The Use of Electrochemical Methods to Determine the Effect of Nitrides of Alloying Elements on the Electrochemical Properties of Titanium β-Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Surface Analysis
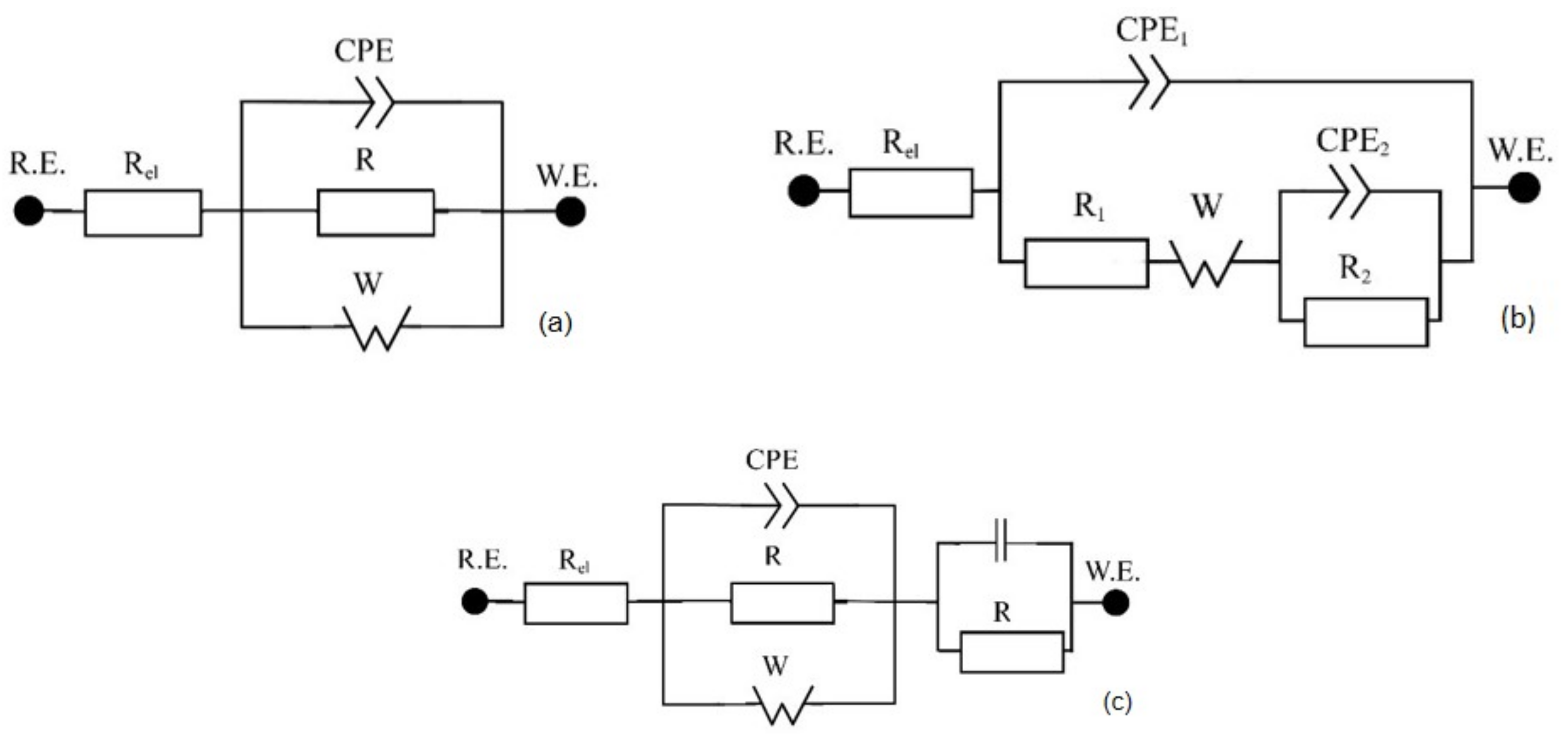
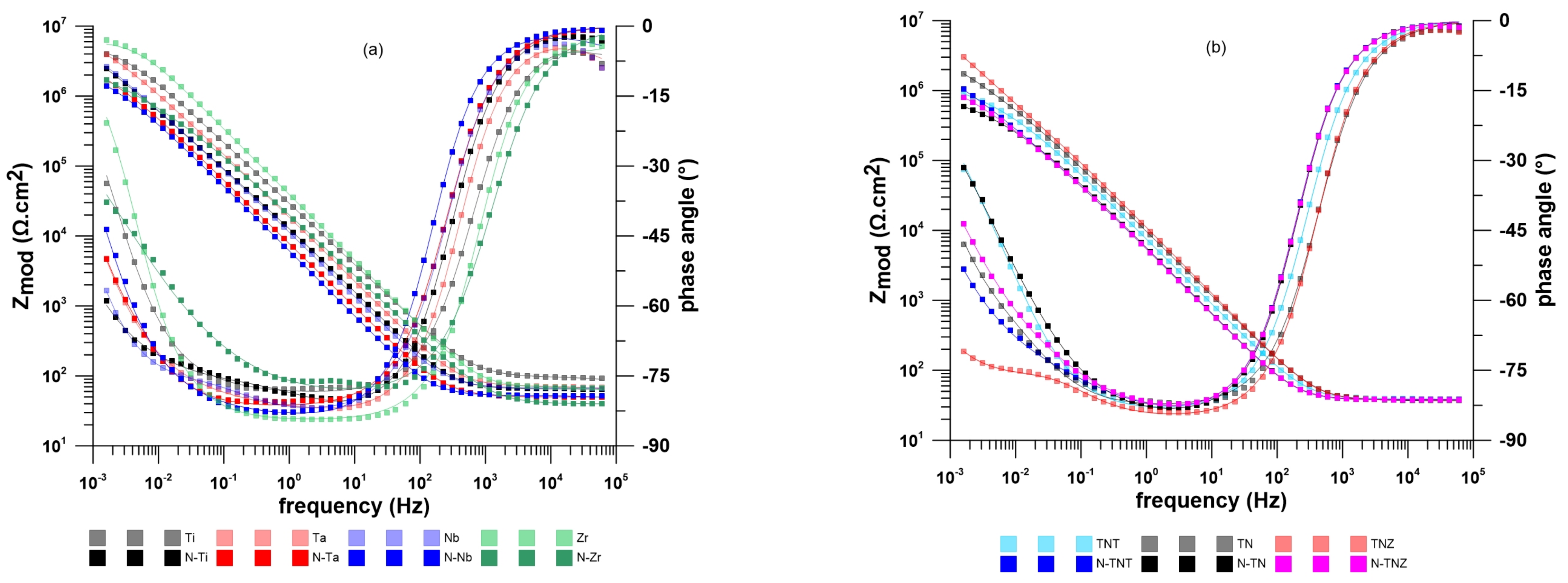
2.2. Electrochemical Behavior
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material Preparation and Surface Modification
3.2. Surface Analysis
3.3. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
- All β-alloys, Ti-36Nb, Ti-36Nb-6Ta, and Ti-36Nb-4Zr, were successfully nitrided by nitrogen ion implantation with fluence 2.1017 cm−2.
- XPS analysis showed the presence of nitrides on all the alloys and pure metals apart from zirconium, more precisely nitrides of titanium, niobium, and tantalum.
- The corrosion behavior of the modified samples was affected by the alloy composition. Better corrosion resistance was exhibited on the treated Ti-36Nb-6Ta rather than on Ti-39Nb and Ti-36Nb-4Zr. This was probably caused by the presence of tantalum in the Ti-36Nb-6Ta alloy. Tantalum formed oxides and a small percentage of nitrides on the surface, making this alloy more resistant to corrosion in comparison with Ti-39Nb alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, D.; Sosnin, K.; Pronin, S.; Konovalov, S.; Moskovskii, S.; Gromov, V.; Ivanov, Y.; Bataev, V.; Semin, A. Electroexplosive hafnium coating on titanium implant modified by nitrogen ions and electron beam processing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 409, 126895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stráský, J.; Harcuba, P.; Václavová, K.; Horváth, K.; Landa, M.; Srba, O.; Janeček, M. Increasing strength of a biomedical Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr alloy by alloying with Fe, Si and O. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 71, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlcak, P.; Fojt, J.; Weiss, Z.; Kopeček, J.; Perina, V. The effect of nitrogen saturation on the corrosion behaviour of Ti-35Nb-7Zr-5Ta beta titanium alloy nitrided by ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 358, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautray, T.; Narayanan, R.; Kim, K.-H. Ion implantation of titanium based biomaterials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2011, 56, 1137–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Bell, T. Enhanced wear resistance of titanium surfaces by a new thermal oxidation treatment. Wear 2000, 238, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzynski, P.; Youssef, A.; Sielanko, J. Surface modification of Ti–6Al–4V alloy by nitrogen ion implantation. Wear 2006, 261, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, J.; Manivasagam, G. Surface Modification and Biological Approaches for Tackling Titanium Wear-Induced Aseptic Loosening. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2021, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hou, X.; Sun, T.; Yao, J.; Wu, P.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Han, J. Cytocompatibility and antibacterial property of N+ ions implanted TiO2 nanotubes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 359, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M. Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 1, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Luo, Z. Biomaterials modification by ion-beam processing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 112, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordin, D.; Busardo, D.; Cimpean, A.; Vasilescu, C.; Höche, D.; Drob, S.; Mitran, V.; Cornen, M.; Gloriant, T. Design of a nitrogen-implanted titanium-based superelastic alloy with optimized properties for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 4173–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Ou, Y.; Wang, K.; Chen, L. Wear and corrosion properties of plasma-based low-energy nitrogen ion implanted titanium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 4602–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hossary, F.; Negm, N.; Khalil, S.; Raaif, M. Surface modification of titanium by radio frequency plasma nitriding. Thin Solid Films 2006, 497, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, S.; Tsubakino, H.; Inoue, S.; Liu, L.; Terasawa, M.; Mitamura, T. Surface modification of titanium by nitrogen ion implantation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 263, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlcak, P.; Drahokoupil, J.; Vertat, P.; Sepitka, J.; Duchon, J. Hardness response to the stability of a Ti(+N) solid solution in an annealed TiN/Ti(+N)/Ti mixture layer formed by nitrogen ion implantation into titanium. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 746, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlcak, P.; Fojt, J.; Koller, J.; Drahokoupil, J.; Smola, V. Surface pre-treatments of Ti-Nb-Zr-Ta beta titanium alloy: The effect of chemical, electrochemical and ion sputter etching on morphology, residual stress, corrosion stability and the MG-63 cell response. Results Phys. 2021, 28, 104613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, M.; Niinomi, M.; Akahori, T.; Ohtsu, N.; Nishimura, H.; Toda, H.; Fukui, H.; Ogawa, M. Surface hardening of biomedical Ti–29Nb–13Ta–4.6Zr and Ti–6Al–4V ELI by gas nitriding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 486, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojt, J.; Hybasek, V.; Joska, L. Electrochemical behaviour of the nanostructured surface of Ti-35Nb-2Zr alloy for biomedical applications. Mater. Corros. 2016, 67, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojt, J.; Joska, L.; Malek, J.; Sefl, V. Corrosion behavior of Ti–39Nb alloy for dentistry. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, P.J. Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 16th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zu, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L. Phase formation and corrosion behavior of nitrogen implanted Zr–Sn–Nb alloy in alkaline environment. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 2006, 246, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kwon, H.; Kim, W.; Choi, B. Effects of compositional and structural change on the corrosion behaviour of nitrogen implanted Zircaloy-4. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 263, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagawa, Y.; Nakao, S.; Baba, K.; Hatada, R.; Ikeyama, M.; Miyagawa, S. Depth profile of nitrogen concentration and nano-hardness in nitrogen implanted Zr at RT and at 600 °C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 103–104, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reger, N.; Balla, V.; Das, M.; Bhargava, A. Wear and corrosion properties of in-situ grown zirconium nitride layers for implant applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 334, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Dhawan, A.; Sharma, S. Influence of nitrogen ion implantation on corrosion behavior of Zr55Cu30Ni5Al10 amorphous alloy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 511, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zu, X.; Qiu, S.; Li, C.; Ma, W.; Huang, X. Surface characteristics and oxidation behavior of nitrogen ion-implanted Zr–Sn–Nb alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 5631–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojt, J.; Joska, L.; Hnilica, F. Tantalum effect on the corrosion behavior of titanium-tantalum alloys in an environment containing fluoride ions. Kov. Mater. 2012, 50, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, K.; Robin, A. Influence of concentration and temperature on the corrosion behavior of titanium, titanium-20 and 40% tantalum alloys and tantalum in sulfuric acid solutions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 103, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Niinomi, M.; Akahori, T.; Fukui, H.; Toda, H. Corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of Ti–Ta alloys for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 398, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Han, C.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, K.; Wei, Q.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y. Improvement on mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of titanium-tantalum alloys in-situ fabricated via selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 804, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metikos-Huković, M.; Kwokal, A.; Piljac, J. The influence of niobium and vanadium on passivity of titanium-based implants in physiological solution. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3765–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.-K.; Kim, J.-Y.; Hwang, M.; Song, H.-J.; Park, Y.-J. Effect of Nb on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Behavior, and Cytotoxicity of Ti-Nb Alloys. Materials 2015, 8, 5986–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnu, D.S.M.; Sure, J.; Liu, Y.; Kumar, R.V.; Schwandt, C. Electrochemical synthesis of porous Ti-Nb alloys for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.-K.; Hwang, M.-J.; Yang, M.-S.; Yang, H.-S.; Song, H.-J.; Park, Y.-J. Effect of zirconium content on the microstructure, physical properties and corrosion behavior of Ti alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 616, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.; Osório, W.; Souza, M.; Caram, R.; Garcia, A. Effects of Zr content on microstructure and corrosion resistance of Ti–30Nb–Zr casting alloys for biomedical applications. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 2809–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, C.; Drob, S.; Neacsu, E.; Rosca, J.M. Surface analysis and corrosion resistance of a new titanium base alloy in simulated body fluids. Corros. Sci. 2012, 65, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanović, M.; Tasić, Ž.; Simonović, A.; Mihajlović, M.P.; Antonijević, M. Corrosion Behavior of Titanium in Simulated Body Solutions with the Addition of Biomolecules. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12768–12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.; Ponthiaux, P.; Henriques, M.; Oliveira, R.; Teughels, W.; Celis, J.; Rocha, L. Corrosion behaviour of titanium in the presence of Streptococcus mutans. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milošev, I.; Kosec, T.; Strehblow, H. XPS and EIS study of the passive film formed on orthopaedic Ti–6Al–7Nb alloy in Hank’s physiological solution. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3547–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazem, M.; Tribollet, B. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yılmaz, E.; Gökçe, A.; Findik, F.; Gulsoy, H.; İyibilgin, O. Mechanical properties and electrochemical behavior of porous Ti-Nb biomaterials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 87, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasia, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Its Applications Springer; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, J.; Johnson, W.; Raistrick, I.D.; Franceschetti, D.R.; Wagner, N.; Mckubre, M.; Macdonald, D.; Sayers, B.; Bonanos, N.; Steele, B.C.H.; et al. Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and Applications, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.; He, F.; Liu, Z. Characterization methods for sulfate ions diffusion coefficient in calcium sulphoaluminate mortar based on AC impedance spectroscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 289, 123169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, Z.; Shu, X.; Liu, E.; Han, Z. A comparative study of the corrosion performance of titanium (Ti), titanium nitride (TiN), titanium dioxide (TiO2) and nitrogen-doped titanium oxides (N–TiO2), as coatings for biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41 Pt B, 11844–11851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-H.; Liu, C.-F.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.-S.; Chang, J.-H. Nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation treatment of Ti6Al7Nb alloy for bone-implant applications: Enhanced in vitro biological responses and in vivo initial bone-implant contact. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Wu, G.; Li, P.; Chu, P. Improved corrosion resistance of Mg-Y-RE alloy coated with niobium nitride. Thin Solid Films 2014, 572, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, G.; Rodil, S.; Arzate, H.; Muhl, S.; Olaya, J. Niobium based coatings for dental implants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2555–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishahi, M.; Mahboubi, F.; Khoie, S.M.; Aparicio, M.; Lopez-Elvira, E.; Méndez, J.; Gago, R. Structural properties and corrosion resistance of tantalum nitride coatings produced by reactive DC magnetron sputtering. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 89061–89072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Xiong, X.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, Z.; Deng, Y.; et al. Tantalum Nitride-Decorated Titanium with Enhanced Resistance to Microbiologically Induced Corrosion and Mechanical Property for Dental Application. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.; Yilbas, B.; Kumar, A.; Drew, R.; Al-Aqeeli, N. Influence of Laser Nitriding on the Surface and Corrosion Properties of Ti-20Nb-13Zr Alloy in Artificial Saliva for Dental Applications. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 4655–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, L.; Antony, R.; Mathews, T.; Walczak, L.; Gopinath, C. A Study on Doped Heterojunctions in TiO2 Nanotubes: An Efficient Photocatalyst for Solar Water Splitting. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Bari, G.; Kang, H.-J.; Lee, T.-G.; Park, J.-W.; Hwang, H.; Hossain, S.; Mun, J.; Suzuki, N.; Fujishima, A.; et al. Synthesis of N-Doped TiO2 for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Atmospheric NOx. Catalysts 2021, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Lu, B.; Luo, J. Study on passivation and erosion-enhanced corrosion resistance by Mott-Schottky analysis. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg. NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database, Version 4.0. 2008. Available online: http://www.xpsfitting.com/p/about.html (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Reference Pages, Surface Science Western. 2009. Available online: https://srdata.nist.gov/xps/Default.aspx (accessed on 6 December 2021).
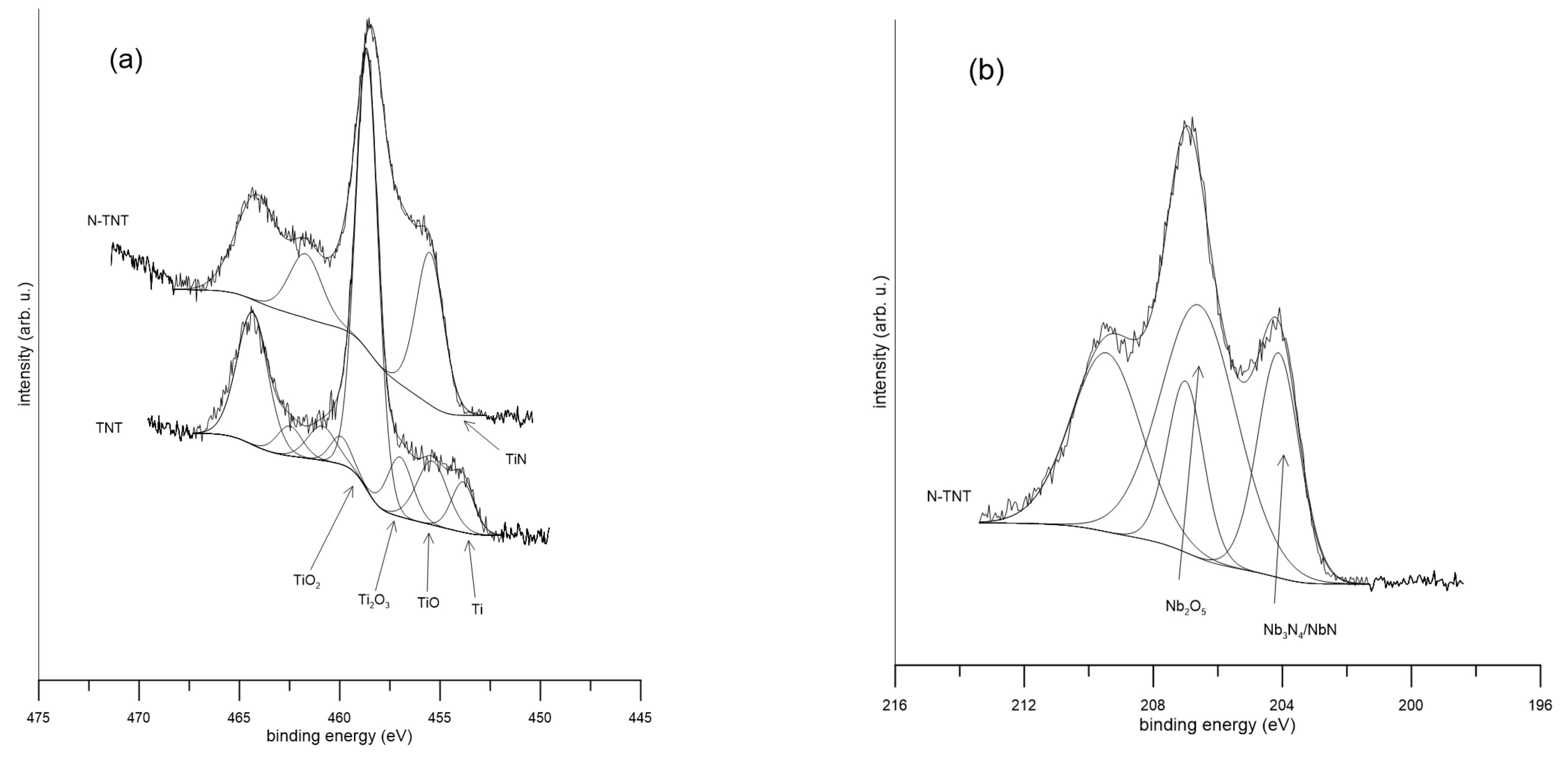
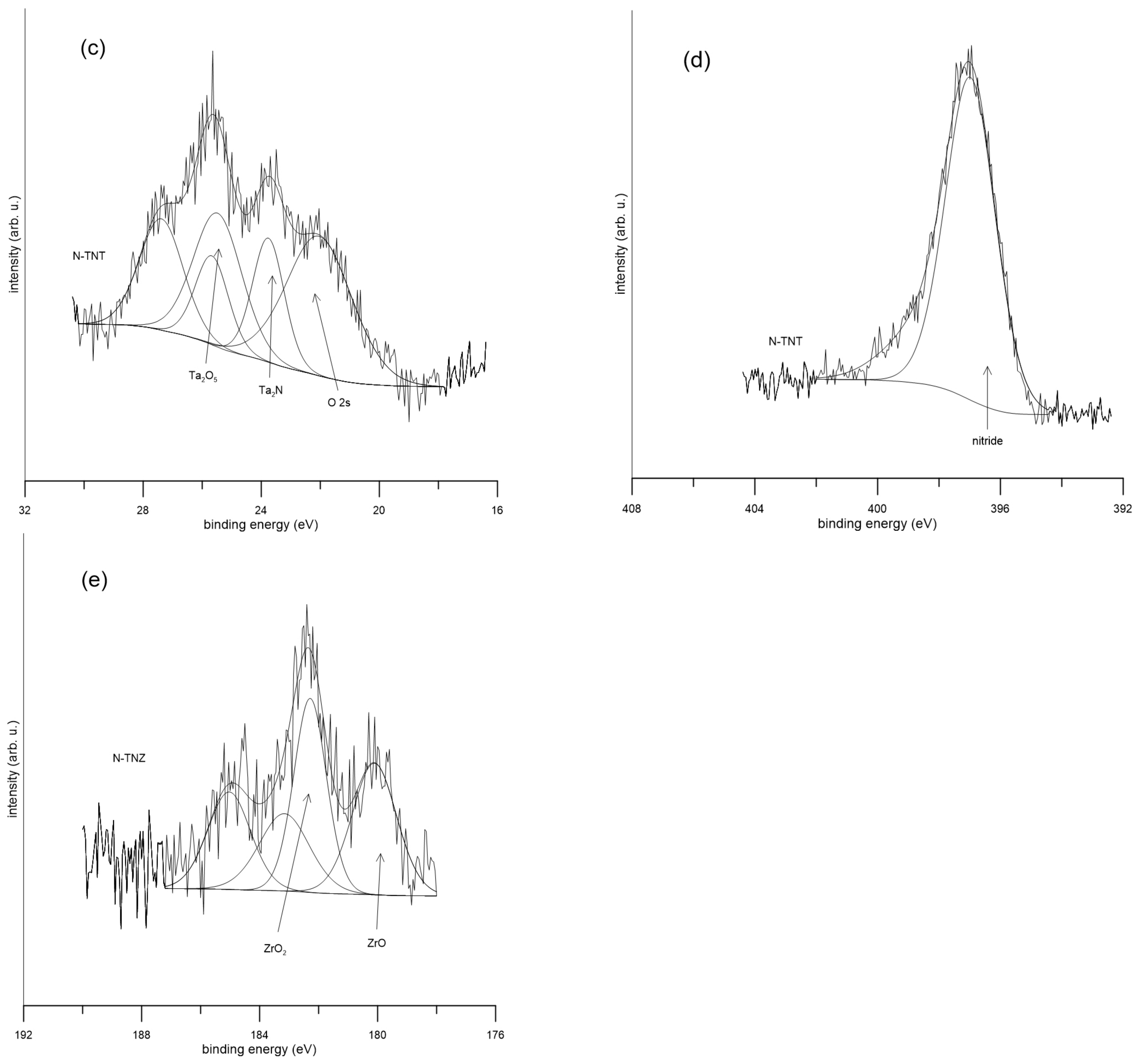
| Ti | Nb | Ta | Zr | O | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | 31.1 | 32.9 | - | - | 36.0 | - |
| N-TN | 26.7 | 42.0 | - | - | 22.6 | 8.7 |
| TNT | 35.2 | 27.8 | 10.5 | - | 26.5 | - |
| N-TNT | 26.2 | 38.2 | 7.0 | - | 19.9 | 8.7 |
| TNZ | 32.3 | 32.7 | - | 1.5 | 33.5 | - |
| N-TNZ | 26.5 | 38.2 | - | 3.5 | 21.3 | 10.5 |
| Ti | N-Ti | Nb | N-Nb | Ta | N-Ta | Zr | N-Zr | TN | N-TN | TNT | N-TNT | TNZ | N-TNZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO | 7.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5.2 | - | 14.2 | - | 9 | - |
| TiO2 | 75.6 | 57.2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 86.3 | 55.6 | 66.8 | 54.4 | 41.3 | 56.5 |
| Ti2O3 | 11.9 | 28.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8.5 | 17.2 | 10.8 | 20 | 8.4 | 19.8 |
| TixOx | 4.6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8.2 | - | 5.7 | - |
| TiN | - | 14.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 27.2 | - | 25.6 | - | 23.7 |
| Nb | - | - | 17.1 | - | - | - | - | - | 5.1 | - | 5.9 | - | 11.3 | - |
| NbO | - | - | 15.1 | - | - | - | - | - | 5.1 | - | 18.1 | - | 18.1 | - |
| NbO2 | - | - | 11.8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 19.4 | - | 16.9 | - |
| Nb2O5 | - | - | 56 | 60.3 | - | - | - | - | 87.7 | 58.8 | 56.6 | 67.1 | 53.7 | 55.8 |
| NbN | - | - | - | 39.7 | - | - | - | - | - | 41.2 | - | 32.9 | - | 44.2 |
| Ta | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 26 | - | - | - |
| Ta2O5 | - | - | - | - | 100 | 59.2 | - | - | - | - | 66.7 | 41.3 | - | - |
| TaN | - | - | - | - | - | 40.8 | - | - | - | - | - | 25.1 | - | - |
| Zr | - | - | - | - | - | - | 12 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ZrO2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 88 | 100 | - | - | - | - | 100 | 60.3 |
| ZrO | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 39.7 |
| Material | R (Ω·cm2) | Eocp (V/SSCE) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native | N- | Native | N- | |
| Ti | 6.2 × 106 | 6.2 × 106 | 0.012 | 0.201 |
| Nb | 9.9 × 105 | 2.2 × 106 | −0.216 | 0.118 |
| Ta | 6.2 × 106 | 3.1 × 106 | 0.030 | 0.104 |
| Zr | 6.7 × 106 | 7.1 × 107 | −0.207 | 0.062 |
| TN | 2.8 × 106 | 7.3 × 105 | 0.067 | 0.001 |
| TNT | 1.4 × 106 | 2.3 × 106 | 0.097 | 0.063 |
| TNZ | 1.6 × 107 | 1.3 × 106 | 0.032 | 0.083 |
| Eq. Circuit | Rel (Ω·cm2) | CPE1 (S.sα/cm2) | α1 | C1 (F/cm2) | R1 (Ω·cm2) | R2 (Ω·cm2) | W (S.s0.5/cm2) | C2 (F/cm2) | CPE2 (S.sα/cm2) | α2 | R3 (Ω·cm2) | C3 (F/cm2) | Χ2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | A | 94.4 | 6.7 × 10−6 | 0.9 | 1.0 × 10−5 | 6.0 × 106 | - | 2.2 × 10−7 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.3 × 10−4 |
| N-Ti | B | 65.2 | 1.3 × 10−5 | 0.9 | 3.3 × 10−5 | - | 1.9 × 106 | 4.3 × 10−6 | 3.9 × 10−5 | - | - | - | - | 6.1 × 10−5 |
| Nb | A | 67.9 | 1.6 × 10−5 | 0.9 | 2.9 × 10−5 | 1.7 × 107 | - | 1.6 × 10−6 | - | - | - | - | - | 4.3 × 10−4 |
| N-Nb | A | 52.1 | 2.9 × 10−5 | 0.9 | 4.7 × 10−5 | 2.6 × 106 | - | 1.6 × 10−6 | - | - | - | - | - | 4.4 × 10−5 |
| Ta | A | 70.1 | 9.6 × 10−6 | 0.9 | 1.6 × 10−5 | 1.3 × 107 | - | 9.5 × 10−7 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.0 × 10−4 |
| N-Ta | A | 50.1 | 2.3 × 10−5 | 0.9 | 3.9 × 10−5 | 4.1 × 106 | - | 1.3 × 10−6 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.3 × 10−4 |
| Zr | A | 68.0 | 4.3 × 10−6 | 0.9 | 6.2 × 10−5 | 6.9 × 106 | - | 9.0 × 10−8 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.5 × 10−4 |
| N-Zr | C | 39.9 | 9.3 × 10−6 | 0.9 | 1.4 × 10−5 | 4.3 × 106 | - | 3.3 × 10−6 | - | - | - | 7.6 × 104 | 1.0 × 10−4 | 2.3 × 10−4 |
| TN | A | 37.1 | 1.7 × 10−5 | 0.9 | 2.9 × 10−5 | 5.6 × 106 | - | 2.7 × 10−6 | - | - | - | - | - | 7.4 × 10−5 |
| N-TN | A | 38.1 | 2.8 × 10−5 | 0.9 | 4.0 × 10−5 | 1.1 × 106 | - | 7.2 × 10−6 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.9 × 10−4 |
| TNT | A | 39.1 | 2.2 × 10−5 | 0.9 | 3.2 × 10−5 | 1.4 × 106 | - | 3.5 × 10−6 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.9 × 10−4 |
| N-TNT | A | 38.3 | 3.1 × 10−5 | 0.9 | 5.6 × 10−5 | 8.0 × 106 | - | 5.8 × 10−6 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.0 × 10−4 |
| TNZ | A | 37.7 | 1.6 × 10−5 | 0.9 | 3.2 × 10−5 | 3.1 × 107 | 5.6 × 105 | - | - | 3.8 × 10−6 | 0.7 | - | - | 4.5 × 10−5 |
| N-TNZ | A | 38.0 | 3.0 × 10−5 | 0.9 | 4.8 × 10−5 | 2.6 × 106 | - | 7.0 × 10−6 | - | - | - | - | - | 6.7 × 10−5 |
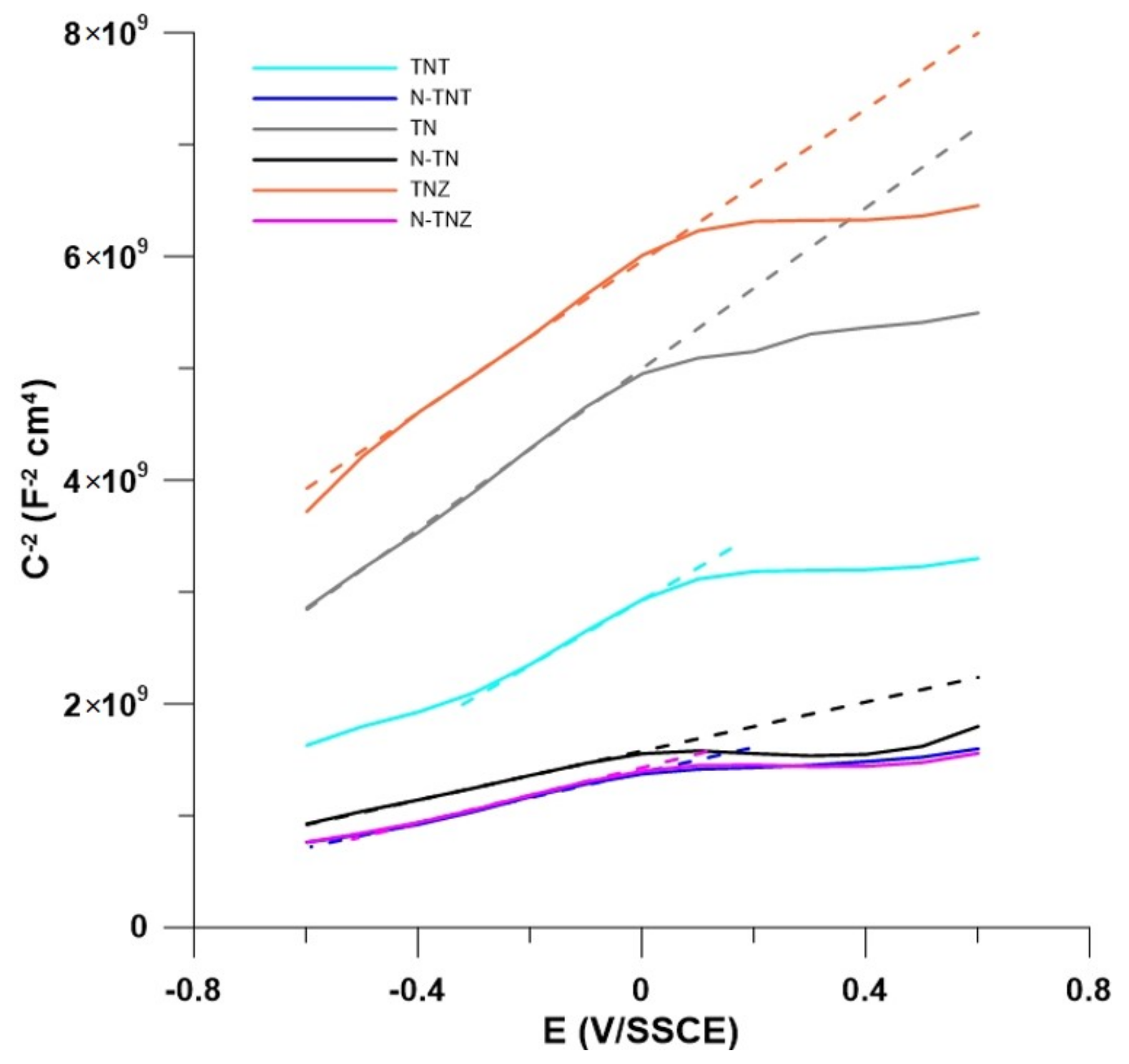
| Efb (V) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Native | N- | |
| TN | −1.249 | −1.264 |
| TNT | −0.997 | −1.233 |
| TNZ | −1.549 | −1.016 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jírů, J.; Hybášek, V.; Vlčák, P.; Fojt, J. The Use of Electrochemical Methods to Determine the Effect of Nitrides of Alloying Elements on the Electrochemical Properties of Titanium β-Alloys. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021656
Jírů J, Hybášek V, Vlčák P, Fojt J. The Use of Electrochemical Methods to Determine the Effect of Nitrides of Alloying Elements on the Electrochemical Properties of Titanium β-Alloys. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021656
Chicago/Turabian StyleJírů, Jitřenka, Vojtěch Hybášek, Petr Vlčák, and Jaroslav Fojt. 2023. "The Use of Electrochemical Methods to Determine the Effect of Nitrides of Alloying Elements on the Electrochemical Properties of Titanium β-Alloys" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021656
APA StyleJírů, J., Hybášek, V., Vlčák, P., & Fojt, J. (2023). The Use of Electrochemical Methods to Determine the Effect of Nitrides of Alloying Elements on the Electrochemical Properties of Titanium β-Alloys. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021656








