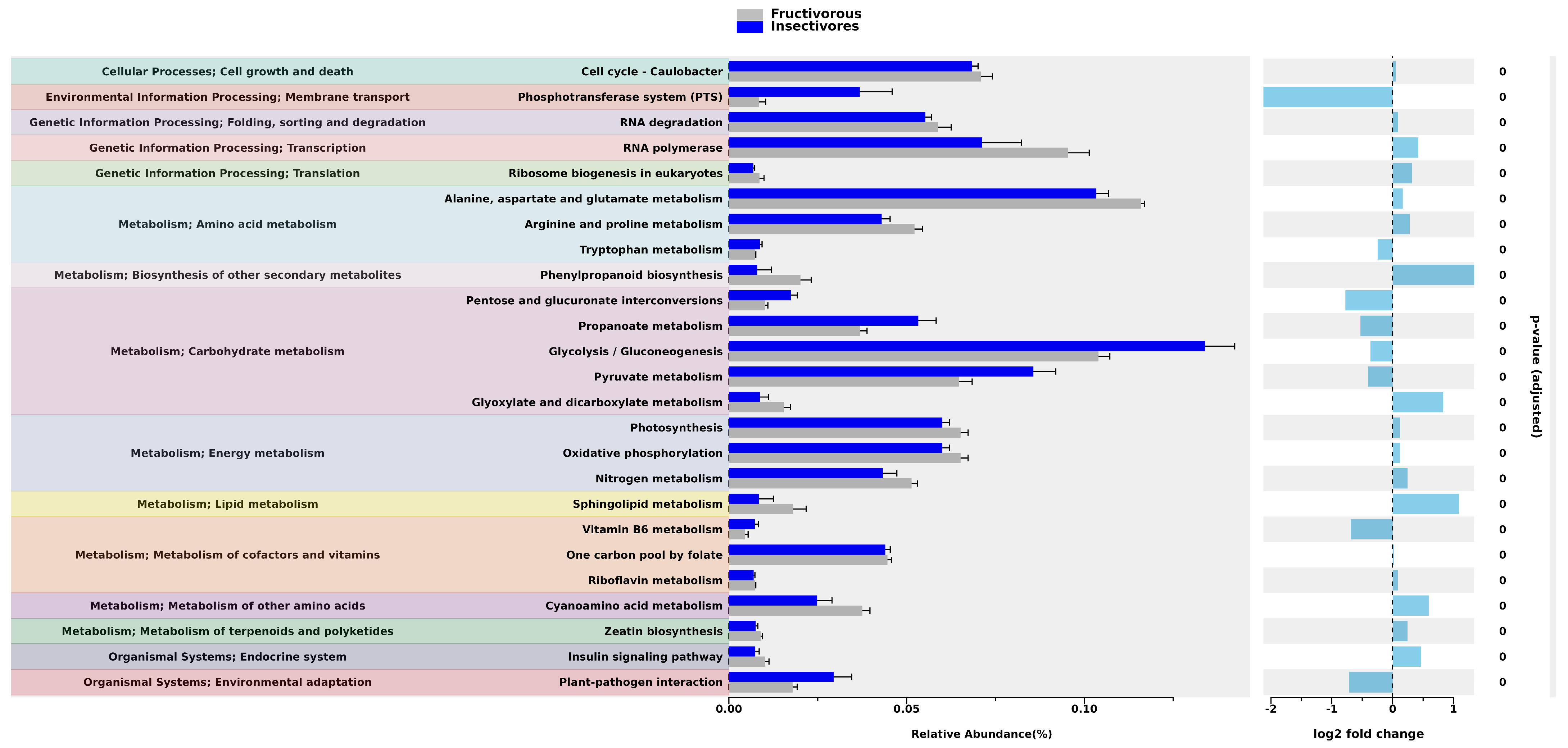
2.3. Prediction of the Functional Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling
4.2. Gut Microbiota Composition and Metagenomes Functions Prediction
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnaout, Y.; Djelouadji, Z.; Robardet, E.; Cappelle, J.; Cliquet, F.; Touzalin, F.; Jimenez, G.; Hurstel, S.; Borel, C.; Picard-Meyer, E. Genetic identification of bat species for pathogen surveillance across France. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, S.A.; Alencastre-Santos, A.B.; da Silva, J.B.; Correia, L.L.; Urbieta, G.L.; Graciolli, G.; Palheta, L.R.; Vieira, T.B. Bats (Mammalia, Chiroptera) and bat flies (Diptera, Streblidae) from the Cazumba-Iracema and Chico Mendes Reserve, Western Brazilian Amazon. Parasitol. Res. 2023, 122, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, M.; Yovel, Y. Revising the paradigm: Are bats really pathogen reservoirs or do they possess an efficient immune system? iScience 2022, 25, 104782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Baker, M.L.; Kulcsar, K.; Misra, V.; Plowright, R.; Mossman, K. Novel Insights Into Immune Systems of Bats. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, A.T.; Ahn, M.; Goh, G.; Anderson, D.E.; Wang, L.F. Lessons from the host defences of bats, a unique viral reservoir. Nature 2021, 589, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Sazzad, H.M.; Satter, S.M.; Sultana, S.; Hossain, M.J.; Hasan, M.; Rahman, M.; Campbell, S.; Cannon, D.L.; Stroher, U.; et al. Nipah Virus Transmission from Bats to Humans Associated with Drinking Traditional Liquor Made from Date Palm Sap, Bangladesh, 2011–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edson, D.; Field, H.; McMichael, L.; Vidgen, M.; Goldspink, L.; Broos, A.; Melville, D.; Kristoffersen, J.; de Jong, C.; McLaughlin, A.; et al. Routes of Hendra Virus Excretion in Naturally-Infected Flying-Foxes: Implications for Viral Transmission and Spillover Risk. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, T.; Anthony, S.J.; Gbakima, A.; Bird, B.H.; Bangura, J.; Tremeau-Bravard, A.; Belaganahalli, M.N.; Wells, H.L.; Dhanota, J.K.; Liang, E.; et al. The discovery of Bombali virus adds further support for bats as hosts of ebolaviruses. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salihi, K.A.; Khalaf, J.M. The emerging SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2: An insight into the viruses zoonotic aspects. Vet. World 2021, 14, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, I.V.; Ohlopkova, O.V.; Donnik, I.M.; Zolotukhin, P.V.; Umanets, A.; Golovin, S.N.; Malinovkin, A.V.; Belanova, A.A.; Lipilkin, P.V.; Lipilkina, T.A.; et al. Detection of coronaviruses in insectivorous bats of Fore-Caucasus, 2021. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnik, I.M.; Popov, I.V.; Sereda, S.V.; Popov, I.V.; Chikindas, M.L.; Ermakov, A.M. Coronavirus Infections of Animals: Future Risks to Humans. Biol. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2021, 48, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, P.; van den Eynde, C.; Baert, F.; D’Hooge, E.; De Pauw, R.; Normand, A.C.; Piarroux, R.; Stubbe, D. Remarkable fungal biodiversity on northern Belgium bats and hibernacula. Mycologia 2023, 115, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devnath, P.; Karah, N.; Graham, J.P.; Rose, E.S.; Asaduzzaman, M. Evidence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bats and Its Planetary Health Impact for Surveillance of Zoonotic Spillover Events: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C.D.; Phelan, G.; Dowd, S.E.; McDonough, M.M.; Ferguson, A.W.; Delton Hanson, J.; Siles, L.; Ordonez-Garza, N.; San Francisco, M.; Baker, R.J. Microbiome analysis among bats describes influences of host phylogeny, life history, physiology and geography. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2617–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, G.P.; Lee, S.M.; Mazmanian, S.K. Gut biogeography of the bacterial microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadelha-Alves, R.; Rozensztranch, A.M.D.; Rocha-Barbosa, O. Comparative Intestinal Histomorphology of Five Species of Phyllostomid Bats (Phyllostomidae, Microchiroptera): Ecomorphological Relations with Alimentary Habits. Int. J. Morphol. 2008, 26, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviedes-Vidal, E.; McWhorter, T.J.; Lavin, S.R.; Chediack, J.G.; Tracy, C.R.; Karasov, W.H. The digestive adaptation of flying vertebrates: High intestinal paracellular absorption compensates for smaller guts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19132–19137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.J.; Sanders, J.G.; Delsuc, F.; Metcalf, J.; Amato, K.; Taylor, M.W.; Mazel, F.; Lutz, H.L.; Winker, K.; Graves, G.R.; et al. Comparative Analyses of Vertebrate Gut Microbiomes Reveal Convergence between Birds and Bats. mBio 2020, 11, 02901-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, H.; Rahnavard, A.; McIver, L.J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, L.H.; Tickle, T.L.; Weingart, G.; Ren, B.; Schwager, E.H.; et al. Multivariable association discovery in population-scale meta-omics studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Mai, J.; Cao, X.; Burberry, A.; Cominelli, F.; Zhang, L. ggpicrust2: An R package for PICRUSt2 predicted functional profile analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuneu-Corral, C.; Puig-Montserrat, X.; Riba-Bertolin, D.; Russo, D.; Rebelo, H.; Cabeza, M.; Lopez-Baucells, A. Pest suppression by bats and management strategies to favour it: A global review. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2023, 98, 1564–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.M.; Jeschke, J.M.; Voigt, C.C.; Itescu, Y. Urban affinity and its associated traits: A global analysis of bats. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 5667–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsengimana, O.; Walker, F.M.; Webala, P.W.; Twizeyimana, I.; Dusabe, M.C.; Sanchez, D.E.; Sobek, C.J.; Ruhagazi, D.; Iribagiza, P.; Muvunyi, R.; et al. Our good neighbors: Understanding ecosystem services provided by insectivorous bats in Rwanda. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, L.M.S.; Bueno-Rocha, I.D.; Oliveira, G.; Pires, E.S.; Vasconcelos, S.; Nunes, G.L.; Frizzas, M.R.; Togni, P.H.B. Going out for dinner-The consumption of agriculture pests by bats in urban areas. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewanzik, D.; Straka, T.M.; Lorenz, J.; Marggraf, L.; Voigt-Heucke, S.; Schumann, A.; Brandt, M.; Voigt, C.C. Evaluating the potential of urban areas for bat conservation with citizen science data. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 297, 118785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Bell, T.; Coleman, C.M.; Harris, D.; Woodward, G.; Worledge, L.; Roberts, H.; McElhinney, L.; Aegerter, J.; Ransome, E.; et al. Testing bats in rehabilitation for SARS-CoV-2 before release into the wild. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2022, 4, e12707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, R.L.; Dopfer, D.; Lemley, E.M.; Thurber, M.I. Factors Impacting Successful Rehabilitation of Big Brown Bats (Eptesicus Fuscus) in a Wisconsin Wildlife Rehabilitation Center: A 5-Year Retrospective. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2023, 54, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.K.; Lee, T.E. Community Ecology and Phylogeography of Bats in the Guianan Savannas of Northern South America. Diversity 2018, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, K.; Veiga, I.B.; Schediwy, M.; Wiederkehr, D.; Meniri, M.; Schneeberger, M.; den Broek, P.R.; Gurtner, C.; Fasel, N.J.; Kittl, S.; et al. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis serotype O:1 infection in a captive Seba’s short tailed-fruit bat (Carollia perspicillata) colony in Switzerland. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Araujo, M.; Tas, N.; Alcantara-Hernandez, R.J.; Gaona, O.; Schondube, J.E.; Medellin, R.A.; Jansson, J.K.; Falcon, L.I. Phyllostomid bat microbiome composition is associated to host phylogeny and feeding strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemieux-Labonte, V.; Tromas, N.; Shapiro, B.J.; Lapointe, F.J. Environment and host species shape the skin microbiome of captive neotropical bats. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corduneanu, A.; Mihalca, A.D.; Sandor, A.D.; Hornok, S.; Malmberg, M.; Viso, N.P.; Bongcam-Rudloff, E. The heart microbiome of insectivorous bats from Central and South Eastern Europe. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 75, 101605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Schlegel, M.L.; Tucker, T.A.; Schrenzel, M.D.; Knight, R.; et al. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.H.; Desai, H.; Sylvetsky, A.C.; LoTempio, J.; Ayanyan, S.; Carrie, J.; Crandall, K.A.; Fochtman, B.C.; Gasparyan, L.; Gulzar, N.; et al. Baseline human gut microbiota profile in healthy people and standard reporting template. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0206484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roswag, A.; Becker, N.I.; Encarnacao, J.A. Inter- and intraspecific comparisons of retention time in insectivorous bat species (Vespertilionidae). J. Zool. 2012, 288, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subudhi, S.; Rapin, N.; Misra, V. Immune System Modulation and Viral Persistence in Bats: Understanding Viral Spillover. Viruses 2019, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Liang, S.; Jin, F. Gut microbiota in antiviral strategy from bats to humans: A missing link in COVID-19. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghi, A.; Massoud, R.; Todorov, S.D.; Chikindas, M.L.; Popov, I.; Smith, S.; Khosravi-Darani, K. Role of the lactobacilli in food bio-decontamination: Friends with benefits. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 150, 109861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebb, D.; Huang, Z.; Pippel, M.; Hughes, G.M.; Lavrichenko, K.; Devanna, P.; Winkler, S.; Jermiin, L.S.; Skirmuntt, E.C.; Katzourakis, A.; et al. Six reference-quality genomes reveal evolution of bat adaptations. Nature 2020, 583, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheben, A.; Mendivil Ramos, O.; Kramer, M.; Goodwin, S.; Oppenheim, S.; Becker, D.J.; Schatz, M.C.; Simmons, N.B.; Siepel, A.; McCombie, W.R. Long-Read Sequencing Reveals Rapid Evolution of Immunity- and Cancer-Related Genes in Bats. Genome Biol. Evol. 2023, 15, evad148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, I.R.; Adams, D.M.; Greville, L.J.S.; Faure, P.A.; Wilkinson, G.S. Big brown bats experience slower epigenetic ageing during hibernation. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2022, 289, 20220635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, G.S.; South, J.M. Life history, ecology and longevity in bats. Aging Cell 2002, 1, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, I.V.; Mazanko, M.S.; Kulaeva, E.D.; Golovin, S.N.; Malinovkin, A.V.; Aleshukina, I.S.; Aleshukina, A.V.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Tverdokhlebova, T.I.; Chikindas, M.L.; et al. Gut microbiota of bats: Pro-mutagenic properties and possible frontiers in preventing emerging disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, D.; Giron, M. Enterobacter Infections; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bandelj, P.; Knapic, T.; Rousseau, J.; Podgorelec, M.; Presetnik, P.; Vengust, M.; Scott Weese, J. Clostridioides difficile in bat guano. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 65, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Q.; Lv, X.; Pu, J.; Zhu, W.; Lu, S.; Jin, D.; Liu, L.; Shi, Z.; et al. The Threat of Potentially Pathogenic Bacteria in the Feces of Bats. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0180222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, S.; Helb, D.; Burday, M.; Connell, N.; Alland, D. A detailed analysis of 16S ribosomal RNA gene segments for the diagnosis of pathogenic bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 69, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Aladid, R.; Fernandez-Barat, L.; Alcaraz-Serrano, V.; Bueno-Freire, L.; Vazquez, N.; Pastor-Ibanez, R.; Palomeque, A.; Oscanoa, P.; Torres, A. Determining the most accurate 16S rRNA hypervariable region for taxonomic identification from respiratory samples. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sens, H.; Trindade, W.A.; Oliveira, A.F.; Zaniolo, M.M.; Serenini, G.F.; Araujo-Ceranto, J.B.; Goncalves, D.D.; Germano, R.M. Bacterial resistance in bats from the Phyllostomidae family and its relationship with unique health. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2018, 38, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbehang Nguema, P.P.; Onanga, R.; Ndong Atome, G.R.; Obague Mbeang, J.C.; Mabika Mabika, A.; Yaro, M.; Lounnas, M.; Dumont, Y.; Zohra, Z.F.; Godreuil, S.; et al. Characterization of ESBL-Producing Enterobacteria from Fruit Bats in an Unprotected Area of Makokou, Gabon. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.A.; Torres, C.; Lopez, A.R.; Rodriguez, C.O.; Valencia, C.S. Antimicrobial Resistance of Enterococcus Species Isolated from Wild Mammals in Aragon, Spain. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 66, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowakiewicz, A.; Zieba, P.; Gnat, S.; Osinska, M.; Lagowski, D.; Kosior-Korzecka, U.; Puzio, I.; Krol, J. Analysis of the occurrence and molecular characteristics of drug-resistant strains of Enterococcus faecalis isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of insectivorous bat species in Poland: A possible essential impact on the spread of drug resistance? Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obodoechi, L.O.; Carvalho, I.; Chenouf, N.S.; Martinez-Alvarez, S.; Sadi, M.; Nwanta, J.A.; Chah, K.F.; Torres, C. Antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli isolates from frugivorous (Eidolon helvum) and insectivorous (Nycteris hispida) bats in Southeast Nigeria, with detection of CTX-M-15 producing isolates. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 75, 101613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavides, J.A.; Shiva, C.; Virhuez, M.; Tello, C.; Appelgren, A.; Vendrell, J.; Solassol, J.; Godreuil, S.; Streicker, D.G. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in common vampire bats Desmodus rotundus and livestock in Peru. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corduneanu, A.; Wu-Chuang, A.; Maitre, A.; Obregon, D.; Sandor, A.D.; Cabezas-Cruz, A. Structural differences in the gut microbiome of bats using terrestrial vs. aquatic feeding resources. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Liu, B.; Wu, H.; Feng, J.; Jiang, T. Seasonal Dietary Shifts Alter the Gut Microbiota of Avivorous Bats: Implication for Adaptation to Energy Harvest and Nutritional Utilization. mSphere 2021, 6, e0046721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingala, M.R.; Simmons, N.B.; Dunbar, M.; Wultsch, C.; Krampis, K.; Perkins, S.L. You are more than what you eat: Potentially adaptive enrichment of microbiome functions across bat dietary niches. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.J.; Mohiuddin, S.S. Biochemistry, Essential Amino Acids; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, C.B.; Reis, N.R.; Rezende, M.I. Nutritional content of bat-consumed fruits in a forest fragment in Southern Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2017, 77, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitai, O.; Holtze, S.; Barkan, S.; Amichai, E.; Korine, C.; Pinshow, B.; Voigt, C.C. Fruit bats (Pteropodidae) fuel their metabolism rapidly and directly with exogenous sugars. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 2693–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, J.T.; Douglas, G.M.; Hayes, M.G.; MacDonald, J.; Desai, D.K.; Allward, N.; Jones, C.M.A.; Wright, R.J.; Dhanani, A.S.; Comeau, A.M.; et al. Microbiome differential abundance methods produce different results across 38 datasets. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, H.L.; Jackson, E.W.; Webala, P.W.; Babyesiza, W.S.; Kerbis Peterhans, J.C.; Demos, T.C.; Patterson, B.D.; Gilbert, J.A. Ecology and Host Identity Outweigh Evolutionary History in Shaping the Bat Microbiome. mSystems 2019, 4, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingala, M.R.; Simmons, N.B.; Wultsch, C.; Krampis, K.; Speer, K.A.; Perkins, S.L. Comparing Microbiome Sampling Methods in a Wild Mammal: Fecal and Intestinal Samples Record Different Signals of Host Ecology, Evolution. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, I.V.; Berezinskaia, I.S.; Popov, I.V.; Martiusheva, I.B.; Tkacheva, E.V.; Gorobets, V.E.; Tikhmeneva, I.A.; Aleshukina, A.V.; Tverdokhlebova, T.I.; Chikindas, M.L. Cultivable Gut Microbiota in Synanthropic Bats: Shifts of Its Composition and Diversity Associated with Hibernation. Animals 2023, 13, 3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Ramos, V.B.; Tomassini, A.; Ferrari, F.; Boga, R.; Russo, D. Admittance to Wildlife Rehabilitation Centres Points to Adverse Effects of Climate Change on Insectivorous Bats. Biology 2023, 12, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D643–D648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
| Bat Species | Food Type | Sampling Location Site | Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nyctalus noctula | Insectivorous | Bat Rehabilitation Center of Don State Technical University, Rostov-on-Don | 30 |
| Vespertilio murinus | Insectivorous | Bat Rehabilitation Center of Moscow Zoo, Moscow | 29 |
| Carollia perspicillata | Fructivorous | Experimental Department of Small Mammals of Moscow Zoo, Moscow | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popov, I.V.; Popov, I.V.; Krikunova, A.A.; Lipilkina, T.A.; Derezina, T.N.; Chikindas, M.L.; Venema, K.; Ermakov, A.M. Gut Microbiota Composition of Insectivorous Synanthropic and Fructivorous Zoo Bats: A Direct Metagenomic Comparison. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417301
Popov IV, Popov IV, Krikunova AA, Lipilkina TA, Derezina TN, Chikindas ML, Venema K, Ermakov AM. Gut Microbiota Composition of Insectivorous Synanthropic and Fructivorous Zoo Bats: A Direct Metagenomic Comparison. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417301
Chicago/Turabian StylePopov, Igor V., Ilia V. Popov, Anastasya A. Krikunova, Tatyana A. Lipilkina, Tatyana N. Derezina, Michael L. Chikindas, Koen Venema, and Alexey M. Ermakov. 2023. "Gut Microbiota Composition of Insectivorous Synanthropic and Fructivorous Zoo Bats: A Direct Metagenomic Comparison" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417301
APA StylePopov, I. V., Popov, I. V., Krikunova, A. A., Lipilkina, T. A., Derezina, T. N., Chikindas, M. L., Venema, K., & Ermakov, A. M. (2023). Gut Microbiota Composition of Insectivorous Synanthropic and Fructivorous Zoo Bats: A Direct Metagenomic Comparison. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417301






