Urinary Long Non-Coding RNA Levels as Biomarkers of Lupus Nephritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
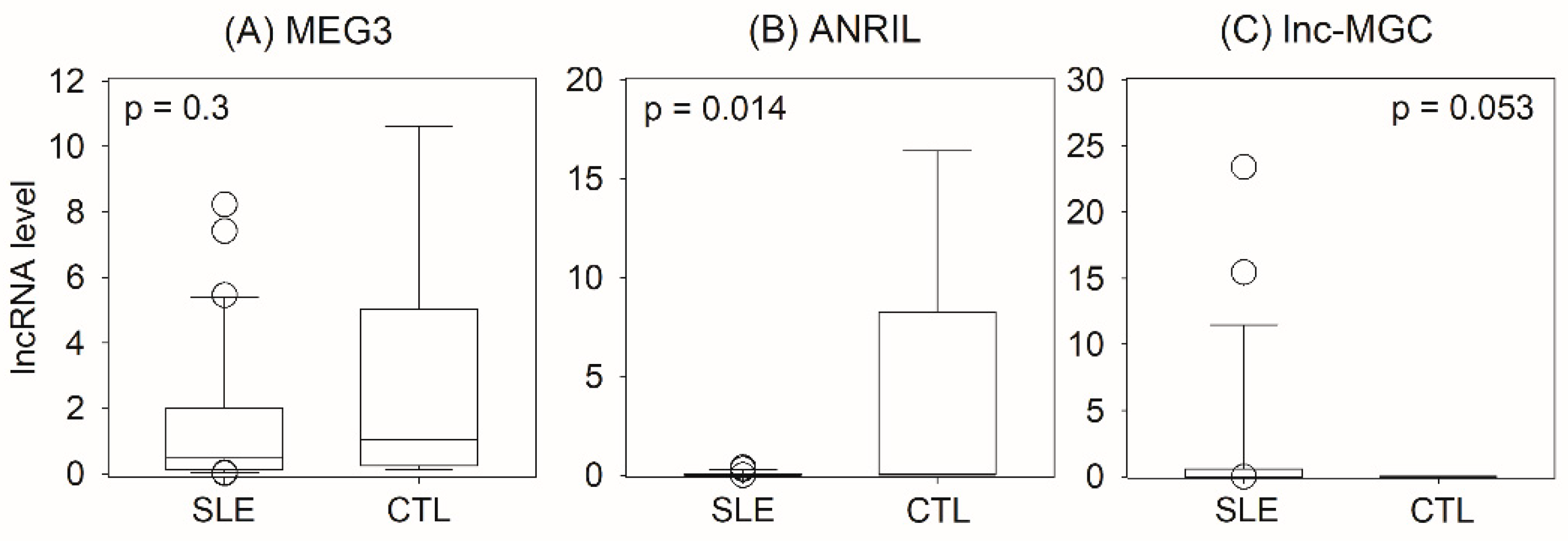
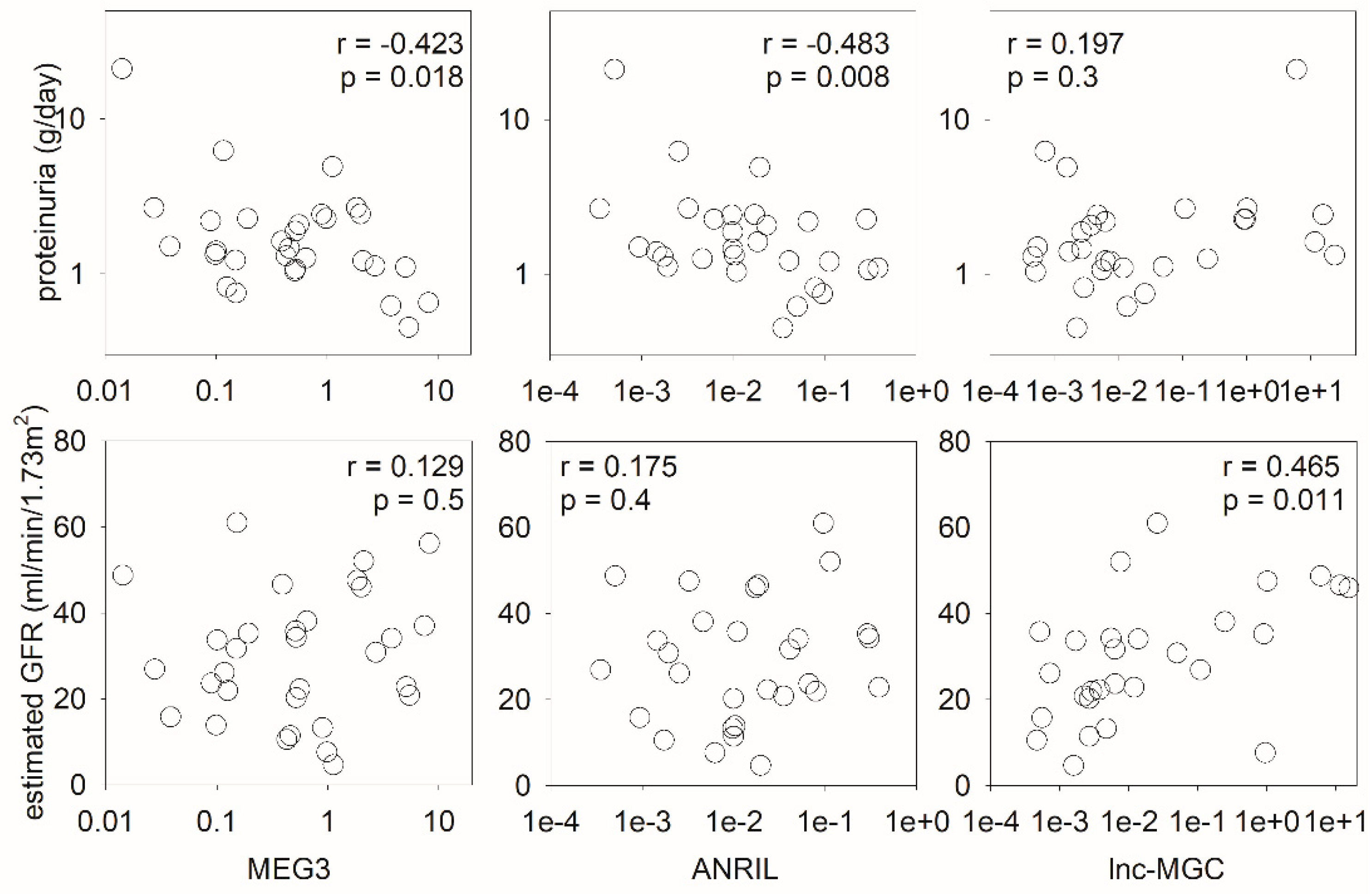
2.1. Urinary lncRNA for Identification of Lupus Nephritis
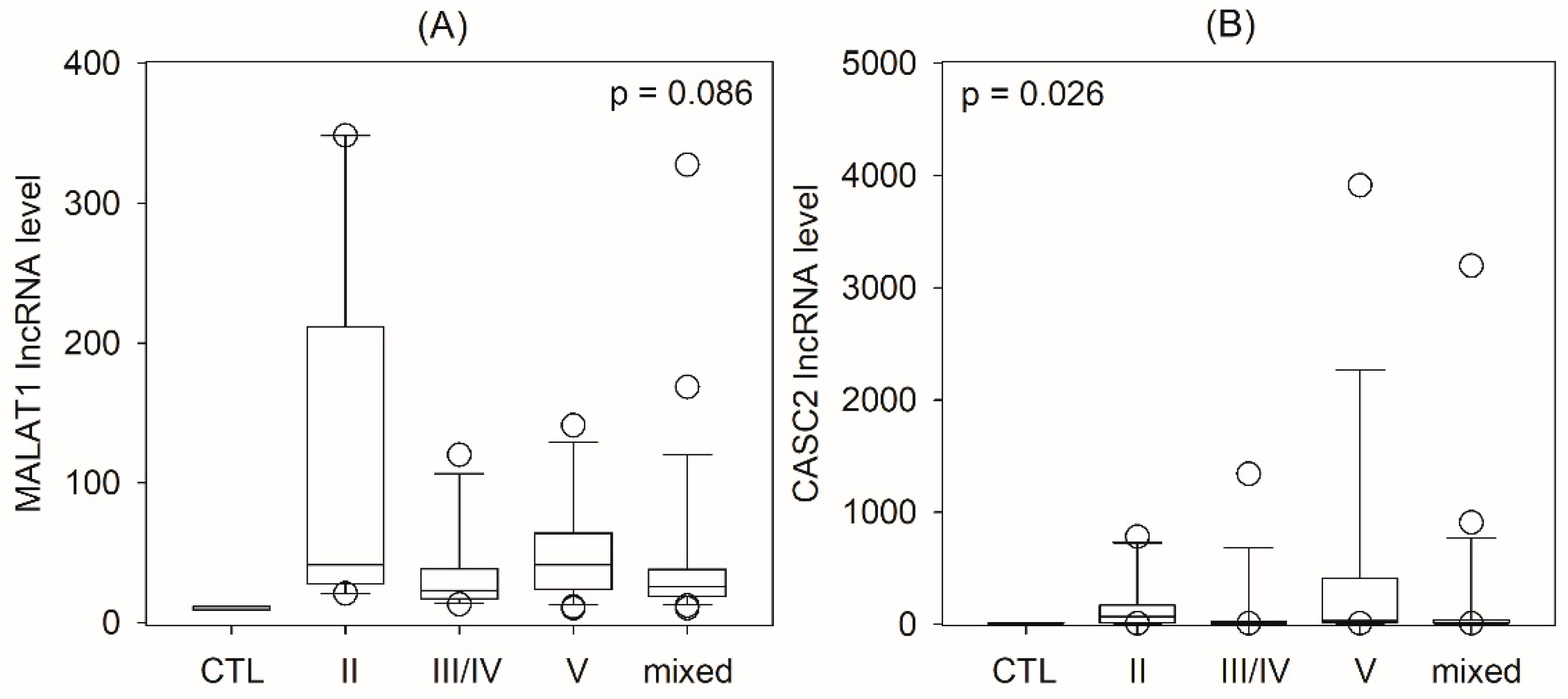
2.2. Urinary lncRNA and Histological Classes of Lupus Nephritis
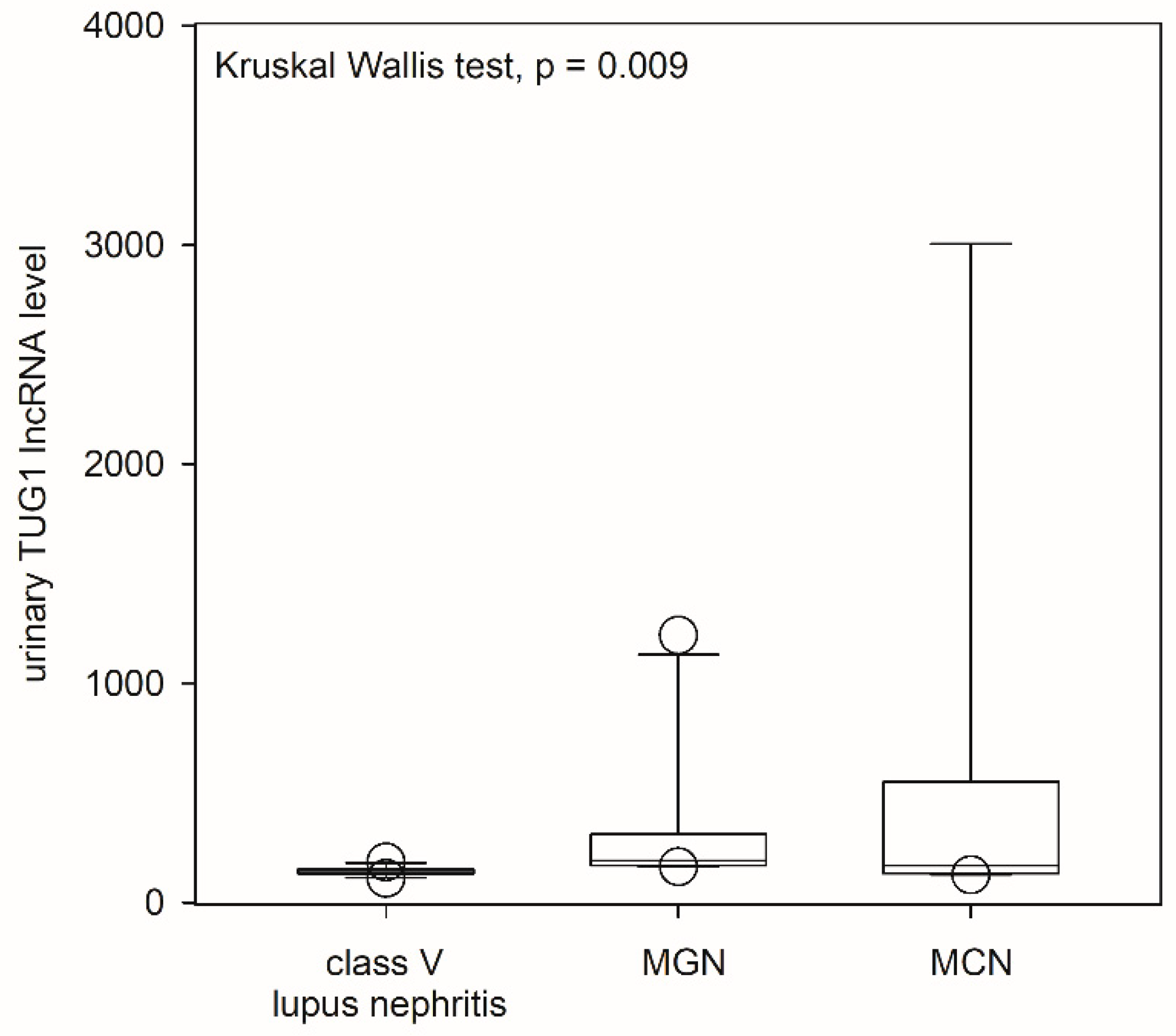
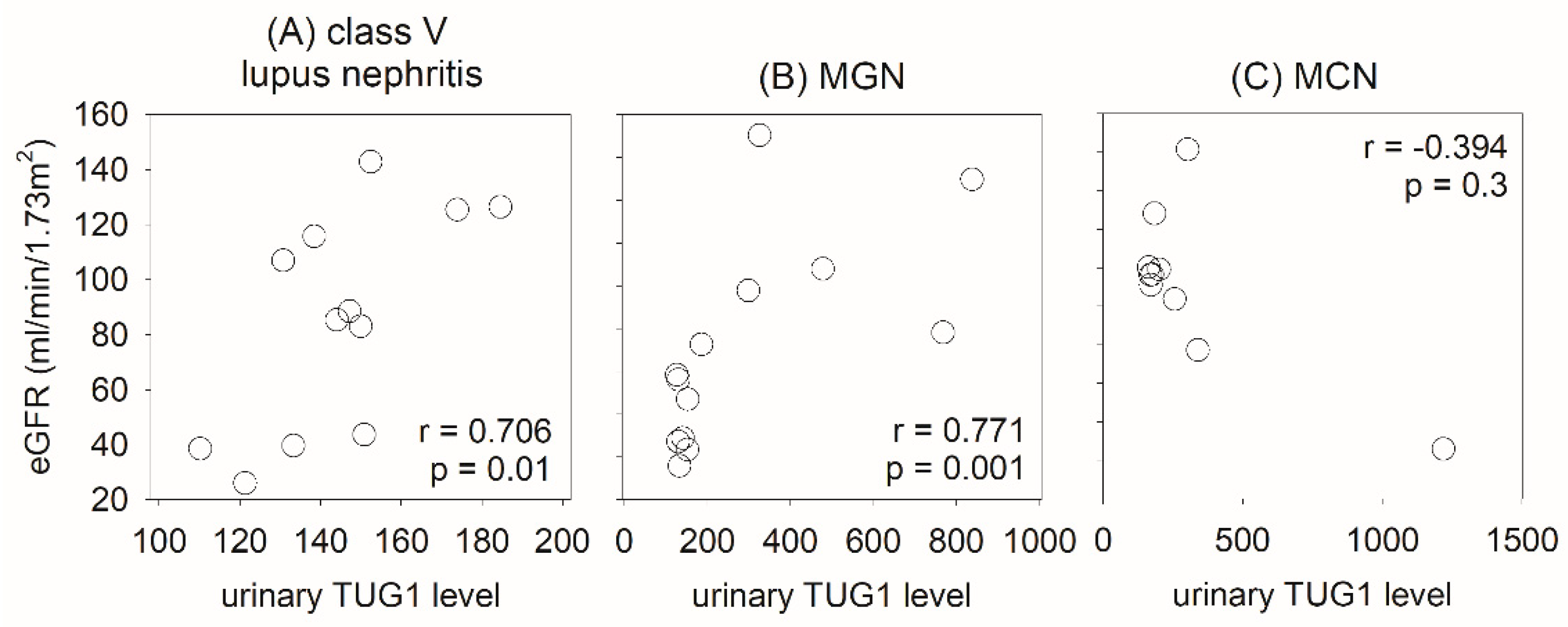
2.3. Urinary lncRNA and Class V Lupus Nephritis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Overall Study Design
4.2. Preparation of RNA
4.3. Quantification of lncRNA
4.4. Histological Study
4.5. Morphometric Study
4.6. Follow-Up and Treatment Response
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cross, J.; Jayne, D. Diagnosis and treatment of kidney disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 19, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, M.; Appel, G.B. Update on the treatment of lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, C.; Hajjar, Y.; Mueller, K.; Waldherr, R.; Ho, A.D.; Andrassy, K. Improved clinical outcome of lupus nephritis during the past decade: Importance of early diagnosis and treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, N.; Michaelson, J.S.; Putterman, C. Lipocalin-2, TWEAK, and other cytokines as urinary biomarkers for lupus nephritis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1109, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Tomosugi, N.; Hisada, Y.; Ohta, S.; Naito, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Mukaida, N.; Matsushima, K. Detection of urinary interleukin-8 in glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Deile, J.; Dannenberg, J.; Liu, P.; Lorenzen, J.; Nyström, J.; Thum, T.; Schiffer, M. Identification of cell and disease specific microRNAs in glomerular pathologies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3927–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaskandan, H.; Pawluczyk, I.; Barratt, J. Clinical application of microRNAs in glomerular diseases. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, T.; Belliere, J.; Bascands, J.L.; Neau, E.; Klein, J.; Schanstra, J.P. miRNAs in urine: A mirror image of kidney disease? Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M.; Rinn, J.L. Modular regulatory principles of large non-coding RNAs. Nature 2012, 482, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chung, A.C.; Huang, X.R.; Dong, Y.; Yu, X.; Lan, H.Y. Identification of novel long noncoding RNAs associated with TGF-β/Smad3-mediated renal inflammation and fibrosis by RNA sequencing. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehana, N.A.; Ghaiad, H.R.; Hassan, M.; Elsabagh, Y.A.; Labib, S.; Abd-Elmawla, M.A. LncRNA MEG3 regulates the interplay between Th17 and Treg cells in Behçet’s disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. Life Sci. 2022, 309, 120965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Ito, S.; Wada, I.; Hosokawa, N. ER-resident protein 46 (ERp46) triggers the mannose-trimming activity of ER degradation-enhancing α-mannosidase-like protein 3 (EDEM3). J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 10663–10674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elmawla, M.A.; Fawzy, M.W.; Rizk, S.M.; Shaheen, A.A. Role of long non-coding RNAs expression (ANRIL, NOS3-AS, and APOA1-AS) in development of atherosclerosis in Egyptian systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 3319–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liang, N.; Wang, M.; Fei, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Guo, C.; Cao, Z.; Li, S.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is a novel inflammatory regulator in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77400–77406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhu, H.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Jiao, J.S.; Xing, X.Y. LncRNA CASC2 regulates high glucose-induced proliferation, extracellular matrix accumulation and oxidative stress of human mesangial cells via miR-133b/FOXP1 axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 802–812. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.Y.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.P.; Lu, H.X.; Sun, J.; Li, H.B. The protection of NF-κB inhibition on kidney injury of systemic lupus erythematosus mice may be correlated with lncRNA TUG1. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congrains, A.; Kamide, K.; Ohishi, M.; Rakugi, H. ANRIL: Molecular mechanisms and implications in human health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1278–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potula, H.H.; Xu, Z.; Zeumer, L.; Sang, A.; Croker, B.P.; Morel, L. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Cdkn2c deficiency promotes B1a cell expansion and autoimmunity in a mouse model of lupus. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2931–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Bhatt, K.; Oh, H.J.; Lanting, L.; Deshpande, S.; Jia, Y.; Lai, J.Y.; O’Connor, C.L.; et al. An endoplasmic reticulum stress-regulated lncRNA hosting a microRNA megacluster induces early features of diabetic nephropathy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.Z.; Tian, W.; Fu, H.T.; Li, C.P.; Liu, B. Long noncoding RNA-MEG3 is involved in diabetes mellitus-related microvascular dysfunction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 471, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, C.; Smyth, D.J.; Maisuria-Armer, M.; Walker, N.M.; Todd, J.A.; Clayton, D.G. The imprinted DLK1-MEG3 gene region on chromosome 14q32.2 alters susceptibility to type 1 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kan, Q.E.; Su, Y.; Man, H. Long Non-Coding RNA CASC2 Improves Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibiting JNK Pathway. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 127, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Su, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G. Clinical Significance of Serum lncRNA Cancer Susceptibility Candidate 2 (CASC2) for Chronic Renal Failure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 6079–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.M.; He, Y.S.; Wu, G.C.; Hu, Y.Q.; Xiang, K.; Liao, T.; Yan, Y.L.; Yang, X.K.; Shuai, Z.W.; Wang, G.H.; et al. Association of MALAT-1 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms with genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2021, 30, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, L. LncRNA TUG1 relieves renal mesangial cell injury by modulating the miR-153-3p/Bcl-2 axis in lupus nephritis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2023, 11, e811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar-Torres, F.J.; Medina-Perez, M.; Melo, Z.; Mendoza-Cerpa, C.; Echavarria, R. Urinary expression of long non-coding RNA TUG1 in non-diabetic patients with glomerulonephritides. Biomed. Rep. 2021, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Xue, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Shang, X.; Liu, Y. The long noncoding RNA TUG1 regulates blood-tumor barrier permeability by targeting miR-144. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 19759–19779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Szeto, C.C. Methods of microRNA quantification in urinary sediment. In Circulating MicroRNAs; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 1024, pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.Y.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.P.; Lu, H.X.; Sun, J.; Li, H.B. Clinical significance of reduced expression of lncRNA TUG1 in the peripheral blood of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, S.; Watson, N.; Long, E.; Sharpe, S.; Zhong, W.; Xu, S.Z.; Atkin, S.L. Expression of somatostatin and somatostatin receptor subtypes 1-5 in human normal and diseased kidney. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2008, 56, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weening, J.J.; D’Agati, V.D.; Schwartz, M.M.; Seshan, S.V.; Alpers, C.E.; Appel, G.B.; Balow, J.E.; Bruijn, J.A.; Cook, T.; Ferrario, F.; et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, J.P.; Balow, J.E. Renal biopsy in lupus nephritis. Lupus 1998, 7, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneval, P.; Bariéty, J.; Bélair, M.F.; Mandet, C.; Heudes, D.; Nicoletti, A. Mesangial expansion associated with glomerular endothelial cell activation and macrophage recruitment is developing in hyperlipidaemic apoE null mice. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KDIGO (Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes). Clinical Practice Guideline for Glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–274. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, R.W.; Szeto, C.C. Advances in the clinical laboratory assessment of urinary sediment. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 340, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.W.; Lai, F.M.; Li, E.K.; Tam, L.S.; Chung, K.Y.; Chow, K.M.; Li, P.K.; Szeto, C.C. Urinary mononuclear cell and disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2006, 15, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs: Definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SLE | Control | |
|---|---|---|
| No. of cases | 31 | 6 |
| Age | 45.6 ± 12.3 | 43.5 ± 10.1 |
| Sex (F:M) | 29:2 | 3:3 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 30.8 (20.2–38.1) | 93.8 (69.1–113.3) |
| Proteinuria (g/day) | 1.4 (1.1–2.3) | -- |
| Glomerulosclerosis (%) | 1.5 (0.0–30.0) | |
| Tubulointerstitial fibrosis (%) | 10.0 (5.0–15.0) | |
| SLEDAI | 12 (9–14) | |
| Activity index | 2 (0–8) | |
| Chronicity index | 2 (1–3) |
| SLE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Case | Class II | Class III or IV | Class V | Mixed | Control | |
| No. of cases | 78 | 10 | 15 | 29 | 24 | 7 |
| Age | 41.7 ± 12.6 | 37.3 ± 14.9 | 40.7 ± 11.8 | 44.9 ± 11.7 | 40.3 ± 13.1 | 44.4 ± 8.3 |
| Sex (F:M) | 73:5 | 9:1 | 14:1 | 29:0 | 21:3 | 6:1 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 47.4 (33.0–67.9) | 55.1 (26.1–85.7) | 44.1 (31.1–64.0) | 55.4 (36.8–72.5) | 45.8 (29.6–73.9) | 93.4 (92.4–104.5) |
| Proteinuria (g/day) | 1.9 (1.2–3.4) | 1.2 (0.9–2.1) | 2.1 (1.4–5.1) | 2.1 (1.3–4.8) | 1.5 (1.2–2.2) | -- |
| Glomerulosclerosis (%) | 0.6 (0.0–3.4) | 0.0 (0.0–8.3) | 2.7 (0.4–5.2) | 0.0 (0.0–2.2) | 1.5 (0.0–3.3) | |
| Tubulointerstitial fibrosis (%) | 1.0 (0.0–6.6) | 0.0 (0.0–16.2) | 4.0 (1.2–7.1) | 0.0 (0.0–4.1) | 1.3 (0.0–7.9) | |
| SLEDAI | 11 (9–13) | 10 (8–11) | 11 (9–13) | 12 (9–14) | 11 (9–14) | |
| Activity index | 3 (1–7) | 1 (0–2) | 7 (6–10) | 1 (1–3) | 7 (4–9) | |
| Chronicity index | 1 (0–2) | 0 (0–3) | 1 (1–2) | 0 (0–1) | 1 (0–2) | |
| SLE | MGN | MCN | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of cases | 12 | 14 | 10 |
| Age | 59.7 ± 16.1 | 60.5 ± 14.1 | 59.1 ± 16.1 |
| Sex (F:M) | 9:3 | 5:9 | 6:4 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 87.0 (40.6–123.0) | 65.5 (28.4–118.4) | 116.4 (97.1–127.3) |
| Proteinuria (g/day) | 5.8 (1.3–10.0) | 1.5 (0.8–4.0) | 6.3 (4.9–10.5) |
| Glomerulosclerosis (%) | 0 (0–12) | 0 (0–12) | 0 (0–9) |
| Tubulointerstitial fibrosis (%) | 0 (0–10) | 2 (0–12) | 0 (0–2) |
| SLEDAI | 7 (5–10) | -- | -- |
| Activity index | 0 (0–2) | -- | -- |
| Chronicity index | 0 (0–1) | -- | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szeto, C.-C.; So, H.; Poon, P.Y.-K.; Luk, C.C.-W.; Ng, J.K.-C.; Fung, W.W.-S.; Chan, G.C.-K.; Chow, K.-M.; Lai, F.M.-M.; Tam, L.-S. Urinary Long Non-Coding RNA Levels as Biomarkers of Lupus Nephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411813
Szeto C-C, So H, Poon PY-K, Luk CC-W, Ng JK-C, Fung WW-S, Chan GC-K, Chow K-M, Lai FM-M, Tam L-S. Urinary Long Non-Coding RNA Levels as Biomarkers of Lupus Nephritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411813
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzeto, Cheuk-Chun, Ho So, Peter Yam-Kau Poon, Cathy Choi-Wan Luk, Jack Kit-Chung Ng, Winston Wing-Shing Fung, Gordon Chun-Kau Chan, Kai-Ming Chow, Fernand Mac-Moune Lai, and Lai-Shan Tam. 2023. "Urinary Long Non-Coding RNA Levels as Biomarkers of Lupus Nephritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411813
APA StyleSzeto, C.-C., So, H., Poon, P. Y.-K., Luk, C. C.-W., Ng, J. K.-C., Fung, W. W.-S., Chan, G. C.-K., Chow, K.-M., Lai, F. M.-M., & Tam, L.-S. (2023). Urinary Long Non-Coding RNA Levels as Biomarkers of Lupus Nephritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411813






