Aβ1-42 Accumulation Accompanies Changed Expression of Ly6/uPAR Proteins, Dysregulation of the Cholinergic System, and Degeneration of Astrocytes in the Cerebellum of Mouse Model of Early Alzheimer Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
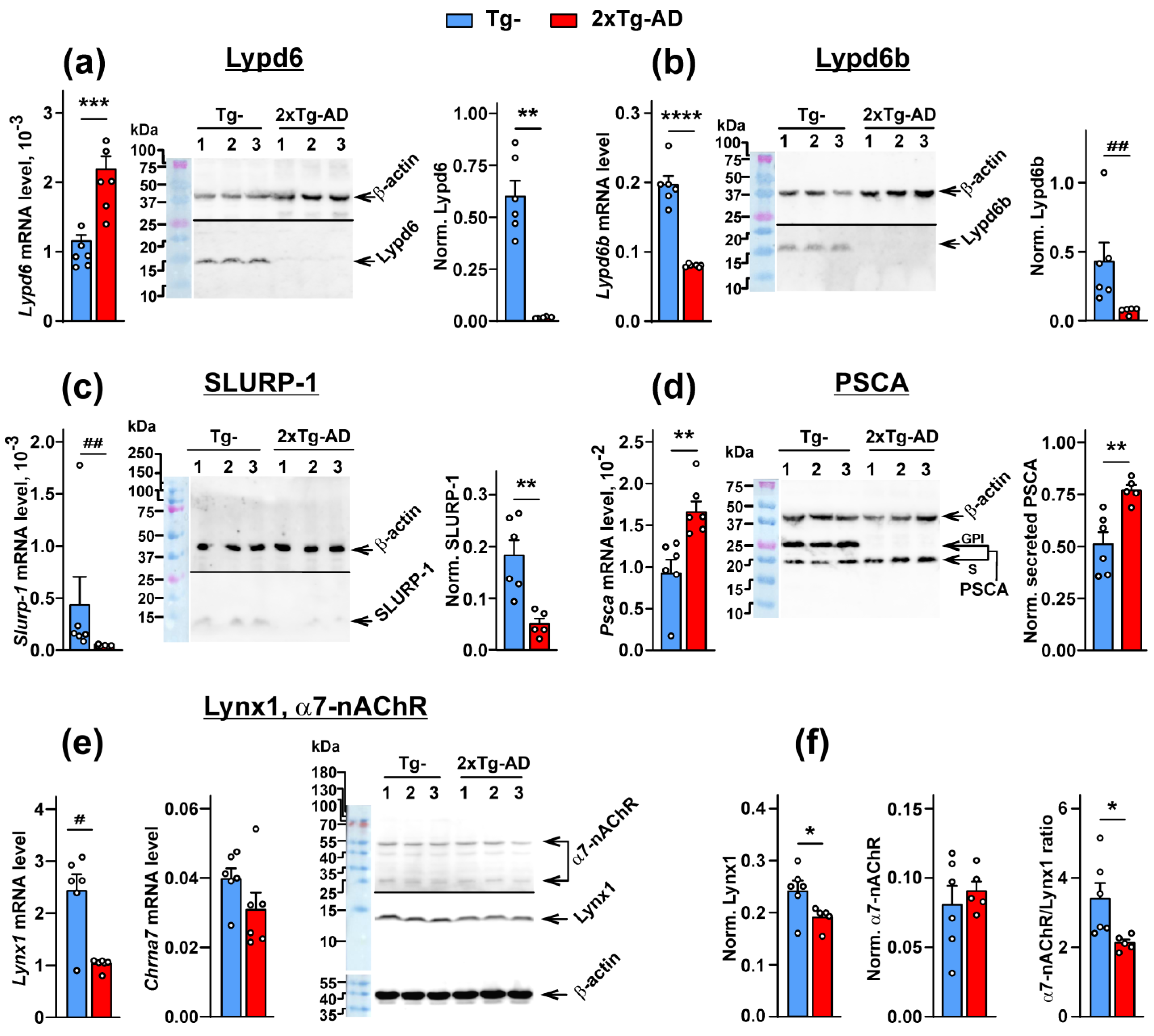
2.1. Expression of the Ly6/uPAR Proteins Is Changed in the Cerebellum of 2xTg-AD Mice
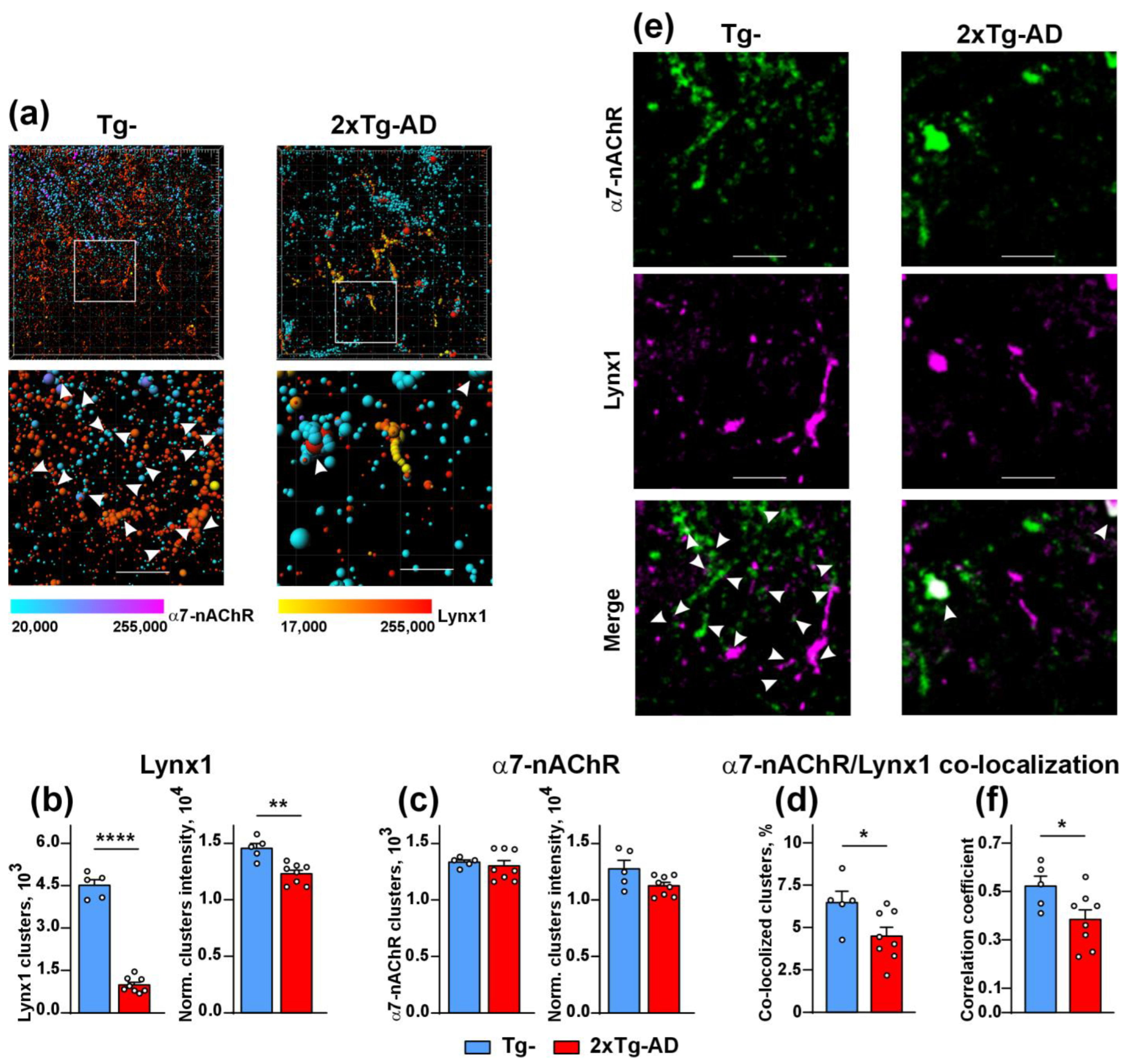
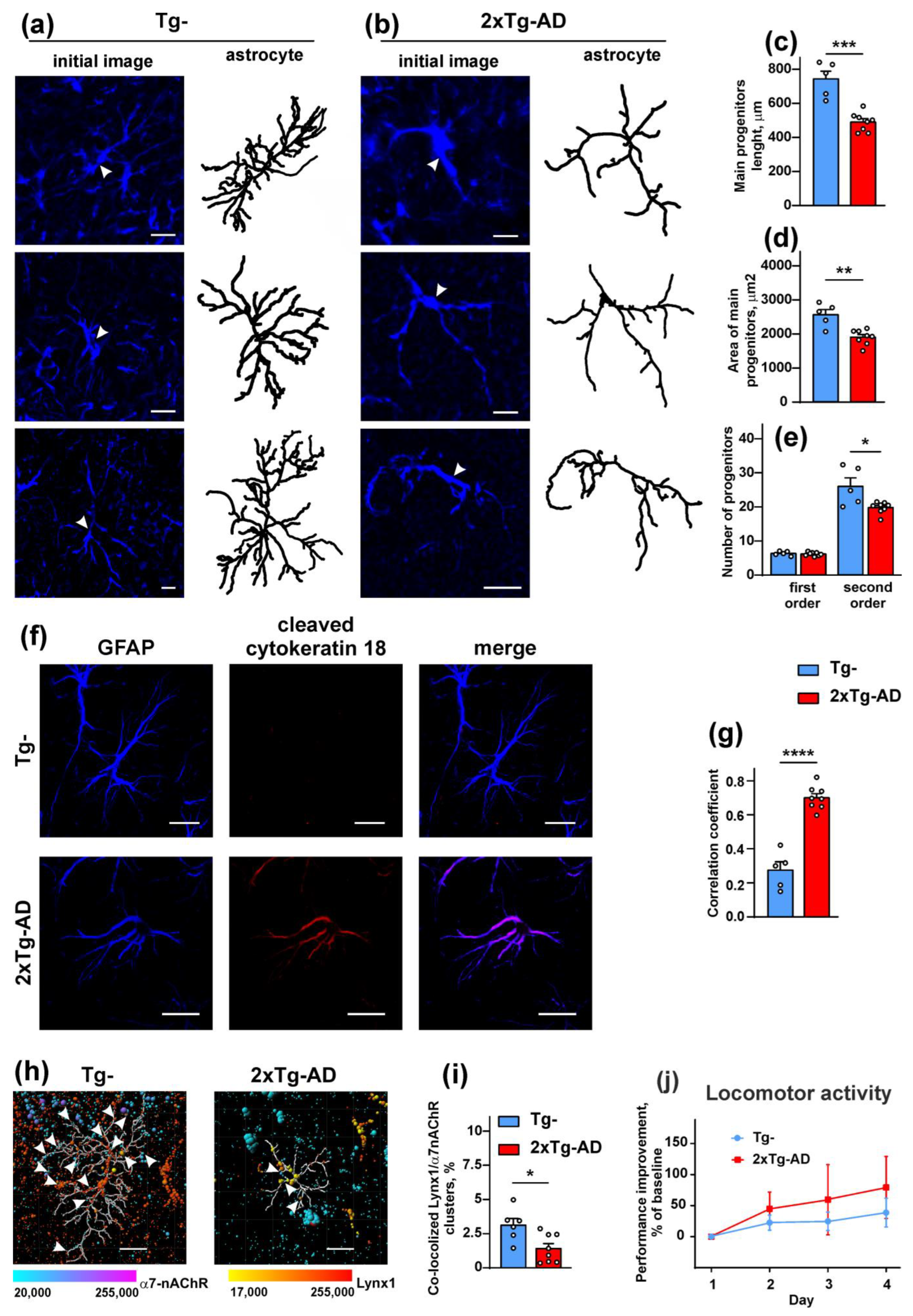
2.2. Colocalization of Lynx1 with α7-nAChR Is Deacreased in the Cerebellum of 2xTg-AD Mice
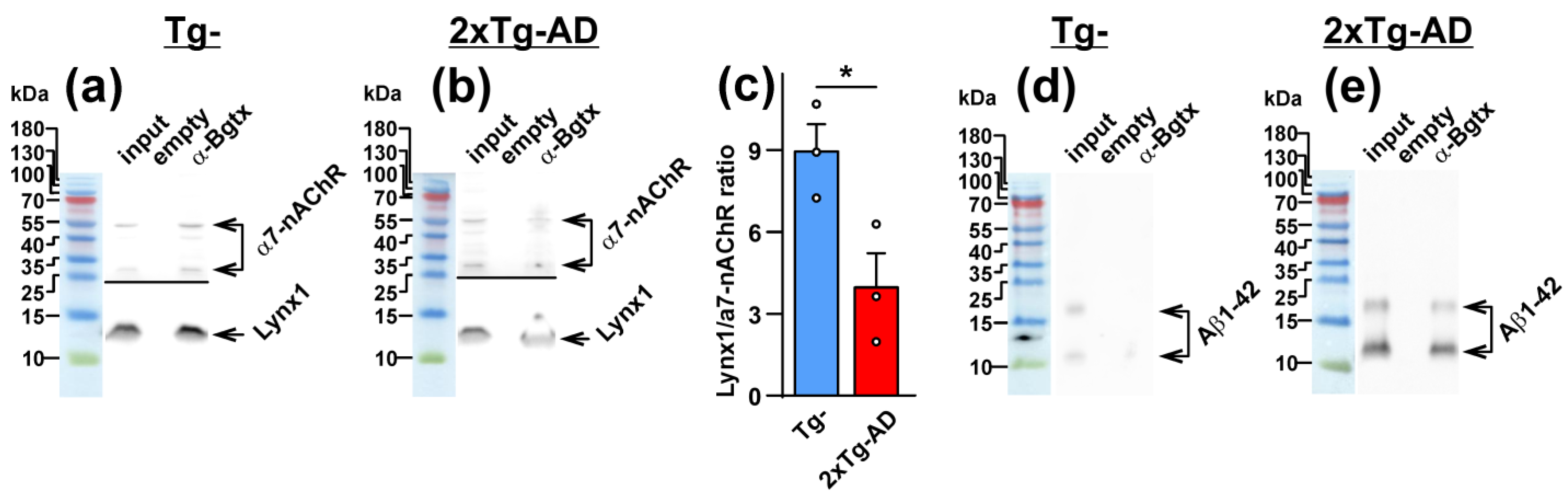
2.3. Increased Co-Localization and Direct Interaction of Aβ1-42 with α7-nAChR in the Cerebellum of 2xTg-AD Mice
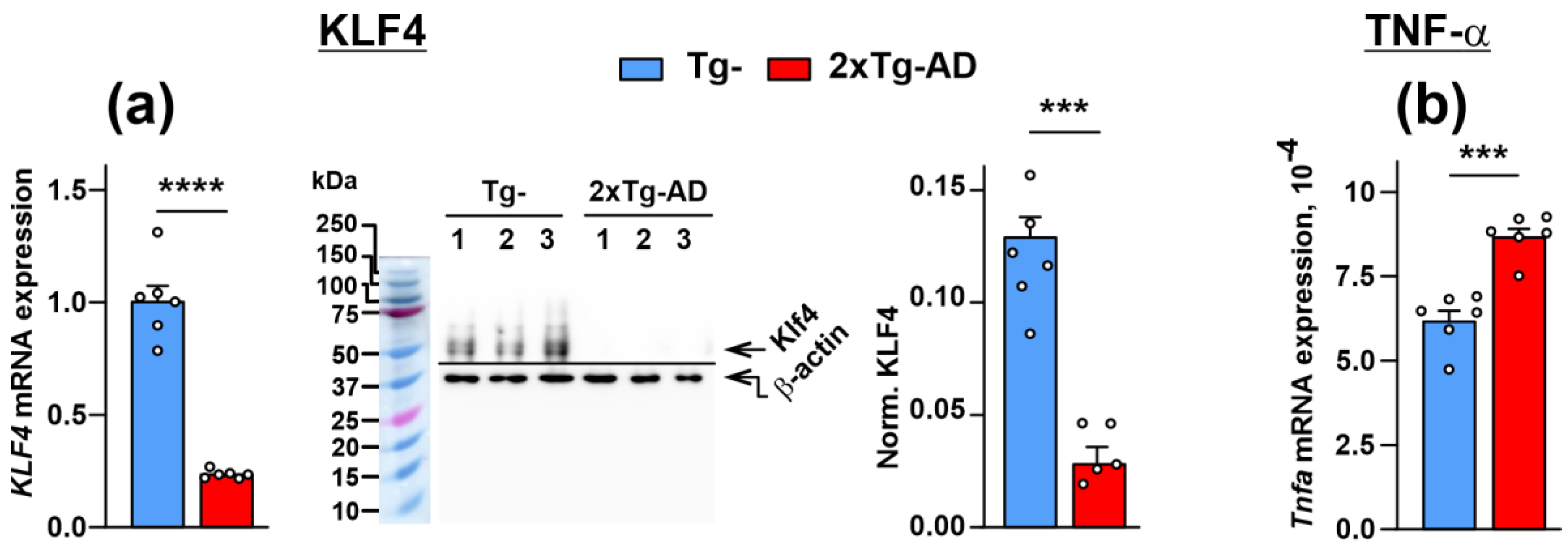
2.4. Dimished Expression of KLF4 Transcription Factor, Lynx1 and SLURP-1 Together with α7-nAChR Dysfunction Results in Activation of Inflammation in the Cerebellum of 2xTg-AD Mice
2.5. Amyloidosis Promotes the Astrocyte Degeneration in the Cerebellum
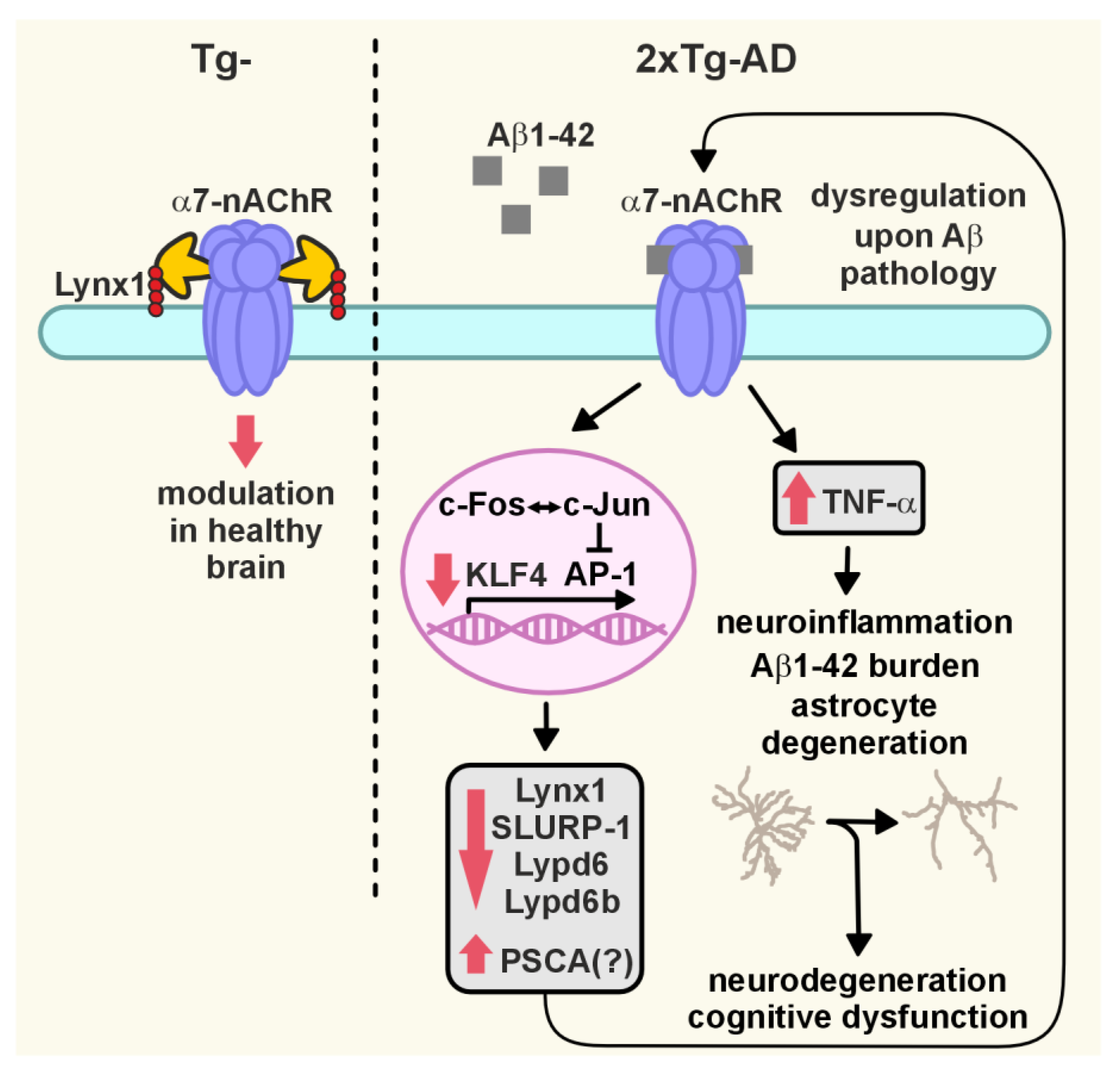
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Real-Time PCR for mRNA Detection
4.3. Western Blotting and Affinity Purification
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Image Analysis
4.6. Rotarod Motor Performance Test
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Action Plan on the Public Health Response to Dementia 2017–2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789241513487 (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Liang, C.-S.; Li, D.-J.; Yang, F.-C.; Tseng, P.-T.; Carvalho, A.F.; Stubbs, B.; Thompson, T.; Mueller, C.; Shin, J.I.; Radua, J.; et al. Mortality Rates in Alzheimer’s Disease and Non-Alzheimer’s Dementias: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2, e479–e488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Hardy, J.; Blennow, K.; Chen, C.; Perry, G.; Kim, S.H.; Villemagne, V.L.; Aisen, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Iwatsubo, T.; et al. The Amyloid-β Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5481–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidar, S.; Ambi, S.V.; Sekaran, S.; Thirumalai, D.; Palaniappan, B. Role of Tau Protein in Alzheimer’s Disease: The Prime Pathological Player. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1599–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasala, M.; Fabiani, C.; Corradi, J.; Antollini, S.; Bouzat, C. Molecular Modulation of Human A7 Nicotinic Receptor by Amyloid-β Peptides. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineley, K.T.; Bell, K.A.; Bui, D.; Sweatt, J.D. Beta-Amyloid Peptide Activates Alpha 7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Expressed in Xenopus Oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25056–25061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oz, M.; Lorke, D.E.; Yang, K.-H.S.; Petroianu, G. On the Interaction of β-Amyloid Peptides and A7-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2013, 10, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; McClatchy, D.B.; Maher, P.; Liang, Z.; Diedrich, J.K.; Soriano-Castell, D.; Goldberg, J.; Shokhirev, M.; Yates, J.R.; Schubert, D.; et al. Intracellular Amyloid Toxicity Induces Oxytosis/Ferroptosis Regulated Cell Death. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiani, C.; Antollini, S.S. Alzheimer’s Disease as a Membrane Disorder: Spatial Cross-Talk Among Beta-Amyloid Peptides, Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors and Lipid Rafts. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, R.; Marutle, A.; Nordberg, A. Modulation of A7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor and Fibrillar Amyloid-β Interactions in Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 33, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckingham, S.D.; Jones, A.K.; Brown, L.A.; Sattelle, D.B. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Signalling: Roles in Alzheimer’s Disease and Amyloid Neuroprotection. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 39–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, H.I.L.; Hopkins, D.A.; Mayrhofer, H.C.; Bruner, E.; van Leeuwen, F.W.; Raaijmakers, W.; Schmahmann, J.D. The Cerebellum in Alzheimer’s Disease: Evaluating Its Role in Cognitive Decline. Brain 2018, 141, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D. The Cerebellum and Cognition. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 688, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellersen, H.M.; Guell, X.; Sami, S. Differential Vulnerability of the Cerebellum in Healthy Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2021, 30, 102605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulbatskii, D.; Shenkarev, Z.; Bychkov, M.; Loktyushov, E.; Shulepko, M.; Koshelev, S.; Povarov, I.; Popov, A.; Peigneur, S.; Chugunov, A.; et al. Human Three-Finger Protein Lypd6 Is a Negative Modulator of the Cholinergic System in the Brain. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 662227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulbatskii, D.S.; Bychkov, M.L.; Lyukmanova, E.N. Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: Part I. Structure, Function, and Role in Neuromuscular Transmission and CNS Functioning. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 44, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkarev, Z.O.; Shulepko, M.A.; Bychkov, M.L.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Shlepova, O.V.; Vasilyeva, N.A.; Andreev-Andrievskiy, A.A.; Popova, A.S.; Lagereva, E.A.; Loktyushov, E.V.; et al. Water-Soluble Variant of Human Lynx1 Positively Modulates Synaptic Plasticity and Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment Associated with A7-nAChR Dysfunction. J. Neurochem. 2020, 155, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Liu, C.Z.; Barrall, E.A.; Rissman, R.A.; Joiner, W.J. Unbalanced Regulation of A7 nAChRs by Ly6h and NACHO Contributes to Neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 8461–8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyukmanova, E.; Shulepko, M.; Kudryavtsev, D.; Bychkov, M.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Kasheverov, I.; Astapova, M.; Feofanov, A.; Thomsen, M.; Mikkelsen, J.; et al. Human Secreted Ly-6/uPAR Related Protein-1 (SLURP-1) Is a Selective Allosteric Antagonist of A7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyukmanova, E.; Shulepko, M.A.; Shenkarev, Z.; Bychkov, M.; Paramonov, A.S.; Chugunov, A.; Kulbatskii, D.; Arvaniti, M.; Dolejsi, E.; Schaer, T.; et al. Secreted Isoform of Human Lynx1 (SLURP-2): Spatial Structure and Pharmacology of Interactions with Different Types of Acetylcholine Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekinay, A.B.; Nong, Y.; Miwa, J.M.; Lieberam, I.; Ibanez-Tallon, I.; Greengard, P.; Heintz, N. A Role for LYNX2 in Anxiety-Related Behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4477–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruska, M.; Keefe, J.; Wert, D.; Tekinay, A.B.; Hulce, J.J.; Ibañez-Tallon, I.; Nishi, R. Prostate Stem Cell Antigen Is an Endogenous Lynx1-like Prototoxin That Antagonizes Alpha7-Containing Nicotinic Receptors and Prevents Programmed Cell Death of Parasympathetic Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14847–14854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Jia, Y.; Pan, P.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, P.; Chen, X.; Jiao, Y.; Kang, G.; Zhang, L.; et al. A5-nAChR Associated with Ly6E Modulates Cell Migration via TGF-Β1/Smad Signaling in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Carcinogenesis 2022, 43, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Puddifoot, C.A.; Taylor, P.; Joiner, W.J. Mechanisms of Inhibition and Potentiation of A4β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors by Members of the Ly6 Protein Family. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24509–24518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Shinagawa, T.; Kai, M.; Miyazawa, M.; Okuda, T.; Kawashima, K.; Yabashi, A.; Waguri, S.; Misawa, H. Primary Sensory Neuronal Expression of SLURP-1, an Endogenous Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Ligand. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 64, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibañez-Tallon, I.; Miwa, J.M.; Wang, H.-L.; Adams, N.C.; Crabtree, G.W.; Sine, S.M.; Heintz, N. Novel Modulation of Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors by Association with the Endogenous Prototoxin Lynx1. Neuron 2002, 33, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, M.S.; Arvaniti, M.; Jensen, M.M.; Shulepko, M.A.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Pinborg, L.H.; Härtig, W.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Mikkelsen, J.D. Lynx1 and Aβ1–42 Bind Competitively to Multiple Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subtypes. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 46, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, M.L.; Kirichenko, A.V.; Paramonov, A.S.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N. Accumulation of β-Amyloid Leads to a Decrease in Lynx1 and Lypd6b Expression in the Hippocampus and Increased Expression of pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Hippocampus and Blood Serum. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 511, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Elder, G.A.; Sosa, M.A.G.; De Gasperi, R.; Dickstein, D.L.; Hof, P.R. Presenilin Transgenic Mice as Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.M.; Arvaniti, M.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Michalski, D.; Pinborg, L.H.; Härtig, W.; Thomsen, M.S. Prostate Stem Cell Antigen Interacts with Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors and Is Affected in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wu, T.; Chen, N. The Amyloid-Beta Clearance: From Molecular Targets to Glial and Neural Cells. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Rezzonico, M.G.; Friedman, B.A.; Huntley, M.H.; Meilandt, W.J.; Pandey, S.; Chen, Y.-J.J.; Easton, A.; Modrusan, Z.; Hansen, D.V.; et al. TREM2-Independent Oligodendrocyte, Astrocyte, and T Cell Responses to Tau and Amyloid Pathology in Mouse Models of Alzheimer Disease. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 110158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, M.S.; Brewer, G.J. Amyloid-β as a Modulator of Synaptic Plasticity. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 22, 741–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.E.; Gu, Z.; Watabe, T.; Thomas, G.; Szigeti, K.; Davis, E.; Wahl, M.; Nisitani, S.; Yamashiro, J.; Le Beau, M.M.; et al. Prostate Stem Cell Antigen: A Cell Surface Marker Overexpressed in Prostate Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Shulepko, M.A.; Mineev, K.S.; D’Hoedt, D.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Filkin, S.Y.; Krivolapova, A.P.; Janickova, H.; Dolezal, V.; et al. NMR Structure and Action on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors of Water-Soluble Domain of Human LYNX1. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10618–10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwabara, Y.; Ishizeki, M.; Watamura, N.; Toba, J.; Yoshii, A.; Inoue, T.; Ohshima, T. Impairments of Long-Term Depression Induction and Motor Coordination Precede Aβ Accumulation in the Cerebellum of APPswe/PS1dE9 Double Transgenic Mice. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, W.J.; Ulloa, L. The Alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor as a Pharmacological Target for Inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 151, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maouche, K.; Polette, M.; Jolly, T.; Medjber, K.; Cloëz-Tayarani, I.; Changeux, J.-P.; Burlet, H.; Terryn, C.; Coraux, C.; Zahm, J.-M.; et al. {alpha}7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Regulates Airway Epithelium Differentiation by Controlling Basal Cell Proliferation. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 1868–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zou, X.; Jin, Y.; Gao, S.; Lv, J.; Li, B.; Cui, R. The Role of KLF4 in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamynathan, S.; Buela, K.-A.; Kinchington, P.; Lathrop, K.L.; Misawa, H.; Hendricks, R.L.; Swamynathan, S.K. Klf4 Regulates the Expression of Slurp1, Which Functions as an Immunomodulatory Peptide in the Mouse Cornea. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 8433–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamynathan, S.K.; Davis, J.; Piatigorsky, J. Identification of Candidate Klf4 Target Genes Reveals the Molecular Basis of the Diverse Regulatory Roles of Klf4 in the Mouse Cornea. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3360–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Majdi, A.; Mahmoudi, J.; Golzari, S.E.J.; Talebi, M. Astrocytic and Microglial Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: An Overlooked Issue in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neural. Transm. 2016, 123, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Reyes, R.E.; Nava-Mesa, M.O.; Vargas-Sánchez, K.; Ariza-Salamanca, D.; Mora-Muñoz, L. Involvement of Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease from a Neuroinflammatory and Oxidative Stress Perspective. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semyanov, A.; Verkhratsky, A. Astrocytic Processes: From Tripartite Synapses to the Active Milieu. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, L.P.; McGill, M.R.; Roberts, D.W.; Hinson, J.A.; Lee, W.M. Advances in Biomarker Development in Acetaminophen Toxicity. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2020, 98, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormina, E.; Petracca, M.; Bommarito, G.; Piaggio, N.; Cocozza, S.; Inglese, M. Cerebellum and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Beyond Conventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. World J. Radiol. 2017, 9, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda-Falla, D.; Barrera-Ocampo, A.; Hagel, C.; Korwitz, A.; Vinueza-Veloz, M.F.; Zhou, K.; Schonewille, M.; Zhou, H.; Velazquez-Perez, L.; Rodriguez-Labrada, R.; et al. Familial Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated Presenilin-1 Alters Cerebellar Activity and Calcium Homeostasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, E.; Lippiello, P.; Zurlo, F.; Balbo, I.; Santamaria, R.; Tempia, F.; Miniaci, M.C. The Emerging Role of Altered Cerebellar Synaptic Processing in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdi, A.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Rahigh Aghsan, S.; Farajdokht, F.; Vatandoust, S.M.; Namvaran, A.; Mahmoudi, J. Amyloid-β, Tau, and the Cholinergic System in Alzheimer’s Disease: Seeking Direction in a Tangle of Clues. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 31, 391–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-R.; Huang, J.-B.; Yang, S.-L.; Hong, F.-F. Role of Cholinergic Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, V.; George, A.A.; Nishi, R.; Whiteaker, P. The Prototoxin LYPD6B Modulates Heteromeric A3β4-Containing Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors, but Not A7 Homomers. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demars, M.P.; Morishita, H. Cortical Parvalbumin and Somatostatin GABA Neurons Express Distinct Endogenous Modulators of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Mol. Brain 2014, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherafat, Y.; Chen, E.; Lallai, V.; Bautista, M.; Fowler, J.P.; Chen, Y.-C.; Miwa, J.; Fowler, C.D. Differential Expression Patterns of Lynx Proteins and Involvement of Lynx1 in Prepulse Inhibition. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 703748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvas, M.; Morsch, M.; Racz, I.; Ahmadi, S.; Swandulla, D.; Zimmer, A. Modulation of the Ca2+ Conductance of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors by Lypd6. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 19, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thomsen, M.S.; Cinar, B.; Jensen, M.M.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shulepko, M.A.; Tsetlin, V.; Klein, A.B.; Mikkelsen, J.D. Expression of the Ly-6 Family Proteins Lynx1 and Ly6H in the Rat Brain Is Compartmentalized, Cell-Type Specific, and Developmentally Regulated. Brain Struct. Funct. 2014, 219, 1923–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarza, R.; Vela, S.; Solas, M.; Ramirez, M.J. C-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Signaling as a Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenki, P.; Khodagholi, F.; Shaerzadeh, F. Inhibition of Phosphorylation of JNK Suppresses Aβ-Induced ER Stress and Upregulates Prosurvival Mitochondrial Proteins in Rat Hippocampus. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 49, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, M.L.; Vasilyeva, N.A.; Shulepko, M.A.; Balaban, P.M.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N. Lynx1 Prevents Long-Term Potentiation Blockade and Reduction of Neuromodulator Expression Caused by Aβ1-42 and JNK Activation. Acta Naturae 2018, 10, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, J.M.; Stevens, T.R.; King, S.L.; Caldarone, B.J.; Ibanez-Tallon, I.; Xiao, C.; Fitzsimonds, R.M.; Pavlides, C.; Lester, H.A.; Picciotto, M.R.; et al. The Prototoxin Lynx1 Acts on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors to Balance Neuronal Activity and Survival in Vivo. Neuron 2006, 51, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monterey, M.D.; Wei, H.; Wu, X.; Wu, J.Q. The Many Faces of Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 619626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Benedetto, G.; Burgaletto, C.; Bellanca, C.M.; Munafò, A.; Bernardini, R.; Cantarella, G. Role of Microglia and Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Neuroinflammation to Ca2+ Homeostasis Dysregulation. Cells 2022, 11, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, J.W.; Bemiller, S.M.; Murtishaw, A.S.; Leisgang, A.M.; Salazar, A.M.; Lamb, B.T. Inflammation as a Central Mechanism in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 4, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulepko, M.A.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Bychkov, M.L.; Lyukmanova, E.N. Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: Part II. Non-Neuronal Cholinergic System. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 45, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; Yang, V.W. Krüppel-like Factor 4 (KLF4): What We Currently Know. Gene 2017, 611, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Olabarria, M.; Noristani, H.N.; Yeh, C.-Y.; Rodriguez, J.J. Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Arellano, J.J.; Parpura, V.; Zorec, R.; Verkhratsky, A. Astrocytes in Physiological Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroscience 2016, 323, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olabarria, M.; Noristani, H.N.; Verkhratsky, A.; Rodríguez, J.J. Concomitant Astroglial Atrophy and Astrogliosis in a Triple Transgenic Animal Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Glia 2010, 58, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preman, P.; Alfonso-Triguero, M.; Alberdi, E.; Verkhratsky, A.; Arranz, A.M. Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathological Significance and Molecular Pathways. Cells 2021, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senitz, D.; Reichenbach, A.; Smith, T.G. Surface Complexity of Human Neocortical Astrocytic Cells: Changes with Development, Aging, and Dementia. J. Hirnforsch. 1995, 36, 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- Khakh, B.S.; Deneen, B. The Emerging Nature of Astrocyte Diversity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 42, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bychkov, M.L.; Isaev, A.B.; Andreev-Andrievskiy, A.A.; Petrov, K.; Paramonov, A.S.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N. Aβ1-42 Accumulation Accompanies Changed Expression of Ly6/uPAR Proteins, Dysregulation of the Cholinergic System, and Degeneration of Astrocytes in the Cerebellum of Mouse Model of Early Alzheimer Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914852
Bychkov ML, Isaev AB, Andreev-Andrievskiy AA, Petrov K, Paramonov AS, Kirpichnikov MP, Lyukmanova EN. Aβ1-42 Accumulation Accompanies Changed Expression of Ly6/uPAR Proteins, Dysregulation of the Cholinergic System, and Degeneration of Astrocytes in the Cerebellum of Mouse Model of Early Alzheimer Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(19):14852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914852
Chicago/Turabian StyleBychkov, Maxim L., Aizek B. Isaev, Alexander A. Andreev-Andrievskiy, Konstantin Petrov, Alexander S. Paramonov, Mikhail P. Kirpichnikov, and Ekaterina N. Lyukmanova. 2023. "Aβ1-42 Accumulation Accompanies Changed Expression of Ly6/uPAR Proteins, Dysregulation of the Cholinergic System, and Degeneration of Astrocytes in the Cerebellum of Mouse Model of Early Alzheimer Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 19: 14852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914852
APA StyleBychkov, M. L., Isaev, A. B., Andreev-Andrievskiy, A. A., Petrov, K., Paramonov, A. S., Kirpichnikov, M. P., & Lyukmanova, E. N. (2023). Aβ1-42 Accumulation Accompanies Changed Expression of Ly6/uPAR Proteins, Dysregulation of the Cholinergic System, and Degeneration of Astrocytes in the Cerebellum of Mouse Model of Early Alzheimer Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(19), 14852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914852






