An Automated High-Throughput Screening (HTS) Spotter for 3D Tumor Spheroid Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
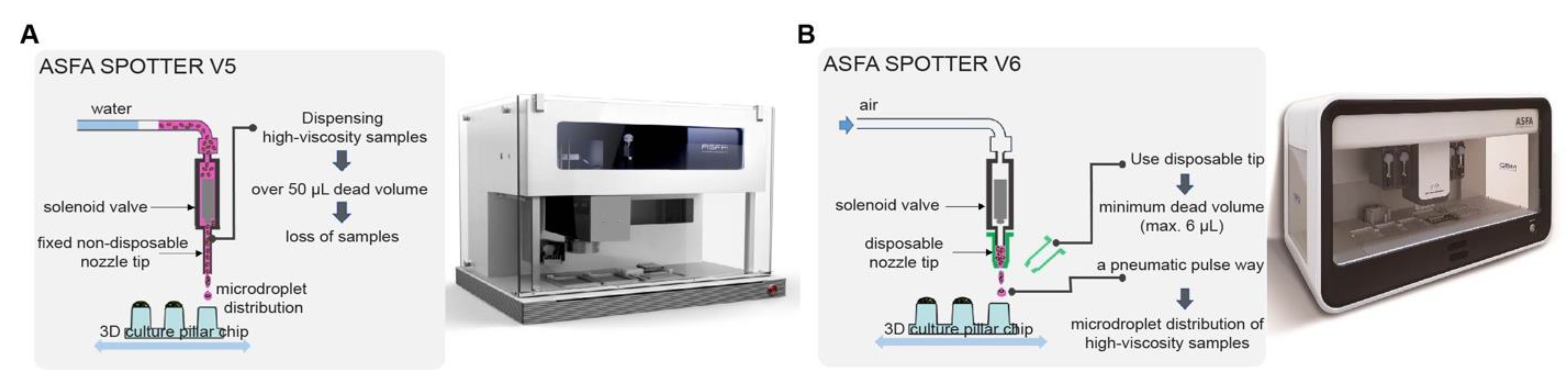
2.1. The Automated Cell Dispenser, ASFA SPOTTER, for HTS
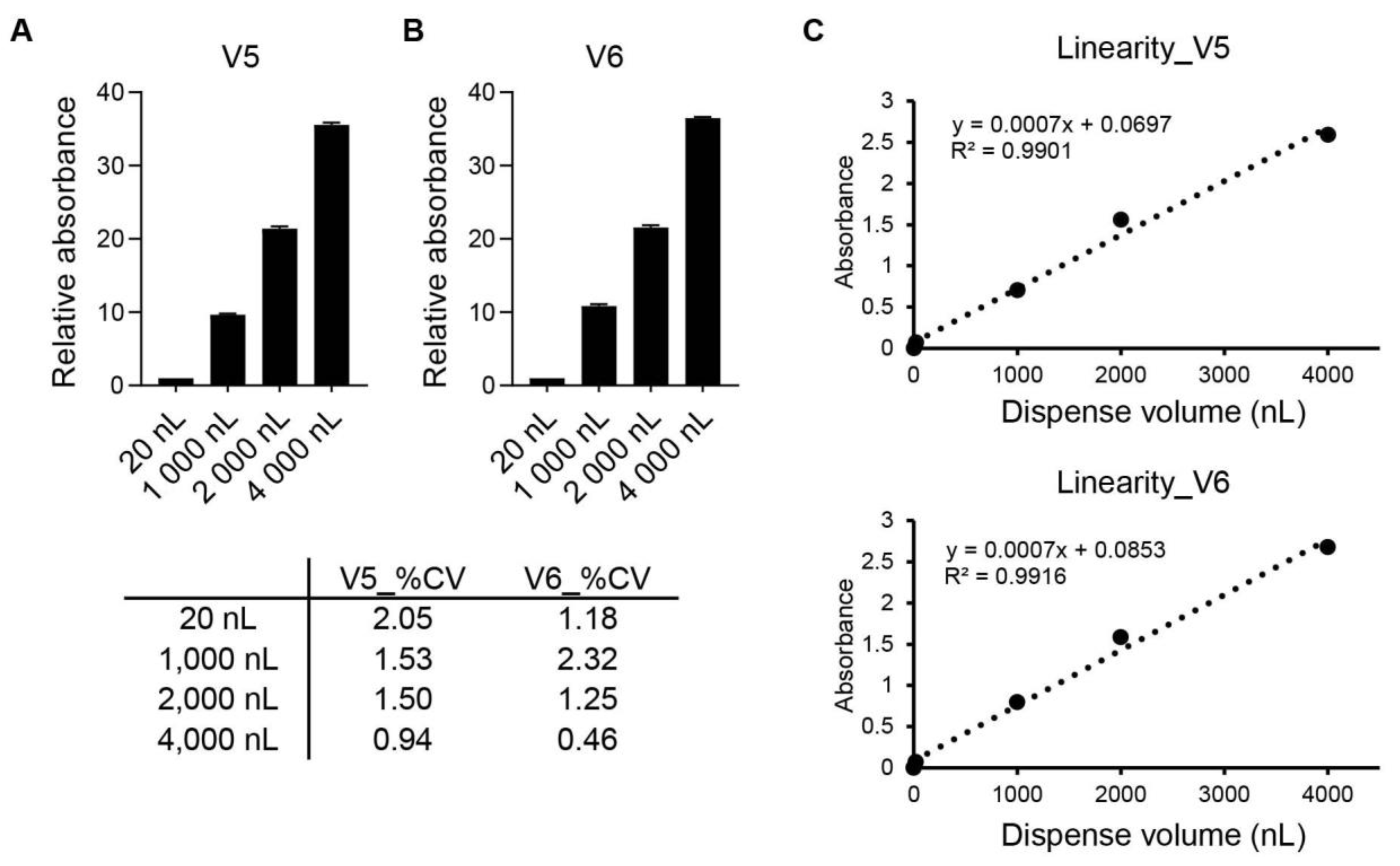
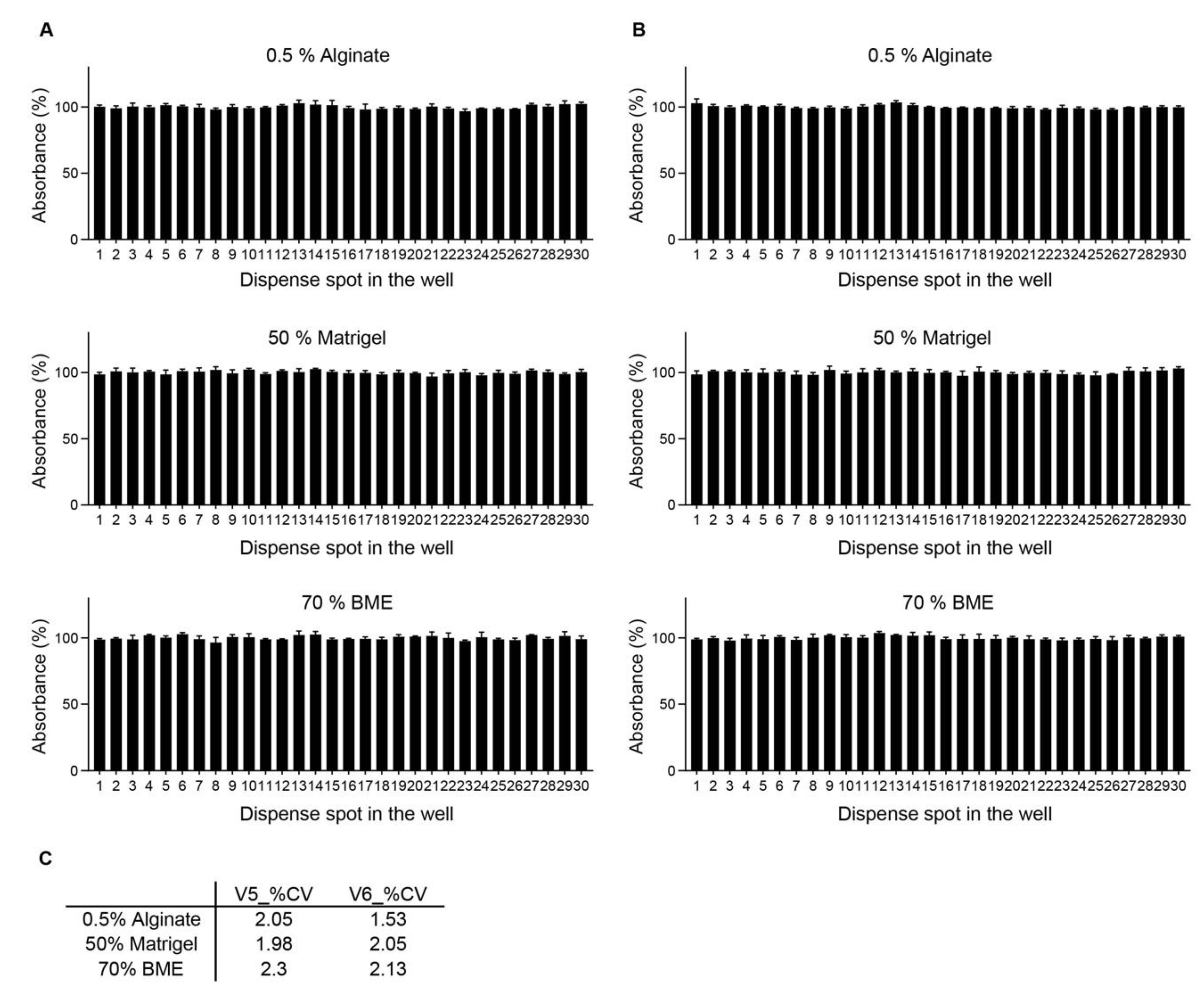
2.2. Dispensing Accuracy and Precision
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- It is composed of a micro-solenoid valve, syringe pump, electro-pneumatic regulator (for V6), nozzle tips, source plate, and target plate.
- It is programmed for dispensing biomaterials with various volumes at nL to μL, with high accuracy and precision.
- The SPOTTER V6 complements the weaknesses (large dead volume, sample dilution, cross-contamination, etc.) of V5 by the application of disposable nozzle tips.
- It can dispense high-viscosity biomaterials with high accuracy and precision.
- It enables self-assembly and the growth of cells in 3D on the micropillar/well chip.
- Good resolution results can be obtained by supporting miniaturized organoid platforms.
- It can support the optimization of drug screening and the selection of an effective treatment in order to improve therapeutic outcomes by the utilization of easy-to-use and rapid in vitro platforms for 3D cultures.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mironov, V.; Kasyanov, V.; Markwald, R.R. Organ printing: From bioprinter to organ biofabrication line. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaei, S.; Parizi, M.S.; Vanaei, S.; Salemizadehparizi, F.; Vanaei, H.R. An Overview on Materials and Techniques in 3D Bioprinting Toward Biomedical Application. Eng. Regen. 2021, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leberfinger, A.N.; Ravnic, D.J.; Dhawan, A.; Ozbolat, I.T. Concise Review: Bioprinting of Stem Cells for Transplantable Tissue Fabrication. Stem. Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1940–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoglu, S.; Demirci, U. Bioprinting for stem cell research. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Al Rashid, A.; Mou, Y.A.; Evis, Z.; Koç, M. Bioprinting: A review of processes, materials and applications. Bioprinting 2021, 23, e00148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudupati, H.; Dey, M.; Ozbolat, I. A Comprehensive Review on Droplet-based Bioprinting- Past, Present and Future. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datar, A.; Joshi, P.; Lee, M.Y. Biocompatible Hydrogels for Microarray Cell Printing and Encapsulation. Biosensors 2015, 5, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.L.; Lee, J.M.; Yeong, W.Y.; Win Naing, M. Microvalve-based bioprinting—Process, bio-inks and applications. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, P. Nanoliter Centrifugal Liquid Dispenser Coupled with Superhydrophobic Microwell Array Chips for High-Throughput Cell Assays. Micromachines 2018, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajalingham, K. Cell-based assays in high-throughput mode (HTS). BioTechnologia 2016, 3, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, G. Automating drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, S.; Gugliandolo, S.G.; Sponchioni, M.; Moscatelli, D.; Colosimo, B.M. 3D bioprinting: Current status and trends—A guide to the literature and industrial practice. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2021, 5, 14–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Henmi, C.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mochizuki, S.; Nakagawa, H.; Takiura, K. Development of a three-dimensional bioprinter: Construction of cell supporting structures using hydrogel and state-of-the-art inkjet technology. J. Biomech. Eng. 2009, 131, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankam, S.; Teo, B.K.; Kukumberg, M.; Yim, E.K. High throughput screening to investigate the interaction of stem cells with their extracellular microenvironment. Organogenesis 2013, 9, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, X.; Ma, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, H.; Qiang, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Developments and Opportunities for 3D Bioprinted Organoids. Int. J. Bioprint. 2021, 7, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BECKMANCOULTER. Biomek i5 Automated Workstation. Available online: https://www.beckman.com/liquid-handlers/biomek-i5 (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- BioDot. BioDot Sphera. Available online: https://www.biodot.com/products/sphera (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Lee, D.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, L.; Kang, M.S.; Kim, M.H.; Doh, I.; Ryu, G.H.; Nam, D.H. High-Throughput Clonogenic Analysis of 3D-Cultured Patient-Derived Cells with a Micropillar and Microwell Chip. SLAS Discov. 2017, 22, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Kim, J.E.; Lee, G.H.; Son, A.; Park, H.C.; Oh, D.; Jo, K.; Choi, C. High-Throughput 3D Tumor Spheroid Array Platform for Evaluating Sensitivity of Proton-Drug Combinations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Joshi, P.; Lee, M.Y. High-Throughput Screening of Compound Neurotoxicity Using 3D-Cultured Neural Stem Cells on a 384-Pillar Plate. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hwang, H.J.; Lee, D.W. Optimization of 3D-aggregated spheroid model (3D-ASM) for selecting high efficacy drugs. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.J.; Lee, D.; Gopal, S.; Ku, A.; Moon, H.; Dordick, J.S. Three-dimensional in vitro cell culture devices using patient-derived cells for high-throughput screening of drug combinations. Med. Devices Sens. 2020, 3, e10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajare, A.A.; Salunkhe, S.S.; Mali, S.S.; Gorde, S.S.; Nadaf, S.J.; Pishawikar, S.A. Review On: High-throughput screening is an approach to drug discovery. Am. J. PharmTech Res. 2014, 4, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Foo, M.A.; You, M.; Chan, S.L.; Sethi, G.; Bonney, G.K.; Yong, W.P.; Chow, E.K.; Fong, E.L.S.; Wang, L.; Goh, B.C. Clinical translation of patient-derived tumour organoids- bottlenecks and strategies. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yu, L.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Huang, W. Patient-derived organoid (PDO) platforms to facilitate clinical decision making. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, D.Y.; Shim, J.; Ku, B.; Oh, D.; Chung, M.K. A novel 3D pillar/well array platform using patient-derived head and neck tumor to predict the individual radioresponse. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 101483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Conventional Automatic Pipette (Biomek i5) | Conventional Spotter (BioDot SpheraTM Platform)  | ASFA Spotter V5 | ASFA Spotter V6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure source | - | water | water | air |
| Target plate number | - | - | 2 | 3 |
| Nozzle tip type | disposable | fixed non-disposable | fixed non-disposable | disposable |
| Nozzle number | max. 6 | max. 4 | ||
| Dispensing volume | 0.5–1000 μL | 2–30 μL | 20–4000 nL | 20–4000 nL |
| Dead volume | - | - | over 50 μL | max. 6 μL |
| Washing step | not necessary | necessary | necessary | not necessary |
| Features |
|
|
|
|
| limitations |
|
|
| - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, M.-H.; Kim, I.; Park, K.; Ku, B.; Lee, D.W.; Park, K.R.; Jeon, S.Y.; Kim, J.E. An Automated High-Throughput Screening (HTS) Spotter for 3D Tumor Spheroid Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021006
Jeong M-H, Kim I, Park K, Ku B, Lee DW, Park KR, Jeon SY, Kim JE. An Automated High-Throughput Screening (HTS) Spotter for 3D Tumor Spheroid Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021006
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Mi-Hyeon, Inhee Kim, Kyunghyun Park, Bosung Ku, Dong Woo Lee, Kyoung Ryeol Park, Sang Youl Jeon, and Jung Eun Kim. 2023. "An Automated High-Throughput Screening (HTS) Spotter for 3D Tumor Spheroid Formation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021006
APA StyleJeong, M.-H., Kim, I., Park, K., Ku, B., Lee, D. W., Park, K. R., Jeon, S. Y., & Kim, J. E. (2023). An Automated High-Throughput Screening (HTS) Spotter for 3D Tumor Spheroid Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021006





