The Sts Proteins: Modulators of Host Immunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sts Catalytic Domains
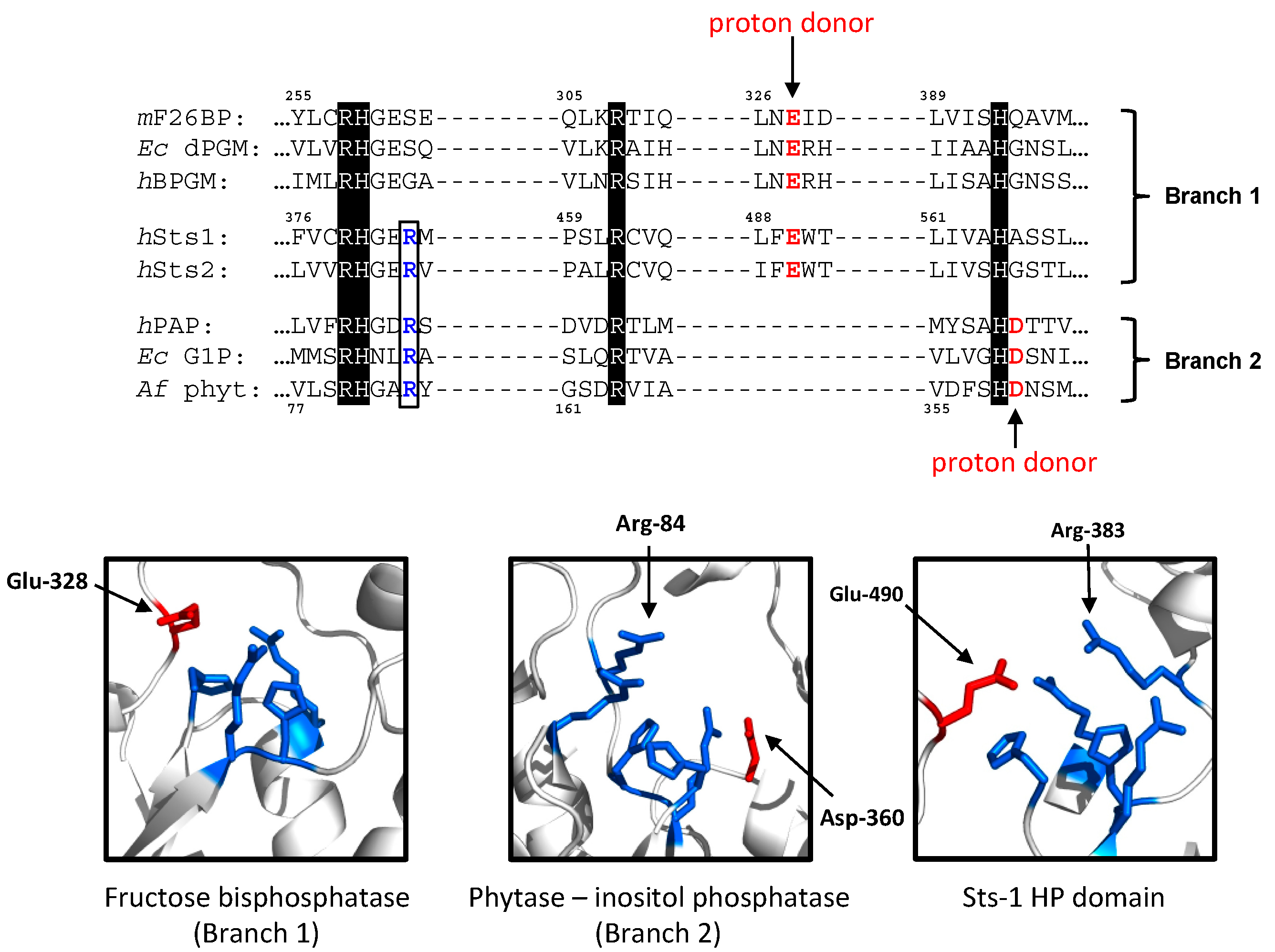
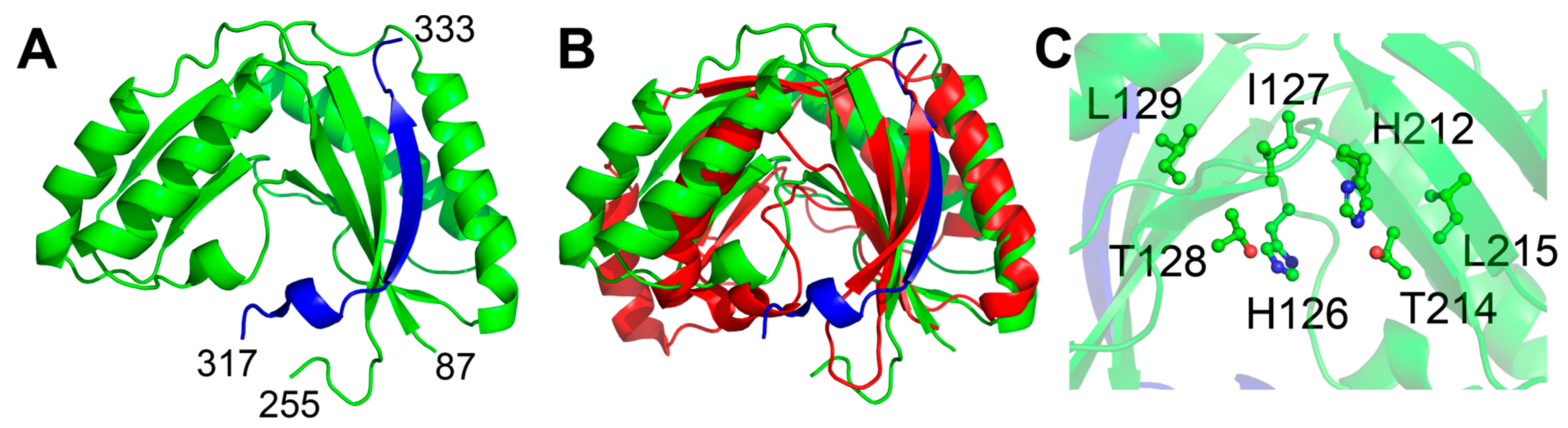
2.1.1. The Sts Histidine Phosphatase (HP) Domain
2.1.2. The Sts Phosphodiesterase (PDE) Domain
2.2. Functional Studies
2.2.1. The Role of Sts in T Cells
2.2.2. The Role of Sts in Additional Cell Types
2.2.3. The Role of Sts in Regulating Anti-Microbial Immunity
- Candida albicans
- 2.
- Francisella tularensis
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsygankov, A.Y. TULA proteins as signaling regulators. Cell Signal. 2020, 65, 109424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.J.; Dixon, J.E.; Manning, G. Genomics and evolution of protein phosphatases. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaag1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpino, N.; Turner, S.; Mekala, D.; Takahashi, Y.; Zang, H.; Geiger, T.L.; Doherty, P.; Ihle, J.N. Regulation of ZAP-70 activation and TCR signaling by two related proteins, Sts-1 and Sts-2. Immunity 2004, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigden, D.J. The histidine phosphatase superfamily: Structure and function. Biochem. J. 2008, 409, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrzejas, M.J. Structure, function, and evolution of phosphoglycerate mutases: Comparison with fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase, acid phosphatase, and alkaline phosphatase. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2000, 73, 263–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, S.I.; Watson, H.C.; Harkins, R.N.; Fothergill, L.A. Structure and activity of phosphoglycerate mutase. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1981, 293, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailik, A.; Ford, B.; Keller, J.; Chen, Y.; Nassar, N.; Carpino, N. A phosphatase activity of Sts-1 contributes to the suppression of TCR signaling. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jakoncic, J.; Carpino, N.; Nassar, N. Structural and functional characterization of the 2H-phosphatase domain of Sts-2 reveals an acid-dependent phosphatase activity. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Luis, B.; Nassar, N.; Carpino, N. New insights into the catalytic mechanism of histidine phosphatases revealed by a functionally essential arginine residue within the active site of the Sts phosphatases. Biochem. J. 2013, 453, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, R.; Sonobe, H. Purification, kinetic characterization, and molecular cloning of a novel enzyme ecdysteroid phosphate phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26365–26373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, L.; Anderson, I.P.; Turner, P.C.; Shirras, A.D.; Rees, H.H.; Rigden, D.J. An unsuspected ecdysteroid/steroid phosphatase activity in the key T-cell regulator, Sts-1, Surprising relationship to insect ecdysteroid phosphate phosphatase. Proteins 2007, 67, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raguz, J.; Wagner, S.; Dikic, I.; Hoeller, D. Suppressor of T-cell receptor signalling 1 and 2 differentially regulate endocytosis and signalling of receptor tyrosine kinases. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 4767–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, R.; Carpino, N.; Tsygankov, A. TULA proteins regulate activity of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ren, L.; Kim, S.; Carpino, N.; Daniel, J.L.; Kunapuli, S.P.; Tsygankov, A.Y.; Pei, D. Determination of the substrate specificity of protein-tyrosine phosphatase TULA-2 and identification of Syk as a TULA-2 substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 31268–31276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Luis, B.; Sondgeroth, B.; Nassar, N.; Carpino, N. Sts-2 is a phosphatase that negatively regulates zeta-associated protein (ZAP)-70 and T cell receptor signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 15943–15954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, R.; Iyer, L.M.; Vasudevan, S.; Aravind, L. Detection of novel members, structure-function analysis and evolutionary classification of the 2H phosphoesterase superfamily. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 5229–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raasakka, A.; Myllykoski, M.; Laulumaa, S.; Lehtimaki, M.; Harlein, M.; Moulin, M.; Kursula, I.; Kursula, P. Determinants of ligand binding and catalytic activity in the myelin enzyme 2′3′-cyclic nucelotide 3′-phosphodiesterase. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raasakka, A.; Kursula, P. The myelin membrane-associated enzyme 2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′-phosphodiesterase: On a highway to structure and function. Neurosci. Bull. 2014, 30, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Frank, D.; Zhou, W.; Kaur, N.; French, J.B.; Carpino, N. An unexpected 2-histidine phosphoesterase activity of suppressor of T-cell receptor signaling protein 1 contributes to the suppression of cell signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 296, 8514–8523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.; Liang, Y.-H.; Li, L.-F.; Su, X.-D. Crystal structure of B. subtilis YjcG characterizing the YjcV-like group of 2H phosphoesterase superfamily. Proteins 2008, 72, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowanetz, K.; Crosetto, N.; Haglund, K.; Schmidt, M.H.; Heldin, C.H.; Dikic, I. Suppressors of T-cell receptor signaling Sts-1 and Sts-2 bind to Cbl and inhibit endocytosis of receptor tyrosine kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 32786–32795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feshchenko, E.A.; Smirnova, E.V.; Swaminathan, G.; Teckchandani, A.M.; Agrawal, R.; Band, H.; Zhang, X.; Annan, R.S.; Carr, S.A.; Tsygankov, A.Y. TULA: An SH3- and UBA-containing protein that binds to c-Cbl and ubiquitin. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4690–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpino, N.; Kobayashi, R.; Zang, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Jou, S.T.; Feng, J.; Nakajima, H.; Ihle, J.N. Identification, cDNA cloning and targeted deletion of p70, a novel, ubiquitiously expressed SH3 domain-containing protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 7491–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, T.N.; Liverani, E.; Ivanova, E.; Russo, G.L.; Carpino, N.; Ganea, D.; Safadi, F.; Kunapuli, S.P.; Tsygankov, A.Y. Members of the novel UBASH3/STS/TULA family of cellular regulators suppress T-cell-driven inflammatory responses in vivo. Immunol. Cell Biol 2014, 92, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, N.; Ohmura, K.; Katayama, M.; Akizuki, S.; Carpino, N.; Murakami, K.; Nakashima, R.; Hashimoto, M.; Imura, Y.; Yoshifuji, H.; et al. Suppressor of TCR signaling-2 (Sts-2) suppresses arthritis development in mice. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 28, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kadlecek, T.A.; Au-Yeung, B.B.; Sjolin Goodfellow, H.E.; Hsu, L.-Y.; Freedman, T.S.; Weiss, A. Zap-70, an essential kinase in T-cell signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a002279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpino, N.; Chen, Y.; Nassar, N.; Oh, H.-W. The Sts proteins target tyrosine phosphorylated, ubiquitinated proteins within TCR signaling pathways. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 3224–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, J.L.; Otero, D.C.; Bae, E.-A.; Stairiker, C.J.; Palete, A.B.; Faso, H.A.; Lin, M.; Henriquez, M.L.; Roy, S.; Seo, H.; et al. PSGL-1 attenuates early TCR signaling to suppress CD8+ T cell progenitor differentiation and elicit terminal CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, T.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Tang, S.; Wang, C.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; et al. K33-linked polyubiquitination of Zap70 by Nrdp1 controls CD8(+) T cell activation. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Jin, J.; Chang, J.H.; Zou, Q.; Xie, X.; Cheng, X.; Sun, S.C. Otud7b facilitates T cell activation and inflammatory responses by regulating Zap70 ubiquitination. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Paisie, T.K.; Newman, J.R.B.; McIntyre, L.M.; Concannon, P. UBASH3 mediates risk for Type 1 diabetes through inhibition of T-cell receptor-induced NF-kB signaling. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2033–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Paisie, T.K.; Chen, S.; Concannon, P. UBASH3 regulates the synthesis and dynamics of the TCR-CD3 complexes. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 2827–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticone, G.; Huang, Z.; Csibi, F.; Leit, S.; Ciccone, D.; Champhekar, A.S.; Austin, J.E.; Ucar, D.A.; Hossain, F.; Ibba, S.V.; et al. Targeting the Cbl-b-Notch1 axis as a novel immuno-therapeutic strategy to boost CD8+ T-cell responses. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 987298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reppschlager, K.; Gosselin, J.; Dangelmaier, C.A.; Thomas, D.H.; Carpino, N.; McKenzie, S.E.; Kunapuli, S.P.; Tsygankov, A.Y. TULA-2 protein phosphatase suppresses activation of Syk through the GPVI platelet receptor for collagen by dephosphorylating Tyr(P)346, a regulatory site of Syk. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 22427–22441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.H.; Getz, T.M.; Newman, T.N.; Dangelmaier, C.A.; Carpino, N.; Kunapuli, S.P.; Tsygankov, A.Y.; Daniel, J.L. A novel histidine tyrosine phosphatase, TULA-2, associates with Syk and negatively regulates GPVI signaling in platelets. Blood 2016, 116, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, R.O.; Zhang, J.; Groves, J.R.; Barbu, E.A.; Siraganian, R.P. Once phosphorylated, tyrosines in carboxyl terminus of protein-tyrosine kinase Syk interact with signaling proteins, including TULA-2, a negative regulator of mast cell degranulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 8194–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, S.H.; Adapala, N.S.; Barbe, M.F.; Carpino, N.; Tsygankov, A.Y.; Sanjay, A. TULA-2, a novel histidine phosphatase, regulates bone remodeling by modulating osteoclast function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Vakhursheva, O.; Bandi, S.R.; Demirel, O.; Kazi, J.U.; Fernandes, R.G.; Jakobi, K.; Eichler, A.; Ronnstrand, L.; Rieger, M.A.; et al. The phosphatases Sts-1 and Sts-2 regulate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell fitness. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, P.G.; Lionakis, M.S.; Arendrup, M.C.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Kullberg, B.J. Invasive candidiasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionakis, M.S. New insights into innate immune control of systemic candidiasis. Med. Mycol. 2014, 52, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellberg, B.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Edwards, J.E., Jr.; Filler, S.G. Mice with disseminated candidiasis die of progressive sepsis. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseem, S.; Frank, D.; Konopka, J.B.; Carpino, N. Protection from systemic Candida albicans infection by inactivation of the Sts phosphatases. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Naseem, S.; Russo, G.L.; Li, C.; Parashar, K.; Konopka, J.B.; Carpino, N. Phagocytes from mice lacking the Sts phosphatases have an enhanced antifungal response to Candida albicans. mBio 2018, 9, e00782-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLendon, M.K.; Apicella, M.A.; Allen, L.-H.H. Francisella tularensis: Taxonomy, genetics, and immunopathogenesis of a potential agent of biowarfare. Annu. Rev. Micobiol. 2006, 60, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashar, K.; Kopping, E.; Frank, D.; Sampath, V.; Thanassi, D.G.; Carpino, N. Increased resistance to intradermal Francisella tularensis LVS infection by inactivation of the Sts phosphatases. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00406-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, K.; Carpino, N. A role for the Sts phosphatases in negatively regulating IFNγ-mediated production of nitric oxide in monocytes. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2020, 8, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, M.R.; Thirawatananond, P.; Peters, L.; Sharp, R.C.; Ogundare, S.; Posgai, A.L.; Perry, D.J.; Brusko, T.M. De-coding genetic risk variants in type 1 diabetes. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2021, 99, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsygankov, A.Y. TULA-family proteins: Jacks of many trades and then some. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaman, A.; French, J.B.; Carpino, N. The Sts Proteins: Modulators of Host Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108834
Zaman A, French JB, Carpino N. The Sts Proteins: Modulators of Host Immunity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):8834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108834
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaman, Anika, Jarrod B. French, and Nick Carpino. 2023. "The Sts Proteins: Modulators of Host Immunity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 8834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108834
APA StyleZaman, A., French, J. B., & Carpino, N. (2023). The Sts Proteins: Modulators of Host Immunity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 8834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108834





