Snapshots of ABCG1 and ABCG5/G8: A Sterol’s Journey to Cross the Cellular Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The General Structure of ABCG1 and ABCG5/G8
3. A Closer Look at the Structures of ABCG1 and ABCG5/G8
3.1. ECD: Hydrophobic Valve, ECLs
3.2. TMD: Polar Relay, Cholesterol-Sensing Motif, Phenylalanine Highway
3.3. NBD: Walker A, Walker B, Signature Motif, NPXDF Motif
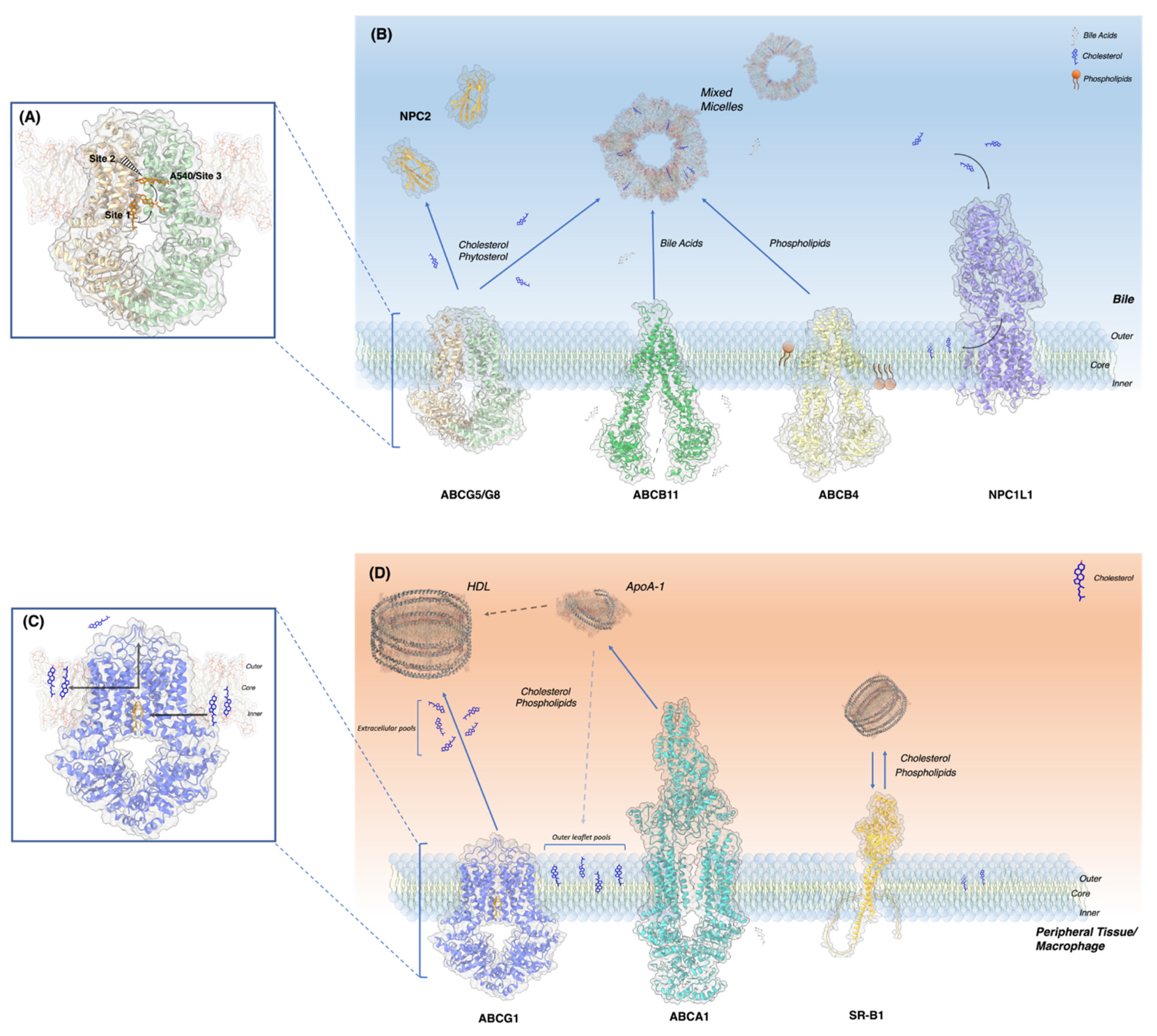
4. Revelation of Cholesterol Binding Sites in ABCG Sterol Transporters and Logical Working Models
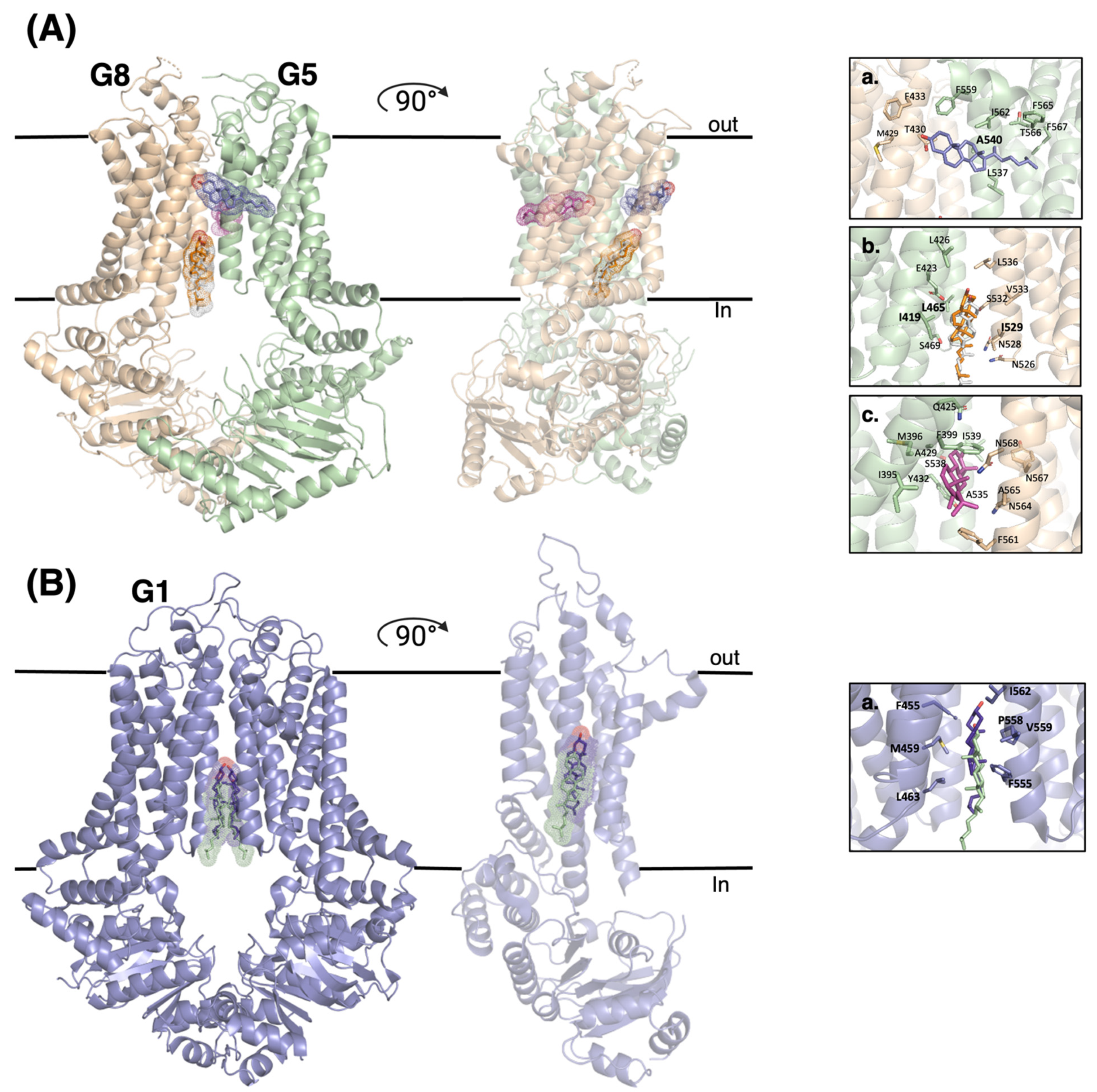
4.1. ABCG5/G8
4.2. ABCG1
5. Outlook
5.1. Challenge to Reveal Conformations of the Catalytic Cycle during the Sterol Transport
5.2. Challenge to Determine Substrate Specificity and Selectivity on ABCG Sterol Transporters
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuchler, K. The ABC of ABCs: Multidrug Resistance and Genetic Diseases; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 278, p. 3189. [Google Scholar]
- Locher, K.P. Mechanistic diversity in ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, D.C.; Johnson, E.; Lewinson, O. ABC transporters: The power to change. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linton, K.J.; Higgins, C.F. Structure and function of ABC transporters: The ATP switch provides flexible control. Pflügers Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2007, 453, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X. ABC family transporters. Drug Transp. Drug Dispos. Eff. Toxic. 2019, 1141, 13–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, I.D.; Hutchison, E.; Gerard, L.; Aleidi, S.M.; Gelissen, I.C. Mammalian ABCG-transporters, sterols and lipids: To bind perchance to transport? Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yutuc, E.; Griffiths, W.J. Cholesterol metabolism pathways–are the intermediates more important than the products? FEBS J. 2021, 288, 3727–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimet, M.; Barrett, T.J.; Fisher, E.A. HDL and reverse cholesterol transport: Basic mechanisms and their roles in vascular health and disease. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrins, C.L.; Ottenhoff, R.; van den Oever, K.; de Waart, D.R.; Kruyt, J.K.; Zhao, Y.; van Berkel, T.J.; Havekes, L.M.; Aerts, J.M.; van Eck, M. Trans-intestinal cholesterol efflux is not mediated through high density lipoprotein. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, I.D.; Haider, A.J.; Gelissen, I.C. The ABCG family of membrane-associated transporters: You don’t have to be big to be mighty. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1767–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, K.E.; Tian, H.; Graf, G.A.; Yu, L.; Grishin, N.V.; Schultz, J.; Kwiterovich, P.; Shan, B.; Barnes, R.; Hobbs, H.H. Accumulation of dietary cholesterol in sitosterolemia caused by mutations in adjacent ABC transporters. Science 2000, 290, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurs, I.; Lammers, B.; Zhao, Y.; Out, R.; Hildebrand, R.B.; Hoekstra, M.; Van Berkel, T.J.; Van Eck, M. The effect of ABCG1 deficiency on atherosclerotic lesion development in LDL receptor knockout mice depends on the stage of atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, M.A.; Barrera, G.C.; Nakamura, K.; Baldán, Á.; Tarr, P.; Fishbein, M.C.; Frank, J.; Francone, O.L.; Edwards, P.A. ABCG1 has a critical role in mediating cholesterol efflux to HDL and preventing cellular lipid accumulation. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Smith, J.D. ABCA1 and nascent HDL biogenesis. Biofactors 2014, 40, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, O.; Kobayashi, A.; Nagao, K.; Kumagai, K.; Kioka, N.; Hanada, K.; Ueda, K.; Matsuo, M. Sphingomyelin-dependence of cholesterol efflux mediated by ABCG1. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavelier, C.; Lorenzi, I.; Rohrer, L.; von Eckardstein, A. Lipid efflux by the ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2006, 1761, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Yu, L. Protein mediators of sterol transport across intestinal brush border membrane. Cholest. Bind. Cholest. Transp. Proteins 2010, 51, 337–380. [Google Scholar]
- Salen, G.; Horak, I.; Rothkopf, M.; Cohen, J.; Speck, J.; Tint, G.; Shore, V.; Dayal, B.; Chen, T.; Shefer, S. Lethal atherosclerosis associated with abnormal plasma and tissue sterol composition in sitosterolemia with xanthomatosis. J. Lipid Res. 1985, 26, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, T.A. Phytosterolaemia, xanthomatosis and premature atherosclerotic arterial disease: A case with high plant sterol absorption, impaired sterol elimination and low cholesterol synthesis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 10, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Lu, K.; Hazard, S.; Yu, H.; Shulenin, S.; Hidaka, H.; Kojima, H.; Allikmets, R.; Sakuma, N.; Pegoraro, R. Identification of a gene, ABCG5, important in the regulation of dietary cholesterol absorption. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salen, G.; Shefer, S.; Nguyen, L.; Ness, G.C.; Tint, G.; Shore, V. Sitosterolemia. J. Lipid Res. 1992, 33, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kinch, L.N.; Borek, D.M.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Urbatsch, I.L.; Xie, X.-S.; Grishin, N.V.; Cohen, J.C.; Otwinowski, Z. Crystal structure of the human sterol transporter ABCG5/ABCG8. Nature 2016, 533, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakulj, L.; Vissers, M.N.; Tanck, M.W.; Hutten, B.A.; Stellaard, F.; Kastelein, J.J.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M. ABCG5/G8 polymorphisms and markers of cholesterol metabolism: Systematic review and meta-analysis [S]. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3016–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuhara, H.; Sugiyama, Y. ATP-binding cassette, subfamily G (ABCG family). Pflügers Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2007, 453, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Long, T.; Qi, X.; Donnelly, L.; Elghobashi-Meinhardt, N.; Esparza, L.; Cohen, J.C.; Xie, X.-S.; Hobbs, H.H. Molecular basis of cholesterol efflux via ABCG subfamily transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2110483118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.; Wagner, M.; Du, D.; Raschka, S.; Nentwig, L.-M.; Gohlke, H.; Smits, S.H.; Luisi, B.F.; Schmitt, L. Structure and efflux mechanism of the yeast pleiotropic drug resistance transporter Pdr5. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okiyoneda, T.; Kono, T.; Niibori, A.; Harada, K.; Kusuhara, H.; Takada, T.; Shuto, T.; Suico, M.A.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kai, H. Calreticulin facilitates the cell surface expression of ABCG5/G8. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemans-Oldehinkel, E.; Doeven, M.K.; Poolman, B. ABC transporter architecture and regulatory roles of accessory domains. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunweeraphong, N.; Szöllősi, D.; Stockner, T.; Kuchler, K. The ABCG2 multidrug transporter is a pump gated by a valve and an extracellular lid. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunweeraphong, N.; Mitchell-White, J.; Szöllősi, D.; Hussein, T.; Kuchler, K.; Kerr, I.D.; Stockner, T.; Lee, J.Y. Picky ABCG5/G8 and promiscuous ABCG2-a tale of fatty diets and drug toxicity. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 4035–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, C.A.; Timachi, M.H.; Hürlimann, L.M.; Zimmermann, I.; Egloff, P.; Göddeke, H.; Kucher, S.; Štefanić, S.; Karttunen, M.; Schäfer, L.V. The extracellular gate shapes the energy profile of an ABC exporter. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodan, A.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakatsu, T.; Matsuoka, K.; Kimura, Y.; Ueda, K.; Kato, H. Inward-and outward-facing X-ray crystal structures of homodimeric P-glycoprotein CmABCB1. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Moreno, A.; Pata, J.; Falson, P.; Prasad, R. ABCG: A new fold of ABC exporters and a whole new bag of riddles! Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2021, 123, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Adachi, T.; Kii, I.; Kobatake, E.; Kudo, A.; Ishikawa, T. Identification of cysteine residues critically involved in homodimer formation and protein expression of human ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2: A new approach using the flp recombinase system. J. Exp. Oncol. 2006, 5, 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Skarda, L.; Kowal, J.; Locher, K.P. Structure of the human cholesterol transporter ABCG1. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 167218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epand, R.M. Cholesterol and the interaction of proteins with membrane domains. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, L.J.; Rao, G.; Jones, P.M.; Glancey, E.; Aleidi, S.M.; George, A.M.; Brown, A.J.; Gelissen, I.C. Cholesterol sensing by the ABCG1 lipid transporter: Requirement of a CRAC motif in the final transmembrane domain. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, D.J.; Plichta, D.R.; Shungin, D.; Koppel, N.; Hall, A.B.; Fu, B.; Vasan, R.S.; Shaw, S.Y.; Vlamakis, H.; Balskus, E.P. Cholesterol metabolism by uncultured human gut bacteria influences host cholesterol level. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 245–257.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristovski, M.; Farhat, D.; Bancud, S.E.M.; Lee, J.-Y. Lipid Transporters Beam Signals from Cell Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, B.M.; Jennings, W.J.; Zein, A.A.; Wang, J.; Lee, J.-Y. Structural snapshot of the cholesterol-transport ATP-binding cassette proteins. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, D.; Rezaei, F.; Ristovski, M.; Yang, Y.; Stancescu, A.; Dzimkova, L.; Samnani, S.; Couture, J.-F.; Lee, J.-Y. Structural analysis of cholesterol binding and sterol selectivity by ABCG5/G8. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.F. ABC transporters: From microorganisms to man. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1992, 8, 67–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, L.-W.; Wang, I.X.; Nikaido, K.; Liu, P.-Q.; Ames, G.F.-L.; Kim, S.-H. Crystal structure of the ATP-binding subunit of an ABC transporter. Nature 1998, 396, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payen, L.F.; Gao, M.; Westlake, C.J.; Cole, S.P.; Deeley, R.G. Role of carboxylate residues adjacent to the conserved core Walker B motifs in the catalytic cycle of multidrug resistance protein 1 (ABCC1). J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38537–38547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauna, Z.E.; Müller, M.; Peng, X.-H.; Ambudkar, S.V. Importance of the conserved Walker B glutamate residues, 556 and 1201, for the completion of the catalytic cycle of ATP hydrolysis by human P-glycoprotein (ABCB1). Biochemistry 2002, 41, 13989–14000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombline, G.; Bartholomew, L.A.; Tyndall, G.A.; Gimi, K.; Urbatsch, I.L.; Senior, A.E. Properties of P-glycoprotein with mutations in the “catalytic carboxylate” glutamate residues. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 46518–46526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Graf, G.A.; Gerard, R.D.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Functional asymmetry of nucleotide-binding domains in ABCG5 and ABCG8. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 4507–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, A.M.; Oram, J.F. ABCG1 redistributes cell cholesterol to domains removable by high density lipoprotein but not by lipid-depleted apolipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30150–30157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, G.; Gu, H.-m.; Zhang, D.-w. Characterization of the role of a highly conserved sequence in ATP binding cassette transporter G (ABCG) family in ABCG1 stability, oligomerization, and trafficking. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 9497–9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, C.-S.; Yu, X.; Lee, J.; Vaish, A.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Z.; Min, X. Cryo-EM structure of ABCG5/G8 in complex with modulating antibodies. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.-X.; Baoukina, S.; Tieleman, D.P. Cholesterol flip-flop in heterogeneous membranes. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 2064–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cao, R.; Wei, S.; Pathan-Chhatbar, S.; Wen, M.; Wu, B.; Schamel, W.W.; Wang, S.; OuYang, B. Cholesterol Binds in a Reversed Orientation to TCRβ-TM in Which Its OH Group is Localized to the Center of the Lipid Bilayer. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 167328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, J.P.; Vestergaard, A.L.; Mikkelsen, S.A.; Mogensen, L.S.; Chalat, M.; Molday, R.S. P4-ATPases as phospholipid flippases—Structure, function, and enigmas. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, P.J.; Wolf, C. The liquid-ordered phase in membranes. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckhardt, E.R.; Moschetta, A.; Renooij, W.; Goerdayal, S.S.; van Berge-Henegouwen, G.P.; Van Erpecum, K.J. Asymmetric distribution of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin between micellar and vesicular phases: Potential implications for canalicular bile formation1. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 2022–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amigo, L.; Mendoza, H.; Zanlungo, S.; Miquel, J.F.; Rigotti, A.; González, S.; Nervi, F. Enrichment of canalicular membrane with cholesterol and sphingomyelin prevents bile salt-induced hepatic damage. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Toomre, D. Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinn, K.P.; Mahoney, M.G. Lipid rafts and detergent-resistant membranes in epithelial keratinocytes. In Epidermal Cells; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Doyen, R.; Lichtenberger, L.M. The role of membrane cholesterol in determining bile acid cytotoxicity and cytoprotection of ursodeoxycholic acid. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Temel, R.E.; Tang, W.; Ma, Y.; Rudel, L.L.; Willingham, M.C.; Ioannou, Y.A.; Davies, J.P.; Nilsson, L.-M.; Yu, L. Hepatic Niemann-Pick C1–like 1 regulates biliary cholesterol concentration and is a target of ezetimibe. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1968–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-S.; Yu, X.; Fordstrom, P.; Choi, K.; Chung, B.C.; Roh, S.-H.; Chiu, W.; Zhou, M.; Min, X.; Wang, Z. Cryo-EM structures of NPC1L1 reveal mechanisms of cholesterol transport and ezetimibe inhibition. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daleke, D.L. Regulation of transbilayer plasma membrane phospholipid asymmetry. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.-y.; Terada, T. Molecular mechanisms for biliary phospholipid and drug efflux mediated by ABCB4 and bile salts. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 954781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elferink, R.O.; Ottenhoff, R.; van Wijland, M.; Smit, J.; Schinkel, A.; Groen, A.K. Regulation of biliary lipid secretion by mdr2 P-glycoprotein in the mouse. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elferink, R.O.; Ottenhoff, R.; van Wijland, M.; Frijters, C.; Van Nieuwkerk, C.; Groen, A. Uncoupling of biliary phospholipid and cholesterol secretion in mice with reduced expression of mdr2 P-glycoprotein. J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langheim, S.; Yu, L.; Von Bergmann, K.; Lütjohann, D.; Xu, F.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. ABCG5 and ABCG8 require MDR2 for secretion of cholesterol into bile. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, H.; Kurata, A.; Onishi, Y.; Sakurai, A.; Saito, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Nagakura, M.; Tarui, S.; Kanamori, Y.; Kitajima, M. High-speed screening and QSAR analysis of human ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCB11 (bile salt export pump) to predict drug-induced intrahepatic cholestasis. Mol. Pharm. 2006, 3, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H. A thermodynamic analysis of charged mixed micelles in water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 15933–15940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosters, A.; Kunne, C.; Looije, N.; Patel, S.B.; Elferink, R.P.O.; Groen, A.K. The mechanism of ABCG5/ABCG8 in biliary cholesterol secretion in mice1. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanashi, Y.; Takada, T.; Yoshikado, T.; Shoda, J.I.; Suzuki, H. NPC2 regulates biliary cholesterol secretion via stimulation of ABCG5/G8-mediated cholesterol transport. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsen, E.M.; Hansen, G.H. Lipid rafts in epithelial brush borders: Atypical membrane microdomains with specialized functions. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2003, 1617, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Sun, C.-R.; Pan, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.-P.; Fang, S.-C.; Yao, X.; Hou, W.-T. Structure and transport mechanism of the human cholesterol transporter ABCG1. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, H.; Kimura, Y.; Kioka, N.; Matsuo, M.; Ueda, K. ATPase activity of human ABCG1 is stimulated by cholesterol and sphingomyelin [S]. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridkis-Hareli, M.; Sharp, A.; Abel, L.; Globerson, A. Thymocyte development in an in vitro constructed chimera of irradiated fetal thymus and lymphohemopoietic cells. Thymus 1991, 18, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pagler, T.A.; Wang, M.; Mondal, M.; Murphy, A.J.; Westerterp, M.; Moore, K.J.; Maxfield, F.R.; Tall, A.R. Deletion of ABCA1 and ABCG1 impairs macrophage migration because of increased Rac1 signaling. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, D.S.; Anzinger, J.J.; Leyva, F.J.; Rubin, N.; Addadi, L.; Kruth, H.S. Extracellular cholesterol-rich microdomains generated by human macrophages and their potential function in reverse cholesterol transport. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.R.; Jin, X.; Anzinger, J.J.; Xu, Q.; Purushothaman, S.; Fessler, M.B.; Addadi, L.; Kruth, H.S. ABCG1-mediated generation of extracellular cholesterol microdomains. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Sviridov, D.; Liu, Y.; Vaisman, B.; Addadi, L.; Remaley, A.T.; Kruth, H.S. ABCA1 mediates ApoA-I and ApoA-I Mimetic Peptide Mobilization of Extracellular Cholesterol Microdomains Deposited by Macrophages. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axmann, M.; Plochberger, B.; Mikula, M.; Weber, F.; Strobl, W.M.; Stangl, H. Plasma Membrane Lipids: An Important Binding Site for All Lipoprotein Classes. Membranes 2021, 11, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigami, M.; Ogasawara, F.; Nagao, K.; Hashimoto, H.; Kimura, Y.; Kioka, N.; Ueda, K. Temporary sequestration of cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine within extracellular domains of ABCA1 during nascent HDL generation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.C. Is ABCA1 a lipid transfer protein? J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedhachalam, C.; Ghering, A.B.; Davidson, W.S.; Lund-Katz, S.; Rothblat, G.H.; Phillips, M.C. ABCA1-induced cell surface binding sites for ApoA-I. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gelissen, I.C.; Harris, M.; Rye, K.-A.; Quinn, C.; Brown, A.J.; Kockx, M.; Cartland, S.; Packianathan, M.; Kritharides, L.; Jessup, W. ABCA1 and ABCG1 synergize to mediate cholesterol export to apoA-I. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karten, B.; Campenot, R.B.; Vance, D.E.; Vance, J.E. Expression of ABCG1, but not ABCA1, correlates with cholesterol release by cerebellar astroglia. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 4049–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezaei, F.; Farhat, D.; Gursu, G.; Samnani, S.; Lee, J.-Y. Snapshots of ABCG1 and ABCG5/G8: A Sterol’s Journey to Cross the Cellular Membranes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010484
Rezaei F, Farhat D, Gursu G, Samnani S, Lee J-Y. Snapshots of ABCG1 and ABCG5/G8: A Sterol’s Journey to Cross the Cellular Membranes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010484
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezaei, Fatemeh, Danny Farhat, Gonca Gursu, Sabrina Samnani, and Jyh-Yeuan Lee. 2023. "Snapshots of ABCG1 and ABCG5/G8: A Sterol’s Journey to Cross the Cellular Membranes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010484
APA StyleRezaei, F., Farhat, D., Gursu, G., Samnani, S., & Lee, J.-Y. (2023). Snapshots of ABCG1 and ABCG5/G8: A Sterol’s Journey to Cross the Cellular Membranes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010484






