A Systematic Review of Circulatory microRNAs in Major Depressive Disorder: Potential Biomarkers for Disease Prognosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
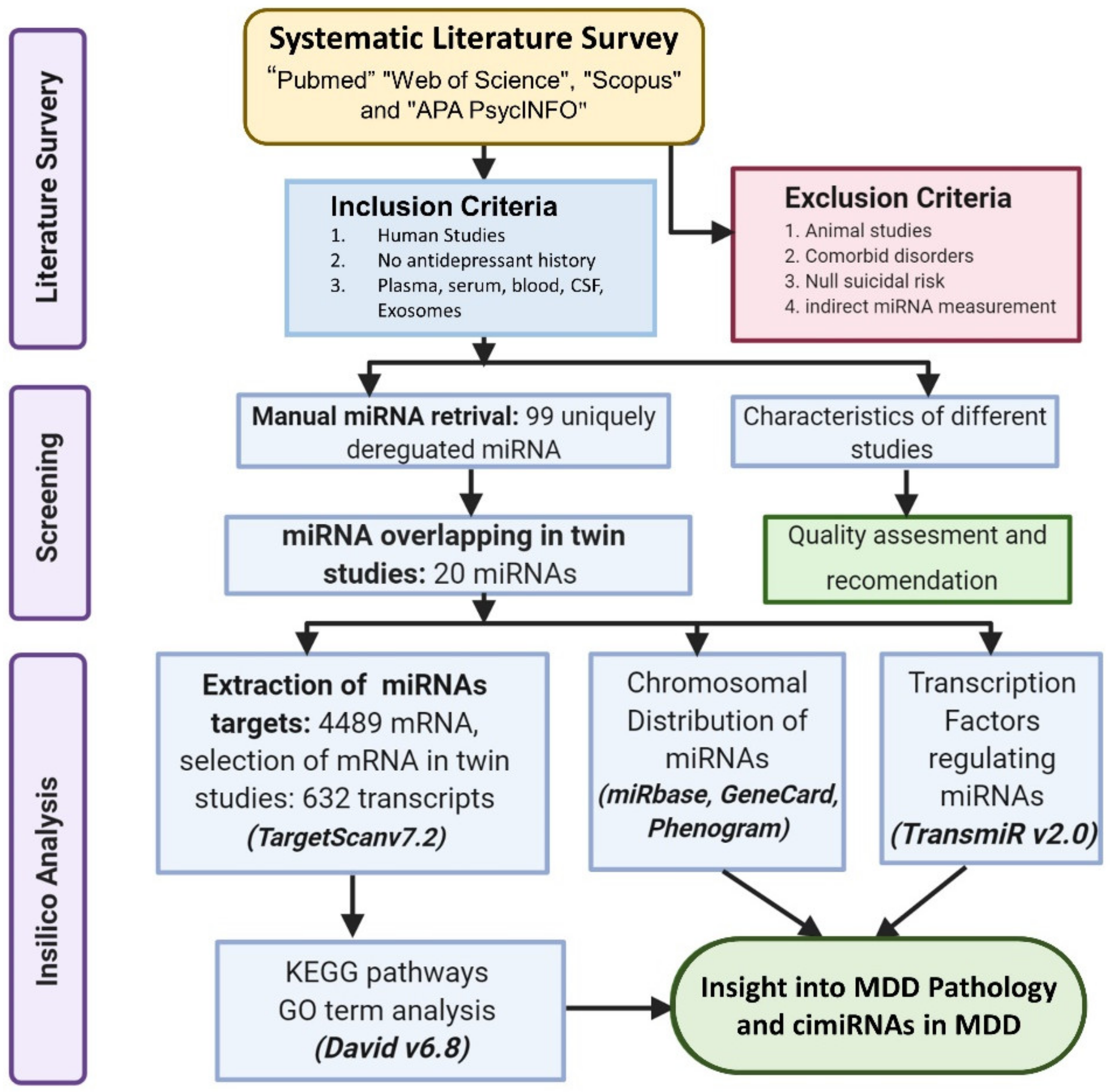
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Selection
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
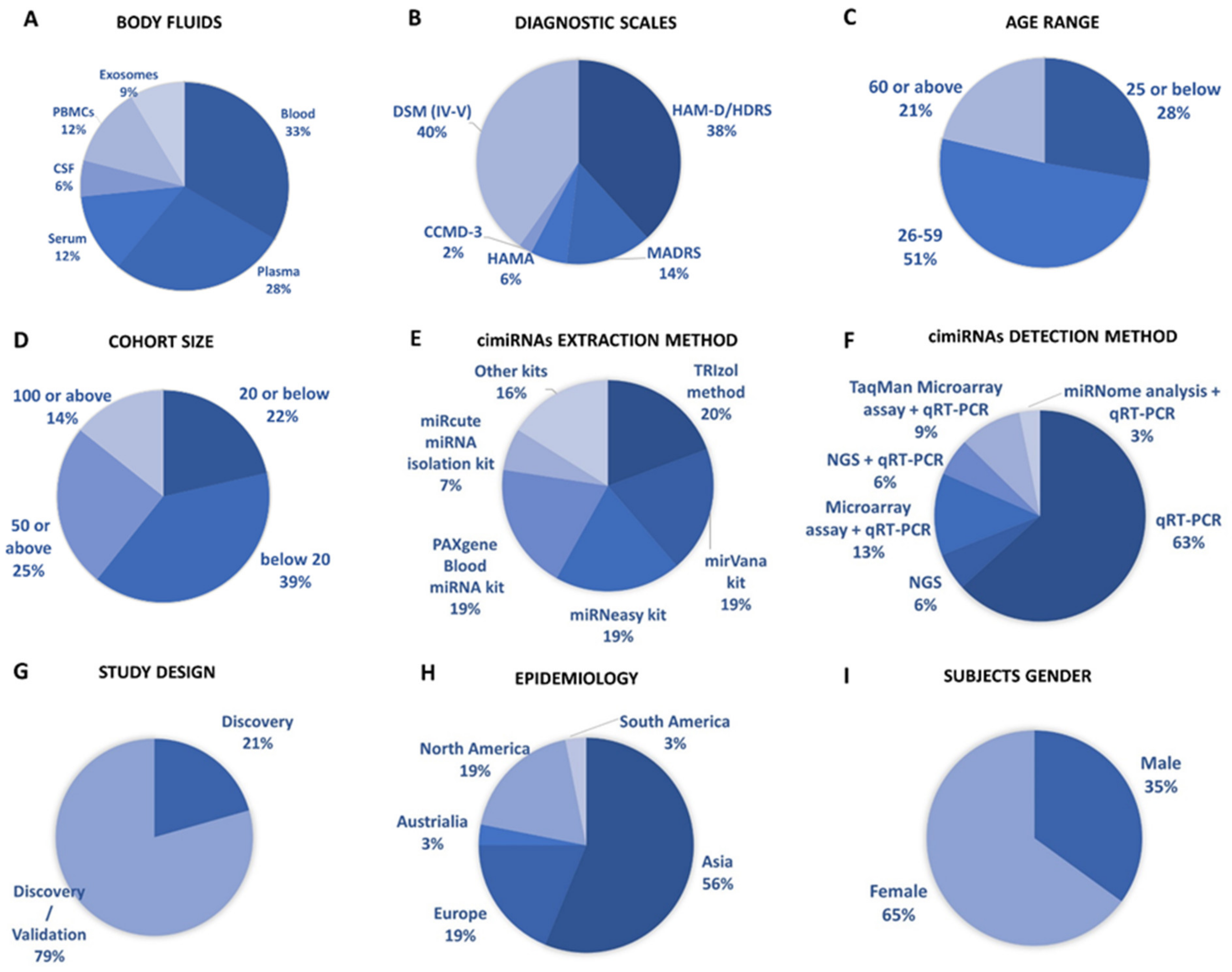
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Prediction of cimiRNA Targets and In-Silico Analysis
2.5. Chromosomal Location of cimiRNAs
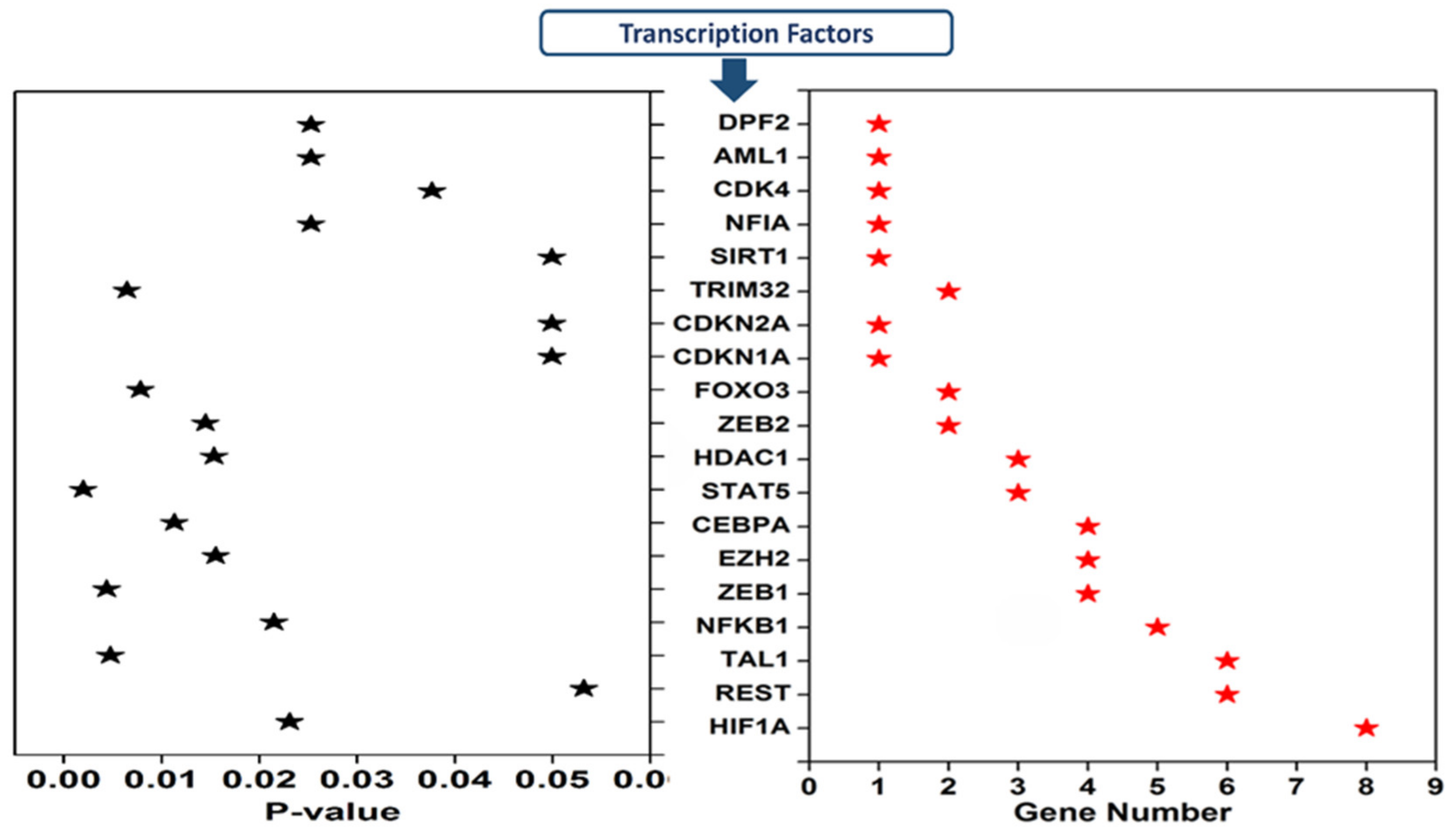
2.6. Transcription Factors Regulating the cimiRNAs
3. Results and Discussion
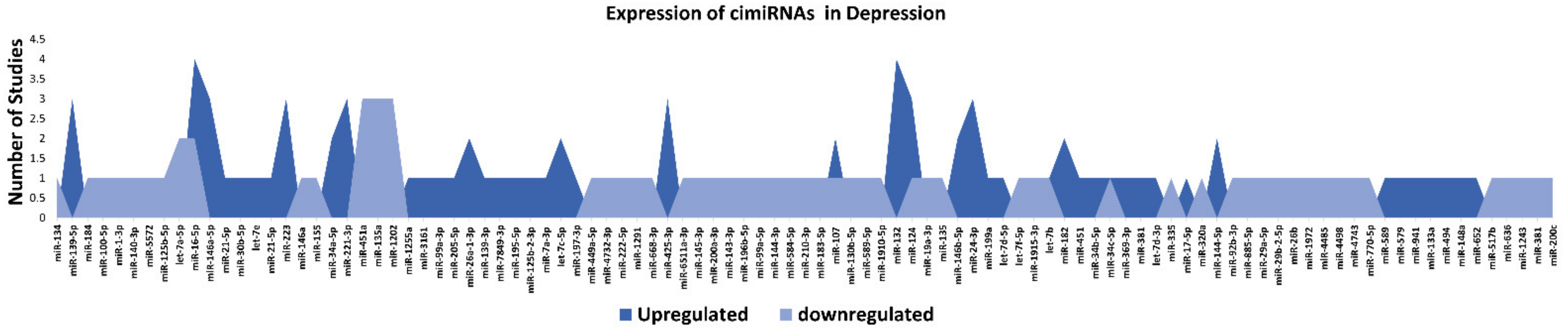
3.1. Profiling of Dysregulated cimiRNAs in MDD
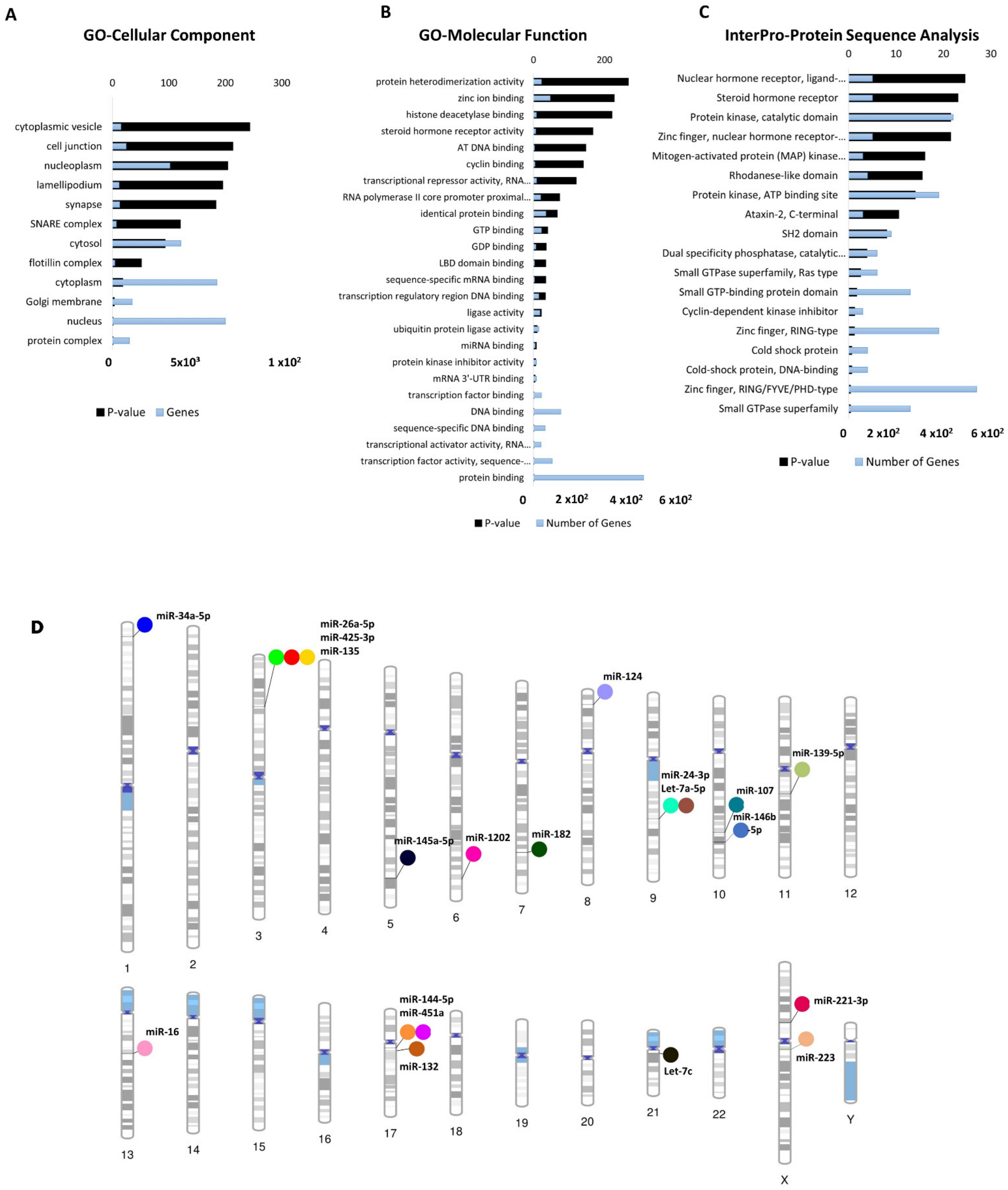
3.2. Profile of Dysregulated cimiRNA Targets in MDD
3.3. Chromosomal Distribution of Dysregulated cimiRNAs in MDD
3.4. Transcription Factors Regulating the Expression of Dysregulated cimiRNAs in MDD
4. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Smith, K. Mental health: A world of depression. Nature 2014, 515, 180–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, A.J.; Patton, G.; Scott, K.M.; Degenhardt, L.; Whiteford, H.A. Global Epidemiology of Mental Disorders: What Are We Missing? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gururajan, A.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Molecular Biomarkers in Depression: Toward Personalized Psychiatric Treatment. In Personalized Psychiatry; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, G.S.; Mann, J.J. Depression. Lancet 2018, 392, 2299–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K. Metabolomics of Major Depressive Disorder and Bipolar Disorder: Overview and Future Perspective. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2018, 84, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiger, T.A.; Samuel, D.B. Diagnostic categories or dimensions? A question for the Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders--fifth edition. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2005, 114, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J.; Vaze, A.; Rao, S. Clinical diagnosis of depression in primary care: A meta-analysis. Lancet 2009, 374, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.-X.; Xia, J.-J.; Deng, F.-L.; Liang, W.-W.; Wu, J.; Yin, B.-M.; Dong, M.-X.; Chen, J.-J.; Ye, F.; Wang, H.-Y.; et al. Diagnosis of major depressive disorder based on changes in multiple plasma neurotransmitters: A targeted metabolomics study. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-J.; Bai, S.-J.; Li, W.-W.; Zhou, C.-J.; Zheng, P.; Fang, L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Xie, P. Urinary biomarker panel for diagnosing patients with depression and anxiety disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wei, X.; Zhuo, Y.; Qin, L.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Song, X. GC-MS-based metabolomics approach to diagnose depression in hepatitis B virus-infected patients with middle or old age. Aging 2018, 10, 2252–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, B.W.; Mayberg, H.S. Neuroimaging Advances for Depression. In Cerebrum: The Dana Forum on Brain Science; Dana Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 2017, pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, R.K.; Asghar, K.; Kanwal, S.; Zulqernain, A. Role of inflammatory cytokines in depression: Focus on interleukin-1β. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 6, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmerich, H.; Patsalos, O.; Lichtblau, N.; Ibrahim, M.; Dalton, B. Cytokine Research in Depression: Principles, Challenges, and Open Questions. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükibrahimoğlu, E.; Saygın, M.Z.; Çalışkan, M.; Kaplan, O.K.; Ünsal, C.; Gören, M.Z. The change in plasma GABA, glutamine and glutamate levels in fluoxetine- or S-citalopram-treated female patients with major depression. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, N.C.; Bischoff, J.R.; Kirn, D.H.; Williams, A.; Heise, C.; Horn, S.; Muna, M.; Ng, L.; Nye, J.A.; Sampson-Johannes, A.; et al. Linking Mind and Brain in the Study of Mental Illnesses: A Project for a Scientific Psychopathology. Science 1997, 275, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazidou, E. The neurobiology of depression. Br. Med. Bull. 2012, 101, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honer, W.G. Assessing the machinery of mind: Synapses in neuropsychiatric disorders. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 1999, 24, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderburg, C.; Beheshti, A. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), the Final Frontier: The Hidden Master Regulators Impacting Biological Response in All Organisms Due to Spaceflight. Available online: https://three.jsc.nasa.gov/articles/miRNA_Beheshti.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- Catalanotto, C.; Cogoni, C.; Zardo, G. MicroRNA in Control of Gene Expression: An Overview of Nuclear Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.-H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2008, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Marin-Muller, C.; Bharadwaj, U.; Chow, K.-H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. MicroRNAs: Control and Loss of Control in Human Physiology and Disease. World J. Surg. 2008, 33, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ingolia, N.T.; Weissman, J.S.; Bartel, D.P. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 2010, 466, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, K.-M.; Mayer, C.; Postepska, A.; Grummt, I. Interaction of noncoding RNA with the rDNA promoter mediates recruitment of DNMT3b and silencing of rRNA genes. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2264–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakama, M.; Kawakami, K.; Kajitani, T.; Urano, T.; Murakami, Y. DNA-RNA hybrid formation mediates RNAi-directed heterochromatin formation. Genes Cells 2012, 17, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.-T.; Hawley, B.R.; Skalka, G.L.; Baldock, R.A.; Smith, E.M.; Bader, A.S.; Malewicz, M.; Watts, F.Z.; Wilczynska, A.; Bushell, M. Drosha drives the formation of DNA:RNA hybrids around DNA break sites to facilitate DNA repair. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, X. Genome-wide DNA methylome analysis reveals epigenetically dysregulated non-coding RNAs in human breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Maruyama, R.; Yamamoto, E.; Kai, M. DNA methylation and microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrba, L.; Munoz-Rodriguez, J.L.; Stampfer, M.R.; Futscher, B.W. miRNA Gene Promoters Are Frequent Targets of Aberrant DNA Methylation in Human Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, W.; Claret, F.X. Mutual regulation of microRNAs and DNA methylation in human cancers. Epigenetics 2017, 12, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohel, M.H. Extracellular/Circulating MicroRNAs: Release Mechanisms, Functions and Challenges. Achiev. Life Sci. 2016, 10, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; e Silva, B.V.R.; Gao, T.; Xu, Z.; Cui, J. Dynamic and Modularized MicroRNA Regulation and Its Implication in Human Cancers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, K.; Malenica, I.; Metpally, R.; Courtright, A.; Rakela, B.; Beach, T.; Shill, H.; Adler, C.; Sabbagh, M.; Villa, S.; et al. Profiles of Extracellular miRNA in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum from Patients with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases Correlate with Disease Status and Features of Pathology. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y. Emerging role of microRNAs in major depressive disorder: Diagnosis and therapeutic implications. Dialog. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 16, 43–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C. Identification of Differential MicroRNAs in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum of Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camkurt, M.A.; Acar, Ş.; Coşkun, S.; Güneş, M.; Güneş, S.; Yılmaz, M.F.; Görür, A.; Tamer, L. Comparison of plasma MicroRNA levels in drug naive, first episode depressed patients and healthy controls. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 69, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marí-Alexandre, J.; Sanchez-Izquierdo, D.; Gilabert-Estellés, J.; Barceló-Molina, M.; Braza-Boïls, A.; Sandoval, J. miRNAs Regulation and Its Role as Biomarkers in Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Huang, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.; Qin, Y.; Duan, Y.; Gong, B.; et al. Salivary MicroRNAs as Promising Biomarkers for Detection of Esophageal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipschitz, D.L.; Kuhn, R.; Kinney, A.Y.; Donaldson, G.W.; Nakamura, Y. Reduction in salivary α-amylase levels following a mind–body intervention in cancer survivors—An exploratory study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Gao, H.C.; Li, Q.; Shao, W.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Cheng, K.; Yang, D.Y.; Fan, S.H.; Chen, L.; Fang, L.; et al. Plasma Metabonomics as a Novel Diagnostic Approach for Major Depressive Disorder. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-B.; Zhang, R.-F.; Luo, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L.; Li, W.-J.; Mu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of plasma from major depressive patients: Identification of proteins associated with lipid metabolism and immunoregulation. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 15, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Schaefer, A.; Steiner, I.; Kempkensteffen, C.; Stephan, C.; Erbersdobler, A.; Jung, K. Robust MicroRNA Stability in Degraded RNA Preparations from Human Tissue and Cell Samples. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Maki, M.; Ding, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xiong, L. Genome-wide survey of tissue-specific microRNA and transcription factor regulatory networks in 12 tissues. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Leidinger, P.; Becker, K.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Pallasch, C.P.; Rheinheimer, S.; Meder, B.; Stähler, C.; Meese, E.; et al. Distribution of miRNA expression across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcells, I.; Cirera, S.; Busk, P.K. Specific and sensitive quantitative RT-PCR of miRNAs with DNA primers. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartova, L.; Berger, A.; Pezawas, L. Is there a personalized medicine for mood disorders? Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 260, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Mischoulon, D.; Fava, M.; Otto, M.W. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for depression: Many candidates, few finalists. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 233, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, M.M.J.; Krauskopf, J.; Ramaekers, J.G.; Kleinjans, J.C.S.; Prickaerts, J.; Briedé, J.J. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 185, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, D.; Dudek, S.; Ritchie, M.D.; Pendergrass, S.A. Visualizing genomic information across chromosomes with PhenoGram. BioData Min. 2013, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Cui, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. TransmiR v2.0: An updated transcription factor-microRNA regulation database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D253–D258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Song, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Han, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, W.; Fan, C. Advances in Roles of miR-132 in the Nervous System. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zheng, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, H. MicroRNA-132 may play a role in coexistence of depression and cardiovascular disease: A hypothesis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2013, 19, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.-T.; Li, J.; Liu, B.-B.; Luo, L.; Liu, Q.; Geng, D. BDNF–ERK–CREB signalling mediates the role of miR-132 in the regulation of the effects of oleanolic acid in male mice. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2014, 39, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Luo, Z.-M.; Guo, X.-M.; Su, D.-F.; Liu, X. An updated role of microRNA-124 in central nervous system disorders: A review. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y. microRNA-124: A putative therapeutic target and biomarker for major depression. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Pan, J.; Chen, L. MiR-124 suppression in the prefrontal cortex reduces depression-like behavior in mice. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Dunbar, M.; Shelton, R.C.; Dwivedi, Y. Identification of MicroRNA-124-3p as a Putative Epigenetic Signature of Major Depressive Disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 42, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururajan, A.; Naughton, M.E.; Scott, K.A.; O’Connor, R.M.; Moloney, G.; Clarke, G.; Dowling, J.; Walsh, A.; Ismail, F.; Shorten, G.; et al. MicroRNAs as biomarkers for major depression: A role for let-7b and let-7c. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhu, H.; Xu, Y.; Ma, C.; Dai, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qin, C. miR-34a, a microRNA up-regulated in a double transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, inhibits bcl2 translation. Brain Res. Bull. 2009, 80, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wu, H.; Pavlosky, A.; Zou, L.-L.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Jevnikar, A.M. Regulatory non-coding RNA: New instruments in the orchestration of cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Le, W. Molecular network of neuronal autophagy in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. Neurosci. Bull. 2015, 31, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.R.; Goldacre, R.; Talbot, K.; Goldacre, M.J. Psychiatric disorders prior to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, G.J.; Vallender, E.J.; Garrett, M.R.; Challagundla, L.; Overholser, J.C.; Jurjus, G.; Dieter, L.; Syed, M.; Romero, D.G.; Benghuzzi, H.; et al. Altered neuro-inflammatory gene expression in hippocampus in major depressive disorder. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 82, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.M.; Grosshans, H.; Shingara, J.; Byrom, M.; Jarvis, R.; Cheng, A.; Labourier, E.; Reinert, K.L.; Brown, D.; Slack, F.J. RAS Is Regulated by the let-7 MicroRNA Family. Cell 2005, 120, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, Y. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Role in depression and suicide. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2009, 5, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Murakami, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Kitagishi, Y. Roles of PI3K/AKT/GSK3 Pathway Involved in Psychiatric Illnesses. Diseases 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karege, F.; Perroud, N.; Burkhardt, S.; Schwald, M.; Ballmann, E.; La Harpe, R.; Malafosse, A. Alteration in Kinase Activity But Not in Protein Levels of Protein Kinase B and Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β in Ventral Prefrontal Cortex of Depressed Suicide Victims. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Hu, Y.; Xin, J.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J. Analyzing the genes and pathways related to major depressive disorder via a systems biology approach. Brain Behav. 2019, 10, e01502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Evinova, A.; Škereňová, M.; Ondrejka, I.; Lehotský, J. Association of EGF, IGFBP-3 and TP53 Gene Polymorphisms with Major Depressive Disorder in Slovak Population. Central Eur. J. Public Health 2016, 24, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J. p53, the Cellular Gatekeeper for Growth and Division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarova, E.A.; Chernov, M.V.; Franks, R.; Wang, K.; Armin, G.; Zelnick, C.R.; Chin, D.M.; Bacus, S.S.; Stark, G.R.; Gudkov, A.V. Transgenic mice with p53-responsive lacZ: p53 activity varies dramatically during normal development and determines radiation and drug sensitivity invivo. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponting, C.P.; Mott, R.; Bork, P.; Copley, R.R. Novel Protein Domains and Repeats in Drosophila melanogaster: Insights into Structure, Function, and Evolution. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1996–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Yoshida, M.; Tsuiki, H.; Ito, K.; Ueno, M.; Nakao, M.; Oka, K.; Tada, M.; Kochi, M.; Kuratsu, J.-I.; et al. Identification of a human homolog of the Drosophila neuralized gene within the 10q25.1 malignant astrocytoma deletion region. Oncogene 1998, 16, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pavlopoulos, E.; Trifilieff, P.; Chevaleyre, V.; Fioriti, L.; Zairis, S.; Pagano, A.; Malleret, G.; Kandel, E.R. Neuralized1 Activates CPEB3: A Function for Nonproteolytic Ubiquitin in Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Storage. Cell 2011, 147, 1369–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Koo, B.-K.; Yoon, K.-J.; Yoon, M.-J.; Yoo, K.-W.; Kim, H.-T.; Oh, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Han, J.-K.; Kim, C.-H.; et al. Neuralized-2 Regulates a Notch Ligand in Cooperation with Mind Bomb-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 36391–36400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasky, J.L.; Wu, H. Notch Signaling, Brain Development, and Human Disease. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Tecott, L.; Jiang, M.-M.; Jan, L.; Jan, Y.N. Ethanol hypersensitivity and olfactory discrimination defect in mice lacking a homolog of Drosophila neuralized. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9907–9912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Xia, Y.; Zong, X.; Sweeney, J.A.; Bishop, J.R.; Liao, Y.; Giase, G.; Li, B.; Rubin, L.H.; Wang, Y. Risperidone-induced changes in DNA methylation from peripheral blood in first-episode schizophrenia parallel neuroimaging and cognitive phenotype. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-P.; Aitchison, K.J.; Malhotra, A.K. The 12th annual pharmacogenetics in psychiatry meeting report. Psychiatr. Genet. 2014, 24, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Holland, S.; Coste, O.; Zhang, D.D.; Pierre, S.C.; Geisslinger, G.; Scholich, K. The Ubiquitin Ligase MYCBP2 Regulates Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Receptor 1 (TRPV1) Internalization through Inhibition of p38 MAPK Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 3671–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Scholich, K.; Poser, S.; Storm, D.R.; Patel, T.B.; Goldowitz, D. Developmental expression of PAM (protein associated with MYC) in the rodent brain. Dev. Brain Res. 2002, 136, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehnert, C.; Tegeder, I.; Pierre, S.; Birod, K.; Nguyen, H.-V.; Schmidtko, A.; Geisslinger, G.; Scholich, K. Protein associated with Myc (PAM) is involved in spinal nociceptive processing. J. Neurochem. 2004, 88, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seno, M.D.J.; de Assis, D.V.; Gouveia, F.V.; Antunes, G.F.; Kuroki, M.; Oliveira, C.C.; Santos, L.C.T.; Pagano, R.L.; Martinez, R.C.R. The critical role of amygdala subnuclei in nociceptive and depressive-like behaviors in peripheral neuropathy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, T.L. The Role of CREB Family Transcription Factors in Depression, Anxiety, and Antidepressant Response. Available online: https://repository.upenn.edu/dissertations/AAI3310377/ (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- Shindo, S.; Yoshioka, N. Polymorphisms of the cholecystokinin gene promoter region in suicide victims in Japan. Forensic Sci. Int. 2005, 150, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangard, L.; Solgy, R.; Salehi, I.; Taheri, S.K.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Haghighi, M.; Brand, S. Cholecystokinin (CCK) level is higher among first time suicide attempters than healthy controls, but is not associated with higher depression scores. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 266, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, S.; Antonelli, F.; Casciati, A. Sonic hedgehog signaling controls dentate gyrus patterning and adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, H.; Wojnowski, L.; Zimmer, A.M.; Hall, J.; Miller, G.; Zimmer, A. Rhabdomyosarcomas and radiation hypersensitivity in a mouse model of Gorlin syndrome. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, F.; Casciati, A.; Tanori, M.; Tanno, B.; Linares, V.; Serra, N.; Belles, M.; Pannicelli, A.; Saran, A.; Pazzaglia, S. Alterations in Morphology and Adult Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus of Patched1 Heterozygous Mice. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, B.; Kohl, Z.; Gage, F.H. Neurodegenerative disease and adult neurogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Bauman, A.L.; Moore, K.R.; Han, H.; Yang-Feng, T.; Chang, A.S.; Ganapathy, V.; Blakely, R.D. Antidepressant-and cocaine-sensitive human serotonin transporter: Molec-ular cloning, expression, and chromosomal localisation (paroxetine/biogenic amine uptake/placenta). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 2542–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heils, A.; Teufel, A.; Petri, S.; Stöber, G.; Riederer, P.; Bengel, D.; Lesch, K.P. Allelic Variation of Human Serotonin Transporter Gene Expression. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 2621–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, K.-P.; Bengel, D.; Heils, A.; Sabol, S.Z.; Greenberg, B.D.; Petri, S.; Benjamin, J.; Müller, C.R.; Hamer, D.H.; Murphy, D.L. Association of Anxiety-Related Traits with a Polymorphism in the Serotonin Transporter Gene Regulatory Region. Science 1996, 274, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heils, A.; Teufel, A.; Petri, S.; Seemann, M.; Bengel, D.; Balling, U.; Riederer, P.; Lesch, K.-P. Functional promoter and polyadenylation site mapping of the human serotonin (5-HT) transporter gene. J. Neural Transm. 1995, 102, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadrina, M.; Bondarenko, E.A.; Slominsky, P.A. Genetics Factors in Major Depression Disease. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Ueno, S.; Sano, A.; Tanabe, H. The human serotonin transporter gene linked polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) shows ten novel allelic variants. Mol. Psychiatry 2000, 5, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Huo, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Luo, X.-J. Regulatory mechanisms of major depressive disorder risk variants. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1926–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Gong, W.; Zhang, J.; Shao, W.; Mu, J.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; et al. Differential co-expression and regulation analyses reveal different mechanisms underlying major depressive disorder and subsyndromal symptomatic depression. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, T.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, M.; Zhu, L. FG-4592 Improves Depressive-Like Behaviors through HIF-1-Mediated Neurogenesis and Synapse Plasticity in Rats. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 17, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malki, K.; Pain, O.; Tosto, M.G.; Du Rietz, E.; Carboni, L.; Schalkwyk, L. Identification of genes and gene pathways associated with major depressive disorder by integrative brain analysis of rat and human prefrontal cortex transcriptomes. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Kastner, R.; van Os, J.; Esquivel, G.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; Rutten, B. An environmental analysis of genes associated with schizophrenia: Hypoxia and vascular factors as interacting elements in the neurodevelopmental model. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, K.; Uchida, S.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Matsubara, T.; Hobara, T.; Funato, H.; Watanabe, Y. Aberrant REST-mediated transcriptional regulation in major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2010, 44, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasheed, M.; Asghar, R.; Firdoos, S.; Ahmad, N.; Nazir, A.; Ullah, K.M.; Li, N.; Zhuang, F.; Chen, Z.; Deng, Y. A Systematic Review of Circulatory microRNAs in Major Depressive Disorder: Potential Biomarkers for Disease Prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031294
Rasheed M, Asghar R, Firdoos S, Ahmad N, Nazir A, Ullah KM, Li N, Zhuang F, Chen Z, Deng Y. A Systematic Review of Circulatory microRNAs in Major Depressive Disorder: Potential Biomarkers for Disease Prognosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031294
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasheed, Madiha, Rabia Asghar, Sundas Firdoos, Nadeem Ahmad, Amina Nazir, Kakar Mohib Ullah, Noumin Li, Fengyuan Zhuang, Zixuan Chen, and Yulin Deng. 2022. "A Systematic Review of Circulatory microRNAs in Major Depressive Disorder: Potential Biomarkers for Disease Prognosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031294
APA StyleRasheed, M., Asghar, R., Firdoos, S., Ahmad, N., Nazir, A., Ullah, K. M., Li, N., Zhuang, F., Chen, Z., & Deng, Y. (2022). A Systematic Review of Circulatory microRNAs in Major Depressive Disorder: Potential Biomarkers for Disease Prognosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031294





