DNA Sensor for the Detection of Brucella spp. Based on Magnetic Nanoparticle Markers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
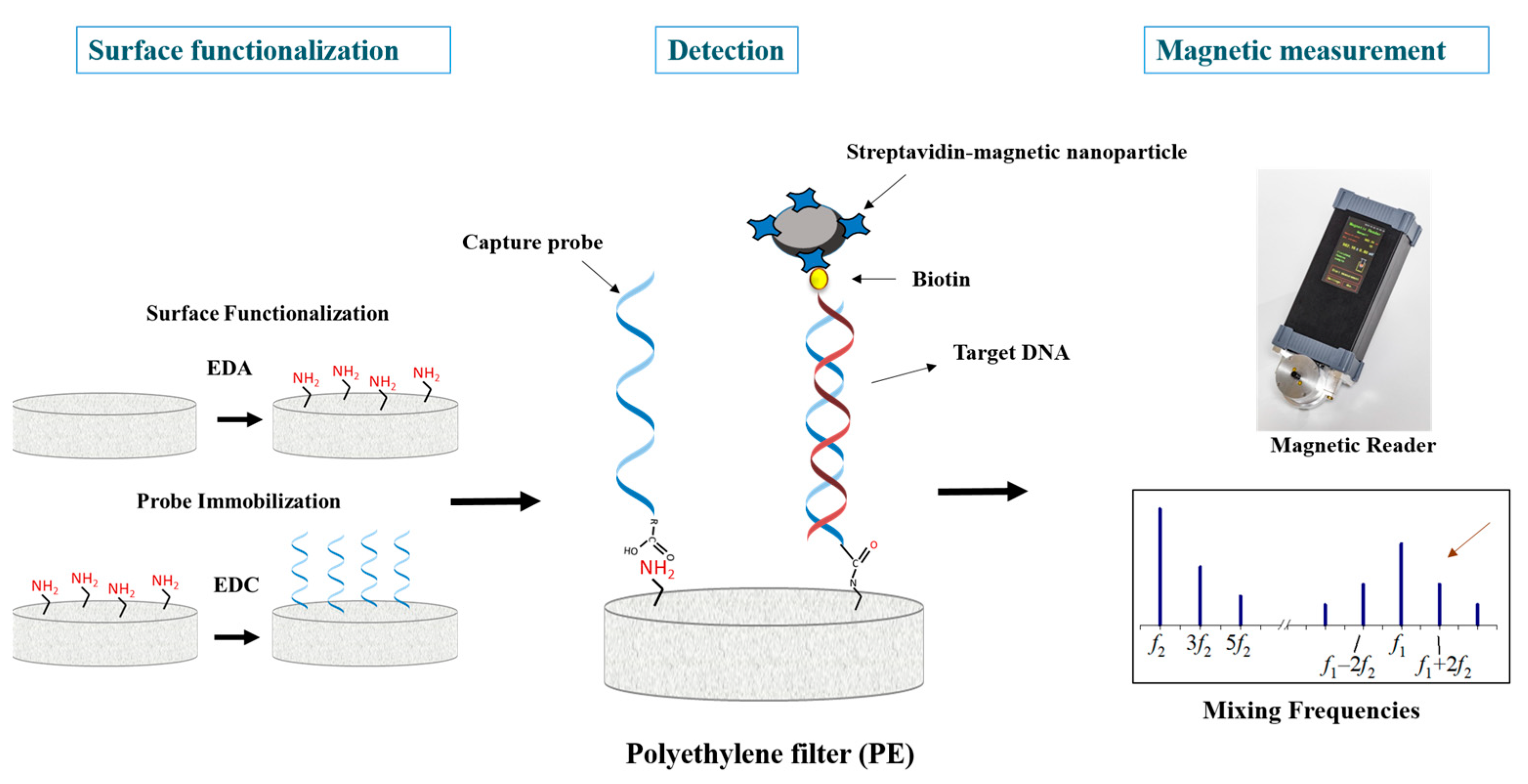
2.1. Principle of the DNA Magnetic Assay
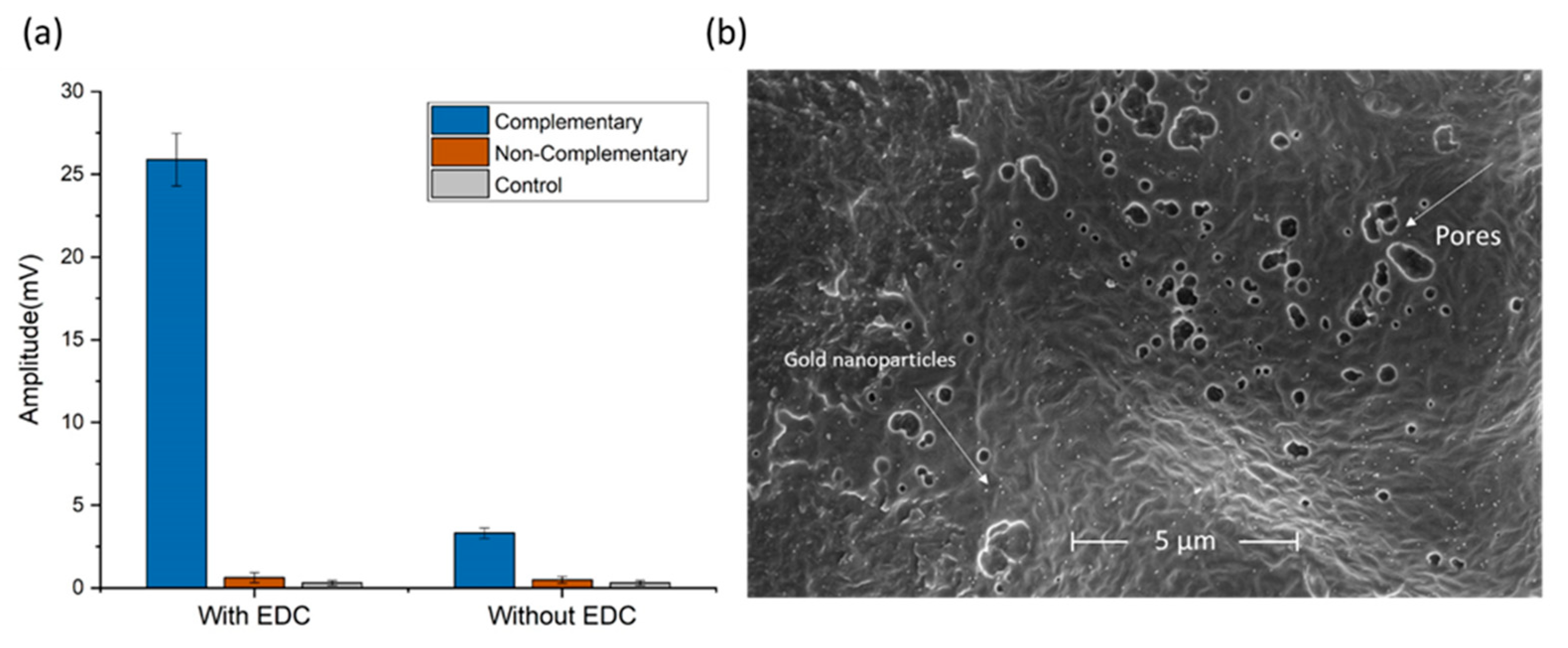
2.2. Surface Functionalization and Probe Immobilization
2.3. Assay Optimization
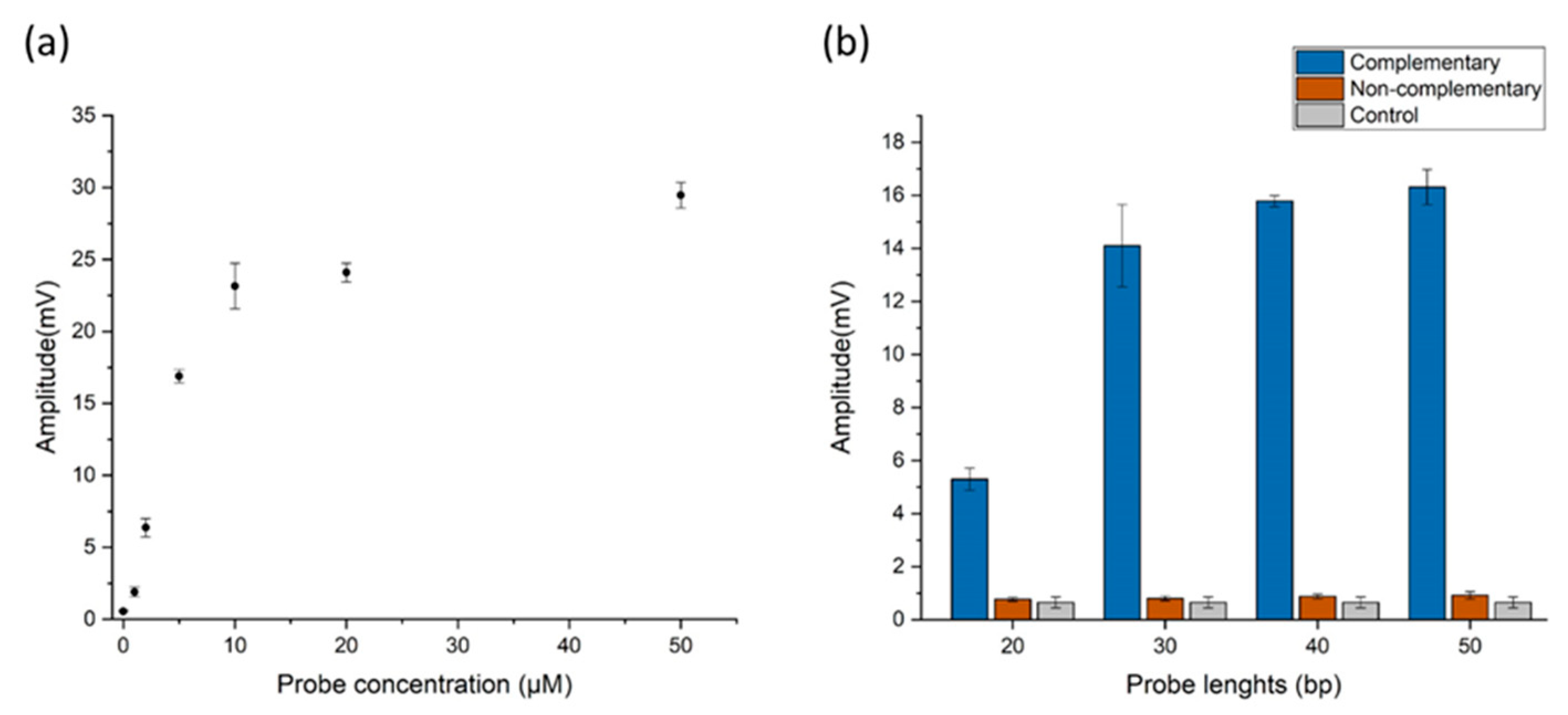
2.3.1. Adjusting Probe Parameters
2.3.2. Optimization of DNA Hybridization
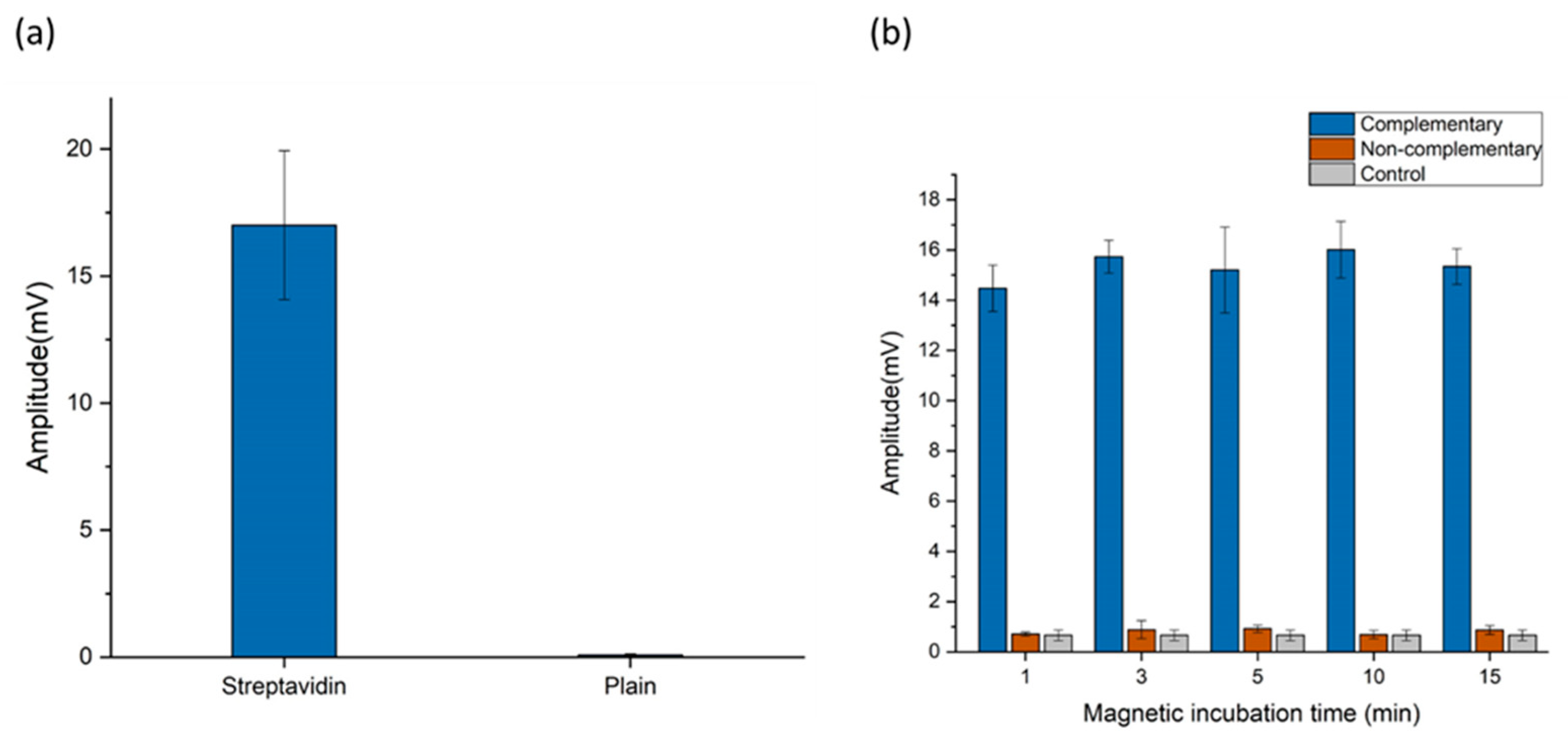
2.3.3. Magnetic Sensing Optimization
2.3.4. Analytical Performance
2.4. Potential for Future Development
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Target Selection and Capture Probes Design
3.2. PE Surface Modification
3.3. Filter Preparation
3.4. Capture Probe Immobilization
3.5. Hybridization and Magnetic Labeling
3.6. Detection of Amplified Brucella Genomic DNA
3.7. Frequency Mixing Magnetic Detection
3.8. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, M.T.; Sobur, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Ievy, S.; Hossain, M.J.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Rahman, A.T.; Ashour, H.M. Zoonotic Diseases: Etiology, Impact, and Control. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, S.K.; Sehrawat, A.; Tiwari, R.; Prasad, M.; Gulati, B.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Chhabra, R.; Karthik, K.; Patel, S.K.; Pathak, M.; et al. Bovine Brucellosis—A Comprehensive Review. Vet. Q. 2021, 41, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljanazreh, B.; Alzatari, K.; Tamimi, A.; Alsaafeen, M.H.; Hassouneh, W.; Ashhab, Y. Brucellosis Re-Emergence after a Decade of Quiescence in Palestine, 2015–2017: A Seroprevalence and Molecular Characterization Study. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e130–e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, A.R.; Baldwin, V.M.; Roy, S.; Essex-Lopresti, A.E.; Prior, J.L.; Harmer, N.J. Zoonoses under Our Noses. Microbes Infect. 2019, 21, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, M. Infectious Pathogens Meet Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 106, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bonaventura, G.; Angeletti, S.; Ianni, A.; Petitti, T.; Gherardi, G. Microbiological Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis: An Overview. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainar-Jaime, R.C.; Muñoz, P.M.; de Miguel, M.J.; Grilló, M.J.; Marín, C.M.; Moriyón, I.; Blasco, J.M. Specificity Dependence between Serological Tests for Diagnosing Bovine Brucellosis in Brucella-Free Farms Showing False Positive Serological Reactions Due to Yersinia Enterocolitica O:9. Can. Vet. J. 2005, 46, 913–916. [Google Scholar]
- Pfukenyi, D.M.; Meletis, E.; Modise, B.; Ndengu, M.; Kadzviti, F.W.; Dipuo, K.; Moesi, K.; Kostoulas, P.; Matope, G. Evaluation of the Sensitivity and Specificity of the Lateral Flow Assay, Rose Bengal Test and the Complement Fixation Test for the Diagnosis of Brucellosis in Cattle Using Bayesian Latent Class Analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 181, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuan-Jimenez, R.; Colmenero, J.D.; Morata, P. Lessons Learned with Molecular Methods Targeting the BCSP-31 Membrane Protein for Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 469, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagupsky, P.; Morata, P.; Colmenero, J.D. Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33, e00073-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syedmoradi, L.; Daneshpour, M.; Alvandipour, M.; Gomez, F.A.; Hajghassem, H.; Omidfar, K. Point of Care Testing: The Impact of Nanotechnology. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; He, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, G.; Xiao, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Deng, Y.; et al. Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Nucleic Acid Detection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloag, L.; Mehdipour, M.; Chen, D.; Tilley, R.D.; Gooding, J.J. Advances in the Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Saha, R.; Su, D.; Krishna, V.D.; Liu, J.; Cheeran, M.C.-J.; Wang, J.-P. Magnetic-Nanosensor-Based Virus and Pathogen Detection Strategies before and during COVID-19. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 9560–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chieh, J.-J.; Wei, W.-C.; Liao, S.-H.; Chen, H.-H.; Lee, Y.-F.; Lin, F.-C.; Chiang, M.-H.; Chiu, M.-J.; Horng, H.-E.; Yang, S.-Y. Eight-Channel AC Magnetosusceptometer of Magnetic Nanoparticles for High-Throughput and Ultra-High-Sensitivity Immunoassay. Sensors 2018, 18, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yari, P.; Rezaei, B.; Dey, C.; Chugh, V.K.; Veerla, N.V.R.K.; Wang, J.-P.; Wu, K. Magnetic Particle Spectroscopy for Point-of-Care: A Review on Recent Advances. Sensors 2023, 23, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achtsnicht, S.; Neuendorf, C.; Faßbender, T.; Nölke, G.; Offenhäusser, A.; Krause, H.-J.; Schröper, F. Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Cholera Toxin Subunit B Using Magnetic Frequency Mixing Detection. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.H.F.; Hartmann, M.; Krause, H.-J.; Blankenstein, G.; Mueller-Chorus, B.; Oster, J.; Miethe, P.; Keusgen, M. CRP Determination Based on a Novel Magnetic Biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietschmann, J.; Voepel, N.; Voß, L.; Rasche, S.; Schubert, M.; Kleines, M.; Krause, H.-J.; Shaw, T.M.; Spiegel, H.; Schroeper, F. Development of Fast and Portable Frequency Magnetic Mixing-Based Serological SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody Detection Assay. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 643275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettcher, S.; Jungk, F.; Kühn, C.; Krause, H.-J.; Nölke, G.; Commandeur, U.; Fischer, R.; Schillberg, S.; Schröper, F. Simple and Portable Magnetic Immunoassay for Rapid Detection and Sensitive Quantification of Plant Viruses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achtsnicht, S.; Pourshahidi, A.M.; Offenhäusser, A.; Krause, H.-J. Multiplex Detection of Different Magnetic Beads Using Frequency Scanning in Magnetic Frequency Mixing Technique. Sensors 2019, 19, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshahidi, A.M.; Achtsnicht, S.; Nambipareechee, M.M.; Offenhäusser, A.; Krause, H.-J. Multiplex Detection of Magnetic Beads Using Offset Field Dependent Frequency Mixing Magnetic Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chern, E.C.; Siefring, S.; Paar, J.; Doolittle, M.; Haugland, R.A. Comparison of Quantitative PCR Assays for Escherichia Coli Targeting Ribosomal RNA and Single Copy Genes. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margulis, M.; Danielli, A. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Repetitive Nucleic Acid Sequences Using Magnetically Modulated Biosensors. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11749–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, J.I.A.; Yusof, N.A. The Strategies of DNA Immobilization and Hybridization Detection Mechanism in the Construction of Electrochemical DNA Sensor: A Review. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2017, 16, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimse, S.B.; Song, K.; Sonawane, M.D.; Sayyed, D.R.; Kim, T. Immobilization Techniques for Microarray: Challenges and Applications. Sensors 2014, 14, 22208–22229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, H.F.; Gong, H.; Dong, X.-D.; Zeng, X.; Lai Kuan Tan, A.; Yang, X.; Tan, S.N. Electrochemical Biosensing of DNA with Capture Probe Covalently Immobilized onto Glassy Carbon Surface. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 551, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elschner, T.; Scholz, F.; Miethe, P.; Heinze, T. Rapid Flow Through Immunoassay for CRP Determination Based on Polyethylene Filters Modified with ω-Aminocellulose Carbamate. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.W.; Heaton, R.J.; Georgiadis, R.M. The Effect of Surface Probe Density on DNA Hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 5163–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.N.; Grainger, D.W. Biophysical Properties of Nucleic Acids at Surfaces Relevant to Microarray Performance. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 436–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wu, L.; Fields, M.W.; Zhou, J. Use of Microarrays with Different Probe Sizes for Monitoring Gene Expression. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5154–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relógio, A.; Schwager, C.; Richter, A.; Ansorge, W.; Valcárcel, J. Optimization of Oligonucleotide-Based DNA Microarrays. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, L.; Reuterswärd, P.; Rasti, R.; Herrmann, B.; Mårtensson, A.; Alfvén, T.; Gantelius, J.; Andersson-Svahn, H. A Vertical Flow Paper-Microarray Assay with Isothermal DNA Amplification for Detection of Neisseria Meningitidis. Talanta 2018, 183, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, M.D.; Jatkoe, T.A.; Stumpf, C.R.; Lu, J.; Thomas, J.D.; Madore, S.J. Assessment of the Sensitivity and Specificity of Oligonucleotide (50mer) Microarrays. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 4552–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.L.; Liu, J. Factors and Methods to Modulate DNA Hybridization Kinetics. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 16, 2000338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, C.S.; Lackey, H.H.; Reece, E.J.; Harris, J.M.; Heemstra, J.M.; Peterson, E.M. Evaluating the Effect of Ionic Strength on PNA:DNA Duplex Formation Kinetics. RSC Chem. Biol. 2021, 2, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dahouk, S.; Nöckler, K. Implications of Laboratory Diagnosis on Brucellosis Therapy. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.P.; Mulder, M.; Gilman, R.H.; Smits, H.L. Human Brucellosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekiri, A.B.; Kilonzo, C.; Bird, B.H.; VanWormer, E.; Wolking, D.J.; Smith, W.A.; Masanja, H.; Kazwala, R.R.; Mazet, J.A.K. Utility of the Rose Bengal Test as a Point-of-Care Test for Human Brucellosis in Endemic African Settings: A Systematic Review. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 2020, 6586182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwida, M.M.; El-Gohary, A.H.; Melzer, F.; Tomaso, H.; Rösler, U.; Wernery, U.; Wernery, R.; Elschner, M.C.; Khan, I.; Eickhoff, M.; et al. Comparison of Diagnostic Tests for the Detection of Brucella Spp. in Camel Sera. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Mesa, J.D.; Sánchez-Gonzalez, J.; Reguera, J.M.; Martín, L.; Lopez-Palmero, S.; Colmenero, J.D. Rose Bengal Test: Diagnostic Yield and Use for the Rapid Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis in Emergency Departments in Endemic Areas. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukambagire, A.S.; Mendes, Â.J.; Bodenham, R.F.; McGiven, J.A.; Mkenda, N.A.; Mathew, C.; Rubach, M.P.; Sakasaka, P.; Shayo, D.D.; Maro, V.P.; et al. Performance Characteristics and Costs of Serological Tests for Brucellosis in a Pastoralist Community of Northern Tanzania. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, A.M. Comparative Assessment of Sensitivity and Specificity of Rose Bengal Test and Modified In-House ELISA by Using IS711 Taqman Real Time PCR Assay as a Gold Standard for the Diagnosis of Bovine Brucellosis. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2018, 11, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memish, Z.A.; Almuneef, M.; Mah, M.W.; Qassem, L.A.; Osoba, A.O. Comparison of the Brucella Standard Agglutination Test with the ELISA IgG and IgM in Patients with Brucella Bacteremia. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2002, 44, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abernethy, D.A.; Menzies, F.D.; McCullough, S.J.; McDowell, S.W.J.; Burns, K.E.; Watt, R.; Gordon, A.W.; Greiner, M.; Pfeiffer, D.U. Field Trial of Six Serological Tests for Bovine Brucellosis. Vet. J. 2012, 191, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho-Martínez, J.C.; Rios-Lugo, M.J.; Gaytán-Hernández, D.; Hernández-Mendoza, H. Comparison of a Brucella Enzyme Immunoassay and the Standard Agglutination with 2-Mercaptoethanol Test in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Brucellosis in Mexican Patients. Clin. Lab. 2020, 66, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGiven, J.A.; Tucker, J.D.; Perrett, L.L.; Stack, J.A.; Brew, S.D.; MacMillan, A.P. Validation of FPA and cELISA for the Detection of Antibodies to Brucella Abortus in Cattle Sera and Comparison to SAT, CFT, and iELISA. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 278, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, W.; Chen, F.; Li, W.; Wang, G. ELISA Is Superior to Bacterial Culture and Agglutination Test in the Diagnosis of Brucellosis in an Endemic Area in China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yin, D.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; Song, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; Song, X.; Li, J. A Sandwich Immunoassay for Brucellosis Diagnosis Based on Immune Magnetic Beads and Quantum Dots. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 141, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, E.; Hou, S.; Xiao, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; et al. Novel Vertical Flow Immunoassay with Au@PtNPs for Rapid, Ultrasensitive, and On-Site Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 29534–29542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nakkas, A.; Mustafa, A.S.; Wright, S.G. Large-Scale Evaluation of a Single-Tube Nested PCR for the Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis in Kuwait. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, L.; Qi, C.; Bao, W.; Ji, X.; Liu, J.; Du, N.; Gao, L.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y. Monitoring the Course of Brucella Infection with qPCR-Based Detection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 89, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattarahmady, N.; Kayani, Z.; Heli, H. Highly Simple and Visual Colorimetric Detection of Brucella Melitensis Genomic DNA in Clinical Samples Based on Gold Nanoparticles. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2015, 12, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangari, A.; Mahmoodi, P.; Mohammadzadeh, A. Biosensors Functionalized with Nanoparticles for Rapid Detection of Brucella. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, A.; Sattarahmady, N.; Heli, H. An Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Genosensor for Brucella Based on Palladium Nanoparticles. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 510, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuker, M. Mfold Web Server for Nucleic Acid Folding and Hybridization Prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holländer, A. Surface Oxidation inside of Macroscopic Porous Polymeric Materials. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, H.-J.; Wolters, N.; Zhang, Y.; Offenhäusser, A.; Miethe, P.; Meyer, M.H.F.; Hartmann, M.; Keusgen, M. Magnetic Particle Detection by Frequency Mixing for Immunoassay Applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Target Element | Assay Time | Safety | Stage of Infection | Cost | Sensitivity/LOD | Specificity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood culture | Living bacteria | Days to weeks | Low | Early to Acute | Moderate to High | 10–90% | 100% | [10,37,38] |
| Rose bengal | Antibodies | Minutes | Moderate | Acute to Chronic | Low | 75–100% | 39–100% | [39,40,41,42,43] |
| Standard agglutination | Antibodies | Hours to days | Moderate | Acute to Chronic | Low to Moderate | 75–96% | 44–99% | [44,45,46,47] |
| ELISA | Antibodies | Hours | Moderate | Acute to Chronic | Moderate to High | 98.7% | 98.4% | [48] |
| Quantum dot | Antibodies | 2 h | Moderate | Acute to Chronic | High | 96.15% | 94.12% | [49] |
| Colorimetric | Antibodies | Hour | Moderate | Acute to Chronic | Moderate | 98.33% | 100% | [50] |
| PCR | DNA | Hours | High | Early to Chronic | Moderate to High | 93-100% | 98–100% | [10,51,52] |
| Colorimetric | DNA | 2 h | High | Early to chronic | Low to Moderate | 3.32 pg/mL | 100% | [53,54] |
| Electrochemical | DNA | 1 h | High | Early to Chronic | Moderate | 2.7 × 10−20 mol dm−3 | 100% | [55] |
| Magnetic | DNA | * Less than 1 h | High | Early to Chronic | Low to Moderate | 0.09 fM | 100% | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abuawad, A.; Ashhab, Y.; Offenhäusser, A.; Krause, H.-J. DNA Sensor for the Detection of Brucella spp. Based on Magnetic Nanoparticle Markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417272
Abuawad A, Ashhab Y, Offenhäusser A, Krause H-J. DNA Sensor for the Detection of Brucella spp. Based on Magnetic Nanoparticle Markers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417272
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbuawad, Abdalhalim, Yaqoub Ashhab, Andreas Offenhäusser, and Hans-Joachim Krause. 2023. "DNA Sensor for the Detection of Brucella spp. Based on Magnetic Nanoparticle Markers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417272
APA StyleAbuawad, A., Ashhab, Y., Offenhäusser, A., & Krause, H.-J. (2023). DNA Sensor for the Detection of Brucella spp. Based on Magnetic Nanoparticle Markers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417272








