miR-877-5p as a Potential Link between Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Development and Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Circulating miRNAs Were Altered in Plasma of Women with AAMS
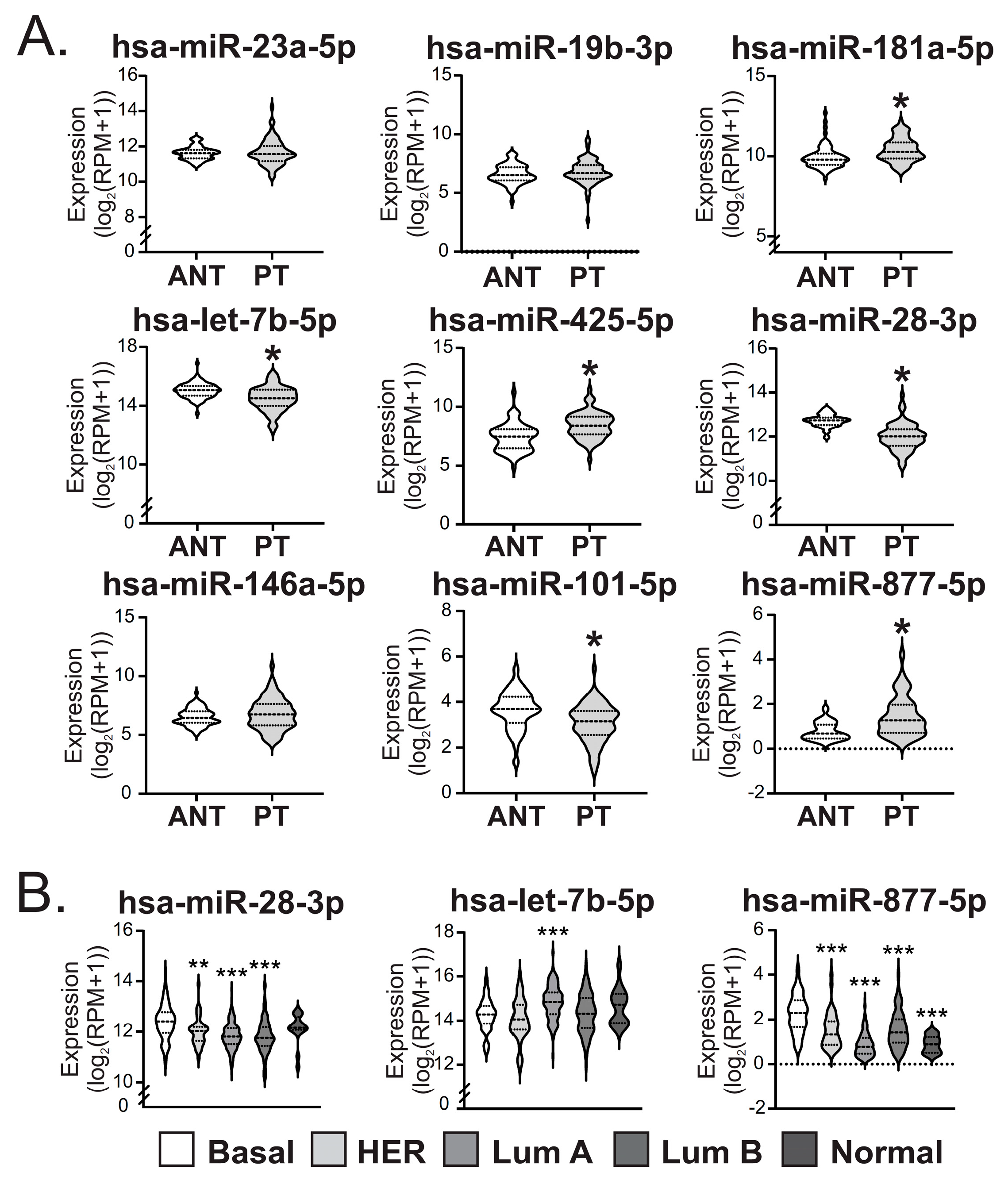
2.2. miR-28-3p, -101-5p and let-7b-5p Were Diminished While miR-181a-5p, -425-5p and -877-5p Were Increased in Primary Tumors of BC Patients
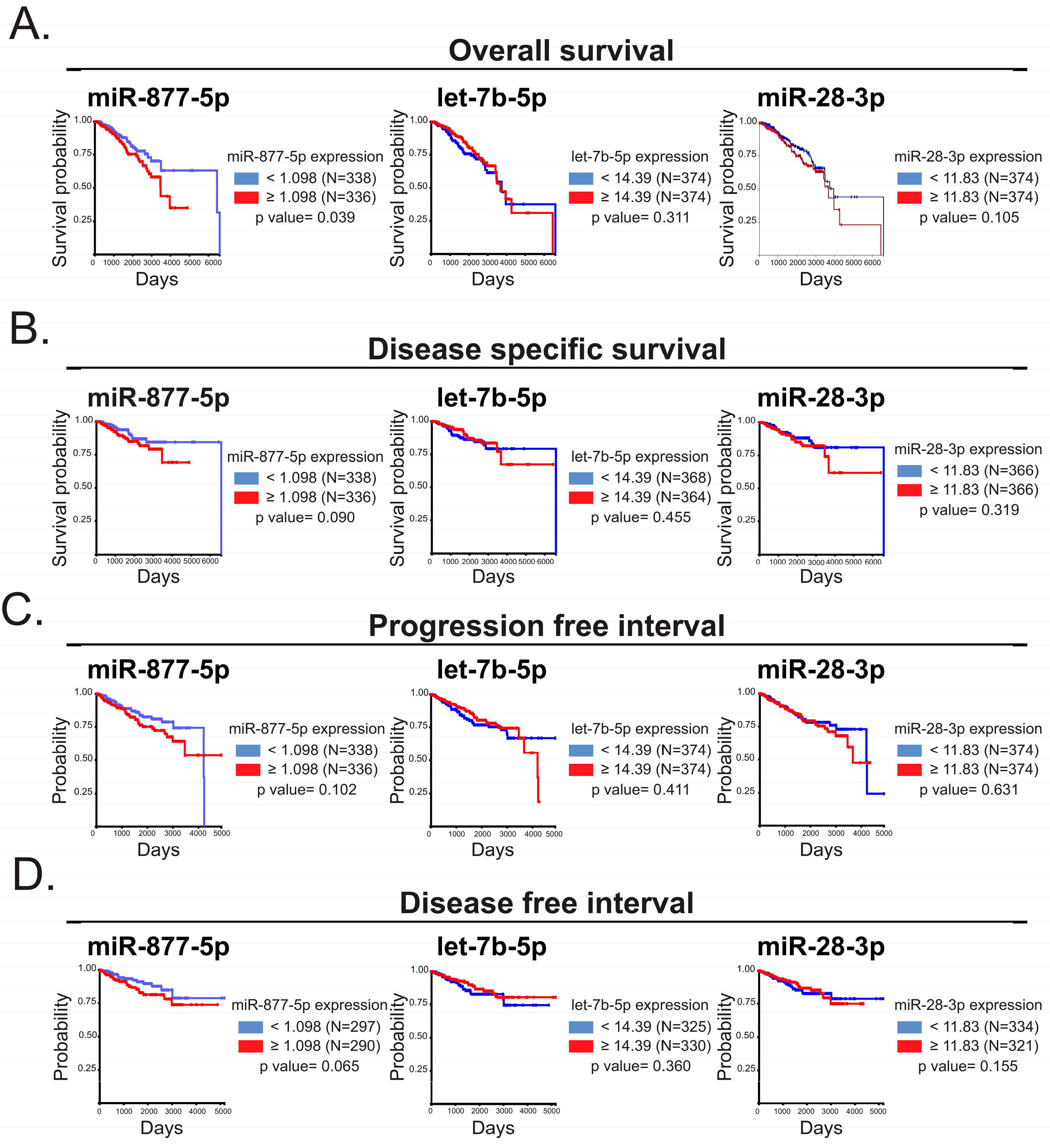
2.3. The miR-877-5p Expression Was Correlated with Diminished Overall Survival of BC Patients
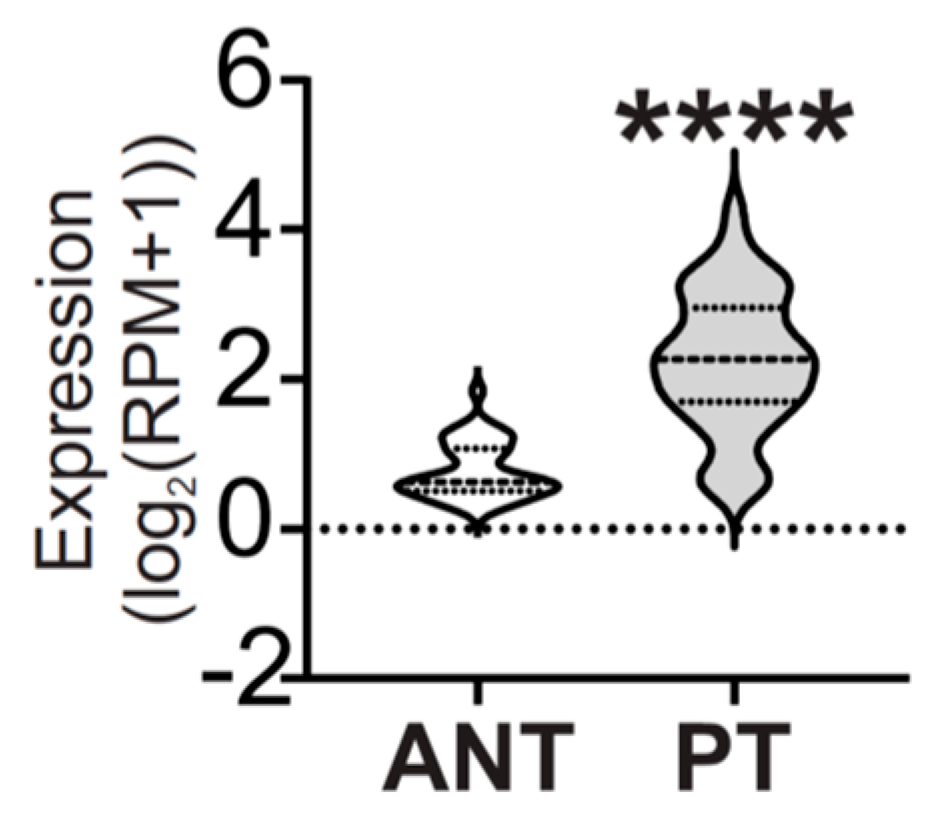
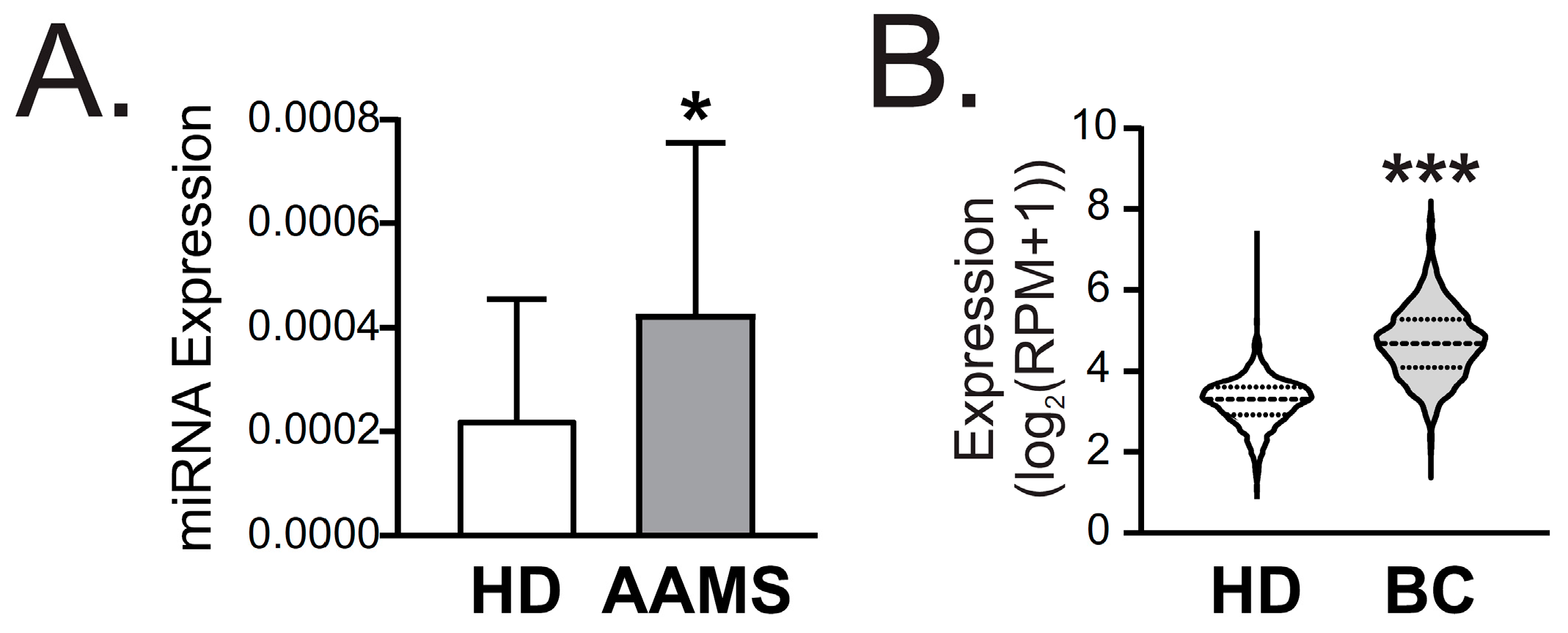
2.4. miR-877-5p Was Increased in Plasma of AAMS Patients and BC Patients
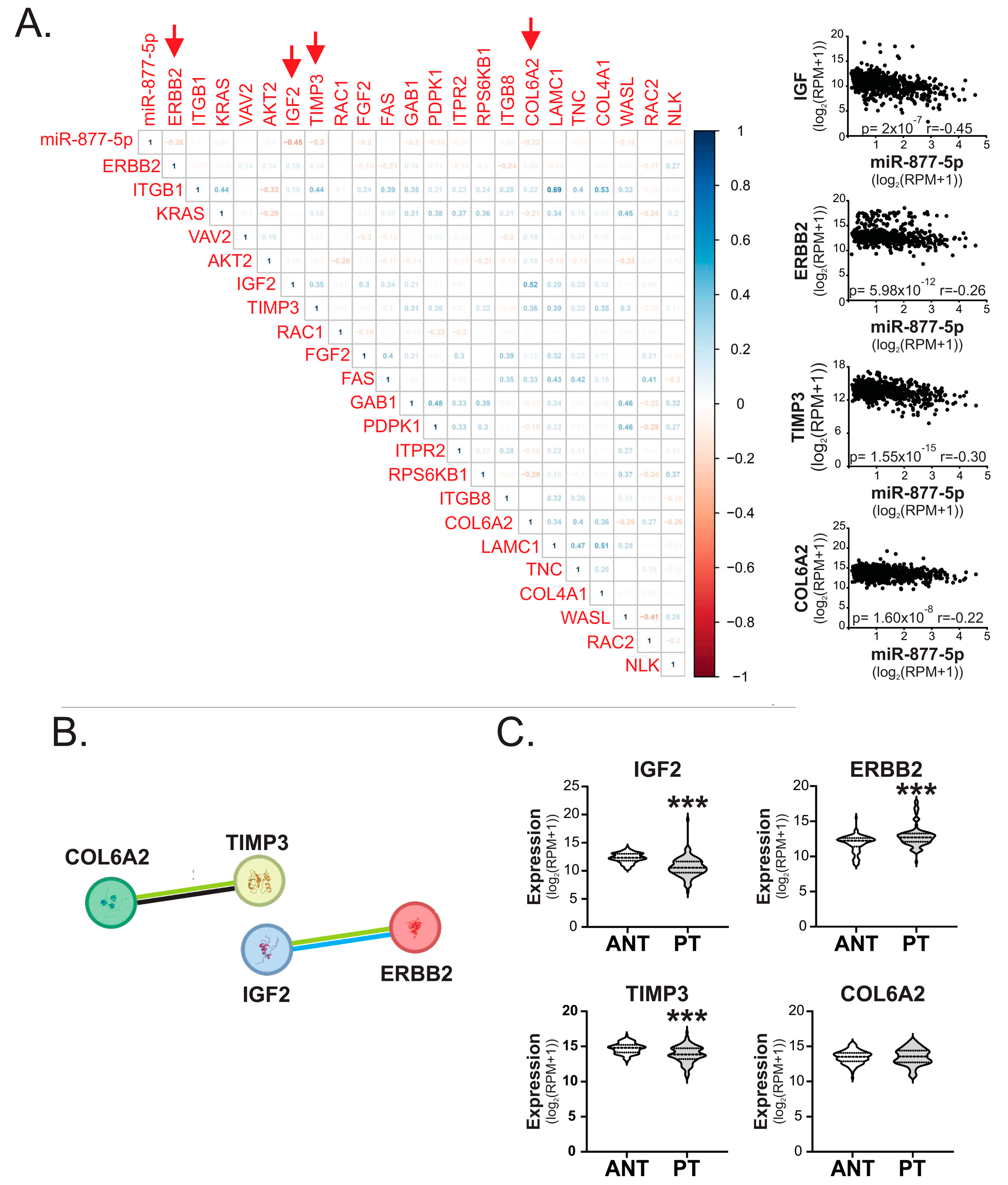
2.5. miR-877-5p Expression Was Inversely Correlated with IGF2, ERBB2, TIMP3 and COL6A2 Levels in Breast Tumors
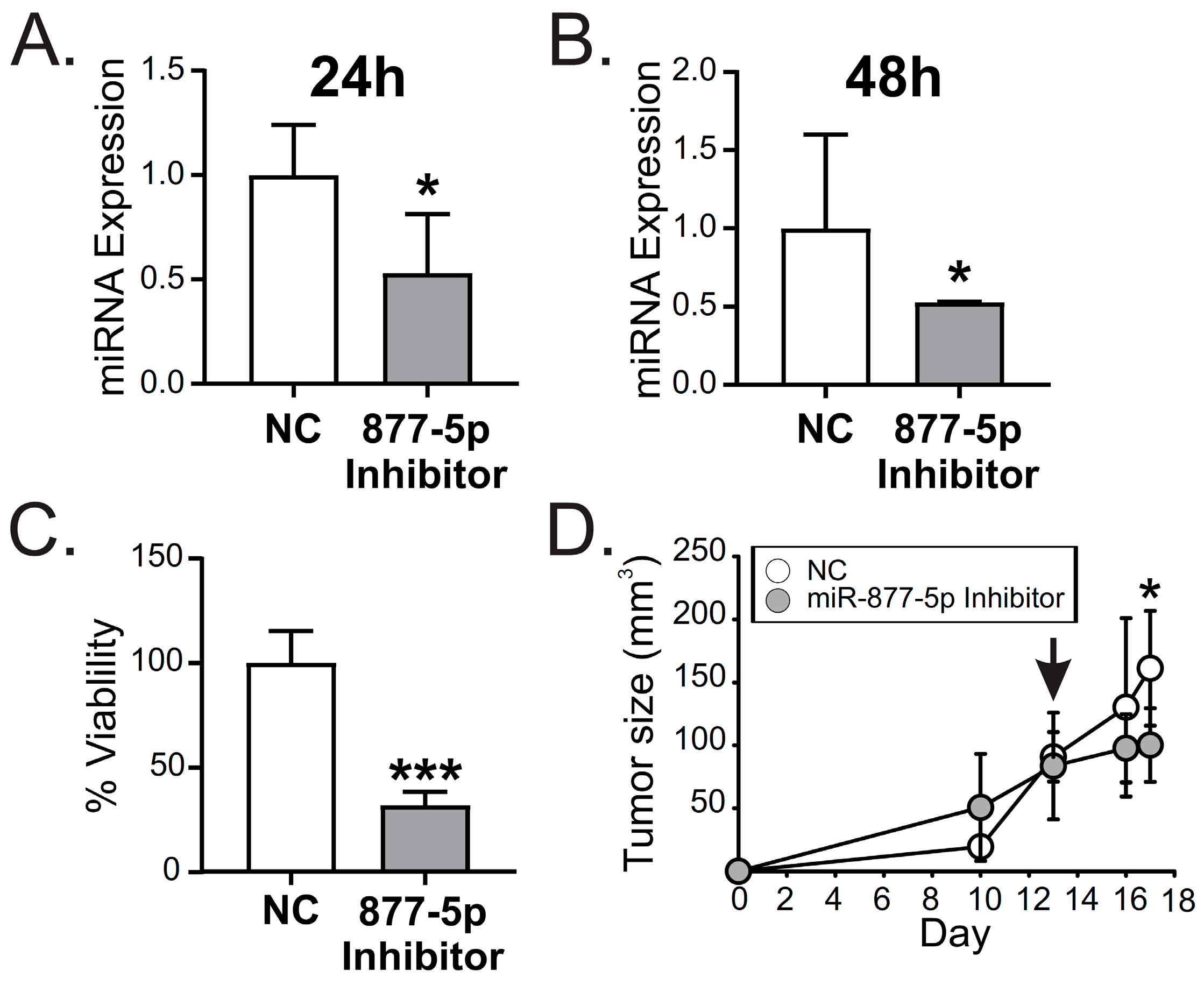
2.6. miR-877-5p Inhibition Decreased Viability and Tumor Growth from the TNBC Model 4T1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Recruitment and Sample Processing
4.2. RNA Isolation
4.3. miRNA Microarrays
4.4. Functional Enrichment Analyses
4.5. TCGA Dataset Analysis
4.6. Correlation Matrix
4.7. miRNA RT-qPCR
4.8. Cell Culture and Transfections
4.9. Cell Viability Assay
4.10. TNBC Syngeneic Transplant Model
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, K.A.; Spruck, C. Triple-negative Breast Cancer Therapy: Current and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.J.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtyping and Treatment Progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czene, K.; Lichtenstein, P.; Hemminki, K. Environmental and Heritable Causes of Cancer among 9.6 Million Individuals in the Swedish Family-Cancer Database. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 99, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.C. Balancing Life-Style and Genomics Research for Disease Prevention. Science 2002, 296, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Final Report. Circulation 2002, 106, 3143–3564. [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome: A Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; And International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Brandt, P.A.; Spiegelman, D.; Yaun, S.S.; Adami, H.O.; Beeson, L.; Folsom, A.R.; Fraser, G.; Goldbohm, R.A.; Graham, S.; Kushi, L.; et al. Pooled Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies on Height, Weight, and Breast Cancer Risk. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Sung, J.; Song, Y.M. Serum Total Cholesterol and the Risk of Breast Cancer in Postmenopausal Korean Women. Cancer Causes Control 2009, 20, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.; Kelley, G.A.; Hartley, T.A.; Rockett, I.R.H. Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated with Increased Breast Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2014, 2014, 189384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, I.; Esposito, E.; Pentimalli, F.; Crispo, A.; Montella, M.; Grimaldi, M.; De Marco, M.; Cavalcanti, E.; D’Aiuto, M.; Fucito, A.; et al. Metabolic Syndrome Affects Breast-Cancer Risk in Postmenopausal Women: National Cancer Institute of Naples Experience. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, R.J.; Eng, S.M.; Abrahamson, P.E.; Britton, J.A.; Teitelbaum, S.L.; Neugut, A.I.; Gammon, M.D. Weight Gain Prior to Diagnosis and Survival from Breast Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2007, 16, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, G.K.; Pirie, K.; Beral, V.; Green, J.; Spencer, E.; Bull, D. Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Relation to Body Mass Index in the Million Women Study: Cohort Study. Br. Med. J. 2007, 335, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Yao, G.; Hu, X.; Chen, L.; Ye, C. Advances in Studies on Metabolic Syndrome and Breast Cancer. Chin. J. Surg. 2015, 53, 966–969. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, B.; Kundranda, M.N.; Spiro, T.P.; Daw, H.A. The Association of Metabolic Syndrome with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 121, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizdar, Ö.; Alyamaç, E. Obesity: An Endocrine Tumor? Med. Hypotheses 2004, 63, 790–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Sen, S. MicroRNA as Biomarkers and Diagnostics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, F.; Nawaz, M. Long Distance Metabolic Regulation through Adipose-Derived Circulating Exosomal MiRNAs: A Trail for RNA-Based Therapies? Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, R.; Van Roosbroeck, K.; Calin, G.A. Cell-to-Cell Communication: MicroRNAs as Hormones. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottiers, V.; Näär, A.M. MicroRNAs in Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.U.; Miyazaki, H.; Ochiya, T. The Roles of MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2015, 7, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asleh, K.; Lluch, A.; Goytain, A.; Barrios, C.; Wang, X.Q.; Torrecillas, L.; Gao, D.; Ruiz-Borrego, M.; Leung, S.; Bines, J.; et al. Triple-Negative PAM50 Non-Basal Breast Cancer Subtype Predicts Benefit from Extended Adjuvant Capecitabine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 17, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yersal, O.; Barutca, S. Biological Subtypes of Breast Cancer: Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overholser, B.R.; Sowinski, K.M. Biostatistics Primer: Part 2. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2008, 23, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowntree, D. Statistics without Tears: A Primer for Non-Mathematicians; Scribner: Troy, MI, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Guilford, J.P. Fundamental Statistics in Psychology and Education. In Fundamental Statistic in Psychology and Education, 3rd ed.; Sci Educ;ation McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1957; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Deiuliis, J.A. MicroRNAs as Regulators of Metabolic Disease: Pathophysiologic Significance and Emerging Role as Biomarkers and Therapeutics. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolina, D.S.; Tavintharan, S.; Armugam, A.; Sepramaniam, S.; Pek, S.L.T.; Wong, M.T.K.; Lim, S.C.; Sum, C.F.; Jeyaseelan, K. Circulating MiRNA Profiles in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E2271–E2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, F.; D’Souza, R.F.; Durainayagam, B.R.; Milan, A.M.; Markworth, J.F.; Miranda-Soberanis, V.; Sequeira, I.R.; Roy, N.C.; Poppitt, S.D.; Mitchell, C.J.; et al. Circulatory MiRNA Biomarkers of Metabolic Syndrome. Acta Diabetol. 2020, 57, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, B.; Hendrayani, S.F.; Silva, G.; Aboussekhra, A. Let-7b Inhibits Cancer-Promoting Effects of Breast Cancerassociated Fibroblasts through IL-8 Repression. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17825–17838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, C.; Tang, S.C.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Du, N.; Qin, S.; Li, G.; Xu, S.; et al. Let-7c Blocks Estrogen-Activated Wnt Signaling in Induction of Self-Renewal of Breast Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Bhardwaj, A.; Embury, M.D.; Singh, H.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Bedrosian, I.; Wang, J. Integrative Analyses of Multilevel Omics Reveal Preneoplastic Breast to Possess a Molecular Landscape That Is Globally Shared with Invasive Basal-like Breast Cancer (Running Title: Molecular Landscape of Basal-like Breast Cancer Progression). Cancers 2020, 12, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, M.; Goto, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Okada, R.; Moriya, S.; Idichi, T.; Noda, M.; Sasaki, K.; Kita, Y.; Kurahara, H.; et al. RNA Sequencing-Based MicroRNA Expression Signature in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Oncogenic Targets by Antitumor MiR-143-5p and MiR-143-3p Regulation. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 65, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.H.; Qiu, C.; Sun, J.; Li, W.H. MiR-877-5p Suppresses Cell Growth, Migration and Invasion by Targeting Cyclin Dependent Kinase 14 and Predicts Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3038–3046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.D.; Zhang, N.; Sha, L. MiR-877-5p Antagonizes the Promoting Effect of Sp on the Gastric Cancer Progression. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Yu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Wei, W.; Xie, D.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, Q. MiR-877-5p Suppresses Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation through Targeting FOXM1. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 4731–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, D.D.; Dang, Y.W.; Lin, P.; Wen, D.Y.; He, R.Q.; Luo, D.Z.; Feng, Z.B.; Chen, G. A CircRNA-MiRNA-MRNA Network Identification for Exploring Underlying Pathogenesis and Therapy Strategy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xiang, L.; Mei, Y. MiR-877-5p Inhibits Epithelial Mesenchymal Transformation of Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting FGB. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 4882375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karginov, F.V.; Hannon, G.J. Remodeling of Ago2-MRNA Interactions upon Cellular Stress Reflects MiRNA Complementarity and Correlates with Altered Translation Rates. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 1624–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, I.; Yang, X.; Brown, J.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Torok-Storb, B.; Kabos, P.; Hesselberth, J.R.; Pillai, M.M. Genome-Wide Analysis of MiRNA-MRNA Interactions in Marrow Stromal Cells. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, W.H.; Yu, S.S.C.; Meng, Q.; Brew, K.; Woessner, J.F. TIMP-3 Binds to Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans of the Extracellular Matrix. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 31226–31232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.R. TIMP-3 and Endocrine Therapy of Breast Cancer: An Apoptosis Connection Emerges. J. Pathol. 2004, 202, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebiler Cavusoglu, A.; Kilic, Y.; Saydam, S.; Canda, T.; Başkan, Z.; Sevinc, A.I.; Sakizli, M. Predicting Invasive Phenotype with CDH1, CDH13, CD44, and TIMP3 Gene Expression in Primary Breast Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, E.L.H.; Loo, W.T.Y.; Zhu, L.; Cheung, M.N.B.; Chow, L.W.C. DNA Hypermethylation of TIMP3 Gene in Invasive Breast Ductal Carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2005, 59, S363–S365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizoso, F.J.; González, L.O.; Corte, M.D.; Rodríguez, J.C.; Vázquez, J.; Lamelas, M.L.; Junquera, S.; Merino, A.M.; García-Mũiz, J.L. Study of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Breast Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, D.; Yee, D. The IGF System and Breast Cancer. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2001, 8, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, N.T.; Zhang, D. Targeting EGFR in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer 2011, 2, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Y.; Aguilar-Mahecha, A.; Krzemien, U.; Hosein, A.; Buchanan, M.; Lafleur, J.; Pollak, M.; Ferrario, C.; Basik, M. Metastatic Breast Carcinoma–Associated Fibroblasts Have Enhanced Protumorigenic Properties Related to Increased IGF2 Expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7229–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, M.; Gariboldi, M.B.; Taiana, E.; Bonzi, M.C.; Craparotta, I.; Pagin, M.; Monti, E. Co-Targeting the IGF System and HIF-1 Inhibits Migration and Invasion by (Triple-Negative) Breast Cancer Cells. Br. J. Cancer. 2014, 110, 2865–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, N.; Márquez-Garbán, D.; Mah, V.; Fernando, G.; Elshimali, Y.; Garbán, H.; Elashoff, D.; Vadgama, J.; Goodglick, L.; Pietras, R. Biologic Roles of Estrogen Receptor- β and Insulin-like Growth Factor-2 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 925703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravia, C.H.; Flores, C.; Schwarz, L.J.; Bravo, L.; Zavaleta, J.; Araujo, J.; Neciosup, S.; Pinto, J.A. Patterns of Mutation Enrichment in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2019, 13, 1179554919868482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, P.L.; Scalise, G.D.; Duca, R.B.; Dalton, G.N.; Massillo, C.; Porretti, J.; Graña, K.; Gardner, K.; De Luca, P.; De Siervi, A. CTBP1 and Metabolic Syndrome Induce an MRNA and MiRNA Expression Profile Critical for Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13848–13858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, G.N.; Massillo, C.; Scalise, G.D.; Duca, R.; Porretti, J.; Farré, P.L.; Gardner, K.; Paez, A.; Gueron, G.; De Luca, P.; et al. CTBP1 Depletion on Prostate Tumors Deregulates MiRNA/MRNA Expression and Impairs Cancer Progression in Metabolic Syndrome Mice. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duca, R.B.; Massillo, C.; Dalton, G.N.; Farré, P.L.; Graña, K.D.; Gardner, K.; De Siervi, A. MiR-19b-3p and MiR-101-3p as Potential Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 2802. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-MiRPath v3.0: Deciphering MicroRNA Function with Experimental Support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W460–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farré, P.L.; Duca, R.B.; Massillo, C.; Dalton, G.N.; Graña, K.D.; Gardner, K.; Lacunza, E.; De Siervi, A. Mir-106b-5p: A Master Regulator of Potential Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Aggressiveness and Prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and Interpreting Cancer Genomics Data via the Xena Platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, P.; Dalton, G.N.; Scalise, G.D.; Moiola, C.P.; Porretti, J.; Massillo, C.; Kordon, E.; Gardner, K.; Zalazar, F.; Flumian, C.; et al. CtBP1 Associates Metabolic Syndrome and Breast Carcinogenesis Targeting Multiple MiRNAs. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18798–18811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Lange-Grünweller, K.; Dayyoub, E.; Bakowsky, U.; Weirauch, U.; Aigner, A.; Hartmann, R.K.; Grünweller, A. PEI-Complexed LNA Antiseeds as MiRNA Inhibitors. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.F.; Weirauch, U.; Thomas, M.; Grünweller, A.; Hartmann, R.K.; Aigner, A. MicroRNA Replacement Therapy for MiR-145 and MiR-33a Is Efficacious in a Model of Colon Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5214–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
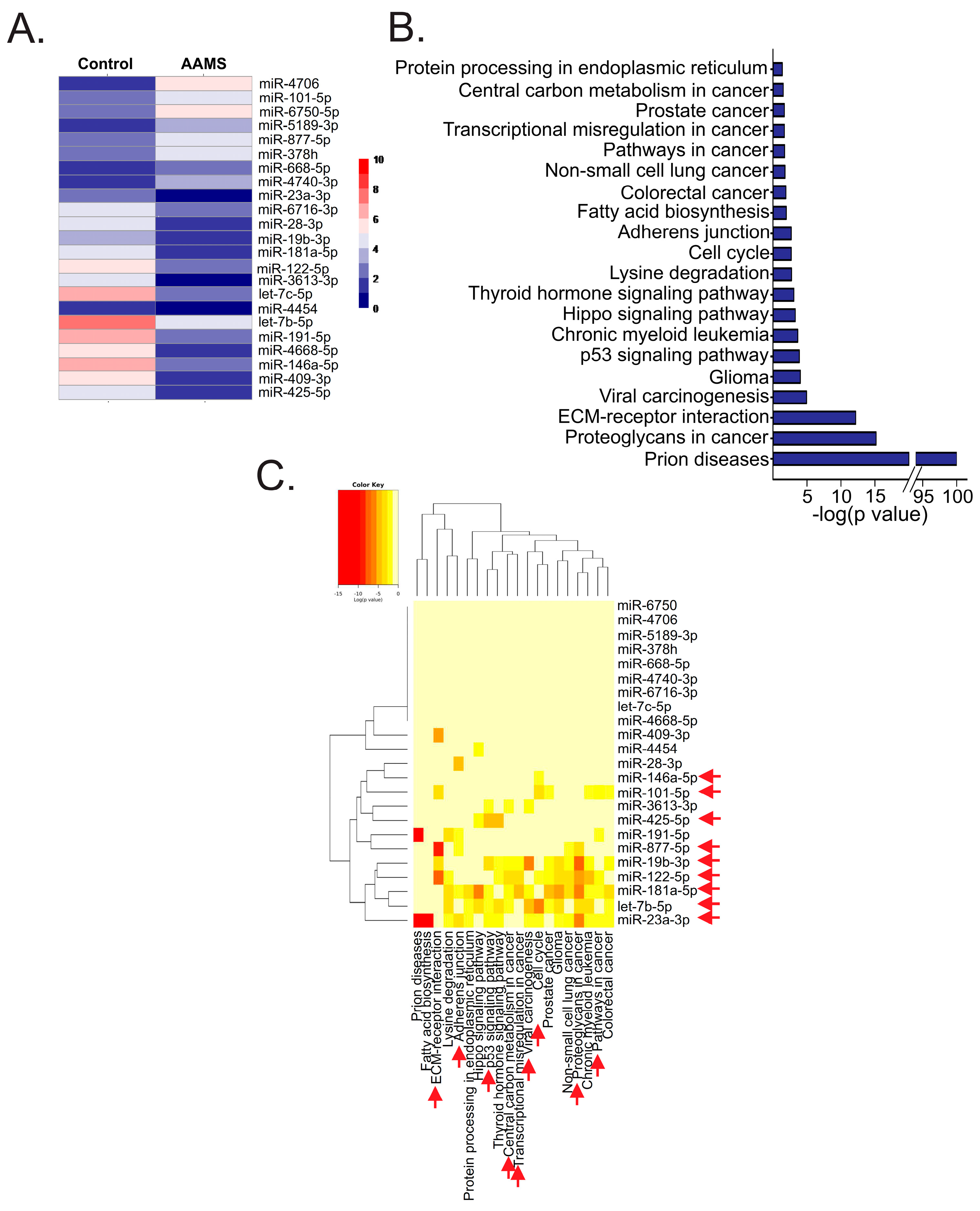

| Transcript_ID | miRNA | p Value | q Value | RP Values | LOG (FC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIMAT0019806 | hsa-miR-4706 | 0 | 0.000 | 1.565 | 3.249 |
| MIMAT0004513 | hsa-miR-101-5p | 2.17 × 10−06 | 0.005 | 6.774 | 2.136 |
| MIMAT0027400 | hsa-miR-6750-5p | 2.17 × 10−06 | 0.005 | 4.738 | 2.348 |
| MIMAT0027088 | hsa-miR-5189-3p | 1.09 × 10−05 | 0.013 | 10.029 | 2.316 |
| MIMAT0004949 | hsa-miR-877-5p | 1.30 × 10−05 | 0.012 | 10.499 | 2.044 |
| MIMAT0018984 | hsa-miR-378h | 3.69 × 10−05 | 0.028 | 13.581 | 1.720 |
| MIMAT0026636 | hsa-miR-668-5p | 5.65 × 10−05 | 0.037 | 16.060 | 1.607 |
| MIMAT0019870 | hsa-miR-4740-3p | 5.87 × 10 −05 | 0.034 | 16.807 | 1.681 |
| MIMAT0000078 | hsa-miR-23a-3p | 1.52 × 10−04 | 0.044 | 24.926 | −2.008 |
| MIMAT0025845 | hsa-miR-6716-3p | 1.04 × 10−04 | 0.032 | 21.203 | −2.269 |
| MIMAT0004502 | hsa-miR-28-3p | 9.56 × 10−05 | 0.031 | 20.584 | −2.285 |
| MIMAT0000074 | hsa-miR-19b-3p | 7.82 × 10−05 | 0.028 | 18.903 | −2.342 |
| MIMAT0000256 | hsa-miR-181a-5p | 5.87 × 10−05 | 0.023 | 16.699 | −2.394 |
| MIMAT0000421 | hsa-miR-122-5p | 6.52 × 10−06 | 0.003 | 7.366 | −3.473 |
| MIMAT0017991 | hsa-miR-3613-3p | 6.52 × 10−06 | 0.003 | 8.144 | −3.599 |
| MIMAT0000064 | hsa-let-7c-5p | 6.52 × 10−06 | 0.003 | 8.050 | −3.415 |
| MIMAT0018976 | hsa-miR-4454 | 6.52 × 10−06 | 0.003 | 9.118 | −3.258 |
| MIMAT0000063 | hsa-let-7b-5p | 2.17 × 10−06 | 0.001 | 5.811 | −3.629 |
| MIMAT0000440 | hsa-miR-191-5p | 2.17 × 10−06 | 0.001 | 4.559 | −3.631 |
| MIMAT0019745 | hsa-miR-4668-5p | 2.17 × 10−06 | 0.001 | 5.091 | −3.910 |
| MIMAT0000449 | hsa-miR-146a-5p | 2.17 × 10−06 | 0.001 | 6.055 | −3.531 |
| MIMAT0001639 | hsa-miR-409-3p | 2.17 × 10−06 | 0.001 | 5.696 | −3.495 |
| MIMAT0003393 | hsa-miR-425-5p | 2-17 × 10−06 | 0.001 | 6.620 | −3.550 |
| KEGG Pathway: Proteoglycans in Cancer (hsa05205) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gene Name | Gene Ensembl ID | Tarbase Methods |
| ERBB2 | ENSG00000141736 | HITS-CLIP |
| ITGB1 | ENSG00000150093 | HITS-CLIP |
| KRAS | ENSG00000133703 | PAR-CLIP |
| VAV2 | ENSG00000160293 | HITS-CLIP |
| AKT2 | ENSG00000105221 | PAR-CLIP |
| IGF2 | ENSG00000167244 | HITS-CLIP |
| TIMP3 | ENSG00000100234 | HITS-CLIP |
| RAC1 | ENSG00000136238 | HITS-CLIP |
| FGF2 | ENSG00000138685 | PAR-CLIP |
| FAS | ENSG00000026103 | HITS-CLIP |
| GAB1 | ENSG00000109458 | PAR-CLIP |
| PDPK1 | ENSG00000140992 | HITS-CLIP |
| ITPR2 | ENSG00000123104 | PAR-CLIP |
| RPS6KB1 | ENSG00000108443 | CLASH |
| KEGG pathway: ECM-receptor interaction (hsa04512) | ||
| Gene Name | Gene Ensembl ID | Tarbase Methods |
| ITGB1 | ENSG00000150093 | HITS-CLIP |
| ITGB8 | ENSG00000105855 | HITS-CLIP |
| COL6A2 | ENSG00000142173 | HITS-CLIP |
| LAMC1 | ENSG00000135862 | Multiple |
| TNC | ENSG00000041982 | HITS-CLIP |
| COL4A1 | ENSG00000187498 | Multiple |
| KEGG pathway: Adherens junction | ||
| Gene Name | Gene Ensembl ID | Tarbase Methods |
| ERBB2 | ENSG00000141736 | HITS-CLIP |
| WASL | ENSG00000106299 | HITS-CLIP |
| RAC2 | ENSG00000128340 | HITS-CLIP |
| NLK | ENSG00000087095 | Multiple |
| RAC1 | ENSG00000136238 | HITS-CLIP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moro, J.; Grinpelc, A.; Farré, P.L.; Duca, R.B.; Lacunza, E.; Graña, K.D.; Scalise, G.D.; Dalton, G.N.; Massillo, C.; Piccioni, F.; et al. miR-877-5p as a Potential Link between Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Development and Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316758
Moro J, Grinpelc A, Farré PL, Duca RB, Lacunza E, Graña KD, Scalise GD, Dalton GN, Massillo C, Piccioni F, et al. miR-877-5p as a Potential Link between Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Development and Metabolic Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(23):16758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316758
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoro, Juana, Agustina Grinpelc, Paula Lucía Farré, Rocío Belén Duca, Ezequiel Lacunza, Karen Daniela Graña, Georgina Daniela Scalise, Guillermo Nicolás Dalton, Cintia Massillo, Flavia Piccioni, and et al. 2023. "miR-877-5p as a Potential Link between Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Development and Metabolic Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 23: 16758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316758
APA StyleMoro, J., Grinpelc, A., Farré, P. L., Duca, R. B., Lacunza, E., Graña, K. D., Scalise, G. D., Dalton, G. N., Massillo, C., Piccioni, F., Dimase, F., Batagelj, E., De Siervi, A., & De Luca, P. (2023). miR-877-5p as a Potential Link between Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Development and Metabolic Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(23), 16758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242316758






