Impact of Gut Recolonization on Liver Regeneration: Hepatic Matrisome Gene Expression after Partial Hepatectomy in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
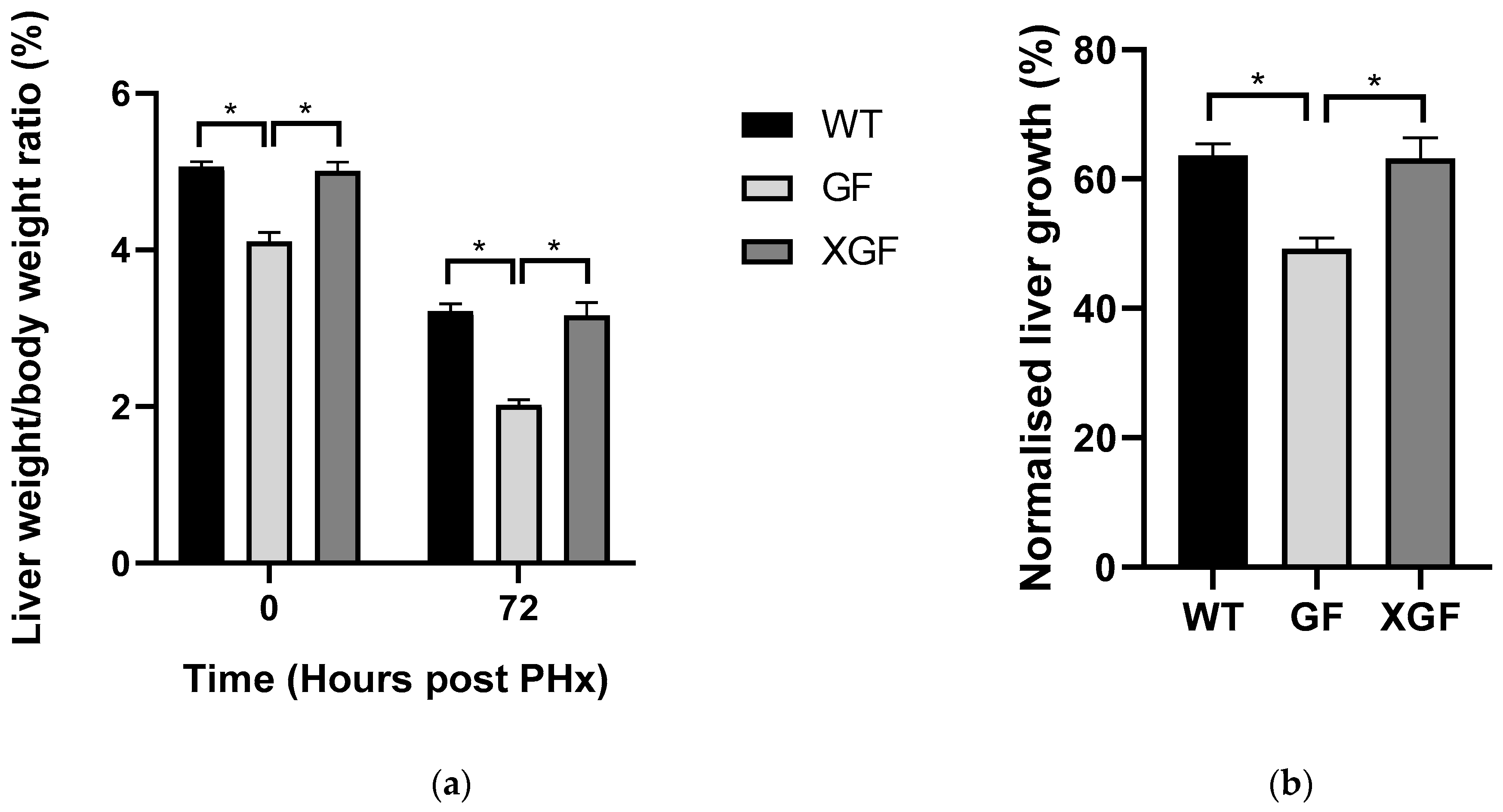
2.1. LW/BW Ratio and Liver Growth Percentage
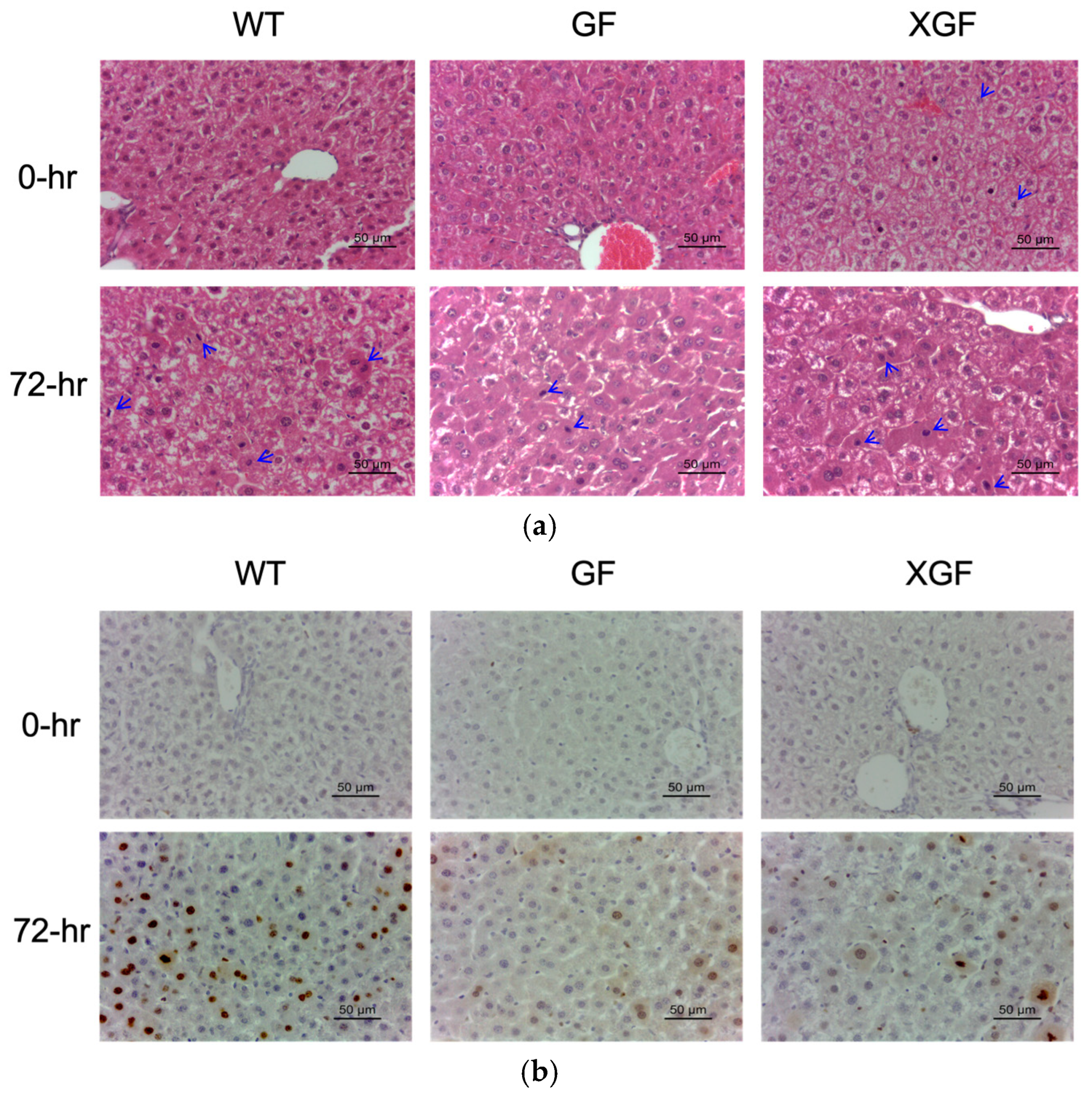
2.2. Proliferative Index
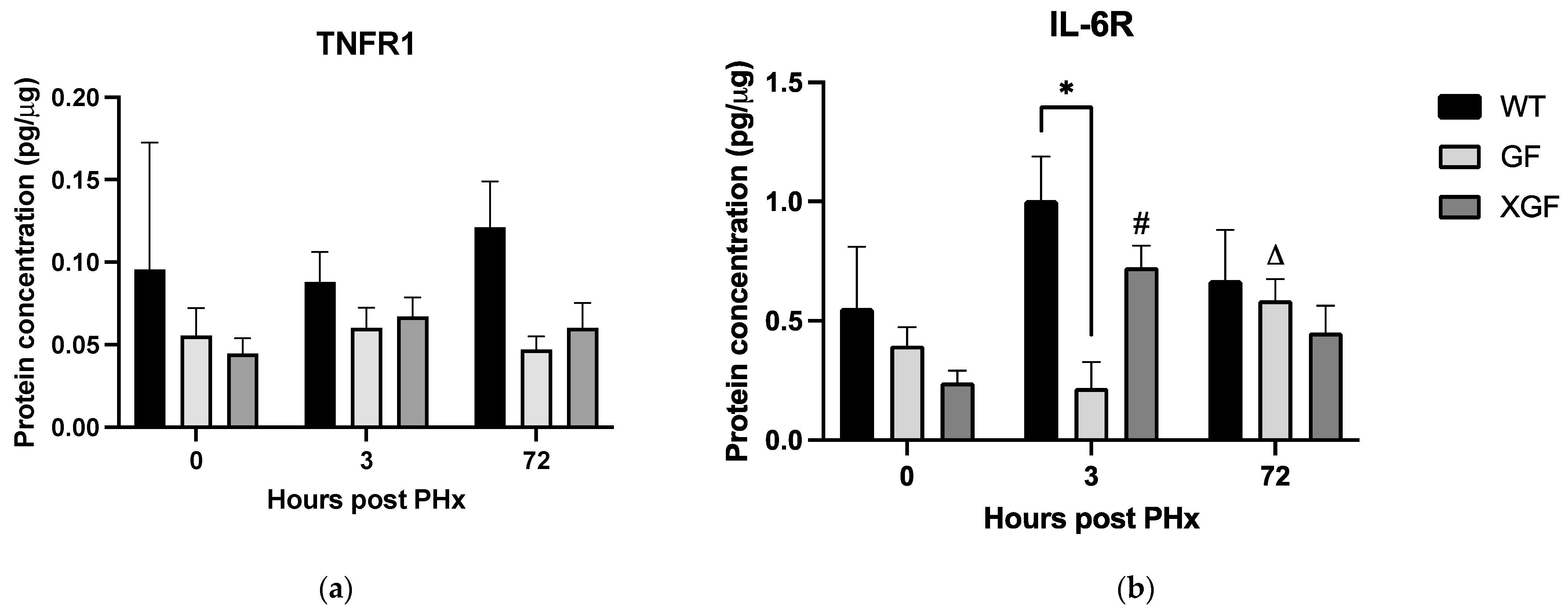
2.3. Cytokine and Growth Factor Responses
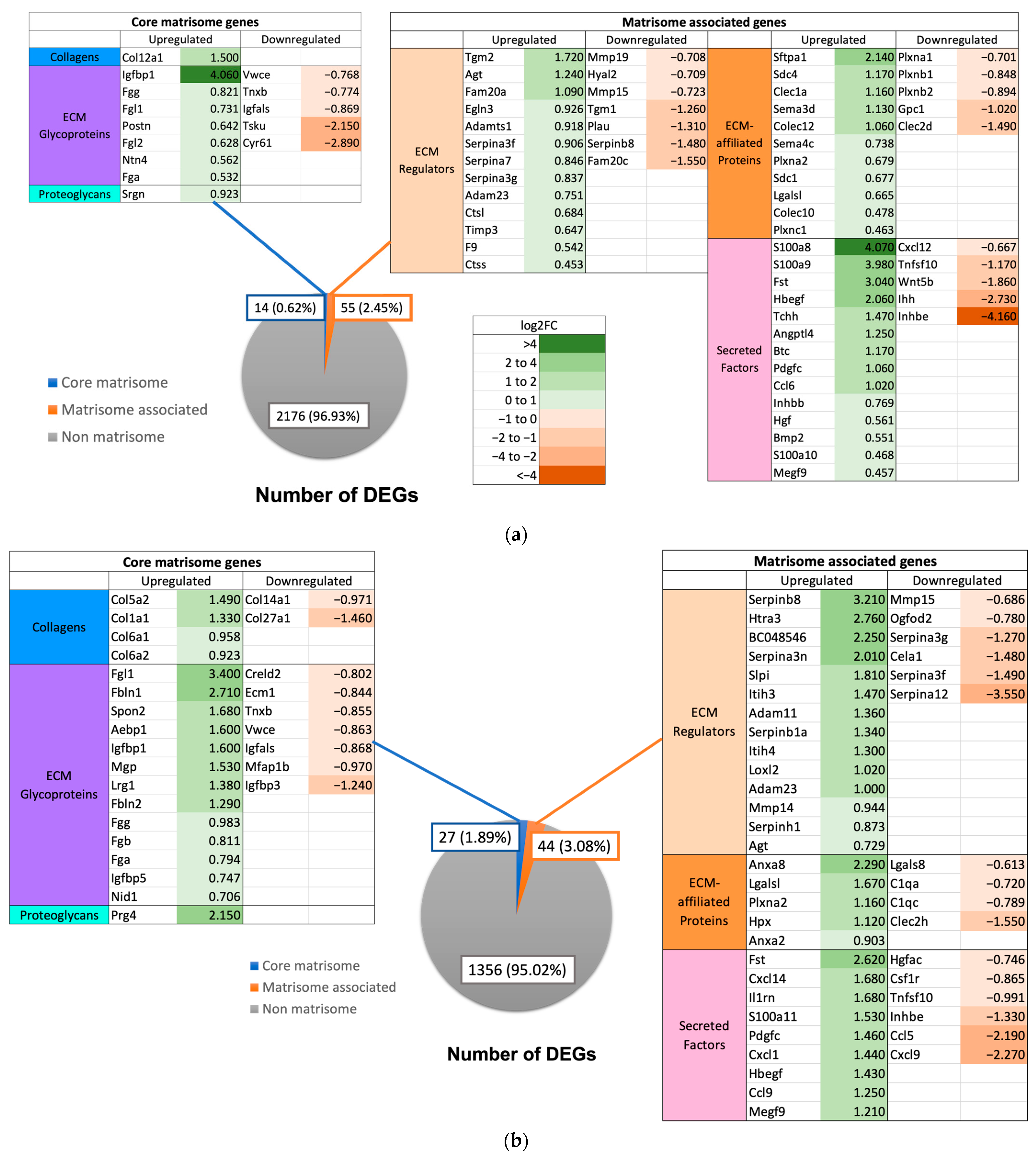
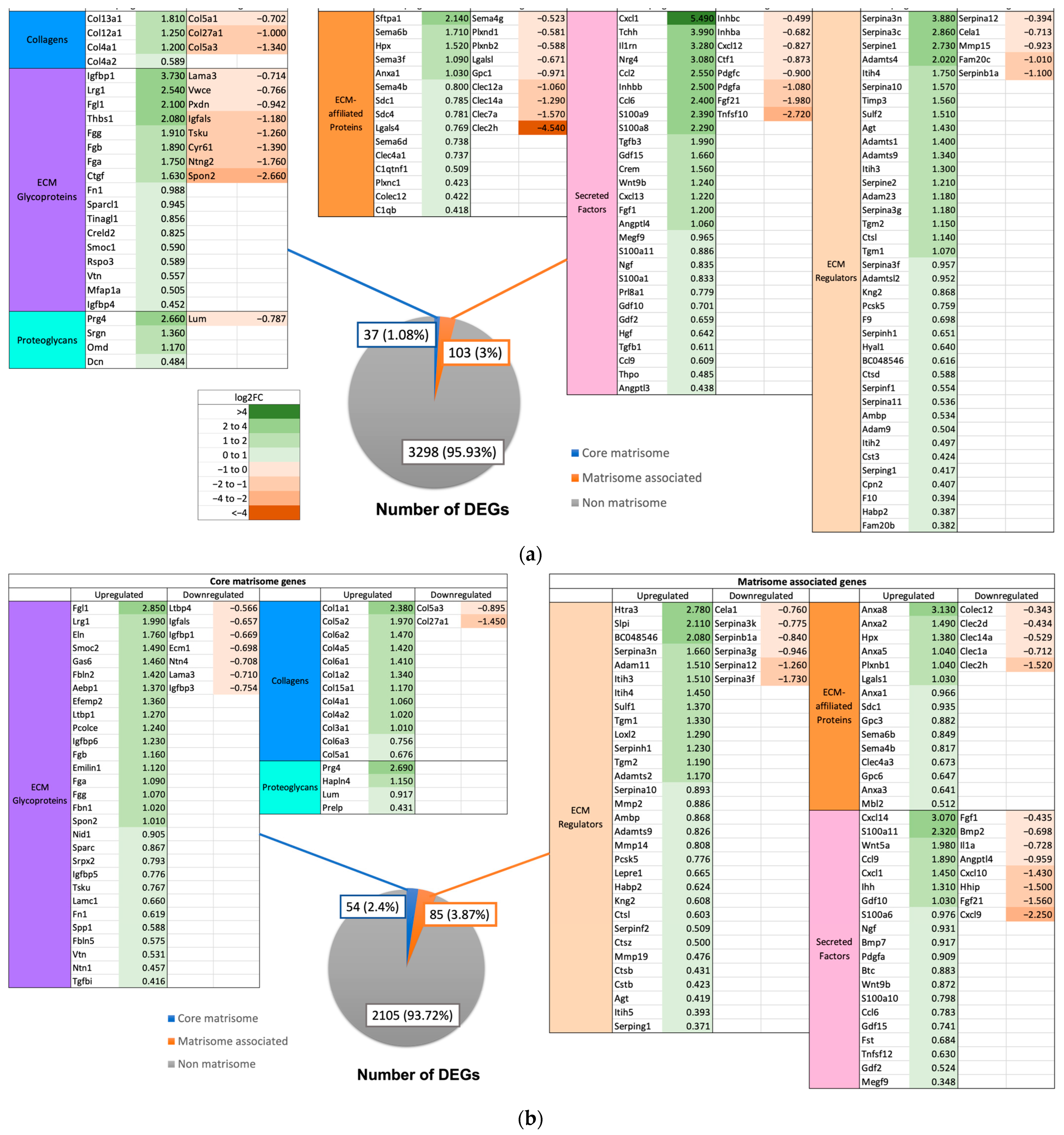
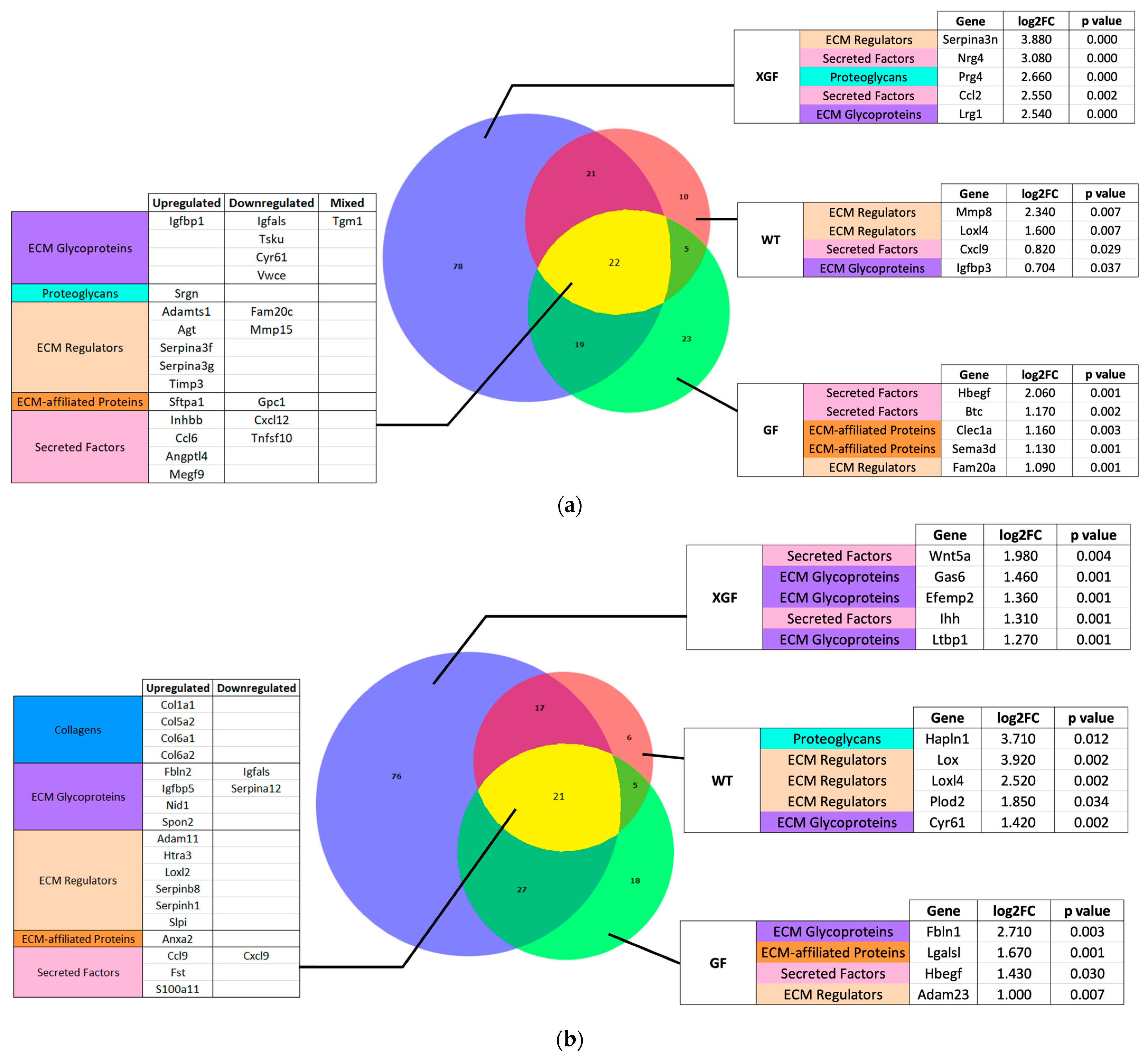
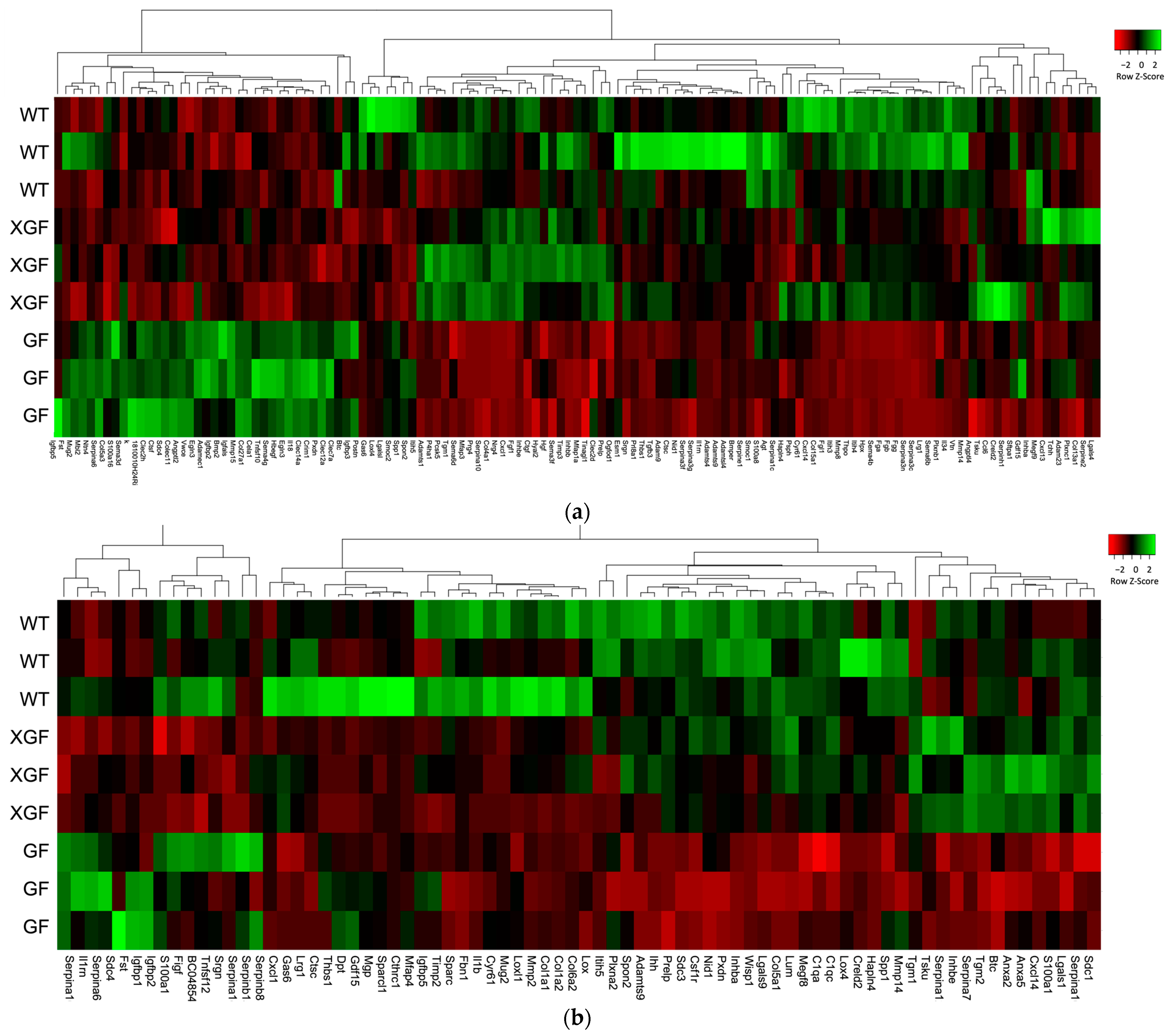
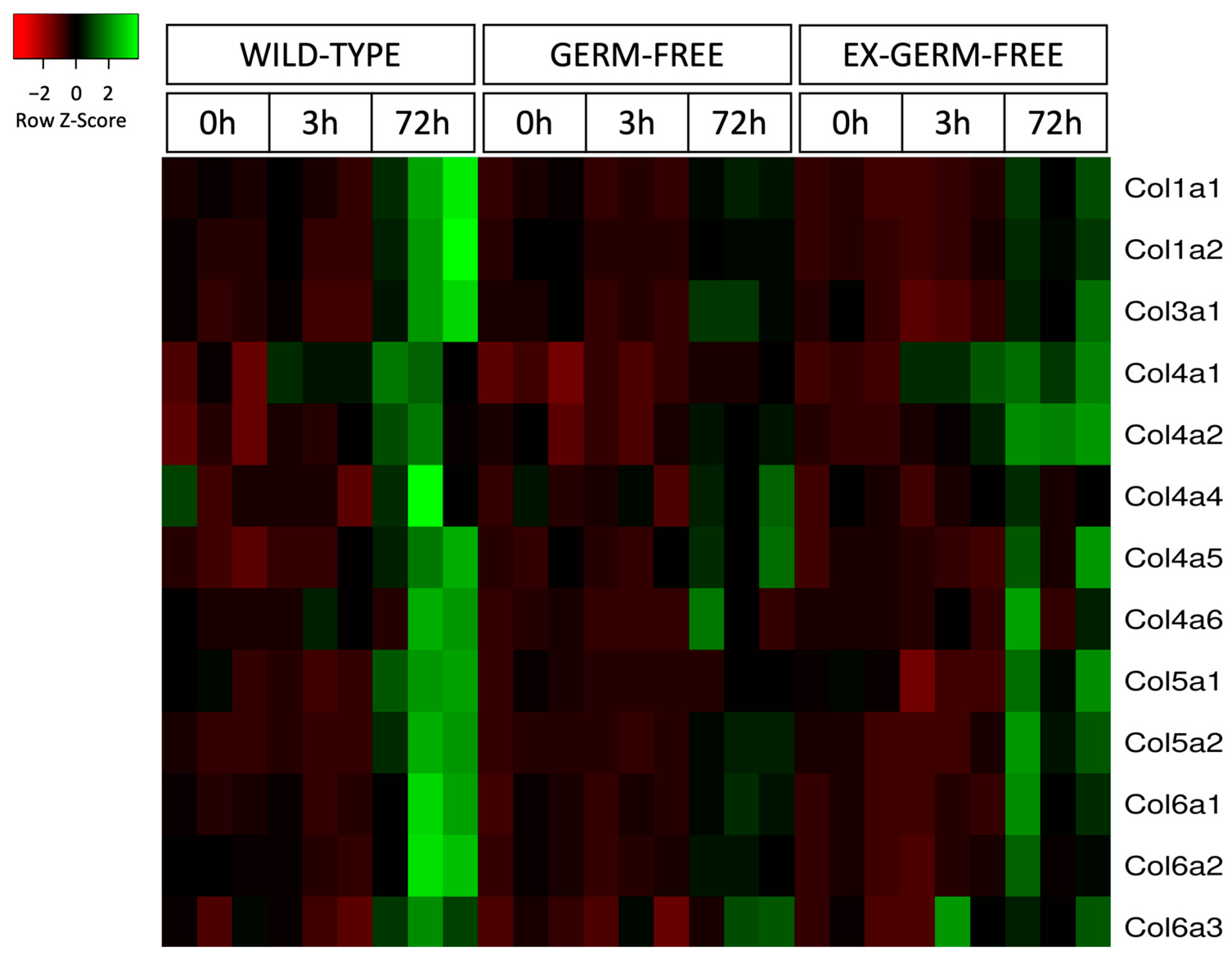
2.4. Expression of Matrisome Genes
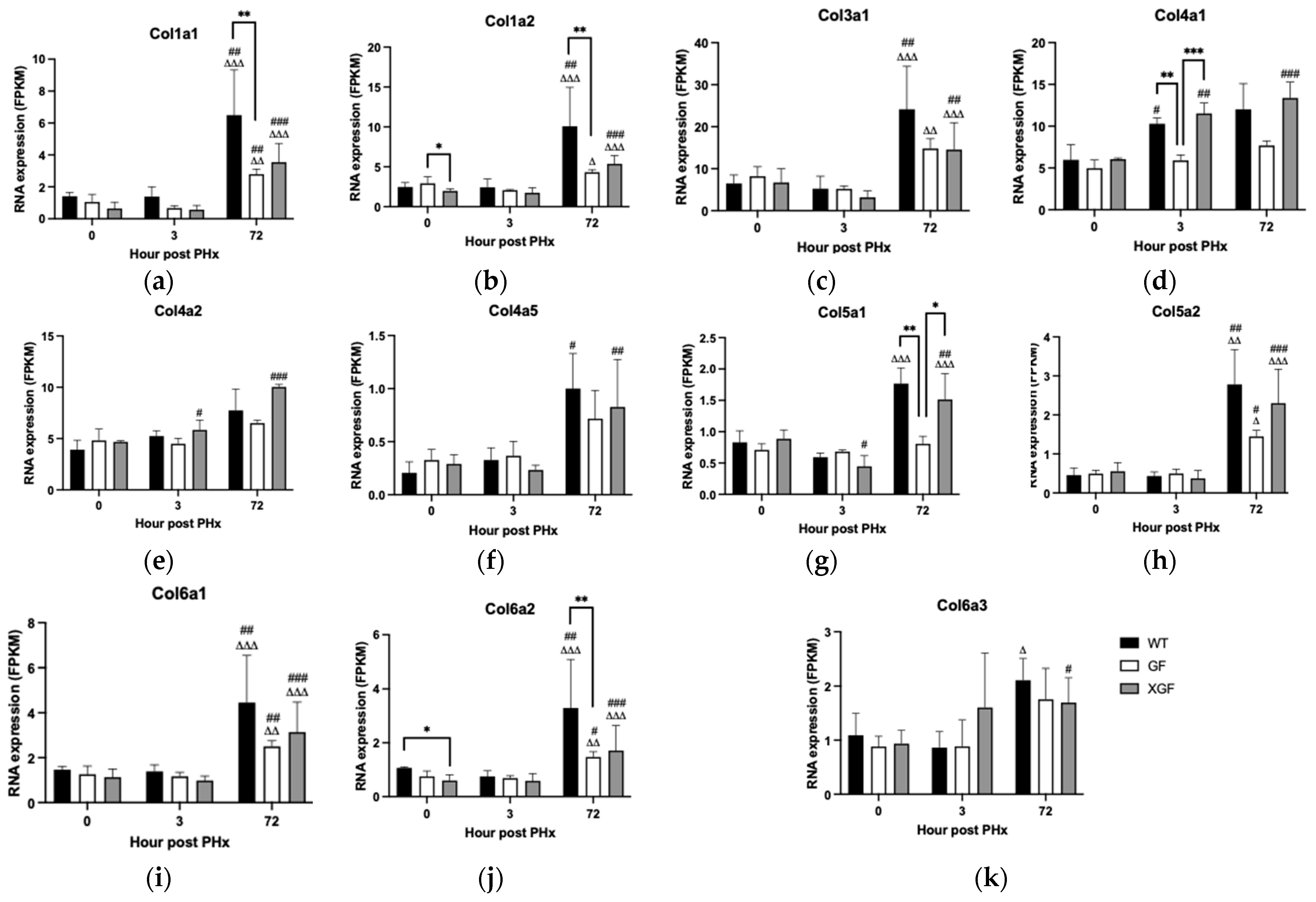
2.5. Expression of Collagen Genes
3. Discussion
3.1. Reduced Liver Mass Restoration, Hepatocyte Proliferation, and Immune Response in GF Mice
3.2. Improved Liver Regeneration in XGF Mice
3.3. Role of Cytokine Receptors in Liver Regeneration
3.4. Role of Matrisome in Liver Regeneration
3.5. Matrisome Expression in GF and XGF Mice
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Animal Ethics
4.3. Anesthetic Protocols
4.4. Partial Hepatectomy and Sampling of Tissues
4.5. Liver Weight/Body Weight Ratio (LW/BW)
4.6. Histology
4.6.1. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining, and Mitotic Count
4.6.2. Ki67 Immunohistochemical Staining and Proliferative Index
4.7. Protein Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
4.9. RNA Sequencing and Analysis
4.9.1. RNA Sequencing
4.9.2. Transcriptome Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fausto, N.; Campbell, J.S.; Riehle, K.J. Liver regeneration. Hepatology 2006, 43, S45–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, R. Liver regeneration: From myth to mechanism. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadri, A.-R.; Jeschke, M.G.; Amini-Nik, S. Cellular and Molecular Cascades during Liver Regeneration. Surg. Res. Open J. 2016, 2, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-X.; Keane, R.; Sheng, L.; Wan, Y.-J.Y. Implications of microbiota and bile acid in liver injury and regeneration. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.P.; Liljequist, B.L.; Bartizal, K.F. Depressed liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy of germ-free, athymic and lipopolysaccharide-resistant mice. Hepatology 1990, 11, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell, R.P. Restriction of gut-derived endotoxin impairs DNA synthesis for liver regeneration. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1985, 249, R563–R569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strey, C.W.; Markiewski, M.; Mastellos, D.; Tudoran, R.; Spruce, L.A.; Greenbaum, L.E.; Lambris, J.D. The Proinflammatory Mediators C3a and C5a Are Essential for Liver Regeneration. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-P.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.-C.; Han, D.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.-C. Dynamic changes and mechanism of intestinal endotoxemia in partially hepatectomized rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 3592–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, E.; Tang, H. Liver Regeneration: Analysis of the Main Relevant Signaling Molecules. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 4256352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mars, W. Immediate early detection of urokinase receptor after partial hepatectomy and its implications for initiation of liver regeneration. Hepatology 1995, 21, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalopoulos, G.K.; Bhushan, B. Liver regeneration: Biological and pathological mechanisms and implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.P. Gut-derived endotoxin elicits hepatotrophic factor secretion for liver regeneration. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1985, 249, R551–R562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlini, M.; Mabuchi, A.; Mallard, B.; Hairulhisyam, N.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Miyata, H.; Harper, J.; Wheatley, A. Impaired Liver Regenerative Response following Administration of Anti-TLR4 Antibody in Mice. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, Y.; Hongo, S.; Hikiba, Y.; Ohmura, K.; Nagura, T.; Okano, K.; Kamii, K.; Tanaka, T.; Komatsu, Y.; Ochiai, T.; et al. Role of macrophages in regeneration of liver. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1996, 41, 1939–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolin, C.E.; Arteel, G.E. The Matrisome, Inflammation, and Liver Disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2020, 40, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andez, A.M.; Amenta, P.S. The extracellular matrix in hepatic regeneration. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabuchi, A. Role of hepatic stellate cell/hepatocyte interaction and activation of hepatic stellate cells in the early phase of liver regeneration in the rat. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walesky, C.; Apte, U. Chapter 7—Mechanisms of Termination of Liver Regeneration. In Liver Regeneration; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouse-Smith, E.; Tzeng, A.; Starnbach, M.N. The Intestinal Flora Is Required to Support Antibody Responses to Systemic Immunization in Infant and Germ Free Mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sun, R.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Bai, L.; Lian, Z.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Oral ampicillin inhibits liver regeneration by breaking hepatic innate immune tolerance normally maintained by gut commensal bacteria. Hepatology 2015, 62, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C.L.; Dong, J.; Galipeau, H.J.; Jury, J.; McCarville, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.-Y.; Naidoo, A.; Anbazhagan, A.N.; Libertucci, J.; et al. Commensal microbiota induces colonic barrier structure and functions that contribute to homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalopoulos, G.K. Principles of Liver Regeneration and Growth Homeostasis. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 485–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, F.; Köhler, U.A.; Speicher, T.; Werner, S. Regulation of liver regeneration by growth factors and cytokines. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, M. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of liver regeneration: Proliferation, growth, death and protection of hepatocytes. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 100, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Mars, W.M.; Stolz, D.B.; Petersen, B.E.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Extracellular matrix remodeling at the early stages of liver regeneration in the rat. Hepatology 1997, 26, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-H.; Mars, W.M.; Stolz, D.B.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Expression and activation of pro-MMP-2 and pro-MMP-9 during rat liver regeneration. Hepatology 2000, 31, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, F.F.; Smookler, D.S.; Taylor, S.E.M.; Fingleton, B.; Kassiri, Z.; Sanchez, O.H.; English, J.L.; Matrisian, L.M.; Au, B.; Yeh, W.-C.; et al. Abnormal TNF activity in Timp3−/− mice leads to chronic hepatic inflammation and failure of liver regeneration. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, F.F.; Pennington, C.J.; Kassiri, Z.; Rubin, J.S.; Soloway, P.D.; Ruther, U.; Edwards, D.R.; Khokha, R. Metalloproteinase inhibitor TIMP-1 affects hepatocyte cell cycle via HGF activation in murine liver regeneration. Hepatology 2005, 41, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaas, M.; Kangur, T.; Viil, J.; Mäemets-Allas, K.; Minajeva, A.; Vadi, K.; Antsov, M.; Lapidus, N.; Järvekülg, M.; Jaks, V. The alterations in the extracellular matrix composition guide the repair of damaged liver tissue. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, H.M.; Li, W. Lysyl oxidase: Properties, specificity, and biological roles inside and outside of the cell. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 88, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.R.; Erler, J.T. The Importance of LOX Family Members on Modulating Cell-ECM Interactions in Carcinogenesis. J. Carcinog. Mutagen. 2013, S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, S.P.; Ellero, S.L.; Berger, B.; Krause, L.; Bruttin, A.; Molina, J.; Paris, A.; Want, E.J.; de Waziers, I.; Cloarec, O.; et al. Colonization-Induced Host-Gut Microbial Metabolic Interaction. mBio 2011, 2, e00271-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roy, T.; Llopis, M.; Lepage, P.; Bruneau, A.; Rabot, S.; Bevilacqua, C.; Martin, P.; Philippe, C.; Walker, F.; Bado, A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota determines development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut 2012, 62, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; Jorquera, F.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Functional Interactions between Gut Microbiota Transplantation, Quercetin, and High-Fat Diet Determine Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Development in Germ-Free Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Xue, X.; Deng, L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, C. Genetically obese human gut microbiota induces liver steatosis in germ-free mice fed on normal diet. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Pachter, L.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; Van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, A.R.; Hairulhisyam, N.M.; Aqilah, R.N.F.; Nur Fariha, M.M.; Mallard, B.L.; Shanahan, F.; Wheatley, A.M.; Marlini, M. Impact of Gut Recolonization on Liver Regeneration: Hepatic Matrisome Gene Expression after Partial Hepatectomy in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310774
Amin AR, Hairulhisyam NM, Aqilah RNF, Nur Fariha MM, Mallard BL, Shanahan F, Wheatley AM, Marlini M. Impact of Gut Recolonization on Liver Regeneration: Hepatic Matrisome Gene Expression after Partial Hepatectomy in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):10774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310774
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Abdul Rahman, Ngatiman M. Hairulhisyam, Raman Nur Fatin Aqilah, Mohd Manzor Nur Fariha, Beth L. Mallard, Fergus Shanahan, Antony M. Wheatley, and Muhamad Marlini. 2023. "Impact of Gut Recolonization on Liver Regeneration: Hepatic Matrisome Gene Expression after Partial Hepatectomy in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 10774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310774
APA StyleAmin, A. R., Hairulhisyam, N. M., Aqilah, R. N. F., Nur Fariha, M. M., Mallard, B. L., Shanahan, F., Wheatley, A. M., & Marlini, M. (2023). Impact of Gut Recolonization on Liver Regeneration: Hepatic Matrisome Gene Expression after Partial Hepatectomy in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 10774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310774





