Influence of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Vitamin D Receptor Expression in Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts as a Response to Orthodontic Compression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
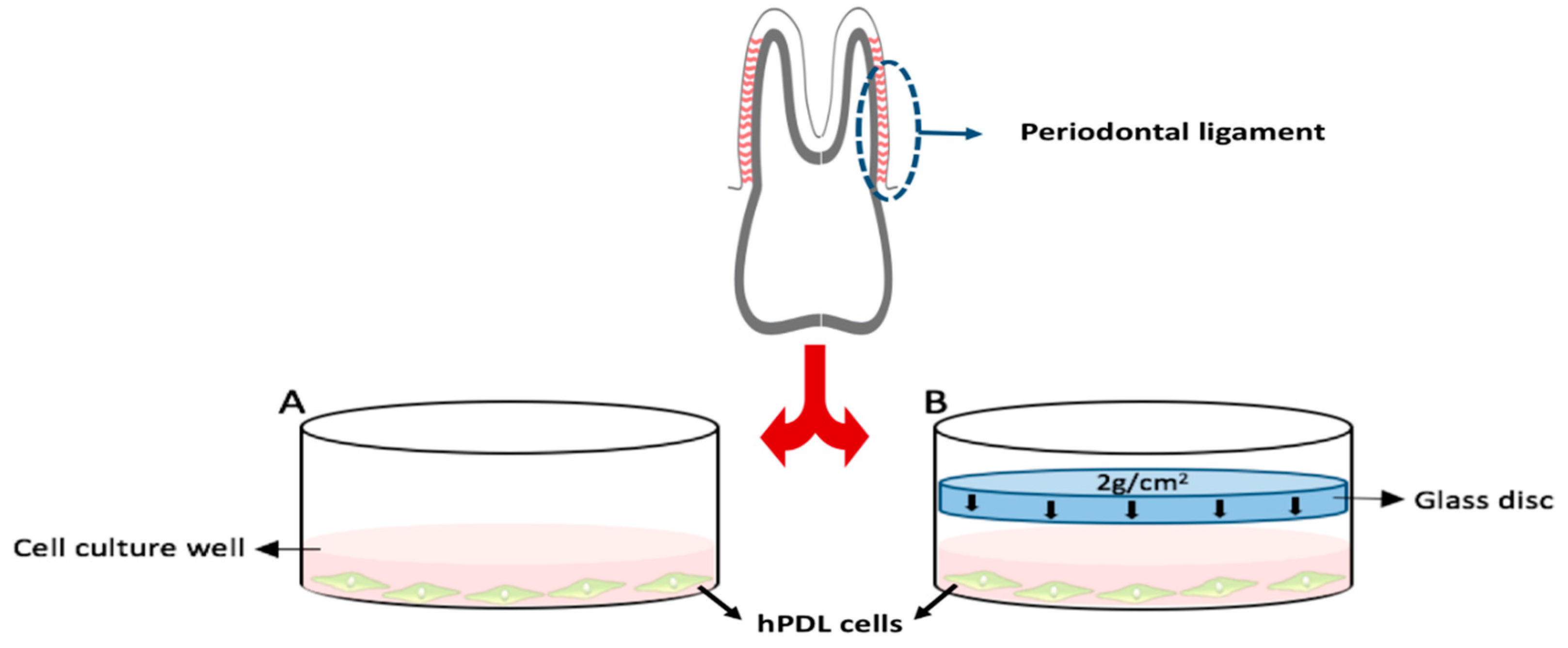
4.2. Sample Collection and In Vitro Compression Model for Orthodontic Tooth Movement
4.3. Total RNA Isolation and Quantification of Relative Gene Expression (RT-qPCR)
4.4. DNA Extraction and Genotyping Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jönsson, D.; Nebel, D.; Bratthall, G.; Nilsson, B.O. The human periodontal ligament cell: A fibroblast-like cell acting as an immune cell. J. Periodontal. Res. 2011, 46, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meikle, M.C. The tissue, cellular, and molecular regulation of orthodontic tooth movement: 100 years after Carl Sandstedt. Eur. J. Orthod. 2006, 28, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jacox, L.A.; Little, S.H.; Co, C.C. Orthodontic tooth movement: The biology and clinical implications. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfondrini, M.F.; Butera, A.; Michele, P.; Luccisano, C.; Ottini, B.; Sangalli, E.; Gallo, S.; Pascadopoli, M.; Gandini, P.; Scribante, A. Microbiological Changes during Orthodontic Aligner Therapy: A Prospective Clinical Trial. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoammar, K. Vitamin D and orthodontics: An insight review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2018, 10, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.K.; Sinclair, P.M. The local use of vitamin D to increase the rate of orthodontic tooth movement. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1988, 94, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, S.; Kocadereli, I.; Atilla, P.; Asan, E. Comparison of the effects of 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol and prostaglandin E2 on orthodontic tooth movement. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2004, 125, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, M.; Takano-Yamamoto, T. Local injection of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhanced bone formation for tooth stabilization after experimental tooth movement in rats. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2004, 22, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Velden, U.; Kuzmanova, D.; Chapple, I.L.C. Micronutritional approaches to periodontal therapy. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Taketani, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Morita, K.; Tonai, T.; Nishisho, T.; Mori, S.; Takeda, E. A vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism in the translation initiation codon: Effect on protein activity and relation to bone mineral density in Japanese women. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1997, 12, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitterlinden, A.G.; Fang, Y.; Van Meurs, J.B.; Pols, H.A.P.; Van Leeuwen, J.P.T.M. Genetics and biology of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms. Gene 2004, 338, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, F.S.; Martelli, M.; Rosati, C.; Fanti, E. Vitamin D: Relevance in dental practice. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2014, 11, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito Júnior, R.B.; Scarel-Caminaga, R.M.; Trevilatto, P.C.; Souza, A.P.; Barros, S.P. Polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor gene are associated with periodontal disease. J. Periodontol. 2004, 75, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Miyake, Y.; Hanioka, T.; Arakawa, M. VDR gene polymorphisms, interaction with smoking and risk of periodontal disease in Japanese women: The Kyushu Okinawa maternal and child health study. Scand. J. Immunol. 2013, 78, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, L.; Xie, C.; Fan, W.; Sun, S.; Xie, B.; Zhang, J. Association between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and severe chronic periodontitis in a Chinese population. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.L.; de Souza, C.M.; Bernardino, J.F.; Hoette, F.; Hoette, M.L.; Thum, L.; Ozawa, T.O.; Capelozza Filho, L.; Olandoski, M.; Trevilatto, P.C. Association analysis of clinical aspects and vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism with external apical root resorption in orthodontic patients. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2012, 142, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatturi, A.L.; Menoncin, B.L.; Reyes, M.T.; Meger, M.; Scariot, R.; Brancher, J.A.; Kuchler, E.C.; Feltrin-Souza, J. The relationship between molar incisor hypomineralization, dental caries, socioeconomic factors, and polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor gene: A population-based study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 3971–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.C.F.; Lima, D.C.; Reis, C.L.B.; Reis, A.L.M.; Rigo, D.; Segato, R.A.B.; Storrer, C.L.M.; Küchler, E.C.; Oliveira, D.S.B. Vitamin D receptor FokI and BglI genetic polymorphisms, dental caries, and gingivitis. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2020, 30, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, T.A.; Madalena, I.R.; Silva, R.A.B.; Silva, L.A.B.; Silva, M.J.B.; De Rossi, A.; Küchler, E.C.; Fukada, S.Y. Vitamin D deficiency is a risk factor for delayed tooth eruption associated with persistent primary tooth. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2021, 79, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.; Küchler, E.C.; Reis, C.L.B.; Paddenberg, E.; Zbidat, N.; Mattos, N.H.R.; Schröder, A.; Proff, P.; Kirschneck, C. Association of third molar agenesis and microdontia with genetic polymorphisms in vitamin-D-related genes. Ann. Anat. 2022, 20, 151972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küchler, E.C.; Carelli, J.; Morais, N.D.; Brancher, J.A.; Lopes, C.M.C.F.; Baratto-Filho, F.; Paddenberg, E.; Menezes, M.A.H.O.; Moro, A.; Kirschneck, C. Assessing the association between vitamin D receptor and dental age variability. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küchler, E.C.; Reis, C.L.B.; Marañón-Vásquez, G.; Nelson-Filho, P.; Matsumoto, M.A.N.; Stuani, M.B.S.; Oliveira, M.A.H.M.; Proff, P.; Kirschneck, C. Parathyroid hormone gene and genes involved in the maintenance of vitamin D levels association with mandibular retrognathism. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küchler, E.C.; Schröder, A.; Teodoro, V.B.; Nazet, U.; Scariot, R.; Spanier, G.; Proff, P.; Kirschneck, C. The role of 25-hydroxyvitamin-D3 and vitamin D receptor gene in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts as response to orthodontic compressive strain: An in vitro study. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Meng, H.; Hou, J. Characterization of the autocrine/paracrine function of vitamin D in human gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Han, B.; Meng, H.; Hou, J. Influence of rs2228570 on transcriptional activation by the vitamin D receptor in human gingival fibroblasts and periodontal ligament cells. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Han, B.; Hou, J.; Meng, H. Preliminary investigation on the molecular mechanisms underlying the correlation between VDR-FokI genotype and periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrukhov, O.; Andrukhova, O.; Hulan, U.; Tang, Y.; Bantleon, H.P.; Rausch-Fan, X. Both 25-Hydroxyvitamin-D3 and 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin-D3 reduces inflammatory response in human periodontal ligament cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.H.; Teixeira, H.; Tsai, A. Mechanistic insight into orthodontic tooth movement based on animal studies: A critical review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Maltha, J.C.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M. Optimum force magnitude for orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic literature review. Angle Orthod. 2003, 73, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, L.X.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. Expression of OPG, RANKL, and RUNX2 in rabbit periodontium under orthodontic force. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 19382–19388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Jeon, H.H.; Alshabab, A.; Lee, W.J.; Chung, C.; Graves, D.T. RANKL deletion in periodontal ligament and bone lining cells blocks orthodontic tooth movement. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butera, A.; Gallo, S.; Maiorani, C.; Molino, D.; Chiesa, A.; Preda, D.; Esposito, F.; Scribante, A. Probiotic Alternative to Chlorhexidine in Periodontal Therapy: Evaluation of Clinical and Microbiological Parameters. Microorganisms 2020, 29, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küchler, E.C.; Schröder, A.; Corso, P.; Scariot, R.; Spanier, G.; Proff, P.; Kirschneck, C. Genetic polymorphisms influence gene expression of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts in the early phases of orthodontic tooth movement. Odontology 2019, 108, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschneck, C.; Batschkus, S.; Proff, P.; Köstler, J.; Spanier, G.; Schröder, A. Valid gene expression normalization by RT-qPCR in studies on hPDL fibroblasts with focus on orthodontic tooth movement and periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, A.; Bauer, K.; Spanier, G.; Proff, P.; Wolf, M.; Kirschneck, C. Expression kinetics of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts in the early phases of orthodontic tooth movement. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2018, 79, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejentsev, S.; Godfrey, L.; Snook, H.; Rance, H.; Nutland, S.; Walker, N.M.; Lam, A.C.; Guja, C.; Tirgoviste, C.I.; Undlien, D.E.; et al. Comparative high-resolution analysis of linkage disequilibrium and tag single nucleotide polymorphisms between populations in the vitamin D receptor gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurutka, P.W.; Remus, L.S.; Whitfield, G.K.; Thompson, P.D.; Hsieh, J.C.; Zitzer, H.; Tavakkoli, P.; Galligan, M.A.; Dang, H.T.; Hausller, C.A.; et al. The polymorphic N terminus in human vitamin D receptor isoforms influences transcriptional activity by modulating interaction with transcription factor IIB. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimirah, F.; Peng, X.; Murillo, G.; Mehta, R.G. Functional significance of vitamin D receptor FokI polymorphism in human breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, C.; Krishnan, A.V.; Malloy, P.J.; Eccleshall, T.R.; Zhao, X.Y.; Feldman, D. The vitamin D receptor gene start codon polymorphism: A functional analysis of FokI variants. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1998, 13, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SNP | Reference Sequence | # Base Change | # Gene Function and Location | * Genotyping Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BgII | rs739837 | G/T | 3 Prime UTR Variant | 54/57 (94.6%) |
| BsmI | rs1544410 | T/C | Intron Variant | 55/57 (96.5%) |
| Apal | rs7975232 | A/C | Intron Variant | 57/57 (100%) |
| FokI | rs2228570 | A/G | Missense Variant | 57/57 (100%) |
| TaqI | rs731236 | A/G | Synonymous Variant | 53/57 (92.9%) |
| SNP | Genotype | n | Fold Change VDR Expression | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 25th Percentile | 75th Percentile | ||||
| BgII | GG | 12 | 0.78 | 0.36 | 1.18 | 0.874 |
| GT | 27 | 0.74 | 0.52 | 1.16 | ||
| TT | 15 | 0.95 | 0.48 | 1.65 | ||
| BsmI | CC | 17 | 0.97 | 0.36 | 1.61 | 0.579 |
| CT | 34 | 0.68 | 0.54 | 1.12 | ||
| TT | 5 | 1.01 | 0.94 | 1.41 | ||
| Apal | AA | 14 | 0.84 | 0.54 | 1.42 | 0.844 |
| AC | 27 | 0.87 | 0.43 | 1.62 | ||
| CC | 16 | 0.65 | 0.45 | 1.17 | ||
| FokI | AA | 8 | 0.69 | 0.57 | 1.18 | 0.938 |
| AG | 25 | 0.87 | 0.41 | 1.22 | ||
| GG | 24 | 0.89 | 0.50 | 1.20 | ||
| TaqI | AA | 4 | 0.87 | 0.66 | 1.30 | 0.901 |
| AG | 39 | 0.80 | 0.48 | 1.97 | ||
| GG | 12 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 1.22 | ||
| Variable | Reference * | Estimate | Standard Error | 95% CI | t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BgII [GT] | GG | −1.33 | 1.50 | −4.37 to 1.71 | 0.88 |
| BgII [TT] | −1.40 | 1.71 | −4.85 to 2.05 | 0.81 | |
| BsmI [CT] | CC | −1.32 | 1.09 | −3.54 to 0.89 | 1.20 |
| BsmI [TT] | 0.36 | 2.05 | −3.77 to 4.51 | 0.17 | |
| Apal [AC] | CC | 0.18 | 1.25 | −2.36 to 2.72 | 0.14 |
| Apal [AA] | 0.56 | 1.66 | −2.79 to 3.92 | 0.33 | |
| FokI [AA] | AG | 0.01 | 1.27 | −2.55 to 2.59 | 0.01 |
| FokI [GG] | 0.67 | 1.03 | −1.41 to 2.76 | 0.65 | |
| TaqI [GG] | AA | 0.19 | 2.30 | −4.45 to 4.84 | 0.08 |
| TaqI [AG] | 1.55 | 2.10 | −2.70 to 5.80 | 0.73 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Küchler, E.C.; Schröder, A.; Spanier, G.; Thedei, G., Jr.; Carvalho Ribeiro de Oliveira, M.B.; de Menezes-Oliveira, M.A.H.; Proff, P.; Kirschneck, C. Influence of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Vitamin D Receptor Expression in Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts as a Response to Orthodontic Compression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415948
Küchler EC, Schröder A, Spanier G, Thedei G Jr., Carvalho Ribeiro de Oliveira MB, de Menezes-Oliveira MAH, Proff P, Kirschneck C. Influence of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Vitamin D Receptor Expression in Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts as a Response to Orthodontic Compression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):15948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415948
Chicago/Turabian StyleKüchler, Erika Calvano, Agnes Schröder, Gerrit Spanier, Geraldo Thedei, Jr., Maria Beatriz Carvalho Ribeiro de Oliveira, Maria Angélica Hueb de Menezes-Oliveira, Peter Proff, and Christian Kirschneck. 2022. "Influence of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Vitamin D Receptor Expression in Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts as a Response to Orthodontic Compression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 15948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415948
APA StyleKüchler, E. C., Schröder, A., Spanier, G., Thedei, G., Jr., Carvalho Ribeiro de Oliveira, M. B., de Menezes-Oliveira, M. A. H., Proff, P., & Kirschneck, C. (2022). Influence of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Vitamin D Receptor Expression in Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts as a Response to Orthodontic Compression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415948








