Microneedle-Integrated Sensors for Extraction of Skin Interstitial Fluid and Metabolic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MN Structure Designs
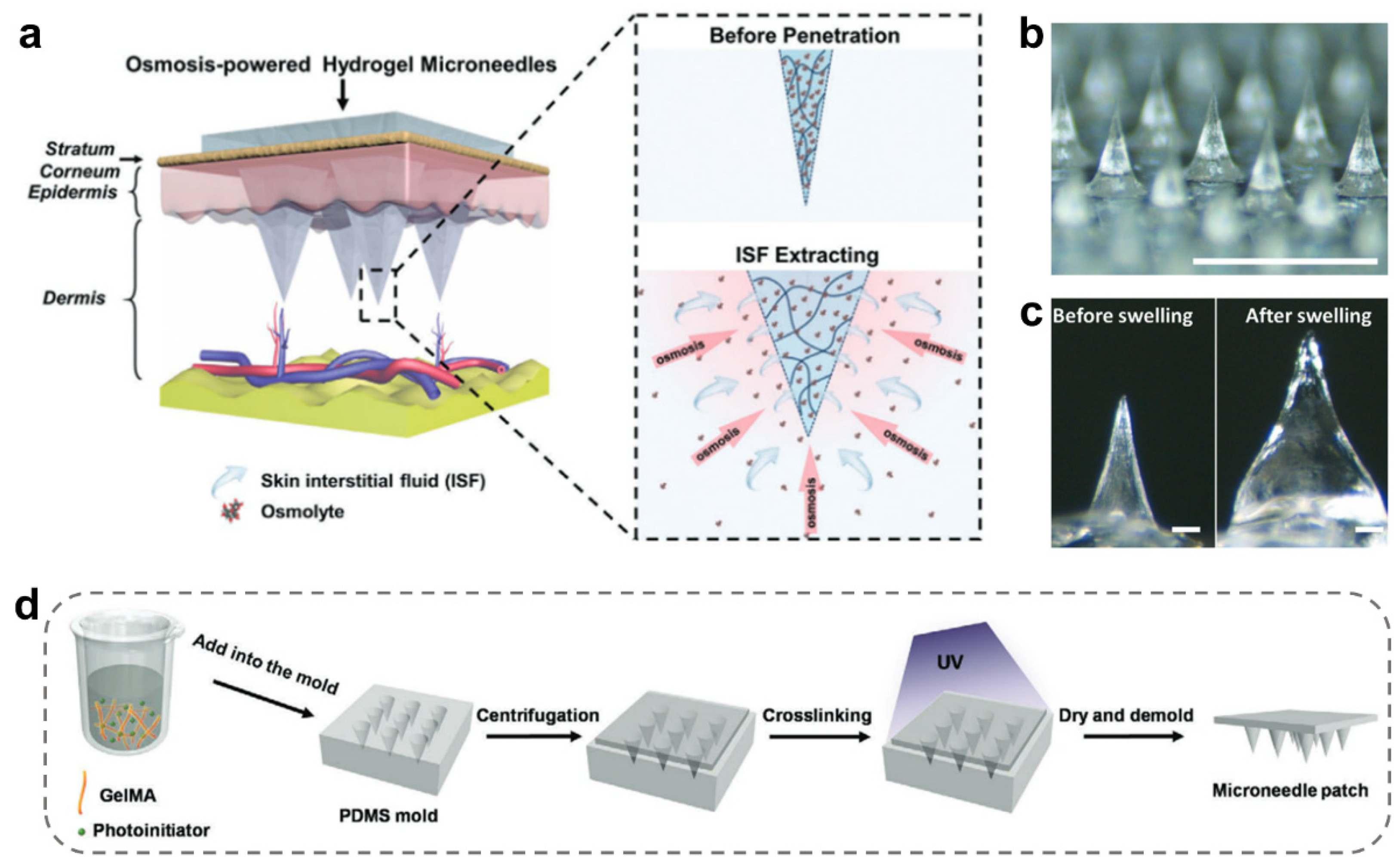
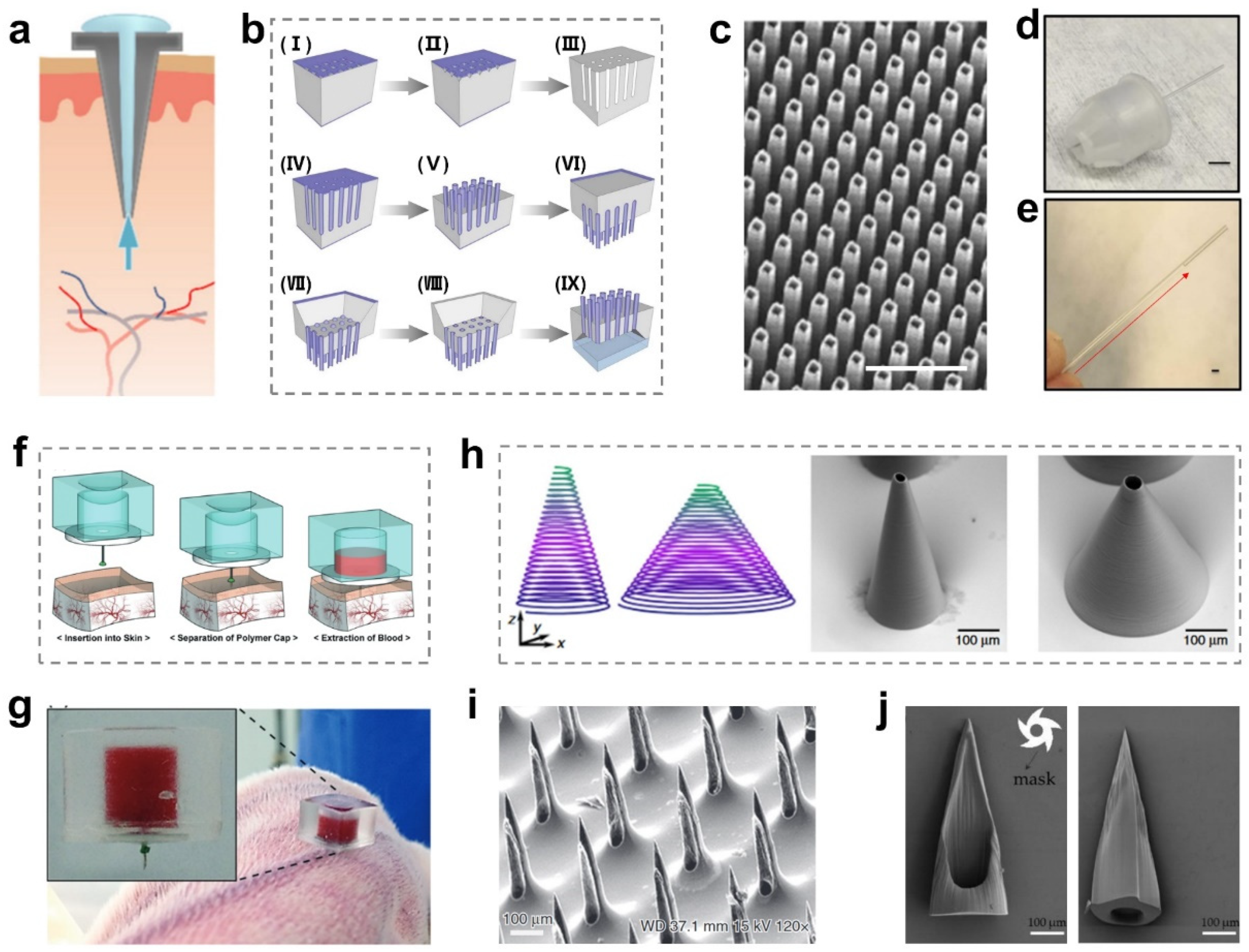
2.1. Solid MNs
2.2. Hollow MNs
2.3. Porous MNs
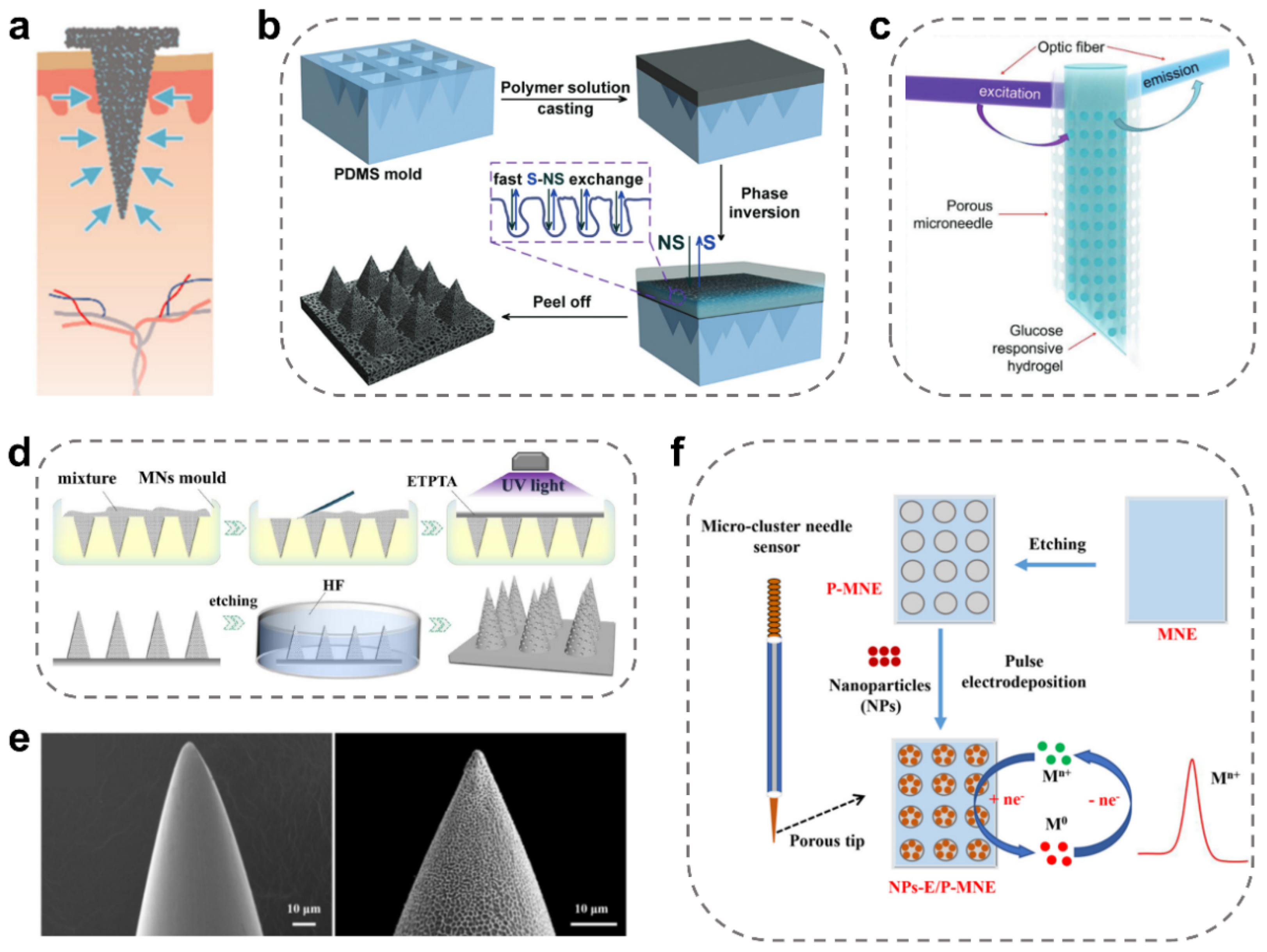
2.4. Coated MNs
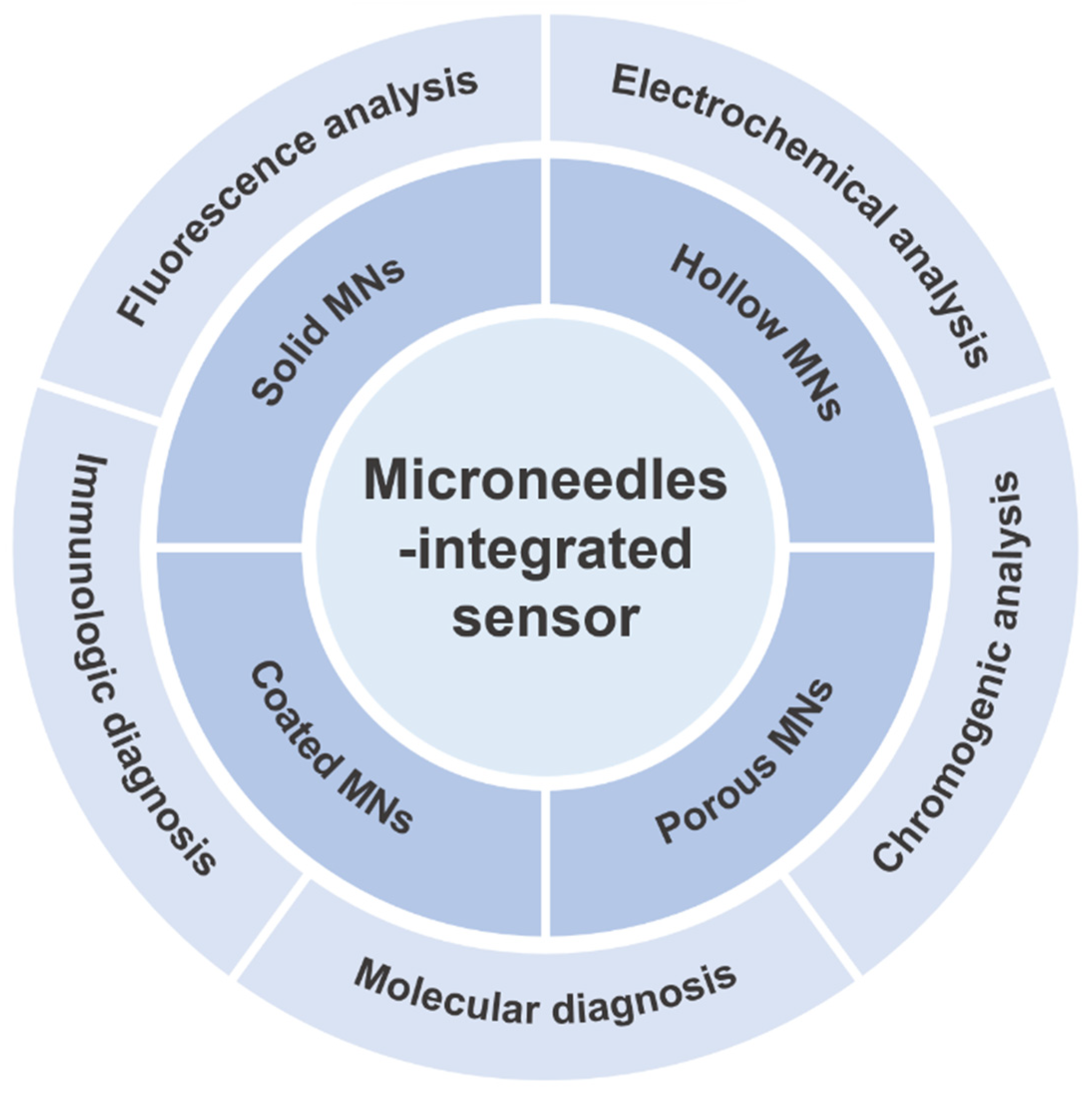
3. Construction of MN-Integrated Sensors
3.1. Electrochemical MN-Integrated Sensors
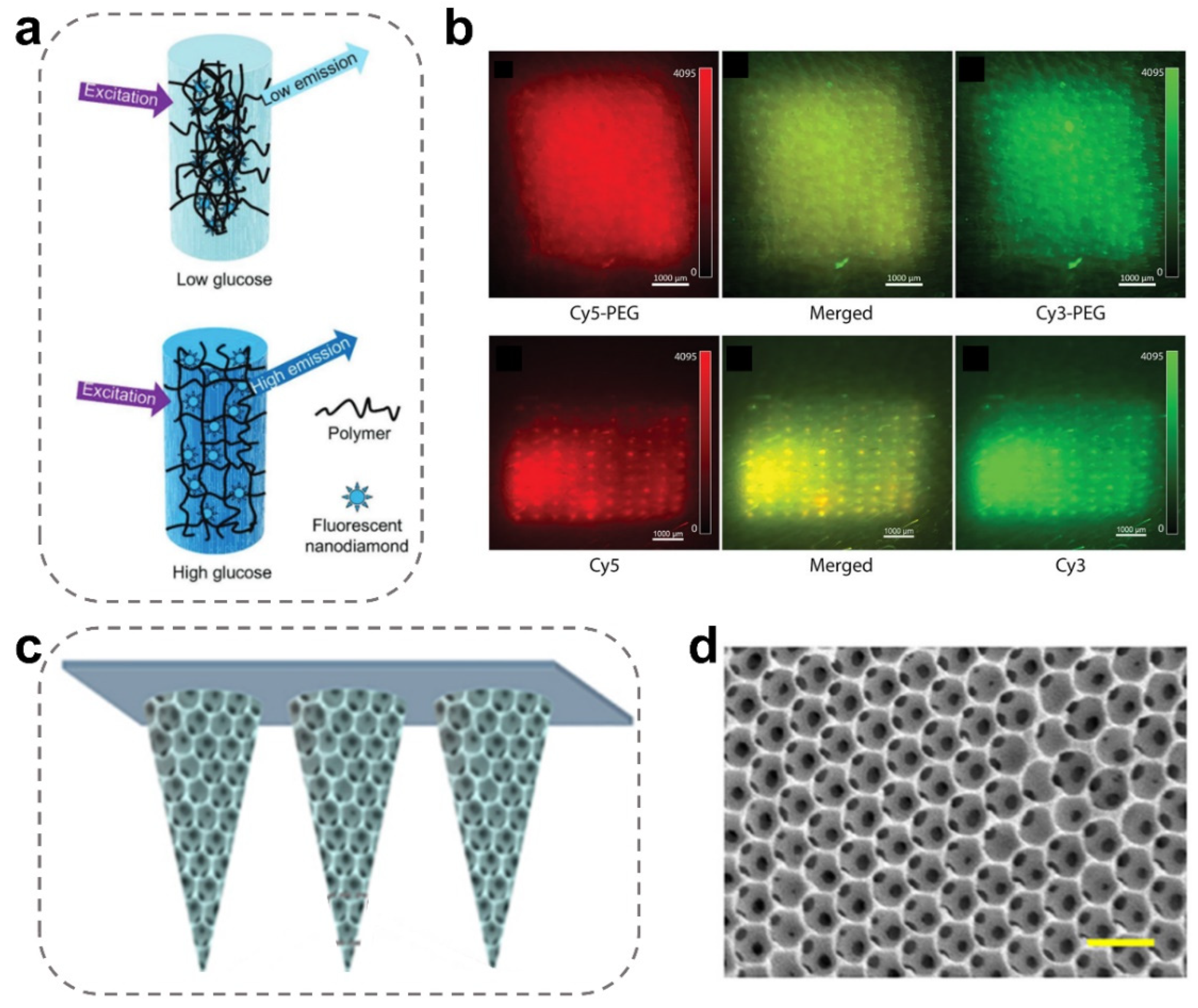
3.2. Fluorescent MN-Integrated Sensors
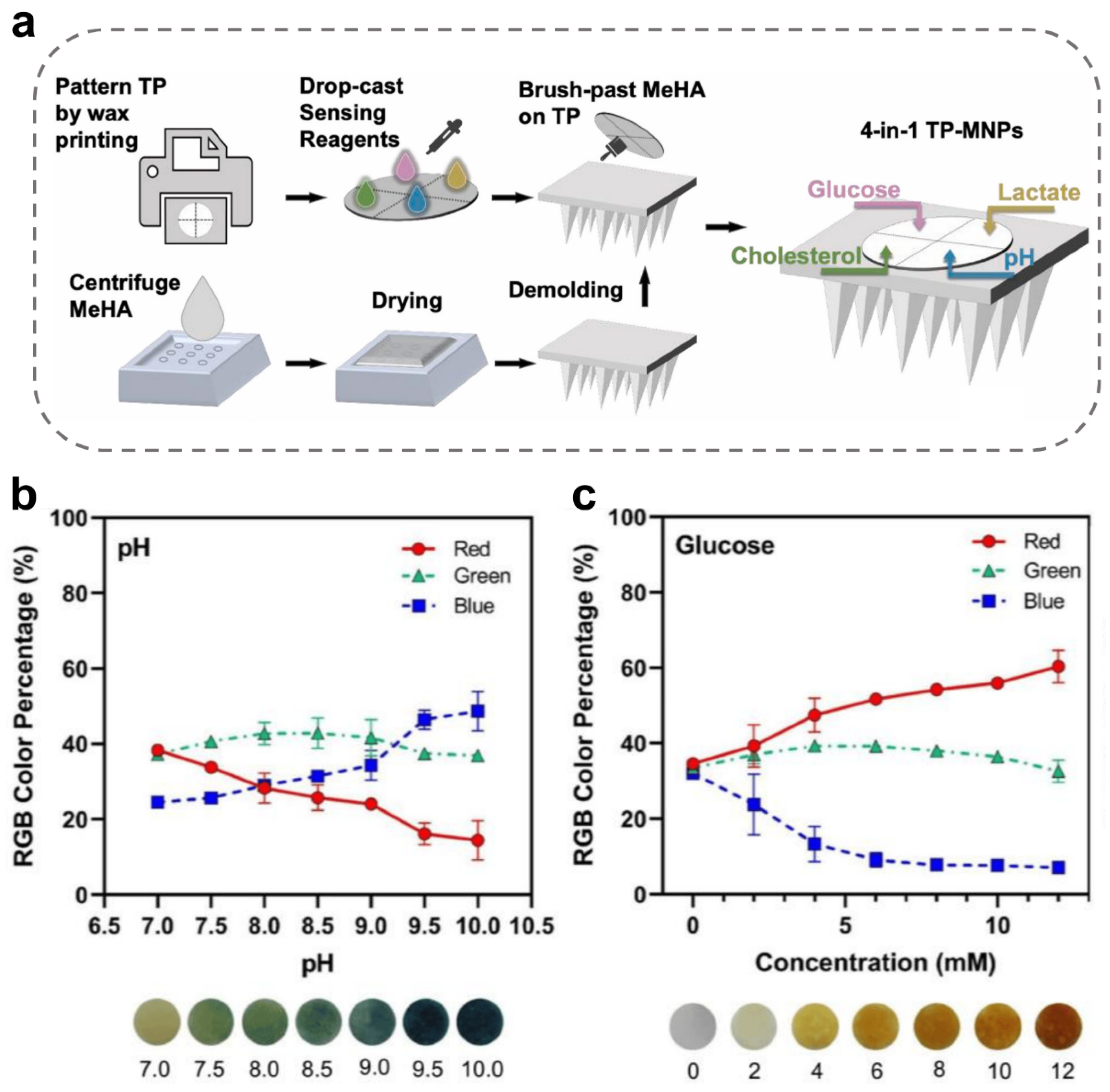
3.3. Chemical Chromogenic MN-Integrated Sensors
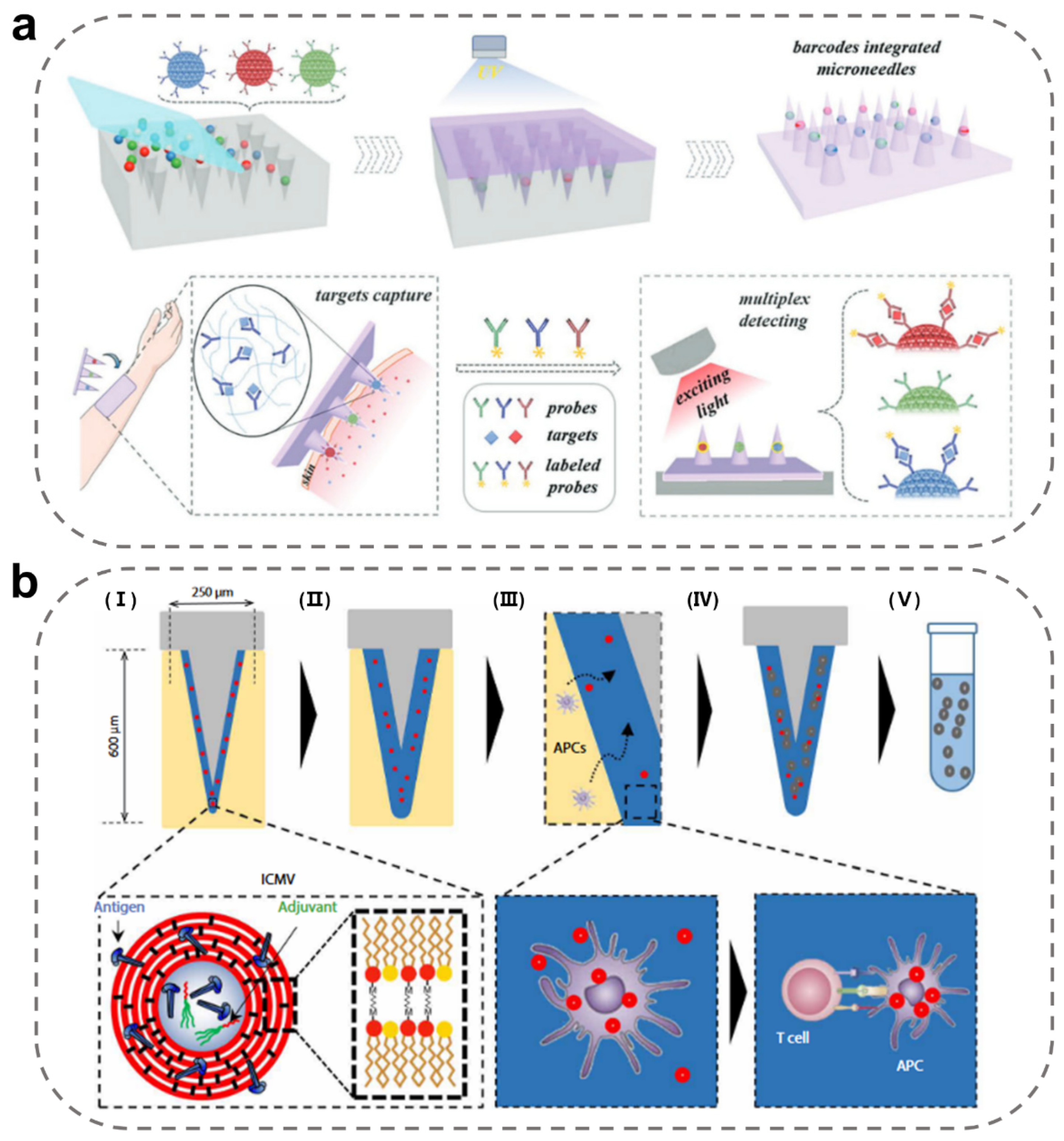
3.4. Immunodiagnostic MN-Integrated Sensors
3.5. Molecular Diagnostic MN-Integrated Sensors
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sim, D.; Brothers, M.C.; Slocik, J.M.; Islam, A.E.; Maruyama, B.; Grigsby, C.C.; Naik, R.R.; Kim, S.S. Biomarkers and Detection Platforms for Human Health and Performance Monitoring: A Review. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedel, M.; Thompson, I.A.P.; Kasting, G.; Polsky, R.; Cunningham, D.; Soh, H.T.; Heikenfeld, J. Opportunities and challenges in the diagnostic utility of dermal interstitial fluid. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Tehrani, F.; Mahato, K.; Wang, J. Lab under the Skin: Microneedle Based Wearable Devices. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2002255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; He, M.; Yao, C.; Huang, X.; Ma, D.; Huang, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, F.; Wen, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Petromyzontidae-Biomimetic Multimodal Microneedles-Integrated Bioelectronic Catheters for Theranostic Endoscopic Surgery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, E.; Palomäki, T.; Ruuth, I.A.; Boeva, Z.A.; Nurminen, T.A.; Vänskä, R.T.; Zschaechner, L.K.; Pérez, A.G.; Hakala, T.A.; Wardale, M.; et al. Influence of enzyme immobilization and skin-sensor interface on non-invasive glucose determination from interstitial fluid obtained by magnetohydrodynamic extraction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 206, 114123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.R.; Taylor, R.M.; Tran, B.Q.; Boyd, G.; Glaros, T.; Chavez, V.H.; Krishnakumar, R.; Sinha, A.; Poorey, K.; Williams, K.P.; et al. Extraction and biomolecular analysis of dermal interstitial fluid collected with hollow microneedles. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, V.F.J.; Ashton, N.J.; Posti, J.P.; Glocker, B.; Manktelow, A.; Chatfield, D.A.; Winzeck, S.; Needham, E.; Correia, M.M.; Williams, G.B.; et al. Post-acute blood biomarkers and disease progression in traumatic brain injury. Brain 2022, 145, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, R.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Haick, H. Microneedle Sensors for Multiplex Applications: Toward Advanced Biomedical and Environmental Analysis. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, 2, 2200032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrycko, A.; Mateu-Gelabert, P.; Ciervo, C.; Linn-Walton, R.; Eckhardt, B. Severe bacterial infections in people who inject drugs: The role of injection-related tissue damage. Harm. Reduct. J. 2022, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbar, L.; Yee, J. Current Concepts in Hemodialysis Vascular Access Infections. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019, 26, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noushin, T.; Tabassum, S. WRRIST: A wearable, rapid, and real-time infection screening tool for dual-mode detection of inflammatory biomarkers in sweat. Microfluid. BioMEMS Med. Microsyst. 2022, 11955, 1195502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xia, Z.; Fodjo, E.K.; Deng, W.; Li, D. A dual-responsive nanozyme sensor with ultra-high sensitivity and ultra-low cross-interference towards metabolic biomarker monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 3023–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiko, G. Feasibility of Skin Water Content Imaging Using CMOS Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdel, N.; Hjort, K.; Sperlich, B.; Holmberg, H.-C.; Supej, M. Use of smart patches by athletes: A concise SWOT analysis. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashaninejad, N.; Nguyen, N.-T. Microfluidic solutions for biofluids handling in on-skin wearable systems. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 913–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiig, H.; Heir, S.; Aukland, K. Colloid osmotic pressure of interstitial fluid in rat subcutis and skeletal muscle: Comparison of various wick sampling techniques. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1988, 133, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laszlo, E.; De Crescenzo, G.; Nieto-Argüello, A.; Banquy, X.; Brambilla, D. Superswelling Microneedle Arrays for Dermal Interstitial Fluid (Prote)Omics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samant, P.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Mechanisms of sampling interstitial fluid from skin using a microneedle patch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noddeland, H. Colloid osmotic pressure of human subcutaneous interstitial fluid sampled by nylon wicks: Evaluation of the method. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1982, 42, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, G.C.; Sibley, L.; Aukland, K.; Renkin, E.M. Wick sampling of interstitial fluid in rat skin: Further analysis and modifications of the method. Microvasc. Res. 1986, 32, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svedman, C.; Yu, B.B.; Ryan, T.J.; Svensson, H. Plasma proteins in a standardised skin mini-erosion (II): Effects of extraction pressure. BMC Dermatol. 2002, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodley, D.; Sauder, D.; Talley, M.J.; Silver, M.; Grotendorst, G.; Qwarnstrom, E. Localization of Basement Membrane Components After Dermal-Epidermal Junction Separation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1983, 81, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, S.R.; Poulos, J.T.; Rainier, J.B.; Zopp, W.E.; Janle, E.; Kissinger, P.T. Subcutaneous capillary filtrate collector for measurement of blood glucose. ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs. 1992, 38, M416–M420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nightingale, A.M.; Leong, C.L.; Burnish, R.A.; Hassan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Clough, G.F.; Boutelle, M.G.; Voegeli, D.; Niu, X. Monitoring biomolecule concentrations in tissue using a wearable droplet microfluidic-based sensor. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collison, M.E.; Stout, P.J.; Glushko, T.S.; Pokela, K.N.; Mullins-Hirte, D.J.; Racchini, J.R.; Walter, M.A.; Mecca, S.P.; Rundquist, J.; Allen, J.J.; et al. Analytical Characterization of Electrochemical Biosensor Test Strips for Measurement of Glucose in Low-Volume Interstitial Fluid Samples. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, M.J.; Jayalakshmi, Y.; Parris, N.A.; Reidy, M.P.; Uhegbu, C.; Vijayakumar, P. Design of a Biosensor for Continual, Transdermal Glucose Monitoring. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 1681–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikenfeld, J.; Jajack, A.; Feldman, B.; Granger, S.W.; Gaitonde, S.; Begtrup, G.; Katchman, B.A. Accessing analytes in biofluids for peripheral biochemical monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouissou, C.C.; Sylvestre, J.-P.; Guy, R.H.; Delgado-Charro, M.B. Reverse Iontophoresis of Amino Acids: Identification and Separation of Stratum Corneum and Subdermal Sources In Vitro. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2630–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhart, S.; Faupel, M.; Fowler, R.; Kapsner, C.; Lincoln, D.; McGee, V.; Pasqua, J.; Steed, L.; Wangsness, M.; Xu, F.; et al. Glucose Sensing in Transdermal Body Fluid Collected Under Continuous Vacuum Pressure Via Micropores in the Stratum Corneum. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2004, 5, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttaswamy, S.V.; Lubarsky, G.V.; Kelsey, C.; Zhang, X.; Finlay, D.; McLaughlin, J.A.; Bhalla, N. Nanophotonic-Carbohydrate Lab-on-a-Microneedle for Rapid Detection of Human Cystatin C in Finger-Prick Blood. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 11939–11949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Guzmán, J.J.; Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Cuartero, M.; Crespo, G.A. Toward In Vivo Transdermal pH Sensing with a Validated Microneedle Membrane Electrode. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heifler, O.; Borberg, E.; Harpak, N.; Zverzhinetsky, M.; Krivitsky, V.; Gabriel, I.; Fourman, V.; Sherman, D.; Patolsky, F. Clinic-on-a-Needle Array toward Future Minimally Invasive Wearable Artificial Pancreas Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12019–12033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harpak, N.; Borberg, E.; Raz, A.; Patolsky, F. The “Bloodless” Blood Test: Intradermal Prick Nanoelectronics for the Blood Extraction-Free Multiplex Detection of Protein Biomarkers. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 13800–13813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; GhavamiNejad, A.; GhavamiNejad, P.; Samarikhalaj, M.; Giacca, A.; Poudineh, M. Hydrogel Microneedle-Assisted Assay Integrating Aptamer Probes and Fluorescence Detection for Reagentless Biomarker Quantification. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 2387–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.V.; Skaria, E.; Lau, W.M.; Manning, P.; Birch-Machin, M.A.; Moghimi, S.M.; Ng, K.W. Microneedle-based devices for point-of-care infectious disease diagnostics. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2344–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GhavamiNejad, P.; GhavamiNejad, A.; Zheng, H.; Dhingra, K.; Samarikhalaj, M.; Poudineh, M. A Conductive Hydrogel Microneedle-Based Assay Integrating PEDOT:PSS and Ag-Pt Nanoparticles for Real-Time, Enzyme-Less, and Electrochemical Sensing of Glucose. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2202362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, S.; Hong, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, K.; Ryu, W. Rapid Extraction and Detection of Biomolecules via a Microneedle Array of Wet-Crosslinked Methacrylated Hyaluronic Acid. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2100874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Namjoshi, S.; Benson, H.A.E.; Mohammed, Y.; Kumeria, T. Dissolvable polymer microneedles for drug delivery and diagnostics. J. Control. Release 2022, 347, 561–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.; Kwon, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Siriaraya, P.; Choi, J.; Otkhmezuri, B.; Kang, K.; Yu, K.J.; Jang, Y.C.; et al. Wireless Soft Scalp Electronics and Virtual Reality System for Motor Imagery-Based Brain-Machine Interfaces. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah, K.M.; Faraji Rad, Z. Sampling Dermal Interstitial Fluid Using Microneedles: A Review of Recent Developments in Sampling Methods and Microneedle-Based Biosensors. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10, 2201763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himawan, A.; Vora, L.K.; Permana, A.D.; Sudir, S.; Nurdin, A.R.; Nislawati, R.; Hasyim, R.; Scott, C.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Where Microneedle Meets Biomarkers: Futuristic Application for Diagnosing and Monitoring Localized External Organ Diseases. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2202066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrole, R.S.J.; Azizoglu, E.; Dul, M.; Birchall, J.C.; Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Trends of microneedle technology in the scientific literature, patents, clinical trials and internet activity. Biomaterials 2021, 267, 120491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, H.C.; Nguyen, P.Q.; Gonzalez-Macia, L.; Morales-Narváez, E.; Güder, F.; Collins, J.J.; Dincer, C. End-to-end design of wearable sensors. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 887–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, M.S.; Yang, H.S.; Jung, J.H. Enhanced extraction of skin interstitial fluid using a 3D printed device enabling tilted microneedle penetration. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, F.; Teymourian, H.; Wuerstle, B.; Kavner, J.; Patel, R.; Furmidge, A.; Aghavali, R.; Hosseini-Toudeshki, H.; Brown, C.; Zhang, F.; et al. An integrated wearable microneedle array for the continuous monitoring of multiple biomarkers in interstitial fluid. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Niu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, A.; Yang, H.; Xu, F.; Li, F. A Hydrogel Microneedle Patch for Point-of-Care Testing Based on Skin Interstitial Fluid. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 1901201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Wang, Z.; Chang, H.; Wang, L.; Chew, S.W.T.; Lio, D.C.S.; Cui, M.; Liu, L.; Tee, B.C.K.; Xu, C. Osmosis-Powered Hydrogel Microneedles for Microliters of Skin Interstitial Fluid Extraction within Minutes. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 1901683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhou, X.; Kim, H.; Qu, M.; Jiang, X.; Lee, K.; Ren, L.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhu, X.; et al. Gelatin Methacryloyl Microneedle Patches for Minimally Invasive Extraction of Skin Interstitial Fluid. Small 2020, 16, 1905910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, J.; Xiang, Q.; Dong, H. Hollow microneedle microfluidic paper-based chip for biomolecules rapid sampling and detection in interstitial fluid. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1255, 341101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strambini, L.M.; Longo, A.; Scarano, S.; Prescimone, T.; Palchetti, I.; Minunni, M.; Giannessi, D.; Barillaro, G. Self-powered microneedle-based biosensors for pain-free high-accuracy measurement of glycaemia in interstitial fluid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lillehoj, P.B. Microneedle-based skin patch for blood-free rapid diagnostic testing. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, E.M.; Keaveney, S.; Stuettgen, V.; Eberts, P.; Ramos-Luna, P.; Zhang, N.; Dangol, M.; O’Cearbhaill, E.D. Metallic microneedles with interconnected porosity: A scalable platform for biosensing and drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2018, 80, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, J.; Hoover, A.; King, S.A.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Lin, Q.; Yu, C.; Zhu, L.; et al. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Enabled by Fluorescent Nanodiamond Boronic Hydrogel. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2203943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciui, B.; Martin, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Brunetti, B.; Nakagawa, T.; Dawkins, T.J.; Lyu, M.; Cristea, C.; Sandulescu, R.; Wang, J. Wearable Wireless Tyrosinase Bandage and Microneedle Sensors: Toward Melanoma Screening. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrilla, M.; Detamornrat, U.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Donnelly, R.F.; De Wael, K. Wearable hollow microneedle sensing patches for the transdermal electrochemical monitoring of glucose. Talanta 2022, 249, 123695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Cheng, J.; Wei, W.; Yang, F.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Microneedle Array Encapsulated with Programmed DNA Hydrogels for Rapidly Sampling and Sensitively Sensing of Specific MicroRNA in Dermal Interstitial Fluid. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 18366–18375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Bian, F.; Cai, L.; Zhao, Y. Encoded Microneedle Arrays for Detection of Skin Interstitial Fluid Biomarkers. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, M.; Seyfoori, A.; Pagan, E.; Askari, E.; Najafabadi, A.H.; Akbari, M. 3D Printed Hydrogel Microneedle Arrays for Interstitial Fluid Biomarker Extraction and Colorimetric Detection. Polymers 2023, 15, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbariamin, D.; Samandari, M.; Ghelich, P.; Shahbazmohamadi, S.; Schmidt, T.A.; Chen, Y.; Tamayol, A. Cleanroom-Free Fabrication of Microneedles for Multimodal Drug Delivery. Small 2023, 2207131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Su, C.; Chen, Y.; Tian, S.; Lu, C.; Huang, W.; Lv, Q. Current Understanding of the Applications of Photocrosslinked Hydrogels in Biomedical Engineering. Gels 2022, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.S.; Gulfam, S.; Zafar, S.; Jalil, N.A.; Ahmad, N.; Qutachi, O.; Chang, M.-W.; Singh, N.; Ahmad, Z. Engineering of tetanus toxoid-loaded polymeric microneedle patches. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolabi, H.; Davari, N.; Khajehmohammadi, M.; Malektaj, H.; Nazemi, K.; Vahedi, S.; Ghalandari, B.; Reis, R.L.; Ghorbani, F.; Oliveira, J.M. Progress of Microfluidic Hydrogel-Based Scaffolds and Organ-on-Chips for the Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Adv. Mater. 2023, 2208852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dervisevic, M.; Alba, M.; Adams, T.E.; Prieto-Simon, B.; Voelcker, N.H. Electrochemical immunosensor for breast cancer biomarker detection using high-density silicon microneedle array. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 192, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strambini, L.M.; Longo, A.; Diligenti, A.; Barillaro, G. A minimally invasive microchip for transdermal injection/sampling applications. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3370–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.G.; Dangol, M.; Lee, C.Y.; Jang, M.; Jung, H. A self-powered one-touch blood extraction system: A novel polymer-capped hollow microneedle integrated with a pre-vacuum actuator. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautmann, A.; Roth, G.-L.; Nujiqi, B.; Walther, T.; Hellmann, R. Towards a versatile point-of-care system combining femtosecond laser generated microfluidic channels and direct laser written microneedle arrays. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, R.; Laffitte, Y.; Schmill, U.; Hu, W.; Kaddoura, M.; Blondeel, E.J.M.; Cui, B. Fabrication of sharp silicon hollow microneedles by deep-reactive ion etching towards minimally invasive diagnostics. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; You, X.; Chen, Z. Hollow Microneedles on a Paper Fabricated by Standard Photolithography for the Screening Test of Prediabetes. Sensors 2022, 22, 4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Collins, S.D.; Duy, J.; Minogue, T.D. Silicon microneedle array for minimally invasive human health monitoring. Microfluid. BioMEMS Med. Microsyst. XVI 2018, 10491, 1049102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappini, C.; De Rosa, E.; Martinez, J.O.; Liu, X.; Steele, J.; Stevens, M.M.; Tasciotti, E. Biodegradable silicon nanoneedles delivering nucleic acids intracellularly induce localized in vivo neovascularization. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, P.; Jamaledin, R.; Chen, G.; Baghbantaraghdari, Z.; Zare, E.N.; Natale, C.D.; Onesto, V.; Vecchione, R.; Lee, J.; Tay, F.R.; et al. Stimuli-responsive transdermal microneedle patches. Mater. Today 2021, 47, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terutsuki, D.; Segawa, R.; Kusama, S.; Abe, H.; Nishizawa, M. Frustoconical porous microneedle for electroosmotic transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2023, 354, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dervisevic, M.; Dervisevic, E.; Esser, L.; Easton, C.D.; Cadarso, V.J.; Voelcker, N.H. Wearable microneedle array-based sensor for transdermal monitoring of pH levels in interstitial fluid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 222, 114955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Du, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Mao, J.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; Zhu, J. Polymer microneedles with interconnected porous structures via a phase inversion route for transdermal medical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Park, J.; Qin, B.; Kim, B. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG antibodies detection using a patch sensor containing porous microneedles and a paper-based immunoassay. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, C.; Borazan, I.; Gencel, O.; Erdogmus, E.; Sutcu, M. Effect of nanofiber as nanopore maker agent on the performance of clinker bricks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Takama, N.; Sharma, K.; Paul, O.; Ruther, P.; Suga, T.; Kim, B. Microfluidic chip connected to porous microneedle array for continuous ISF sampling. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusama, S.; Sato, K.; Matsui, Y.; Kimura, N.; Abe, H.; Yoshida, S.; Nishizawa, M. Transdermal electroosmotic flow generated by a porous microneedle array patch. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Wang, Y.; Shi, K.; Chi, J.; Lyu, J.; Zhao, Y. Aptamer-decorated porous microneedles arrays for extraction and detection of skin interstitial fluid biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 190, 113404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugo, S.M.; Lu, W.; Wood, M.; Lemieux, S. Wearable microneedle dual electrochemical sensor for simultaneous pH and cortisol detection in sweat, Electrochem. Sci. Adv. 2022, 2, e2100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, J.; Pan, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Tip-porous microneedle: A highly stable sensing platform for direct determination of labile metals in natural seawater. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aich, K.; Singh, T.; Dang, S. Advances in microneedle-based transdermal delivery for drugs and peptides. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittard, S.D.; Miller, P.R.; Jin, C.; Martin, T.N.; Boehm, R.D.; Chisholm, B.J.; Stafslien, S.J.; Daniels, J.W.; Cilz, N.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; et al. Deposition of antimicrobial coatings on microstereolithography-fabricated microneedles. JOM 2011, 63, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.K.; Ingrole, R.S.J.; Joshi, G.; Uddin, M.J.; Anvari, S.; Davis, C.M.; Gill, H.S. Microneedles coated with peanut allergen enable desensitization of peanut sensitized mice. J. Control. Release 2019, 314, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; O’Cearbhaill, E.D.; Sisk, G.C.; Park, K.M.; Cho, W.K.; Villiger, M.; Bouma, B.E.; Pomahac, B.; Karp, J.M. A bio-inspired swellable microneedle adhesive for mechanical interlocking with tissue. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sulaiman, D.; Chang, J.Y.H.; Bennett, N.R.; Topouzi, H.; Higgins, C.A.; Irvine, D.J.; Ladame, S. Hydrogel-Coated Microneedle Arrays for Minimally Invasive Sampling and Sensing of Specific Circulating Nucleic Acids from Skin Interstitial Fluid. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9620–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Jing, X.; Hu, Y.; Lin, J.; Fu, H.; Ji, X.; et al. A Plasmonic Fluor-Lightened Microneedle Array Enables Ultrasensitive Multitarget Whole Blood Diagnosis of Anemia in A Paper Origami-Based Device. Small 2023, 2023, 2300464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, G.; Weng, Z.; Sun, H.; Nistala, R.; Zhang, Y. Microneedle-Based Potentiometric Sensing System for Continuous Monitoring of Multiple Electrolytes in Skin Interstitial Fluids. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odinotski, S.; Dhingra, K.; GhavamiNejad, A.; Zheng, H.; GhavamiNejad, P.; Gaouda, H.; Mohammadrezaei, D.; Poudineh, M. A Conductive Hydrogel-Based Microneedle Platform for Real-Time pH Measurement in Live Animals. Small 2022, 18, 2200201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Si, Q.; Pan, Z.; Jia, F.; Cui, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Fluorescence-Amplified Origami Microneedle (FAOM) Device for Quantitatively Monitoring Blood Glucose. Adv. Mater. 2023, 2023, 2208820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, K.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Inverse opal microneedles arrays for fluorescence enhanced screening skin interstitial fluid biomarkers. Nano Today 2022, 47, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.D.; Zheng, L.W.; Duong, P.K.; Cheah, R.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Wong, J.R.; Wang, W.J.; Guan, S.T.T.; Zheng, X.T.; Chen, P. Colorimetric microneedle patches for multiplexed transdermal detection of metabolites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 212, 114412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Boopathy, A.V.; Lam, L.K.W.; Moynihan, K.D.; Welch, M.E.; Bennett, N.R.; Turvey, M.E.; Thai, N.; Van, J.H.; Love, J.C.; et al. Cell and fluid sampling microneedle patches for monitoring skin-resident immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaar2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, W.; Lee, C.H. Electrochemically active materials and wearable biosensors for the in situ analysis of body fluids for human healthcare. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, K.Y.; Mahato, K.; Teymourian, H.; Longardner, K.; Litvan, I.; Wang, J. Wearable electrochemical microneedle sensing platform for real-time continuous interstitial fluid monitoring of apomorphine: Toward Parkinson management. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 354, 131234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugo, S.M.; Robertson, S.V.; Lu, W. A molecularly imprinted electrochemical microneedle sensor for multiplexed metabolites detection in human sweat. Talanta 2023, 259, 124531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, J.; O’Mahony, C.; Thompson, M.; O’Riordan, A.; Galvin, P. Biosensing in dermal interstitial fluid using microneedle based electrochemical devices. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 29, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, K.J.; Jing, L.; Severt, S.Y.; Cruz, M.; Sarmadi, M.; Jayawardena, H.S.N.; Perkinson, C.F.; Larusson, F.; Rose, S.; Tomasic, S.; et al. Biocompatible near-infrared quantum dots delivered to the skin by microneedle patches record vaccination. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaay7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, S.N.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Hui, S.W.; Sen, A. Electroporation and transcutaneous extraction (ETE) for pharmacokinetic studies of drugs. J. Control. Release 2005, 105, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasseb, A.A.; Ghani, N.D.T.A.; Shehab, O.R.; El Nashar, R.M. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers for electrochemical detection of some important biomedical markers and pathogens. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 31, 100848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Gong, X.; Yang, J.; Zheng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Nie, G.; Xie, X.; Chen, M.; et al. A touch-actuated glucose sensor fully integrated with microneedle array and reverse iontophoresis for diabetes monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 203, 114026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, H.; Gong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lv, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. In vitro and in vivo detection of lactate with nanohybrid-functionalized Pt microelectrode facilitating assessment of tumor development. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 191, 113474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Zhang, G.; Chai, H.; Qu, L.; Shan, D.; Zhang, X. Two-stage ligand exchange in Mn(III)-based porphyrinic metal−organic frameworks for fluorescence water sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 362, 131808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babity, S.; Polomska, A.K.; Couture, F.; Bonmarin, M.; Fehr, D.; Detmar, M.; Brambilla, D. Rational design of a fluorescent microneedle tattoo for minimally invasive monitoring of lymphatic function. J. Control. Release 2020, 327, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babity, S.; Couture, F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Hedtrich, S.; Hagen, R.; Fehr, D.; Bonmarin, M.; Brambilla, D. A Naked Eye-Invisible Ratiometric Fluorescent Microneedle Tattoo for Real-Time Monitoring of Inflammatory Skin Conditions. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, L.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Microfluidic Chip-Based Wearable Colorimetric Sensor for Simple and Facile Detection of Sweat Glucose. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14803–14807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Bian, F.; Wang, Y.; Shi, K.; Ye, F.; Zhao, Y. Stomatocyte structural color-barcode micromotors for multiplex assays. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribet, F.; Bendes, A.; Fredolini, C.; Dobielewski, M.; Böttcher, M.; Beck, O.; Schwenk, J.M.; Stemme, G.; Roxhed, N. Microneedle Patch for Painless Intradermal Collection of Interstitial Fluid Enabling Multianalyte Measurement of Small Molecules, SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies, and Protein Profiling. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2202564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrollahi, F.; Haghniaz, R.; Hosseini, V.; Davoodi, E.; Mahmoodi, M.; Karamikamkar, S.; Darabi, M.A.; Zhu, Y.; Lee, J.; Diltemiz, S.E.; et al. Micro and Nanoscale Technologies for Diagnosis of Viral Infections. Small 2021, 17, 2100692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolluru, C.; Williams, M.; Yeh, J.S.; Noel, R.K.; Knaack, J.; Prausnitz, M.R. Monitoring drug pharmacokinetics and immunologic biomarkers indermal interstitial fluid using a microneedle patch. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.R.; Joe, C.; Mitchell, R.J.; Gu, M.B. Biosensors for healthcare: Current and future perspectives. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 374–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, M.; Alizadeh, E.; Zarebkohan, A.; Seidi, K.; Ayoubi-Joshaghani, M.H.; Azizi, M.; Dadashi, H.; Mahmudi, H.; Javaheri, T.; Jaymand, M.; et al. Advanced Bioresponsive Multitasking Hydrogels in the New Era of Biomedicine. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, A.M.; Bolotsky, A.; Weaver, B.M.; Bennett, H.; Wolff, N.; Polsky, R.; Miller, P.R. Microneedle electrochemical aptamer-based sensing: Real-time small molecule measurements using sensor-embedded, commercially-available stainless steel microneedles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 236, 115408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kostal, E.; Matylitskaya, V.; Partel, S.; Ryu, W. Highly-sensitive single-step sensing of levodopa by swellable microneedle-mounted nanogap sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 220, 114912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Riley, P.R.; Mishra, R.; Machekposhti, S.A.; Narayan, R. Transdermal Polymeric Microneedle Sensing Platform for Fentanyl Detection in Biofluid. Biosensors 2022, 12, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.M.; Cornwell, M.; Prausnitz, M.R. Minimally Invasive Extraction of Dermal Interstitial Fluid for Glucose Monitoring Using Microneedles. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2005, 7, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.K.M.; Thakor, N.V.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.-H. Real-time modulated nanoparticle separation with an ultra-large dynamic range. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortolini, C.; Cass, A.E.G.; Pofi, R.; Lenzi, A.; Antiochia, R. Microneedle-based nanoporous gold electrochemical sensor for real-time catecholamine detection. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, L.F.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Ray, T.; Folch, A. Microfluidics for interrogating live intact tissues. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-S.; Li, C.G.; Ihm, C.; Jung, H. A three-dimensional and bevel-angled ultrahigh aspect ratio microneedle for minimally invasive and painless blood sampling. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Mustafa, Y.L.; Turner, J.G.; Lay, E.; Jungwirth, U.; Marken, F.; Leese, H.S. Conductive Polymer-Coated 3D Printed Microneedles: Biocompatible Platforms for Minimally Invasive Biosensing Interfaces. Small 2023, 19, 2206301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, R.; Carvalho, V.; Lima, R.; Minas, G.; Rodrigues, R.O. Microneedles in Advanced Microfluidic Systems: A Systematic Review throughout Lab and Organ-on-a-Chip Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, B.; Battisti, M.; De Martino, S.; Nocerino, V.; Dardano, P.; De Stefano, L.; Cangiano, G. Hollow Microneedle-based Plasmonic Sensor for on Patch Detection of Molecules in Dermal Interstitial Fluid. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 2023, 2300037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detamornrat, U.; McAlister, E.; Hutton, A.R.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. The Role of 3D Printing Technology in Microengineering of Microneedles. Small 2022, 18, 2106392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Ma, B.; Xu, C.; Liu, H. Emerging tumor-on-chips with electrochemical biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 153, 116640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeeva, N.V.; Arnold, M.A. Impact of Tissue Heterogeneity on Noninvasive Near-Infrared Glucose Measurements in Interstitial Fluid of Rat Skin. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 1041–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Pu, Z.; Liang, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Xu, K. Non-invasive measurement of normal skin impedance for determining the volume of the transdermally extracted interstitial fluid. Measurement 2015, 62, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Structures | Materials | Extracts | Fabrication Methods | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid MNs | Polyvinyl alcohol and chitosan | Glucose, chlorine, lactate | Micro-molding method | [46] |
| Methacrylated hyaluronic acid | Glucose and cholesterol | Micro-molding method | [11] | |
| Maltose and methacrylated hyaluronic acid | Glucose | Micro-molding method | [47] | |
| Gelatin methacryloyl | Glucose and vancomycin | Micro-molding method | [48] | |
| Hollow MNs | Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) | Glucose and lactic acid | Three-dimensional (3D) printer and micro stereolithography (PμSL) technology | [49] |
| Silicon-dioxide | Glucose | Standard lithography, buffered hydrofluoric acid (HF) and potassium hydroxide (KOH) etching et al. | [50] | |
| Stainless steel | Exosomes | Photoetching | [6] | |
| Polymerized SU-8 photoresist | Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 | Photoetching | [51] | |
| Porous MNs | Stainless steel | Glucose | Sintering at 1100 °C and subsequent electropolishing | [52] |
| Dopamine and hyaluronic acid | Glucose | Micro-molding method | [36] | |
| Acrylic resin | Glucose | Salt leaching method | [53] | |
| Coated MNs | Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (coated), maltose (solid) | Cystatin C | Drawing and wrapping method | [30] |
| Catechol(coated), photocurable acrylate (hollow) | Tyrosinase enzyme | Coating method | [54] |
| Classification | Materials | Extracts | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical MN-integrated sensors | Stainless-steel (hollow) | Na+ and K+ | Hollow MN-based potentiometric sensor consisting of a sodium/potassium ion-selective electrode and an Ag/AgCl reference electrode. Ref. [88]. |
| Hyaluronic acid | pH | Solid MNs made up of dopamine (DA) conjugated HA, and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT: PSS) to increase conductivity. Ref. [89]. | |
| Fluorescent MN-integrated sensors | Maltose and methacrylated hyaluronic acid | Glucose | The porous MNs were integrated with a fluorescent nanodiamond boronic hydrogel system. Ref. [90]. |
| Acrylic resin (porous) | Glucose | Surface functionalization using the fluorescent nanodiamond embedded in the boronic polymer hydrogels. Ref. [53]. | |
| Ethoxylated trimethylolpropane triacrylate (porous) | Lipopolysaccharide | The MNs had an inverse opal structure with fluorescence enhanced signal. Ref. [91]. | |
| Chemical colorimetric MN-integrated sensors | Methacrylated hyaluronic acid and hyaluronic acid (solid) | Glucose, lactate, cholesterol, and pH | The MeHA MNs was incorporated with multiplexed colorimetric and sensing-reagent-decorated test paper. Ref. [92]. |
| Immunodiagnostic MN-integrated sensors | poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (solid) | TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 | PEGDA MNs containing photonic crystal barcodes connecting specific antibody. Ref. [57]. |
| Poly-l-lactide (solid), alginate (coated) | Memory T cells | The immune adjuvants and specific antigens nanocapsules were embedded in the MN coating. Ref. [93]. | |
| Molecular diagnostic MN-integrated sensors | Methacrylate hyaluronic acid (solid) | miRNA | The MeHA MNs were equipped with the DNA displacement signal amplification system. Ref. [56]. |
| Alginate, Poly-L-Lactide (coated) | miRNA | The surface of Poly-L-Lactide MNs were coated with an alginate-peptide nucleic acid hybrid system for sequence-specific sampling. Ref. [86]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Luo, R.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y. Microneedle-Integrated Sensors for Extraction of Skin Interstitial Fluid and Metabolic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129882
Yang J, Luo R, Yang L, Wang X, Huang Y. Microneedle-Integrated Sensors for Extraction of Skin Interstitial Fluid and Metabolic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(12):9882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129882
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jie, Ruiyu Luo, Lei Yang, Xiaocheng Wang, and Yong Huang. 2023. "Microneedle-Integrated Sensors for Extraction of Skin Interstitial Fluid and Metabolic Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12: 9882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129882
APA StyleYang, J., Luo, R., Yang, L., Wang, X., & Huang, Y. (2023). Microneedle-Integrated Sensors for Extraction of Skin Interstitial Fluid and Metabolic Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(12), 9882. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24129882





