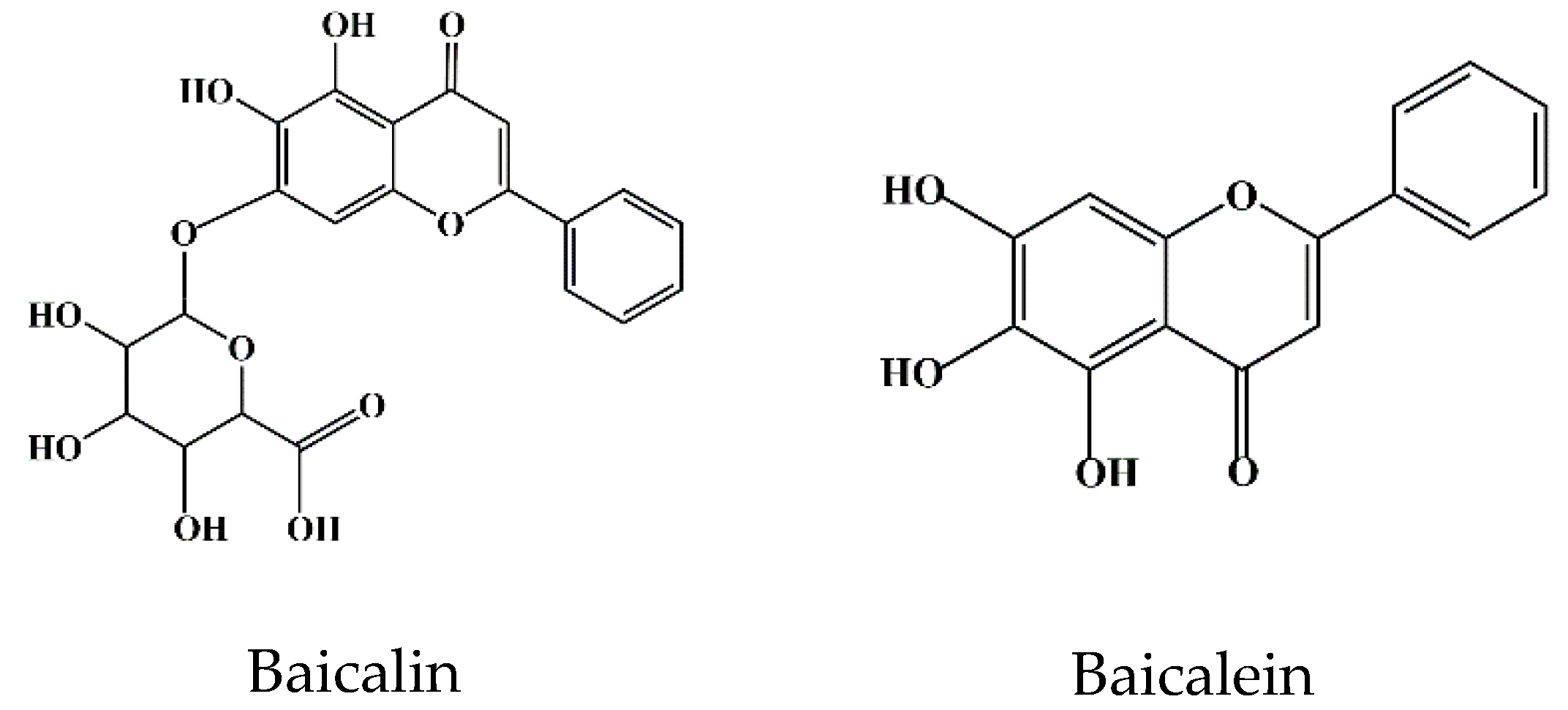
The Pharmacological Efficacy of Baicalin in Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
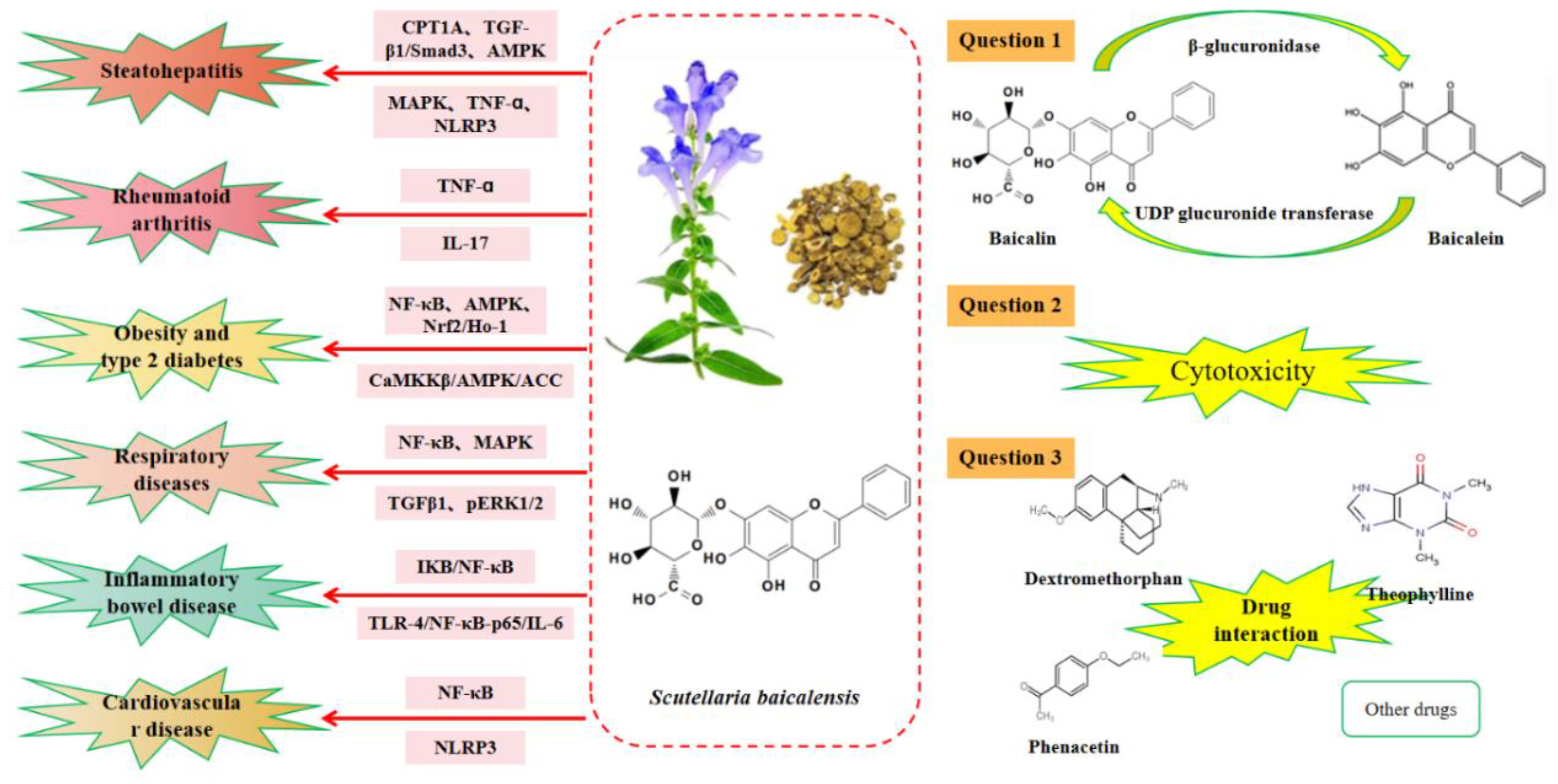
2. Bioavailability of Baicalin
3. Toxicity of Baicalin
4. Interaction between Baicalin and Other Drugs
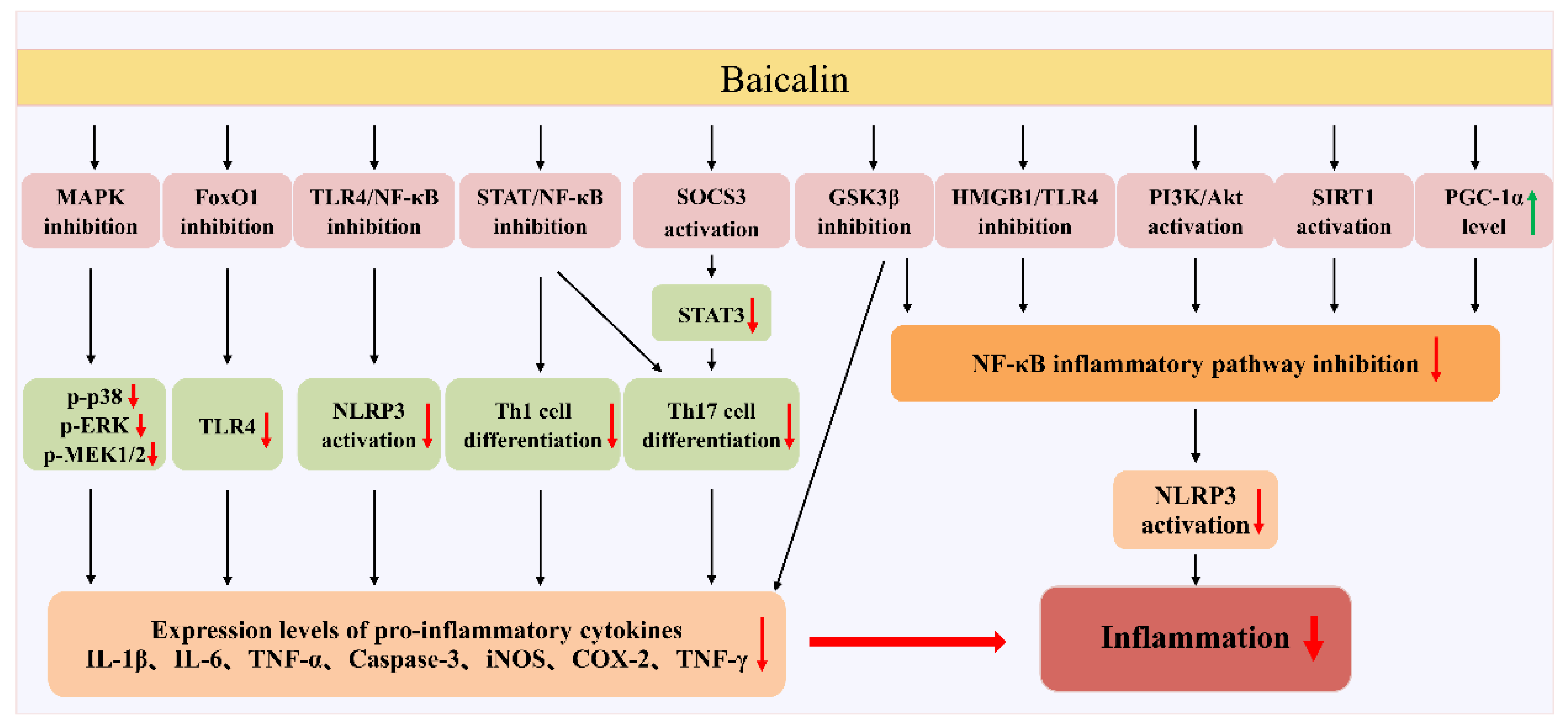
5. Therapeutic Effects of Baicalin
5.1. Effect of Baicalin on Hepatitis
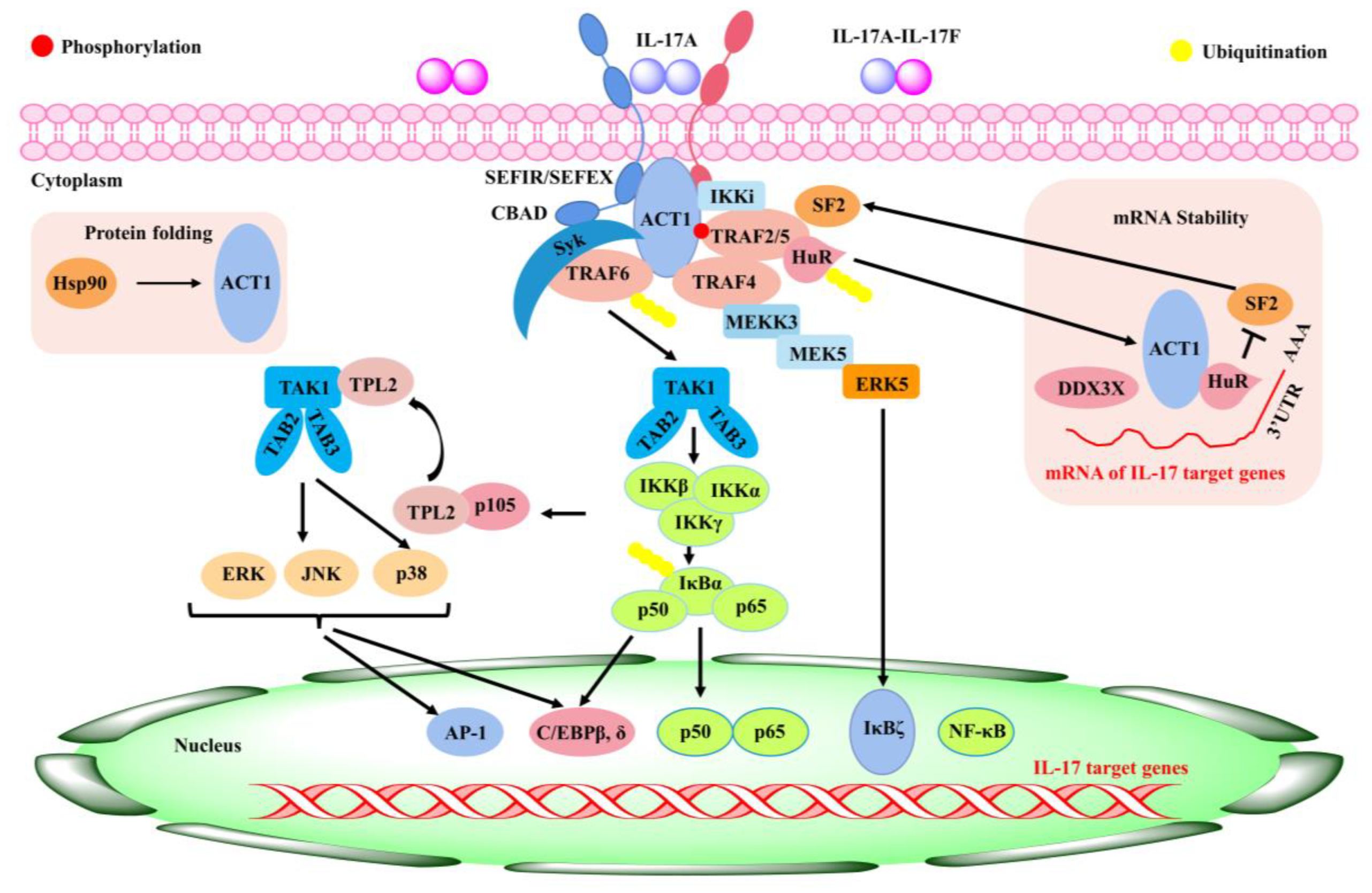
5.2. Role of Baicalin in Rheumatoid Arthritis
5.3. Anti-Inflammatory Role of Baicalin in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
5.4. Role of Baicalin in Respiratory-Related Inflammation
5.5. Therapeutical Effects of Baicalin in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
5.6. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Baicalin in Cardiovascular Diseases
6. Prospects
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, H.; Ye, J.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y. The main bioactive compounds of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. for alleviation of inflammatory cytokines: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Meng, F.; Zhou, G.; Li, Y.; Lu, H. Assessing the suitable cultivation areas for Scutellaria baicalensis in China using the Maxent model and multiple linear regression. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2020, 90, 104052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhou, C.; Dong, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, H.; et al. A candidate drug screen strategy: The discovery of oroxylin a in scutellariae radix against sepsis via the correlation analysis between plant metabolomics and pharmacodynamics. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 861105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, S.; Paul, S.; Manna, A.; Majumder, C.; Pal, K.; Casarcia, N.; Mondal, A.; Banerjee, S.; Nelson, V.K.; Ghosh, S.; et al. Phenolic phytochemicals for prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer: A critical evaluation of in vivo studies. Cancers 2023, 15, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, X.-Y.; Martin, C. Scutellaria baicalensis, the golden herb from the garden of Chinese medicinal plants. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.-E.; Kim, J.-A.; Nagappan, A.; Yumnam, S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, E.-H.; Lee, W.-S.; Shin, S.-C.; Park, H.-S.; Kim, G.-S. Flavonoids Identified from Korean Scutellaria baicalensis georgi inhibit inflammatory signaling by suppressing activation of NF-κB and MAPK in RAW 264.7 cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 912031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.-E.; Song, J.-H.; Song, H.-H.; Kang, J.W.; Hwang, S.N.; Rhee, K.-J.; Shim, A.; Hong, E.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jeon, S.-M.; et al. Antiviral activity of oroxylin a against coxsackievirus b3 alleviates virus-induced acute pancreatic damage in mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e155784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Chu, F.; Wu, C.; Huo, Q.; Gan, H.; Li, X.; Liu, H. Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi extract protects against alcohol-induced acute liver injury in mice and affects the mechanism of ER stress. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3052–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hong, G. Comparative metabolomics of flavonoids in twenty vegetables reveal their nutritional diversity and potential health benefits. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Liang, K.; Zhao, S.; Jia, W.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Lv, J.; Cao, C.; Chen, T.; Zhuang, S.; et al. Chemoproteomics reveals baicalin activates hepatic CPT1 to ameliorate diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5896–E5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.R.; Nabavi, S.F.; Habtemariam, S.; Erdogan, O.I.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.M. The effects of baicalein and baicalin on mitochondrial function and dynamics: A review. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 100, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, H.; Dong, S.; Luo, E.; Gu, M.; Shen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Baicalin attenuates high fat diet-induced obesity and liver dysfunction: Dose-response and potential role of CaMKKβ/AMPK/ACC pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 2349–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-B.; Chen, F. Isolation and purification of baicalein, wogonin and oroxylin a from the medicinal plant Scutellaria baicalensis by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1074, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Nwafor, E.-O.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Dang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, C.; et al. Baicalin-berberine complex nanocrystals orally promote the co-absorption of two components. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 3017–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Han, S.; Wang, M.; Han, L.; Huang, Y.; Bo, P.; Fang, P.; Zhang, Z. Baicalin protects against insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction through activation of GALR2/GLUT4 signaling. Phytomedicine 2022, 95, 153869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, X.; Shen, Q.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, M.; Wu, G. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of COVID-19. Curr. Drug Metab. 2022, 23, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, B.; Dinda, S.; DasSharma, S.; Banik, R.; Chakraborty, A.; Dinda, M. Therapeutic potentials of baicalin and its aglycone, baicalein against inflammatory disorders. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 131, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Kumar, S.; Singh, S.; Bhatia, S.; Albarrati, A.; Albratty, M.; Meraya, A.M.; Najmi, A.; Bungau, S. Reviving the mutual impact of SARS-COV-2 and obesity on patients: From morbidity to mortality. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Tian, J.; Xin, G.; Liu, L.; Sun, X.; Li, B. Advanced approaches for improving bioavailability and controlled release of anthocyanins. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artursson, P.; Karlsson, J. Correlation between oral drug absorption in humans and apparent drug permeability coefficients in human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 175, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Long, X.; Yuan, F.; Chen, L.; Pan, S.; Liu, Y.; Stowell, Y.; Li, X. Combined use of phospholipid complexes and self-emulsifying microemulsions for improving the oral absorption of a BCS class IV compound, baicalin. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalapos-Kovács, B.; Magda, B.; Jani, M.; Fekete, Z.; Szabó, P.T.; Antal, I.; Krajcsi, P.; Klebovich, I. Multiple ABC transporters efflux baicalin. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1987–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, K.; Kang, Y.; Nepal, M.R.; Jeong, K.S.; Oh, D.G.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, S.; Kang, W.; Jeong, H.G.; Jeong, T.C. Role of intestinal microbiota in baicalin-induced drug interaction and its pharmacokinetics. Molecules 2016, 21, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, Y.K.; Li, C.R.; Wo, S.K.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Lin, G.; Zuo, Z. In vitro and in situ evaluation of herb–drug interactions during intestinal metabolism and absorption of baicalein. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Yuan, T.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, D.; Liu, C.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y. Mechanistic and therapeutic perspectives of baicalin and baicalein on pulmonary hypertension: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, T.; Kawabata, K.; Yanagisawa, E.; Ishihara, K.; Mizuhara, Y.; Wakui, Y.; Sakashita, Y.; Kobashi, K. Balicalin, the predominant flavone glucuronide of scutellariae radix, is absorbed from the rat gastrointestinal tract as the aglycone and restored to its original form. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 52, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovrlić, M.; Mrkalić, E.; Jelić, R.; Cendic, S.M.; Stojanović, S.; Prodanović, N.; Tomović, J. Effect of caffeine and flavonoids on the binding of tigecycline to human serum albumin: A spectroscopic study and molecular docking. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bao, W.; Ding, H.; Jang, J.; Zou, G. Binding modes of flavones to human serum albumin: Insights from experimental and computational studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 12938–12947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Wu, T.; Peng, Z.; Tan, Q.; Peng, X.; Zhan, Z.; Song, L.; Wei, B. Baicalin induces apoptosis and autophagy in human osteosarcoma cells by increasing ROS to inhibit PI3K/Akt/mTOR, ERK1/2 and β-catenin signaling pathways. J. Bone Oncol. 2022, 33, 100415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.-Y.; Hsiu, S.-L.; Tsai, S.-Y.; Hou, Y.-C.; Chao, P.-D.L. Comparison of metabolic pharmacokinetics of baicalin and baicalein in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, J.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, T.; Guo, P.; Liu, Z.; Qi, D. The Flavonoid components of Scutellaria baicalensis: Biopharmaceutical properties and their improvement using nanoformulation techniques. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, N.; Mudgal, D.; Anand, R.; Jindal, S.; Mishra, V. Recent development in nanoencapsulation and delivery of natural bioactives through chitosan scaffolds for various biological applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 537–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariadoss, A.; Sivakumar, A.S.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, S.J. Diabetes mellitus and diabetic foot ulcer: Etiology, biochemical and molecular based treatment strategies via gene and nanotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shi, A.; Pang, H.; Xue, W.; Li, Y.; Cao, G.; Yan, B.; Dong, F.; Li, K.; Xiao, W.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of a single ascending dose of baicalein chewable tablets in healthy subjects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Sun, Y.; Gu, X.; Shi, M.; Bo, P.; Zhang, Z.; Bu, L. Baicalin ameliorates hepatic insulin resistance and gluconeogenic activity through inhibition of p38 MAPK/PGC-1α pathway. Phytomedicine 2019, 64, 153074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Z.; Hu, F.; Zhang, T.; Wei, M.; Bai, Q.; Lu, B.; Ji, L. Baicalin promotes liver regeneration after acetaminophen-induced liver injury by inducing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Muhammad, I.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, X. Baicalin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver inflammation in chicken by suppressing TLR4-Mediated NF-κB pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K. Baicalin protects AML-12 cells from lipotoxicity via the suppression of ER stress and TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 278, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhong, R.; Tang, S.; Han, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. Baicalin alleviates short-term lincomycin-induced intestinal and liver injury and inflammation in infant mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keumhan, N.; Youra, K.; Mahesh, N.; Ki, J.; Do, O.; Mi, K.; Sangkyu, L.; Wonku, K.; Hye, J.; Tae, J. Role of intestinal microbiota in baicalin-induced drug interaction and its pharmacokinetics. Molecules 2016, 21, 337. [Google Scholar]
- Khanal, T.; Kim, H.G.; Choi, J.H.; Park, B.H.; Do, M.T.; Kang, M.J.; Yeo, H.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kang, W.; Jeong, T.C. Protective role of intestinal bacterial metabolism against baicalin-induced toxicity in HepG2 cell cultures. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 37, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Ao, H.; Peng, C.; Yan, D. Gut microbiota, a new frontier to understand traditional Chinese medicines. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Zheng, L.; Cong, H.; Wu, B.; Huo, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; et al. Catechol-O-Methyltransferase and UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases in the metabolism of baicalein in different species. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Luan, Y.; Zhong, D. Interaction of baicalin and baicalein with antibiotics in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Guan, Y.; Hu, W.; Xu, Z.; Ishfaq, M. An overview of pharmacological activities of baicalin and its aglycone baicalein: New insights into molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Qi, B.; Liu, F.-J.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jia, L.-J.; Qiao, H.-L. Inhibition of baicalin on metabolism of phenacetin, a probe of CYP1A2, in human liver microsomes and in rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Fang, Y.; Qi, B.; Jia, L.-J.; Jin, H.; Qiao, H.-L. Pharmacokinetic changes of unbound theophylline are due to plasma protein binding displacement and CYP1A2 activity inhibition by baicalin in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.-Y.; Zhou, M.-H.; Cao, S.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, P.-J.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X.-X.; Yang, Q.-M.; Gao, X.-L. Effect of polyethylene glycol 400 on the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of baicalin by intravenous injection based on the enzyme activity of UGT1A8/1A9. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 180, 106328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.-L.; Li, T.-T.; Yang, F.; Tzeng, C.-M. Baicalin ameliorates dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis by regulation of the RANK/RANKL/OPG signaling pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Cheng, Z.-Y.; He, J.; Jia, L.-J.; Qiao, H.-L. Concentration-dependent inhibitory effects of baicalin on the metabolism of dextromethorphan, a dual probe of CYP2D and CYP3A, in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 203, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; He, L.-L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Ye, X.; Jing, J.-J.; Zhang, J.-F.; Gao, M.; Wang, X. Spectroscopic investigation on the food components–drug interaction: The influence of flavonoids on the affinity of nifedipine to human serum albumin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.-Y.; Tian, X.; Gao, J.; Li, H.-M.; Jia, L.-J.; Qiao, H.-L. Contribution of baicalin on the plasma protein binding displacement and CYP3A activity inhibition to the pharmacokinetic changes of nifedipine in rats in vivo and in vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Zhang, W.; Guo, D.; Tan, Z.-R.; Xu, P.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Zhang, L.; He, T.-Y.; Hu, D.-L.; et al. The effect of herbal medicine baicalin on pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin, substrate of organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Cheng, Z.-Y.; Jin, H.; Gao, J.; Qiao, H.-L. Inhibitory effects of baicalin on the expression and activity of CYP3A induce the pharmacokinetic changes of midazolam in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 179643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.-L.; Wang, Z.-X.; Wang, Y.-X.; Liu, X.-P.; Yang, Y.-J.; Gao, Y.-P.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, X. Studies on the interaction between promethazine and human serum albumin in the presence of flavonoids by spectroscopic and molecular modeling techniques. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, T.A.; Bakheit, A.H.; Zargar, S.; Alanazi, Z.S.; Al-Majed, A.A. Influence of antioxidant flavonoids quercetin and rutin on the in-vitro binding of neratinib to human serum albumin. Spectroc. Acta Pt. A. Molec. Biomolec. Spectr. 2021, 246, 118977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, L.-L.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.-F.; Sun, T. Decrease of the affinity of theophylline bind to serum proteins induced by flavonoids and their synergies on protein conformation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, X.-Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, B.; Zhou, L.-L.; Wang, X.-F.; Wang, D.; Sun, T. Studies on the competitive binding of cleviprex and flavonoids to plasma protein by multi-spectroscopic methods: A prediction of food-drug interaction. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 175, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felemban, A.H.; Alshammari, G.M.; Yagoub, A.; Al-Harbi, L.N.; Alhussain, M.H.; Yahya, M.A. Activation of AMPK entails the protective effect of royal jelly against high-fat-diet-induced hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, F.; Shi, C.; Pei, M.; Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Gong, Z. TNF-α/HMGB1 inflammation signalling pathway regulates pyroptosis during liver failure and acute kidney injury. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, N.; Hövelmeyer, N.; Waisman, A.; Straub, B.K.; Weinmann-Menke, J.; Wörns, M.A.; Galle, P.R.; Schattenberg, J.M. Hepatocyte-specific deletion of IL1-RI attenuates liver injury by blocking IL-1 driven autoinflammation. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Liu, Z.; Shang, J.; Zhou, X.; Yu, S.; Tian, H.; Bao, Y. Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides play anti-cancer effect through TLR4-MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, L.; Liu, M.; Cheng, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, M. Pien-Tze-Huang attenuates neuroinflammation in cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats through the TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Deng, X.; Zhang, N.; Liu, B.; Xin, S.; Li, G.; Xu, K. Baicalin attenuates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by suppressing key regulators of lipid metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in mice. Life Sci. 2018, 192, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Gong, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Kuang, G.; Yin, X.; et al. Baicalin and its nanoliposomes ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via suppression of TLR4 signaling cascade in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Liu, H. Baicalin attenuates diet induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress via suppressing JNK signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wei, M.; Lu, B.; Wang, Z.; Ji, L. Baicalein and baicalin alleviate acetaminophen-induced liver injury by activating Nrf2 antioxidative pathway: The involvement of ERK1/2 and PKC. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 150, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemtsova, M.V.; Zaletaev, D.V.; Bure, I.V.; Mikhaylenko, D.S.; Kuznetsova, E.B.; Alekseeva, E.A.; Beloukhova, M.I.; Deviatkin, A.A.; Lukashev, A.N.; Zamyatnin, A.J. Epigenetic changes in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.-M.; Ketharnathan, S.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Rajakumar, G. Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Stride from Research to Clinical Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: A review. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2018, 320, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Sundrud, M.S.; Skepner, J.; Yamagata, T. Targeting Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeuchi, T.; Moutsopoulos, N.M. Osteoimmunology in periodontitis; a paradigm for Th17/IL-17 inflammatory bone loss. Bone 2022, 163, 116500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selimov, P.; Karalilova, R.; Damjanovska, L.; Delcheva, G.; Stankova, T.; Stefanova, K.; Maneva, A.; Selimov, T.; Batalov, A. Rheumatoid arthritis and the proinflammatory cytokine IL-17. Folia Med. 2023, 65, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schett, G.; Rahman, P.; Ritchlin, C.; McInnes, I.B.; Elewaut, D.; Scher, J.U. Psoriatic arthritis from a mechanistic perspective. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Misra, R.; Aggarwal, A. Interleukin 17 levels are increased in juvenile idiopathic arthritis synovial fluid and induce synovial fibroblasts to produce proinflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-W.; Cho, M.-L.; Park, M.-K.; Yoon, C.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.-Y. Increased interleukin-17 production via a phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt and nuclear factor κB-dependent pathway in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R139–R148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatya, N.; Garg, A.V.; Gaffen, S.L. IL-17 Signaling: The Yin and the Yang. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Zou, H. Baicalin inhibits IL-17-mediated joint inflammation in murine adjuvant-induced arthritis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 268065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Chu, Y.; Li, M. Identification of baicalin as an immunoregulatory compound by controlling TH17 cell differentiation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.W.; Zhang, C.; Hong, T.; Liu, D.H.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; He, X.K.; Xu, W.D. Silibinin alleviates inflammation and induces apoptosis in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes and has a therapeutic effect on arthritis in rats. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohm, T.V.; Meier, D.T.; Olefsky, J.M.; Donath, M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity 2022, 55, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olefsky, J.M.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Barnes, G.T.; Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Yang, D.; Chou, C.J.; Sole, J.; Nichols, A.; Ross, J.S.; Tartaglia, L.A.; et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganami, T.; Tanimoto-Koyama, K.; Nishida, J.; Itoh, M.; Yuan, X.; Mizuarai, S.; Kotani, H.; Yamaoka, S.; Miyake, K.; Aoe, S.; et al. Role of the toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB pathway in saturated fatty acid–induced inflammatory changes in the interaction between adipocytes and macrophages. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legaki, A.-I.; Moustakas, I.I.; Sikorska, M.; Papadopoulos, G.; Velliou, R.-I.; Chatzigeorgiou, A. Hepatocyte mitochondrial dynamics and bioenergetics in obesity-related non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chi, X.; Wang, Y.; Setrerrahmane, S.; Xie, W.; Xu, H. Trends in insulin resistance: Insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Jiao, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Ni, X.; Fang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, X.; Sun, L.; Yang, Z.; et al. The roles of cell-cell and organ-organ crosstalk in the type 2 diabetes mellitus associated inflammatory microenvironment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022, 66, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingrui, W.; Zheng, L.; Guoyan, L.; Hongjie, W. Research progress of active ingredients of Scutellaria baicalensis in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and its complications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, F.; Shao, Q.; Chen, G.; Xu, L.; Lu, F. Baicalin alleviates oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy via Nrf2 and MAPK signaling pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 3207–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritopoulos, G.A.; Romagnoli, M.; Poletti, V.; Siafakas, N.M.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M. Recent advances in the pathogenesis and clinical evaluation of pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2012, 21, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.R.; Peters, S.P.; Busse, W.W. Asthma exacerbations: Pathogenesis, Prevention, and Treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2017, 5, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zuo, H.; Yang, Z.; Qu, J. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An update on pathogenesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 797292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Friggeri, A.; Yang, Y.; Milosevic, J.; Ding, Q.; Thannickal, V.J.; Kaminski, N.; Abraham, E. miR-21 mediates fibrogenic activation of pulmonary fibroblasts and lung fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekelmann, T.J.; Limper, A.H.; Colby, T.V.; McDonald, J.A. Transforming growth factor beta 1 is present at sites of extracellular matrix gene expression in human pulmonary fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 6642–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, P.; Gui, D.; Cai, H.; Chen, A.; Chen, M.; Dai, C.; Yao, D.; et al. Baicalin attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via adenosine A2a receptor related TGF-β1-induced ERK1/2 signaling pathway. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibner, K.A.; Boodoo, S.; Collins, S.; Black, K.E.; Chan-Li, Y.; Zarek, P.; Powell, J.D.; Horton, M.R. The adenosine a2a receptor inhibits matrix-induced inflammation in a novel fashion. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 40, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Goncharov, D.A.; Pena, A.; Baust, J.; Chavez, B.A.; Ray, A.; Rode, A.; Bachman, T.N.; Chang, B.; Jiang, L.; et al. Cross-talk between TSC2 and the extracellular matrix controls pulmonary vascular proliferation and pulmonary hypertension. Sci. Signal. 2022, 15, n2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, A.; Chen, M.; Yao, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, X. Baicalin attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension to improve hypoxic cor pulmonale by reducing the activity of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway and MMP-9. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 2546402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, S.; Eisenstein, S. Inflammatory bowel disease presentation and diagnosis. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 99, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, V.; Ferlazzo, N.; Currò, M.; Isola, G.; Matarese, M.; Bertuccio, M.P.; Caccamo, D.; Matarese, G.; Ientile, R. Baicalin-induced autophagy preserved LPS-stimulated intestinal cells from inflammation and alterations of paracellular permeability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F.; Leppkes, M. Resolution of ulcerative colitis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungaro, R.; Mehandru, S.; Allen, P.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Colombel, J.-F. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xie, L.; Long, J.; Liu, K.; Lu, J.; Liang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Dai, X.; Li, X. Therapeutic effect of baicalin on inflammatory bowel disease: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Pisano, M.; Xu, L.; Sun, F.; Xu, J.; Zheng, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, R.; Cui, X. Baicalin regulates autophagy to interfere with small intestinal acute graft-versus-host disease. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, J.; Ye, Q.; Xu, Y.; Dong, H.; Zheng, X. Regulating effect of baicalin on IKK/IKB/NF-kB signaling pathway and apoptosis-related proteins in rats with ulcerative colitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 73, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Bin Jia, X. The anti-inflammation effect of baicalin on experimental colitis through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB pathway activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Deng, X.; Lei, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ai, J.; Chen, L.; Xiong, H.; Mei, Z.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Ren, Y. The comparative study of the therapeutic effects and mechanism of baicalin, baicalein, and their combination on ulcerative colitis rat. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Zhang, S.; He, W.X.; Lu, J.L.; Xu, Y.J.; Yang, J.Y.; Liu, D. Baicalin may alleviate inflammatory infiltration in dextran sodium sulfate-induced chronic ulcerative colitis via inhibiting IL-33 expression. Life Sci. 2017, 186, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Guo, C.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, X. Baicalin down regulates the expression of TLR4 and NFkB-p65 in colon tissue in mice with colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 4063–4072. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.-X.; Zou, Y.; Feng, Y.-L.; Liu, H.-B.; Zheng, X.-B. Baicalin down-regulates the expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) effectively for rats with ulcerative colitis. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Chen, Z.; Bai, W.; Hao, J.; Heng, Z.; Meng, C.; Wang, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; et al. Taurohyodeoxycholic acid alleviates trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid induced ulcerative colitis via regulating Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg cells balance. Life Sci. 2023, 318, 121501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, L.-Z.; Zhao, S.; Shen, Z.-F.; Shen, H.; Zhan, L.-B. Protective effect of baicalin on the regulation of Treg/Th17 balance, gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in rats with ulcerative colitis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 5449–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Dai, S.-X.; Chi, H.-G.; Li, T.; He, Z.-W.; Wang, J.; Ye, C.-G.; Huang, G.-L.; Zhao, B.; Li, W.-Y.; et al. Baicalin attenuates TNBS-induced colitis in rats by modulating the Th17/Treg paradigm. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.-Y.; Huang, S.-G.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Ye, H.; Chi, H.-G.; Zou, Y.; Lv, R.-X.; Zheng, X.-B. Effects of baicalin in CD4 + CD29 + T cell subsets of ulcerative colitis patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15299–15309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, S.K.; Ranjan, P.; Dutta, R.K.; Verma, S.K. Management of inflammation in cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 173, 105912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, H.N.; Packard, C.J.; Chapman, M.J.; Borén, J.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Averna, M.; Ference, B.A.; Gaudet, D.; Hegele, R.A.; Kersten, S.; et al. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants: Metabolic insights, role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and emerging therapeutic strategies—A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur. Hear. J. 2021, 42, 4791–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, D.; Ley, K. Immunity and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nègre-Salvayre, A.; Augé, N.; Camaré, C.; Bacchetti, T.; Ferretti, G.; Salvayre, R. Dual signaling evoked by oxidized LDLs in vascular cells. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 106, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Mao, S.; Zhou, M. Effect of the flavonoid baicalein as a feed additive on the growth performance, immunity, and antioxidant capacity of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2790–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Fang, X.; Guan, S. Baicalin and geniposide attenuate atherosclerosis involving lipids regulation and immunoregulation in ApoE-/-mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, X.; Li, Z. The mechanism of efferocytosis in the pathogenesis of periodontitis and its possible therapeutic strategies. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2023, 113, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutuk, O.; Basaga, H. Inflammation meets oxidation: NF-κB as a mediator of initial lesion development in atherosclerosis. Trends Mol. Med. 2003, 9, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Tan, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; et al. Perfluorooctane sulfonate promotes atherosclerosis by modulating M1 polarization of macrophages through the NF-κB pathway. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2023, 249, 114384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liao, P.P.; Liu, L.H.; Fang, X.; Li, W.; Guan, S.M. Baicalin and geniposide inhibit the development of atherosclerosis by increasing Wnt1 and inhibiting dickkopf-related protein-1 expression. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 846–854. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Gang, X.; Yang, S.; Cui, M.; Sun, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, G. The alterations in and the role of the Th17/Treg balance in metabolic diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 678355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekhina, A.V.; Pylaeva, E.; Provatorov, S.; Ruleva, N.; Masenko, V.; Noeva, E.; Krasnikova, T.; Arefieva, T. Treg/Th17 balance in stable CAD patients with different stages of coronary atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2015, 238, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, L.; Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Xiang, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Gao, L.; Xie, R. Baicalin inhibits IgG production by regulating Treg/Th17 axis in a mouse model of red blood cell transfusion. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 66, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Li, M. Baicalin, a natural compound, promotes regulatory T cell differentiation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ding, L.; Tang, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T. Baicalin protects against hypertension-associated intestinal barrier impairment in part through enhanced microbial production of short-chain fatty acids. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Jia, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T. Baicalin relaxes vascular smooth muscle and lowers blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Wang, Q.; Qi, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Yang, F. Promoting effect of baicalin on nitric oxide production in CMECs via activating the PI3K-AKT-eNOS pathway attenuates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine 2019, 63, 153035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Mao, Y.; Ding, L.; Zeng, X.-A. Dihydromyricetin: A review on identification and quantification methods, biological activities, chemical stability, metabolism and approaches to enhance its bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, B.; Wang, J. The Pharmacological Efficacy of Baicalin in Inflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119317
Wen Y, Wang Y, Zhao C, Zhao B, Wang J. The Pharmacological Efficacy of Baicalin in Inflammatory Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119317
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Yongqiang, Yazhou Wang, Chenxu Zhao, Baoyu Zhao, and Jianguo Wang. 2023. "The Pharmacological Efficacy of Baicalin in Inflammatory Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119317
APA StyleWen, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, C., Zhao, B., & Wang, J. (2023). The Pharmacological Efficacy of Baicalin in Inflammatory Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119317






