Is Atopic Dermatitis Only a Skin Disease?
Abstract
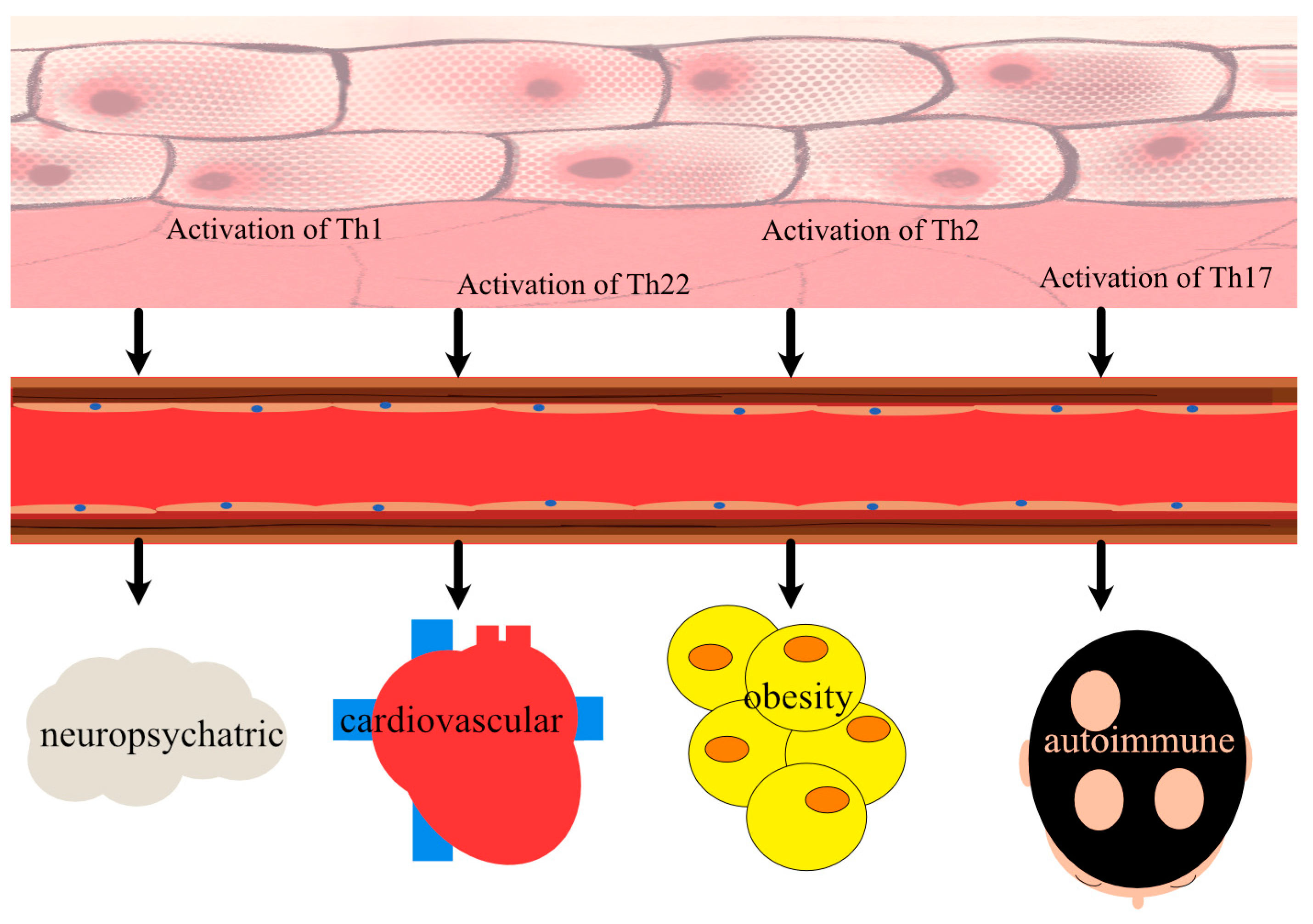
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Discussion
3.1. AD Patients Behaviours That May Enhance Comorbidity Prevalence
3.2. Cardiovascular Diseases
3.3. Neurologic and Psychiatric Diseases in AD
3.3.1. Neuro-Immune Crosstalk in AD
3.3.2. Epilepsy
3.3.3. Autism
3.3.4. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
3.3.5. Depression
3.4. Autoimmune Diseases
3.4.1. Alopecia Areata
3.4.2. Vitiligo
3.4.3. Rheumatoid Diseases
3.4.4. Type I Diabetes
3.5. Obesity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sroka-Tomaszewska, J.; Trzeciak, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Atopic Dermatitis Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.H.; Chung, B.Y.; Kim, H.O.; Park, C.W. Clinical Features of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults Are Different according to Onset. J. Korean Med Sci. 2017, 32, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokura, Y.; Hayano, S. Subtypes of atopic dermatitis: From phenotype to endotype. Allergol. Int. 2021, 71, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, Y.M.; Egeberg, A.; Skov, L.; Thyssen, J.P. Comorbidities of Atopic Dermatitis: Beyond Rhinitis and Asthma. Curr. Dermatol. Rep. 2017, 6, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Kim, J.; Park, H.-J.; Hahm, D.-H. Comparative Analysis of the Microbiome across the Gut–Skin Axis in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamari, M.; Hirota, T. Genome-wide association studies of atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternoster, L.; Standl, M.; Waage, J.; Baurecht, H.; Hotze, M.; Strachan, D.P.; Curtin, J.; Bønnelykke, K.; Tian, C.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Multi-ethnic genome-wide association study of 21,000 cases and 95,000 controls identifies new risk loci for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1449. [Google Scholar]
- Paller, A.; Jaworski, J.C.; Simpson, E.L.; Boguniewicz, M.; Russell, J.J.; Block, J.K.; Tofte, S.; Dunn, J.D.; Feldman, S.R.; Clark, A.R.; et al. Major Comorbidities of Atopic Dermatitis: Beyond Allergic Disorders. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I. Comorbidities and the impact of atopic dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 123, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, D.E.R.; Nicol, C.W.; Bredin, S.S.D. Health benefits of physical activity: The evidence. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2006, 174, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Song, J.; Pinto, D.; Yu, S.H.; Gilbert, A.L.; Dunlop, D.D.; Chang, R.W. Atopic Dermatitis Is Associated with Less Physical Activity in US Adults. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1714–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strom, M.A.; Silverberg, J.I. Associations of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior with Atopic Disease in United States Children. J. Pediatr. 2016, 174, 247–253.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-H.; Chen, P.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Chang, W.-H.; Chang, L.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Kuo, H.-C. Adolescents with Atopic Dermatitis Have Lower Peak Exercise Load Capacity and Exercise Volume Compared with Unaffected Peers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonmann, Y.; Mansfield, K.E.; Hayes, J.F.; Abuabara, K.; Roberts, A.; Smeeth, L.; Langan, S.M. Atopic Eczema in Adulthood and Risk of Depression and Anxiety: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 8, 248–257.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.J.; Shin, A.; Kang, D. Active smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke and their relationship to depressive symptoms in the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES). BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.; Cucullo, L. Pathobiology of tobacco smoking and neurovascular disorders: Untied strings and alternative products. Fluids Barriers CNS 2015, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, S.; Frei, R.; Schmaußer-Hechfellner, E.; von Mutius, E.; Pekkanen, J.; Karvonen, A.M.; Kirjavainen, P.V.; Dalphin, J.; Divaret-Chauveau, A.; Riedler, J.; et al. Association between antibiotic treatment during pregnancy and infancy and the development of allergic diseases. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 30, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Liao, X.; Fu, M.; Shi, H.; Lin, B.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Q.; Mai, B.; Liu, R. Association between the use of antibiotics during pregnancy and obesity in 5-year-old children. Transl. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubanga, M.; Lundholm, C.; D’Onofrio, B.M.; Stratmann, M.; Hedman, A.; Almqvist, C. Association of Early Life Exposure to Antibiotics with Risk of Atopic Dermatitis in Sweden. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e215245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Shang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Qi, K. Early-life antibiotic exposure increases the risk of childhood overweight and obesity in relation to dysbiosis of gut microbiota: A birth cohort study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2022, 21, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, S.; Jokelainen, J.; Timonen, M.; Tasanen, K.; Huilaja, L. Atopic dermatitis and the risk of eating disorders: A population-based cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 87, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agüera, Z.; Lozano-Madrid, M.; Mallorquí-Bagué, N.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Menchón, J.M.; Fernández-Aranda, F. A review of binge eating disorder and obesity. Neuropsychiatrie 2020, 35, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollenberg, A.; Kinberger, M.; Arents, B.; Aszodi, N.; Valle, G.A.; Barbarot, S.; Bieber, T.; Brough, H.; Pinton, P.C.; Christen-Zäch, S.; et al. European guideline (EuroGuiDerm) on atopic eczema: Part I–systemic therapy. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1409–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, J.I. Association between adult atopic dermatitis, cardiovascular disease, and increased heart attacks in three population-based studies. Allergy 2015, 70, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standl, M.; Tesch, F.; Baurecht, H.; Rodríguez, E.; Müller-Nurasyid, M.; Gieger, C.; Peters, A.; Wang-Sattler, R.; Prehn, C.; Adamski, J.; et al. Association of Atopic Dermatitis with Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 137, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascott, A.; Mulick, A.; Yu, A.M.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Schmidt, M.; Abuabara, K.; Smeeth, L.; Roberts, A.; Langan, S.M. Atopic eczema and major cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based studies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, Y.M.F.; Egeberg, A.; Hamann, C.R.; Skov, L.; Gislason, G.H.; Skaaby, T.; Linneberg, A.; Thyssen, J.P. Poor agreement in questionnaire-based diagnostic criteria for adult atopic dermatitis is a challenge when examining cardiovascular comorbidity. Allergy 2017, 73, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.M.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; He, H.; Malik, K.; Wen, H.-C.; Gonzalez, J.; Chan, T.C.-C.; Estrada, Y.; Zheng, X.; Khattri, S.; et al. Author Correction: The atopic dermatitis blood signature is characterized by increases in inflammatory and cardiovascular risk proteins. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, A.P.; Pavel, A.B.; Wu, J.; Fernandes, M.; Maari, C.; Proulx, E.S.; Jack, C.; Glickman, J.; Choi, S.; He, H.; et al. Vascular inflammation in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis is associated with enhanced Th2 response. Allergy 2021, 76, 3107–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Olesen, C.M.; Pavel, A.B.; Clausen, M.-L.; Wu, J.; Estrada, Y.; Zhang, N.; Agner, T.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Tape-Strip Proteomic Profiling of Atopic Dermatitis on Dupilumab Identifies Minimally Invasive Biomarkers. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, R.; Choi, S.; Zhou, L.; Pavel, A.; Estrada, Y.D.; Krueger, J.G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Increased cardiovascular and atherosclerosis markers in blood of older patients with atopic dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 124, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, P.M.; He, H.; Pavel, A.B.; Czarnowicki, T.; Lefferdink, R.; Erickson, T.; Canter, T.; Puar, N.; Rangel, S.M.; Malik, K.; et al. The blood proteomic signature of early-onset pediatric atopic dermatitis shows systemic inflammation and is distinct from adult long-standing disease. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colas, L.; Magnan, A.; Brouard, S. Immunoglobulin E response in health and disease beyond allergic disorders. Allergy 2022, 77, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandher, K.; Ghamrawi, R.I.; Heron, C.E.; Feldman, S.R. Controversial cardiovascular and hematologic comorbidities in atopic dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2021, 314, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastałek, M.; Wojas-Pelc, A.; Undas, A. Plasma fibrin clot properties in atopic dermatitis: Links between thrombosis and atopy. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2010, 30, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.M.; Drucker, A.M.; Alikhan, A.; Bercovitch, L.; Cohen, D.E.; Darr, J.M.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Frazer-Green, L.; Paller, A.S.; Silverberg, J.I.; et al. American Academy of Dermatology Guidelines: Awareness of comorbidities associated with atopic dermatitis in adults. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 1335–1336.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Silverberg, J.I. Screening for cardiovascular comorbidity in United States outpatients with psoriasis, hidradenitis, and atopic dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 313, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollanazar, N.K.; Smith, P.K.; Yosipovitch, G. Mediators of Chronic Pruritus in Atopic Dermatitis: Getting the Itch Out? Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 51, 263–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, S.; Okayama, Y. Neuro-allergology: Mast cell–nerve cross-talk. Allergol. Int. 2022, 71, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, Y.; Fischer, M.J.M.; Steinhoff, M.; Chen, W.; Wang, J. Th2 Modulation of Transient Receptor Potential Channels: An Unmet Therapeutic Intervention for Atopic Dermatitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikbas, F.; Wang, X.; Akiyama, T.; Kempkes, C.; Savinko, T.; Antal, A.; Kukova, G.; Buhl, T.; Ikoma, A.; Buddenkotte, J.; et al. A Sensory Neuron-expressed Interleukin-31 Receptor Mediates T helper Cell-dependent Itch: Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPA1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.R.; Thé, L.; Batia, L.M.; Beattie, K.; Katibah, G.E.; McClain, S.P.; Pellegrino, M.; Estandian, D.; Bautista, D. The Epithelial Cell-derived Atopic Dermatitis Cytokine TSLP Activates Neurons to Induce Itch. Cell 2013, 155, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochiai, S.; Jagot, F.; Kyle, R.L.; Hyde, E.; White, R.F.; Prout, M.; Schmidt, A.J.; Yamane, H.; Lamiable, O.; Le Gros, G.; et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin drives the development of IL-13+ Th2 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, B.; Tong, X.; Yan, S.; Lu, J. Current views on neuropeptides in atopic dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Su, T.-P.; Chen, Y.-S.; Hsu, J.-W.; Huang, K.-L.; Li, C.-T.; Lin, W.-C.; Chang, W.-H.; Chen, T.-J.; et al. Risk of epilepsy among patients with atopic dermatitis: A nationwide longitudinal study. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Joks, R.; Durkin, H.G. Allergic disease is associated with epilepsy in childhood: A US population-based study. Allergy 2013, 69, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaboushan, A.S.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Rezaei, N. Neuroinflammation and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Epileptogenesis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 1724–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, E.; van Bergeijk, D.; Oosting, R.S.; Redegeld, F.A. Mast cells in neuroinflammation and brain disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 79, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, J.; Ginsburg, D.; Ormon, R.; Stewart, M.; Amassian, V.; Durkin, H. Blood T and B Lymphocytes Enter Mouse Brain After a Single Seizure and Some Switch to IL-4+ and IgE+ Cells in Neocortex: Epilepsy as an Allergic Disease? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, L.; Lu, D.; Wu, Z.; Han, Y.; Xu, P.; Chang, L.; Wu, Q. Interleukin 4 Affects Epilepsy by Regulating Glial Cells: Potential and Possible Mechanism. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 554547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson-Cowan, L.; Cole, E.F.; Arbiser, J.L.; Silverberg, J.I.; Lawley, L.P. TH2 sensitization in the skin-gut-brain axis: How early-life Th2-mediated inflammation may negatively perpetuate developmental and psychologic abnormalities. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2021, 38, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Luo, C.; Yao, Y.; Huang, J.; Fu, H.; Xia, C.; Ye, G.; Yu, L.; Han, J.; Fan, Y.; et al. IL-33 Alleviated Brain Damage via Anti-apoptosis, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Inflammation After Epilepsy. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.P.; Lin, S.P.; Chern, S.R.; Tsai, F.J.; Wu, P.C.; Lee, C.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, W.L.; Wang, W. A de novo 7.9 Mb deletion in 22q13.2→qter in a boy with autistic features, epilepsy, developmental delay, atopic dermatitis and abnormal immunological findings. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 53, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billeci, L.; Tonacci, A.; Tartarisco, G.; Ruta, L.; Pioggia, G.; Gangemi, S. Association Between Atopic Dermatitis and Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameson, C.; Boulton, K.A.; Silove, N.; Guastella, A.J. Eczema and related atopic diseases are associated with increased symptom severity in children with autism spectrum disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eve, M.; Gandawijaya, J.; Yang, L.; Oguro-Ando, A. Neuronal Cell Adhesion Molecules May Mediate Neuroinflammation in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 842755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Tong, G.; Sun, Y. Association of food hypersensitivity in children with the risk of autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 180, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.-H.; He, H.-J.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Jia, X.-Y.; Srivastava, K.; Miao, M.-S.; Li, X.-M. Food Allergy-Induced Autism-Like Behavior is Associated with Gut Microbiota and Brain mTOR Signaling. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 645–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.-O.; Crumrine, D.A.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, B.; Abuabara, K.; Park, C.; Uchida, Y.; Wakefield, J.S.; Meyer, J.M.; et al. Phenotypic overlap between atopic dermatitis and autism. BMC Neurosci. 2021, 22, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.Y.; Ha, E.K.; Cha, H.R.; Han, M.Y.; Baek, H.-S. Neurodevelopment at 6 years of age in children with atopic dermatitis. Allergol. Int. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, J.; Buske-Kirschbaum, A.; Tesch, F.; Trikojat, K.; Stephan, V.; Abraham, S.; Bauer, A.; Nemat, K.; Plessow, F.; Roessner, V. Increased attention-deficit/hyperactivity symptoms in atopic dermatitis are associated with history of antihistamine use. Allergy 2017, 73, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Schans, J.; Çiçek, R.; de Vries, T.W.; Hak, E.; Hoekstra, P.J. Association of atopic diseases and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 74, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-Y.; Huang, W.-L.; Wang, L.-J.; Kuo, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-J. Two meta-analyses of the association between atopic diseases and core symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-H.; Tai, Y.-H.; Dai, Y.-X.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, T.-J.; Chen, M.-H. Risk of Atopic Diseases among Siblings of Patients with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 180, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrmann, S.; Tesch, F.; Romanos, M.; Abraham, S.; Schmitt, J. ADHD in school-age children is related to infant exposure to systemic H1-antihistamines. Allergy 2020, 75, 2956–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-C.; Wang, J.-P.; Zhu, W.-J.; Li, P. Childhood atopic dermatitis as a precursor for developing attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 2058738420962902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Immaneni, S.; Singam, V.; Rastogi, S.; Silverberg, J.I. Association between atopic dermatitis, depression, and suicidal ideation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 80, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønnstad, A.T.M.; Halling-Overgaard, A.-S.; Hamann, C.R.; Skov, L.; Egeberg, A.; Thyssen, J.P. Association of atopic dermatitis with depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation in children and adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 448–456.e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cork, M.; Eckert, L.; Simpson, E.L.; Armstrong, A.; Barbarot, S.; Puig, L.; Girolomoni, G.; De Bruin-Weller, M.; Wollenberg, A.; Kataoka, Y.; et al. Dupilumab improves patient-reported symptoms of atopic dermatitis, symptoms of anxiety and depression, and health-related quality of life in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Analysis of pooled data from the randomized trials SOLO 1 and SOLO 2. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2019, 31, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrazzo, M.; Cipolla, S.; Signoriello, S.; Camerlengo, A.; Calabrese, G.; Giordano, G.M.; Argenziano, G.; Galderisi, S. A systematic review on shared biological mechanisms of depression and anxiety in comorbidity with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa. Eur. Psychiatry 2021, 64, E71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buske-Kirschbaum, A.; Geiben, A.; Höllig, H.; Morschhäuser, E.; Hellhammer, D. Altered Responsiveness of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis and the Sympathetic Adrenomedullary System to Stress in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 4245–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, B.J.; Cassidy, F.; Naftolowitz, D.; Tatham, N.E.; Wilson, W.H.; Iranmanesh, A.; Liu, P.Y.; Veldhuis, J.D. Pathophysiology of hypercortisolism in depression. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2007, 115, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinnik, T.; Kreinin, A.; Abildinova, G.; Batpenova, G.; Kirby, M.; Pinhasov, A. Biological Sex and IgE Sensitization Influence Severity of Depression and Cortisol Levels in Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology 2020, 236, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, I.; Inoue, Y.; Shimada, T.; Aikawa, T. Brain Mast Cells Act as an Immune Gate to the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis in Dogs. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson-Cowan, L.D.; Cole, E.F.; Silverberg, J.I.; Lawley, L.P. Childhood atopic dermatitis is associated with cognitive dysfunction: A National Health Interview Survey study from 2008 to 2018. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, G.C.; Silverberg, J.I. Association of Vitiligo and Alopecia Areata with Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, R.C.; Pforr, J.; Flaquer, A.; Redler, S.; Hanneken, S.; Eigelshoven, S.; Kortüm, A.-K.; Tüting, T.; Lambert, J.; De Weert, J.; et al. Loss-of-Function Mutations in the Filaggrin Gene and Alopecia Areata: Strong Risk Factor for a Severe Course of Disease in Patients Comorbid for Atopic Disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2539–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, R.; Ito, T.; Hanai, S.; Morishita, N.; Nakazawa, S.; Fujiyama, T.; Honda, T.; Tokura, Y. Immunological Properties of Atopic Dermatitis-Associated Alopecia Areata. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; Bares, J.; Chima, M.; Hawkes, J.E.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; Singer, G.K.; Garcet, S.; Pavel, A.B.; et al. Phase 2a randomized clinical trial of dupilumab (anti-IL-4Rα) for alopecia areata patients. Allergy 2021, 77, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.; Owais, R.; Sheikh, A.; Shaikh, A. Olumniant (Baricitinib) oral tablets: An insight into FDA-approved systemic treatment for Alopecia Areata. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 80, 104157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olumiant|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/olumiant (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Uchida, H.; Kamata, M.; Nagata, M.; Fukaya, S.; Hayashi, K.; Fukuyasu, A.; Tanaka, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Tada, Y. Baricitinib improved alopecia areata concomitant with atopic dermatitis: A case report. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lusignan, S.; Alexander, H.; Broderick, C.; Dennis, J.; McGovern, A.; Feeney, C.; Flohr, C. Atopic dermatitis and risk of autoimmune conditions: Population-based cohort study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campione, E.; Lanna, C.; Diluvio, L.; Cannizzaro, M.V.; Grelli, S.; Galluzzo, M.; Talamonti, M.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; Mancini, M.; Melino, G.; et al. Skin immunity and its dysregulation in atopic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa and vitiligo. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Silverberg, N.B. Association Between Vitiligo and Atopic Disorders: A Pilot Study. JAMA Dermatol. 2013, 149, 963–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittiphairoj, T.; Charoenngam, N.; Ben Ponvilawan, B.; Tornsatitkul, S.; Wattanachayakul, P.; Rujirachun, P.; Ungprasert, P.M. Atopic Dermatitis is a Risk Factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dermatitis 2021, 32, S15–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, B.; Craig, T.J. Small molecule drugs for atopic dermatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and hereditary angioedema. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 128, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.S.; Bieber, T.; Williams, H.C. Does “autoreactivity” play a role in atopic dermatitis? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1209–1215.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronzer, V.L.; Westerlind, H.; Alfredsson, L.; Crowson, C.S.; Klareskog, L.; Holmqvist, M.; Askling, J. Original research: Allergic conditions and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A Swedish case–control study. RMD Open 2022, 8, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.-P.; Tsai, J.-D.; Muo, C.-H.; Tsai, C.-H.; Sung, F.-C.; Liao, Y.-T.; Chang, Y.-J.; Yang, J.-H. Atopic Diseases and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An Epidemiological Study of the Risks and Correlations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8112–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, N.; Rivera, J. Basophils and Autoreactive IgE in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011, 11, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wen, D.; Du, X.; Qiao, Y.; Dong, J.-Z.; Ma, C.-S. RANTES Gene Polymorphisms Are Not Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Atopic Dermatitis: A Meta-Analysis. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 34, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, D.J.; Mitra, N.; Monos, D.S. Rheumatoid Arthritis Known HLA Associations Are Unlikely to Be Associated with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 48, 308–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, J.; Schwarz, K.; Baurecht, H.; Hotze, M.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Rodríguez, E.; Lee, Y.A.; Franke, A.; Degenhardt, F.; Lieb, W.; et al. Atopic dermatitis is associated with an increased risk for rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, and a decreased risk for type 1 diabetes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 137, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinvoq|European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/rinvoq (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Stene, L.C.; Joner, G. The Norwegian Childhood Diabetes Study Group Atopic disorders and risk of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes in individuals. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Wei, C.; Lin, W.; Kao, C. Childhood type 1 diabetes may increase the risk of atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 174, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fsadni, P.; Fsadni, C.; Fava, S.; Montefort, S. Correlation of worldwide incidence of type 1 diabetes (DiaMond) with prevalence of asthma and atopic eczema (ISAAC). Clin. Respir. J. 2011, 6, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, J.-F.; Chatenoud, L. The Hygiene Hypothesis: An Explanation for the Increased Frequency of Insulin-Dependent Diabetes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a007799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krischer, J.P.; Cuthbertson, D.; Couluris, M.; Knip, M.; Virtanen, S.M. Association of diabetes-related autoantibodies with the incidence of asthma, eczema and allergic rhinitis in the TRIGR randomised clinical trial. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardwell, C.R.; Shields, M.D.; Carson, D.J.; Patterson, C.C. A Meta-Analysis of the Association Between Childhood Type 1 Diabetes and Atopic Disease. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2568–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thomsen, S.F.; Duffy, D.L.; Kyvik, K.O.; Skytthe, A.; Backer, V. Relationship between type 1 diabetes and atopic diseases in a twin population. Allergy 2010, 66, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Silverberg, J.I. Association of atopic dermatitis with being overweight and obese: A systematic review and metaanalysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 606–616.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanItallie, T.B. Worldwide epidemiology of obesity. Pharmacoeconomics 1994, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, B.; Nino, M.; Perrino, N.; Laccetti, R.; Trio, R.; Labella, S.; Balato, N. The impact of obesity on skin disease and epidermal permeability barrier status. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.-J. Emerging Roles of Adipose Tissue in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis in Obesity. JID Innov. 2021, 2, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek, A.K.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Szafraniec, K.; Jaworek, M.; Hałubiec, P.; Wojas-Pelc, A.; Pokorski, M. Adipokines as Biomarkers of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, S.; Lorentz, A. Obesity–A Promoter of Allergy? Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 162, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapat, S.P.; Whitty, C.; Mowery, C.T.; Liang, Y.; Yoo, A.; Jiang, Z.; Peters, M.C.; Zhang, L.-J.; Vogel, I.; Zhou, C.; et al. Obesity alters pathology and treatment response in inflammatory disease. Nature 2022, 604, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savastano, D.M.; Gorbach, A.M.; Eden, H.S.; Brady, S.M.; Reynolds, J.C.; Yanovski, J. Adiposity and human regional body temperature. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mesjasz, A.; Zawadzka, M.; Chałubiński, M.; Trzeciak, M. Is Atopic Dermatitis Only a Skin Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010837
Mesjasz A, Zawadzka M, Chałubiński M, Trzeciak M. Is Atopic Dermatitis Only a Skin Disease? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010837
Chicago/Turabian StyleMesjasz, Alicja, Marta Zawadzka, Maciej Chałubiński, and Magdalena Trzeciak. 2023. "Is Atopic Dermatitis Only a Skin Disease?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010837
APA StyleMesjasz, A., Zawadzka, M., Chałubiński, M., & Trzeciak, M. (2023). Is Atopic Dermatitis Only a Skin Disease? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010837




