Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous and Intrathecal Delivery of AAV9-Mediated ARSA in Minipigs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
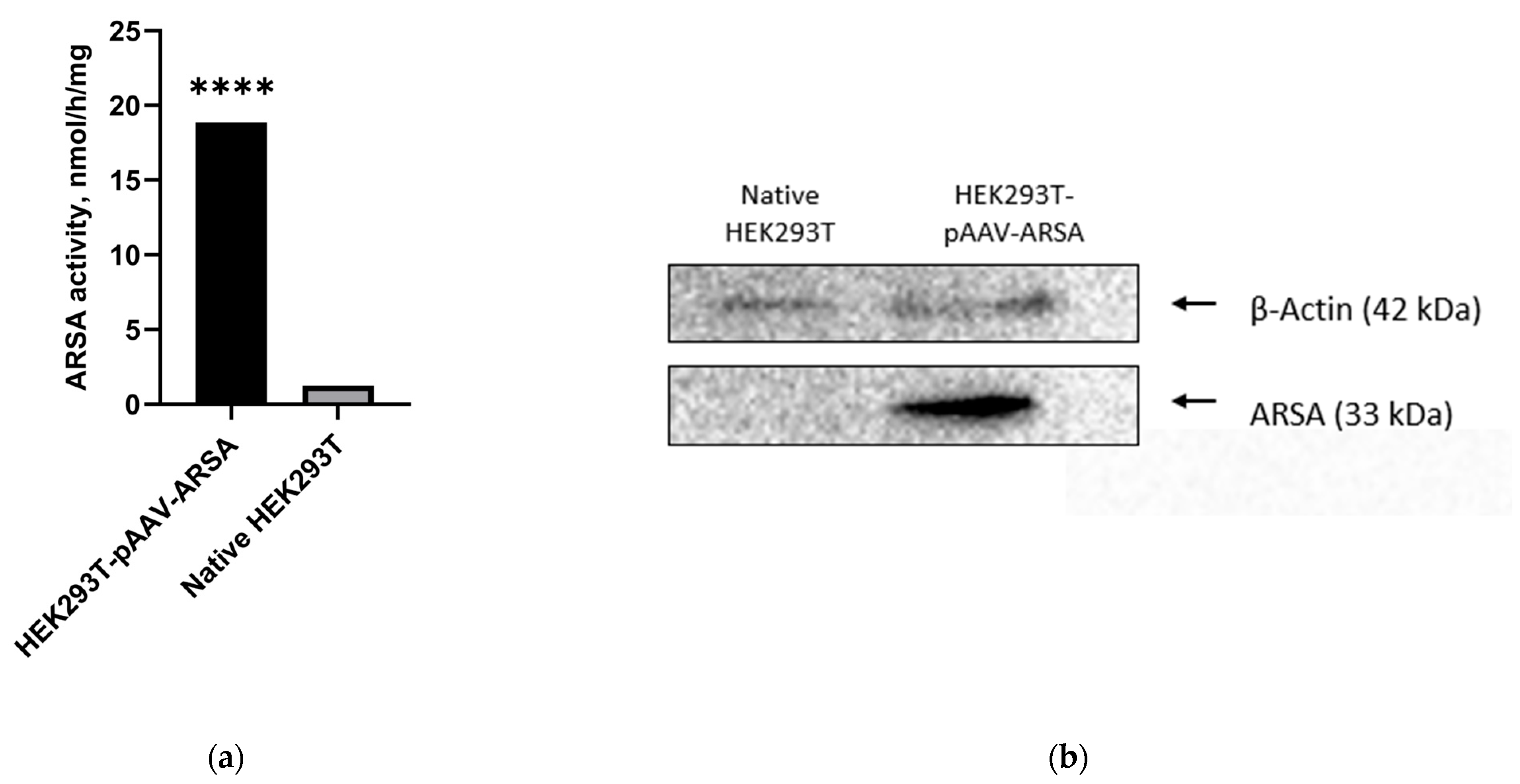
2.1. Codon Optimization
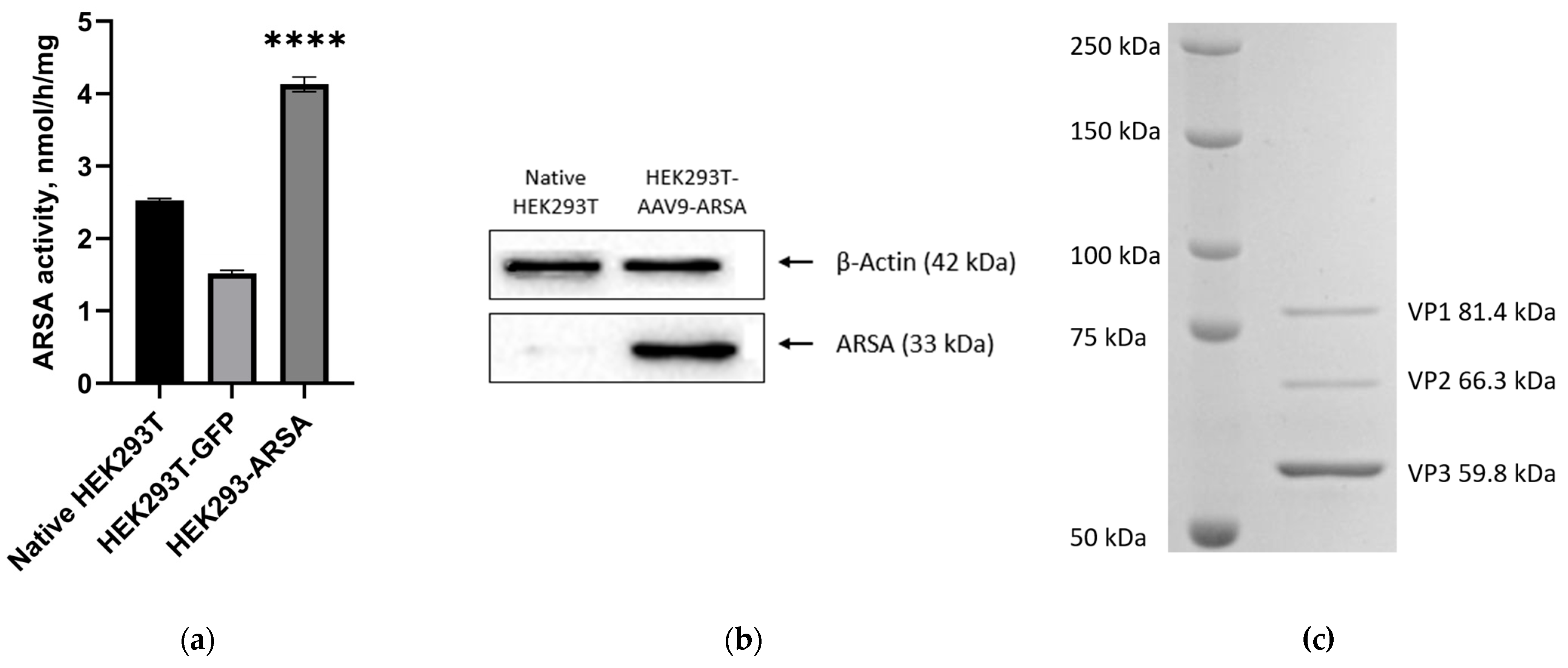
2.2. Analysis of ARSA Enzymatic Activity
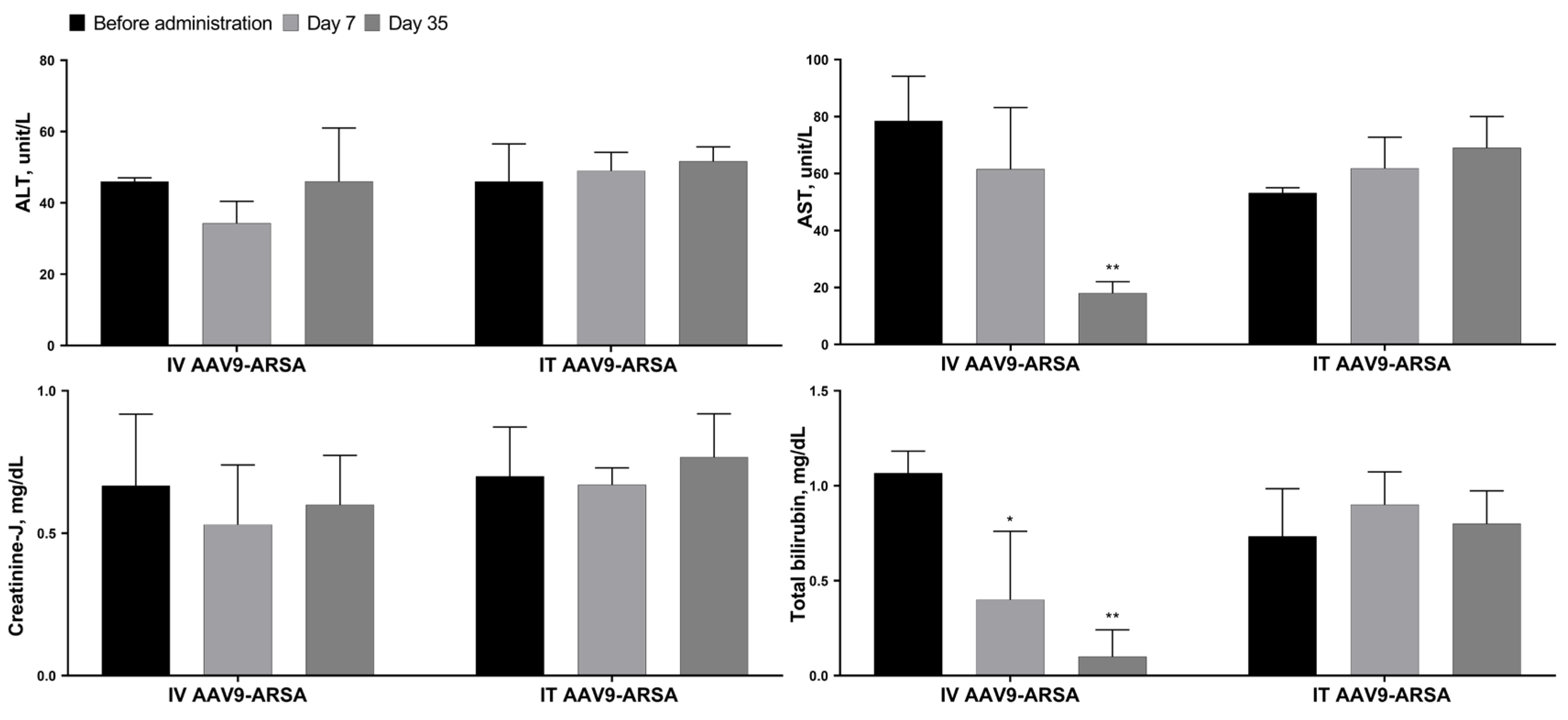
2.3. Biochemical Blood Analysis
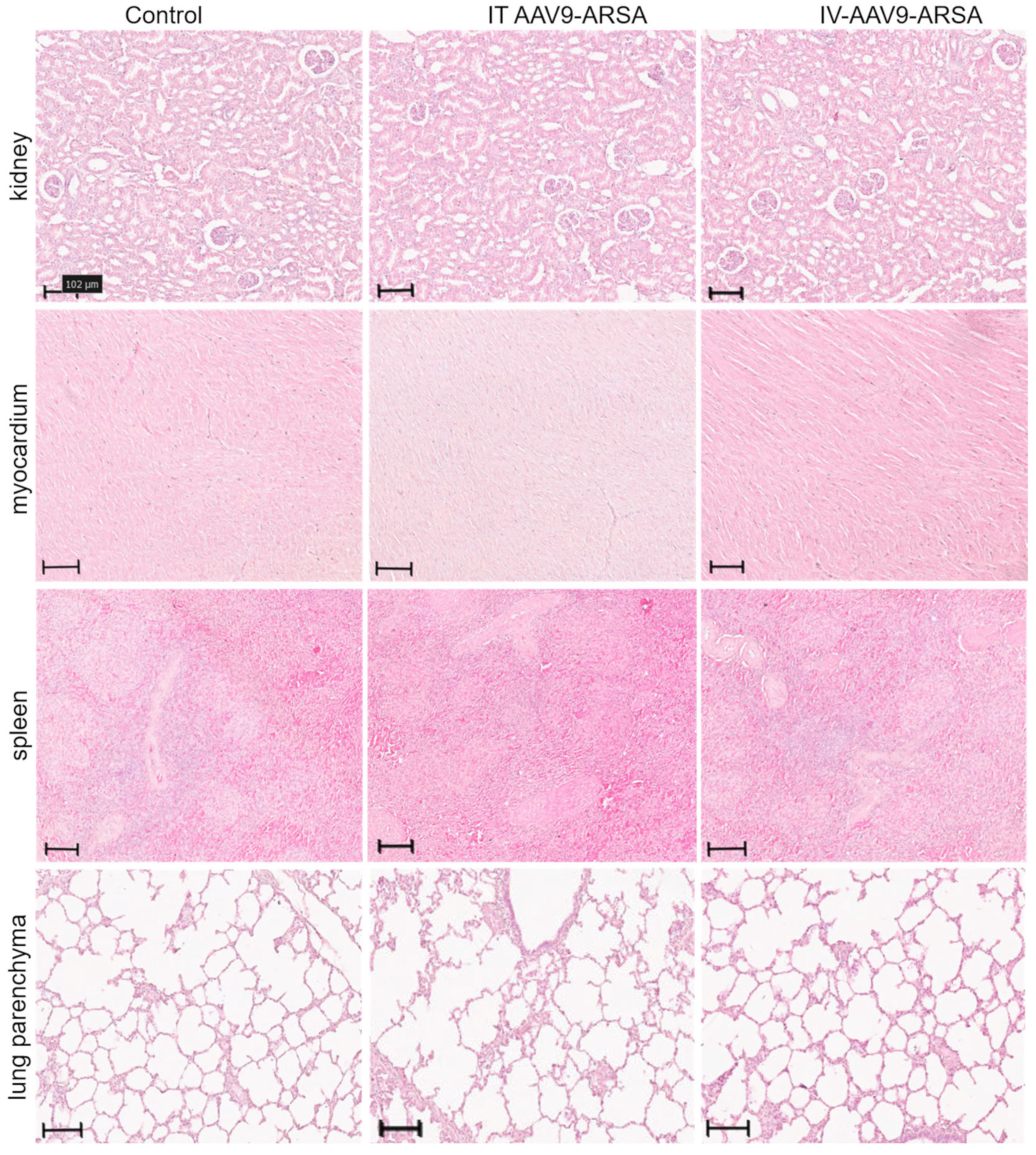
2.4. Pathomorphological Analysis
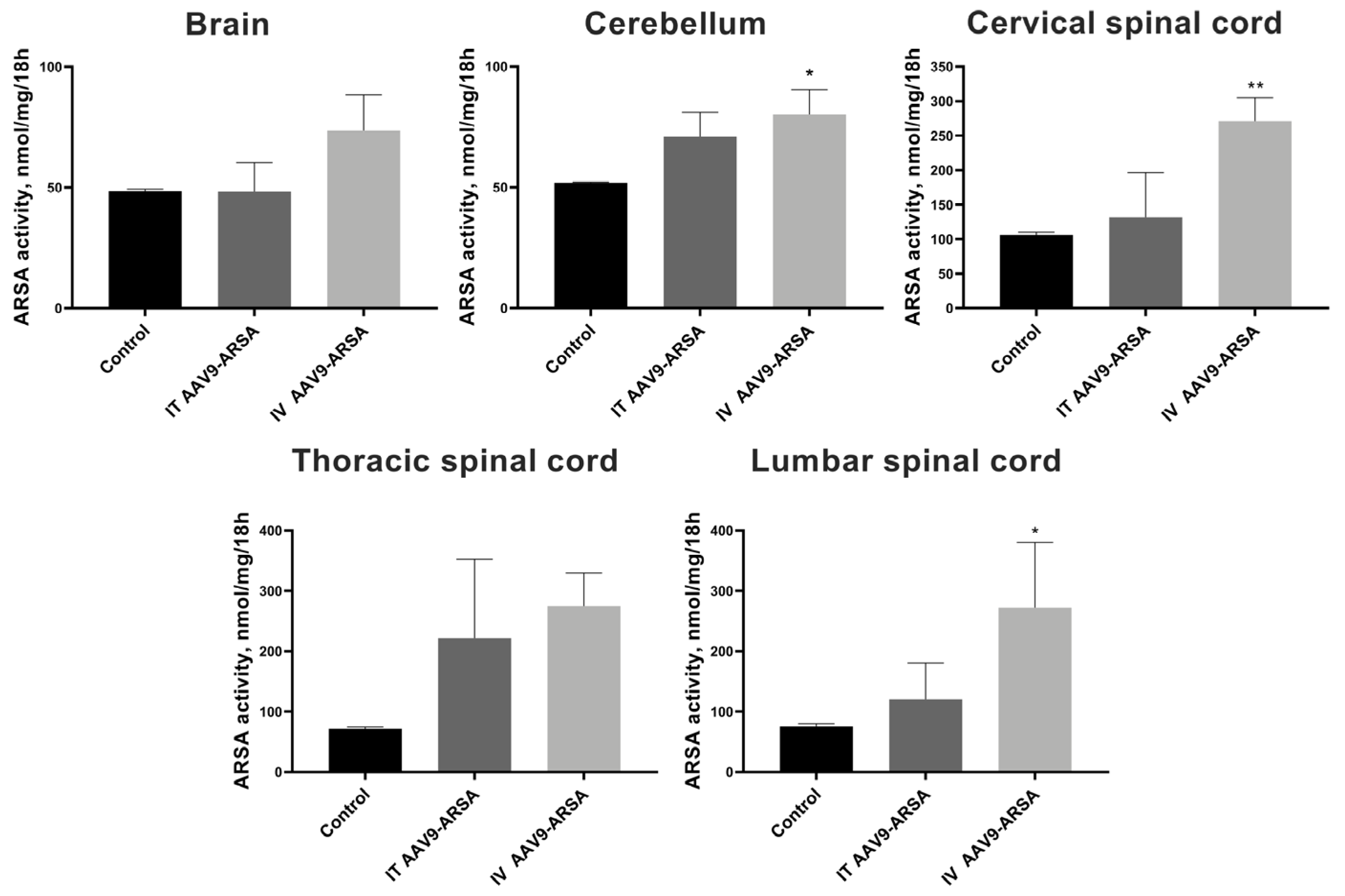
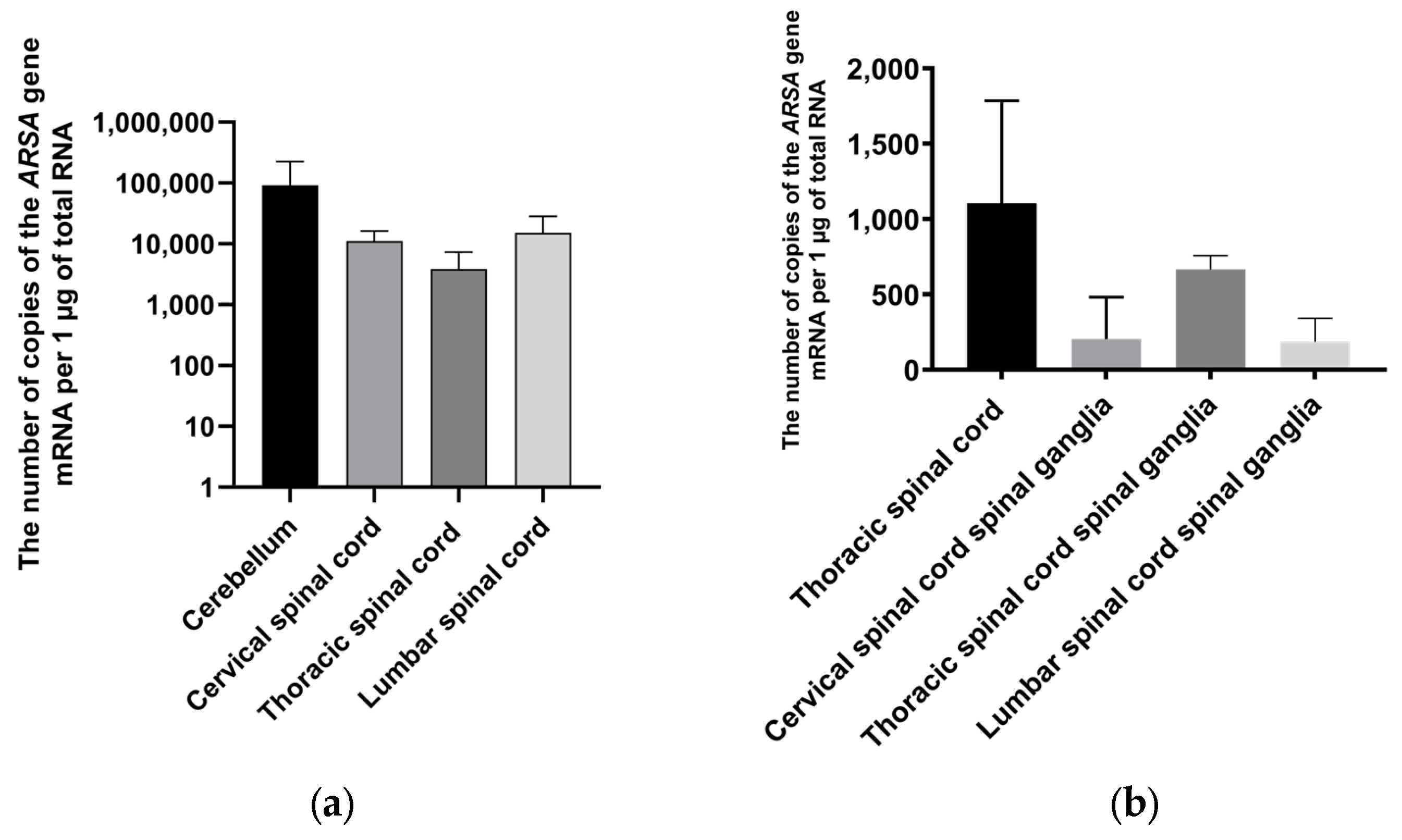
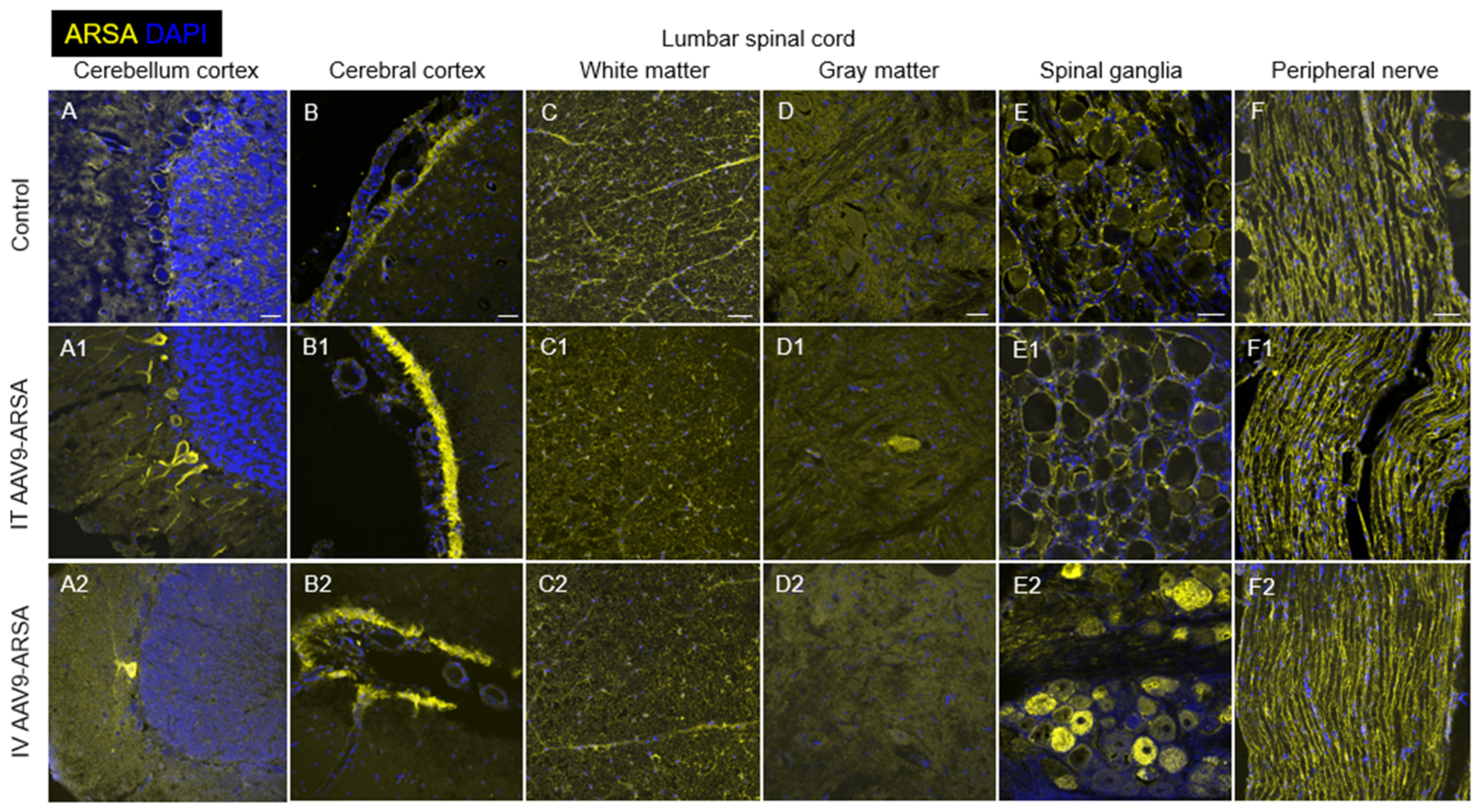
2.5. Assessment of ARSA Expression in Nervous Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genetic Construct Design and Analysis
4.2. Production of Preparative Amounts of Plasmid Constructs Required for AAV Assembly
4.3. Preparation and Purification of Recombinant AAV
4.4. Determination of the Overall Purity of Virus Particles
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Animals
4.7. Material Sampling
4.8. Determination of ARSA Enzymatic Activity
4.9. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.10. Biochemical Blood Analysis and Cytokine Profile Analysis
4.11. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaimardanova, A.A.; Chulpanova, D.S.; Solovyeva, V.V.; Mullagulova, A.I.; Kitaeva, K.V.; Allegrucci, C.; Rizvanov, A.A. Metachromatic leukodystrophy: Diagnosis, modeling, and treatment approaches. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 576221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Ospina, N. Arylsulfatase a deficiency. In Genereviews; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wanner, M.R.; Karmazyn, B.; Fan, R. Multidetector ct diagnosis of massive hemobilia due to gallbladder polyposis in a child with metachromatic leukodystrophy. Pediatr. Radiol. 2015, 45, 2017–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almarzooqi, S.; Quadri, A.; Albawardi, A. Gallbladder polyps in metachromatic leukodystrophy. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2018, 37, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Sun, Z.; Ezekian, B.; Schooler, G.R.; Prasad, V.K.; Kurtzberg, J.; Rice, H.E.; Tracy, E.T. Gallbladder abnormalities in children with metachromatic leukodystrophy. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 208, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, K.; Ranganathan, S. Pathology of the gallbladder in a child with metachromatic leukodystrophy. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2015, 18, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, J.J.; Jacob, T.J.K. An unusual presentation of gall bladder papillomatosis in association with metachromatic leukodystrophy. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr–2017–224162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Knaap, M.S.; Bugiani, M. Leukodystrophies: A proposed classification system based on pathological changes and pathogenetic mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 351–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, T.M.; Ziegler, J.C.; Weinberger, D.R. Psychiatric disturbances in metachromatic leukodystrophy: Insights into the neurobiology of psychosis. Arch. Neurol. 1992, 49, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Mallick, M.S.; Godil, A.; Khetpal, A.; Rizvi, A.H.; Khan, F. Infantile metachromatic leukodystrophy in an 18 month old girl. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2016, 66, 1197–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, H.R.; Lee, H.F.; Chi, C.S.; Tsai, C.R. Late infantile metachromatic leukodystrophy: Clinical manifestations of five taiwanese patients and genetic features in Asia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkovich, A.J. Concepts of myelin and myelination in neuroradiology. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2000, 21, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Thibert, K.A.; Raymond, G.V.; Tolar, J.; Miller, W.P.; Orchard, P.J.; Lund, T.C. Cerebral spinal fluid levels of cytokines are elevated in patients with metachromatic leukodystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, C.L.; Vanguri, P.; Shin, M.L. Activation of the alternative pathway of complement by human peripheral nerve myelin. J. Immunol. 1985, 134, 1810–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerepoot, S.; Nierkens, S.; Boelens, J.J.; Lindemans, C.; Bugiani, M.; Wolf, N.I. Peripheral neuropathy in metachromatic leukodystrophy: Current status and future perspective. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, K.; Frazier, S.B.; Clark, M.; Childers, A.; Pruthi, S.; Wenger, D.A.; Duis, J. A closer look at arsa activity in a patient with metachromatic leukodystrophy. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2019, 19, 100460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluharty, A.L.; Meek, W.E.; Kihara, H. Pseudo arylsulfatase a deficiency: Evidence for a structurally altered enzyme. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1983, 112, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieselmann, V.; Polten, A.; Kreysing, J.; Von Figura, K. Arylsulfatase a pseudodeficiency: Loss of a polyadenylylation signal and n-glycosylation site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9436–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.A.; Khaliq, S.; Amar, A.; Mahmood, S. Metachromatic leukodystrophy (mld): A pakistani family with novel arsa gene mutation. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 63, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.T.; Akhter, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, K.A.; Siddique, R.; Helaly, L.; Ahmed, S. A rare case of metachromatic leukodystrophy confirmed by Arylsulfatase A. Mymensingh Med. J. 2015, 24, 864–867. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rappard, D.F.; De Vries, A.L.C.; Oostrom, K.J.; Boelens, J.J.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Van der Knaap, M.S.; Wolf, N.I. Slowly progressive psychiatric symptoms: Think metachromatic leukodystrophy. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2018, 57, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.M.; Martin, S.; Fehnel, S.E.; Deal, L.S. Development of the impact of juvenile metachromatic leukodystrophy on physical activities scale. J. Patient-Rep. Outcomes 2017, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumperscak, H.G.; Paschke, E.; Gradisnik, P.; Vidmar, J.; Bradac, S.U. Adult metachromatic leukodystrophy: Disorganized schizophrenia-like symptoms and postpartum depression in 2 sisters. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2005, 30, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Black, D.N.; Taber, K.H.; Hurley, R.A. Metachromatic leukodystrophy: A model for the study of psychosis. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2003, 15, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espejo, L.M.; De la Espriella, R.; Hernandez, J.F. Metachromatic leukodystrophy. Case presentation. Rev. Colomb. Psiquiatr. 2017, 46, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostantjopoulou, S.; Katsarou, Z.; Michelakaki, H.; Kazis, A. Seizures as a presenting feature of late onset metachromatic leukodystrophy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2000, 102, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, A.A.; Miller, W.; Shanley, R.; Ziegler, R.; Lund, T.; Raymond, G.; Orchard, P.J. Long-term outcomes after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for metachromatic leukodystrophy: The largest single-institution cohort report. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeschel, S.; Kuhl, J.S.; Bley, A.E.; Kehrer, C.; Weschke, B.; Doring, M.; Bohringer, J.; Schrum, J.; Santer, R.; Kohlschutter, A.; et al. Long-term outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with juvenile metachromatic leukodystrophy compared with nontransplanted control patients. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevin, C.; Roujeau, T.; Cartier, N.; Baugnon, T.; Adamsbaum, C.; Piraud, M.; Martino, S.; Mouiller, P.; Couzinie, C.; Bellesme, C.; et al. Intracerebral gene therapy in children with metachromatic leukodystrophy: Results of a phase i/ii trial. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 123, S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, N.; Miyake, K.; Asakawa, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Shimada, T. Long-term correction of biochemical and neurological abnormalities in mld mice model by neonatal systemic injection of an aav serotype 9 vector. Gene Ther. 2014, 21, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, O.N.; Day, J.; Nieder, M.; Gerson, S.L.; Lazarus, H.M.; Krivit, W. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell infusion for treatment of metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) and hurler syndrome (MPS-IH). Bone Marrow Transpl. 2002, 30, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuleman, N.; Vanhaelen, G.; Tondreau, T.; Lewalle, P.; Kwan, J.; Bennani, J.; Martiat, P.; Lagneaux, L.; Bron, D. Reduced intensity conditioning haematopoietic stem cell transplantation with mesenchymal stromal cells infusion for the treatment of metachromatic leukodystrophy: A case report. Haematologica 2008, 93, e11–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, M.; Lorioli, L.; Fumagalli, F.; Acquati, S.; Redaelli, D.; Baldoli, C.; Canale, S.; Lopez, I.D.; Morena, F.; Calabria, A.; et al. Lentiviral haemopoietic stem-cell gene therapy in early-onset metachromatic leukodystrophy: An ad-hoc analysis of a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellettato, C.M.; Scarpa, M. Possible strategies to cross the blood-brain barrier. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X. Current strategies for brain drug delivery. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, B.; Chou, X.L.; Zhang, Z.G.; Mesik, L.; Liang, F.X.; Tao, H.W.; Zhang, L.I. Aav-mediated anterograde transsynaptic tagging: Mapping corticocollicular input-defined neural pathways for defense behaviors. Neuron 2017, 93, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschauer, D.F.; Kreuz, S.; Rumpel, S. Analysis of transduction efficiency, tropism and axonal transport of aav serotypes 1, 2, 5, 6, 8 and 9 in the mouse brain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevin, C.; Benraiss, A.; Van Dam, D.; Bonnin, D.; Nagels, G.; Verot, L.; Laurendeau, I.; Vidaud, M.; Gieselmann, V.; Vanier, M.; et al. Intracerebral adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer in rapidly progressive forms of metachromatic leukodystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cearley, C.N.; Wolfe, J.H. Transduction characteristics of adeno-associated virus vectors expressing cap serotypes 7, 8, 9, and rh10 in the mouse brain. Mol. Ther. 2006, 13, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piguet, F.; Sondhi, D.; Piraud, M.; Fouquet, F.; Hackett, N.R.; Ahouansou, O.; Vanier, M.T.; Bieche, I.; Aubourg, P.; Crystal, R.G.; et al. Correction of brain oligodendrocytes by aavrh.10 intracerebral gene therapy in metachromatic leukodystrophy mice. Hum. Gene Ther. 2012, 23, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deverman, B.E.; Pravdo, P.L.; Simpson, B.P.; Kumar, S.R.; Chan, K.Y.; Banerjee, A.; Wu, W.L.; Yang, B.; Huber, N.; Pasca, S.P.; et al. Cre-dependent selection yields aav variants for widespread gene transfer to the adult brain. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.Y.; Jang, M.J.; Yoo, B.B.; Greenbaum, A.; Ravi, N.; Wu, W.L.; Sanchez-Guardado, L.; Lois, C.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Deverman, B.E.; et al. Engineered aavs for efficient noninvasive gene delivery to the central and peripheral nervous systems. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audouard, E.; Oger, V.; Meha, B.; Cartier, N.; Sevin, C.; Piguet, F. Complete correction of brain and spinal cord pathology in metachromatic leukodystrophy mice. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 677895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzner, U.; Hartmann, D.; Lullmann-Rauch, R.; Coenen, R.; Rothert, F.; Mansson, J.E.; Fredman, P.; D’Hooge, R.; De Deyn, P.P.; Gieselmann, V. Bone marrow stem cell-based gene transfer in a mouse model for metachromatic leukodystrophy: Effects on visceral and nervous system disease manifestations. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biffi, A.; Capotondo, A.; Fasano, S.; Del Carro, U.; Marchesini, S.; Azuma, H.; Malaguti, M.C.; Amadio, S.; Brambilla, R.; Grompe, M.; et al. Gene therapy of metachromatic leukodystrophy reverses neurological damage and deficits in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3070–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, F.; Calbi, V.; Natali Sora, M.G.; Sessa, M.; Baldoli, C.; Rancoita, P.M.V.; Ciotti, F.; Sarzana, M.; Fraschini, M.; Zambon, A.A.; et al. Lentiviral haematopoietic stem-cell gene therapy for early-onset metachromatic leukodystrophy: Long-term results from a non-randomised, open-label, phase 1/2 trial and expanded access. Lancet 2022, 399, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci, F.; Scaramuzza, S.; Aiuti, A.; Mortellaro, A. Update on clinical ex vivo hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy for inherited monogenic diseases. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyeva, V.V.; Shaimardanova, A.A.; Chulpanova, D.S.; Kitaeva, K.V.; Chakrabarti, L.; Rizvanov, A.A. New approaches to tay-sachs disease therapy. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantor, B.; Bailey, R.M.; Wimberly, K.; Kalburgi, S.N.; Gray, S.J. Methods for gene transfer to the central nervous system. Adv. Genet. 2014, 87, 125–197. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, Y. Crossing the blood-brain barrier with aav vectors. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, J.; Nobre, R.J.; Pereira de Almeida, L. Gene therapy for the cns using aavs: The impact of systemic delivery by aav9. J. Control. Release 2016, 241, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foust, K.D.; Nurre, E.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hernandez, A.; Chan, C.M.; Kaspar, B.K. Intravascular aav9 preferentially targets neonatal neurons and adult astrocytes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.S.; Li, H.; Cao, C.; Sikoglu, E.M.; Denninger, A.R.; Su, Q.; Eaton, S.; Liso Navarro, A.A.; Xie, J.; Szucs, S.; et al. A single intravenous raav injection as late as p20 achieves efficacious and sustained cns gene therapy in canavan mice. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 2136–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, N.; Miyake, K.; Sakai, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Suzuki, H.; Shimada, T. Treatment of adult metachromatic leukodystrophy model mice using intrathecal administration of type 9 aav vector encoding arylsulfatase a. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, C.; Bell, P.; Gurda, B.L.; Wang, Q.; Louboutin, J.P.; Zhu, Y.; Bagel, J.; O’Donnell, P.; Sikora, T.; Ruane, T.; et al. Intrathecal gene therapy corrects cns pathology in a feline model of mucopolysaccharidosis i. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hordeaux, J.; Hinderer, C.; Buza, E.L.; Louboutin, J.P.; Jahan, T.; Bell, P.; Chichester, J.A.; Tarantal, A.F.; Wilson, J.M. Safe and sustained expression of human iduronidase after intrathecal administration of adeno-associated virus serotype 9 in infant rhesus monkeys. Hum. Gene Ther. 2019, 30, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.M.; Rozenberg, A.; Gray, S.J. Comparison of high-dose intracisterna magna and lumbar puncture intrathecal delivery of aav9 in mice to treat neuropathies. Brain Res. 2020, 1739, 146832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, D.J.; Dykstra, J.A.; Riedl, M.S.; Kitto, K.F.; Belur, L.R.; McIvor, R.S.; Elde, R.P.; Fairbanks, C.A.; Vulchanova, L. Biodistribution of adeno-associated virus serotype 9 (aav9) vector after intrathecal and intravenous delivery in mouse. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Z.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. Intravenous aav9 administration results in safe and widespread distribution of transgene in the brain of mini-pig. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1115348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderer, C.; Katz, N.; Buza, E.L.; Dyer, C.; Goode, T.; Bell, P.; Richman, L.K.; Wilson, J.M. Severe toxicity in nonhuman primates and piglets following high-dose intravenous administration of an adeno-associated virus vector expressing human smn. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.B.; Chen, A.; De, B.P.; Dyke, J.P.; Ballon, D.J.; Monette, S.; Ricart Arbona, R.J.; Kaminsky, S.M.; Crystal, R.G.; Sondhi, D. Safety of direct intraparenchymal aavrh.10-mediated central nervous system gene therapy for metachromatic leukodystrophy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2021, 32, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Shang, C.; Dong, H.; Meng, K. Interleukin-1 in cerebrospinal fluid for evaluating the neurological outcome in traumatic brain injury. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartfai, T.; Sanchez-Alavez, M.; Andell-Jonsson, S.; Schultzberg, M.; Vezzani, A.; Danielsson, E.; Conti, B. Interleukin-1 system in cns stress: Seizures, fever, and neurotrauma. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 1113, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mullagulova, A.; Shaimardanova, A.; Solovyeva, V.; Mukhamedshina, Y.; Chulpanova, D.; Kostennikov, A.; Issa, S.; Rizvanov, A. Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous and Intrathecal Delivery of AAV9-Mediated ARSA in Minipigs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119204
Mullagulova A, Shaimardanova A, Solovyeva V, Mukhamedshina Y, Chulpanova D, Kostennikov A, Issa S, Rizvanov A. Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous and Intrathecal Delivery of AAV9-Mediated ARSA in Minipigs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119204
Chicago/Turabian StyleMullagulova, Aysilu, Alisa Shaimardanova, Valeriya Solovyeva, Yana Mukhamedshina, Daria Chulpanova, Alexander Kostennikov, Shaza Issa, and Albert Rizvanov. 2023. "Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous and Intrathecal Delivery of AAV9-Mediated ARSA in Minipigs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119204
APA StyleMullagulova, A., Shaimardanova, A., Solovyeva, V., Mukhamedshina, Y., Chulpanova, D., Kostennikov, A., Issa, S., & Rizvanov, A. (2023). Safety and Efficacy of Intravenous and Intrathecal Delivery of AAV9-Mediated ARSA in Minipigs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119204