Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: The Impact of Pharmacological Properties and Genetic Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Incretin System
3. Pharmacological Properties of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
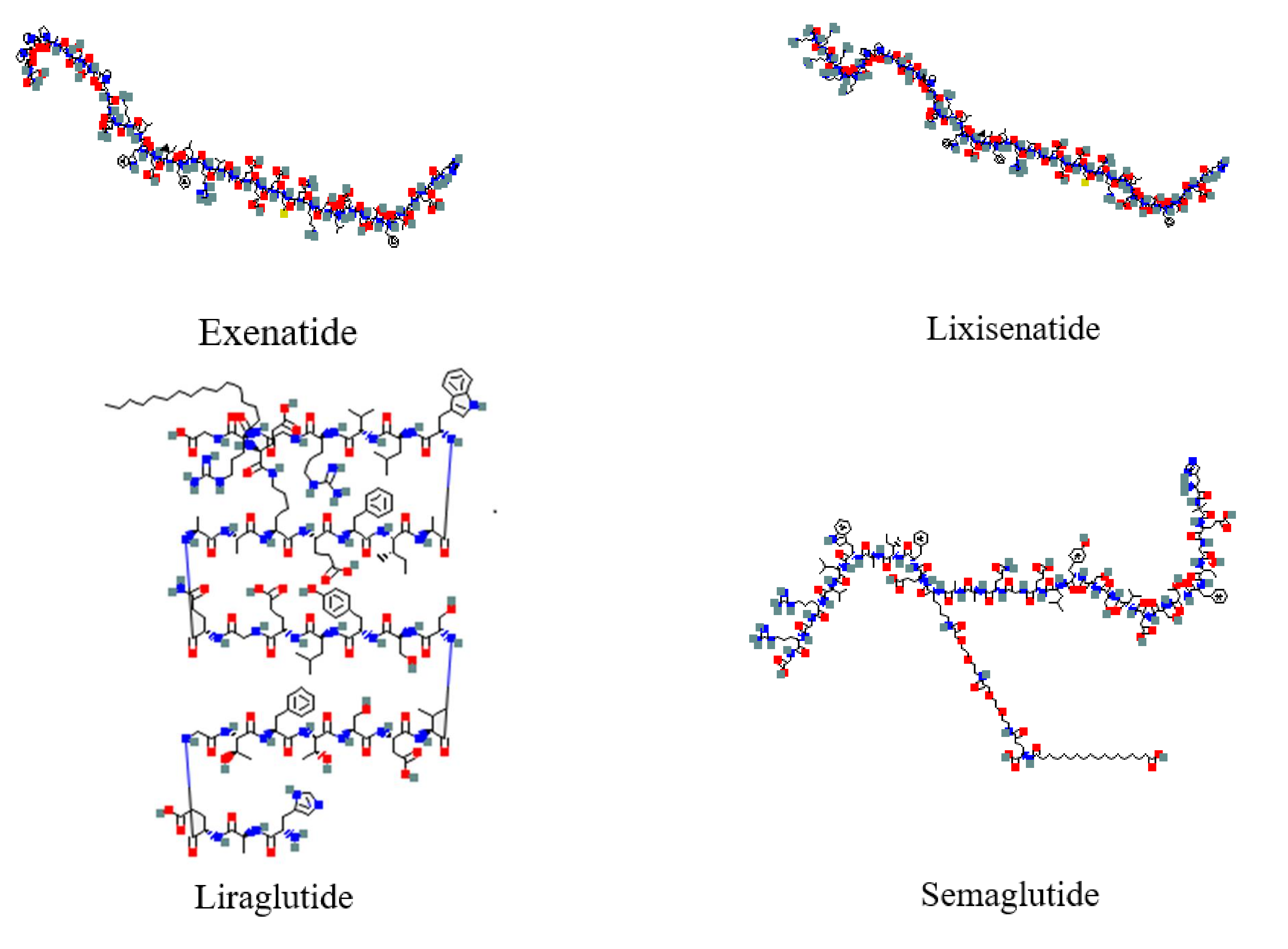
3.1. Short-Acting GLP-1 RAs
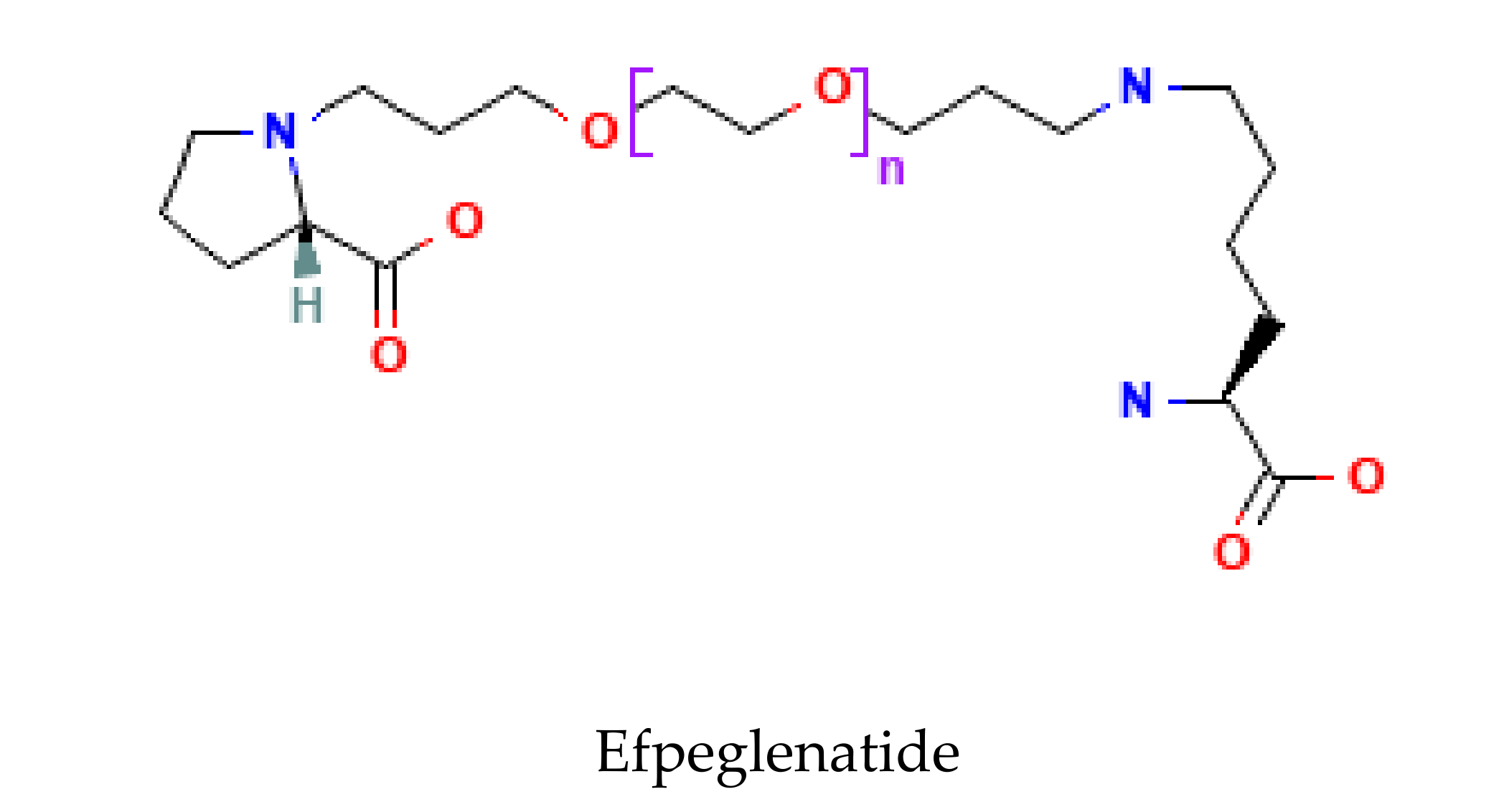
3.2. Long-Acting GLP-1 RAs
4. Clinical Efficacy of GLP-1 RAs
5. Side Effects of GLP-1 RAs
6. Cardiovascular Benefits and Outcomes
7. Obesity and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
8. Genetic Variability of the Incretin System
8.1. Associations of GLP1R Variants with Glycemic Traits and Incretin Effect
8.2. Associations of GLP1R Variants with Obesity and T2DM
8.3. Associations of GLP1R Variants with Cardiovascular Risk Factors
8.4. Associations of GLP1R Variants with Body Weight Lowering Potential of Dietary Interventions in Obese Subjects
8.5. Associations of GLP1R Variants with Response to GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
9. Future Perspectives
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Association, A.D. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Kaabi, J. Al Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes-Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piché, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, F.X. The obesity epidemic: Pathophysiology and consequences of obesity. Obes. Res. 2002, 10 (Suppl. 2), 97S–104S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. The in cretin effect in healthy individuals and those with type 2 diabetes: Physiology, pathophysiology, and response to therapeutic interventions. lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz-Chaves, Y.; Herrera-Pérez, S.; González-Matías, L.C.; Lamas, J.A.; Mallo, F. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) in the Integration of Neural and Endocrine Responses to Stress. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, D. The structure and function of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and its ligands. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willard, F.S.; Sloop, K.W. Physiology and emerging biochemistry of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 470851, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, T.M.; Hahn, J.D.; Konanur, V.R.; Lam, A.; Kanoski, S.E. Hippocampal GLP-1 receptors influence food intake, meal size, and effort-based responding for food through volume transmission. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. Incretin hormones: Their role in health and disease. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2018, 20 (Suppl. 1), 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Vilsbøll, T.; Gallwitz, B.; Garber, A.; Madsbad, S. Incretin-based therapies: Viewpoints on the way to consensus. Diabetes Care 2009, 32 (Suppl. 2), 223S–231S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Alessio, D. Is GLP-1 a hormone: Whether and When? J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7 (Suppl. 1), 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nauck, M. Incretin therapies: Highlighting common features and differences in the modes of action of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, S.; Isaacs, D.; Clements, J.N. Pharmacokinetics and Clinical Implications of Semaglutide: A New Glucagon-Like Peptide (GLP)-1 Receptor Agonist. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.H.; Kang, J.; Kwon, S.C.; Trautmann, M.E.; Hompesch, M.; Stewart, J.; Sorli, C.H. Pharmacokinetic and dose-finding studies on efpeglenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettge, K.; Kahle, M.; Abd El Aziz, M.S.; Meier, J.J.; Nauck, M.A. Occurrence of nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea reported as adverse events in clinical trials studying glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: A systematic analysis of published clinical trials. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trujillo, J. Safety and tolerability of once-weekly GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2020, 45 (Suppl. 1), 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Claggett, B.; Diaz, R.; Dickstein, K.; Gerstein, H.C.; Køber, L.V.; Lawson, F.C.; Ping, L.; Wei, X.; Lewis, E.F.; et al. Lixisenatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Acute Coronary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kim, C.H. Differential Risk of Cancer Associated with Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists: Analysis of Real-world Databases. Endocr. Res. 2022, 47, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, M.; Rosebraugh, C. Weighing risks and benefits of liraglutide--the FDA’s review of a new antidiabetic therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gier, B.; Butler, P.C.; Lai, C.K.; Kirakossian, D.; DeNicola, M.M.; Yeh, M.W. Glucagon like peptide-1 receptor expression in the human thyroid gland. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sherman, S.I.; Kloos, R.T.; Tuttle, R.M.; Pontecorvi, A.; Völzke, H.; Harper, K.; Vance, C.; Alston, J.T.; Usborne, A.L.; Sloop, K.W.; et al. No calcitonin change in a person taking dulaglutide diagnosed with pre-existing medullary thyroid cancer. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignarelli, A.; Genchi, V.A.; Caruso, I.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Diabetes and cancer: Pathophysiological fundamentals of a “dangerous affair”. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 143, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosenzon, O.; Alguwaihes, A.; Leon, J.L.A.; Bayram, F.; Darmon, P.; Davis, T.M.E.; Dieuzeide, G.; Eriksen, K.T.; Hong, T.; Kaltoft, M.S.; et al. CAPTURE: A multinational, cross-sectional study of cardiovascular disease prevalence in adults with type 2 diabetes across 13 countries. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.M.; Jung, C.H. Cardiovascular Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M.M.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; Tonneijck, L.; Hoekstra, T.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Diamant, M.; Van Raalte, D.H. Exenatide acutely increases heart rate in parallel with augmented sympathetic nervous system activation in healthy overweight males. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendis, B.; Simpson, E.; Macdonald, I.; Mansell, P. Investigation of the haemodynamic effects of exenatide in healthy male subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 74, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Courrèges, J.P.; Vilsbøll, T.; Zdravkovic, M.; Le-Thi, T.; Krarup, T.; Schmitz, O.; Verhoeven, R.; Bugáñová, I.; Madsbad, S. Beneficial effects of once-daily liraglutide, a human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue, on cardiovascular risk biomarkers in patients with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 1129–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y.; Ali, F. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A review of initiators and protective factors. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurkan, E.; Tarkun, I.; Sahin, T.; Cetinarslan, B.; Canturk, Z. Evaluation of exenatide versus insulin glargine for the impact on endothelial functions and cardiovascular risk markers. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 106, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blonde, L.; Klein, E.J.; Han, J.; Zhang, B.; Mac, S.M.; Poon, T.H.; Taylor, K.L.; Trautmann, M.E.; Kim, D.D.; Kendall, D.M. Interim analysis of the effects of exenatide treatment on A1C, weight and cardiovascular risk factors over 82 weeks in 314 overweight patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2006, 8, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Greevenbroek, M.M.J.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Stehouwer, C.D.A. Obesity-associated low-grade inflammation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Causes and consequences. Neth. J. Med. 2013, 71, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nezu, T.; Hosomi, N.; Aoki, S.; Matsumoto, M. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness for Atherosclerosis. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2016, 23, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, M.; Chandalia, M.; Patti, A.M.; Di Bartolo, V.; Rizvi, A.A.; Montalto, G.; Abate, N. Liraglutide decreases carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes: 8-month prospective pilot study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkins, N.D.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Kemp, G.J.; Pugh, C.; Green, D.J.; Cable, N.T.; Jones, H. Effects of 6 months glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist treatment on endothelial function in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, P.A.; Khan, F.Z.; Dutka, D.P. Cardioprotection against ischaemia induced by dobutamine stress using glucagon-like peptide-1 in patients with coronary artery disease. Heart 2012, 98, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozue, T.; Yamada, M.; Tsunoda, T.; Katoh, H.; Ito, S.; Iwaki, T.; Michishita, I. Effects of liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, on left ventricular remodeling assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Heart Vessels 2016, 31, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskiet, M.H.A.; Tonneijck, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, M.; Saremi, A.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; van Raalte, D.H. Lixisenatide and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome: An exploratory analysis of the ELIXA randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Bethel, M.A.; Mentz, R.J.; Thompson, V.P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Buse, J.B.; Chan, J.C.; Choi, J.; Gustavson, S.M.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Effects of Once-Weekly Exenatide on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; Xavier, D.; et al. Design and baseline characteristics of participants in the Researching cardiovascular Events with a Weekly INcretin in Diabetes (REWIND) trial on the cardiovascular effects of dulaglutide. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Sattar, N.; Rosenstock, J.; Ramasundarahettige, C.; Pratley, R.; Lopes, R.D.; Lam, C.S.P.; Khurmi, N.S.; Heenan, L.; Del Prato, S.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Efpeglenatide in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iepsen, E.W.; Torekov, S.S.; Holst, J.J. Therapies for inter-relating diabetes and obesity-GLP-1 and obesity. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 2487–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes-state-of-the-art. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, X.; Astrup, A.; Fujioka, K.; Greenway, F.; Halpern, A.; Krempf, M.; Lau, D.C.W.; le Roux, C.W.; Violante Ortiz, R.; Jensen, C.B.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of 3.0 mg of Liraglutide in Weight Management. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, R. Pharmacotherapy in obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of anti-obesity drugs. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Hollander, P.; Klein, S.; Niswender, K.; Woo, V.; Hale, P.M.; Aronne, L. Weight maintenance and additional weight loss with liraglutide after low-calorie-diet-induced weight loss: The SCALE Maintenance randomized study. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoffel, M.; Espinosa, R.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bell, G.I. Human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene. Localization to chromosome band 6p21 by fluorescence in situ hybridization and linkage of a highly polymorphic simple tandem repeat DNA polymorphism to other markers on chromosome 6. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyama, Y.; Matsui, K.; Egashira, T.; Nozaki, O.; Ishizuka, T.; Kanatsuka, A. Five missense mutations in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor gene in Japanese population. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2004, 66, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beinborn, M.; Worrall, C.I.; McBride, E.W.; Kopin, A.S. A human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor polymorphism results in reduced agonist responsiveness. Regul. Pept. 2005, 130, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koole, C.; Wootten, D.; Simms, J.; Miller, L.J.; Christopoulos, A.; Sexton, P.M. Differential impact of amino acid substitutions on critical residues of the human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor involved in peptide activity and small-molecule allostery. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 353, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sathananthan, A.; Dalla Man, C.; Micheletto, F.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Camilleri, M.; Giesler, P.D.; Laugen, J.M.; Toffolo, G.; Rizza, R.A.; Cobelli, C.; et al. Common genetic variation in GLP1R and insulin secretion in response to exogenous GLP-1 in nondiabetic subjects: A pilot study. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2074–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Li, P.; Li, R.; Yu, Z.; Sun, X.; Ji, G.; Yang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, S. GLP1R Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms rs3765467 and rs10305492 Affect β Cell Insulin Secretory Capacity and Apoptosis Through GLP-1. DNA Cell Biol. 2020, 39, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, J.; Chu, A.Y.; Willems, S.M.; Wang, S.; Yaghootkar, H.; Brody, J.A.; Dauriz, M.; Hivert, M.F.; Raghavan, S.; Lipovich, L.; et al. Low-frequency and rare exome chip variants associate with fasting glucose and type 2 diabetes susceptibility. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wishart, J.M.; Horowitz, M.; Morris, H.A.; Jones, K.L.; Nauck, M.A. Relation between gastric emptying of glucose and plasma concentrations of glucagon-like peptide-1. Peptides 1998, 19, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, A.M.W.; McLaughlin, J.; Maughan, R.J.; Gilmore, W.; Ashworth, J.J.; Evans, G.H. A Pilot Study Investigating the Influence of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Gastric Emptying Rate in Caucasian Men. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; Carlson, P.; Laurenti, M.; Vella, A.; Camilleri, M.; Desai, A.; Feuerhak, K.; Bharucha, A.E. Association between allelic variants in the glucagon-like peptide 1 and cholecystokinin receptor genes with gastric emptying and glucose tolerance. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, D.A.; Bachiller, R.; Izaola, O.; De La Fuente, B.; Aller, R. Relation of the rs6923761 gene variant in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor to metabolic syndrome in obese subjects. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 65, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luis, D.A.; Ballesteros, M.; Lopez Guzman, A.; Ruiz, E.; Muñoz, C.; Penacho, M.A.; Iglesias, P.; Maldonado, A.; Puigdevall, V.; Delgado, M. rs6923761 gene variant in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor: Allelic frequencies and influence on cardiovascular risk factors in a multicenter study of Castilla-Leon. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2144–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, S.M.; Zidan, H.E.; Shokry, A.; Saeed, J.; El-Sokkary, R.H. Association of incretin receptors genetic polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Egyptian patients. J. Gene Med. 2017, 19, e2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.A.; Freitag, D.F.; Li, L.; Chu, A.Y.; Surendran, P.; Young, R.; Grarup, N.; Stancáková, A.; Chen, Y.; Varga, T.V.; et al. A genomic approach to therapeutic target validation identifies a glucose-lowering GLP1R variant protective for coronary heart disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 341ra76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buse, J.B.; The LEADER Steering Committee. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1798–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ban, K.; Noyan-Ashraf, M.H.; Hoefer, J.; Bolz, S.S.; Drucker, D.J.; Husain, M. Cardioprotective and vasodilatory actions of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor are mediated through both glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. Circulation 2008, 117, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; Bachiller, R. Role of rs6923761 gene variant in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in basal GLP-1 levels, cardiovascular risk factor and serum adipokine levels in naïve type 2 diabetic patients. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Lu, R.; Gu, N.; Wei, X.; Bai, G.; Zhang, J.; Deng, R.; Feng, N.; Li, J.; Guo, X. Polymorphisms in the Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor (GLP-1R) Gene Are Associated with the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Chinese Han Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 1054192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; De La Fuente, B.; Primo, D.; Conde, R.; Sagrado, M.G. Evaluation of weight loss and adipocytokine levels after two hypocaloric diets with different macronutrient distribution in obese subjects with the rs6923761 gene variant of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 63, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; Bachiller, R.; Pacheco, D. Cardiovascular risk factors and adipocytokines levels after two hypocaloric diets with different fat distribution in obese subjects and rs6923761 gene variant of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2014, 37, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; Lopez, J.J.; Gomez, E.; Torres, B.; Soto, G.D. Effect of rs6923761 gene variant of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor on metabolic response and weight loss after a 3-month intervention with a hypocaloric diet. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2014, 37, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, D.A.; Aller, R.; Izaola, O.; Romero, E. Effects of a high-protein/low-carbohydrate versus a standard hypocaloric diet on adipocytokine levels and cardiovascular risk factors during 9 months, role of rs6923761 gene variant of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, D.A.; Diaz Soto, G.; Izaola, O.; Romero, E. Evaluation of weight loss and metabolic changes in diabetic patients treated with liraglutide, effect of RS 6923761 gene variant of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javorský, M.; Gotthardová, I.; Klimčáková, L.; Kvapil, M.; Židzik, J.; Schroner, Z.; Doubravová, P.; Gala, I.; Dravecká, I.; Tkáč, I. A missense variant in GLP1R gene is associated with the glycaemic response to treatment with gliptins. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Huang, Y.Y.; Hsieh, S.H.; Chen, Z.S.; Tsai, C.N. Polymorphisms of GLP-1 receptor gene and response to GLP-1 analogue in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 176949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chedid, V.; Vijayvargiya, P.; Carlson, P.; Van Malderen, K.; Acosta, A.; Zinsmeister, A.; Camilleri, M. Allelic variant in the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor gene associated with greater effect of liraglutide and exenatide on gastric emptying: A pilot pharmacogenetics study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensterle, M.; Pirš, B.; Goričar, K.; Dolžan, V.; Janež, A. Genetic variability in GLP-1 receptor is associated with inter-individual differences in weight lowering potential of liraglutide in obese women with PCOS: A pilot study. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.H.; Del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pratley, R.E.; et al. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schernthaner, G.; Shehadeh, N.; Ametov, A.S.; Bazarova, A.V.; Ebrahimi, F.; Fasching, P.; Janež, A.; Kempler, P.; Konrāde, I.; Lalić, N.M.; et al. Worldwide inertia to the use of cardiorenal protective glucose-lowering drugs (SGLT2i and GLP-1 RA) in high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatachalapathy, P.; Padhilahouse, S.; Sellappan, M.; Subramanian, T.; Kurian, S.J.; Miraj, S.S.; Rao, M.; Raut, A.A.; Kanwar, R.K.; Singh, J.; et al. Pharmacogenomics and Personalized Medicine in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Potential Implications for Clinical Practice. Pharmgenomics. Pers. Med. 2021, 14, 1441–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GLP-1 Receptor Agonists | Median Follow Up (Years) | Mortality | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparator | Study | No. of Patients | MACE | Cardiovascular | General | Heart Failure | Renal Failure | Reference | ||
| Liraglutide | Placebo | LEADER | 9340 | 3.8 | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | [18] |
| Lixisenatide | Placebo | ELIXA | 6068 | 2.1 | neutral | neutral | neutral | neutral | impact on macroalbumin uria | [20] |
| Exenatide-LAR | Placebo | EXSCEL | 14,752 | 3.2 | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | neutral | ↓ | [41] |
| Dulaglutide | Placebo | REWIND | 9901 | 5.0 | ↓ | ↓ | neutral | neutral | ↓ | [42] |
| Semaglutide | Placebo | SUSTAIN-6 | 3297 | 2.1 | ↓ | neutral | neutral | neutral | ↓ | [14] |
| Efpeglenatide | Placebo | AMPLITUDE-O | 4076 | 1.8 | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | [43] | |
| GLP1R Polymorphisms | Outcomes Studied | Study Population | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP1R region sequencing; PCR-RFLP validation of Pro7Leu, Arg44His, Arg131Gln, Thr149Met, Leu260Phe, Arg48Arg, Lys130Lys, Arg176Arg, Ile400Ile | T2DM risk, BMI, insulin secretion, insulin usage | 36 Japanese T2DM patients, validation: 791 T2DM and 318 control subjects | Thr149Met found in T2DM patients with decreased insulin secretion; no associations with BMI, T2DM risk, or insulin usage | [51] |
| 21 GLP1R tag SNPs | insulin secretion stimulated by hyperglycemia and GLP-1 infusion | 88 non-diabetic subjects | rs6923761 (Gly168Ser) and rs3765467 (Arg131Gln) nominally associated with decreased insulin secretion stimulated by hyperglycemia and GLP-1 infusion | [54] |
| HumanExome BeadChip | fasting glucose and insulin levels, incretin effect | 60,564 non-diabetic subjects | rs10305492 (Ala316Thr) associated with lower fasting glucose | [56] |
| HumanExome BeadChip | T2DM risk | 16,491 T2DM and 81,877 control subjects | no association with T2DM risk | [56] |
| 27 Tag SNPs | gastric emptying | 48 healthy Caucasian males | faster gastric emptying in rs742764 CC vs. TT and TC; slower in rs2254336 AA vs. TT and TA genotypes | [58] |
| rs6923761 and rs1042044 | gastric emptying, plasma glucose, and GLP-1 levels | 51 individuals with dyspepsia | no significant associations | [59] |
| rs6923761 | anthropometric parameters, glycemia, and metabolic traits; cardiovascular risk factors | 341 Spanish obese subjects | higher BMI, weight, fat mass, waist to hip ratio, waist circumference, triglycerides, insulin levels, HOMA-IR index values, and lower HDL cholesterol in GG vs. GA or AA genotypes | [61] |
| rs6923761 | anthropometric parameters, metabolic syndrome components | 1122 Spanish obese subjects | higher BMI, weight, fat mass, waist to hip ratio, waist circumference in GG vs. GA or AA genotypes; no association with the metabolic syndrome | [60] |
| rs367543060 | T2D risk | 150 Egyptian T2DM patients and 150 healthy controls | no association with T2DM risk | [62] |
| Targeted exome sequencing and genotyping | metabolic traits, T2D risk | T2DM risk: 11,806 (sequencing) and 39,979 (genotyping) individuals | rs10305492 (Ala316Thr) associated with lower fasting glucose and T2D risk | [63] |
| Targeted exome sequencing and genotyping | cardiovascular risk | 61,846 patients with coronary heart disease and 163,728 controls | rs10305492 (Ala316Thr) associated with lower CAD risk | [63] |
| rs6923761 | anthropometric parameters, metabolic traits, cardiovascular risk | 104 Spanish treatment-naïve T2DM patients | basal GLP-1 levels higher in A allele carriers vs. non-carriers; no associations with other traits or cardiovascular risk factors | [66] |
| 11 tagSNPs | cardiovascular disease risk | Han Chinese T2D patients: 394 with CAD vs. 217 without CAD | rs4714210 GG genotype associated with lower CAD risk | [67] |
| rs6923761 | anthropometric parameters and weight loss after 5 months of a hypocaloric diet | 280 obese Spanish patients randomized to a diet low in carbohydrates or low in fats | polymorphic rs6923761 A allele associated with better anthropometric parameters, but not weight loss | [68] |
| rs6923761 | anthropometric and metabolic parameters of cardiovascular risk after 3 months of a hypocaloric diet | 391 obese Spanish patients randomized to a diet with high monounsaturated fat or high polyunsaturated fat content | polymorphic rs6923761 A allele associated with better anthropometric parameters, but not weight loss | [69] |
| rs6923761 | metabolic responses and weight loss after 3 months of a hypocaloric diet | 91 obese Spanish patients on a hypocaloric diet | polymorphic rs6923761 A allele associated with better anthropometric parameters and triglyceride levels, but not weight loss | [70] |
| rs6923761 | cardiovascular risk factors, adipokine levels, and weight loss after 9 months of a hypocaloric diet | 211 obese Spanish patients randomized to a high protein/low carbohydrate versus standard hypocaloric diet | polymorphic rs6923761 A allele associated with better anthropometric parameters, but not weight loss | [71] |
| GLP1R Polymorphisms | Outcomes Studied | Study Population | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs6923761 | metabolic changes and weight loss after liraglutide add-on treatment | 90 overweight Spanish T2DM patients on liraglutide add-on treatment | carriers of polymorphic rs6923761 A allele achieved higher reductions in BMI, weight, and fat mass; no association of rs6923761 genotypes with the decrease in basal glucose levels, HOMA-R index, and HbA1c | [72] |
| rs6923761 | glycemic response after 6 months of gliptin treatment | T2DM patients on sitagliptin (n = 92) or vildagliptin (n = 48) | significantly lower reduction in HbA1c levels in carriers of rs6923761 polymorphism | [73] |
| all exons and intron-exon junctions | plasma glucose levels after 3 days of exenatide co-treatment | 36 patients with poorly controlled T2D on combination treatment with insulin and exenatide | no associations with rs3765467 and rs761386 after adjustment for multiple testing | [74] |
| rs6923761 | gastric emptying and weight loss | obese individuals on liraglutide (n = 20) for 16 weeks or exenatide (n = 40) for 30 days | significantly greater delay in gastric emptying in rs6923761 A-allele carriers compared to non-carriers; no association with weight loss | [75] |
| rs6923761, rs10305420 | weight loss, glycemic control, insulin resistance after 12 weeks of liraglutide | 57 obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome treated with liraglutide for 12 weeks | rs10305420 polymorphism associated with poor treatment response, while carriers of at least one polymorphic rs6923761 allele tended to lose more weight | [76] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klen, J.; Dolžan, V. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: The Impact of Pharmacological Properties and Genetic Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073451
Klen J, Dolžan V. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: The Impact of Pharmacological Properties and Genetic Factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(7):3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073451
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlen, Jasna, and Vita Dolžan. 2022. "Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: The Impact of Pharmacological Properties and Genetic Factors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 7: 3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073451
APA StyleKlen, J., & Dolžan, V. (2022). Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: The Impact of Pharmacological Properties and Genetic Factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(7), 3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073451






