Sevoflurane Exposure in Neonates Perturbs the Expression Patterns of Specific Genes That May Underly the Observed Learning and Memory Deficits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
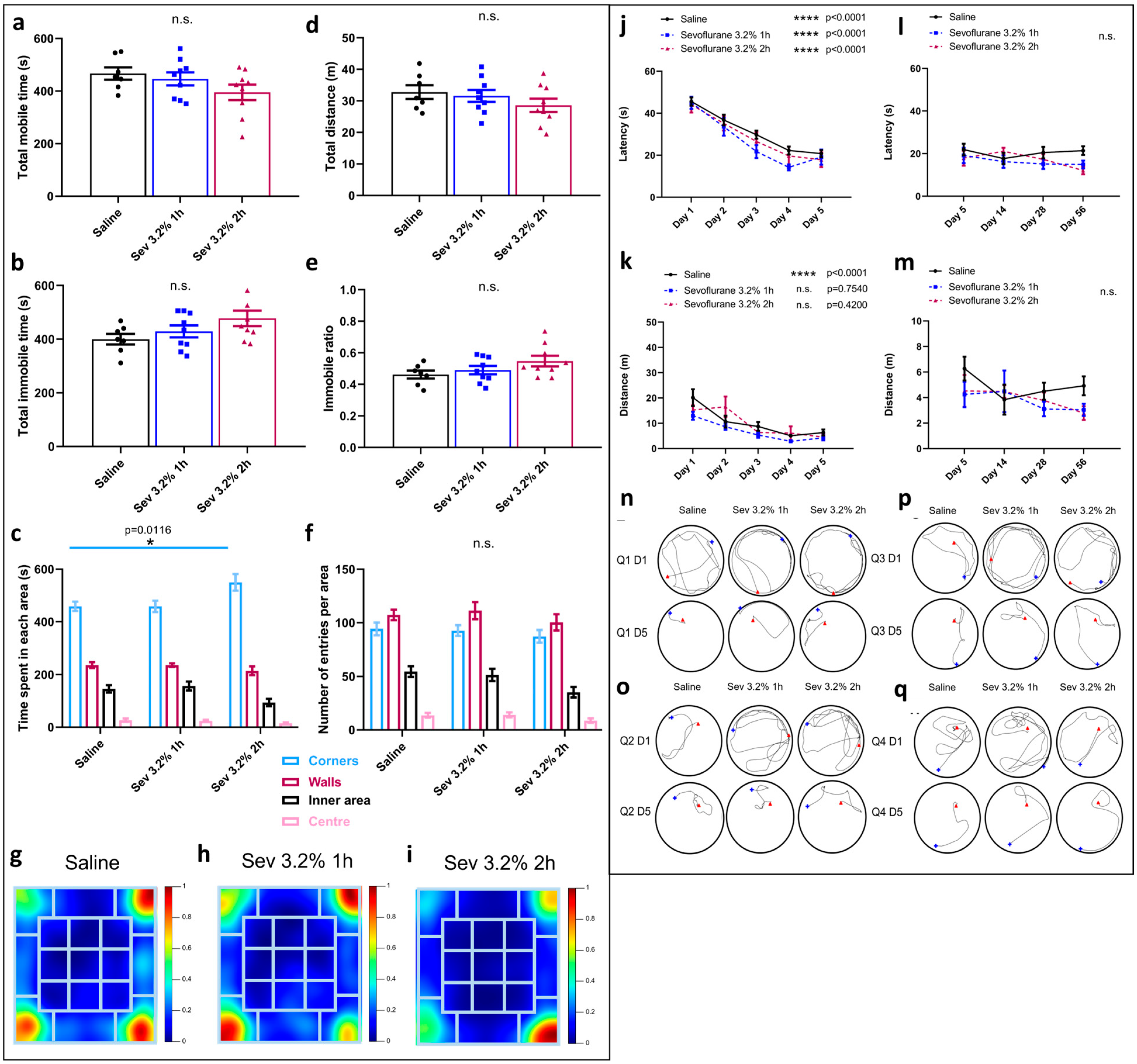
2.1. Sevoflurane Exposure Did Not Compromise Locomotor Skills but Impacted Various Aspects of Exploratory Behaviours
2.2. Sevoflurane Exposure Resulted in Erratic Swimming Patterns but Did Not Impact Spatial Memory
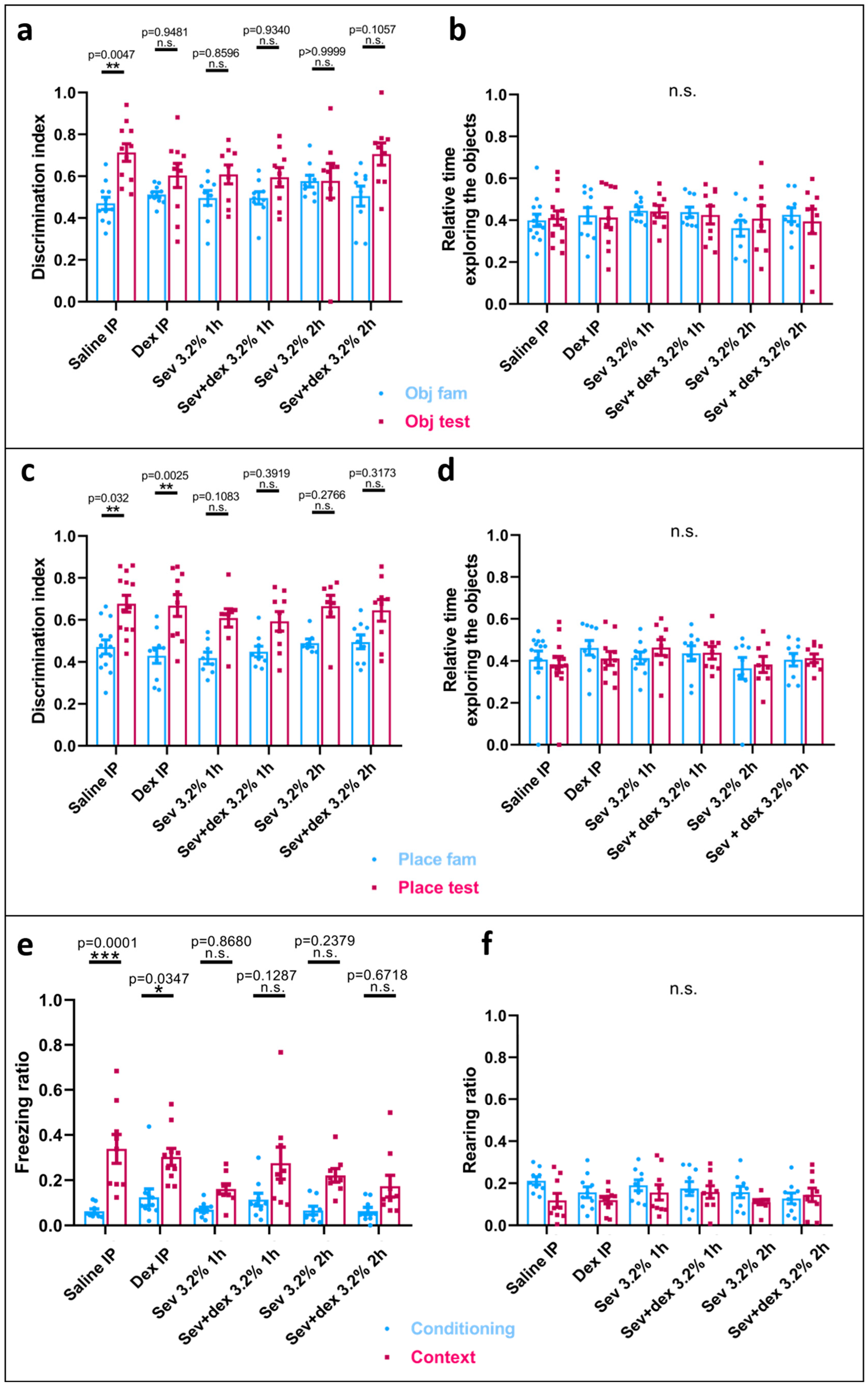
2.3. Sevoflurane Exposure Resulted in Object Recognition Deficits
2.4. Sevoflurane Exposure Compromised Hippocampal-Dependent Memory
2.5. DEX IP Pre-Treatment Resulted in a Significant Respiratory Depression
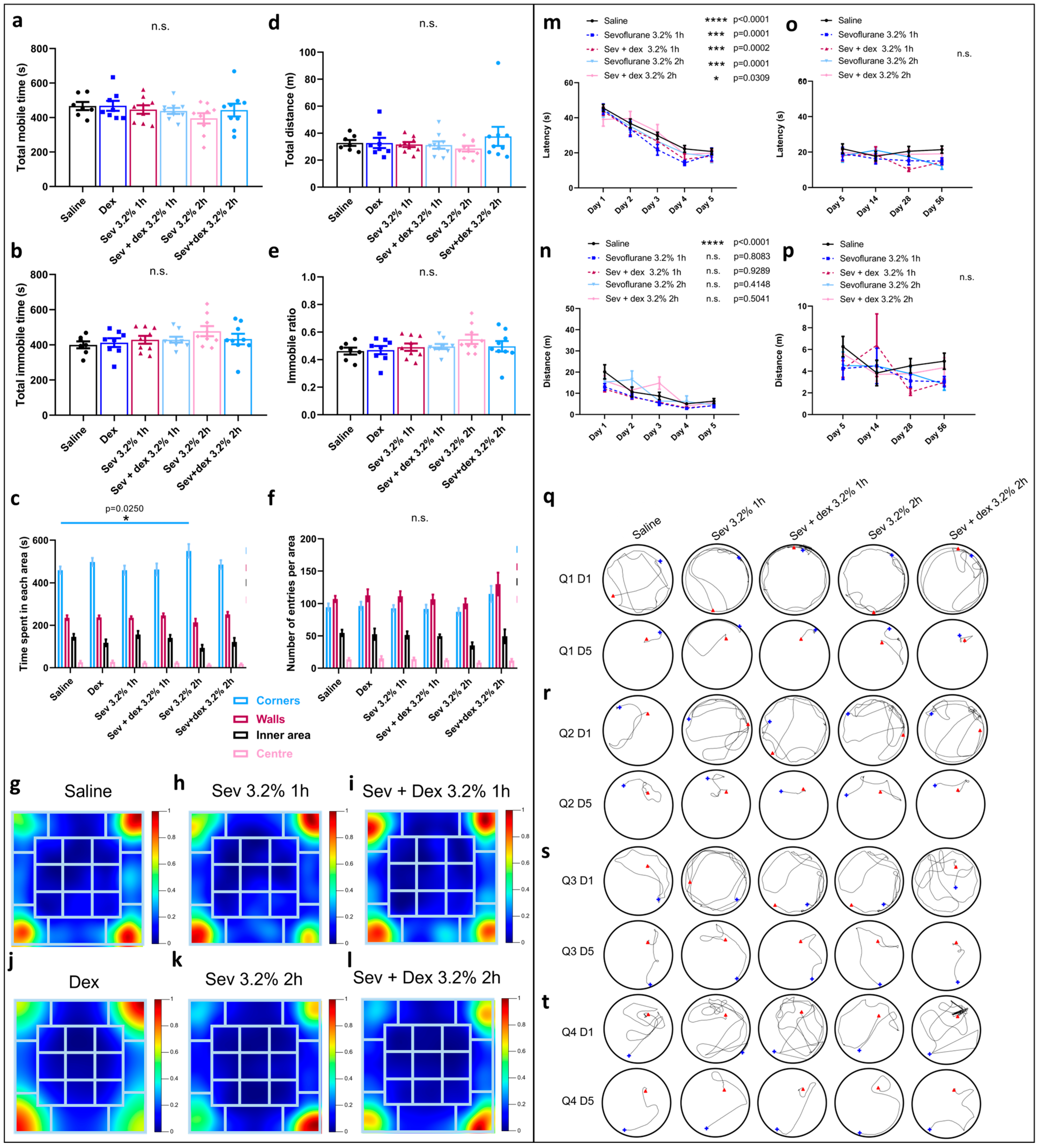
2.6. DEX Pre-Treatment Via IP Mode of Administration Impacted the Exploratory Behaviour
2.7. DEX Pre-Treatment Did Not Significantly Impact Spatial Memory
2.8. DEX Pre-Treatment Did Not Prevent Recognition Memory Deficits Caused by Sevoflurane Exposure
2.9. DEX IP Pre-Treatment Did Not Prevent Hippocampal-Dependent Memory Deficits
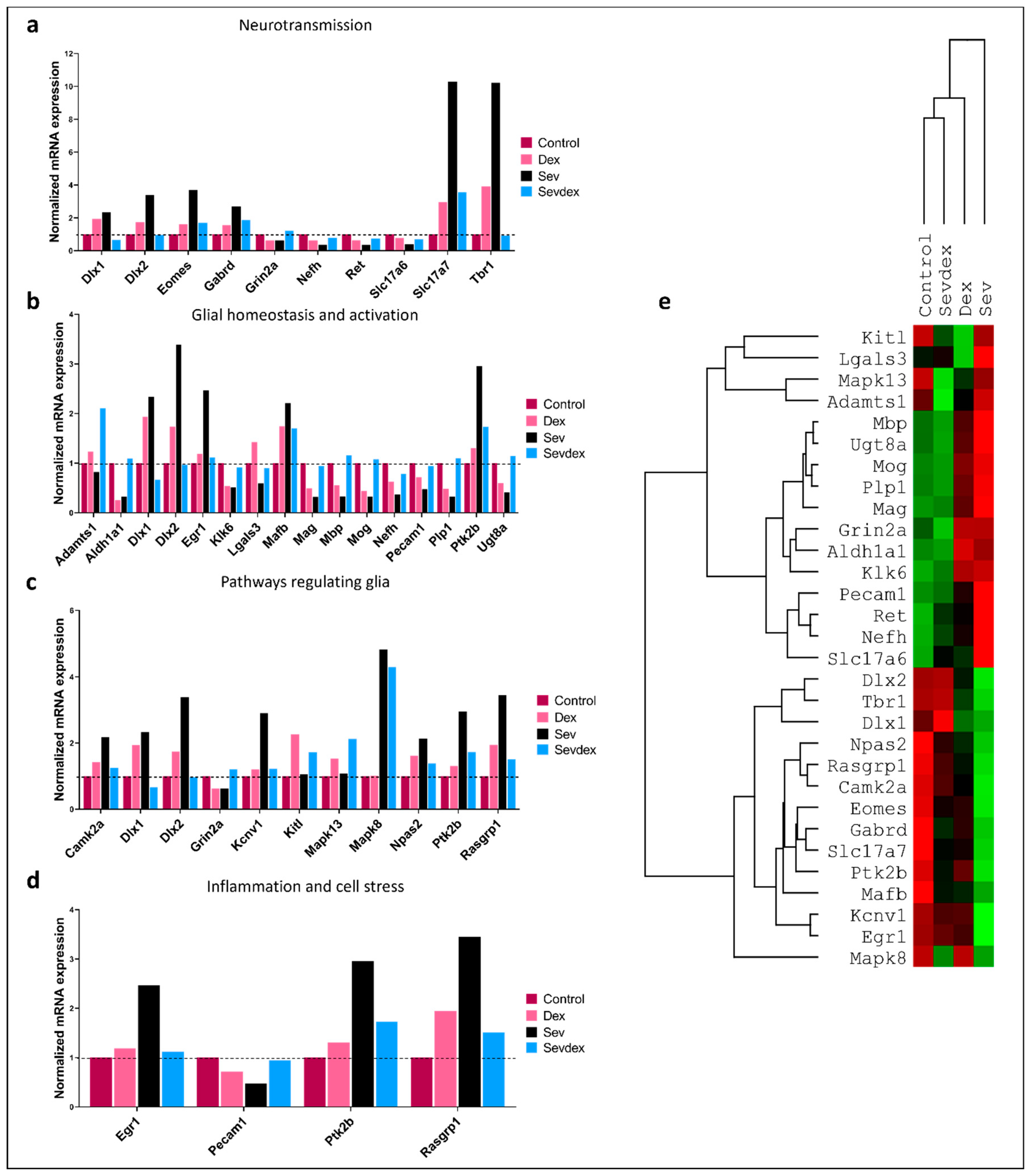
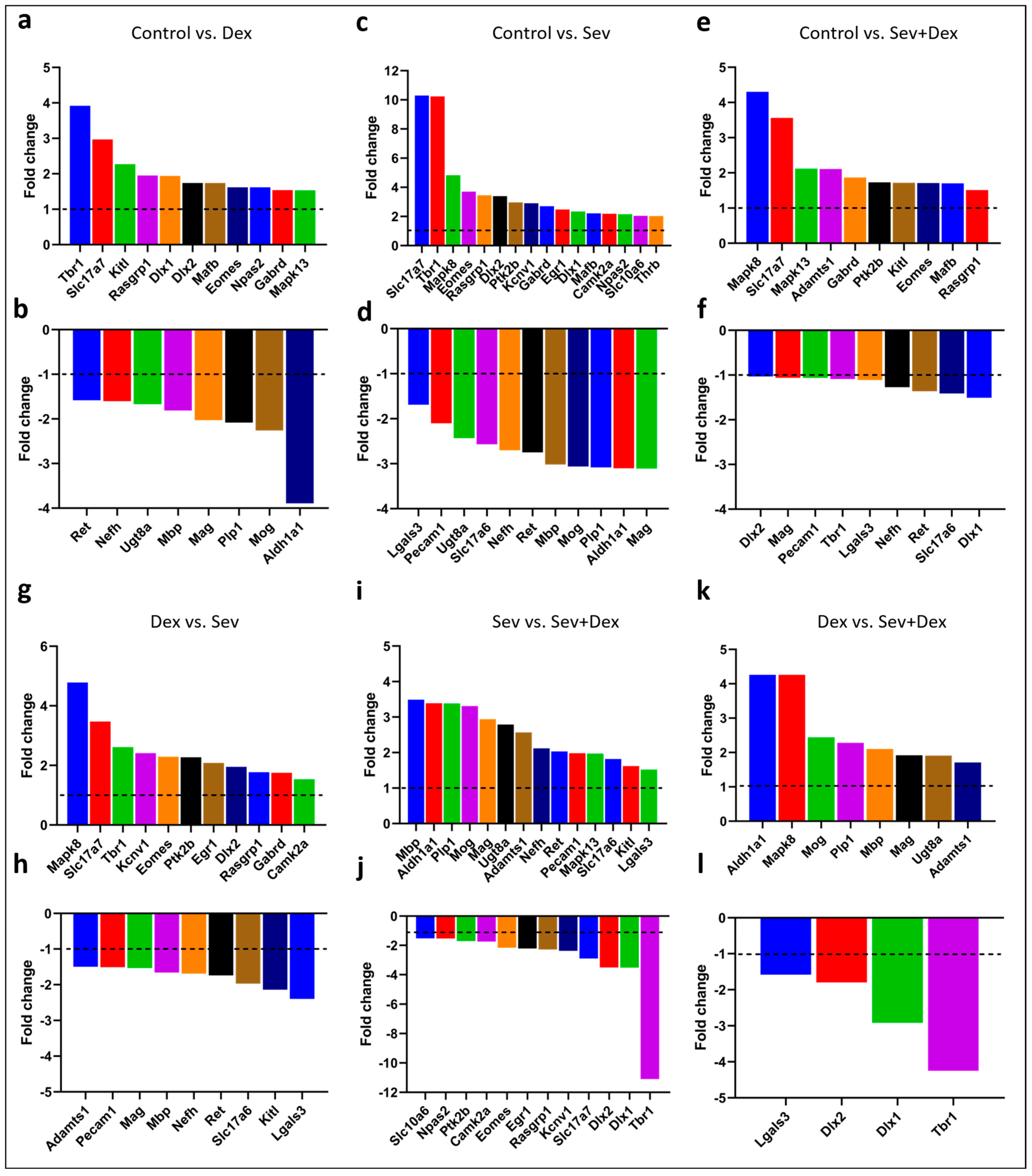
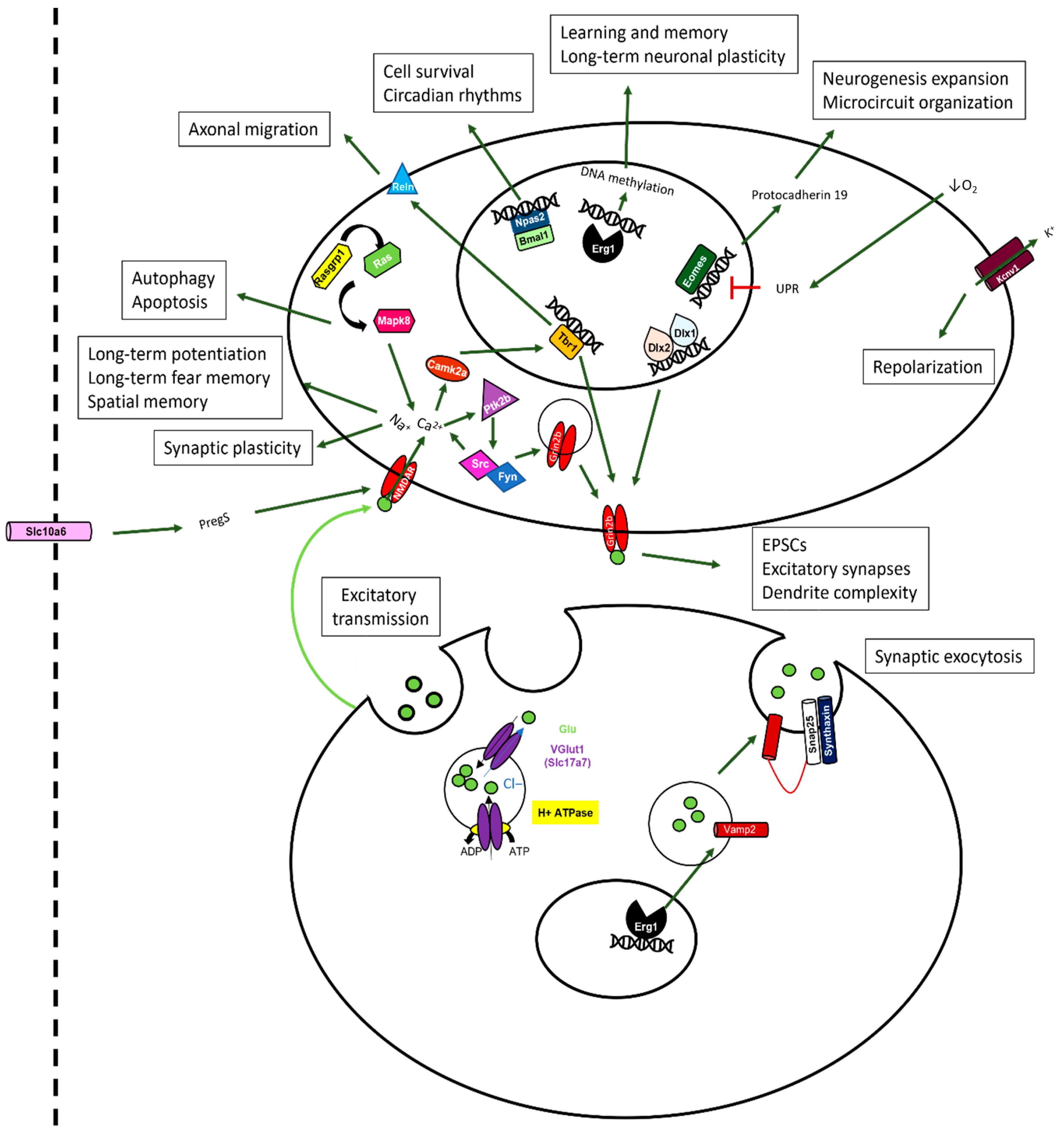
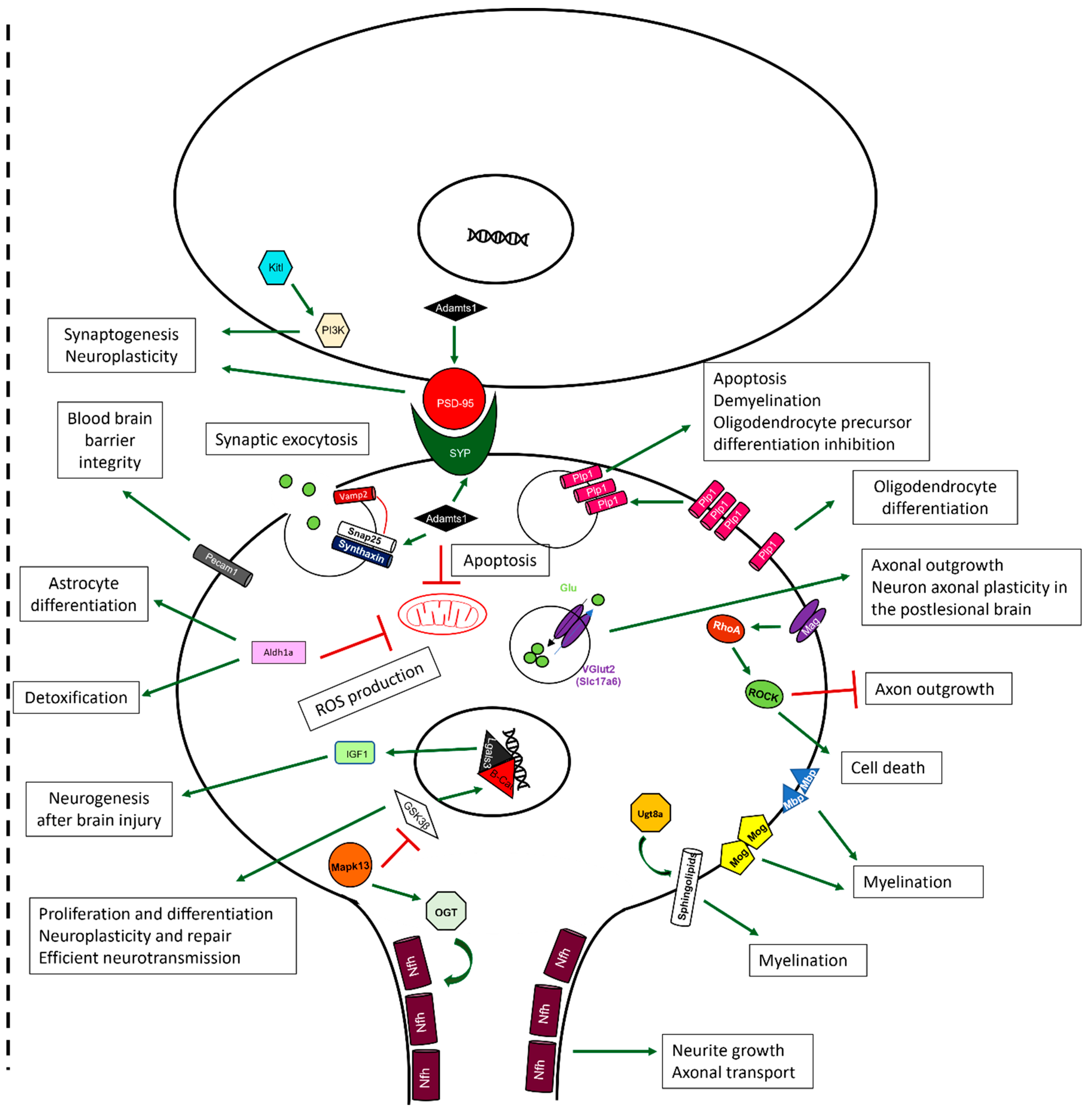
2.10. Sevoflurane and Dexmedetomidine Differentially Affected Patterns of Gene Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Dexmedetomidine Treatment
4.3. Sevoflurane Exposure
4.4. Morris Water Maze
4.5. Novel Object Recognition
4.6. Open Field
4.7. Contextual Fear Conditioning
4.8. RNA Isolation
4.9. Nanostring RNA Expression Quantification
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiser, T.G.; Haynes, A.B.; Molina, G.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Esquivel, M.M.; Uribe-Leitz, T.; Fu, R.; Azad, T.; Chao, T.E.; Berry, W.R.; et al. Size and Distribution of the Global Volume of Surgery in 2012. Bull World Health Organ 2016, 94, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkalayci, O.; Araz, C.; Cehreli, S.B.; Tirali, R.E.; Kayhan, Z. Effects of Music on Sedation Depth and Sedative Use during Pediatric Dental Procedures. J. Clin. Anesth. 2016, 34, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soehle, M.; Bochem, J. Anesthesia for Electroconvulsive Therapy. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2018, 31, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickey, B.J.; White, A.T.; Arp, A.M.; Leonardi, K.; Torres, M.M.; Larson, A.L.; Odell, D.H.; Whittingham, S.A.; Beck, M.M.; Jessop, J.E.; et al. Propofol for Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 21, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitilian, H.; Eckenhoff, R.; Raines, D. Anesthetic Drug Development: Novel Drugs and New Approaches. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2013, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzma, P.J.; Kline, M.D.; Calkins, M.D.; Staats, P.S. Progress in the Development of Ultra-Long-Acting Local Anesthetics. Reg. Anesth. 1998, 22, 543–551. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, F.; Thompson, A.J.; Riaz, S.; Pehar, M.; Rice, T.; Syed, N.I. Anesthetics: From Modes of Action to Unconsciousness and Neurotoxicity. J. Neurophysiol. 2019, 122, 760–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA Approves Label Changes for Use of General Anesthetic and Sedation Drugs in Young Children|FDA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communication-fda-approves-label-changes-use-general-anesthetic-and-sedation-drugs (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- Brioni, J.D.; Varughese, S.; Ahmed, R.; Bein, B. A Clinical Review of Inhalation Anesthesia with Sevoflurane: From Early Research to Emerging Topics. J. Anesth. 2017, 31, 764–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Zoghbi, J.F.; Zhu, W.; Grafe, M.R.; Brambrink, A.M. Dexmedetomidine-Mediated Neuroprotection against Sevoflurane-Induced Neurotoxicity Extends to Several Brain Regions in Neonatal Rats. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Joseph, B.; Hofacer, R.; Upton, B.; Lee, S.; Ewing, L.; Zhang, B.; Danzer, S.; Loepke, A. Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Sevoflurane-Induced Neurodegeneration in Neonatal Rats. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.-J.; Yu, P.-X.; Zhang, F.-Z.; Dong, Z.-M. Dexmedetomidine Mitigates Sevoflurane-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest in Hippocampus. J. Anesth. 2018, 32, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Fu, Z.; Luo, X. Dexmedetomidine on Autophagy of Hippocampal Neurons in Aged Rats under Sevoflurane Anesthesia. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, M.C.; Murphy, K.L.; Baxter, M.G. Visual Recognition Memory Is Impaired in Rhesus Monkeys Repeatedly Exposed to Sevoflurane in Infancy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Newport, G.; Paule, M.; Callicott, R.; Thompson, J.; Liu, F.; Patterson, T.; Berridge, M.; Apana, S.; et al. In Vivo Monitoring of Sevoflurane-Induced Adverse Effects in Neonatal Nonhuman Primates Using Small-Animal Positron Emission Tomography. Anesthesiology 2016, 125, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.E.; Berde, C.; Soriano, S.; Marmor, J.; Bellinger, D.; de Graaff, J.C.; de Graaff, J.C.; Dorris, L.; Bell, G.; Morton, N.; et al. Neurodevelopmental Outcome at 5 Years of Age after General Anaesthesia or Awake-Regional Anaesthesia in Infancy (GAS): An International, Multicentre, Randomised, Controlled Equivalence Trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A.J.; Disma, N.; De Graaff, J.C.; Withington, D.E.; Dorris, L.; Bell, G.; Stargatt, R.; Bellinger, D.C.; Schuster, T.; Arnup, S.J.; et al. Neurodevelopmental Outcome at 2 Years of Age after General Anaesthesia and Awake-Regional Anaesthesia in Infancy (GAS): An International Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.S.; Li, G.; Miller, T.L.K.; Salorio, C.; Byrne, M.W.; Bellinger, D.C.; Ing, C.; Park, R.; Radcliffe, J.; Hays, S.R.; et al. Association between a Single General Anesthesia Exposure before Age 36 Months and Neurocognitive Outcomes in Later Childhood. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 315, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, D.O.; Zaccariello, M.J.; Katusic, S.K.; Schroeder, D.R.; Hanson, A.C.; Schulte, P.J.; Buenvenida, S.L.; Gleich, S.J.; Wilder, R.T.; Sprung, J.; et al. Neuropsychological and Behavioral Outcomes after Exposure of Young Children to Procedures Requiring General Anesthesia: The Mayo Anesthesia Safety in Kids (MASK) Study. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Hong, W.; Tang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, H. Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Neurotoxicity in Developing Rats Induced by Sevoflurane through Upregulating BDNF-TrkB-CREB and Downregulating ProBDNF-P75NRT-RhoA Signaling Pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 5458061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, D.; Yan, J.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, H. Sevoflurane Inhibits Neuronal Migration and Axon Growth in the Developing Mouse Cerebral Cortex. Aging 2020, 12, 6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liang, F.; Huang, L.; Fang, F.; Yang, G.; Tanzi, R.E.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, Q.; Xie, Z. The Anesthetic Sevoflurane Induces Tau Trafficking from Neurons to Microglia. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Dong, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, F.; Zhang, J.; Soriano, S.G.; Xie, Z. Dexmedetomidine and Clonidine Attenuate Sevoflurane-Induced Tau Phosphorylation and Cognitive Impairment in Young Mice via α-2 Adrenergic Receptor. Anesth. Analg. 2021, 132, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Hong, W.; Tang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, H. Sevoflurane Leads to Learning and Memory Dysfunction via Breaking the Balance of TPA/PAI-1. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 139, 104789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, L.; Wang, M. Dexmedetomidine Alleviates Sevoflurane-Induced Neurotoxicity via Mitophagy Signaling. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 7893–7901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Shen, J.; Yu, L.; Sun, J.; McQuillan, P.M.; Hu, Z.; Yan, M. Role of Autophagy in Sevoflurane-Induced Neurotoxicity in Neonatal Rat Hippocampal Cells. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 140, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Tellez, N.; Pehar, M.; Iqbal, F.; Casas-Ortiz, A.; Rice, T.; Syed, N.I. Dexmedetomidine Pre-Treatment of Neonatal Rats Prevents Sevoflurane-Induced Deficits in Learning and Memory in the Adult Animals. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Dong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Crosby, G.; Culley, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z. Sevoflurane Anesthesia in Pregnant Mice Induces Neurotoxicity in Fetal and Offspring Mice. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Liu, J.; Kramberg, L.; Ruggiero, A.; Cottrell, J.; Kass, I.S. Early-Life Single-Episode Sevoflurane Exposure Impairs Social Behavior and Cognition Later in Life. Brain Behav. 2016, 6, e00514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.; Park, S.; Hong, J.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Heo, J.; Kim, D.; Ko, Y. Sevoflurane Exposure during the Neonatal Period Induces Long-Term Memory Impairment but Not Autism-Like Behaviors. Pediatr. Anesth. 2015, 25, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Uchida, Y.; Chiba, T.; Kurimoto, R.; Matsushima, T.; Inotsume, M.; Ishikawa, C.; Li, H.; Shiga, T.; Muratani, M.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Sevoflurane Exposure Effects at the Different Brain Regions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.-Y.; Meng, X.-W.; Xia, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.-C.; Liu, H.-Y.; Ji, F.-H.; Peng, K. Cognitive Impairment and Transcriptomic Profile in Hippocampus of Young Mice after Multiple Neonatal Exposures to Sevoflurane. Aging 2019, 11, 8386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayase, T.; Tachibana, S.; Yamakage, M. Effect of Sevoflurane Anesthesia on the Comprehensive MRNA Expression Profile of the Mouse Hippocampus. Med. Gas Res. 2016, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, G.; Hori, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Tanaka, S.; Sakamoto, A. Changes in the Gene Expression Levels of MicroRNAs in the Rat Hippocampus by Sevoflurane and Propofol Anesthesia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.; Yang, V. Krüppel-Like Factor 4 (KLF4): What We Currently Know. Gene 2017, 611, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Israr, M.; Li, B.; Yu, P.; Gao, G.; Chang, Y.-Z.; Shi, Z. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Molecular Mechanism of Alzheimer-Related Neuropathology Induced by Sevoflurane in Mice. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 17555–17565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.-Y.; Lu, Z.-P.; Zhao, W.; Zou, J.-Q.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Zhou, L.-B.; Lei, H.-Y. The Role of Klotho Protein Against Sevoflurane-Induced Neuronal Injury. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 47, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, D.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yan, J.; Hu, R.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H. Multiple Sevoflurane Exposures during Pregnancy Inhibit Neuronal Migration by Upregulating Prostaglandin D2 Synthase. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2019, 78, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Lu, X.F.; Shao, C.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Ma, T.; Zhang, L.C.; Cao, J.L. The Effects of Sevoflurane Anesthesia on Rat Hippocampus: A Genomic Expression Analysis. Brain Res. 2011, 1381, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huitink, J.; Heimerikxs, M.; Nieuwland, M.; Loer, S.; Brugman, W.; Velds, A.; Sie, D.; Kerkhoven, R. Volatile Anesthetics Modulate Gene Expression in Breast and Brain Tumor Cells. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 111, 1411–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culley, D.; Yukhananov, R.; Xie, Z.; Gali, R.; Tanzi, R.; Crosby, G. Altered Hippocampal Gene Expression 2 Days after General Anesthesia in Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 549, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broad, K.D.; Kawano, G.; Fierens, I.; Rocha-Ferreira, E.; Hristova, M.; Ezzati, M.; Rostami, J.; Alonso-Alconada, D.; Chaban, B.; Hassell, J.; et al. Surgery Increases Cell Death and Induces Changes in Gene Expression Compared with Anesthesia Alone in the Developing Piglet Brain. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, D.H.; Popovic, K.; Fulton, R.; Kassiou, M. Anaesthetic-Dependent Changes in Gene Expression Following Acute and Chronic Exposure in the Rodent Brain. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekny, T.; Andersson, D.; Wilhemsson, U.; Pekna, M.; Pekny, M. Short General Anaesthesia Induces Prolonged Changes in Gene Expression in the Mouse Hippocampus. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2014, 58, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Paule, M.; Ali, S.; Wang, C. Ketamine-Induced Neurotoxicity and Changes in Gene Expression in the Developing Rat Brain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2011, 9, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Suen, K.C.; Hana, Z.; Sanders, R.D.; Maze, M.; Ma, D. Neuroprotection and Neurotoxicity in the Developing Brain: An Update on the Effects of Dexmedetomidine and Xenon. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 60, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ari, Y. Excitatory Actions of Gaba during Development: The Nature of the Nurture. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, E.; Steinmann, M.E. Structure, Function, and Modulation of GABA(A) Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40224–40231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, X. Basic Pharmacology of NMDA Receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 1558–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou, Q. NMDA Receptor Subunit Diversity: Impact on Receptor Properties, Synaptic Plasticity and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, A.; Niu, K.; Wang, G. Meta-Analysis of Dexmedetomidine on Emergence Agitation and Recovery Profiles in Children after Sevoflurane Anesthesia: Different Administration and Different Dosage. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Yang, F.; Tang, Z.; Bi, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Dexmedetomidine Ameliorates the Neurotoxicity of Sevoflurane on the Immature Brain Through the BMP/SMAD Signaling Pathway. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Chen, Y.; Luan, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y. Dexmedetomidine Reduces Inflammation in Traumatic Brain Injury by Regulating the Inflammatory Responses of Macrophages and Splenocytes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lai, I.K.; Pan, J.Z.; Zhang, P.; Maze, M. Dexmedetomidine Exerts an Anti-Inflammatory Effect via A2 Adrenoceptors to Prevent Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cognitive Decline in Mice. Anesthesiology 2020, 133, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Tellez, N.; Iqbal, F.; Pehar, M.; Casas-Ortiz, A.; Rice, T.; Syed, N.I. Dexmedetomidine Does Not Compromise Neuronal Viability, Synaptic Connectivity, Learning and Memory in a Rodent Model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturman, O.; Germain, P.L.; Bohacek, J. Exploratory Rearing: A Context- and Stress-Sensitive Behavior Recorded in the Open-Field Test. Stress 2018, 21, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.R.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.X.; Zhang, Y.X. Expression of VGLUTs Contributes to Degeneration and Acquisition of Learning and Memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2011, 95, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Mahnke, A.H.; Doyle, S.; Fan, N.; Wang, C.-C.; Hall, B.J.; Tang, Y.-P.; Inglis, F.M.; Chen, C.; Erickson, J.D. Neurodevelopmental Role for VGLUT2 in Pyramidal Neuron Plasticity, Dendritic Refinement, and in Spatial Learning. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 15886–15901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.-C.; Huang, T.-N.; Hsueh, Y.-P. Neuronal Excitation Upregulates Tbr1, a High-Confidence Risk Gene of Autism, Mediating Grin2b Expression in the Adult Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Shirakami, G.; Tazuke-Nishimura, M.; Matsuura, S.; Tanimoto, K.; Fukuda, K. Effect of Single-Dose Dexmedetomidine on Emergence Agitation and Recovery Profiles after Sevoflurane Anesthesia in Pediatric Ambulatory Surgery. J. Anesth. 2010, 24, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Abdellatif, A.A. Prevention of Sevoflurane Related Emergence Agitation in Children Undergoing Adenotonsillectomy: A Comparison of Dexmedetomidine and Propofol. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2013, 7, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Guo, R.; Sun, L. Dexmedetomidine for Preventing Sevoflurane-Related Emergence Agitation in Children: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2014, 58, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurky, M.; Clyde, M.; Kalarickal, P.; Ramadhyani, U. Does Dexmedetomidine Prevent Emergence Delirium in Children after Sevoflurane-Based General Anesthesia? Pediatr. Anesth. 2005, 15, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Miao, S.; Gu, T.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Dexmedetomidine for the Prevention of Emergence Delirium and Postoperative Behavioral Changes in Pediatric Patients with Sevoflurane Anesthesia: A Double-Blind, Randomized Trial. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Qian, B.; Lin, Y.; Wu, W.; Ye, H.; Chen, Y. Intranasal Dexmedetomidine Premedication Reduces Minimum Alveolar Concentration of Sevoflurane for Laryngeal Mask Airway Insertion and Emergence Delirium in Children: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Pediatr. Anesth. 2015, 25, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, C.R.; Engineer, S.R.; Shah, B.J.; Madhu, S. The Effect of Dexmedetomidine Continuous Infusion as an Adjuvant to General Anesthesia on Sevoflurane Requirements: A Study Based on Entropy Analysis. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 29, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Kil, H.K. Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Sevoflurane Requirements and Emergence Agitation in Children Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery. Yonsei Med. J. 2014, 55, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.; Yoon, S.; Shin, Y.S. Multiple Exposures of Sevoflurane during Pregnancy Induces Memory Impairment in Young Female Offspring Mice. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2017, 70, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.; Ryu, M.J.; Heo, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Yoon, S.; Park, H.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Yoon, S.H.; et al. Sevoflurane Exposure during the Critical Period Affects Synaptic Transmission and Mitochondrial Respiration but Not Long-Term Behavior in Mice. Anesthesiology 2017, 126, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Gong, X.; Fang, X.; Xing, F.; Xia, T.; Gu, X. Sevoflurane Plays a Reduced Role in Cognitive Impairment Compared with Isoflurane: Limited Effect on Fear Memory Retention. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Su, J.; Cai, D.; Xu, Q. Sevoflurane Postconditioning Improves Long-Term Learning and Memory of Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Brain Damage Rats via the PI3K/Akt-MPTP Pathway. Brain Res. 2016, 1630, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, J.K.; Jones, N.C.; Royse, A.G.; Royse, C.F. Sevoflurane Anesthesia Does Not Impair Acquisition Learning or Memory in the Morris Water Maze in Young Adult and Aged Rats. Anesthesiology 2012, 117, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.S.O.; Gomes, H.S.; Sado-Filho, J.; Costa, L.R.; Costa, P.S. Does Sevoflurane Add to Outpatient Procedural Sedation in Children? A Randomised Clinical Trial. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedenstierna, G. Oxygen and Anesthesia: What Lung Do We Deliver to the Post-Operative Ward? Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2012, 56, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinsasser, A.T.; Pircher, I.; Truebsbach, S.; Knotzer, H.; Loeckinger, A.; Treml, B. Pulmonary Function after Emergence on 100% Oxygen in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseA Randomized, Controlled Trial. Anesthesiology 2014, 120, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, J.; Van der Walt, J. Oxygen in Neonatal and Infant Anesthesia—Current Practice in the UK. Pediatr. Anesth. 2008, 18, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vento, M.; Asensi, M.; Sastre, J.; García-Sala, F.; Pallardó, F.; Viña, J. Resuscitation with Room Air Instead of 100% Oxygen Prevents Oxidative Stress in Moderately Asphyxiated Term Neonates. Pediatrics 2001, 107, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, S.G.E.; Mure, M. Dosing Oxygen: A Tricky Matter or a Piece of Cake? Anesth. Analg. 2002, 95, 1472–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greif, R.; Laciny, S.; Rapf, B.; Hickle, R.; Sessler, D. Supplemental Oxygen Reduces the Incidence of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting. Anesthesiology 1999, 91, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greif, R.; Akça, O.; Horn, E.; Kurz, A.; Sessler, D. Supplemental Perioperative Oxygen to Reduce the Incidence of Surgical-Wound Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Manaenko, A.; Xu, T.; Guo, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Traumatic Brain Injury: Bench-to-Bedside. Med. Gas Res. 2016, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Meng, X.; Cui, Y.; Gou, X.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, X.; Gao, C.; Xu, L.; Luo, E. The Neuroprotective Effect of Hyperoxygenate Hydrogen-Rich Saline on CO-Induced Brain Injury in Rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 67, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerman, J.; Sikich, N.; Kleinman, S.; Yentis, S. The Pharmacology of Sevoflurane in Infants and Children. Anesthesiology 1994, 80, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, T.J.; Kritzmire, S.M. Neonatal Anesthesia. In A Practical Approach to Neonatal Diseases; ResearchGate: Berlin, Germany, 2021; pp. 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J. Learning, Memory and Synaptic Plasticity in Hippocampus in Rats Exposed to Sevoflurane. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2016, 48, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satomoto, M.; Satoh, Y.; Terui, K.; Miyao, H.; Takishima, K.; Ito, M.; Imaki, J. Neonatal Exposure to Sevoflurane Induces Abnormal Social Behaviors and Deficits in Fear Conditioning in Mice. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.-S.; Jia, M.; Sun, J.; Sun, X.-R.; Zhang, H.; Ji, M.-H.; Yang, J.-J.; Wang, Z.-Y. Hypermethylation of Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity-Related Genes Is Involved in Neonatal Sevoflurane Exposure-Induced Cognitive Impairments in Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2016, 29, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Satomoto, M.; Adachi, Y.U.; Kinoshita, H.; Makita, K. Inhibiting NADPH Oxidase Protects against Long-Term Memory Impairment Induced by Neonatal Sevoflurane Exposure in Mice. BJA Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 117, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yang, F.; Wu, X.; Liu, H. Dexmedetomidine Protects Hippocampal Neurons against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Apoptosis through Activation HIF-1α/P53 Signaling. Life Sci. 2019, 232, 116611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Cui, E.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Yan, M.; Sun, J. Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Sevoflurane-induced Neurocognitive Impairment through α2-adrenoceptors. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z.H. Molecular Mechanisms of Excitotoxicity and Their Relevance to Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov Kirdajova, D.; Kriska, J.; Tureckova, J.; Anderova, M. Ischemia-Triggered Glutamate Excitotoxicity From the Perspective of Glial Cells. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Bell, J.D.; Baker, A.J. Traumatic Brain Injury: Can the Consequences Be Stopped? CMAJ 2008, 178, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannenberg, R.; Scott, H.; Westphalen, R.; Dodd, P. The Identification and Characterization of Excitotoxic Nerve-Endings in Alzheimer Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2004, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Wills, Z.; Chu, C.T. Excitatory Dendritic Mitochondrial Calcium Toxicity: Implications for Parkinson’s and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girling, K.D.; Demers, M.J.; Laine, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.T.; Graham, R.K. Activation of Caspase-6 and Cleavage of Caspase-6 Substrates Is an Early Event in NMDA Receptor-Mediated Excitotoxicity. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, H.R. Role of Calpain in Apoptosis. Cell J. 2011, 13, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Conforti, L.; Gilley, J.; Coleman, M.P. Wallerian Degeneration: An Emerging Axon Death Pathway Linking Injury and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 394–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanou, E.; Catterall, W.A. Calcium Channels, Synaptic Plasticity, and Neuropsychiatric Disease. Neuron 2018, 98, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patergnani, S.; Danese, A.; Bouhamida, E.; Aguiari, G.; Previati, M.; Pinton, P.; Giorgi, C. Various Aspects of Calcium Signaling in the Regulation of Apoptosis, Autophagy, Cell Proliferation, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Reddy, P.H. Role of Glutamate and NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 57, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Hoed, J.; Sollis, E.; Venselaar, H.; Estruch, S.B.; Deriziotis, P.; Fisher, S.E. Functional Characterization of TBR1 Variants in Neurodevelopmental Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandel, E. The Molecular Biology of Memory: CAMP, PKA, CRE, CREB-1, CREB-2, and CPEB. Mol. Brain 2012, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duclot, F.; Kabbaj, M. The Role of Early Growth Response 1 (EGR1) in Brain Plasticity and Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, R.; Stanco, A.; Howard, M.A.; Rubin, A.N.; Vogt, D.; Mortimer, N.; Cobos, I.; Potter, G.B.; Lindtner, S.; Price, J.D.; et al. Dlx1 and Dlx2 Promote Interneuron GABA Synthesis, Synaptogenesis, and Dendritogenesis. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 3797–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paşca, A.M.; Park, J.-Y.; Shin, H.-W.; Qi, Q.; Revah, O.; Krasnoff, R.; O’Hara, R.; Willsey, A.J.; Palmer, T.D.; Paşca, S.P. Human 3D Cellular Model of Hypoxic Brain Injury of Prematurity. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Ren, S.-Q.; Zhang, X.-J.; Shen, Z.; Ghosh, T.; Xianyu, A.; Gao, P.; Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Yu, Y.; et al. TBR2 Coordinates Neurogenesis Expansion and Precise Microcircuit Organization via Protocadherin 19 in the Mammalian Cortex. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endesfelder, S.; Makki, H.; von Haefen, C.; Spies, C.D.; Bührer, C.; Sifringer, M. Neuroprotective Effects of Dexmedetomidine against Hyperoxia-Induced Injury in the Developing Rat Brain. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, M.H.; Kumaresan, V.; Farb, D.H. Neurosteroid Actions in Memory and Neurologic/Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giralt, A.; Brito, V.; Chevy, Q.; Simonnet, C.; Otsu, Y.; Cifuentes-Díaz, C.; de Pins, B.; Coura, R.; Alberch, J.; Ginés, S.; et al. Pyk2 Modulates Hippocampal Excitatory Synapses and Contributes to Cognitive Deficits in a Huntington’s Disease Model. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, M.; Torres-Collado, A.; Iruela-Arispe, M.; Gottschall, P. Selective Decline of Synaptic Protein Levels in the Frontal Cortex of Female Mice Deficient in the Extracellular Metalloproteinase ADAMTS1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschall, P.E.; Howell, M.D. ADAMTS Expression and Function in Central Nervous System Injury and Disorders. Matrix Biol. 2015, 44–46, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.D.A.; Ricciardelli, C.; Russell, D.L. The Metalloproteinase ADAMTS1: A Comprehensive Review of Its Role in Tumorigenic and Metastatic Pathways. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2263–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, H.; Hara, A.; Kunisada, T. Induced Haploinsufficiency of Kit Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Impairs Brain Development. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e94385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruvolo, P.P. Galectin 3 as a Guardian of the Tumor Microenvironment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Brocker, C.; Koppaka, V.; Ying, C.; Jackson, B.; Matsumoto, A.; Thompson, D.C.; Vasiliou, V. Aldehyde Dehydrogenases in Cellular Responses to Oxidative/Electrophilic Stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 56, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Torii, T.; Tanoue, A.; Yamauchi, J. Pelizaeus–Merzbacher Disease-Associated Proteolipid Protein 1 Inhibits Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cell Differentiation via Extracellular-Signal Regulated Kinase Signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 424, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xu, X. RhoA/Rho Kinase in Spinal Cord Injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugmann, B.; Radulescu, A.; Appavou, M.-S.; Koutsioubas, A.; Stingaciu, L.R.; Dulle, M.; Förster, S.; Stadler, A.M. Membrane Stiffness and Myelin Basic Protein Binding Strength as Molecular Origin of Multiple Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wei, W.J.; Wang, G.; Gaertig, M.A.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X.J.; Li, S. Mutant Huntingtin Downregulates Myelin Regulatory Factor-Mediated Myelin Gene Expression and Affects Mature Oligodendrocytes. Neuron 2015, 85, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosio, A.; Binczek, E.; Le Beau, M.M.; Fernald, A.A.; Stoffel, W. The Human Gene CGT Encoding the UDP-Galactose Ceramide Galactosyl Transferase (Cerebroside Synthase): Cloning, Characterization, and Assignment to Human Chromosome 4, Band Q26. Genomics 1996, 34, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, N.; Razavi, S.; Nikzad, E. Multiple Sclerosis: Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Diagnoses andCell-Based Therapy. Cell J. 2017, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, N.; Mullins, P. The Development of Myelin in the Brain of the Juvenile Rat. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 42, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, A.; Kang, M.S.; Blinder, S.; Bouhachi, R.; Soucy, J.P.; Aliaga-Aliaga, A.; Massarweh, G.; Stroobants, S.; Staelens, S.; Rosa-Neto, P.; et al. PET Imaging of Freely Moving Interacting Rats. Neuroimage 2019, 191, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeoka, A.; Jindrich, D.L.; Muñoz-Quiles, C.; Zhong, H.; Van Den Brand, R.; Pham, D.L.; Ziegler, M.D.; Ramón-Cueto, A.; Roy, R.R.; Edgerton, V.R.; et al. Axon Regeneration Can Facilitate or Suppress Hindlimb Function after Olfactory Ensheathing Glia Transplantation. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 4298–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, H.; Suemitsu, S.; Murakami, S.; Kitamura, N.; Wani, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Ishihara, T. Feeding Behavior of Mice under Different Food Allocation Regimens. Behav. Neurol. 2019, 2019, 1581304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, D.E.; Schöttle, V.A.; Nemcova, P.; Binder, F.P.; Ebert, T.; Domschke, K.; Wotjak, C.T. Exploratory Drive, Fear, and Anxiety Are Dissociable and Independent Components in Foraging Mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xue, H.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, P. Effects of Early Postnatal Sevoflurane Exposure on Oligodendrocyte Maturation and Myelination in Cerebral White Matter of the Rat. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, D. Principles and Standards for Reporting Animal Experiments in The Journal of Physiology and Experimental Physiology. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 2547–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, F.; Pehar, M.; Thompson, A.J.; Azeem, U.; Jahanbakhsh, K.; Jimenez-Tellez, N.; Sabouny, R.; Batool, S.; Syeda, A.; Chow, J.; et al. A Synthetic Peptide Rescues Rat Cortical Neurons from Anesthetic-Induced Cell Death, Perturbation of Growth and Synaptic Assembly. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jimenez-Tellez, N.; Pehar, M.; Visser, F.; Casas-Ortiz, A.; Rice, T.; Syed, N.I. Sevoflurane Exposure in Neonates Perturbs the Expression Patterns of Specific Genes That May Underly the Observed Learning and Memory Deficits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108696
Jimenez-Tellez N, Pehar M, Visser F, Casas-Ortiz A, Rice T, Syed NI. Sevoflurane Exposure in Neonates Perturbs the Expression Patterns of Specific Genes That May Underly the Observed Learning and Memory Deficits. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):8696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108696
Chicago/Turabian StyleJimenez-Tellez, Nerea, Marcus Pehar, Frank Visser, Alberto Casas-Ortiz, Tiffany Rice, and Naweed I. Syed. 2023. "Sevoflurane Exposure in Neonates Perturbs the Expression Patterns of Specific Genes That May Underly the Observed Learning and Memory Deficits" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 8696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108696
APA StyleJimenez-Tellez, N., Pehar, M., Visser, F., Casas-Ortiz, A., Rice, T., & Syed, N. I. (2023). Sevoflurane Exposure in Neonates Perturbs the Expression Patterns of Specific Genes That May Underly the Observed Learning and Memory Deficits. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 8696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108696








