Chromosomal Microarray Study in Prader-Willi Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
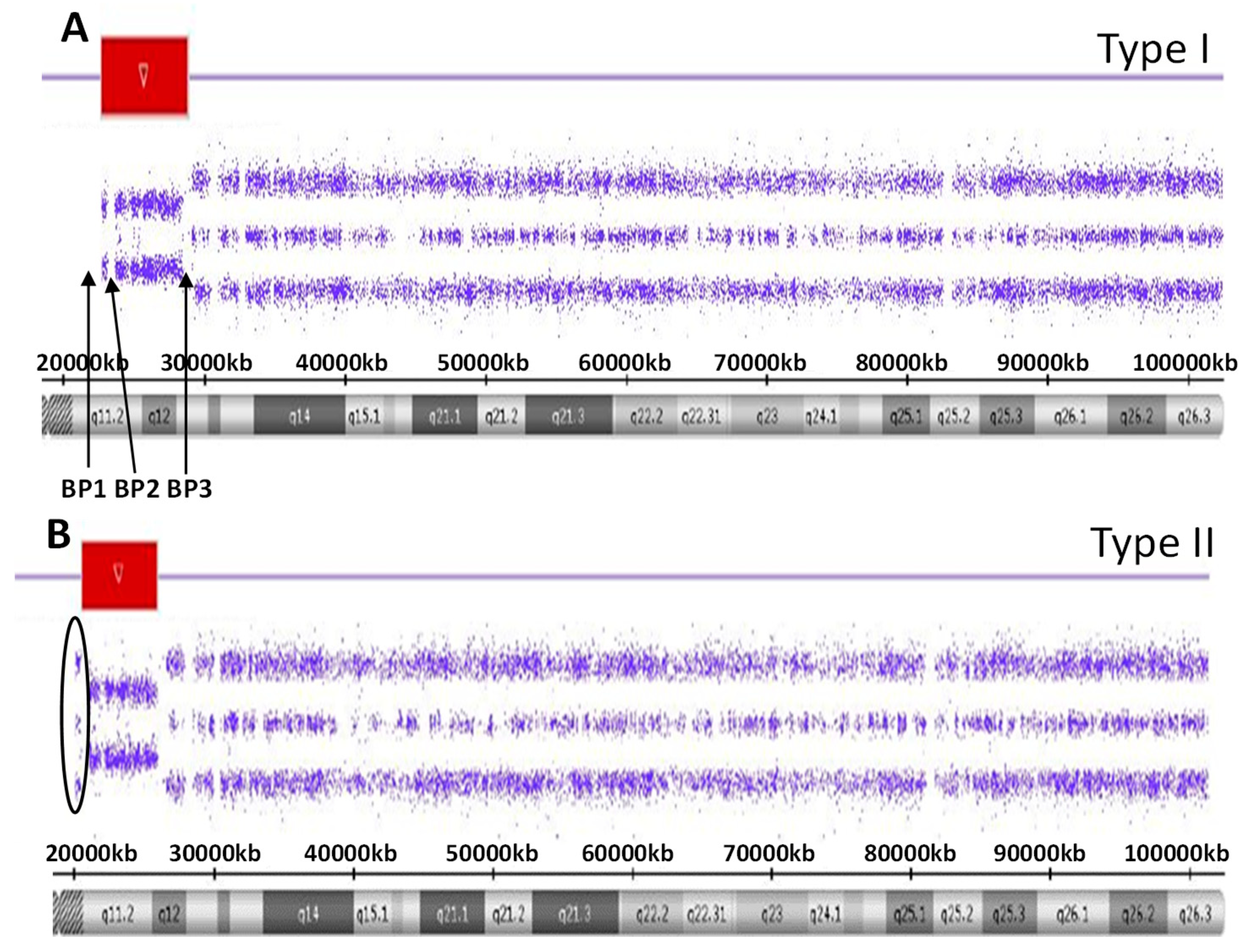
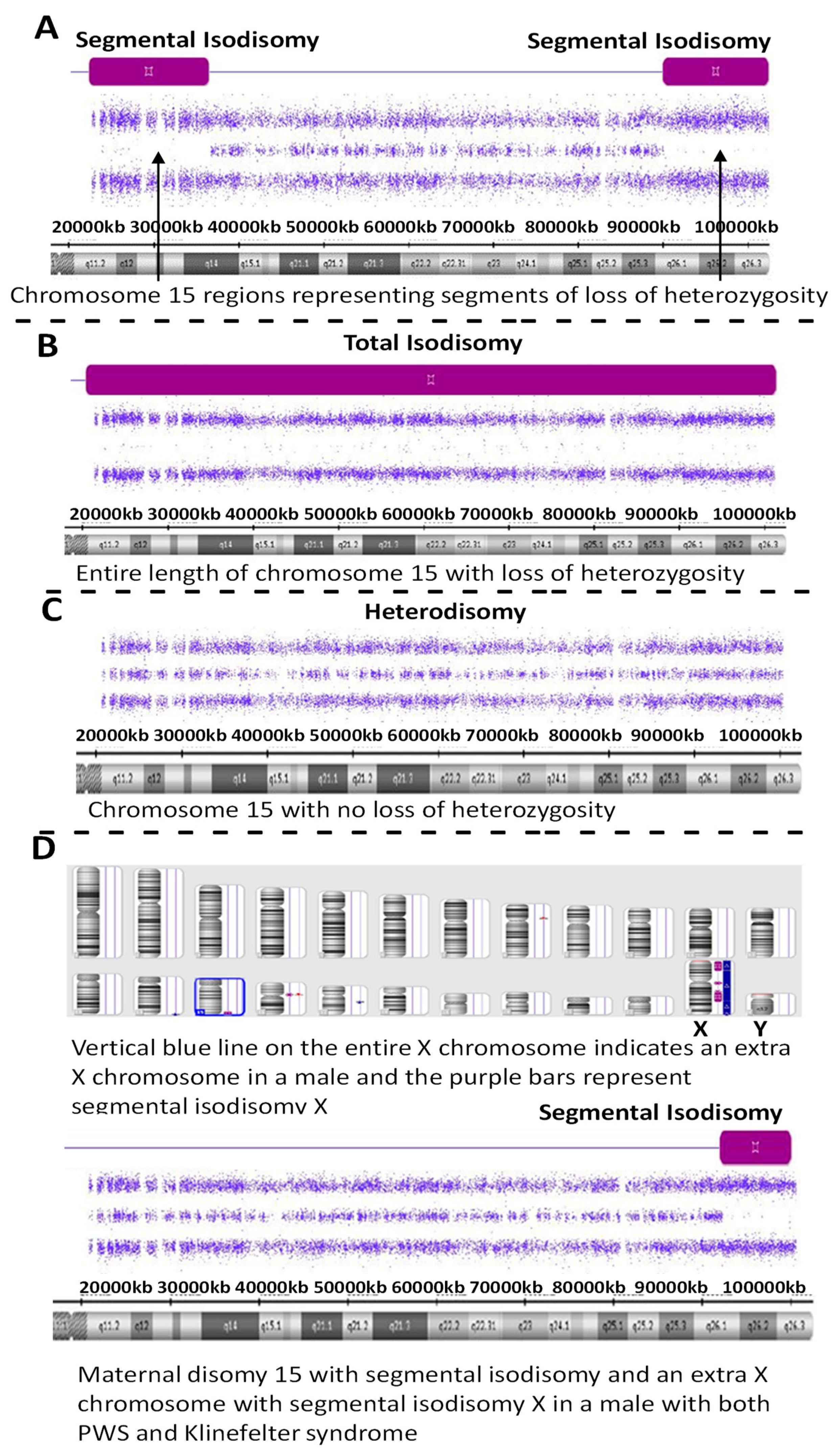
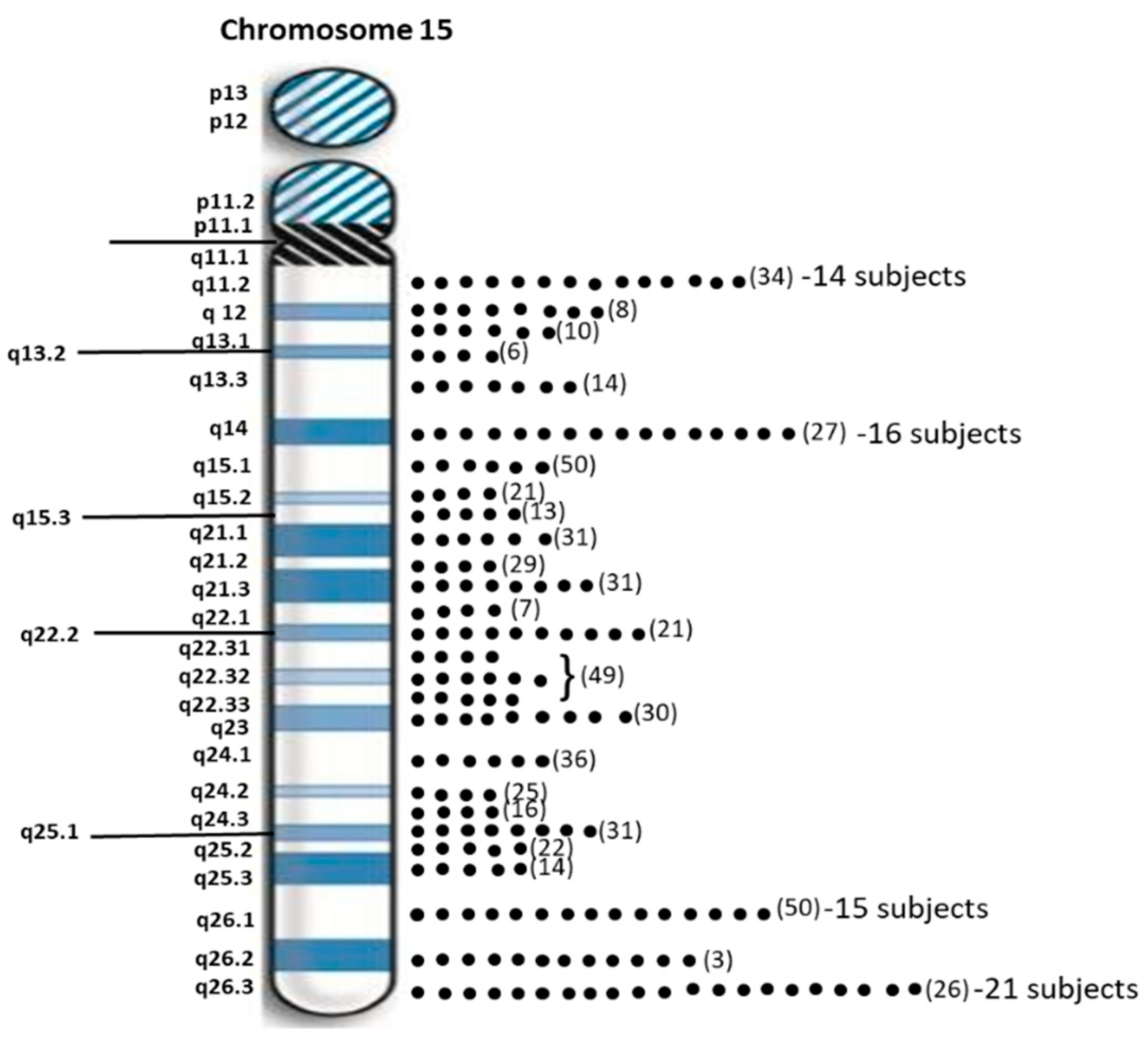
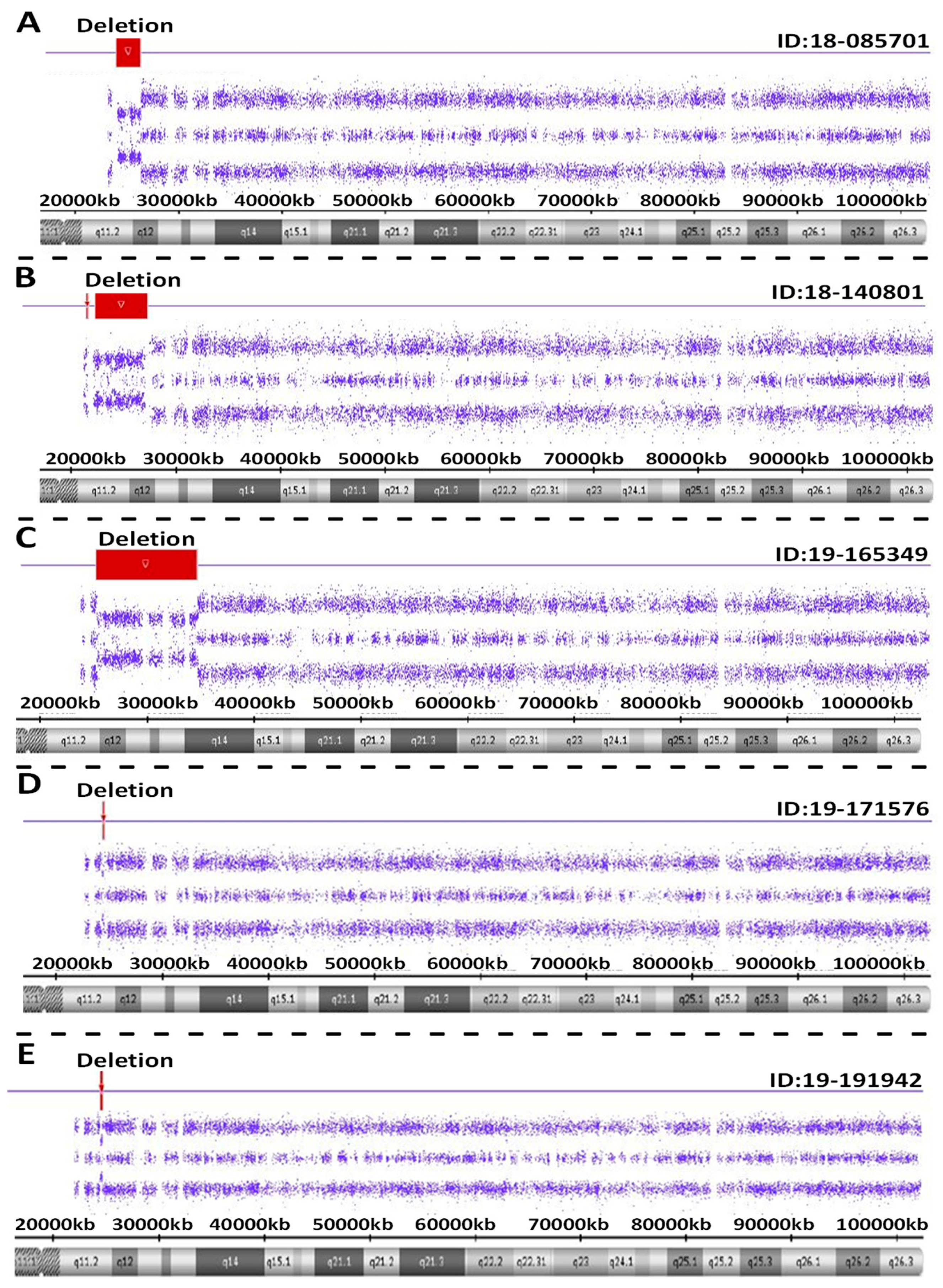
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ledbetter, D.H.; Riccardi, V.M.; Airhart, S.D.; Strobel, R.J.; Keenan, B.S.; Crawford, J.D. Deletions of chromosome 15 as a cause of the Prader-Willi syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1981, 5, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delach, J.A.; Rosengren, S.; Kaplan, L.; Greenstein, R.M.; Cassidy, S.B.; Benn, P.A. Comparison of high- resolution chromosome banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for the laboratory evaluation of Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1994, 52, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.G.; Fischer, W.; Kibiryeva, N.; Bittel, D.C. Array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) analysis in Prader-Willi syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2008, 146A, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.G.; Duis, J. Chromosome 15 Imprinting Disorders: Genetic Laboratory Methodology and Approaches. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papenhausen, P.; Schwartz, S.; Risheg, H.; Keitges, E.; Gadi, I.; Burnside, R.D.; Jaswaney, V.; Pappas, J.; Pasion, R.; Friedman, K.; et al. UPD detection using homozygosity profiling with a SNP genotyping microarray. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2011, 155A, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.G. Single Gene and Syndromic Causes of Obesity: Illustrative Examples. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2016, 140, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.G.; Lee, P.D.K.; Whitman, B.Y. Management of Prader-Willi Syndrome. In Management of Prader-Willi Syndrome, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–550. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, M.G.; Thompson, T. Prader-Willi Syndrome: Clinical and Genetic Findings. Endocrinologist. 2000, 10 (Suppl. 1), 3S–16S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittel, D.C.; Butler, M.G. Prader-Willi syndrome: Clinical genetics, cytogenetics and molecular biology. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2005, 25, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.G.; Hartin, S.N.; Hossain, W.A.; Manzardo, A.M.; Kimonis, V.; Dykens, E.; Gold, J.A.; Kim, S.J.; Weisensel, N.; Tamura, R.; et al. Molecular genetic classification in Prader-Willi syndrome: A multisite cohort study. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 56, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.G.; Bittel, D.C.; Kibiryeva, N.; Talebizadeh, Z.; Thompson, T. Behavioral differences among subjects with Prader-Willi syndrome and type I or type II deletion and maternal disomy. Pediatrics 2004, 113 Pt 1, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarcone, J.; Napolitano, D.; Peterson, C.; Breidbord, J.; Ferraioli, S.; Caruso-Anderson, M.; Holsen, L.; Butler, M.G.; Thompson, T. The relationship between compulsive behaviour and academic achievement across the three genetic subtypes of Prader-Willi syndrome. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2007, 51 Pt 6, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roof, E.; Stone, W.; MacLean, W.; Feurer, I.D.; Thompson, T.; Butler, M.G. Intellectual characteristics of Prader-Willi syndrome: Comparison of genetic subtypes. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2000, 44, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.G.; Matthews, N.A.; Pate, N.; Surampalli, A.; Gold, J.A.; Khare, M.; Thompson, T.; Cassidy, S.B.; Kimonis, V.E. Impact of genetic subtypes of Prader-Willi syndrome with growth hormone therapy on intelligence and body mass index. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2019, 179, 1826–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.L.; Yanovski, J.; Bird, L.; Salehi, P.; Abuzzahab, J.; Shoemaker, A.; Fleishman, A.; Stevenson, D.; Angulo, M.; Viskochil, D.; et al. Long-term Ssfety and efficacy evaluation of diazoxide choline Eetended-release (DCCR) tablets in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome. In Proceedings of the 11th International Prader-Willi Syndrome Organisation Conference, Limerick, Ireland, 6–10 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, M.G.; Hedges, L.K.; Rogan, P.K.; Seip, J.R.; Cassidy, S.B.; Moeschler, J.B. Klinefelter and trisomy X syndromes in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome and uniparental maternal disomy of chromosome 15--a coincidence? Am. J. Med. Genet. 1997, 72, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, H.M.; Kearney, J.B.; Conlin, L.K. Diagnostic implications of excessive homozygosity detected by SNP-based microarrays: Consanguinity, uniparental disomy, and recessive single-gene mutations. Clin. Lab. Med. 2011, 4, 595–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.G.; Bittel, D.C.; Kibiryeva, N.; Cooley, L.D.; Yu, S. An interstitial 15q11-q14 deletion: Expanded Prader-Willi syndrome phenotype. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 404–408, Erratum in: Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 1331–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkhaus, R.S.; Kim, S.J.; Kimonis, V.E.; Gold, J.A.; Dykens, E.M.; Driscoll, D.J.; Butler, M.G. Methylation-specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification and identification of deletion genetic subtypes in Prader-Willi syndrome. Genet. Test Mol. Biomark. 2012, 16, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buiting, K.; Nazlican, H.; Galetzka, D.; Wawrzik, M.; Gross, S.; Horsthemke, B. C15orf2 and a novel noncoding transcript from the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region show monoallelic expression in fetal brain. Genomics 2007, 89, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multhusamy, K.; Macke, E.L.; Klee, E.W.; Tebben, P.J.; Hand, J.L.; Hasadsri, L.; Marcou, C.A.; Schimmenti, L.A. Congenital ichthyosis in Prader-Willi syndrome associated with maternal chromosome 15 uniparental disomy: Case report and review of autosomal recessive conditions unmasked by UPD. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2020, 182, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.G.; Theodoro, M.F.; Bittel, D.C.; Kuipers, P.J.; Driscoll, D.J.; Talebizadeh, Z. X-chromosome inactivation patterns in females with Prader-Willi syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2007, 143A, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, D.; Shinawi, M.; Astbury, C.; Tayeh, M.K.; Deak, L.; Raca, G. ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. Diagnostic testing for uniparental disomy: A point to consider statement from the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cytogenetic Location | Genomic Coordinates | Gene Symbol | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15q12-q13.1 | 15:27719008-28099315 | OCA2 | Albinism, brown oculocutaneous, Albinism, oculocutaneous, type II |
| 15q13.1 | 15:28111040-28322179 | HERC2 | Intellectual developmental disorder |
| 15q13.1 | 15:29264989-29269822 | NSMCE3 | Lung disease, immunodeficiency, chromosome breakage syndrome |
| 15q13.1-q15.1 | 15:27800001-42500000 | CILD4 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, 4 |
| 15q13.3 | 15:30903852-30943108 | FAN1 | Interstitial nephritis, karyomegalic |
| 15q14 | 15:34341719-34343136 | NOP10 | Dyskeratosis congenita |
| 15q14 | 15:36579626-36810244 | CDIN1 | Dyserythropoietic anemia, congenital, type Ib |
| 15q14 | 15:38488103-38564814 | RASGRP1 | Immunodeficiency 64 |
| 15q14 | 15:34229784-34338057 | SLC12A6 | Agenesis of the corpus callosum with peripheral neuropathy |
| 15q14 | 15:33400001-39800000 | EIG7 | Epilepsy, juvenile myoclonic |
| 15q15.1 | 15:40161069-40221123 | BUB1B | Mosaic variegated aneuploidy syndrome 1 |
| 15q15.1 | 15:42359501-42412317 | CAPN3 | Muscular dystrophy, limb-girdle |
| 15q15.1 | 15:40520993-40565042 | CCDC32 | Cardiofacioneurodevelopmental syndrome |
| 15q15.1 | 15:41231268-41281887 | CHP1 | ?Spastic ataxia 9, autosomal recessive |
| 15q15.1 | 15:40470984-40473158 | CHST14 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, musculocontractural type 1 |
| 15q15.1 | 15:39934115-40035591 | EIF2AK4 | Pulmonary venoocclusive disease 2 |
| 15q15.1 | 15:40405795-40435947 | IVD | Isovaleric acidemia |
| 15q15.1 | 15:40594249-40664342 | KNL1 | Microcephaly 4, primary, autosomal recessive |
| 15q15.1 | 15:41774484-41827855 | MAPKBP1 | Nephronophthisis 20 |
| 15q15.1 | 15:41387353-41403026 | NDUFAF1 | Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 11 |
| 15q15.1 | 15:40807089-40815084 | ZFYVE19 | Cholestasis, progressive familial intrahepatic, 9 |
| 15q15.2 | 15:42723544-42737128 | CDAN1 | Dyserythropoietic anemia, congenital, type Ia |
| 15q15.2 | 15:43232590-43266928 | TGM5 | Peeling skin syndrome 2 |
| 15q15.2 | 15:42942897-43106038 | UBR1 | Johanson-Blizzard syndrome |
| 15q15.3 | 15:43599563-43618800 | STRC | Deafness, autosomal recessive 16 |
| 15q15.3 | 15:43371101-43409771 | TUBGCP4 | Microcephaly and chorioretinopathy |
| 15q21.1 | 15:44711517-44718145 | B2M | Immunodeficiency 43 |
| 15q21.1 | 15:45587123-45609716 | BLOC1S6 | ?Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 9 |
| 15q21.1 | 15:48729083-48811069 | CEP152 | Microcephaly 9, primary, autosomal recessive, Seckel syndrome 5 |
| 15q21.1 | 15:45092650-45114172 | DUOX2 | Thyroid dyshormonogenesis 6 |
| 15q21.1 | 15:45114326-45118421 | DUOXA2 | Thyroid dyshormonogenesis 5 |
| 15q21.1 | 15:45361124-45402227 | GATM | Cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome 3 |
| 15q21.1 | 15:44665732-44711390 | PATL2 | Oocyte maturation defect 4 |
| 15q21.1 | 15:48206302-48304078 | SLC12A1 | Bartter syndrome, type 1 |
| 15q21.1 | 15:48120990-48142672 | SLC24A5 | Albinism, oculocutaneous, type VI, [Skin/hair/eye pigmentation 4, fair/dark skin] |
| 15q21.1 | 15:45023195-45077185 | SORD | Sorbitol dehydrogenase deficiency with peripheral neuropathy |
| 15q21.1 | 15:45402336-45421415 | SPATA5L1 | Deafness, autosomal recessive 119, Neurodevelopmental disorder with hearing loss and spasticity |
| 15q21.1 | 15:44562696-44663662 | SPG11 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 5, juvenile, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, axonal, type 2X, Spastic paraplegia 11, autosomal recessive |
| 15q21.1 | 15:45631148-45691281 | SQOR | Sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase deficiency |
| 15q21.1 | 15:44956687-44979229 | TERB2 | ?Spermatogenic failure 59 |
| 15q21.2 | 15:50907492-51005895 | AP4E1 | Spastic paraplegia 51, autosomal recessive |
| 15q21.2 | 15:51447791-51622771 | DMXL2 | ?Polyendocrine-polyneuropathy syndrome, Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 81 |
| 15q21.2 | 15:51341655-51413365 | GLDN | Lethal congenital contracture syndrome 11 |
| 15q21.2 | 15:52115100-52191392 | GNB5 | Intellectual developmental disorder with cardiac arrhythmia, Language delay and ADHD/cognitive impairment with or without cardiac arrhythmia |
| 15q21.2 | 15:52307283-52529050 | MYO5A | Griscelli syndrome, type 1 |
| 15q21.2 | 15:50702266-50765706 | SPPL2A | Immunodeficiency 86, mycobacteriosis |
| 15q21.3 | 15:55417755-55508234 | DNAAF4 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, 25 |
| 15q21.3 | 15:58410554-58569844 | LIPC | Hepatic lipase deficiency |
| 15q21.3 | 15:56428724-56465137 | MNS1 | Heterotaxy, visceral, 9, autosomal, with male infertility |
| 15q21.3 | 15:55319222-55355648 | PIGB | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 80 |
| 15q21.3 | 15:55202966-55289813 | RAB27A | Griscelli syndrome, type 2 |
| 15q21.3 | 15:53513741-53762878 | WDR72 | Amelogenesis imperfecta, type IIA3 |
| 15q22.2 | 15:63321378-63381846 | CA12 | Hyperchlorhidrosis, isolated |
| 15q22.2 | 15:59132434-59372871 | MYO1E | Glomerulosclerosis, focal segmental, 6 |
| 15q22.2 | 15:61852389-62060447 | VPS13C | Parkinson disease 23, autosomal recessive, early onset |
| 15q22.31 | 15:63608618-63833948 | HERC1 | Macrocephaly, dysmorphic facies, and psychomotor retardation |
| 15q22.31 | 15:65001512-65029639 | MTFMT | Combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 15, Mitochondrial complex I deficiency, nuclear type 27 |
| 15q22.31 | 15:64155817-64163022 | PPIB | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type IX |
| 15q22.31 | 15:65611350-65661002 | SLC24A1 | Night blindness, congenital stationary (complete), 1D, autosomal recessive |
| 15q22.31 | 15:65045387-65053397 | SLC51B | ?Bile acid malabsorption, primary, 2 |
| 15q22.31 | 15:64963022-64989914 | SPG21 | MAST syndrome |
| 15q22.31 | 15:64387836-64455303 | TRIP4 | ?Muscular dystrophy, congenital, Davignon-Chauveau type, Spinal muscular atrophy with congenital bone fractures 1 |
| 15q23 | 15:68206992-68257215 | CLN6 | Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, 6A, Ceroid lipofuscinosis, neuronal, 6B (Kufs type) |
| 15q23 | 15:72340924-72376014 | HEXA | GM2-gangliosidosis, several forms, Tay-Sachs disease, [Hex A pseudo deficiency] |
| 15q23 | 15:71822291-72118600 | MYO9A | Myasthenic syndrome, congenital, 24, presynaptic |
| 15q23 | 15:71810554-71818253 | NR2E3 | Enhanced S-cone syndrome |
| 15q24.1 | 15:72686207-72738473 | BBS4 | Bardet-Biedl syndrome 4 |
| 15q24.1 | 15:74630558-74696024 | EDC3 | ?Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 50 |
| 15q24.1 | 15:73443164-73560013 | REC114 | Oocyte maturation defect 10 |
| 15q24.1 | 15:74409289-74433958 | SEMA7A | ?Cholestasis, progressive familial intrahepatic, 11 |
| 15q24.1 | 15:74179466-74212259 | STRA6 | Microphthalmia, isolated, with coloboma 8, Microphthalmia, syndromic 9 |
| 15q24.1-q24.2 | 15:74890042-74902219 | MPI | Congenital disorder of glycosylation, type Ib |
| 15q24.2 | 15:74919791-74938073 | COX5A | ?Mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, nuclear type 20 |
| 15q24.2 | 15:75355792-75368607 | MAN2C1 | Congenital disorder of deglycosylation 2 |
| 15q24.2-q24.3 | 15:76215353-76311469 | ETFA | Glutaric acidemia IIA |
| 15q24.3 | 15:77613027-77820900 | LINGO1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 64 |
| 15q24.3 | 15:76347904-76905340 | SCAPER | Intellectual developmental disorder and retinitis pigmentosa |
| 15q24.3-q25.1 | 15:77994985-78077711 | TBC1D2B | Neurodevelopmental disorder with seizures and gingival overgrowth |
| 15q24-q25 | 15:72400001-88500000 | CILD8 | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, 8 |
| 15q25.1 | 15:80404382-80597933 | ARNT2 | ?Webb-Dattani syndrome |
| 15q25.1 | 15:78593052-78620996 | CHRNA3 | Bladder dysfunction, autonomic, with impaired pupillary reflex and secondary CAKUT |
| 15q25.1 | 15:78104606-78131535 | CIB2 | Deafness, autosomal recessive 48, Usher syndrome, type IJ |
| 15q25.1 | 15:80152789-80186949 | FAH | Tyrosinemia, type I |
| 15q25.1 | 15:78149362-78171945 | IDH3A | Retinitis pigmentosa 90 |
| 15q25.1 | 15:78437431-78501453 | IREB2 | Neurodegeneration, early-onset, with choreoathetoid movements and microcytic anemia |
| 15q25.1 | 15:80946289-80989819 | MESD | Osteogenesis imperfecta, type XX |
| 15q25.1 | 15:79843547-79897285 | MTHFS | Neurodevelopmental disorder with microcephaly, epilepsy, and hypomyelination |
| 15q25.2 | 15:82659281-82709875 | AP3B2 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 48 |
| 15q25.2 | 15:82130233-82262734 | EFL1 | Shwachman-Diamond syndrome 2 |
| 15q25.2 | 15:84639285-84654283 | WDR73 | Galloway-Mowat syndrome 1 |
| 15q25.3 | 15:84817356-84873479 | ALPK3 | Cardiomyopathy, familial hypertrophic 27 |
| 15q25.3 | 15:84884662-84975649 | SLC28A1 | [Uridine-cytidineuria] |
| 15q26.1 | 15:88803436-88875353 | ACAN | Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, aggrecan type |
| 15q26.1 | 15:90717346-90816166 | BLM | Bloom syndrome |
| 15q26.1 | 15:90229975-90265759 | CIB1 | Epidermodysplasia verruciformis 3 |
| 15q26.1 | 15:89243979-89317259 | FANCI | Fanconi anemia, complementation group I |
| 15q26.1 | 15:89617309-89663049 | KIF7 | ?Al-Gazali-Bakalinova syndrome, ?Hydrolethalus syndrome 2, Acrocallosal syndrome, Joubert syndrome 12 |
| 15q26.1 | 15:89776332-89778754 | MESP2 | Spondylocostal dysostosis 2, autosomal recessive |
| 15q26.1 | 15:89316320-89334824 | POLG | Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 4A (Alpers type), Mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome 4B (MNGIE type), Mitochondrial recessive ataxia syndrome (includes SANDO and SCAE), Progressive external ophthalmoplegia, autosomal recessive 1 |
| 15q26.1 | 15:89209869-89221579 | RLBP1 | Bothnia retinal dystrophy |
| 15q26.1 | 15:90930180-90954093 | UNC45A | Osteo-oto-hepato-enteric syndrome |
| 15q26.1 | 15:90998416-91022621 | VPS33B | Arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction, and cholestasis 1, Cholestasis, progressive familial intrahepatic, 12, Keratoderma-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome, autosomal recessive |
| 15q26.3 | 15:99971437-100341975 | ADAMTS17 | Weill-Marchesani 4 syndrome, recessive |
| 15q26.3 | 15:100879831-100916626 | ALDH1A3 | Microphthalmia, isolated 8 |
| 15q26.3 | 15:100400395-100544683 | CERS3 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive 9 |
| 15q26.3 | 15:101175727-101252048 | CHSY1 | Temtamy preaxial brachydactyly syndrome |
| 15q26.3 | 15:100566924-100602184 | LINS1 | Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal recessive 27 |
| 15q26.3 | 15:100919357-101078257 | LRRK1 | Osteosclerotic metaphyseal dysplasia |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Butler, M.G.; Hossain, W.A.; Cowen, N.; Bhatnagar, A. Chromosomal Microarray Study in Prader-Willi Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021220
Butler MG, Hossain WA, Cowen N, Bhatnagar A. Chromosomal Microarray Study in Prader-Willi Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021220
Chicago/Turabian StyleButler, Merlin G., Waheeda A. Hossain, Neil Cowen, and Anish Bhatnagar. 2023. "Chromosomal Microarray Study in Prader-Willi Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021220
APA StyleButler, M. G., Hossain, W. A., Cowen, N., & Bhatnagar, A. (2023). Chromosomal Microarray Study in Prader-Willi Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021220







