Analysis of Proteins and Peptides of Highly Purified CD9+ and CD63+ Horse Milk Exosomes Isolated by Affinity Chromatography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
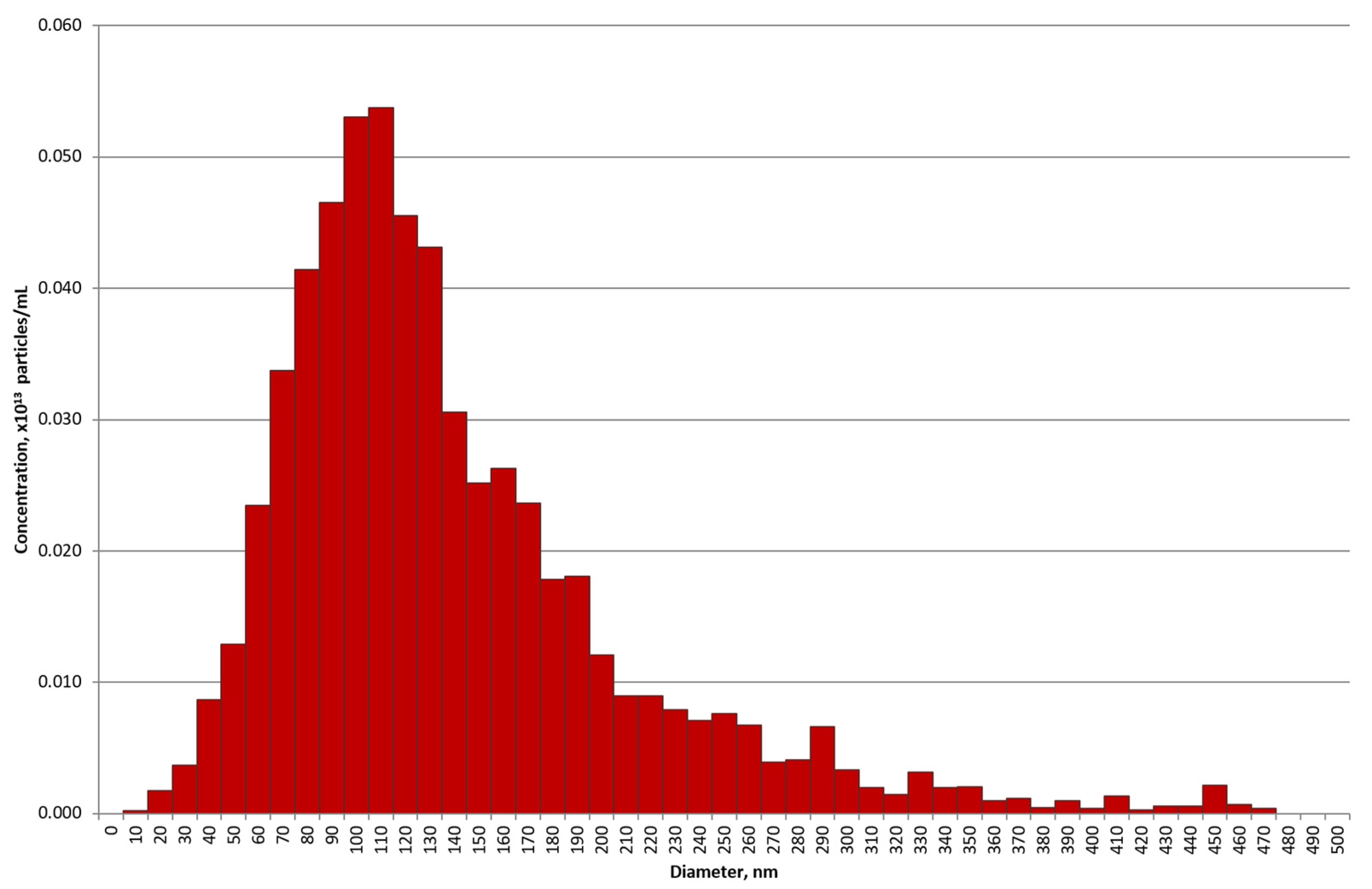
2.1. Purification of Exosomes
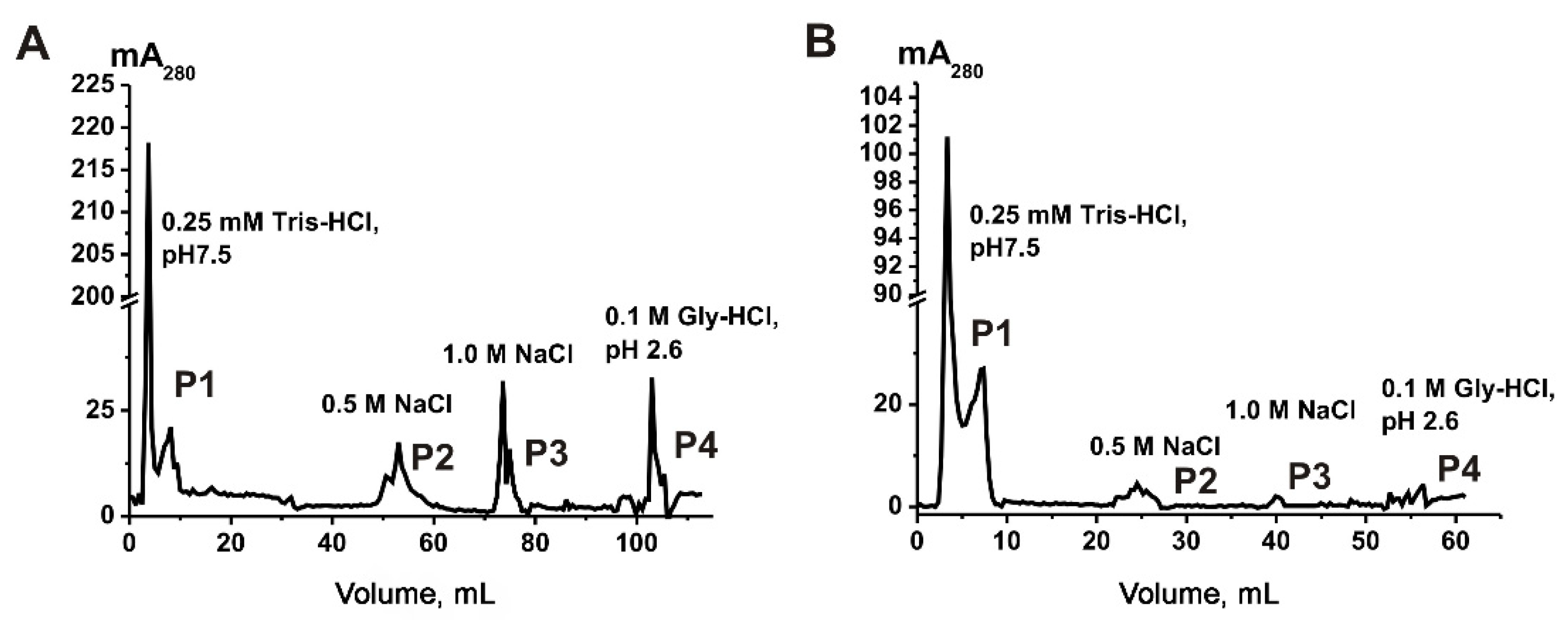
2.2. Affinity Chromatography on Anti-CD9/CD63-Sepharose
2.3. Electron Microscopy Analysis
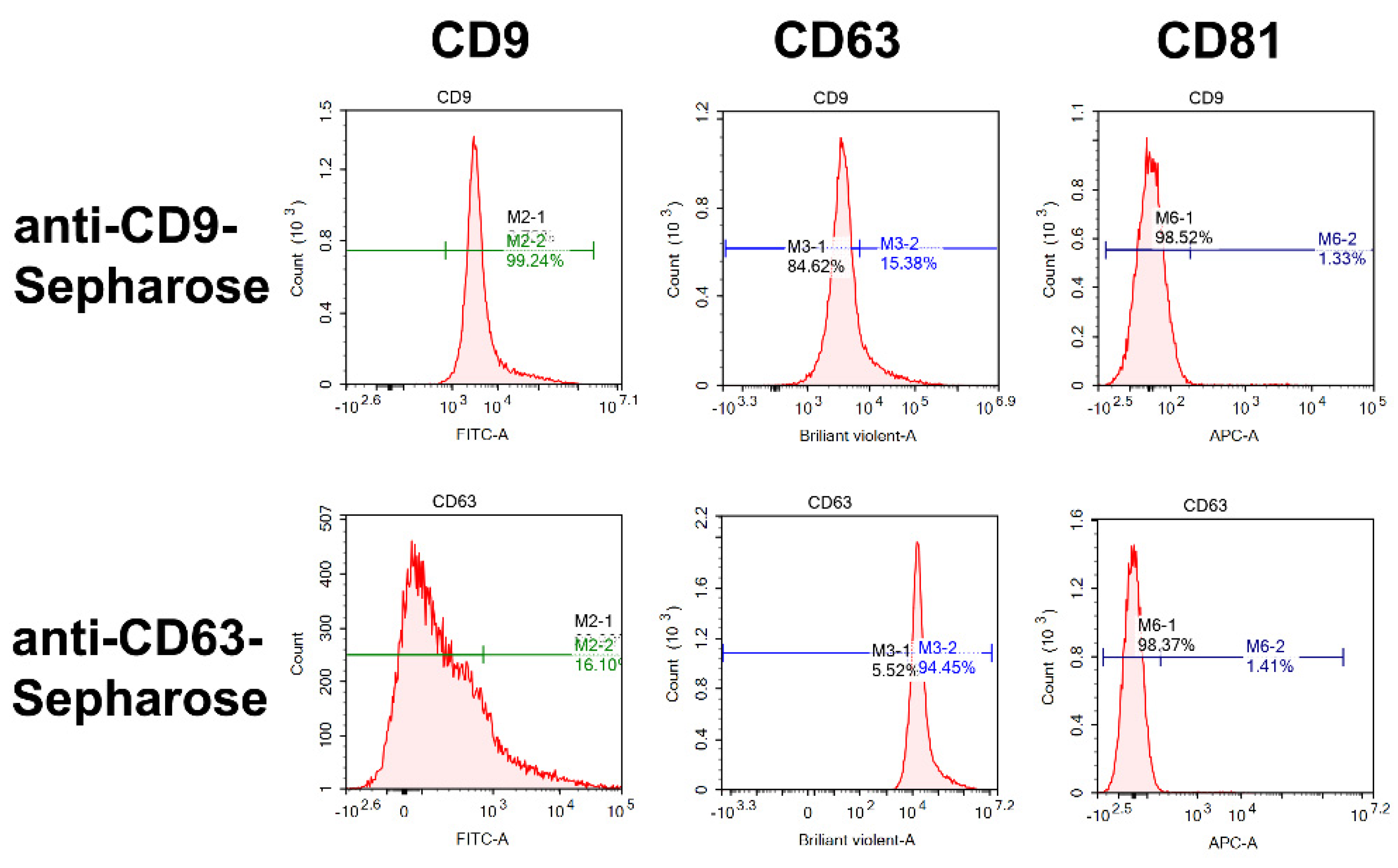
2.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Peptides and Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Isolation of Exosomes from Horse Milk
4.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Nano Tracking Analysis
4.4. Affinity Chromatography on Anti-CD9- and Anti-CD63-Sepharose
4.5. Analysis of Proteins and Peptides
4.6. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Proteins and Peptides
4.7. Flow Cytometry Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsieh, C.-C.; Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Fernández-Tomé, S.; Weinborn, V.; Barile, D.; de Moura Bell, J.M.L.N. Milk Proteins, Peptides, and Oligosaccharides: Effects against the 21st Century Disorders. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 146840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, D.P.; Mohapatra, S.; Misra, S.; Sahu, P.S. Milk derived bioactive peptides and their impact on human health—A review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedykh, S.E.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Human Milk Lactoferrin and Antibodies: Catalytic Activities, Complexes, and Other Features. In Milk Proteins—From Structure to Biological Properties and Health Aspects; InTech: London, UK, 2016; pp. 51–80. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Milk Lipids. In Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 69–144. [Google Scholar]
- Thorell, L.; Sjöberg, L.-B.; Hernell, O. Nucleotides in Human Milk: Sources and Metabolism by the Newborn Infant. Pediatr. Res. 1996, 40, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipkin, E.; Shalom, A.; Khatib, H.; Soller, M.; Friedmann, A. Milk as a Source of Deoxyribonucleic Acid and as a Substrate for the Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Dairy Sci. 1993, 76, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.A.; Lawrence, R.M. Breastfeeding, 7th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 9781437707885. [Google Scholar]
- Melnik, B.C.; John, S.M.; Schmitz, G. Milk is not just food but most likely a genetic transfection system activating mTORC1 signaling for postnatal growth. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, T.A.; Lippolis, J.D.; Nonnecke, B.J.; Sacco, R.E. Bovine milk exosome proteome. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, K.B.; Gudbergsson, J.M.; Skov, M.N.; Pilgaard, L.; Moos, T.; Duroux, M. A comprehensive overview of exosomes as drug delivery vehicles—Endogenous nanocarriers for targeted cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2014, 1846, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, J.R. Q&A: What are exosomes, exactly? BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkova, E.E.; Sedykh, S.E.; Nevinsky, G.A. Human Placenta Exosomes: Biogenesis, Isolation, Composition, and Prospects for Use in Diagnostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Mahajan, V.; Deygen, I.; Klyachko, N.L.; Inskoe, E.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Okolie, O.; et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshkov, A.; Purvinsh, L.; Brodskaia, A.; Vasin, A. Exosomes as Natural Nanocarriers for RNA-Based Therapy and Prophylaxis. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wu, S.Y. The Advances and Challenges in Utilizing Exosomes for Delivering Cancer Therapeutics. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuma, R.J.; Manca, S.; Frieme, T.; Sukreet, S.; Nguyen, C.; Zempleni, J. Human vascular endothelial cells transport foreign exosomes from cow’s milk by endocytosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2016, 310, C800–C807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Du, X.; Li, J.; Lönnerdal, B. Human milk exosomes and their microRNAs survive digestion in vitro and are taken up by human intestinal cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; Fan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qi, C.; Huang, N.; Xiao, Z.; Lu, Z.; Tannous, B.A.; et al. Biomaterials Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 150, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Su, C. Design strategies and application progress of therapeutic exosomes. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunggulawa, E.J.; Wang, W.; Yin, T.; Wang, N.; Durkan, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. Recent advancements in the use of exosomes as drug delivery systems. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimisiaris, S.G.; Mourtas, S.; Marazioti, A. Exosomes and Exosome-Inspired Vesicles for Targeted Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admyre, C.; Johansson, S.M.; Qazi, K.R.; Filen, J.-J.; Lahesmaa, R.; Norman, M.; Neve, E.P.A.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S.; Filén, J.-J.J.-J.; et al. Exosomes with Immune Modulatory Features Are Present in Human Breast Milk. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Inoshima, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Ishiguro, N. Comparison of Methods for Isolating Exosomes from Bovine Milk. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 1523–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munagala, R.; Aqil, F.; Jeyabalan, J.; Gupta, R.C. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soboleva, S.E.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Verkhovod, T.D.; Buneva, V.N.; Sedykh, S.E.; Nevinsky, G.A. Very stable high molecular mass multiprotein complex with DNase and amylase activities in human milk. J. Mol. Recognit. 2015, 28, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkova, E.E.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Sedykh, S.E.; Buneva, V.N.; Soboleva, S.E.; Nevinsky, G.A. Extremely Stable Soluble High Molecular Mass Multi-Protein Complex with DNase Activity in Human Placental Tissue. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sedykh, S.E.; Burkova, E.E.; Purvinsh, L.V.; Klemeshova, D.A.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Nevinsky, G.A. Milk Exosomes: Isolation, Biochemistry, Morphology, and Perspectives of Use. In Extracellular Vesicles and Their Importance in Human Health; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sedykh, S.E.; Purvinish, L.V.; Burkova, E.E.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Vlassov, V.V.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Nevinsky, G.A. Analysis of peptides and small proteins in preparations of horse milk exosomes, purified on anti-CD81-Sepharose. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 117, 104994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedykh, S.; Kuleshova, A.; Nevinsky, G. Milk Exosomes: Perspective Agents for Anticancer Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigor’eva, A.E.; Dyrkheeva, N.S.; Bryzgunova, O.E.; Tamkovich, S.N.; Chelobanov, B.P.; Ryabchikova, E.I. Contamination of exosome preparations, isolated from biological fluids. Biochem. (Mosc.) Suppl. Ser. B Biomed. Chem. 2017, 11, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Herwijnen, M.J.C.; Zonneveld, M.I.; Goerdayal, S.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.M.; Garssen, J.; Stahl, B.; Maarten Altelaar, A.F.; Redegeld, F.A.; Wauben, M.H.M. Comprehensive Proteomic Analysis of Human Milk-derived Extracellular Vesicles Unveils a Novel Functional Proteome Distinct from Other Milk Components. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2016, 15, 3412–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, C.; Long, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Jin, L.; Tang, Q.; Jiang, A.; Wang, X.; Tian, S.; et al. Exosomal microRNAs in giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) breast milk: Potential maternal regulators for the development of newborn cubs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, H.; Tsuda, M.; Sato, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Namba, K.; Takeda, Y. Bovine milk exosomes contain microRNA and mRNA and are taken up by human macrophages. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2920–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedykh, S.E.; Purvinish, L.V.; Monogarov, A.S.; Burkova, E.E.; Grigor’eva, A.E.; Bulgakov, D.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Vlassov, V.V.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Nevinsky, G.A. Purified horse milk exosomes contain an unpredictable small number of major proteins. Biochim. Open 2017, 4, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkova, E.E.; Grigor’eva, A.E.; Bulgakov, D.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Vlassov, V.V.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Sedykh, S.E.; Nevinsky, G.A. Extra Purified Exosomes from Human Placenta Contain an Unpredictable Small Number of Different Major Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkova, E.E.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Bulgakov, D.V.; Vlassov, V.V.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Nevinsky, G.A. Exosomes from human placenta purified by affinity chromatography on sepharose bearing immobilized antibodies against CD81 tetraspanin contain many peptides and small proteins. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverdlov, E.D. Amedeo Avogadro’s cry: What is 1 µg of exosomes? BioEssays 2012, 34, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedykh, S.E.; Kuleshova, A.E.; Purvinsh, L.V.; Burkova, E.E.; Grigorieva, A.E.; Evtushenko, E.G.; Stepanov, G.A.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Nevinskii, G.A. Horse Milk Exosomes: Isolation, Microscopic and Biochemical Analysis, and Prospects of Use. Biotekhnologiya 2020, 36, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firer, M. Efficient elution of functional proteins in affinity chromatography. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2001, 49, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, M. Proteomics for routine identification of microorganisms. Proteomics 2011, 11, 3143–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, G.A.; Wiker, H.G. A proteomic view of mycobacteria. Proteomics 2011, 11, 3118–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.; Stepaniak, L.; De Angelis, M.; Corsetti, A.; Di Cagno, R. Latent Bioactive Peptides in Milk Proteins: Proteolytic Activation and Significance in Dairy Processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2002, 42, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.T.; Ross, R.P.; Bolton, D.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Bioactive peptides from muscle sources: Meat and fish. Nutrients 2011, 3, 765–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Sharma, H.; Deshwal, G.K.; Rao, P.S. A comprehensive review on bioactive peptides derived from milk and milk products of minor dairy species. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2021, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


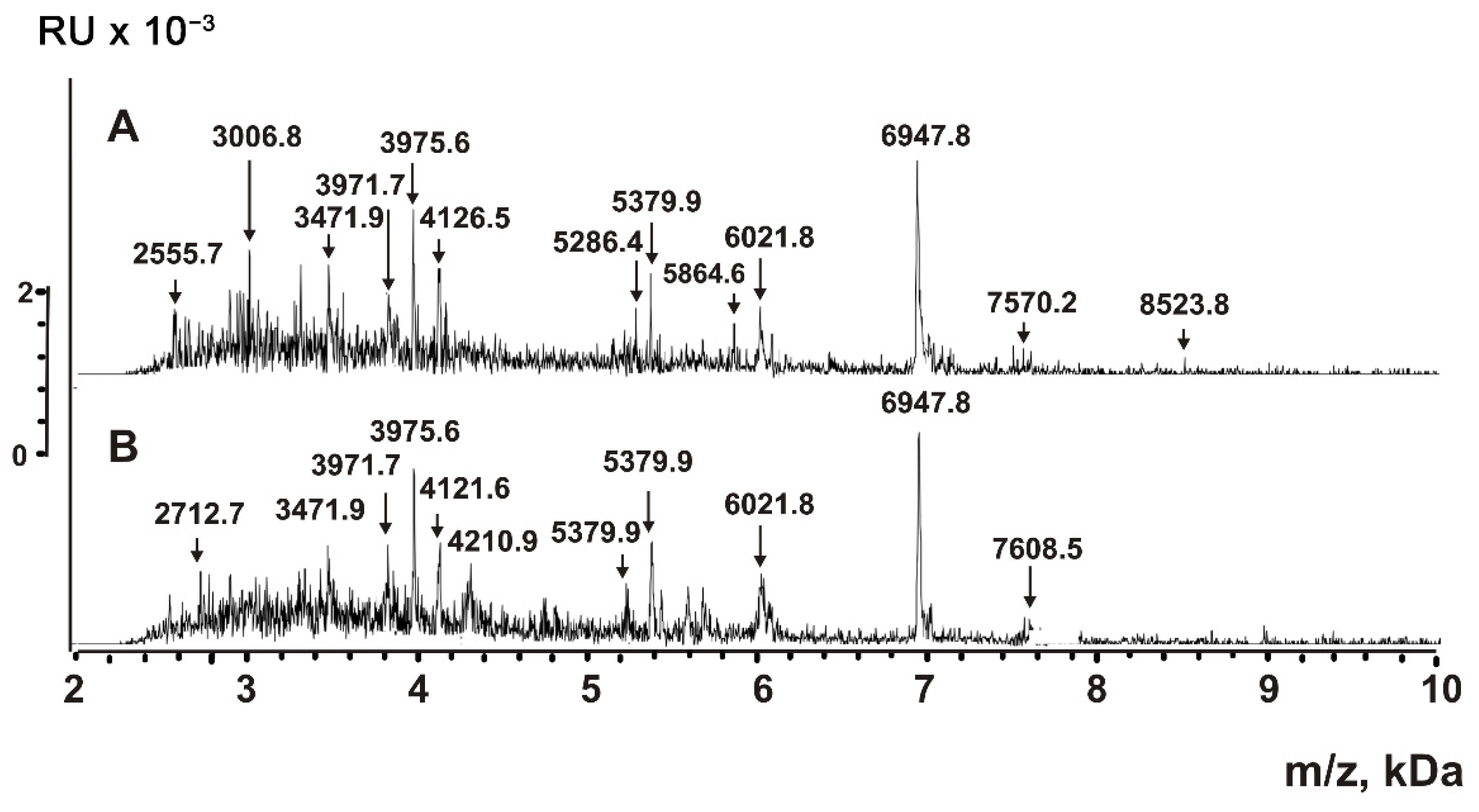
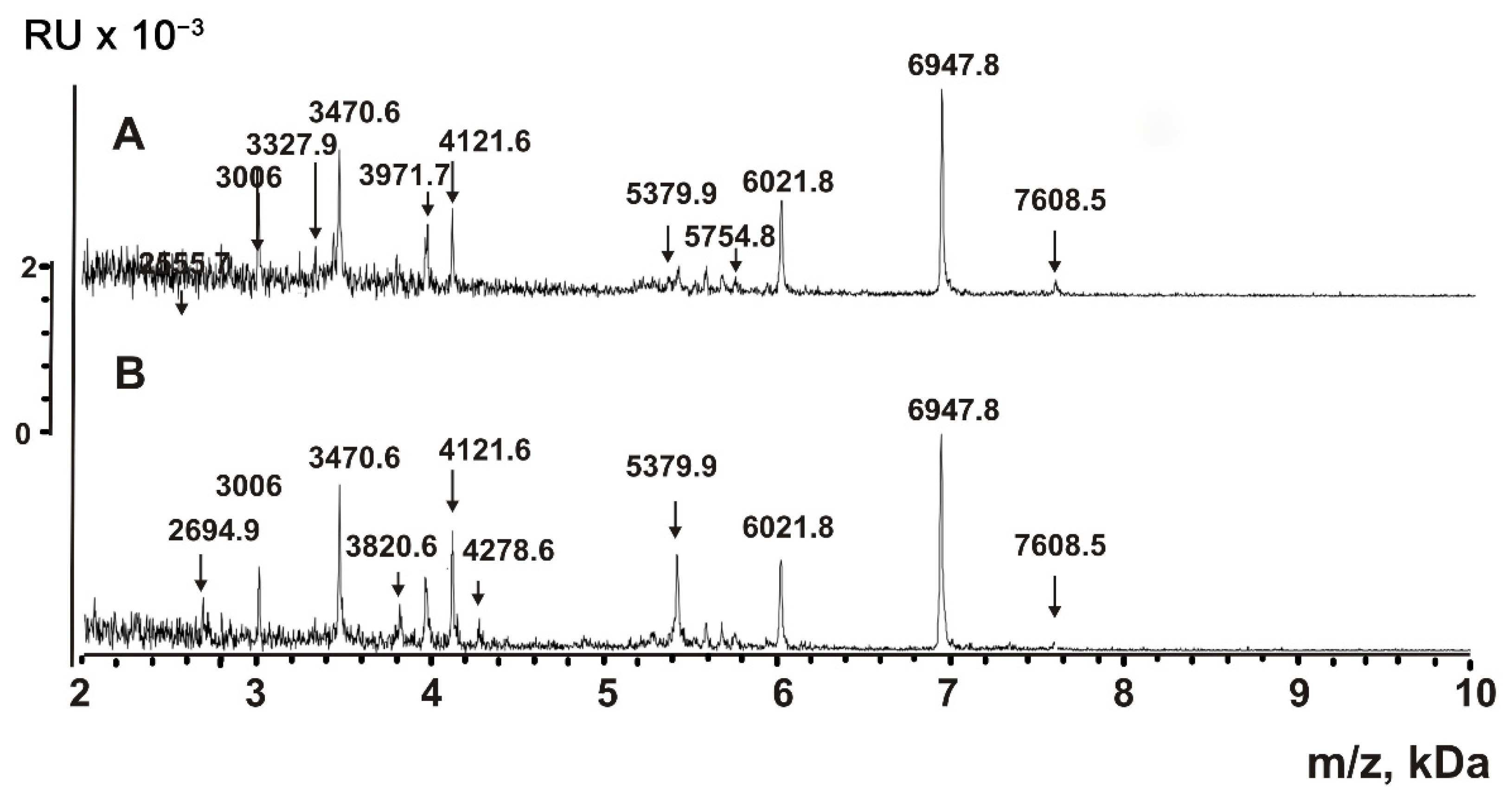
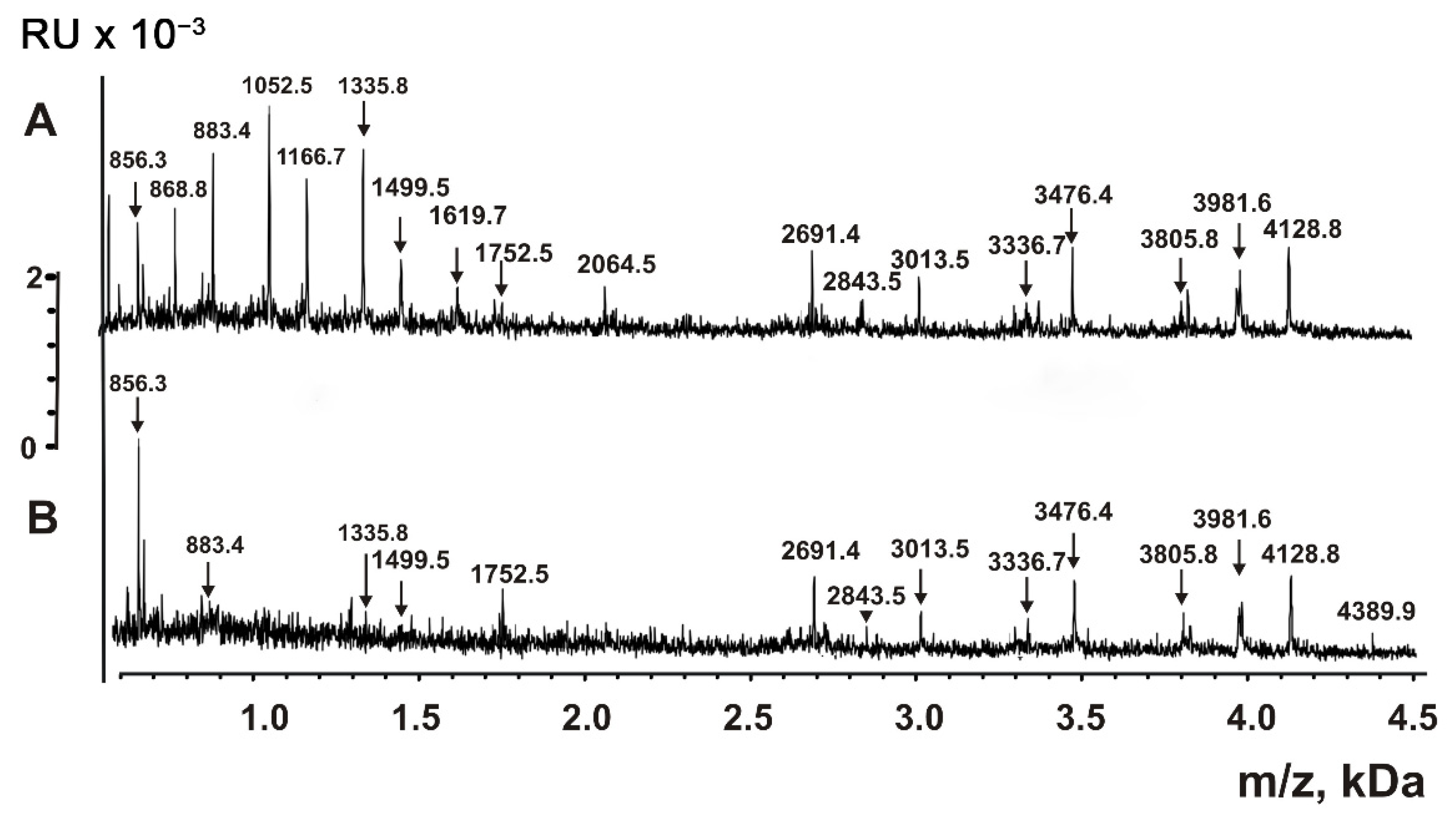
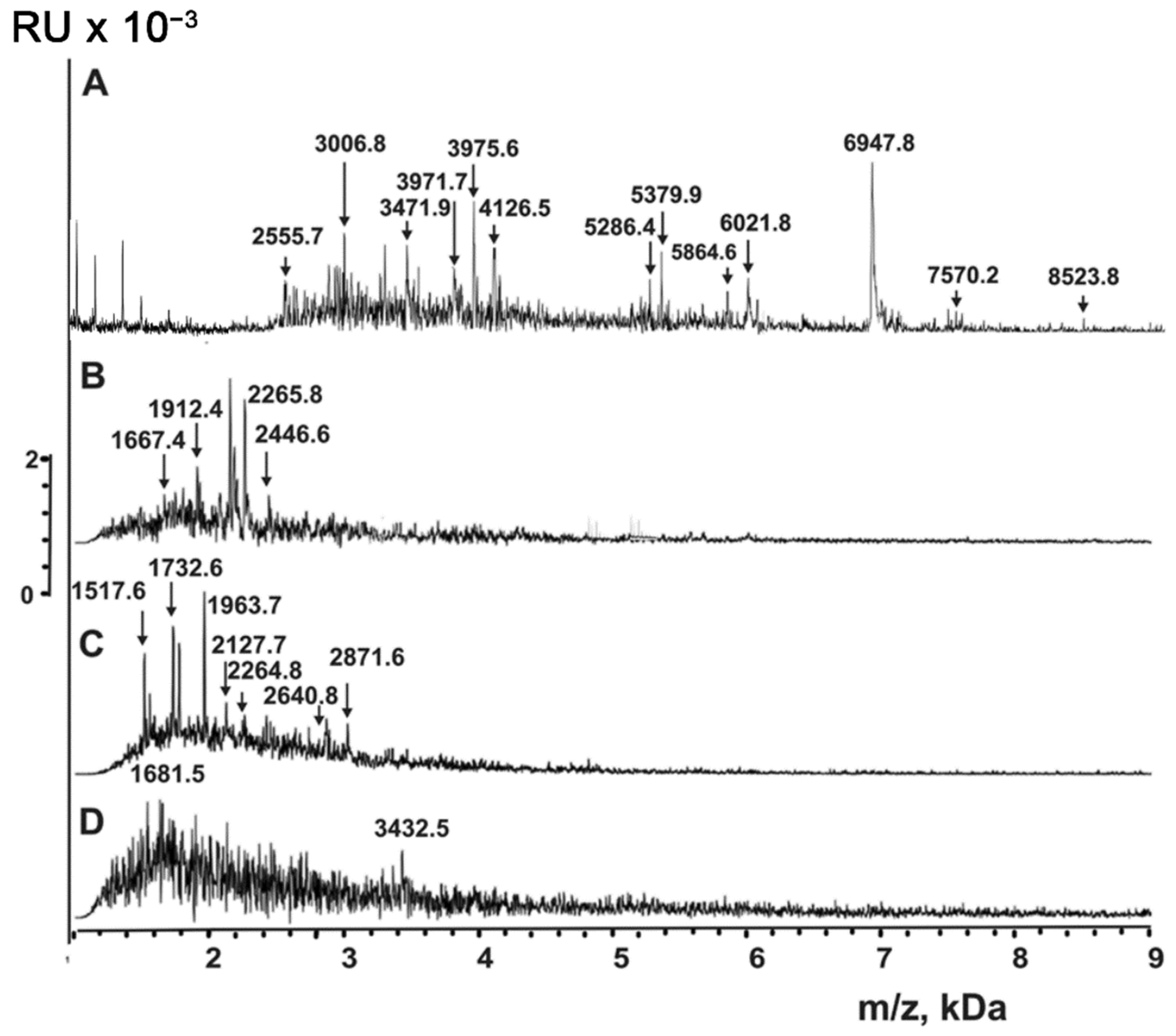
| Peptide | Molecular mass, Da * | Peptide | Molecular mass, Da |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 856.3 **,*** | 17 | 3471.7 |
| 2 | 868.8 *** | 18 | 3476.4 |
| 3 | 883.4 *** | 19 | 3805.8 |
| 4 | 1052.5 | 20 | 3971.7 |
| 5 | 1166.7 *** | 21 | 3981.6 *** |
| 6 | 1335.8 *** | 22 | 4121.6 *** |
| 7 | 1499.5 *** | 23 | 4128.8 *** |
| 8 | 1619.7 *** | 24 | 4210.9 *** |
| 9 | 1752.5 *** | 25 | 5286.4 |
| 10 | 2064.5 | 26 | 5379.9 *** |
| 11 | 2691.4 *** | 27 | 6021.8 *** |
| 12 | 2843.0 | 28 | 6947.8 *** |
| 13 | 3006.0 *** | 29 | 7608.5 *** |
| 14 | 3013.5 *** | 30 | 8848.5 *** |
| 15 | 3327.9 *** | 31 | 8523.8 |
| 16 | 3336.7 *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sedykh, S.E.; Purvinsh, L.V.; Burkova, E.E.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Nevinsky, G.A. Analysis of Proteins and Peptides of Highly Purified CD9+ and CD63+ Horse Milk Exosomes Isolated by Affinity Chromatography. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16106. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416106
Sedykh SE, Purvinsh LV, Burkova EE, Dmitrenok PS, Ryabchikova EI, Nevinsky GA. Analysis of Proteins and Peptides of Highly Purified CD9+ and CD63+ Horse Milk Exosomes Isolated by Affinity Chromatography. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):16106. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416106
Chicago/Turabian StyleSedykh, Sergey E., Lada V. Purvinsh, Evgeniya E. Burkova, Pavel S. Dmitrenok, Elena I. Ryabchikova, and Georgy A. Nevinsky. 2022. "Analysis of Proteins and Peptides of Highly Purified CD9+ and CD63+ Horse Milk Exosomes Isolated by Affinity Chromatography" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 16106. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416106
APA StyleSedykh, S. E., Purvinsh, L. V., Burkova, E. E., Dmitrenok, P. S., Ryabchikova, E. I., & Nevinsky, G. A. (2022). Analysis of Proteins and Peptides of Highly Purified CD9+ and CD63+ Horse Milk Exosomes Isolated by Affinity Chromatography. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 16106. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416106









