Dextran Sulfate Nanocarriers: Design, Strategies and Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
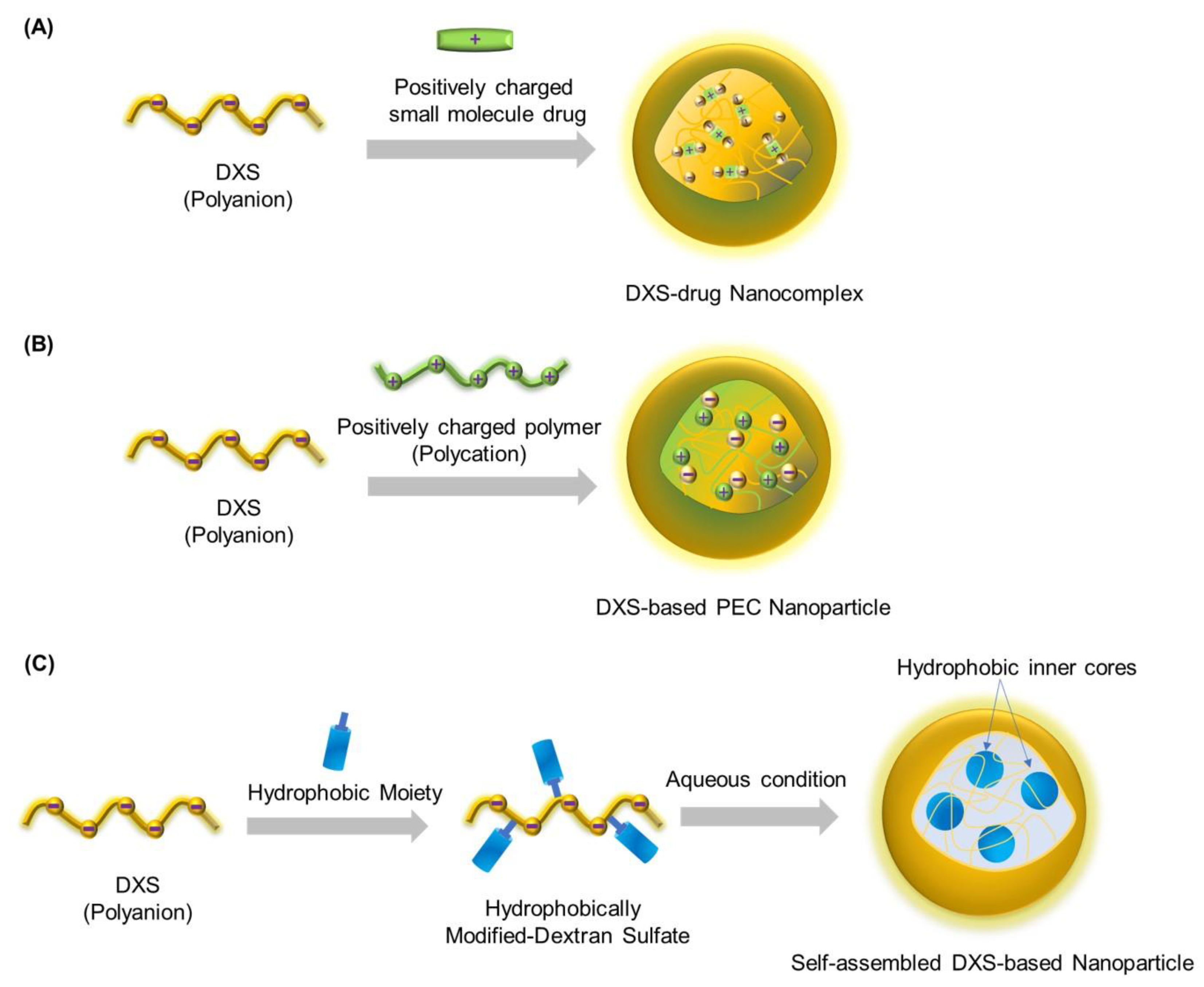
2. Strategies for the Preparation of DXS-Based Nanoparticles
2.1. DXS-Drug Nanocomplexes
2.2. DXS-Based Polyelectrolyte Complex (PEC) Nanoparticles
2.3. Self-Assembled DXS-Based Nanoparticles
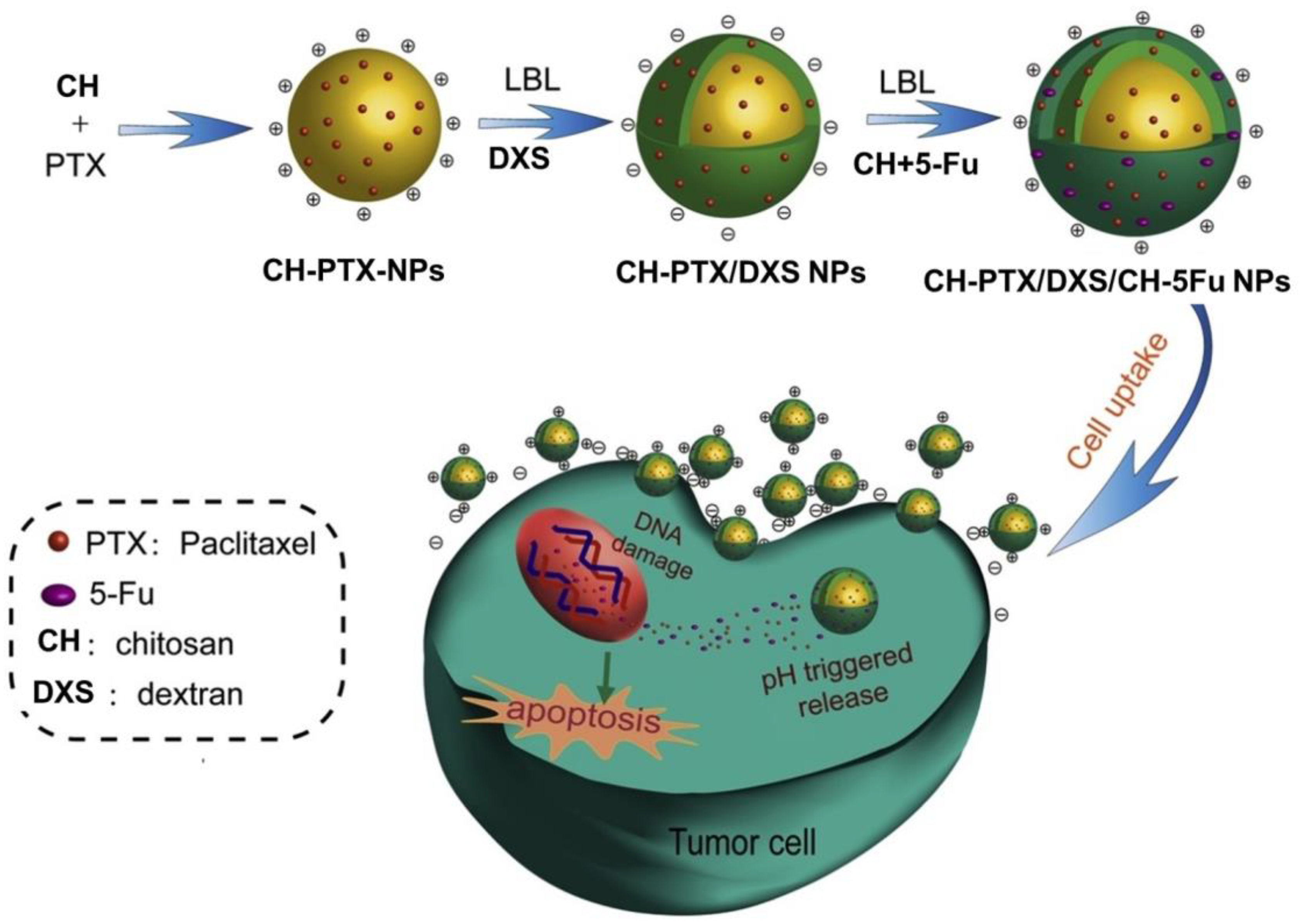
3. Therapeutic Applications of DXS Nanoparticles
3.1. Cancer
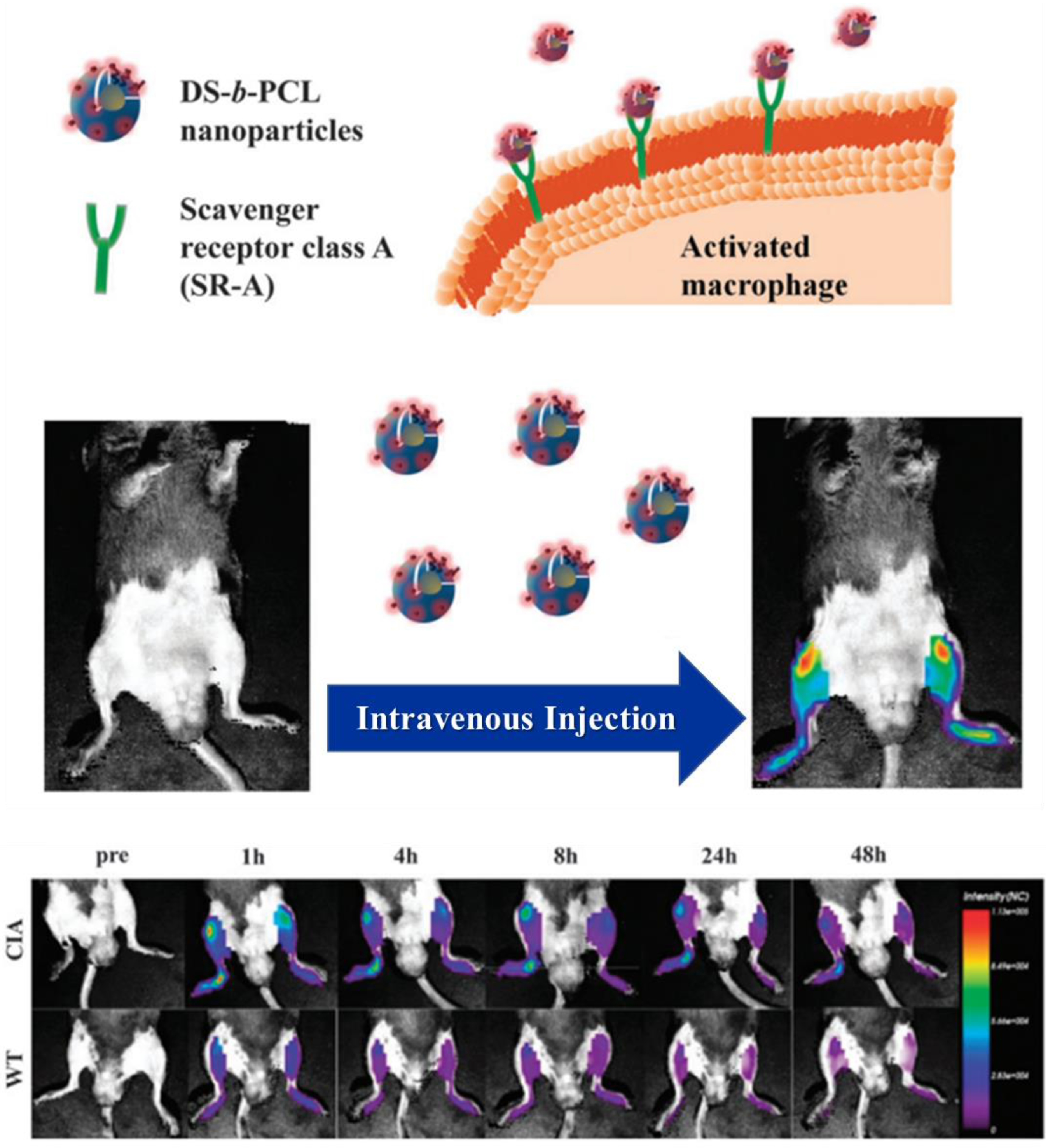
3.2. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
3.3. Ocular Disease
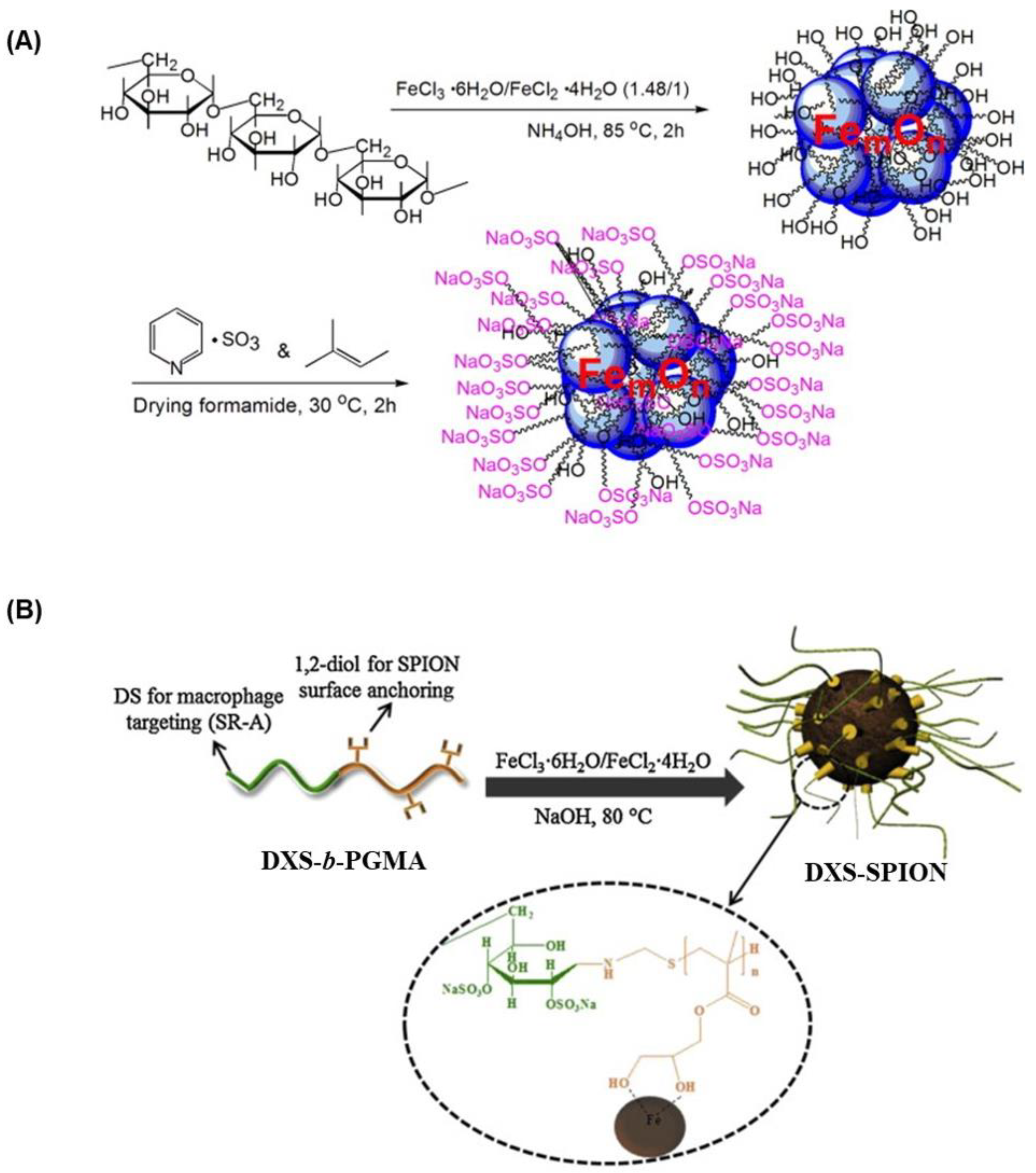
4. Diagnostic Applications of DXS Nanoparticles
4.1. DXS Nanoparticles for MRI
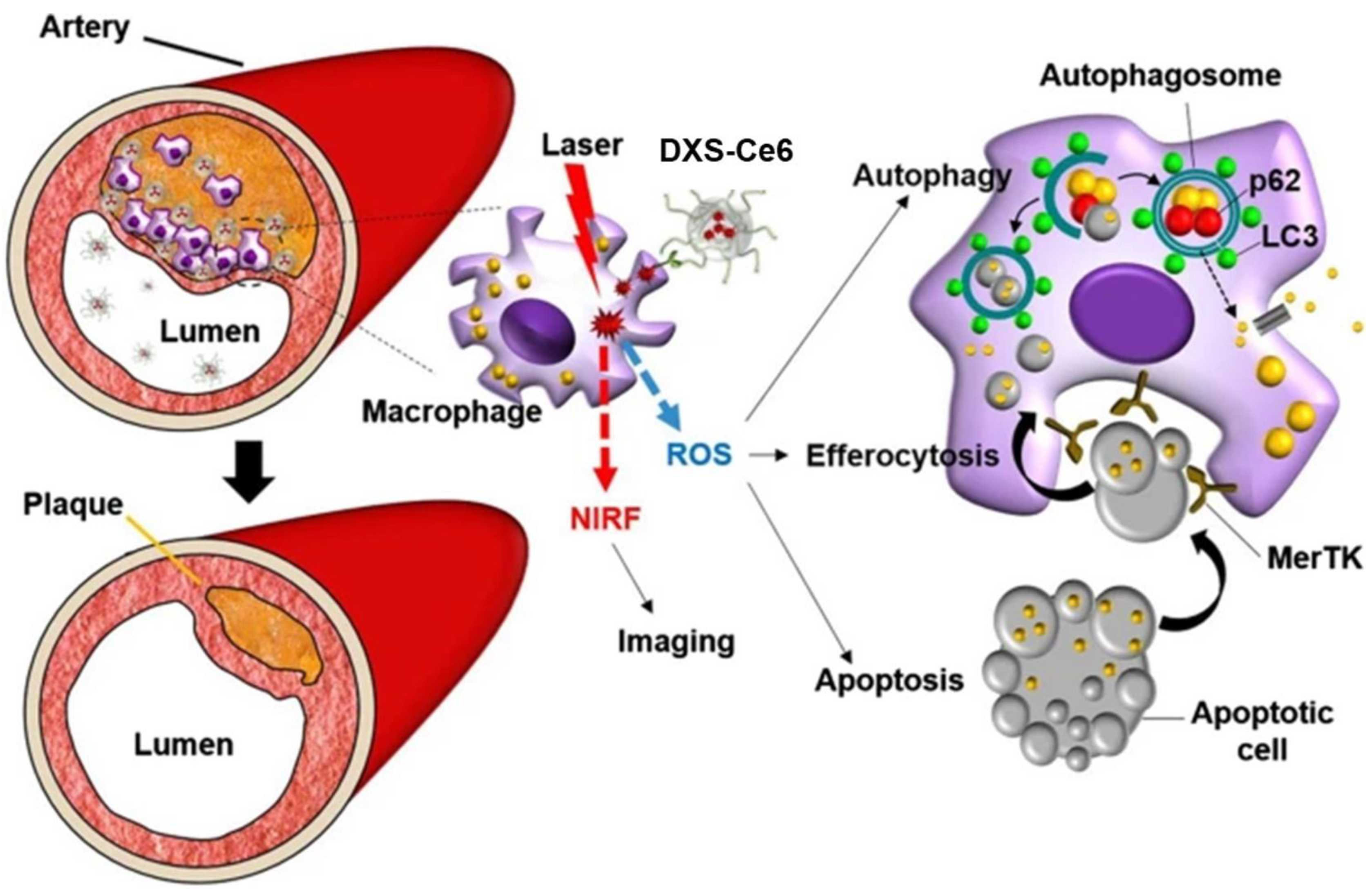
4.2. DXS Nanoparticles for Optical Imaging
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delair, T. Colloidal polyelectrolyte complexes of chitosan and dextran sulfate towards versatile nanocarriers of bioactive molecules. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 78, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Bandopadhyay, R. Use of dextran nanoparticle: A paradigm shift in bacterial exopolysaccharide based biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricketts, C.R. Dextran sulphate—A synthetic analogue of heparin. Biochem. J. 1952, 51, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricketts, C.R.; Walton, K.W.; Saddington, S.M. Preparation of dextran [35S]sulphate and tracer experiments in the rabbit. Biochem. J. 1954, 58, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Majumder, A.; Goyal, A. Potentials of Exopolysaccharides from Lactic Acid Bacteria. Indian J. Microbiol. 2012, 52, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkhali, O.A.; Sivagurunathan Moni, S.; Sultan, M.H.; Bukhary, H.A.; Ghazwani, M.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Meraya, A.M.; Alshahrani, S.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Bakkari, M.A.; et al. Formulation and evaluation of injectable dextran sulfate sodium nanoparticles as a potent antibacterial agent. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammassam Veettil, R.; Marcano, D.C.; Yuan, X.; Zaheer, M.; Adumbumkulath, A.; Lee, R.; Isenhart, L.C.; Soriano, N.; Mhatre, K.; Joseph, R.; et al. Dextran Sulfate Polymer Wafer Promotes Corneal Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, A.A.; Swinkels, D.W.; van Dongen, P.W.J.; Stalenhoef, A.F.H. Pregnancy in a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia treated with long-term low-density lipoprotein apheresis. Metabolism 1994, 43, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Raucourt, E.; Mauray, S.; Chaubet, F.; Maiga-Revel, O.; Jozefowicz, M.; Fischer, A.M. Anticoagulant activity of dextran derivatives. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 41, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.M.; van Zanten, J.H.; Betenbaugh, M.J., II. Electrostatic effect in the aggregation of heat-denatured RNase A and implications for protein additive design. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1998, 59, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.; Kim, J.; Cho, B.-K.; Ko, B.-J.; Hwang, B.-Y.; Kim, B.-G. How does dextran sulfate prevent heat induced aggregation of protein?: The mechanism and its limitation as aggregation inhibitor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1774, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, I. The application of sodium dextran sulfate to the field of cosmetics. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2007, 29, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirig, R.; Gajanayake, T.; Korsgren, O.; Nilsson, B.; Rieben, R. Low molecular weight dextran sulfate as complement inhibitor and cytoprotectant in solid organ and islet transplantation. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 4084–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, T.; Sakakura, C.; Kin, S.; Nakase, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Shimomura, K.; Ito, T.; Fujiyama, J.; Yamasaki, J.; Tsujimoto, H.; et al. Dextran Sulfate Suppresses Cell Adhesion and Cell Cycle Progression of Melanoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 895. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, C. Delivery of protein drugs using nanoparticles self-assembled from dextran sulfate and quaternized chitosan. J. Control. Release 2011, 152, e170–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasseri, R.; Karimi, M.; Tian, L.; Naderi-Manesh, H.; Ramakrishna, S. Hydrophobic lapatinib encapsulated dextran-chitosan nanoparticles using a toxic solvent free method: Fabrication, release property & in vitro anti-cancer activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Vitharana, S.N.; Peek, L.J.; Coop, T.; Berkland, C. Polyelectrolyte Complexes Stabilize and Controllably Release Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.G.; dos Santos, A.M.; Silvestre, A.L.P.; Meneguin, A.B.; Ferreira, L.M.B.; Chorilli, M.; Gremião, M.P.D. New insights into physicochemical aspects involved in the formation of polyelectrolyte complexes based on chitosan and dextran sulfate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiyama, T.; Takata, H.; Kikuchi, M.; Nakanishi, K. Polyelectrolyte complex gel with high pH-sensitivity prepared from dextran sulfate and chitosan. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 73, 2227–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, G.T.; Humphries, W.H.; Fay, N.C.; Payne, C.K. Cellular binding, motion, and internalization of synthetic gene delivery polymers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cock, L.J.; De Koker, S.; De Geest, B.G.; Grooten, J.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.P.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Antipina, M.N. Polymeric Multilayer Capsules in Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6954–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, N.; Suzuki, H.; Kurihara, Y.; Kodama, T.; Gordon, S. Role for the class A macrophage scavenger receptor in the phagocytosis of apoptotic thymocytes in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1996, 93, 12456–12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, S.T.; Taylor, P.C. Role of biological agents in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahy, S.; Peer, D. Polysaccharides as building blocks for nanotherapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2623–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanakumar, G.; Jo, D.G.; Park, J.H. Polysaccharide-Based Nanoparticles: A Versatile Platform for Drug Delivery and Biomedical Imaging. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3212–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plucinski, A.; Lyu, Z.; Schmidt, B.V.K.J. Polysaccharide nanoparticles: From fabrication to applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7030–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, E.; Osada, Y.; Sanada, K. Interaction of poly(styrene sulfonate) with polycations carrying charges in the chain backbone. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-1 Polym. Chem. 1972, 10, 3397–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, V.A.; Zezin, A.B. A new class of complex water-soluble polyelectrolytes. Die Makromol. Chem. 1984, 6, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, H.; Kikuchi, Y. Polyelectrolyte complexes of sodium dextran sulfate with chitosan, 2. Die Makromol. Chem. 1977, 178, 2895–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalat, M.; David, L.; Delair, T. Reversible controlled assembly of chitosan and dextran sulfate: A new method for nanoparticle elaboration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Drogoz, A.; David, L.; Domard, A.; Charles, M.-H.; Verrier, B.; Delair, T. Polysaccharide-based vaccine delivery systems: Macromolecular assembly, interactions with antigen presenting cells, and in vivo immunomonitoring. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 93A, 1322–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, V.A.; Blau, A.; Alvarenga, J.; Loscalzo, J.; Zhang, Y.-Y. A crosslinked dextran sulfate-chitosan nanoparticle for delivery of therapeutic heparin-binding proteins. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.H.; Park, K.; Kim, Y.-S.; Bae, S.M.; Lee, S.; Jo, H.G.; Park, R.-W.; Kim, I.-S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, K.; et al. Hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles-encapsulated camptothecin enhance the drug stability and tumor targeting in cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.Y.; Min, K.H.; Na, J.H.; Choi, K.; Kim, K.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, I.C.; Jeong, S.Y. Self-assembled hyaluronic acid nanoparticles as a potential drug carrier for cancer therapy: Synthesis, characterization, and in vivo biodistribution. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 4102–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, G.; Choi, K.Y.; Yoon, H.Y.; Kim, K.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, I.C.; Park, K. Hydrotropic hyaluronic acid conjugates: Synthesis, characterization, and implications as a carrier of paclitaxel. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 394, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, L.; Fish, P.V.; Mano, T. Bridging solubility between drug discovery and development. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gala, U.H.; Miller, D.A.; Williams, R.O. Harnessing the therapeutic potential of anticancer drugs through amorphous solid dispersions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2020, 1873, 188319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefpour, P.; Atyabi, F.; Farahani, E.V.; Sakhtianchi, R.; Dinarvand, R. Polyanionic carbohydrate doxorubicin-dextran nanocomplex as a delivery system for anticancer drugs: In vitro analysis and evaluations. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, K.A.; Fresneau, M.P.; Marazuela, A.; Fabra, A.; Alonso, M.a.J. Chitosan nanoparticles as delivery systems for doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2001, 73, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Deepagan, V.G.; Divya Rani, V.V.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Preparation, characterization, in vitro drug release and biological studies of curcumin loaded dextran sulphate–chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, J.; Tang, X.; Huang, K.; Chen, L. Polyelectrolyte three layer nanoparticles of chitosan/dextran sulfate/chitosan for dual drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboutaleb, E.; Atyabi, F.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Vatanara, A.R.; Ostad, S.N.; Kobarfard, F.; Dinarvand, R. Improved brain delivery of vincristine using dextran sulfate complex solid lipid nanoparticles: Optimization and in vivo evaluation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, A.K.; Singh, A.; Ganta, S.; Amiji, M.M. Role of integrated cancer nanomedicine in overcoming drug resistance. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2013, 65, 1784–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markman, J.L.; Rekechenetskiy, A.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.Y. Nanomedicine therapeutic approaches to overcome cancer drug resistance. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2013, 65, 1866–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Ling, G.; Pan, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, T.; Pu, X.; Yin, S.; He, Z. Novel nanostructured lipid-dextran sulfate hybrid carriers overcome tumor multidrug resistance of mitoxantrone hydrochloride. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.L.; Wolfe, F.; Huizinga, T.W.J. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Steiner, G. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chang, Y.; Wei, W. Emerging role of targeting macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis: Focus on polarization, metabolism and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Ding, J.; Feng, X.; Chang, F.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Scavenger Receptor-Mediated Targeted Treatment of Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Dextran Sulfate-Methotrexate Prodrug. Theranostics 2017, 7, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Xu, X.; Su, M.; Xi, M.; Yin, Z. Dextran sulfate–modified pH-sensitive layered double hydroxide nanocomposites for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Liu, H.; Guo, C.; Chen, Q.; Su, Y.; Guo, H.; Hou, X.; Zhao, F.; Fan, H.; Xu, H.; et al. Dextran sulfate-based MMP-2 enzyme-sensitive SR-A receptor targeting nanomicelles for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, C.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Choonara, Y.E.; du Toit, L.C.; Ally, N.; Pillay, V. Advances in Biodegradable Nano-Sized Polymer-Based Ocular Drug Delivery. Polymers 2019, 11, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyasan, W.; Srinivas, S.P.; Tiyaboonchai, W. Crosslinked chitosan-dextran sulfate nanoparticle for improved topical ocular drug delivery. Mol. Vis. 2015, 21, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaiyasan, W.; Srinivas, S.P.; Tiyaboonchai, W. Mucoadhesive Chitosan–Dextran Sulfate Nanoparticles for Sustained Drug Delivery to the Ocular Surface. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 29, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyasan, W.; Praputbut, S.; Kompella, U.B.; Srinivas, S.P.; Tiyaboonchai, W. Penetration of mucoadhesive chitosan-dextran sulfate nanoparticles into the porcine cornea. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2017, 149, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, C.; Bala, P.; Pal, K.; Kale, S.N. Cross-linked chitosan-dextran sulphate vehicle system for controlled release of ciprofloxaxin drug: An ophthalmic application. OpenNano 2017, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Park, J.S.; Kang, M.J. Nanocomplex System of Bupivacaine with Dextran Sulfate for Parenteral Prolonged Delivery. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2020, 41, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.R.; Gambhir, S.S. Nanomaterials for In Vivo Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 901–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, J.; Park, K. Multicomponent, Tumor-Homing Chitosan Nanoparticles for Cancer Imaging and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.; Park, S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, K.; Choi, K.; Song, I.C.; Han, M.H.; Leary, J.J.; Yuk, S.A.; Kwon, I.C.; et al. Tumor Targeting Chitosan Nanoparticles for Dual-Modality Optical/MR Cancer Imaging. Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassa, C.; Shaw, S.Y.; Weissleder, R. Dextran-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: A Versatile Platform for Targeted Molecular Imaging, Molecular Diagnostics, and Therapy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Hsu, J.C.; Koo, H.; Cormode, D.P. Repurposing ferumoxytol: Diagnostic and therapeutic applications of an FDA-approved nanoparticle. Theranostics 2022, 12, 796–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrett, B.R.; Frendo, M.; Vogan, J.; Louie, A.Y. Size-controlled synthesis of dextran sulfate coated iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 035603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Ng, T.S.C.; Sohi, H.K.; Palko, H.A.; House, A.; Jacobs, R.E.; Louie, A.Y. Receptor-targeted iron oxide nanoparticles for molecular MR imaging of inflamed atherosclerotic plaques. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7209–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Z.-T.; Tsai, F.-Y.; Yang, W.-C.; Wang, J.-F.; Liu, C.-L.; Shen, C.-R.; Yen, T.-C. Preparation and Characterization of Ferrofluid Stabilized with Biocompatible Chitosan and Dextran Sulfate Hybrid Biopolymer as a Potential Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) T2 Contrast Agent. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2403–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.G.; Saravanakumar, G.; Son, S.; Han, H.S.; Heo, R.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.H. Dextran sulfate-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a contrast agent for atherosclerosis imaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.-S.; Chiu, D.T. Soft fluorescent nanomaterials for biological and biomedical imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4699–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Antaris, A.L.; Dai, H. Near-infrared fluorophores for biomedical imaging. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisch, A.; Klymchenko, A.S. Fluorescent Polymer Nanoparticles Based on Dyes: Seeking Brighter Tools for Bioimaging. Small 2016, 12, 1968–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Wei, Z.; Song, C.; Tang, C.; Han, W.; Dong, X. Optical nano-agents in the second near-infrared window for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; You, D.G.; Saravanakumar, G.; Yoon, H.Y.; Choi, K.Y.; Thambi, T.; Deepagan, V.G.; Jo, D.-G.; Park, J.H. Self-assembled dextran sulphate nanoparticles for targeting rheumatoid arthritis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10349–10351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, R.; You, D.G.; Um, W.; Choi, K.Y.; Jeon, S.; Park, J.-S.; Choi, Y.; Kwon, S.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; et al. Dextran sulfate nanoparticles as a theranostic nanomedicine for rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials 2017, 131, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.W.; Ahn, J.W.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, D.O.; Kim, R.H.; Kang, U.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, J.; Park, Y.H.; et al. Targeted theranostic photoactivation on atherosclerosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramasundaram, S.; Saravanakumar, G.; Sobha, S.; Oh, T.H. Dextran Sulfate Nanocarriers: Design, Strategies and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010355
Ramasundaram S, Saravanakumar G, Sobha S, Oh TH. Dextran Sulfate Nanocarriers: Design, Strategies and Biomedical Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010355
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamasundaram, Subramaniyan, Gurusamy Saravanakumar, Sivasangu Sobha, and Tae Hwan Oh. 2023. "Dextran Sulfate Nanocarriers: Design, Strategies and Biomedical Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010355
APA StyleRamasundaram, S., Saravanakumar, G., Sobha, S., & Oh, T. H. (2023). Dextran Sulfate Nanocarriers: Design, Strategies and Biomedical Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010355




