Anti-Fibrotic Effects of RF Electric Currents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
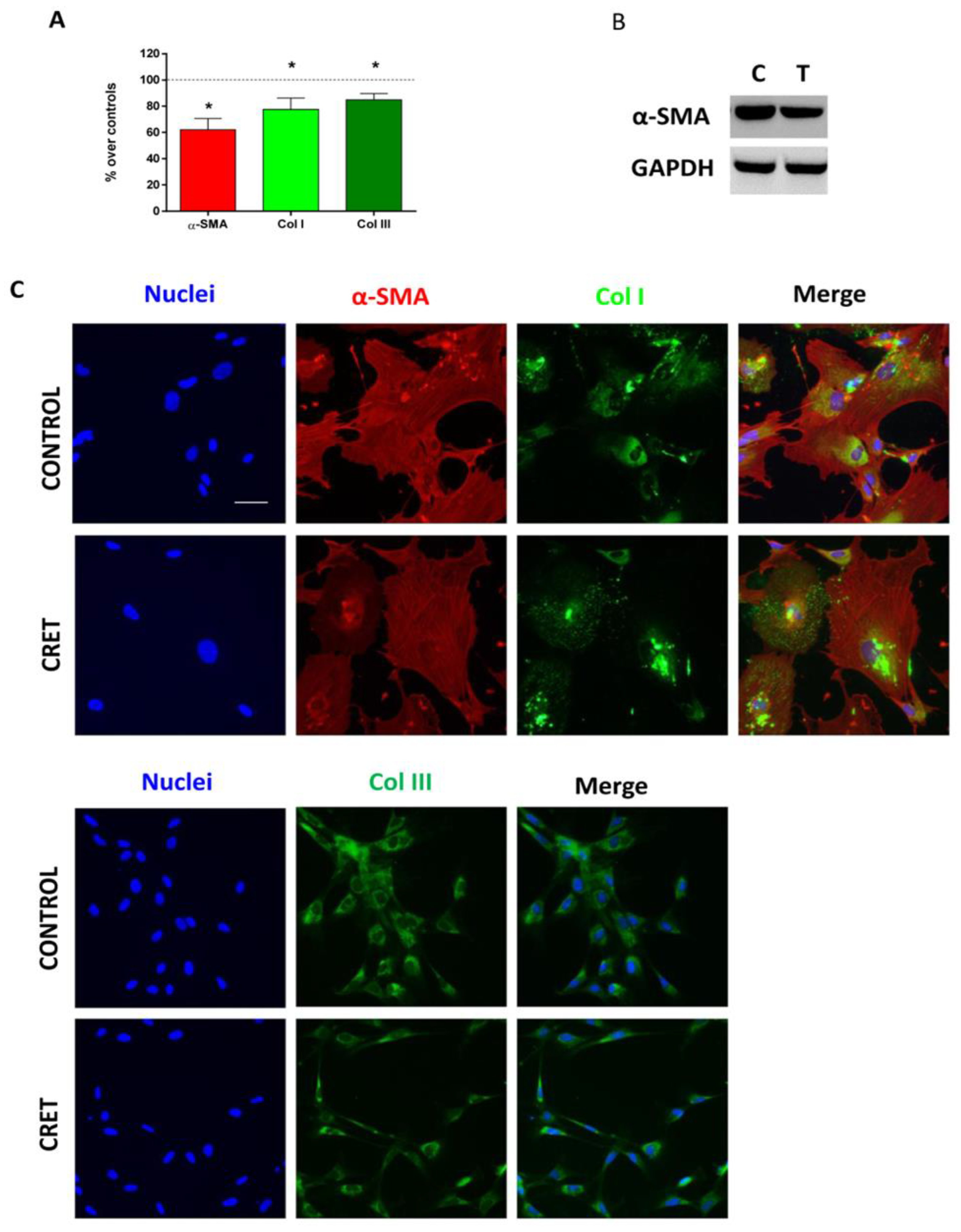
2.1. Extracellular Matrix Production
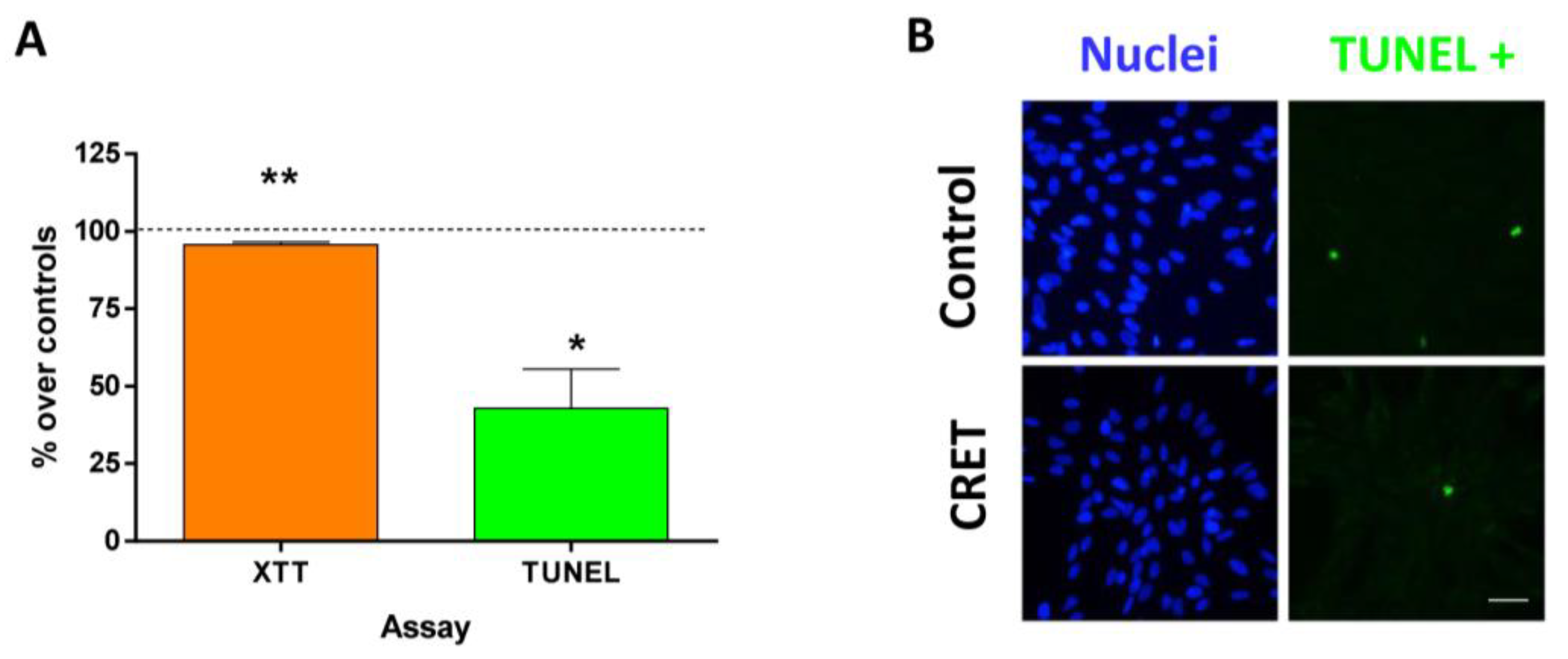
2.2. Cell Proliferation and Death
2.3. Cell Migration
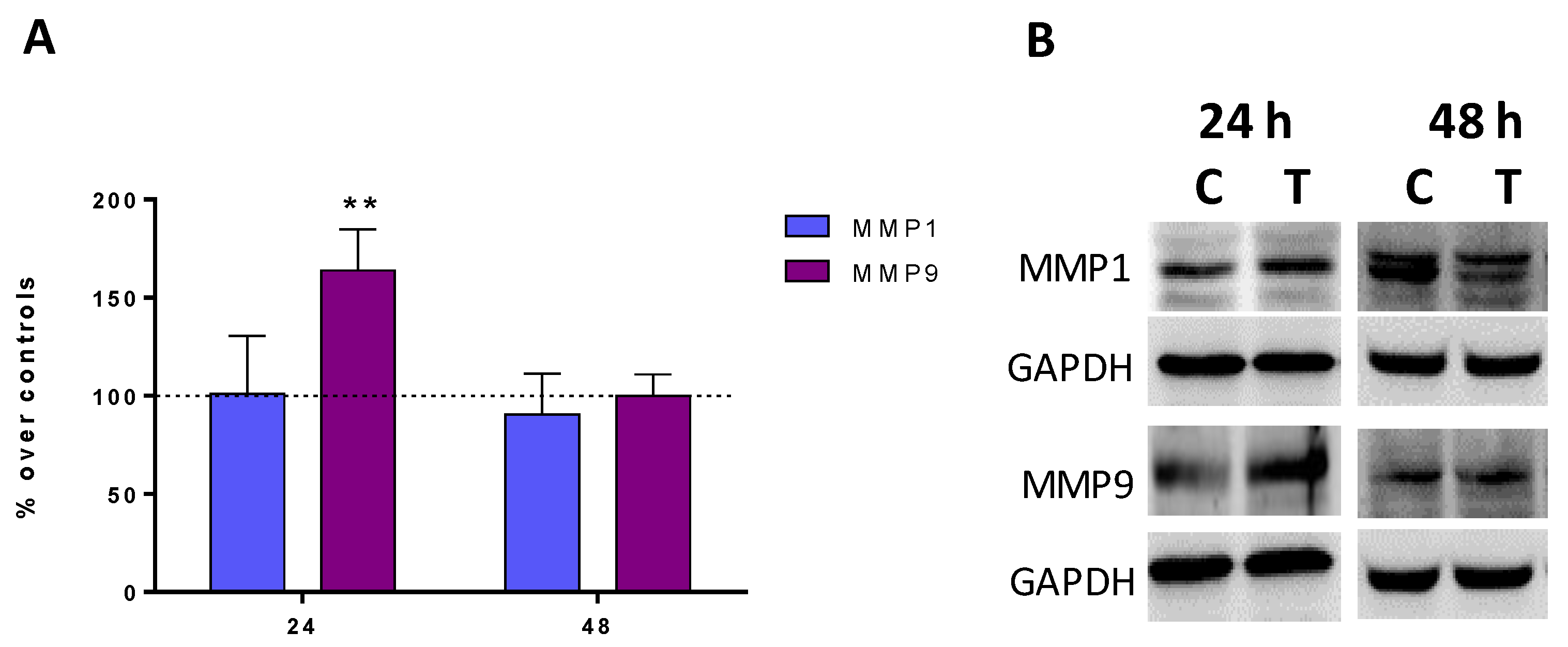
2.4. Expression of Metalloproteinases MMP1 and MMP9
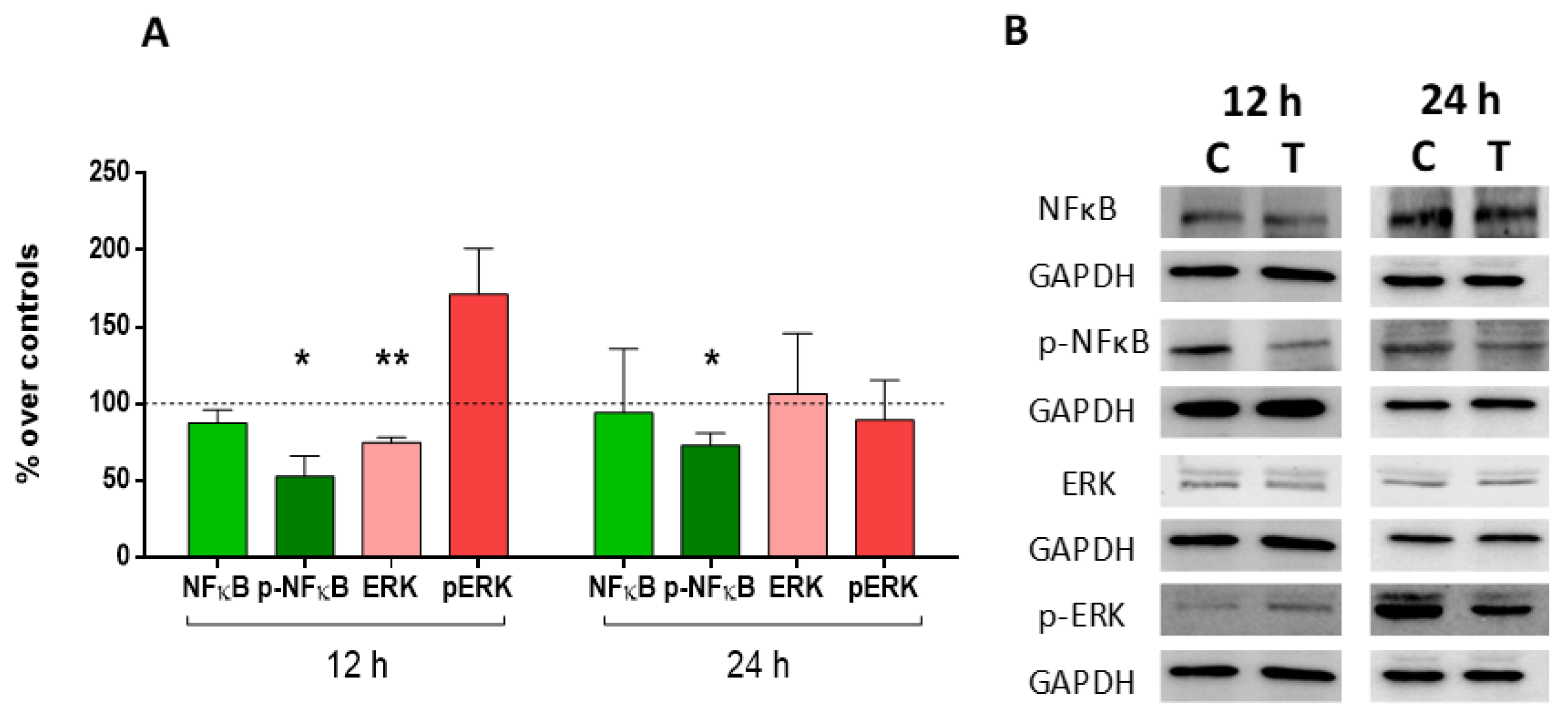
2.5. Expression and Activation of MAP-Kinase ERK1/2 and Nuclear Factor (NF)-Kappa B p65
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Electric Treatment
4.3. XTT Proliferation Assay
4.4. TUNEL Assay
4.5. Wound Assay
4.6. Immunofluorescence for α-SMA, Collagen Type I and Collagen Type III
4.7. Immunoblot for α-SMA, MMP1, MMP9, ERK, P-ERK, NF-κB and p-NF-κB
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, P.; Nunan, R. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Repair in Acute and Chronic Wound Healing. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Bule, M.L.; Toledano-Macías, E.; Naranjo, A.; de Andrés-Zamora, M.; Úbeda, A. In Vitro Stimulation with Radiofrequency Currents Promotes Proliferation and Migration in Human Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2021, 40, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Guarino, M.; Bacci, S.; Pérez González, L.A.; Bermejo-Martínez, M.; Cecilia-Matilla, A.; Hernández-Bule, M.L. The Role of Physical Therapies in Wound Healing and Assisted Scarring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.R.; Sultan, M.T.; Park, H.J.; Lee, J.M.; Ju, H.W.; Lee, O.J.; Lee, D.J.; Kaplan, D.L.; Park, C.H. NF-ΚB Signaling Is Key in the Wound Healing Processes of Silk Fibroin. Acta Biomater. 2018, 67, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Jang, Y.J. Recent Understandings of Biology, Prophylaxis and Treatment Strategies for Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, J.P.; Marttala, J.; Macarak, E.; Rosenbloom, J.; Uitto, J. Keloids: The Paradigm of Skin Fibrosis—Pathomechanisms and Treatment. Matrix Biol. 2016, 51, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinaik, R.; Barayan, D.; Auger, C.; Abdullahi, A.; Jeschke, M.G. Regulation of Glycolysis and the Warburg Effect in Wound Healing. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e138949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-C.; Zhao, W.-Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Sun, Q.; Shi, P.; Cai, J.-Q.; Shen, X.Z.; Tan, W.-Q. The Roles of Inflammation in Keloid and Hypertrophic Scars. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 603187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingzhi, Z.; Meirong, L.; Xiaobing, F. Biological Approaches for Hypertrophic Scars. Int. Wound J. 2020, 17, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Rinkevich, Y. Scars or Regeneration?—Dermal Fibroblasts as Drivers of Diverse Skin Wound Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-S.; Yosipovitch, G.; Chan, Y.-H.; Goh, C.-L. Pruritus, Pain, and Small Nerve Fiber Function in Keloids: A Controlled Study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, N.; Goldberg, D.J. Update on the Treatment of Scars. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2019, 18, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arno, A.I.; Gauglitz, G.G.; Barret, J.P.; Jeschke, M.G. Up-to-Date Approach to Manage Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars: A Useful Guide. Burns 2014, 40, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, N.M.; Melo, P.R.; Crema, V.O.; Mendonça, A.C. Effects of Radiofrequency Procedure on Hypertrophic Scar Due to Burns. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshkinpour, A.; Ghasri, P.; Pope, K.; Lyubovitsky, J.G.; Risteli, J.; Krasieva, T.B.; Kelly, K.M. Treatment of Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids with a Radiofrequency Device: A Study of Collagen Effects. Lasers Surg. Med. 2005, 37, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khedr, M.M.; Mahmoud, W.H.; Sallam, F.A.; Elmelegy, N. Comparison of Nd:YAG Laser and Combined Intense Pulsed Light and Radiofrequency in the Treatment of Hypertrophic Scars: A Prospective Clinico-Histopathological Study. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2020, 84, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelles, M.A.; Martínez-Carpio, P.A. Clinical and Histological Results in the Treatment of Atrophic and Hypertrophic Scars Using a Combined Method of Radiofrequency, Ultrasound, and Transepidermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, G.; Perugini, P.; Bellino, S.; Capra, P.; Malovini, A.; Jaber, O.; Tresoldi, M.; Faga, A. Scar Remodeling with the Association of Monopolar Capacitive Radiofrequency, Electric Stimulation, and Negative Pressure. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2017, 35, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, P.F.; de Oliveira, P.; Silva, F.K.B.A.; da Costa, A.C.S.; Pereira, C.R.A.; Casenave, S.; Valentim Silva, R.M.; Araújo-Neto, L.G.; Santos-Filho, S.D.; Aizamaque, E.; et al. Radiofrequency Treatment Induces Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 Expression and Subsequently Promotes Neocollagenesis and Neoangiogenesis in the Skin Tissue. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Bule, M.L.; Paíno, C.L.; Trillo, M.Á.; Úbeda, A. Electric Stimulation at 448 KHz Promotes Proliferation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Bule, M.L.; Angeles Trillo, M.; Martinez Garcia, M.A.; Abilahoud, C.; Ubeda, A. Chondrogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by Radiofrequency Electric Stimulation. J. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memariani, H.; Memariani, M.; Moravvej, H.; Shahidi-Dadras, M. Emerging and Novel Therapies for Keloids: A Compendious Review. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2021, 21, e22–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.-Q.; Wang, X.-F.; Zhao, W.-Y.; Ding, S.-L.; Shi, B.-H.; Xia, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, L.-H.; Li, C.-Y.; Tan, W.-Q. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Reduces Scar Formation by Inhibiting Both Canonical and Noncanonical TGF-Β1 Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-S.; Wu, P.-H.; Fang, A.-H.; Lan, C.-C.E. FK506 Inhibits the Enhancing Effects of Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)-Β1 on Collagen Expression and TGF-β/Smad Signalling in Keloid Fibroblasts: Implication for New Therapeutic Approach. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-J.; Ko, J.-Y.; Chou, W.-Y.; Cheng, J.-H.; Kuo, Y.-R. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Treatment of Keloid Scars. Wound Repair Regen. 2018, 26, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.S.; Hong, A.R.; Kim, J.-B.; Yu, J.H.; Cho, Y.S.; Joo, S.Y.; Seo, C.H. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Alters the Expression of Fibrosis-Related Molecules in Fibroblast Derived from Human Hypertrophic Scar. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Lopes, L.R.; Soares-Lopes, I.M.; Filho, L.L.; Alencar, A.P.; da Silva, B.B. Morphological and Morphometric Analysis of the Effects of Intralesional Tamoxifen on Keloids. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Miyake, K.; Ogawa, R.; Dohi, T.; Akaishi, S.; Hyakusoku, H.; Shimada, T. SiRNA Knockdown of Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 in Keloid Fibroblasts Leads to Degradation of Collagen Type I. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, D.; Colthurst, J.; Giddings, P.; McGrouther, D.A.; Morris, J.; Bayat, A. Treatment of Symptomatic Abnormal Skin Scars with Electrical Stimulation. J. Wound Care 2010, 19, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, G.; Cornaglia, A.I.; Faga, A.; Scevola, S. The Biological Effects of Quadripolar Radiofrequency Sequential Application: A Human Experimental Study. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2014, 32, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.-M.; Chen, Y.-S.; Harn, H.-J. The Versatile Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase for the Diverse Results of Fibrosis Treatment. Molecules 2019, 24, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, H.; Suga, H.; Aoi, N.; Kato, H.; Doi, K.; Kuno, S.; Tabata, Y.; Yoshimura, K. Therapeutic Potential of Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 for Hypertrophic Scars: Upregulation of MMP-1 and HGF Expression. Lab. Investig. 2012, 92, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Jackson, C.J. Extracellular Matrix Reorganization During Wound Healing and Its Impact on Abnormal Scarring. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yang, J. Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Inhibit Bioactivity of Keloid Fibroblasts. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Kuan-hong, S.; Hong-gang, W. Pressure Therapy Upregulates Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression and Downregulates Collagen Expression in Hypertrophic Scar Tissue. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 3321–3324. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, E.; Koo, E.; Jagdeo, J. The Cellular Response of Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars to Botulinum Toxin A: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 44, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Holeyfield, K.C.; Uitto, J. Doxorubicin-Induced Inhibition of Prolyl Hydroxylation during Collagen Biosynthesis in Human Skin Fibroblast Cultures. Relevance to Imparied Wound Healing. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 80, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, D.C.; Balmayor, E.R.; Schantz, J.-T.; Xu, C. Microneedle Physical Contact as a Therapeutic for Abnormal Scars. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2017, 22, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Huang, R.-L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, M.; Huo, R. Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit the Proliferative and Profibrotic Phenotype of Hypertrophic Scar Fibroblasts and Keloid Fibroblasts through Paracrine Signaling. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2016, 83, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-C.; Liou, S.-H.; Kotsuchibashi, Y. Development and Characterisation of the Imiquimod Poly(2-(2-Methoxyethoxy)Ethyl Methacrylate) Hydrogel Dressing for Keloid Therapy. Polymers 2017, 9, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liu, X.; Jin, Z. Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells-sourced Exosomal microRNA-7846-3p Suppresses Proliferation and Pro-angiogenic Role of Keloid Fibroblasts by Suppressing Neuropilin 2. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, ahead of print. [CrossRef]
- Linge, C.; Richardson, J.; Vigor, C.; Clayton, E.; Hardas, B.; Rolfe, K.J. Hypertrophic Scar Cells Fail to Undergo a Form of Apoptosis Specific to Contractile Collagen—The Role of Tissue Transglutaminase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, A.; Syed, F.; McGrouther, D.A.; Colthurst, J.; Paus, R.; Bayat, A. A Novel in Vitro Assay for Electrophysiological Research on Human Skin Fibroblasts: Degenerate Electrical Waves Downregulate Collagen I Expression in Keloid Fibroblasts. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Wortsman, J. Neuroendocrinology of the Skin1. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 457–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.T.; Slominski, R.M.; Raman, C.; Chen, J.Y.; Athar, M.; Elmets, C. Neuroendocrine Signaling in the Skin with a Special Focus on the Epidermal Neuropeptides. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C1757–C1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbytek, B.; Pfeffer, L.; Slominski, A. Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Stimulates NF-KappaB in Human Epidermal Keratinocytes. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 181, R1–R7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodeneva, N.; Sugimoto, M.A.; Davan-Wetton, C.S.A.; Montero-Melendez, T. Melanocortin Therapies to Resolve Fibroblast-Mediated Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1084394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Bule, M.L.; Trillo, M.A.; Cid, M.A.; Leal, J.; Ubeda, A. In Vitro Exposure to 0.57-MHz Electric Currents Exerts Cytostatic Effects in HepG2 Human Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 30, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Bule, M.L.; Trillo, M.Á.; Úbeda, A. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Antiproliferative and Differentiating Responses of Hepatocarcinoma Cells to Subthermal Electric Stimulation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Bule, M.L.; Martínez-Botas, J.; Trillo, M.Á.; Paíno, C.L.; Úbeda, A. Antiadipogenic Effects of Subthermal Electric Stimulation at 448 KHz on Differentiating Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Bule, M.L.; Toledano-Macías, E.; Pérez-González, L.A.; Martínez-Pascual, M.A.; Fernández-Guarino, M. Anti-Fibrotic Effects of RF Electric Currents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310986
Hernández-Bule ML, Toledano-Macías E, Pérez-González LA, Martínez-Pascual MA, Fernández-Guarino M. Anti-Fibrotic Effects of RF Electric Currents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):10986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310986
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Bule, María Luisa, Elena Toledano-Macías, Luis Alfonso Pérez-González, María Antonia Martínez-Pascual, and Montserrat Fernández-Guarino. 2023. "Anti-Fibrotic Effects of RF Electric Currents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 10986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310986
APA StyleHernández-Bule, M. L., Toledano-Macías, E., Pérez-González, L. A., Martínez-Pascual, M. A., & Fernández-Guarino, M. (2023). Anti-Fibrotic Effects of RF Electric Currents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 10986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310986





