Role of Senescent Astrocytes in Health and Disease
Abstract
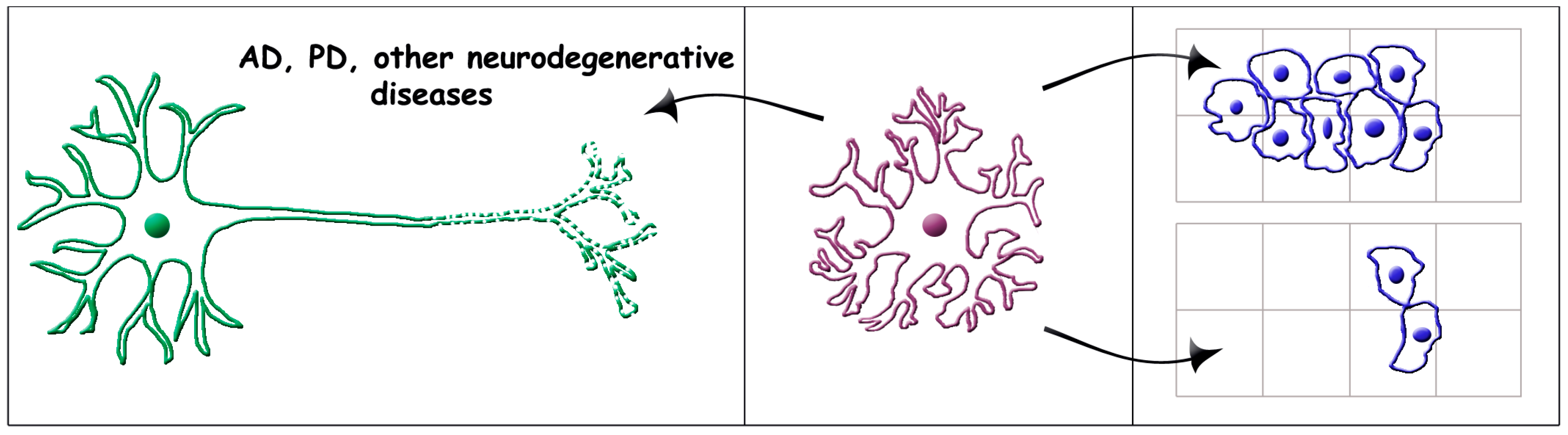
1. Introduction
2. Astrocyte Senescence Development from Young Physiology
2.1. Physiology of Early Astrocytes
2.2. Astrocyte Senescence
2.3. Processes Co-Operative to Astrocyte Senescence
3. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Aging
4. Role of Senescent Astrocytes in Brain Diseases
4.1. Role of Senescent Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Diseases
4.2. Role of Senescent Astrocytes in Other Brain Diseases
4.3. Role of Senescent Astrocytes in Brain Cancers
5. Final Comments
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD. | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ARTAG | aging related tau astrogliopathy |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| IL | Interleukin |
| miR | microRNA |
| NAD | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| SASP | senescence-associated secretory phenotype |
| TBI | traumatic brain injury |
| UPS | unconventional protein secretion |
References
- Kettenmann, H.; Faissner, A.; Trotter, J. Neuron-glia interactions in homeostasis and degeneration. In Human Physiology; Greger, R., Windhorst, U., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 533–543. [Google Scholar]
- Araque, A.; Parpura, V.; Sanzgiri, R.P.; Haydon, P.G. Tripartite synapses: Glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezzi, P.; Volterra, A. A neuron-glia signalling network in the active brain. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volterra, A.; Meldolesi, J. Astrocytes, from glue to communication elements: The revolution continues. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Semyanov, A. The great astroglial metabolic revolution: Mitochondria fuel astrocyte homeostatic support and neuroprotection. Cell Calcium 2022, 104, 102583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelucci, A.; Bithell, A.; Burney, M.J.; Johnston, C.E.; Wong, K.-Y.; Teng, S.-W.; Desai, J.; Gumbleton, N.; Anderson, G.; Stanton, L.W.; et al. The neurogenic potential of astrocytes is regulated by inflammatory signals. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 3724–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.B.; Bhutani, A.; Stary, C.M. Adult neurogenesis from reprogrammed astrocytes. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Lin, Y.X.; Lin, L.; Zhang, B.Q.; Xu, S.H.; Wang, W. Identification of potential candidate proteins for reprogramming spinal cord-derived astrocytes into neurons: A proteomic analysis. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 2257–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, A.; Bills, E.H.; DeSchepper, K.M.; Williamson, J.C.; Henderson, B.J.; Risher, W.C. Astrocyte-derived thrombospondin induces cortical synaptogenesis in a sex-specific manner. Eneuro 2021, 8, 8328272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.D.R. New tricks for an old (hedge)hog: Sonic hedgehog regulation of astrocyte function. Cells 2021, 10, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.L.; Ousman, S.S. Astrocytes and aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, E.P.; Tuzer, F.; Gregory, B.D.; Donahue, G.; Gosai, S.J.; Cohen, J.; Leung, Y.Y.; Yetkin, E.; Nativio, R.; Wang, L.S.; et al. Changes in the transcriptome of human astrocytes accompanying oxidative stress-induced senescence. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzuoli, M.R.; Facchinetti, R.; Valenza, M.; Cassano, T.; Leardo, L.; Scuderi, C. Astrocyte function is affected by aging and not Alzheimer’s disease: A preliminary investigation in hippocampi of 3xTg-AD mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Matas, S.; Paul, R.K.; Molina-Martínez, P.; Palacios, H.; Gutierrez, V.M.; Corpas, R.; Pallas, M.; Cristòfol, R.; Cabo, R.; Sanfeliu, C. In vitro caloric restriction induces protective genes and functional rejuvenation in senescent astrocytes. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Cui, C.; Kim, S.; Sung, C.; Choi, C. Ginsenoside F1 suppresses astrocyte senescence-associated secretory phenotype. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 283, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.R.J.; Cassidy, L.D.; Narita, M. Autophagy and senescence converging roles in pathophysiology as seen through mouse models. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 150, 113–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damulewicz, M.; Szypulski, K.; Pyza, E. Glia-neurons cross-talk regulated through autophagy. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 886273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Xu, C.J. Astrocytes autophagy in aging and neurodegenerative disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldolesi, J. Astrocytes: News about brain health and diseases. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldolesi, J. Extracellular vesicles (exosomes and ectosomes) play key roles in the pathology of brain diseases. Mol. Biomed. 2021, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavreul, S.; Dumas, L.; Loulier, K. Astrocyte development in the cerebral cortex: Complexity of their origin, genesis, and maturation. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 916055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, I.; Morgado, J.; Carvalho Alcantara Gomes, F. Astrocyte heterogeneity: Impact to brain aging and diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, J.M.; Schardien, K.; Wigdahl, B.; Nonetmacher, M.R. Roles of neuropathology-associated reactive astrocytes: A systematic review. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 1, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sompol, P.; Norris, C.M. Ca2+, astrocyte activation and calcineurin/NFAT signaling in age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xue, M.; Zhang, J.; Leng, L. Brain energy metabolism: Astrocytes in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; Spinelli, C.C.; Martucciello, S.; Nori, S.L.; Capunzo, M.; Puca, A.A.; Ciaglia, E. Innate immunity and cellular senescence: The good and bad in the development and aged brain. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.E.; Liddelow, S.A.; Chakraborty, C.; Munch, A.E.; Heiman, M.; Barres, B.A. Normal aging induces A1-like astrocyte reactivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1896–E1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, T.C.; Geoffroy, C.G. The influence of neuron-extrinsic factors and aging on injury progression and axonal repair in the central nervous system. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preininger, M.K.; Zaytseva, D.; Lin, J.M.; Kaufer, D. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction promotes astrocyte senescence through albumin-induced TGFβ signaling activation. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villablanca, C.; Vidal, R.; Gonzalez-Billault, C. Actin cytoskeleton changes observed in astrocytes functionally linked to aging? Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 196, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lye, J.J.; Latorre, E.; Lee, B.P.; Bandinelli, S.; Holley, J.E.; Gutowski, N.J.; Ferrucci, L.; Harries, L.W. Astrocyte senescence may drive alterations in GFPAa, CDKN2A, p14(ARF) and TAU3 transcript expression and contribution to cognitive decline. Geroscience 2019, 41, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisvert, M.M.; Erikson, G.A.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Allen, N.A. The aging astrocyte transcriptome from multiple regions of the mouse brain. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsan, E.; Velmeshev, D.; Ramsey, A.; Patel, R.K.; Zhang, J.; Koontz, M.; Andrews, M.G.; de Majo, M.; Mora, C.; Blumenfeld, J.; et al. Astrogial toxicity promotes synaptic degeneration in the thalamocortical circuit in frontotemporal dementia with GRN mutations. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e164919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.; Gharagozloo, M.; Simard, C.; Gris, D. Astrocytes maintain glutamate homeostasis in the CNS by controlling the balance between glutamate uptake and release. Cells 2019, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, I.; Diniz, L.P.; Araujo, A.P.B.; Damico, I.V.; de Moura, P.; Cabral-Miranda, F.; Diniz, F.; Parmeggiani, B.; Coelho, V.D.M.; Leite, R.E.P.; et al. Age-associated upregulation of glutamate transporters and glutamine synthetase is senescent astrocytes in vitro and in the mouse and human hippocampus. ASN Neuro 2023, 15, 17590914231157974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbad, C.; Oron, T.R.; Alimirah, F.; Davalos, A.R.; Tracy, T.E.; Gan, L.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Campisi, J. Astrocyte senescence promotes glutamate toxicity in cortical neurons. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escartin, C.; Galea, E.; Lakatos, A.; O’callaghan, J.P.; Petzold, G.C.; Serrano-Pozo, A.; Steinhäuser, C.; Volterra, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Agarwal, A.; et al. Reactive astrocyte nomenclature, definitions, and future directions. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.-S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanslik, K.I.; Marino, K.M.; Ulland, T.K. Modulation of glial function in health, ageing and neurodegenerative disease. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 718324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, K.-T. Region-specific characteristics of astrocytes and microglia: A possible involvement in aging and diseases. Cells 2022, 11, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.G. Astroglia and tau: New perspectives review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Amari, M.; Fukuda, T.; Suzuki, K.; Takatama, M. Astrocytic tau pathologies in aged human brain. Neuropathology 2019, 39, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I.; García, M.A.; González, I.L.; Lucena, D.D.; Villalonga, A.R.; Tech, M.C.; Llorens, F.; Garcia-Esparcia, P.; Martinez-Maldonado, A.; Mendez, M.F.; et al. Aging-regulated tau astrogliopathy (ARTAG): Not only tau phosphorylation in astrocytes. Brain Pathol. 2018, 28, 965–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musi, N.; Valentine, J.M.; Sickora, K.R.; Baeuerle, E.; Thompson, C.S.; Shen, Q.; Orr, M.E. Tau protein aggregation is associated with cellular senescence in the brain. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussian, T.J.; Aziz, A.; Meyer, C.F.; Swenson, B.L.; van Deursen, J.M.; Baker, D.J. Clearance of senescent glial cells prevents tau-dependent pathology and cognitive decline. Nature 2018, 562, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J.; Petersen, R.C. Cellular senescence in brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases: Evidence and perspectives. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burda, J.E.; Bernstein, A.M.; Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocyte roles in traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 275 Pt 3, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early, A.N.; Gorman, A.A.; Van Eldik, L.J.; Bachstetter, A.D.; Morganti, J.M. Effects of advanced age upon astrocyte-specific responses to acute traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revuelta, M.; Elicegui, A.; Moreno-Cugnon, L.; Buhrer, C.; Matheu, A.; Schmitz, T. Ischemic stroke in neonatal and adult astrocytes. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 183, 111147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite Santos, C.; Bobermin, L.D.; Onofre Sousa, D.; Quincozes-Santos, A. Leptin stimulates the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in hypothalamic astrocyte cultures from adult and aged rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, J.; Gao, F.; Hashem, J.; Kingsley, P.; Marnett, L.J.; Mackie, K.; Chen, C. Enhancing endocannabinoid signaling in astrocytes promotes recovery from traumatic brain injury. Brain 2022, 145, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raihan, O.; Brishti, A.; Molla, R.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, P.; Khan, M.I.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q. The age-dependent elevation of miR-335-3p leads to reduced cholesterol and impaired memory in brain. Neuroscience 2018, 390, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsegiani, A.S.; Shah, Z.A. The role of cofilin in age-related neuroinflammation. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1451–14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, G.; Gaetani, S.; Cacci, E.; Biagioni, S.; Regri, R. Molecular signatures of the aging brain: Finding the links between genes and phenotypes. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, M.; Richardson, J.R. Epigenetic regulation of astrocyte function in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chucair-Elliott, A.J.; Ocañas, S.R.; Stanford, D.R.; Ansere, V.A.; Buettner, K.B.; Porter, H.; Eliason, N.L.; Reid, J.J.; Sharpe, A.L.; Stout, M.B.; et al. Inducible cell-specific mouse models for paired epigenetic and transcriptomic studies of microglia and astroglia. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ma, N.; Yu, B.; Zhang, W.; Wan, J. Transcriptomic profiling of microglia and astrocytes throughout aging. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, G. Novel therapeutic strategies for ischemic stroke: Recent insights into autophagy. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 3450207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, H.; Fan, Y.; Yang, L.; Yin, M.; Miao, W.; He, J.; Wang, Y. Autophagy protects against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting neuroinflammation. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 4726–4737. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Tian, M.; Hua, T.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, H. Combination of autophagy and NFE2L2/NRF2 activation as a treatment approach for neuropathic pain. Autophagy 2021, 17, 4062–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.; Kataura, T.; Korsgen, M.E.; Sun, C.; Sarkar, S.; Korolchuk, V.I. The autophagy-NAD axis in longevity and disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, J.; Rosser, G.; Kancheva, D.; Vinel, C.; Lim, Y.M.; Pomella, N.; Zhang, X.; Guglielmi, L.; Sheer, D.; Barnes, M.; et al. Global hypo-methylation of glioblastoma enriched for an astrocytic signature is associated with increased invasion and altered immune landscape. eLife 2022, 11, e77335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Hernández, A.; López-Santaella, T.; Torres-Caballero, A.; Serrato, A.; Torres-Flores, U.; Montesinos-Valencia, D.; de León, F.C.-P.; González-Carranza, V.; Torres-García, S.; Rebollar-Vega, R.; et al. The transcriptomic landscape of pediatric astrocytoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trovato, F.; Stefani, F.R.; Li, J.; Zetterdahl, O.G.; Canals, I.; Ahlenius, H.; Bengzon, J. Transcription factor-forced astrocytes differentiation impairs human glioblastoma growth in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2023, 22, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Strooper, B.; Karran, E. The cellular phase of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 2016, 164, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Nievas, B.G.; Serrano-Pozo, A. Deciphering the astrocyte reaction in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz, A.M.; De Strooper, B. The role of astroglia in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preman, P.; Tcw, J.; Calafate, S.; Snellinx, A.; Alfonso-Triguero, M.; Corthout, N.; Munck, S.; Thal, D.R.; Goate, A.M.; De Strooper, B.; et al. Human iPSC-derived astrocytes transplanted into the mouse brain undergo morphological changes in response to amyloid-β plaques. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzer, F.; Torres, C. Involvement of astrocyte senescence in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2022, 76, 102594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazic, A.; Balint, V.; Stanisavljevic Ninkovic, D.; Peric, M.; Stevanovic, M. Reactive and senescent astroglIal phenotypes as hallmarks of brain pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middeldorp, J.; Min, R.; Benetatos, J.; Bodea, L.-G. The neuron-glia crosstalk and beyond. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1157597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Ortiz, A.; Castellino, J.; Kinney, J. Diabetes: Risk factor and translational therapeutic implications in Alzheimer’s diseases. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 56, 5727–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Gsell, W.; Wahis, J.; Luckett, E.S.; Jamoulle, T.; Vermaercke, B.; Preman, P.; Moechars, D.; Hendrickx, V.; Jaspers, T.; et al. Astrocyte calcium dysfunction causes early network hyperactivity in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Huang, H.; Shao, J.; Huang, W. MicroRNA-mediated regulation of reactive astrocytes in central nervous diseases. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1061343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.; McCabe, C.; Medina, S.; Varshavsky, M.; Kitsberg, D.; Dvir-Szternfeld, R.; Green, G.; Dionne, D.; Nguyen, L.; Marshall, J.L.; et al. Disease-associated astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease and aging. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, C.; Do, K.V.; Jun, B.; Hjorth, E.; Alcalde, S.G.; Kautzmann, M.-A.I.; Gordon, W.C.; Nilsson, P.; Bazan, N.G.; Schultzberg, M. Age-related changes in brain phospholipids and bioactive lipids in APP knock-in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Nauropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnitskaya, E.A.; Kozlova, T.A.; Burnyasheva, A.O.; Stefanova, N.A.; Kolosova, N.G. Glia not neurons: Uncovering brain dysmaturation in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, G.S.; Fujita, M.; Yang, H.S.; Taga, M.; McCabe, C.; Cain, A.; White, C.C.; Schmidtner, A.K.; Wang, Y.; Regev, A.; et al. Cellular dynamics across aged human brains uncovers a multicellular cascade leading to Alzheimer’s disease. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, G.; Cragnolini, A.B.; Lampitella, G.; Virtuoso, A.; Viscovo, I.; Panetsos, F.; Papa, M. Regional brain susceptibility to neurodegeneration: What is the role of glial cells? Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, K.; Li, E.; Eser, R.; Piergies, A.; Sit, R.; Tan, M.; Neff, N.; Li, S.H.; Rodriguez, R.D.; Suemoto, C.K.; et al. Molecular characterization of selectively vulnerable neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Koistinen, N.A.; Malarte, M.-L.; Nennesmo, I.; Ingelsson, M.; Ghetti, B.; Lemoine, L.; Nordberg, A. Astrogeal tracer BU99008 detects multiple binding sites in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5833–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Fontana, I.C.; Nordberg, A. Reactive astrogliosis: A friend or foe in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2023, 164, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Fan, J.; Kulic, I.; Koh, C.; Clark, A.; Meuller, J.; Engkvist, O.; Barichievy, S.; Raynoschek, C.; Hicks, R.; et al. Axl receptor tyrosine is a regulator of apolipoprotein E. Mol. Brain 2020, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, C.A.; Lananna, B.V.; Musiek, E.S. Circadian regulation of astrocyte function: Implications for Alzheimer’s diseases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shentu, Y.-P.; Hu, W.-T.; Zhang, Q.; Huo, Y.; Liang, J.-W.; Liuyang, Z.-Y.; Zhou, H.; Wei, H.; Ke, D.; Wang, X.-C.; et al. CIP2A-promoted astrogliosis induces AD-like synaptic degeneration and cognitive deficits. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 75, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, L.P.; Matias, I.; Siqueira, M.; Stipursky, I.; Carvalho Alcantara Gomes, F. Astrocytes and the TGF-β1 pathway in the healthy and diseased brain: A double-edged sword. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 4653–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyzériat, K.; Ben Haim, L.; Denizot, A.; Pommier, D.; Matos, M.; Guillemaud, O.; Palomares, M.-A.; Abjean, L.; Petit, F.; Gipchtein, P.; et al. Modulation of astrocyte reactivity improves functional deficits in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.S.; Wolf, F.; De Strooper, B.; Busche, M.A. Tipping the scales: Peptide-dependent dysregulation of neural circuit dynamics in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2020, 107, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Quin, S. Reactive astrocytes in neurodegenerative diseases. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Astrocytes: Role and function in brain pathologies. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, T.; Yokota, O.; Haraguchi, T.; Ishizu, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Ishihara, T.; Ueno, S.; Takenoshita, S.; Terada, S.; Yamada, N. Factors associated with development and distribution of granular/fuzzy astrocytes in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 811–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.S.; Janrao, S.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, S.B.; Vora, L.; Khatri, D.K. GSK-3β: An exuberant neuroinflammatory mediator in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 210, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abjean, L.; Ben Haim, L.; Riquelme-Perez, M.; Gipchtein, P.; Derbois, C.; Palomares, M.-A.; Petit, F.; Hérard, A.-S.; Gaillard, M.-C.; Guillermier, M.; et al. Reactive astrocytes promote proteostasis in Huntington’s disease through the JAK2-STAT3 pathway. Brain 2023, 146, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemaud, O.; Ceyzériat, K.; Saint-Georges, T.; Cambon, K.; Petit, F.; Ben Haim, L.; Sauvage, M.-A.C.-D.; Guillermier, M.; Bernier, S.; Hérard, A.-S.; et al. Complex roles for reactive astrocytes in the triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’ disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 90, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini-Stoica, H.; Cole, A.L.; Swartzlander, D.B.; Chen, F.; Wan, Y.-W.; Bajaj, L.; Bader, D.A.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Liu, Z.; et al. TFEB enhances astroglial uptake of extracellular tau species and reduces tau spreading. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 2355–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Komine, O. The multidimensional role of astrocytes in ALS. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 126, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trias, E.; Barbeito, L.; Yamanaka, K. Phenotypic heterogeneity of astrocytes in motor neuron disease. Clin. Exp. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 9, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suruga, Y.; Satomi, K.; Otani, Y.; Fujii, K.; Ishida, J.; Uneda, A.; Tsuboi, N.; Makino, K.; Hirano, S.; Kemmotsu, N.; et al. The utility of DNA methylation analysis in elderly patients with pilocytic astrocytoma morphology. J. Neurooncol. 2022, 160, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelroizen, R.; Bar Philosof, B.; Budick-Harmelin, N.; Chernobylsky, T.; Ron, A.; Katzir, R.; Shimon, D.; Tessler, A.; Adir, O.; Gaoni-Yogev, A.; et al. Astrocyte immunometabolic regulation of the tumour microenvironment drives glioblastoma pathogenicity. Brain 2020, 145, 3288–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racchetti, G.; Meldolesi, J. Extracellular vesicles of mesenchymal stem cells: Therapeutic properties discovered with extraordinary success. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meldolesi, J. Role of Senescent Astrocytes in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108498
Meldolesi J. Role of Senescent Astrocytes in Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):8498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108498
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeldolesi, Jacopo. 2023. "Role of Senescent Astrocytes in Health and Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 8498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108498
APA StyleMeldolesi, J. (2023). Role of Senescent Astrocytes in Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 8498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108498





