A Regulatory Loop Involving miR-200c and NF-κB Modulates Mortalin Expression and Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity in an Ovarian Cancer Cell Line Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
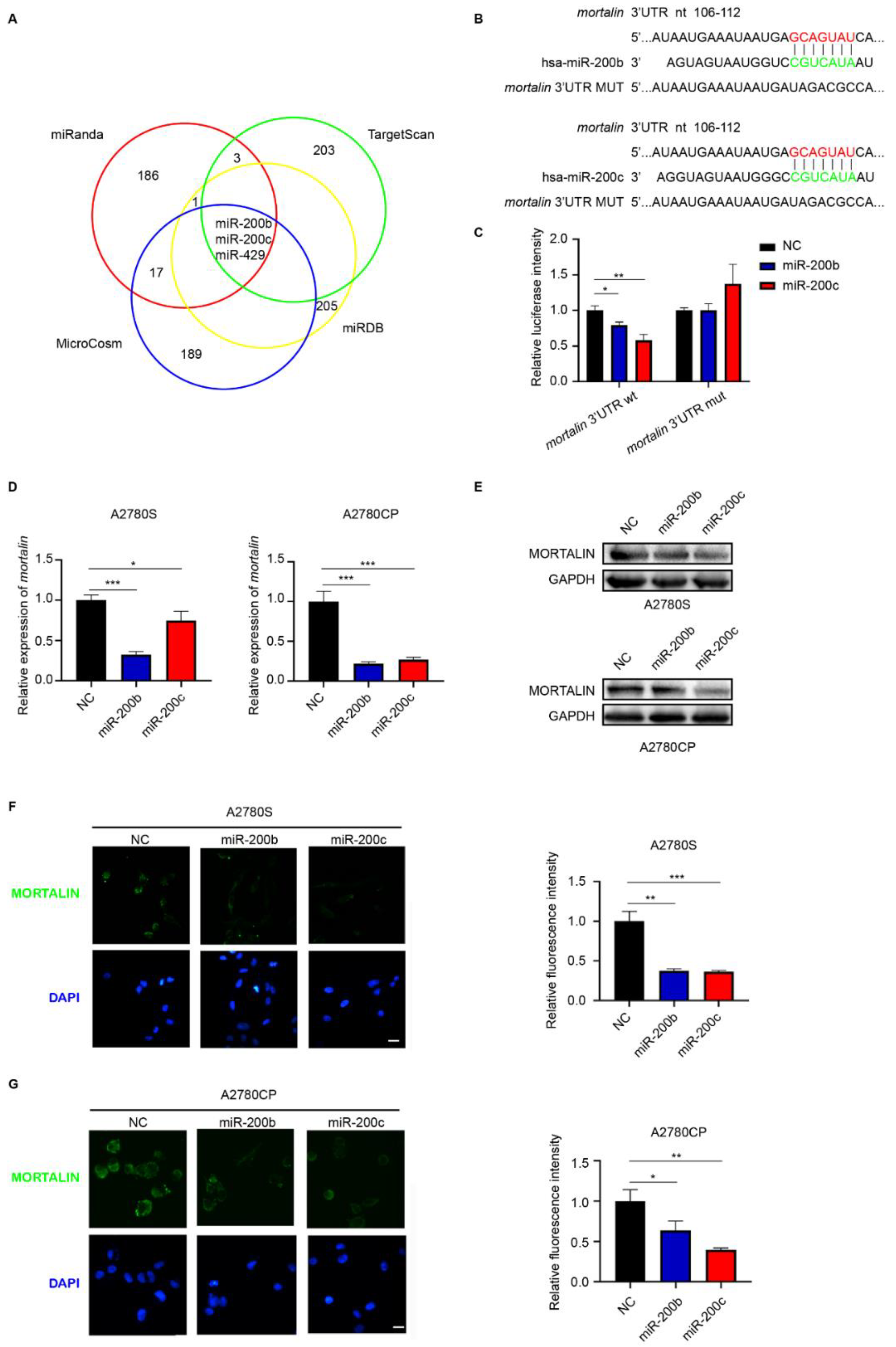
2.1. Mortalin Is a Direct Target of miR-200b/c
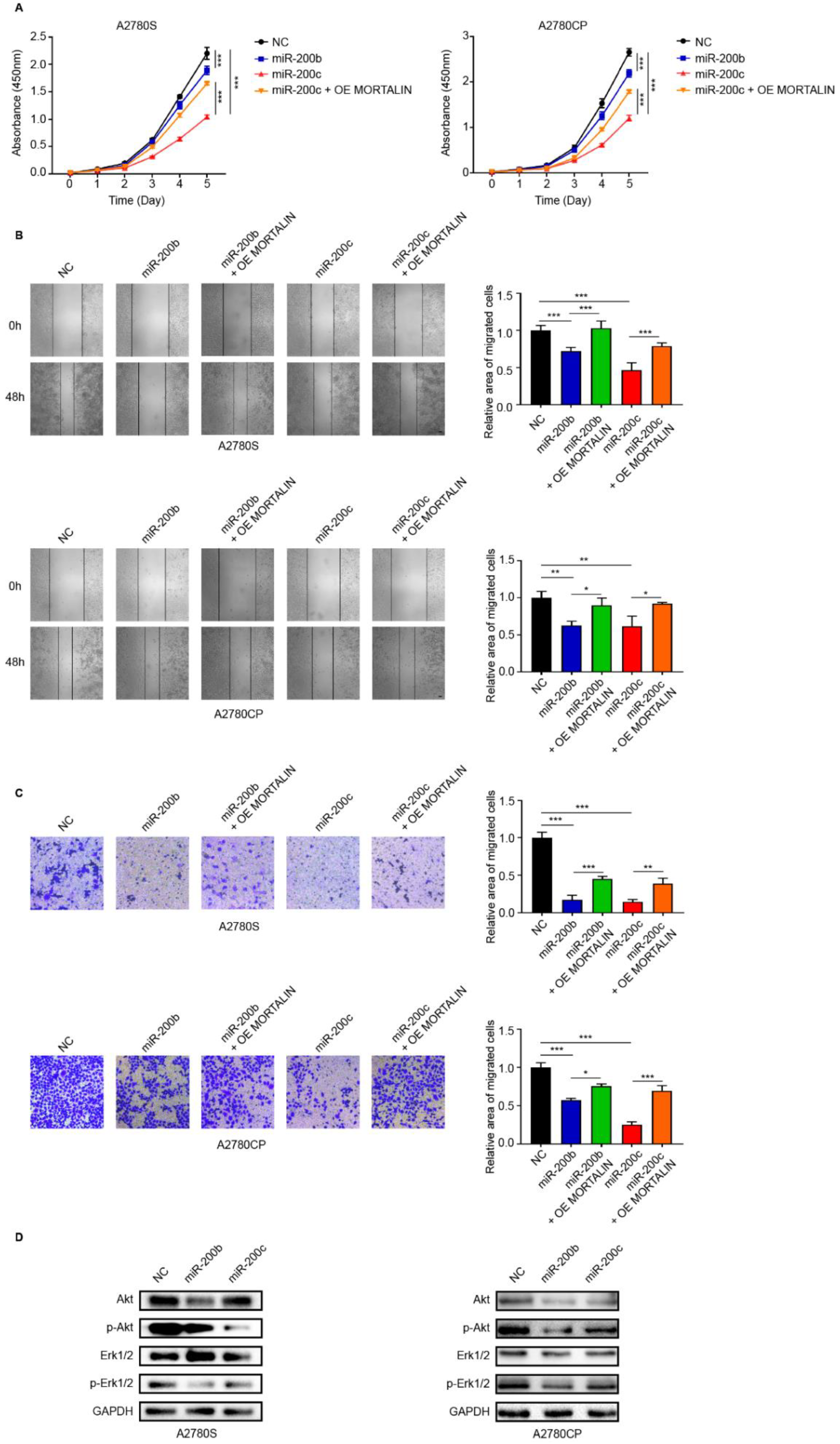
2.2. miR-200b/c Decrease the Proliferation and Migration of Ovarian Cancer Cells Via Mortalin
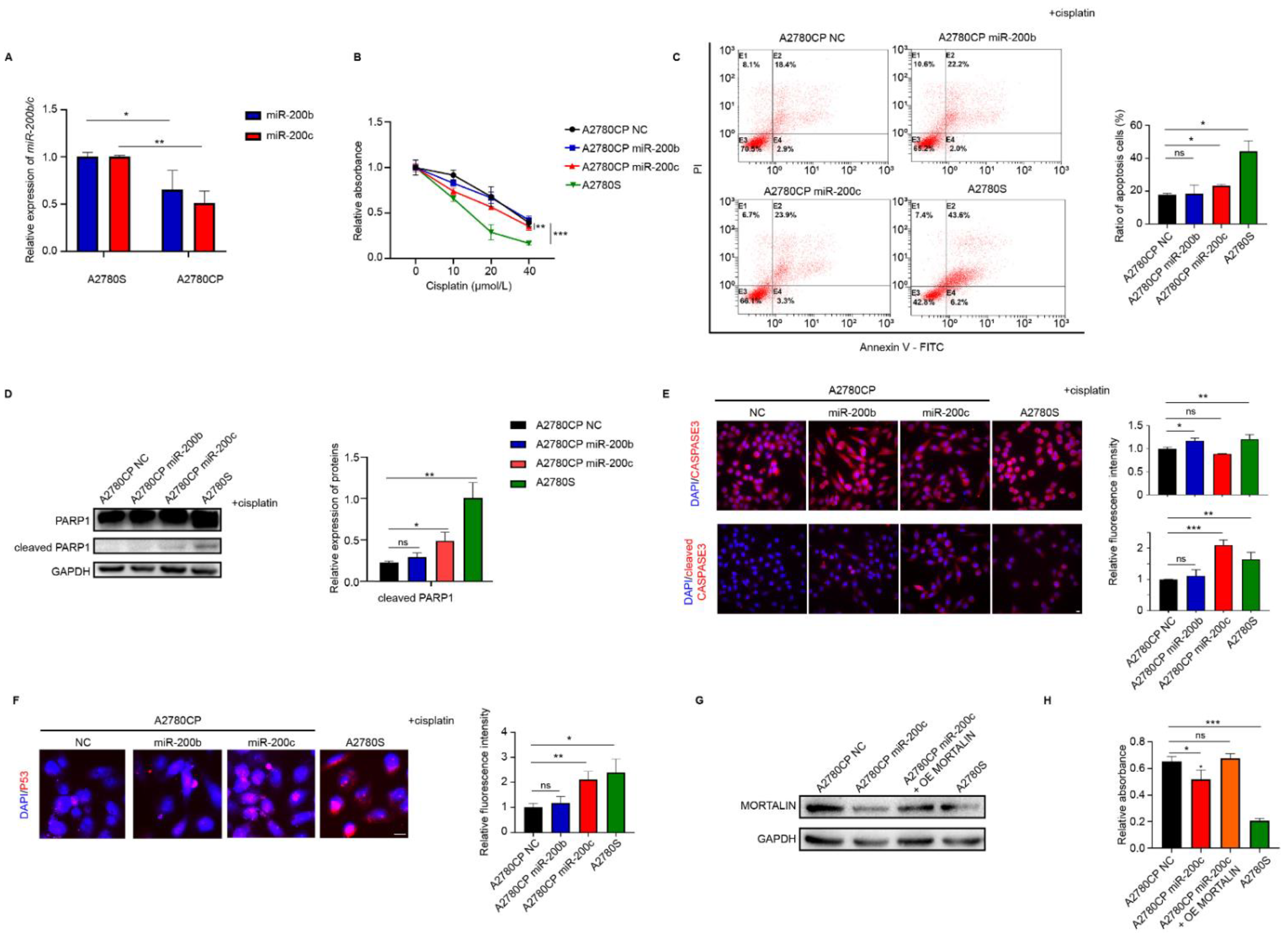
2.3. miR-200c Increases the Sensitivity of Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin
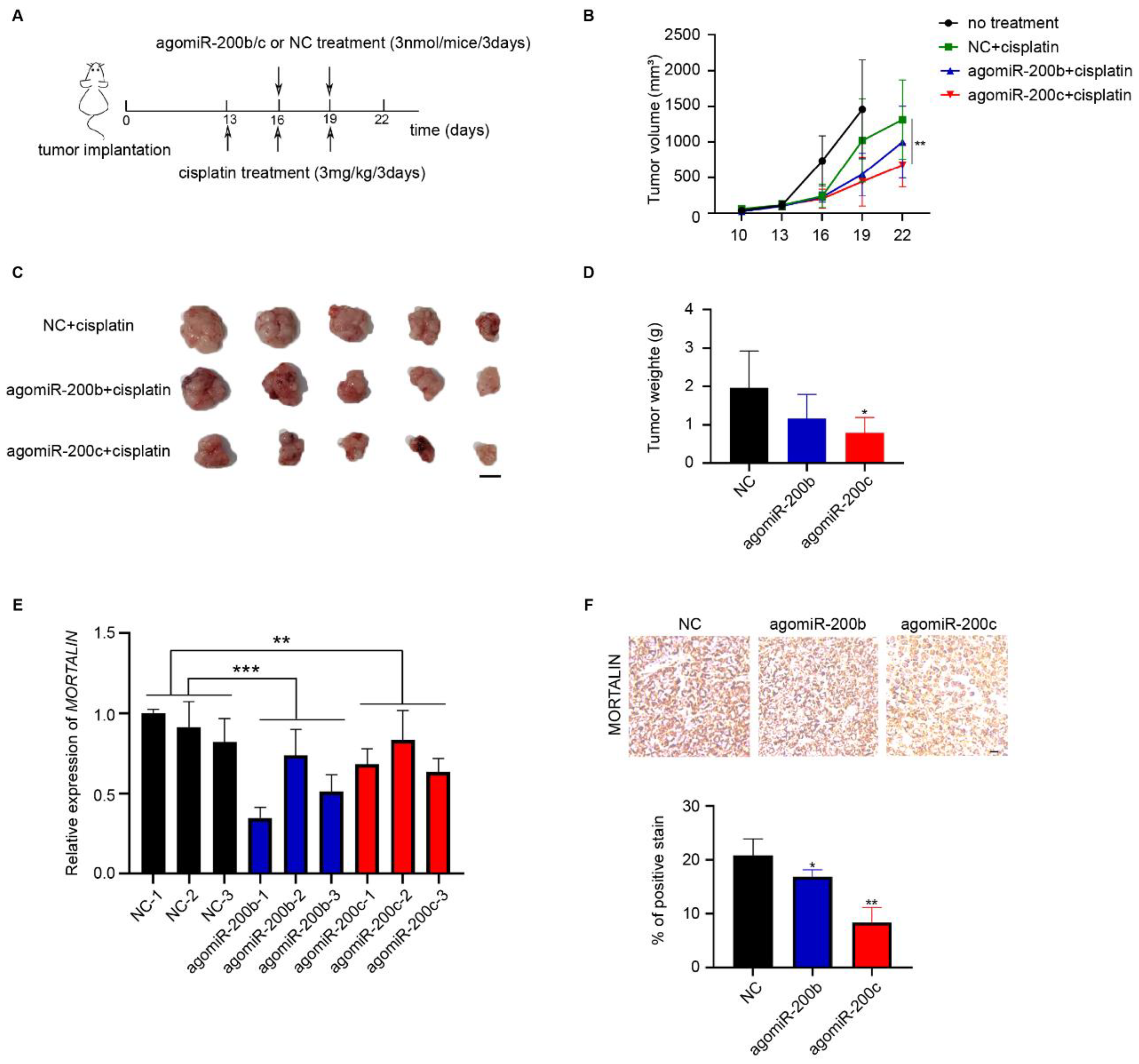
2.4. miR-200c Suppresses the Chemoresistance of Ovarian Cancer Cells In Vivo
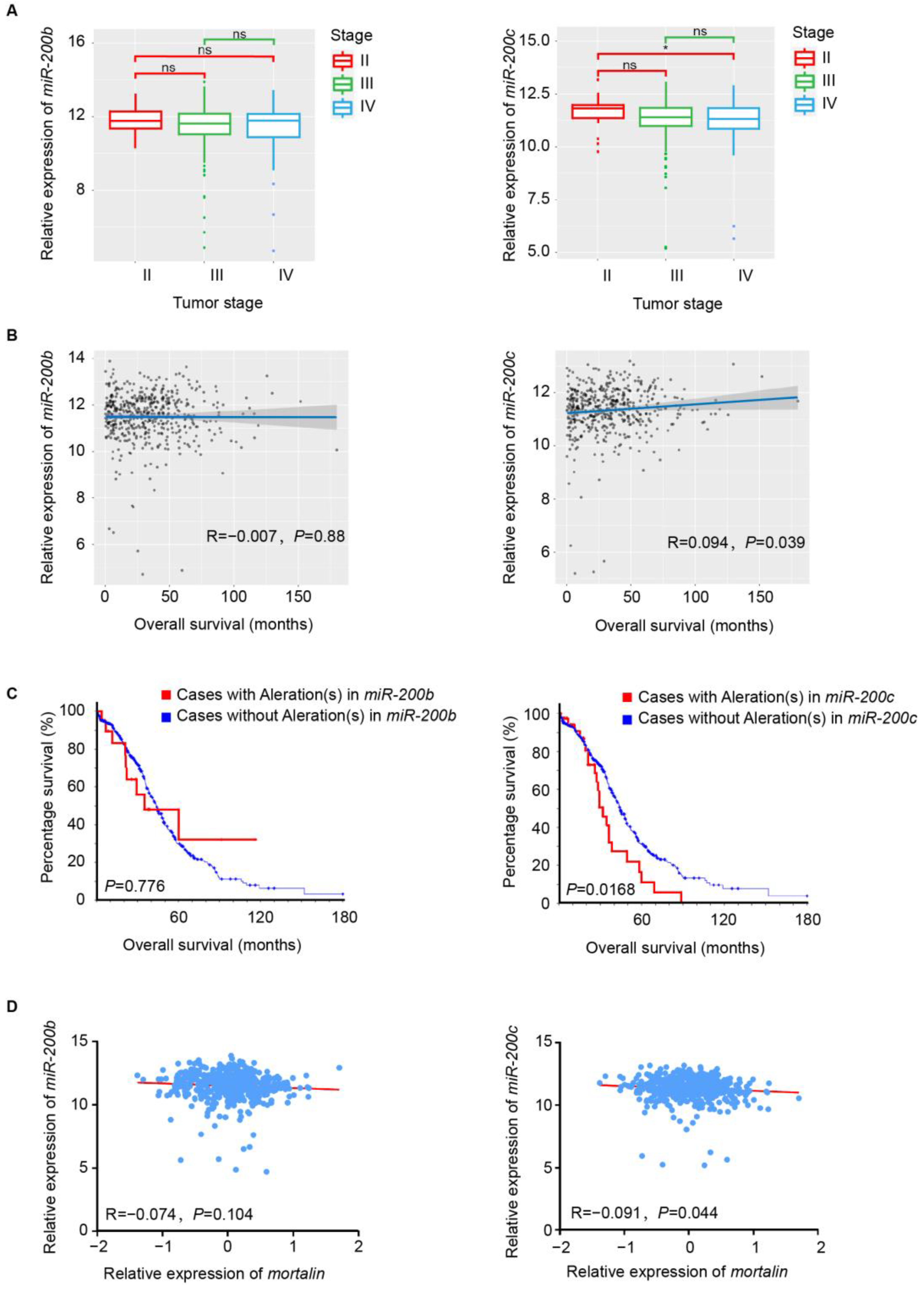
2.5. miR-200c Expression Levels Are Associated with Patient Prognosis
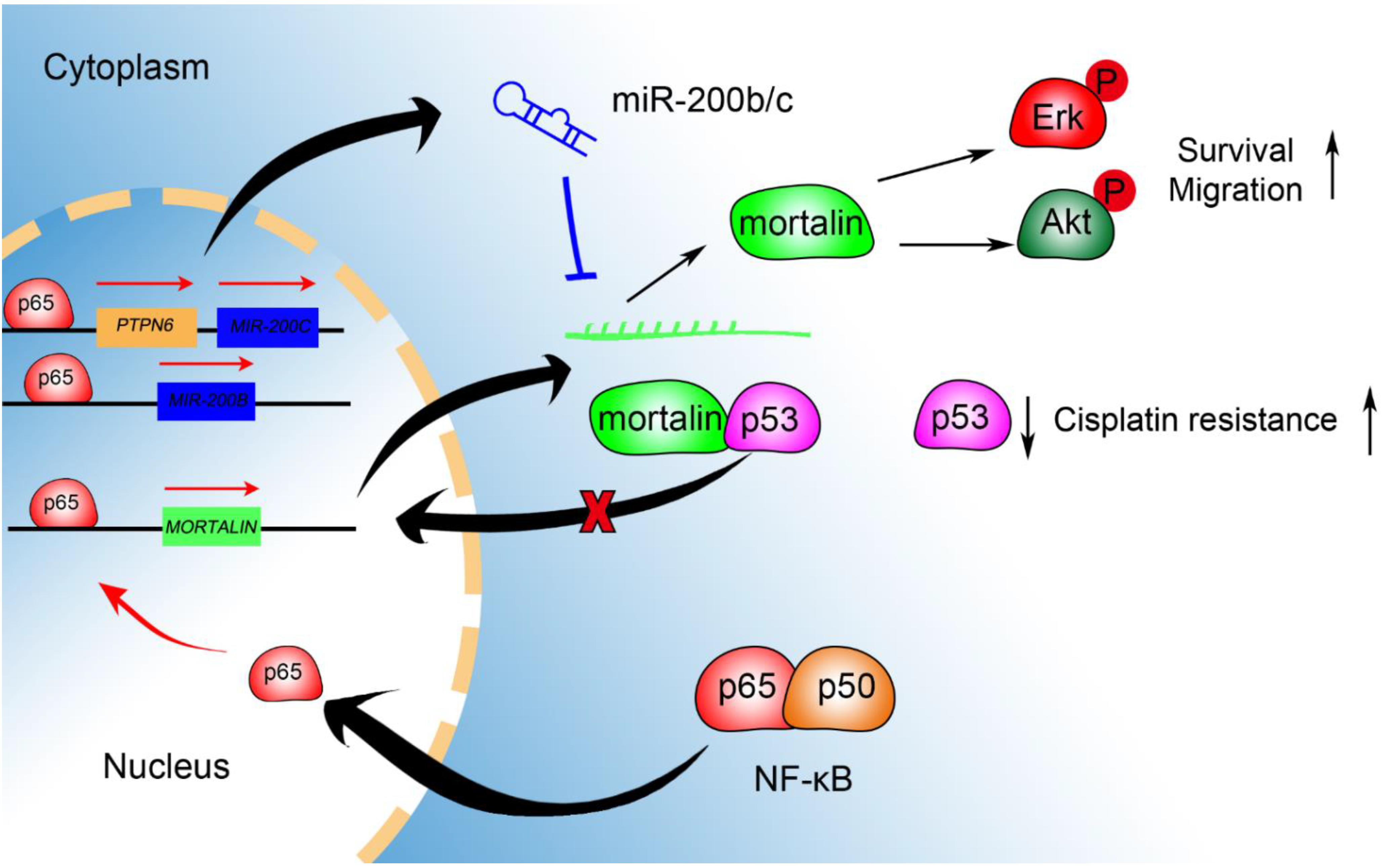
2.6. NF-κB and miR-200b/c Co-Regulate Mortalin Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.2. Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay and Mortalin 3′-UTR Site Mutagenesis
4.3. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR Assay
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.6. Wound Healing Assay
4.7. Transwell Assay
4.8. Determination of Cell Viability
4.9. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.10. Xenograft Tumor Growth Study
4.11. Immunohistochemistry
4.12. Analysis of Clinical Ovarian Cancer Data from TCGA Dataset
4.13. ChIP Assay
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecorelli, S. Annual report on the results of treatment in gynecologic cancer. J. Epidemiol. Biostat. 1998, 3, 75–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidman, J.D.; Kurman, R.J. Ovarian serous borderline tumors: A critical review of the literature with emphasis on prognostic indicators. Hum. Pathol. 2000, 31, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Qureshi, A.N.; Kazmi, A.; Rasool, A.; Gul, M.; Ashfaq, M.; Batool, L.; Rehman, R.A.; Ahmad, J. Muniba First cancer statistics report from Hazara division. JAMC 2014, 25, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, A.; Zheng, H.; Ziebarth, A.; Sakati, W.; Branham-O’Connor, M.; Blumer, J.B.; Liu, Y.; Kistner-Griffin, E.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; et al. EDD enhances cell survival and cisplatin resistance and is a therapeutic target for epithelial ovarian cancer. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starenki, D.; Sosonkina, N.; Hong, S.-K.; Lloyd, R.V.; Park, J.-I. Mortalin (GRP75/HSPA9) Promotes Survival and Proliferation of Thyroid Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Oki, E.; Zhao, Y.; Ikawa-Yoshida, A.; Kitao, H.; Saeki, H.; Kimura, Y.; Ida, S.; Morita, M.; Kusumoto, T.; et al. Mortalin is a prognostic factor of gastric cancer with normal p53 function. Gastric Cancer 2014, 17, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Zou, H.; Yang, X.; Cai, J.B.; Liu, L.X.; Xie, N.; Wang, L.M.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, X.W. Characterization and prognostic significance of mortalin, Bcl-2 and Bax in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zuo, J.; Liu, W. Inhibition of mortalin expression reverses cisplatin resistance and attenuates growth of ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013, 336, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zuo, J. Oncogenic role of mortalin contributes to ovarian tumorigenesis by activating the MAPK–ERK pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M.R.; Sonenberg, N.; Filipowicz, W. Regulation of mRNA Translation and Stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmell, M.A.; Xuan, Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Hannon, G.J. The Argonaute family: Tentacles that reach into RNAi, developmental control, stem cell maintenance, and tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquinelli, A.E.; Ruvkun, G. Control of Developmental Timing by MicroRNAs and Their Targets. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 18, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennecke, J.; Hipfner, D.R.; Stark, A.; Russell, R.B.; Cohen, S.M. bantam Encodes a Developmentally Regulated microRNA that Controls Cell Proliferation and Regulates the Proapoptotic Gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 2003, 113, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-M.; Gaur, A.B.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.A.; Pietenpol, J.A.; Moses, H.L. A tale of two proteins: Differential roles and regulation of Smad2 and Smad3 in TGF-β signaling. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 101, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, H.; Pelakh, L.; Chuang, T.-D.; Luo, X.; Bukulmez, O.; Chegini, N. Endometrial miR-200c is Altered During Transformation into Cancerous States and Targets the Expression of ZEBs, VEGFA, FLT1, IKKβ, KLF9, and FBLN5. Reprod. Sci. 2012, 19, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.; Dai, X.; Hu, J.; Xue, J.; Liu, T.; Liang, Y.; Wu, G. miR-200c Increases the Radiosensitivity of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line A549 by Targeting VEGF-VEGFR2 Pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecot, C.V.; Rupaimoole, R.; Yang, D.; Akbani, R.; Ivan, C.; Lu, C.; Wu, S.; Han, H.-D.; Shah, M.Y.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; et al. Tumour angiogenesis regulation by the miR-200 family. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lv, M.; Qiu, S.; Meng, J.; Liu, W.; Zuo, J.; Yang, L. NF-κB p65 promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration via regulating mortalin. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4338–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalgi, R.; Lieber, D.; Oren, M.; Pilpel, Y. Global and Local Architecture of the Mammalian microRNA–Transcription Factor Regulatory Network. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Mei, Y.; Hawthorn, L.; Cowell, J.K. WASF3 regulates miR-200 inactivation by ZEB1 through suppression of KISS1 leading to increased invasiveness in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2013, 33, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wendlandt, E.B.; Graff, J.W.; Gioannini, T.L.; McCaffrey, A.P.; Wilson, M.E. The role of MicroRNAs miR-200b and miR-200c in TLR4 signaling and NF-κB activation. Innate Immun. 2012, 18, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Brown, M.; Sims, R.J.; Gottlieb, P.D.; Tucker, P.W. Identification and characterization of Smyd2: A split SET/MYND domain-containing histone H3 lysine 36-specific methyltransferase that interacts with the Sin3 histone deacetylase complex. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, G. Emerging roles of microRNAs in intestinal ischemia/reperfusion–induced injury: A review. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 76, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Y.-B.; Giffard, R. MicroRNAs Regulate the Chaperone Network in Cerebral Ischemia. Transl. Stroke Res. 2013, 4, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, Y.; Mazkereth, N.; Farberov, L.; Shomron, N.; Fishelson, Z. Regulation of Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity by MicroRNAs miR-200b, miR-200c, and miR-217. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 5156–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, G.P. Cisplatin: Process and future. J. Buon. 2013, 18, 564–569. [Google Scholar]
- Roossink, F.; De Jong, S.; Wisman, G.B.A.; Van Der Zee, A.G.J.; Schuuring, E. DNA hypermethylation biomarkers to predict response to cisplatin treatment, radiotherapy or chemoradiation: The present state of art. Cell. Oncol. 2012, 35, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidhar, G.G.; Barbolina, M.V. The miR-200 Family: Versatile Players in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16833–16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Luo, F.; Yang, Y.; Shen, C.; Li, S.; Xu, J. Oridonin inhibition and miR-200b-3p/ZEB1 axis in human pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 50, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, J.; Gong, J.; Yang, C.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, H. miR-200c/FUT4 axis prevents the proliferation of colon cancer cells by downregulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, B.; Silvestris, N.; Mohammadi, A.; Khaze, V.; Baghbani, E.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Shanehbandi, D.; Derakhshani, A.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Baradaran, B. miR-34a and miR-200c Have an Additive Tumor-Suppressive Effect on Breast Cancer Cells and Patient Prognosis. Genes 2021, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Yan, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; E, Q.; Gao, P.; Ye, X.; Liu, W.; Zuo, J. Targeting GRP75 Improves HSP90 Inhibitor Efficacy by Enhancing p53-Mediated Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iosefson, O.; Azem, A. Reconstitution of the mitochondrial Hsp70 (mortalin)-p53 interaction using purified proteins—Identification of additional interacting regions. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-J.; Lee, N.P.; Kaul, S.C.; Lan, F.; Poon, R.T.P.; Wadhwa, R.; Luk, J.M. Mortalin–p53 interaction in cancer cells is stress dependent and constitutes a selective target for cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prislei, S.; Martinelli, E.; Mariani, M.; Raspaglio, G.; Sieber, S.; Ferrandina, G.; Shahabi, S.; Scambia, G.; Ferlini, C. miR-200c and HuR in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cittelly, D.M.; Dimitrova, I.; Howe, E.N.; Cochrane, D.R.; Jean, A.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Post, M.D.; Lu, X.; Broaddus, R.R.; Spillman, M.A.; et al. Restoration of miR-200c to Ovarian Cancer Reduces Tumor Burden and Increases Sensitivity to Paclitaxel. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 2556–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescarelli, E.; Gerini, G.; Megiorni, F.; Anastasiadou, E.; Pontecorvi, P.; Solito, L.; De Vitis, C.; Camero, S.; Marchetti, C.; Mancini, R.; et al. miR-200c sensitizes Olaparib-resistant ovarian cancer cells by targeting Neuropilin 1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, T.; Kariya, M.; Higuchi, T.; Mandai, M.; Matsumura, N.; Kondoh, E.; Miyanishi, M.; Fukuhara, K.; Takakura, K.; Fujii, S. Neuropilin-1 promotes unlimited growth of ovarian cancer by evading contact inhibition. Gynecol. Oncol. 2007, 105, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobert, O. Gene Regulation by Transcription Factors and MicroRNAs. Science 2008, 319, 1785–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalanotto, C.; Cogoni, C.; Zardo, G. MicroRNA in Control of Gene Expression: An Overview of Nuclear Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, J.; Yao, P.; Wang, E.; Cui, Q. microRNA evolution in a human transcription factor and microRNA regulatory network. BMC Syst. Biol. 2010, 4, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milo, R.; Shen-Orr, S.; Itzkovitz, S.; Kashtan, N.; Chklovskii, D.; Alon, U. Network Motifs: Simple Building Blocks of Complex Networks. Science 2002, 298, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosh, R.; Shalgi, R.; Liran, A.; Landan, G.; Korotayev, K.; Nguyen, G.H.; Enerly, E.; Johnsen, H.; Buganim, Y.; Solomon, H.; et al. p53-repressed miRNAs are involved with E2F in a feed-forward loop promoting proliferation. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008, 4, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofir, M.; Hacohen, D.; Ginsberg, D. miR-15 and miR-16 Are Direct Transcriptional Targets of E2F1 that Limit E2F-Induced Proliferation by Targeting Cyclin E. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; An, S.; Ye, P.; Luo, S. A negative feedback loop between miR-200b and the nuclear factor-κB pathway via IKBKB/IKK-β in breast cancer cells. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malander, S.; Hjerpe, E.; Carlson, J.; Borg, Å. Ovarian cancer is in many ways a heterogeneous disease. Lakartidningen 2015, 112, DIUR. [Google Scholar]
- Kossaï, M.; Leary, A.; Scoazec, J.-Y.; Genestie, C. Ovarian Cancer: A Heterogeneous Disease. Pathobiology 2018, 85, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.; Berchuck, A.; Birrer, M.; Chien, J.; Cramer, D.W.; Dao, F.; Dhir, R.; DiSaia, P.; Gabra, H.; Glenn, P.; et al. Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature 2011, 474, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Yan, Y.; Gui, A.; Zhu, S.; Qiu, S.; Chen, F.; Liu, W.; Zuo, J.; Yang, L. A Regulatory Loop Involving miR-200c and NF-κB Modulates Mortalin Expression and Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity in an Ovarian Cancer Cell Line Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315300
Huang X, Yan Y, Gui A, Zhu S, Qiu S, Chen F, Liu W, Zuo J, Yang L. A Regulatory Loop Involving miR-200c and NF-κB Modulates Mortalin Expression and Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity in an Ovarian Cancer Cell Line Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):15300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315300
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xin, Yichen Yan, Ailing Gui, Shun Zhu, Shi Qiu, Feng Chen, Wen Liu, Ji Zuo, and Ling Yang. 2022. "A Regulatory Loop Involving miR-200c and NF-κB Modulates Mortalin Expression and Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity in an Ovarian Cancer Cell Line Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 15300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315300
APA StyleHuang, X., Yan, Y., Gui, A., Zhu, S., Qiu, S., Chen, F., Liu, W., Zuo, J., & Yang, L. (2022). A Regulatory Loop Involving miR-200c and NF-κB Modulates Mortalin Expression and Increases Cisplatin Sensitivity in an Ovarian Cancer Cell Line Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 15300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315300






